Hydrogeologic and Paleo-Geographic Characteristics of Riverside Alluvium at an Artificial Recharge Site in Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological and Hydrogeological Setting
3. Methods
4. Results
4.1. Hydrogeologic Characteristics
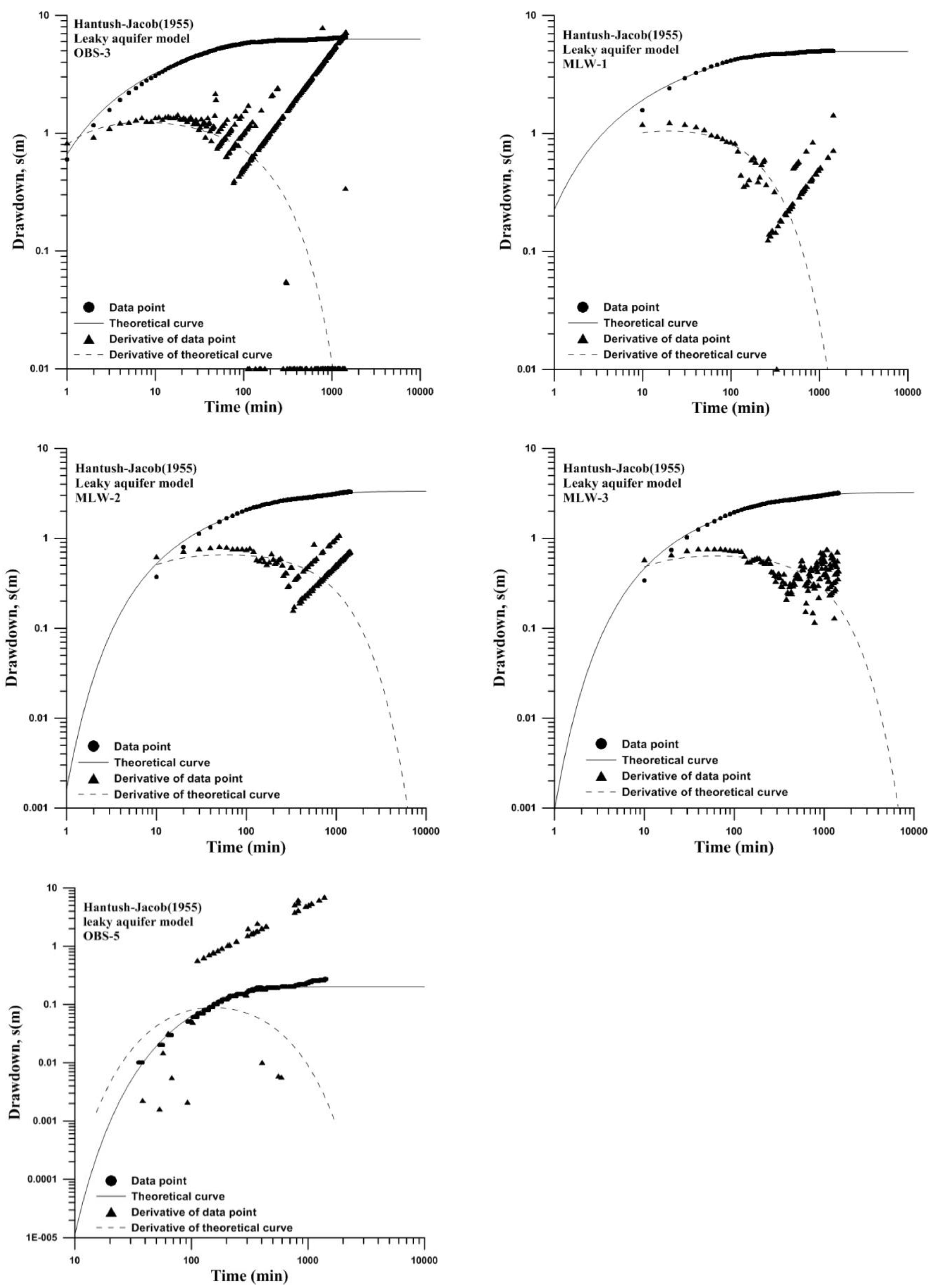
4.2. Hydraulic Parameter Estimation
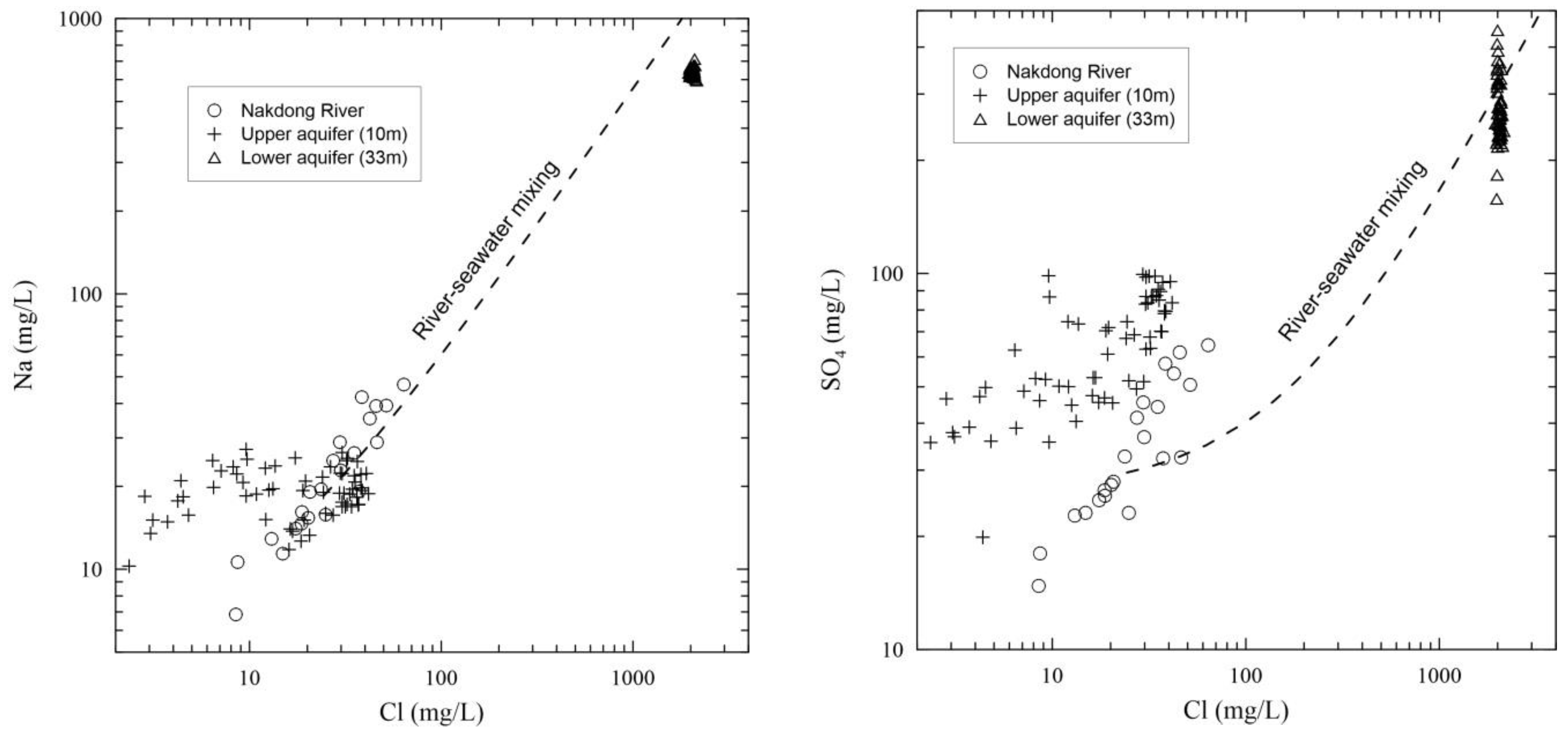
4.3. Estimation of Remnant Paleo-saltwater
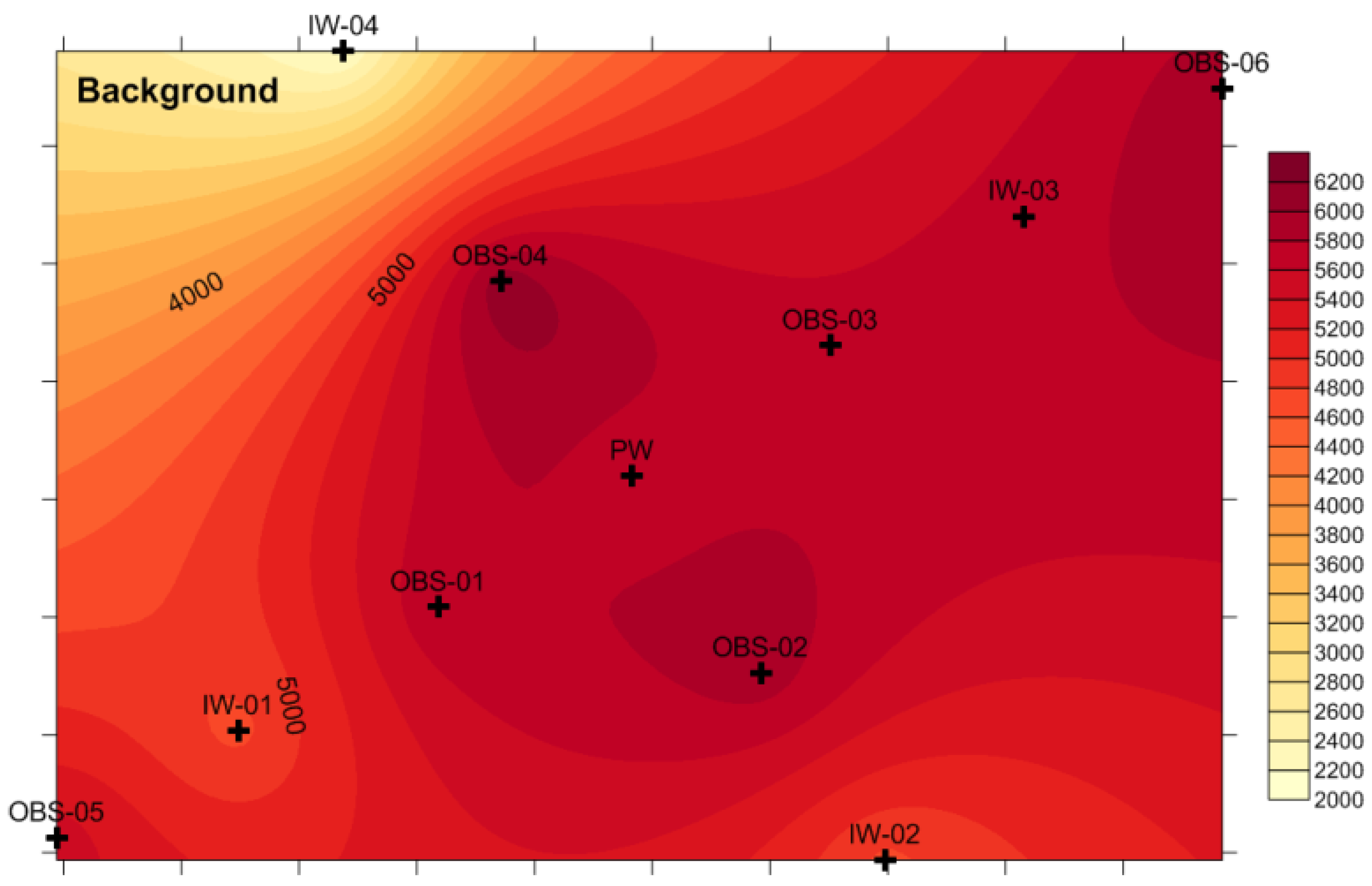
4.4. Spatial Distribution of Paleo-saltwater
4.5. Vertical Profile of Saltwater Bed
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, C. Riverbank Filtration: Understanding Contaminant Biogeochemistry and Pathogen Removal; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; p. 253. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Water Corporation. Report on Pilot Survey of Hydraulic Property of Fluvial Deposits for Water Resource Utilization; Korea Water Corporation: Daejeon, Korea, 1995; p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- Hamm, S.-Y.; Cheong, J.-Y.; Ryu, S.M.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, H.S. Hydrogeological characteristics of bank storage area in Daesan-Myeon, Changwon City, Korea. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2002, 38, 595–610. [Google Scholar]
- Hamm, S.-Y.; Cheong, J.-Y.; Kim, H.S.; Hahn, J.S.; Cha, Y.H. Groundwater flow modeling in a riverbank filtration area, Deasan-Myeon, Changwon City. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2005, 38, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.A.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.J. Site prioritization for artificial recharge in Korea using GIS mapping. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2011, 16, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Seo, J.A.; Ko, K.S. Trend and barrier in the patents of artificial recharge for securing groundwater. j. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2012, 17, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, B.U.; Hardenbol, J.; Vail, P.R. Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic (250 million years ago to present). Science 1987, 235, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldale, R.N.; O’Hara, C.J. New radiocarbon dates from the inner continental shelf off Southeastern Massachusetts and a local sea level rise curve for the past 12,000 yr. Geology 1980, 8, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbanks, R.G. A 17,000-year glacio-eustatic sea level record; influence of glacial melting rates on the Younger Dryas event and deep-ocean circulation. Nature 1989, 342, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plag, H.-P.; Jules-Plag, S. Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Ecosystems. In Vulnerability of Ecosystems to Climate. Climate Vulnerability: Understanding and Addressing Threats to Essential Resources; Pielke, S.R.A., Seastedt, T., Suding, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciopinto, C.; Liso, I.S. Assessment of the impact of sea-level rise due to climate change on coastal groundwater discharge. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Cazenave, A. Sea-level rise and its impact on coastal zones. Science 2010, 328, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Weert, F.; Van der Gun, J.; Reckman, J. Global Overview of Saline Groundwater Occurrence and Genesis; Report nr. GP 2009-1; International Groundwater Resources Assessment Centre: Utrecht, Netherlands, 2009; p. 109. [Google Scholar]
- Post, V.E.A.; Groen, J.; Kooi, H.; Person, M.; Ge, S.; Edmunds, W.M. Offshore fresh groundwater reserves as a global phenomenon. Nature 2013, 504, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delsman, J.R. Saline Groundwater–Surface Water Interaction in Coastal Lowlands; IOS press BV: Amsterdam, The Nerherlands, 2015; p. 194. ISBN 978-1-61499-517-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kooi, H.; Groen, J.; Leijnse, A. Modes of seawater intrusion during transgressions. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 3581–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, V.E.A.; Kooi, H. Rates of salinization by free convection in high-permeability sediments: Insights from numerical modeling and application to the Dutch coastal area. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Park, Y.A.; Han, S.J. Late Quaternary stratigraphy and sea-level change in the tidal flat of Gomso Bay, West Coast of Korea. Sea J. Korean Soc. Ocean. 1996, 1, 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, J.-Y.; Hamm, S-.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Ko, E.J.; Yang, K.; Lee, J.H. Estimating hydraulic conductivity using grain-size analyses, aquifer tests, and numerical modeling in a riverside alluvial system in South Korea. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.J.; Lee, H.K. Geologic map of Yeongsan area (1:50,000); National Geological Survey: Seoul, Korea, 1964; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopulos, I.S.; Cooper, H.H. Drawdown in a well of large diameter. Water Resour. Res. 1967, 3, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantush, M.S.; Jacob, C.E. Non-steady radial flow in an infinite leaky aquifer. EOS 1955, 36, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moench, A.F. Transient flow to a large-diameter well in an aquifer with storative semiconfining layers. Water Resour. Res. 1985, 21, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, S.P. Effect of partial penetration on flow in unconfined aquifers considering delayed gravity response. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.H.; Jacob, C.E. A generalized graphical method for evaluating formation constants and summarizing well field history. Am. Geophys. Union Trans. 1946, 27, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, C.V. The relation between the lowering of the piezometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a well using groundwater storage. Am. Geophys. Union Trans. 1935, 16, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, J.J.; Cherry, J.A.; Lee, C.M. Contribution of the aquitard to the regional groundwater hydrochemistry of the underlying confined aquifer in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Jiao, J.J. Seawater intrusion and coastal aquifer management in China: A review. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2811–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, J.J. Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in the confined Quaternary aquifer of the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 438, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-Y.; Han, W.S.; Park, E. The impact of highly permeable layer on hydraulic system in a coastal aquifer. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 27, 3128–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

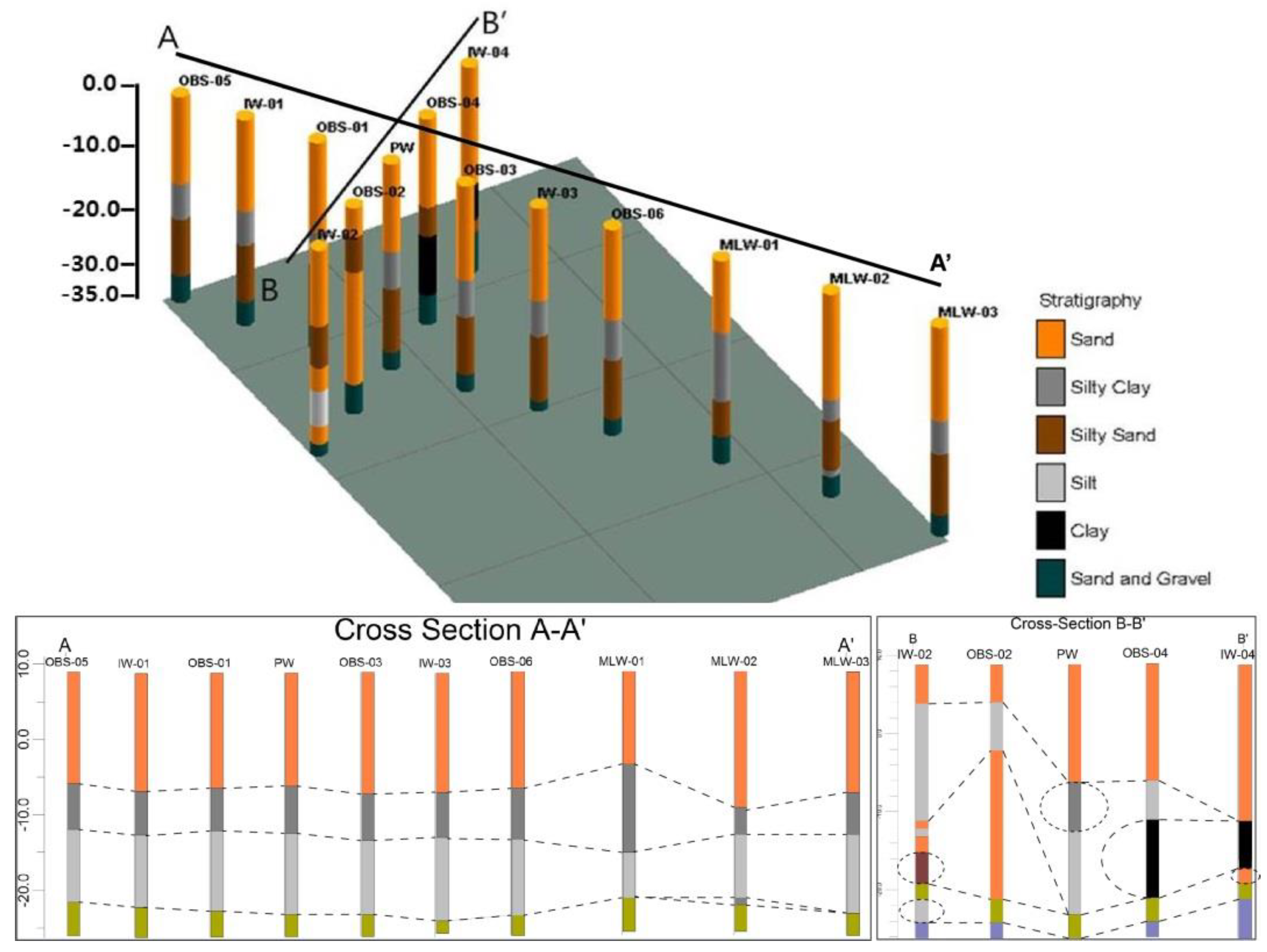
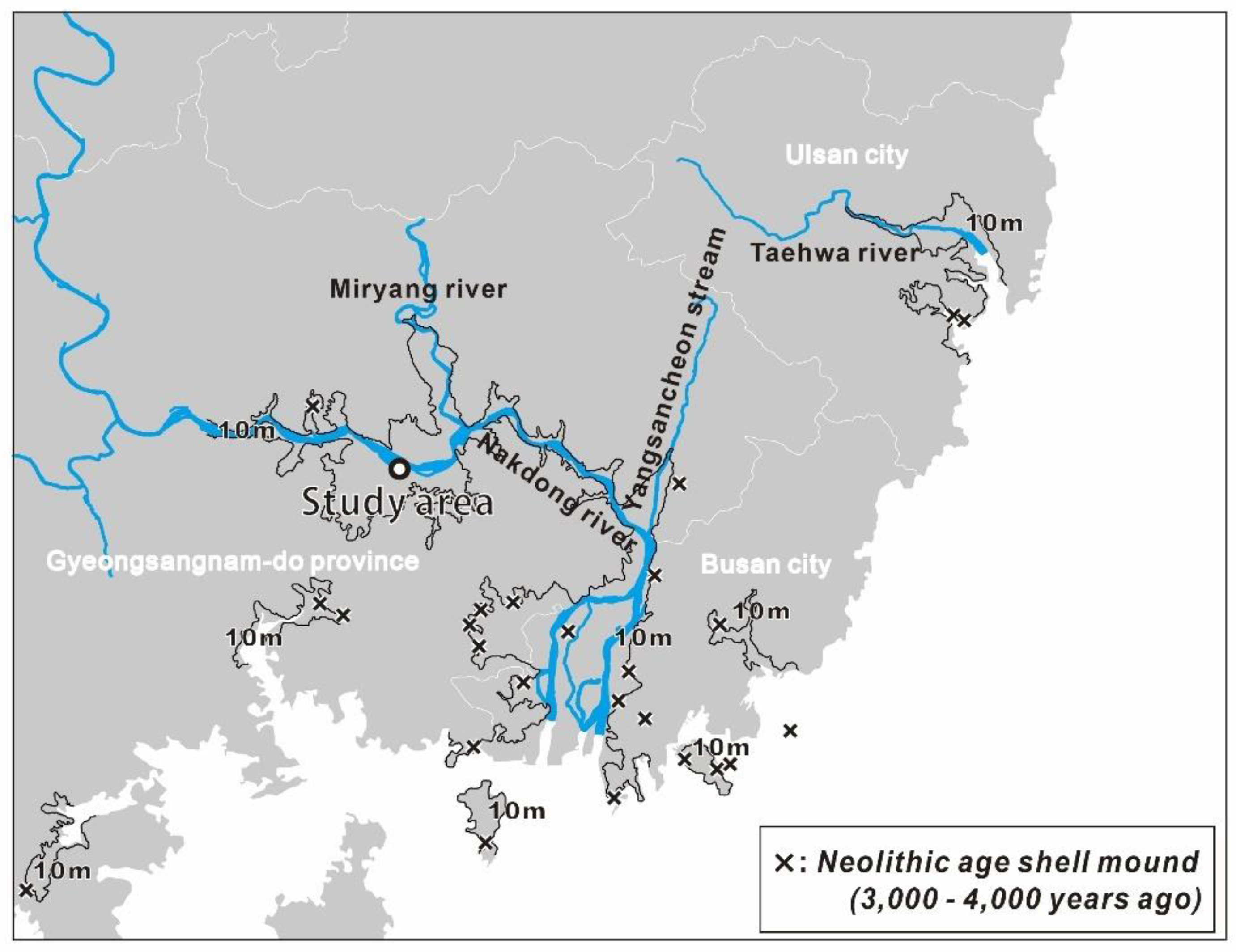

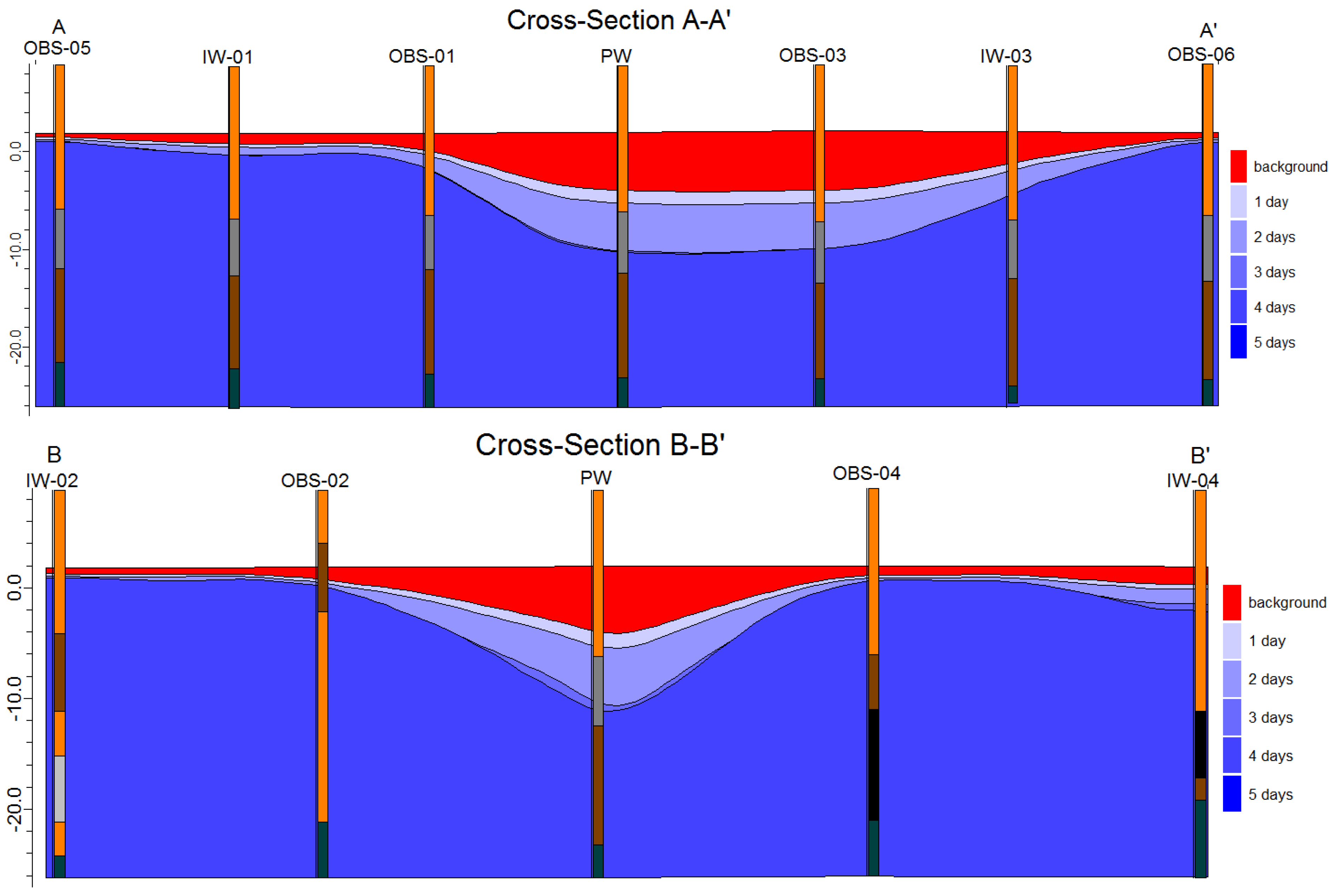




| Well | X | Y | Elevation (EL. m) | Well Depth (m) | DTW (m) | EC Logging Depth (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW | 177,584.1 | 305,371 | 8.817 | 35.0 | 7.02 | - | |
| IW 1 | 177,567.4 | 305,360.2 | 8.725 | 35.0 | 7.0 | - | |
| IW 2 | 177,594.9 | 305,354.7 | 8.815 | 35.0 | - | - | |
| IW 3 | 177,600.8 | 305,382 | 8.779 | 34.5 | 7.08 | - | |
| IW 4 | 177,571.9 | 305,389 | 8.802 | 35.0 | - | - | |
| OBS 1 | 177,575.9 | 305,365.4 | 8.791 | 35.0 | 7.17 | 28.3 | |
| OBS2 | 177,589.6 | 305,362.6 | 8.81 | 35.0 | 7.17 | 29.8 | |
| OBS3 | 177,592.6 | 305,376.5 | 8.886 | 35.0 | 7.07 | 33.8 | |
| OBS4 | 177,578.6 | 305,379.2 | 8.98 | 35.0 | 7.36 | 32.8 | |
| OBS5 | 177,559.7 | 305,355.6 | 8.929 | 35.0 | 7.31 | 24.4 | |
| OBS6 | 177,609.2 | 305,387.4 | 9.002 | 35.0 | 7.36 | 30.5 | |
| MLW1 | 177,621.3 | 305,395.7 | 9.034 | 34.5 | 7.23 | - | |
| MLW2 | 177,633.8 | 305,403.7 | 9.034 | 34.5 | 7.35 | - | |
| MLW3 | 177,646.2 | 305,411.9 | 8.894 | 35.5 | 7.35 | - |
| Well | Aquifer Model | Solution | Drawdown (1 Step, m) | T (m2/s) | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBS-1 | unconfined | Cooper-Jacob (1946) | 0.1 | 4.67 × 10−3 | 0.25 |
| OBS-2 | unconfined | Cooper-Jacob (1946) | 0.04 | 4.76 × 10−3 | 2.26 |
| OBS-3 | leaky | Hantush-Jacob (1955) | 6.48 | 1.14 × 10−4 | 1.7 × 10−4 |
| OBS-4 | unconfined | Neuman (1974) | 0.09 | 4.19 × 10−3 | 5.2 × 10−3 |
| OBS-5 | Leaky | Hantush-Jacob (1955) | 0.27 | 5.52 × 10−4 | 1.1 × 10−2 |
| OBS-6 | unconfined | Neuman (1974) | 0.1 | 1.91 × 10−3 | 9.6 × 10−3 |
| MLW-1 | Leaky | Hantush-Jacob (1955) | 4.97 | 1.22 × 10−4 | 1.5 × 10−5 |
| MLW-2 | Leaky | Hantush-Jacob (1955) | 3.28 | 2.06 × 10−4 | 6.3 × 10−5 |
| MLW-3 | leaky | Hantush-Jacob (1955) | 3.16 | 2.11 × 10−4 | 4.6 × 10−5 |
| Well No. | Distance (m) | Depth to Water (h, m) | EC (mS/cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | ∆h | Initial | Final | ∆EC | ||
| PW | 0 | 6.87 | 22.2 | 15.33 | 5.6 | 3.2 | 2.4 |
| OBS1 | 10m | 6.93 | 7.07 | 0.14 | 5.8 | 2.5 | 3.3 |
| OBS2 | 10m | 6.96 | 7.07 | 0.11 | 5.9 | 0.8 | 5.1 |
| OBS3 | 10m | 6.69 | 19.47 | 12.49 | 5.7 | 5.3 | 0.4 |
| OBS4 | 10m | 6.98 | 7.14 | 0.16 | 6.2 | 5.3 | 0.9 |
| IW1 * | 20m | - | - | - | 4.7 | 2.3 | 2.4 |
| IW2 | 20m | 7.05 | 7.63 | 0.58 | 4.7 | 0.7 | 4.0 |
| IW4 | 20m | 6.95 | 7.37 | 0.42 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 0.2 |
| OBS5 | 30m | 7.06 | 7.7 | 0.64 | 5.5 | 3.7 | 1.8 |
| OBS6 | 30m | 7.05 | 7.21 | 0.16 | 5.9 | 1.0 | 4.9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-H.; Hamm, S.-Y.; Ha, K.; Kim, Y.; Koh, D.-C.; Yoon, H.; Kim, S.-W. Hydrogeologic and Paleo-Geographic Characteristics of Riverside Alluvium at an Artificial Recharge Site in Korea. Water 2018, 10, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070835
Lee S-H, Hamm S-Y, Ha K, Kim Y, Koh D-C, Yoon H, Kim S-W. Hydrogeologic and Paleo-Geographic Characteristics of Riverside Alluvium at an Artificial Recharge Site in Korea. Water. 2018; 10(7):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070835
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Soo-Hyoung, Se-Yeong Hamm, Kyoochul Ha, YongCheol Kim, Dong-Chan Koh, Heesung Yoon, and Sung-Wook Kim. 2018. "Hydrogeologic and Paleo-Geographic Characteristics of Riverside Alluvium at an Artificial Recharge Site in Korea" Water 10, no. 7: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070835
APA StyleLee, S.-H., Hamm, S.-Y., Ha, K., Kim, Y., Koh, D.-C., Yoon, H., & Kim, S.-W. (2018). Hydrogeologic and Paleo-Geographic Characteristics of Riverside Alluvium at an Artificial Recharge Site in Korea. Water, 10(7), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070835






