Physical Hybrid Neural Network Model to Forecast Typhoon Floods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physical Hybrid Neural Network Model
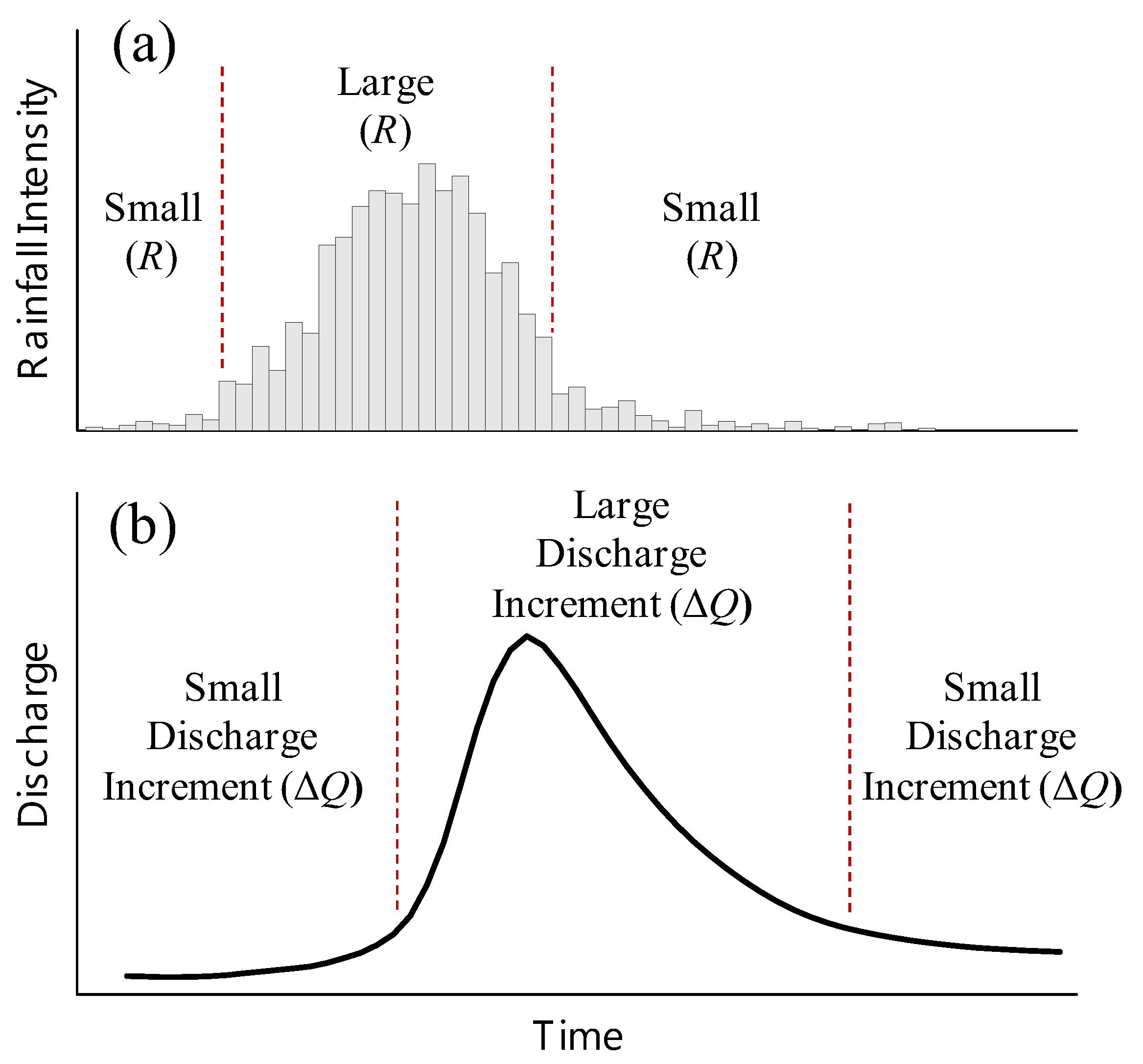
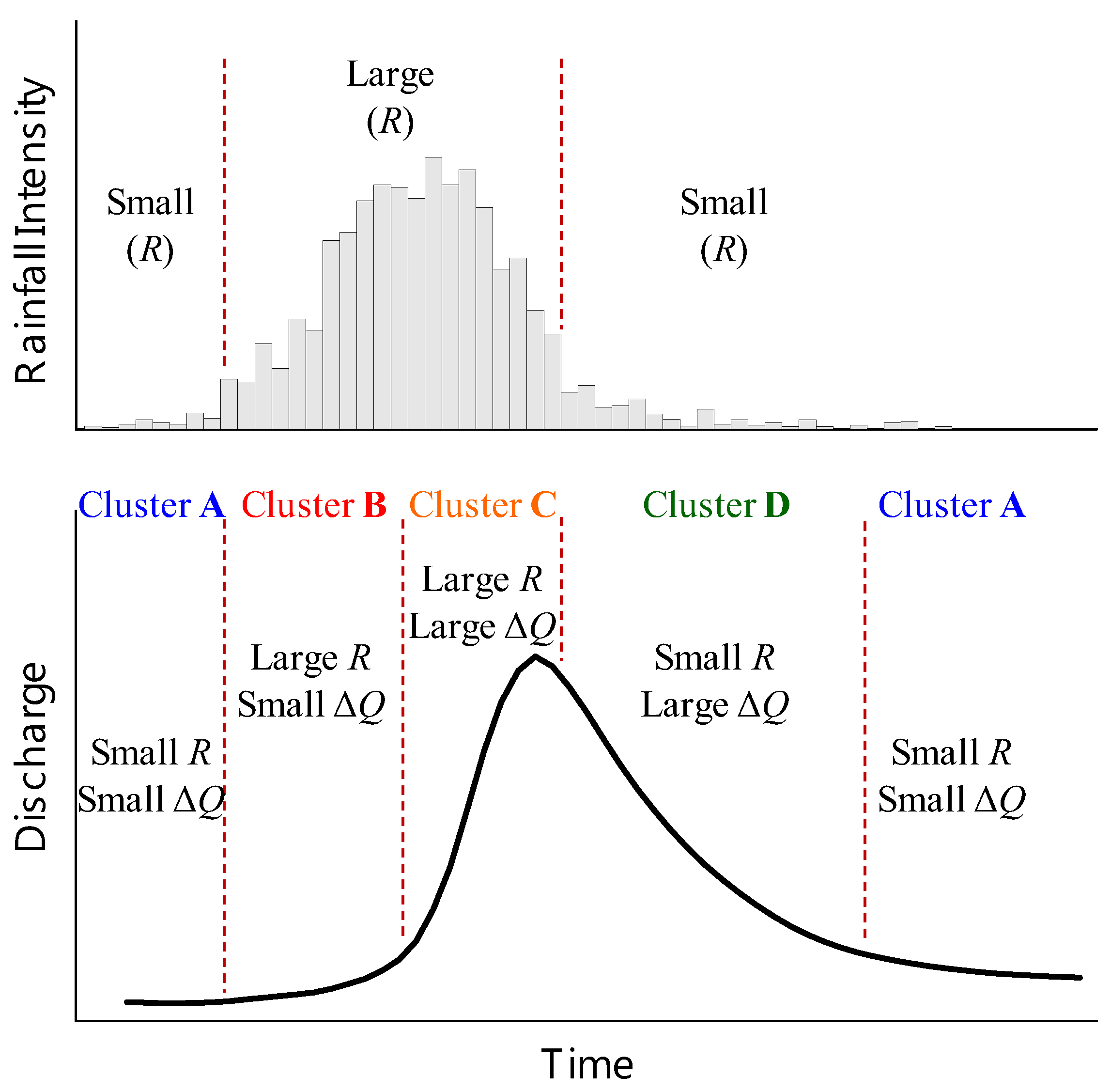
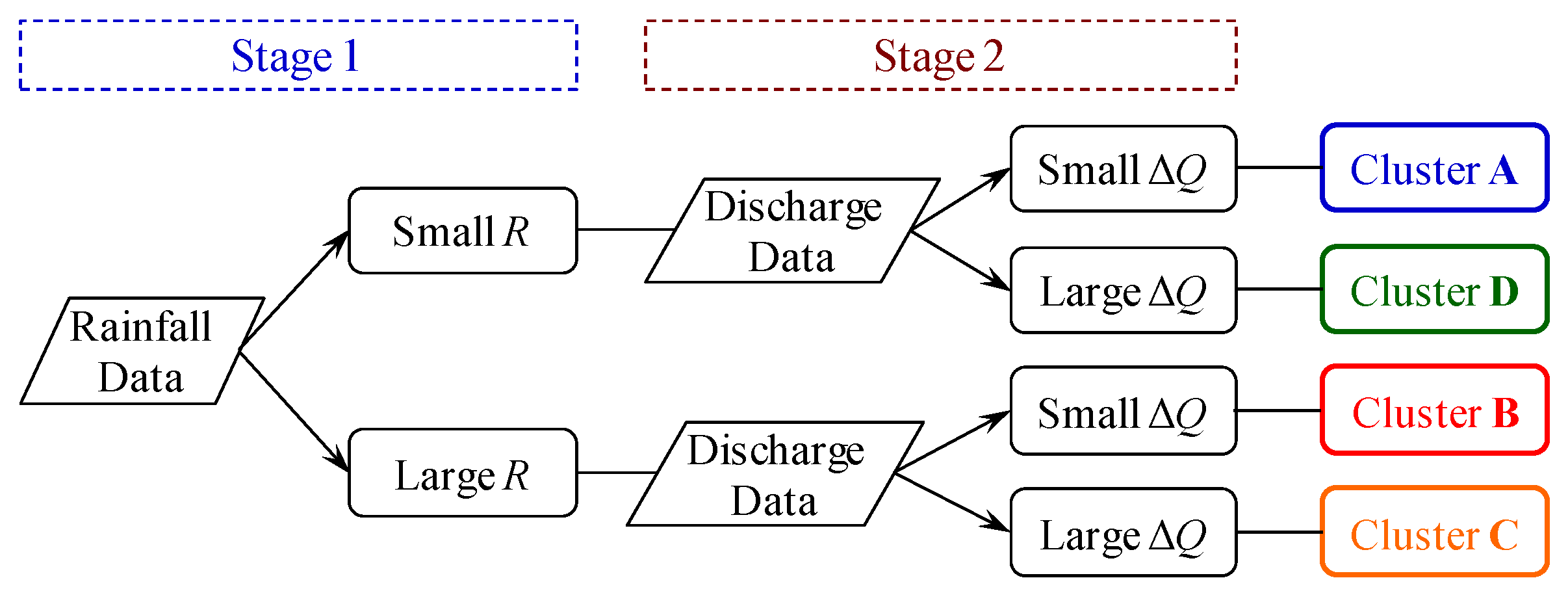
2.1. Rainfall-Runoff Clusters Based on the Hydrologic Process
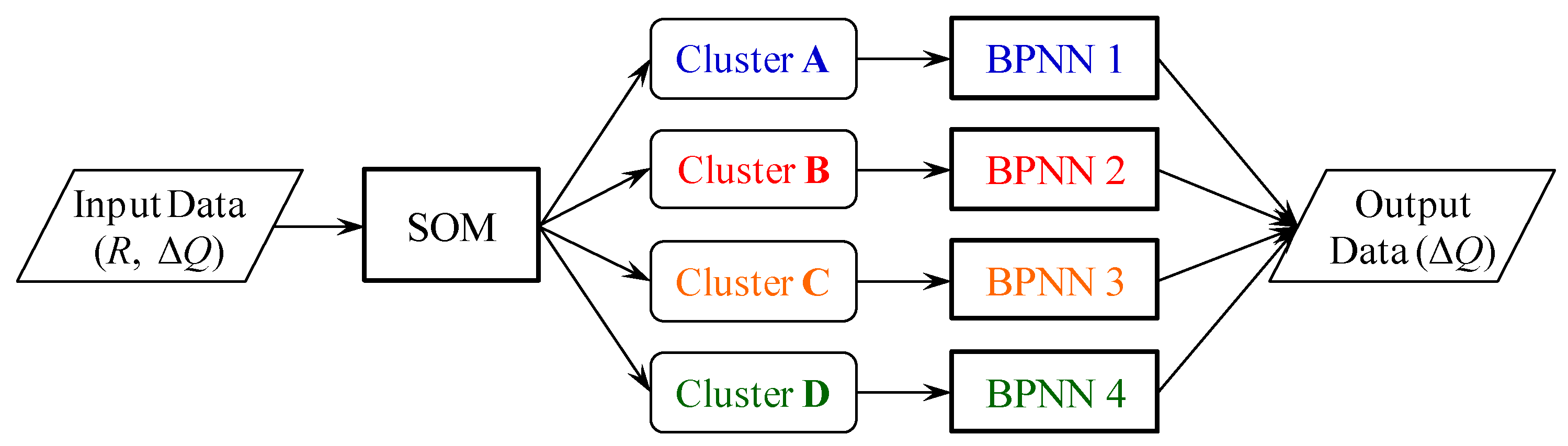
2.2. Hybrid Neural Network Model
2.2.1. SOM
2.2.2. BPNN
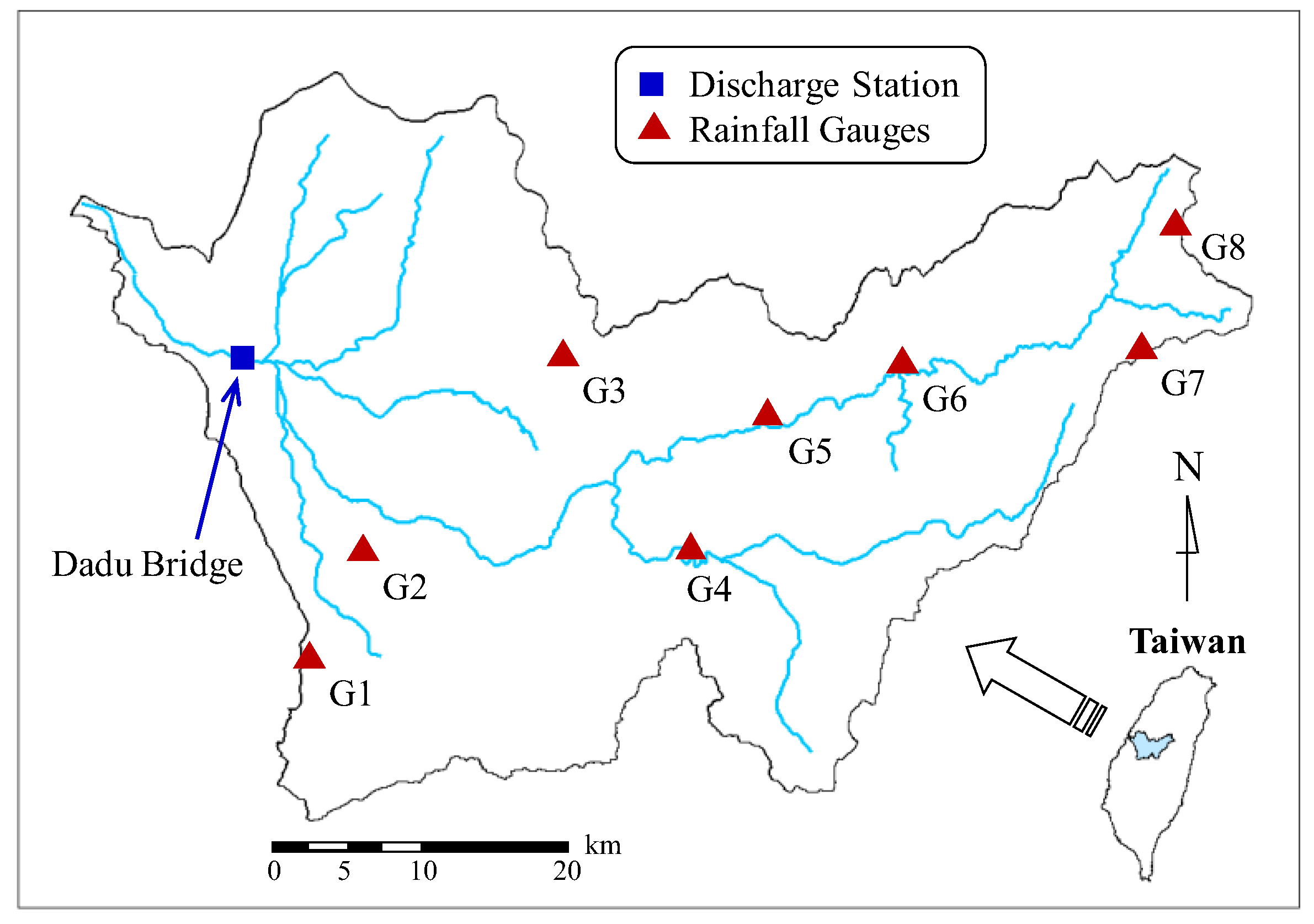
3. Study Area and Hydrologic Data
4. Model Development and Forecasting Results
4.1. Determining the Input Variables
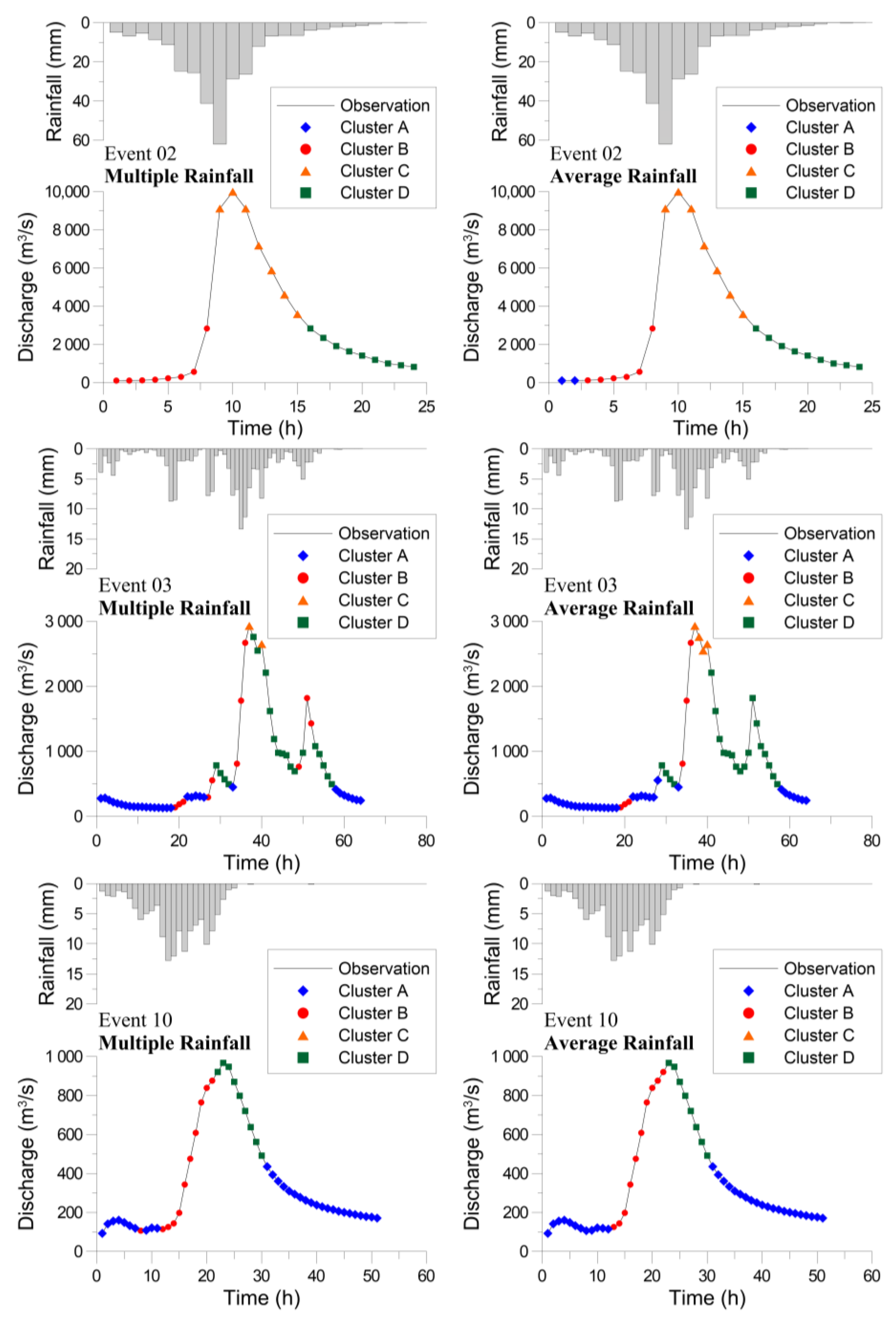
4.2. Clustering by Using the SOM
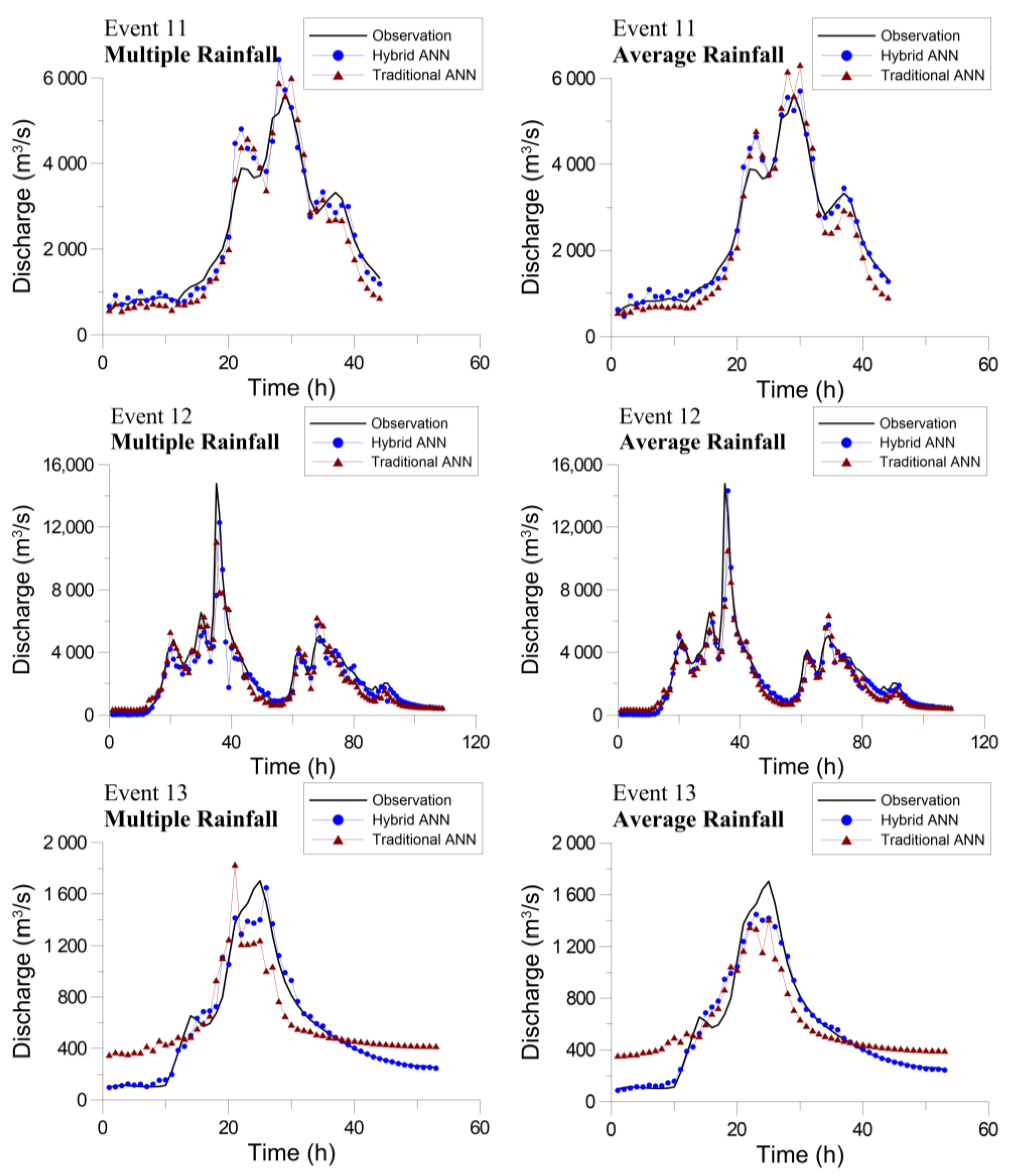
4.3. Flood Forecasting Using the Hybrid Neural Network Model
4.4. Comparison with Traditional Neural Network Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, F.J.; Chiang, Y.M.; Chang, L.C. Multi-step-ahead neural networks for flood forecasting. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2007, 52, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, C.W.; Wilby, R. An artificial neural network approach to rainfall-runoff modelling. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1998, 43, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, M.N.; Krajewski, W.F.; Cuykendall, R.R. Rainfall forecasting in space and time using a neural network. J. Hydrol. 1992, 137, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.F.; Wu, M.C. A hybrid neural network model for typhoon-rainfall forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.F.; Jhong, B.C.; Chang, C.C. Development of an effective data-driven model for hourly typhoon rainfall forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2013, 495, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, L.; Openshaw, S. Applying soft computing approaches to river level forecasting. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1999, 44, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.C.; Liu, W.C. Prediction and modelling of rainfall-runoff during typhoon events using a physically-based and artificial neural network hybrid model. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 2102–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Yu, P.S.; Liu, B.W. Comparison of neural network architectures and inputs for radar rainfall adjustment for typhoon events. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, M.; Han, D. Identification of support vector machines for runoff modeling. J. Hydroinf. 2004, 6, 265–280. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.T. Multiclass support vector classification to estimate typhoon rainfall distribution. Disaster Adv. 2013, 6, 110–121. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.T.; Yu, P.S. Real-time probabilistic forecasting of flood stages. J. Hydrol. 2007, 340, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Yu, P.S. Pruning of support vector networks on flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Chan, L.; Zhu, N. Flood forecasting using support vector machines. J. Hydroinf. 2007, 9, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.F.; Chen, G.R.; Huang, P.Y.; Chou, Y.C. Support vector machine-based models for hourly reservoir inflow forecasting during typhoon-warning periods. J. Hydrol. 2009, 372, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, S.Y.; Sivapragasam, C. Flood stage forecasting with support vector machines. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2002, 38, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.S.; Chen, S.T.; Chang, I.F. Support vector regression for real-time flood stage forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.S.; Yang, T.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Kuo, C.M.; Tseng, H.W. Comparison of random forests and support vector machine for real-time radar-derived rainfall forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, M.; Chua, L.H.C.; Quek, C.; Qin, X. A fully-online Neuro-Fuzzy model for flow forecasting in basins with limited data. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.J.; Chen, Y.C. A counterpropagation fuzzy-neural network modeling approach to real time streamflow prediction. J. Hydrol. 2001, 245, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohani, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Singh, R.D. Hydrological time series modeling: A comparison between adaptive neuro-fuzzy, neural network and autoregressive techniques. J. Hydrol. 2012, 442, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukerji, A.; Chatterjee, C.; Raghuwanshi, N.S. Flood forecasting using ANN, neuro-fuzzy, and neuro-GA models. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.C.; Sudheer, K.P.; Rangan, D.M.; Ramasastri, K.S. A neuro-fuzzy computing technique for modeling hydrological time series. J. Hydrol. 2004, 291, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.C.; Sudheer, K.P.; Rangan, D.P.; Ramasastri, K.S. Short-term flood forecasting with a neurofuzzy model. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W04004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.C.; Sudheer, K.P.; Jain, S.K. Rainfall-runoff modeling through hybrid intelligent system. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W07415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarar, A. A hybrid wavelet and neuro-fuzzy model for forecasting the monthly streamflow data. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Patuwo, B.E.; Hu, M.Y. Forecasting with artificial neural networks: The state of the art. Int. J. Forecas. 1998, 14, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, N.T. New mathematical approaches in hydrological modeling–an application of artificial neural networks. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B 1999, 24, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Sudheer, K.P.; Srinivasulu, S. Identification of physical processes inherent in artificial neural network rainfall runoff models. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T. Mining informative hydrologic data by using support vector machines and elucidating mined data according to information entropy. Entropy 2015, 17, 1023–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furundzic, D. Application example of neural networks for time series analysis: Rainfall–runoff modeling. Signal Process. 1998, 64, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahart, R.J.; See, L. Comparing neural network and autoregressive moving average techniques for the provision of continuous river flow forecasts in two contrasting catchments. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 2157–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.L.; Gupta, H.V.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S.; Imam, B. Self-organizing linear output map (SOLO): An artificial neural network suitable for hydrologic modeling and analysis. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 38-1–38-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Srinivasulu, S. Integrated approach to model decomposed flow hydrograph using artificial neural network and conceptual techniques. J. Hydrol. 2006, 317, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohonen, T. Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps. Biol. Cybern. 1982, 43, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, M.T.; Demuth, H.B.; Beale, M.H. Neural Network Design; PWS Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation; MacMillan: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.S.; Chen, B.P.T.; Chou, F.N.F.; Yang, C.C. Development and application of a decision group back-propagation neural network for flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2010, 385, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Event No. | Date | Typhoon | Total Rainfall (mm) | Peak Discharge (m3/s) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 4 August 1998 | Otto | 100.9 | 1440 | Calibration |
| 02 | 30 July 2001 | Toraji | 290.4 | 10,000 | Calibration |
| 03 | 16 September 2001 | Nari | 165.0 | 2930 | Calibration |
| 04 | 20 June 2012 | Talim | 95.5 | 1067 | Calibration |
| 05 | 1 August 2012 | Saola | 452.1 | 7199 | Calibration |
| 06 | 12 July 2013 | Soulik | 358.6 | 11,004 | Calibration |
| 07 | 21 August 2013 | Trami | 319.6 | 2011 | Calibration |
| 08 | 29 August 2013 | Kongrey | 127.0 | 1786 | Calibration |
| 09 | 7 August 2015 | Soudelor | 138.8 | 720 | Calibration |
| 10 | 28 September 2015 | Dujuan | 134.9 | 967 | Calibration |
| 11 | 31 July 1996 | Herb | 415.3 | 5630 | Validation |
| 12 | 1 July 2004 | Mindulle | 898.4 | 14,802 | Validation |
| 13 | 22 July 2014 | Matmo | 193.8 | 1704 | Validation |
| Cluster | Model I(Multiple Rainfall) | Model II(Average Rainfall) |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster A (Low R, Small ΔQ) | 222 | 231 |
| Cluster B (High R, Small ΔQ) | 98 | 89 |
| Cluster C (High R, Large ΔQ) | 33 | 35 |
| Cluster D (Low R, Large ΔQ) | 135 | 133 |
| Cluster | Rainfall (mm) | Discharge Increment (m3/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | Max. | Min. | Max. | |
| Cluster A | 0 | 4.66 | −80 | 261 |
| Cluster B | 4.67 | 45.21 | −303 | 4756 |
| Cluster C | 4.84 | 51.83 | −3170 | 6280 |
| Cluster D | 0 | 4.56 | −750 | 841 |
| Cluster | Model I(Multiple Rainfall) | Model II(Average Rainfall) |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster A (Low R, Small ΔQ) | 42 | 43 |
| Cluster B (High R, Small ΔQ) | 40 | 40 |
| Cluster C (High R, Large ΔQ) | 59 | 60 |
| Cluster D (Low R, Large ΔQ) | 65 | 62 |
| Cluster | Model I | Model II | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Hidden Nodes | Activation Function | Number of Hidden Nodes | Activation Function | |
| Cluster A (Low R, Small ΔQ) | 3 | Linear | 2 | Linear |
| Cluster B (High R, Small ΔQ) | 3 | Sigmoid | 2 | Sigmoid |
| Cluster C (High R, Large ΔQ) | 2 | Linear | 2 | Linear |
| Cluster D (Low R, Large ΔQ) | 4 | Sigmoid | 2 | Sigmoid |
| Data | Model Type | CE | MAE (m3/s) | ETP (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Model I | 0.97 | 92.9 | –0.2 |
| Model II | 0.98 | 68.2 | –0.1 | |
| Validation | Model I | 0.94 | 188.0 | 0.3 |
| Model II | 0.91 | 248.2 | 0.0 |
| Data | Model Type | CE | MAE (m3/s) | ETP (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Model I | 0.95 | 229.2 | –0.1 |
| Model II | 0.95 | 242.4 | –0.5 | |
| Validation | Model I | 0.85 | 339.8 | –1.0 |
| Model II | 0.85 | 359.1 | 0.7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jhong, Y.-D.; Chen, C.-S.; Lin, H.-P.; Chen, S.-T. Physical Hybrid Neural Network Model to Forecast Typhoon Floods. Water 2018, 10, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050632
Jhong Y-D, Chen C-S, Lin H-P, Chen S-T. Physical Hybrid Neural Network Model to Forecast Typhoon Floods. Water. 2018; 10(5):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050632
Chicago/Turabian StyleJhong, You-Da, Chang-Shian Chen, Hsin-Ping Lin, and Shien-Tsung Chen. 2018. "Physical Hybrid Neural Network Model to Forecast Typhoon Floods" Water 10, no. 5: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050632
APA StyleJhong, Y.-D., Chen, C.-S., Lin, H.-P., & Chen, S.-T. (2018). Physical Hybrid Neural Network Model to Forecast Typhoon Floods. Water, 10(5), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050632




