Adsorption Behaviors and Removal Efficiencies of Inorganic, Polymeric and Organic Phosphates from Aqueous Solution on Biochar Derived from Sewage Sludge of Chemically Enhanced Primary Treatment Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sludge-Based Biochar
2.2. Batch Adsorption Assays
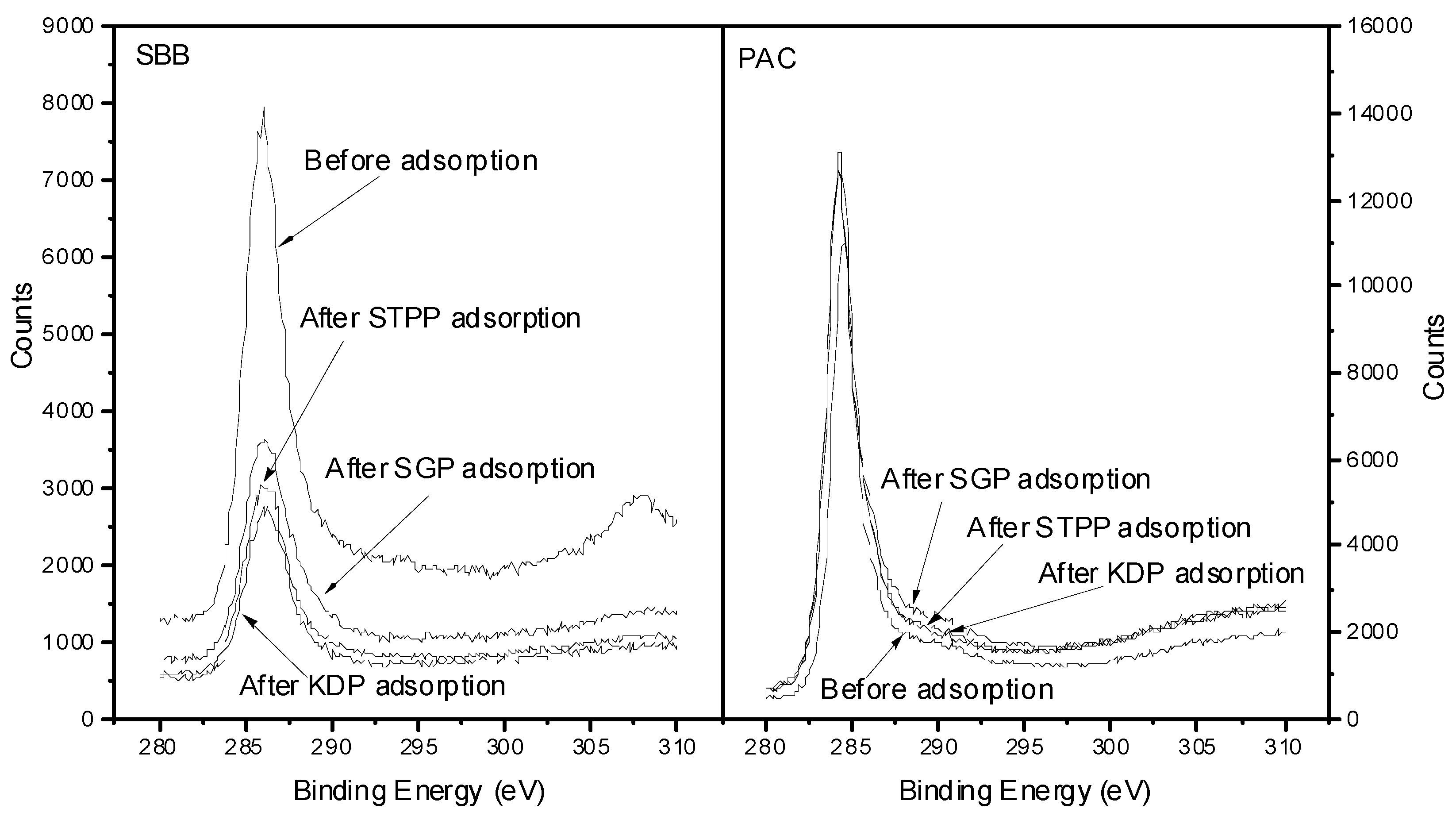
2.3. XPS Analysis
2.4. Adsorption Kinetic Model
2.4.1. Langmuir Isotherm
2.4.2. Freundlich Isotherm
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of SBB and PAC
3.2. Effect of Initial pH on KDP, STPP and SGP Adsorptions
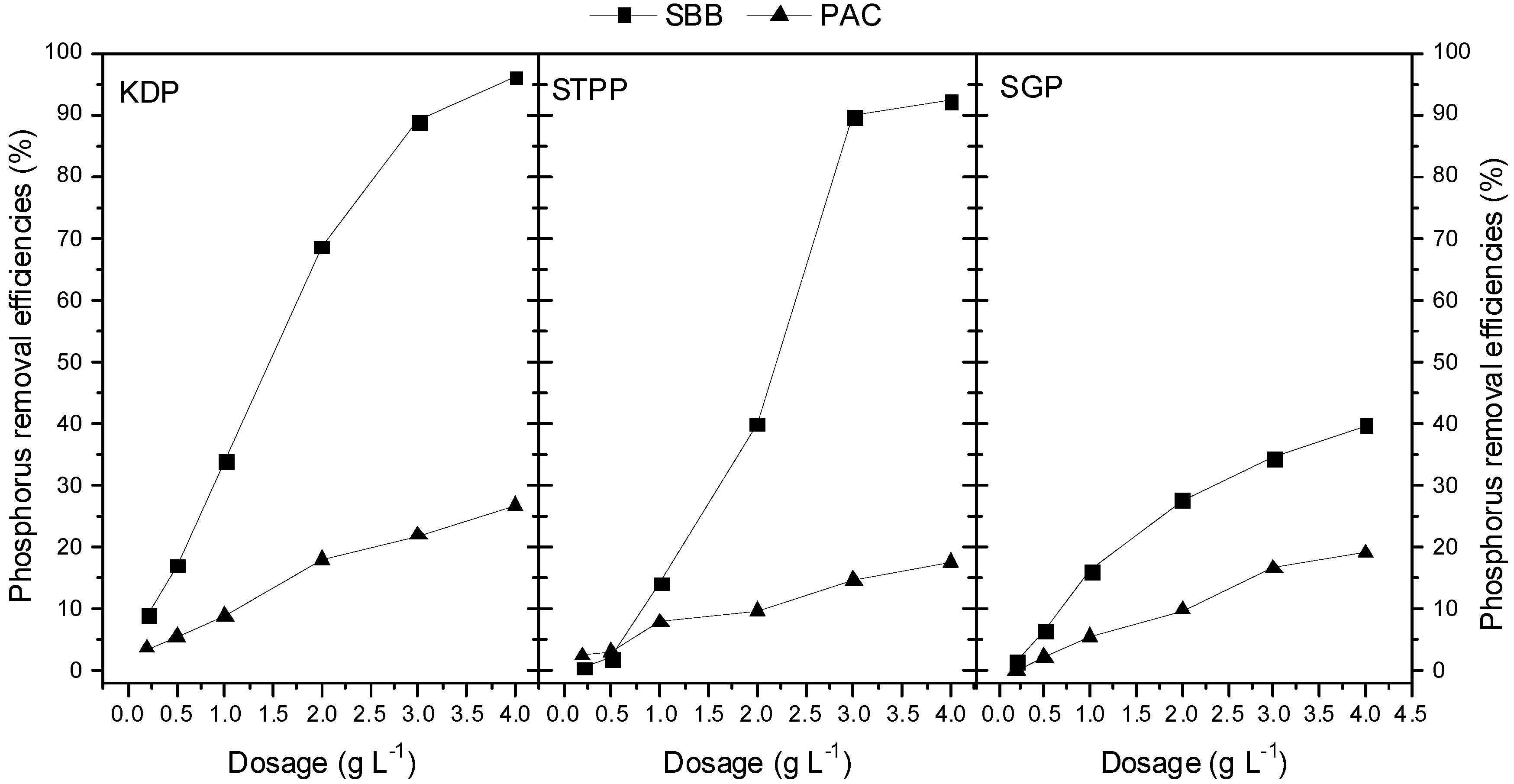
3.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage on KDP, STPP and SGP Adsorptions
3.4. Phosphate Adsorption Characteristics on SBB and PAC
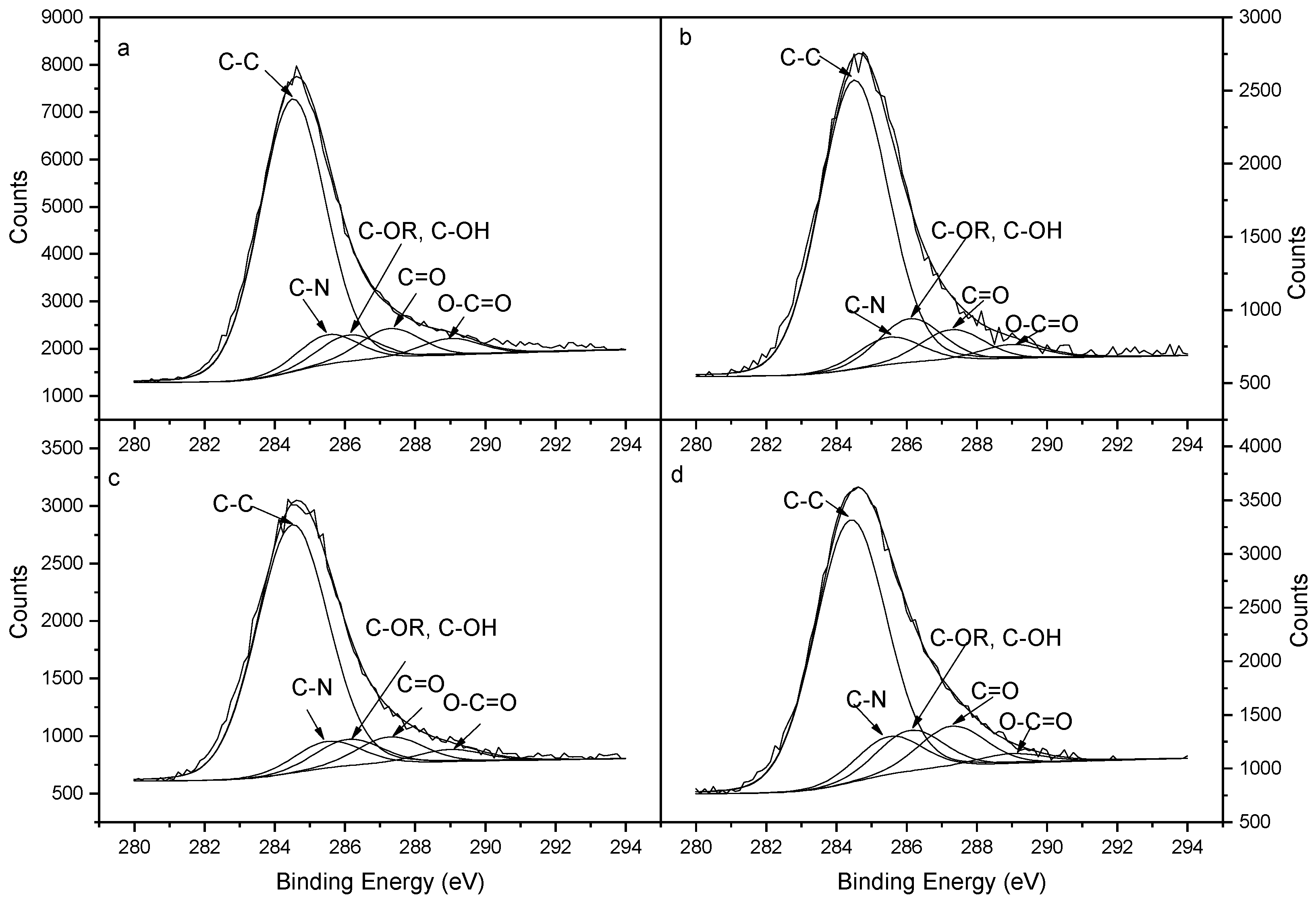
3.4.1. Adsorption Properties of Phosphates on SBB Characterized by XPS Analysis of C Element
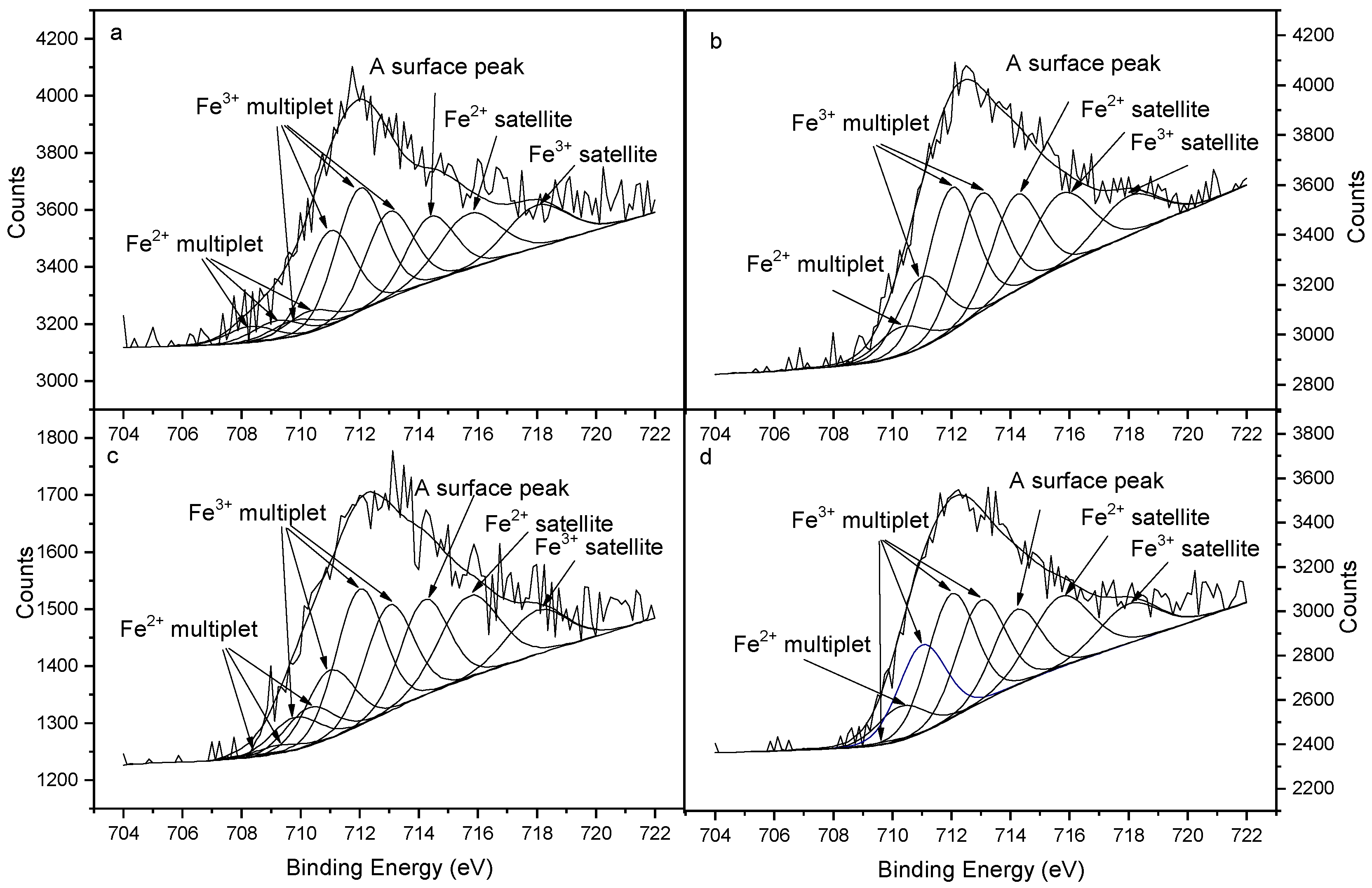
3.4.2. Adsorption Properties of Phosphates on SBB Characterized by XPS Analysis of Fe Element
 ), bidentate (
), bidentate ( ), and monodentate complexes (
), and monodentate complexes ( ). As it has been described, H2PO4− forms monodentate inner-sphere complex by coulombic and Lewis acid-base interaction; HPO42− forms bidentate inner-sphere complex by Lewis acid-base interaction [29].
). As it has been described, H2PO4− forms monodentate inner-sphere complex by coulombic and Lewis acid-base interaction; HPO42− forms bidentate inner-sphere complex by Lewis acid-base interaction [29].4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elser, J.; Bennett, E. Phosphorus cycle: A broken biogeochemical cycle. Nature 2011, 478, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, T.C.; Sharpley, A.N.; Lemunyon, J.L. Agricultural phosphorus and eutrophication: A symposium overview. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, H.P.; Neal, C.; Withers, P.J.A. Sewage-effluent phosphorus: A greater risk to river eutrophication than agricultural phosphorus? Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 360, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darch, T.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Hawkins, J.M.B.; Haygarth, P.M.; Chadwick, D. A meta-analysis of organic and inorganic phosphorus in organic fertilizers, soils, and water: Implications for water quality. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2172–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmidt, E.; Ghyselbrecht, K.; Zhang, Y.; Pinoy, L.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Verstraete, W.; Rabaey, K.; Meesschaert, B. Global Phosphorus scarcity and full-scale p-recovery techniques: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 45, 336–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmann, B.E.; Mayer, B.; Westerhoff, P.; Edwards, M. Capturing the lost phosphorus. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Yang, X.; Spinosa, L. Development of sludge-based adsorbents: Preparation, characterization, utilization and its feasibility assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 151, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.M.; Fowler, G.D.; Pullket, S.; Graham, N.J.D. Sewage sludge-based adsorbents: A review of their production, properties and use in water treatment applications. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2569–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.R.; Zhang, W.T.; Li, G.B. Adsorbent obtained from CEPT sludge in wastewater chemically enhanced treatment. Water Res. 2005, 39, 5175–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.E.; Jeon, P.; Kim, J.G.; Baek, K. Adsorption characteristics of arsenic and phosphate onto iron impregnated biochar derived from anaerobic granular sludge. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, X.; Luo, W.; Sun, J.; Xu, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Yao, F.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Zeng, G. Effectiveness and mechanisms of phosphate adsorption on iron-modified biochars derived from waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, C.A.; Jensen, H.S.; Egemose, S. Phosphate adsorption to iron sludge from waterworks, ochre precipitation basins and commercial ferrihydrite at ambient freshwater phosphate concentrations. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 2185–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W. Nutrients and Heavy Metals in Biochar Produced by Sewage Sludge Pyrolysis: Its Application in Soil Amendment. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Gascó, G.; Gutiérrez, B.; Méndez, A. Soil biochemical activities and the geometric mean of enzyme activities after application of sewage sludge and sewage sludge biochar to soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- American, P.H.A. Water Environment Federation (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, C.; Shilton, A.; Pratt, S.; Haverkamp, R.G.; Elmetri, I. Effects of Redox Potential and pH Changes on Phosphorus Retention by Melter Slag Filters Treating Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6585–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Li, L.; Yao, X.; Rudolph, V.; Haghseresht, F. Phosphate removal from wastewater using red mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, J.; Das, J.; Das, S.; Thakur, R.S. Adsorption of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution Using Activated Red Mud. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 204, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkan, M.; Demirbaş, Ö.; Doğan, M.; Arslan, O. Surface properties of bovine serum albumin—Adsorbed oxides: Adsorption, adsorption kinetics and electrokinetic properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 96, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytianos, K.; Voudrias, E.; Raikos, N. Modelling of phosphorus removal from aqueous and wastewater samples using ferric iron. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 101, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.; Gelbrecht, J. Phosphorus retention at the redox interface of peatlands adjacent to surface waters. Wasser Boden 2002, 54, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Drizo, A.; Cummings, J.; Weber, D.; Twohig, E.; Druschel, G.; Bourke, B. New evidence for rejuvenation of phosphorus retention capacity in EAF steel slag. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6191–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derylo-Marczewska, A.; Swiatkowski, A.; Buczek, B.; Biniak, S. Adsorption equilibria in the systems: Aqueous solutions of organics—Oxidized activated carbon samples obtained from different parts of granules. Fuel 2006, 85, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozada, F.; Otero, M.; Parra, J.B.; Morán, A.; García, A.I. Producing adsorbents from sewage sludge and discarded tyres. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 114, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoudi, S.; Saad, R.; Belkacemi, K. Adsorptive Removal of Phosphate and Nitrate Anions from Aqueous Solutions Using Ammonium-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 8806–8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullet, M.; Khare, V.; Ruby, C. XPS study of Fe(II)Fe(III) (oxy)hydroxycarbonate green rust compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.W.; Han, J.S.; Jang, M.; Min, S.; Park, J.K.; Rowell, R.M. Phosphate Adsorption on Aluminum-Impregnated Mesoporous Silicates: Surface Structure and Behavior of Adsorbents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaney, L.; Cinar, S.; Sengupta, A. Hybrid anion exchanger for trace phosphate removal from water and wastewater. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | C | O | N | Si | S | P | Ca | Fe | O/C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBB | 60.35 | 25.11 | 6.65 | 0.59 | 2.41 | 1.02 | 0.52 | 3.35 | 0.42 |
| KDP-adsorbed SBB | 56.74 | 29.03 | 3.89 | 0.4 | 1.43 | 3.3 | 0 | 5.21 | 0.51 |
| STPP-adsorbed SBB | 56.57 | 29.13 | 4.52 | 0 | 1.48 | 3.79 | 0 | 4.51 | 0.51 |
| SGP-adsorbed SBB | 51.71 | 32.24 | 5.10 | 0.39 | 1.83 | 2.69 | 0.18 | 5.86 | 0.62 |
| PAC | 94.44 | 5.56 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.06 |
| KDP-adsorbed PAC | 93.30 | 6.70 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.07 | |
| STPP-adsorbed PAC | 93.29 | 6.71 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.07 | |
| SGP-adsorbed PAC | 93.50 | 6.50 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.07 |
| Phosphate | Adsorbent | Initial pH of the Phosphate Solutions | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 10.0 | ||
| KDP | SBB | 2.3 | 3.2 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 4.0 |
| PAC | 2.1 | 3.5 | 6.3 | 6.5 | 6.6 | 7.2 | 7.9 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
| STPP | SBB | 2.1 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 4.1 |
| PAC | 2.0 | 3.5 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 9.2 | |
| SGP | SBB | 2.1 | 3.2 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 4.3 | 4.3 | 4.4 |
| PAC | 2.0 | 3.4 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 7.8 | 8.3 | |
| Solution | Adsorbent | Langmuir Constants | Freundlich Constants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Qmax (mg·g−1) | K (L·mg−1) | R2 | Kf (mg·g−1)/(mg·L−1)n | 1/n | ||
| KDP | SBB | 0.978 | 15.15 | 0.0299 | 0.966 | 0.79 | 0.628 |
| PAC | 0.931 | 3.60 | 0.0472 | 0.968 | 0.55 | 0.373 | |
| STPP | SBB | 0.964 | 4.76 | 0.4339 | 0.972 | 1.10 | 0.447 |
| PAC | 0.996 | 1.36 | 0.4502 | 0.972 | 0.36 | 0.381 | |
| SGP | SBB | 0.982 | 7.63 | 0.0312 | 0.982 | 0.47 | 0.580 |
| PAC | 0.912 | 2.66 | 0.0676 | 0.982 | 0.58 | 0.318 | |
| Sample | O-C=O | C=O | C-OR, C-OH | C-N | C-C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBB | 4.16 | 7.35 | 6.55 | 7.35 | 74.60 |
| KDP-adsorbed SBB | 3.24 | 7.08 | 10.14 | 6.31 | 73.23 |
| STPP-adsorbed SBB | 3.36 | 7.33 | 7.33 | 7.33 | 74.65 |
| SGP-adsorbed SBB | 2.40 | 9.80 | 9.80 | 9.07 | 68.93 |
| Sample | Fe | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 3 | Peak 4 | Fe(III)/Fe(Total) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBB | Fe2+ | 2.85 | 3.33 | 3.78 | - | 0.85 |
| Fe3+ | 2.85 | 16.68 | 21.77 | 15.31 | ||
| KDP-adsorbed SBB | Fe2+ | 0 | 0 | 4.75 | - | 0.92 |
| Fe3+ | 0 | 11.76 | 23.88 | 19.69 | ||
| STPP-adsorbed SBB | Fe2+ | 0.46 | 1.28 | 5.95 | - | 0.87 |
| Fe3+ | 5.06 | 10.55 | 21.01 | 16.41 | ||
| SGP-adsorbed SBB | Fe2+ | 0 | 0 | 6.09 | - | 0.91 |
| Fe3+ | 0.46 | 15.50 | 21.90 | 18.06 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, L. Adsorption Behaviors and Removal Efficiencies of Inorganic, Polymeric and Organic Phosphates from Aqueous Solution on Biochar Derived from Sewage Sludge of Chemically Enhanced Primary Treatment Process. Water 2018, 10, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070869
Xu G, Zhang Z, Deng L. Adsorption Behaviors and Removal Efficiencies of Inorganic, Polymeric and Organic Phosphates from Aqueous Solution on Biochar Derived from Sewage Sludge of Chemically Enhanced Primary Treatment Process. Water. 2018; 10(7):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070869
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Guoren, Zhao Zhang, and Linyu Deng. 2018. "Adsorption Behaviors and Removal Efficiencies of Inorganic, Polymeric and Organic Phosphates from Aqueous Solution on Biochar Derived from Sewage Sludge of Chemically Enhanced Primary Treatment Process" Water 10, no. 7: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070869
APA StyleXu, G., Zhang, Z., & Deng, L. (2018). Adsorption Behaviors and Removal Efficiencies of Inorganic, Polymeric and Organic Phosphates from Aqueous Solution on Biochar Derived from Sewage Sludge of Chemically Enhanced Primary Treatment Process. Water, 10(7), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070869




