Data Pre-Analysis and Ensemble of Various Artificial Neural Networks for Monthly Streamflow Forecasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
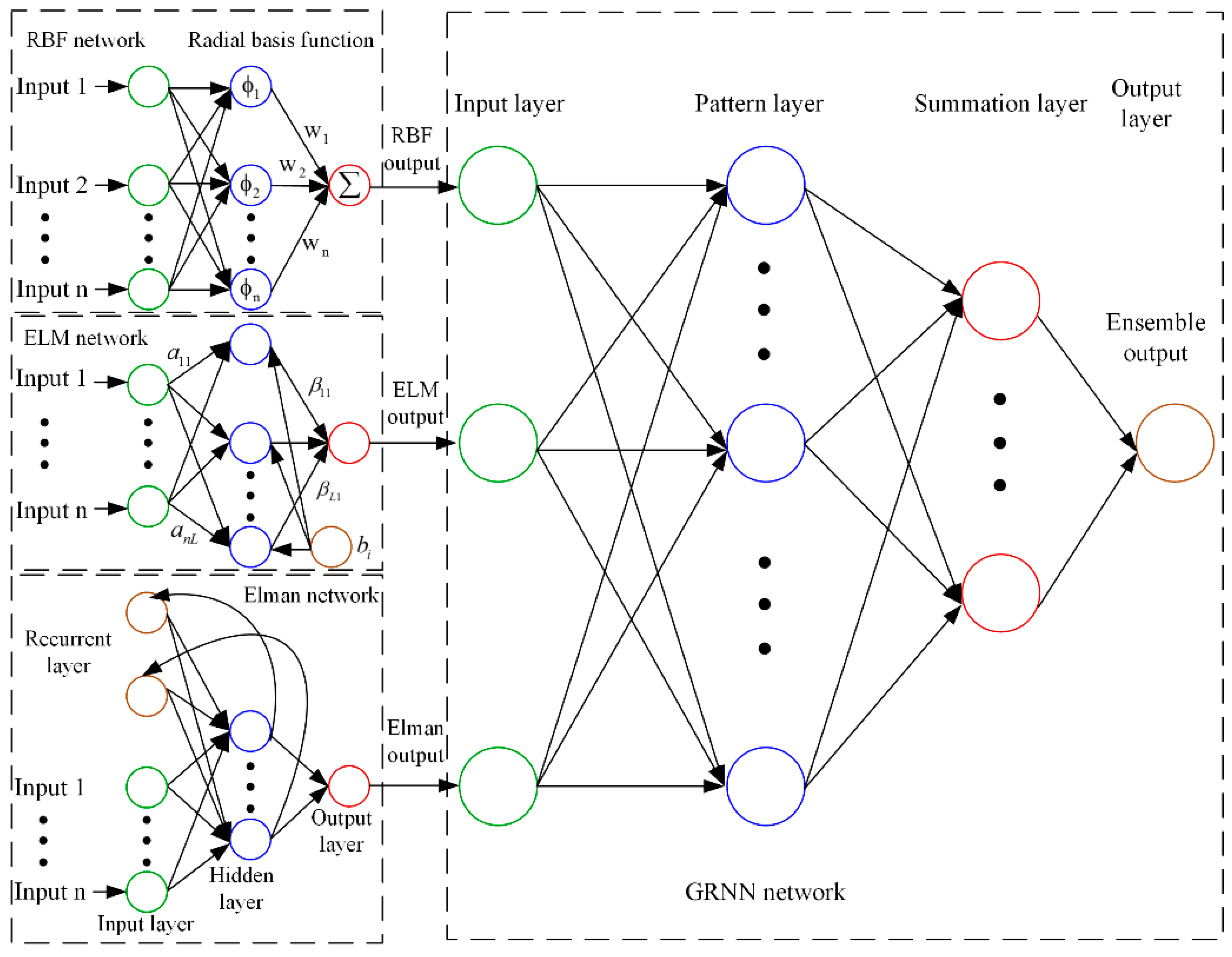
2.1. Artificial Neural Networks
2.1.1. Radial Basis Function Neural Network
2.1.2. Extreme Learning Machine
2.1.3. Elman Neural Network
2.1.4. General Regression Neural Network
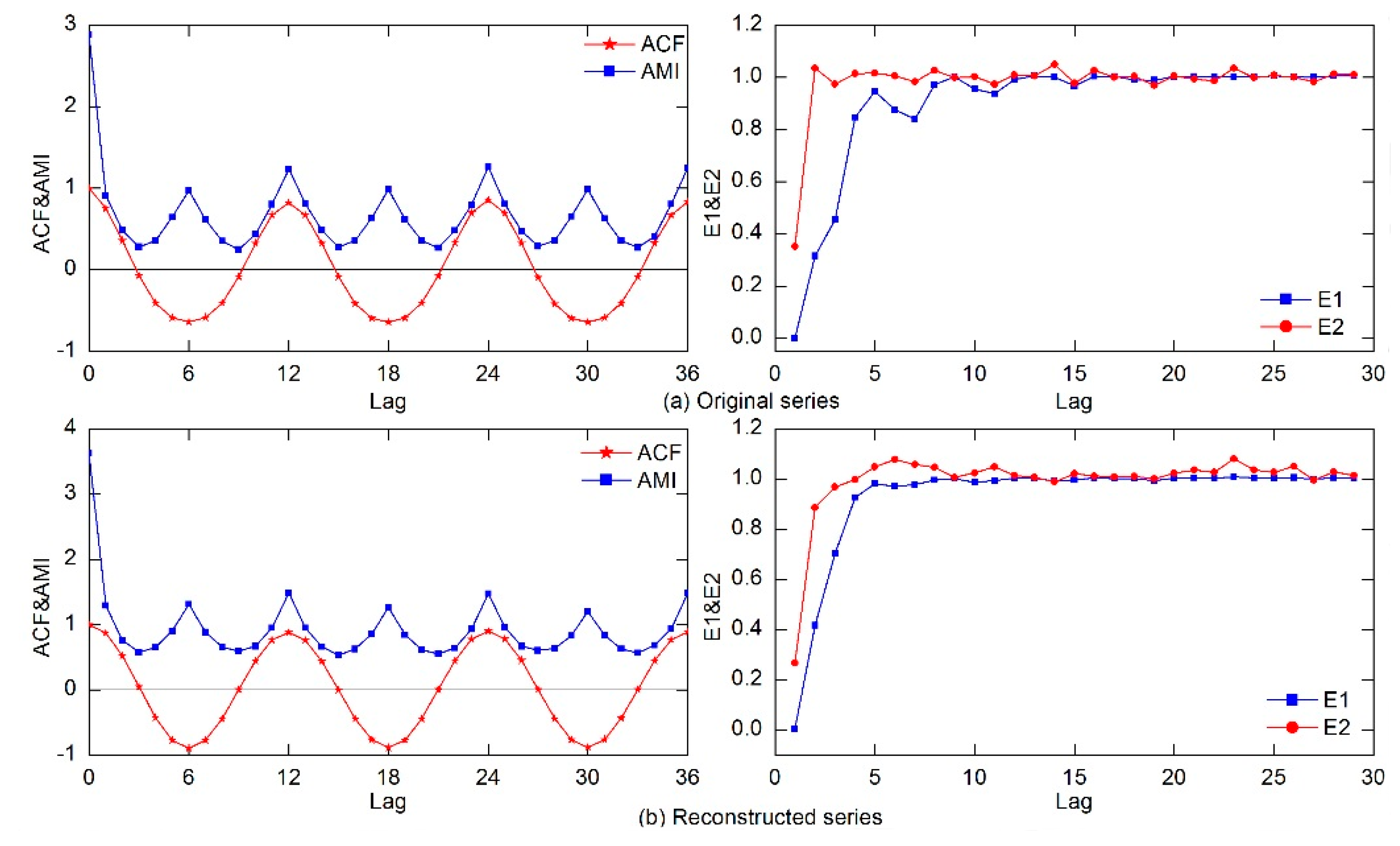
2.2. Phase Space Reconstruction
2.3. Empirical Wavelet Transform
2.4. Ensemble Techniques
2.4.1. Simple Averaging Ensemble
2.4.2. Weighted Averaging Ensemble
2.4.3. Artificial Neural Network-Based Ensemble
2.5. Model Performance Evaluation
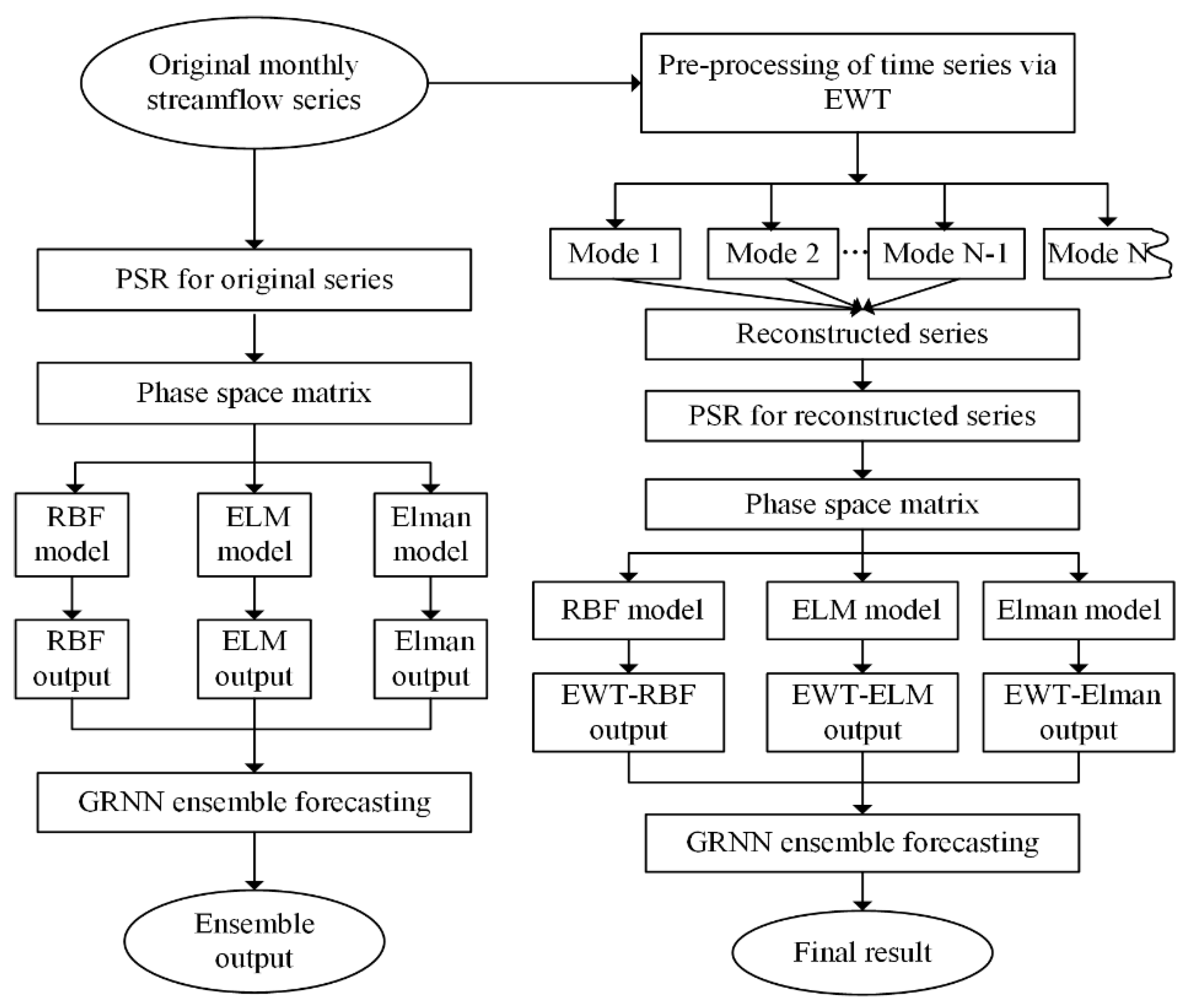
2.6. Modeling Framework
3. Model Construction and Development
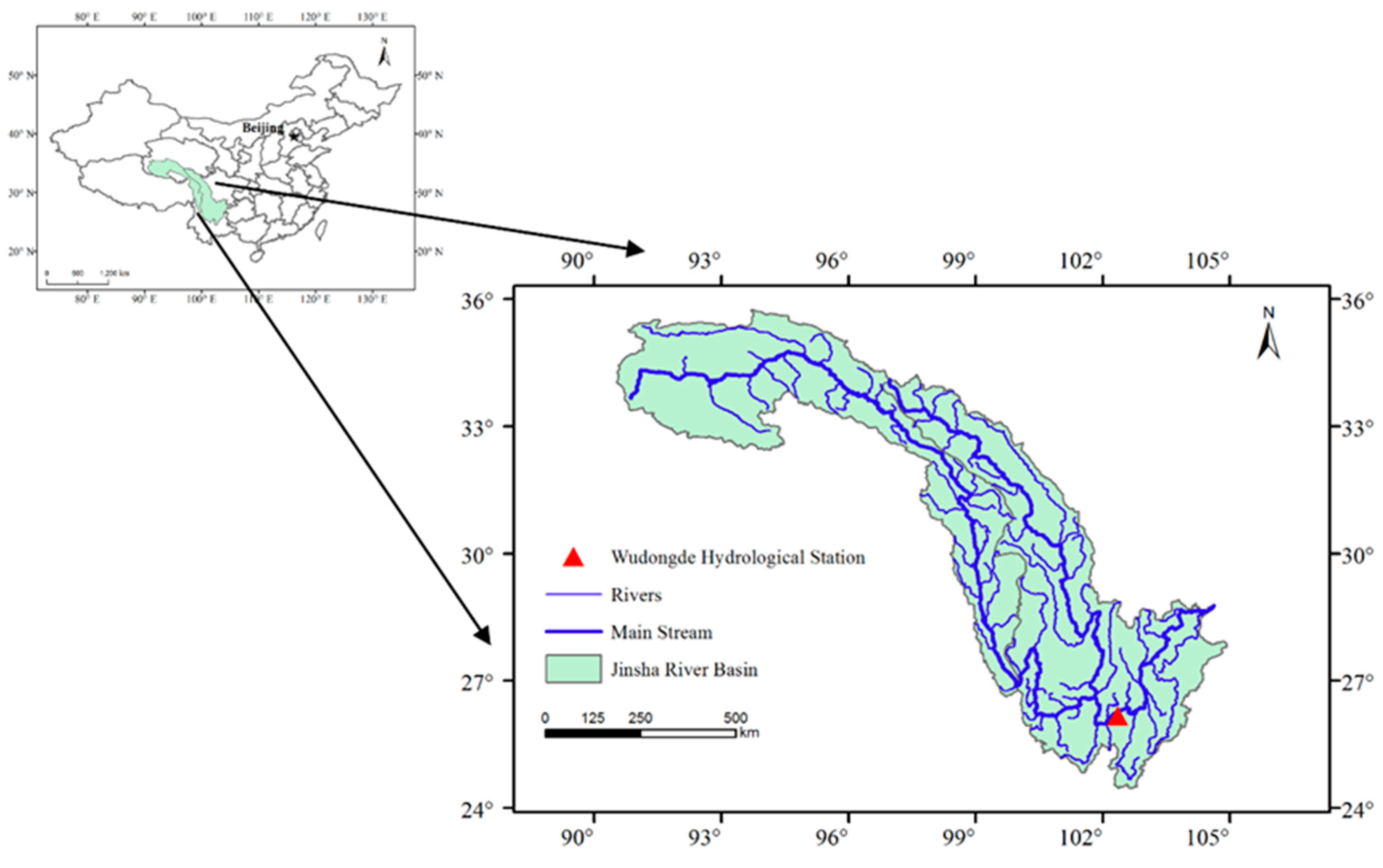
3.1. Study Area and Data Collection
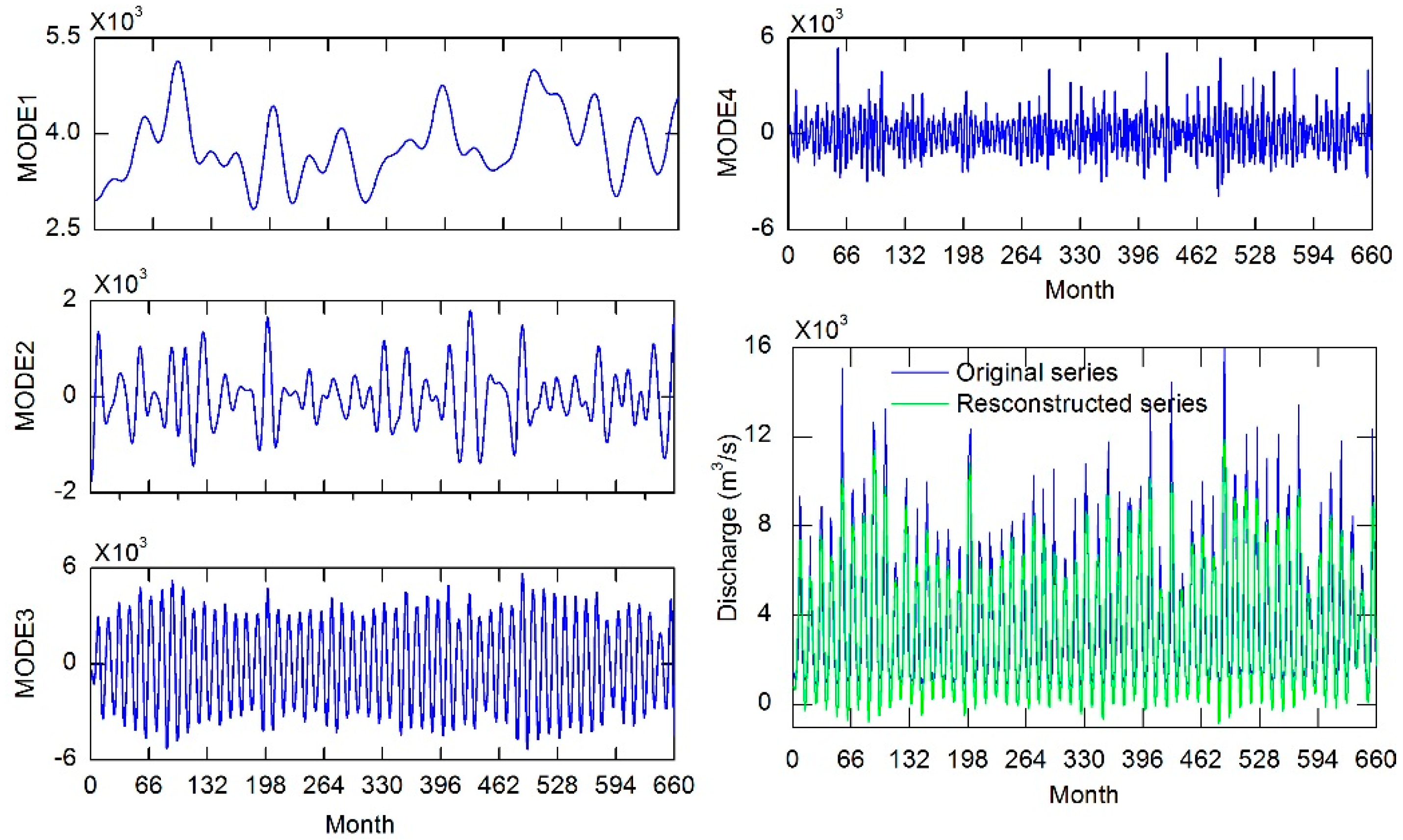
3.2. Data Preprocessing Using Empirical Wavelet Transform
3.3. Determination of Phase Space Reconstruction Parameters
3.4. Parameter Settings of Different ANNs
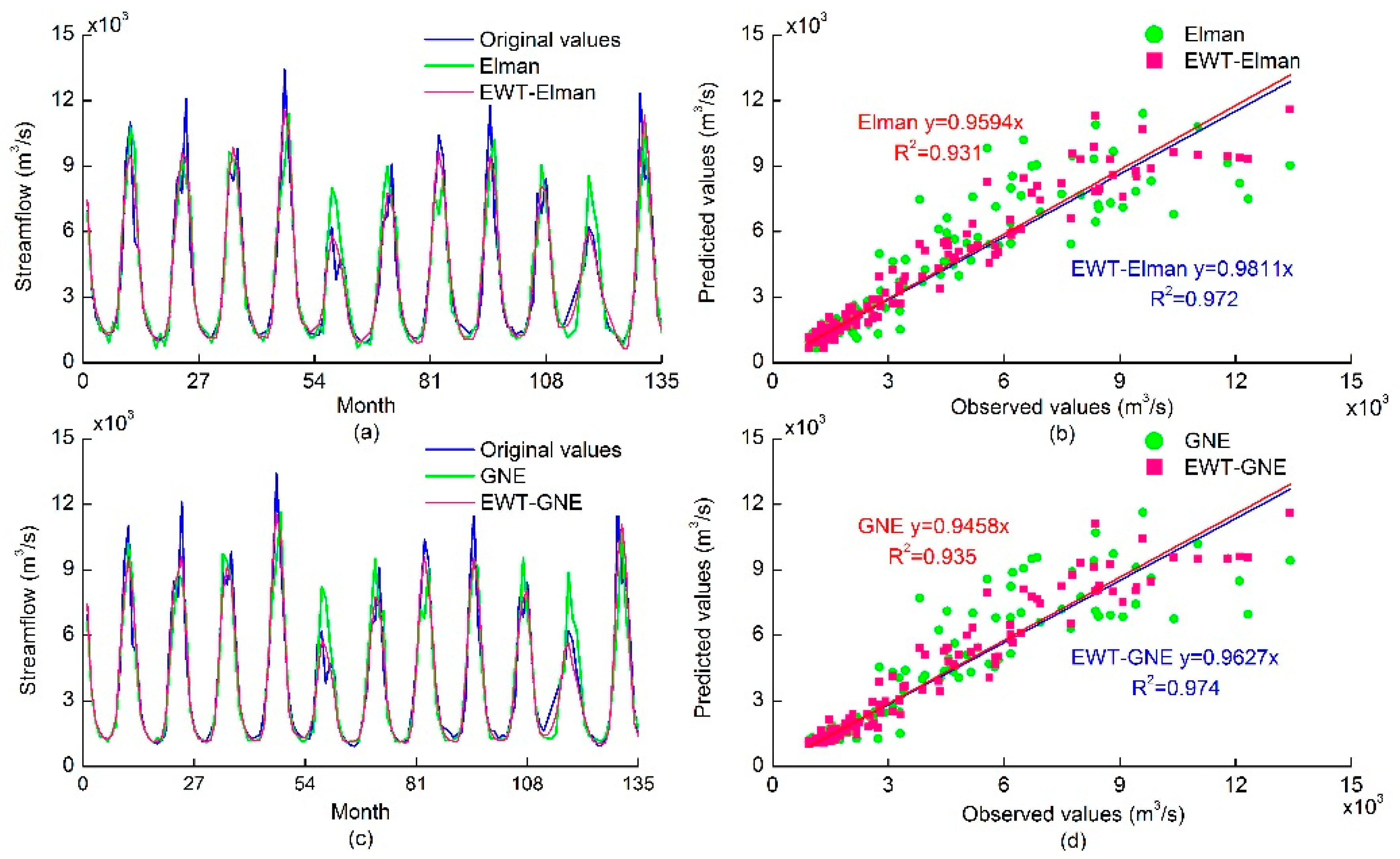
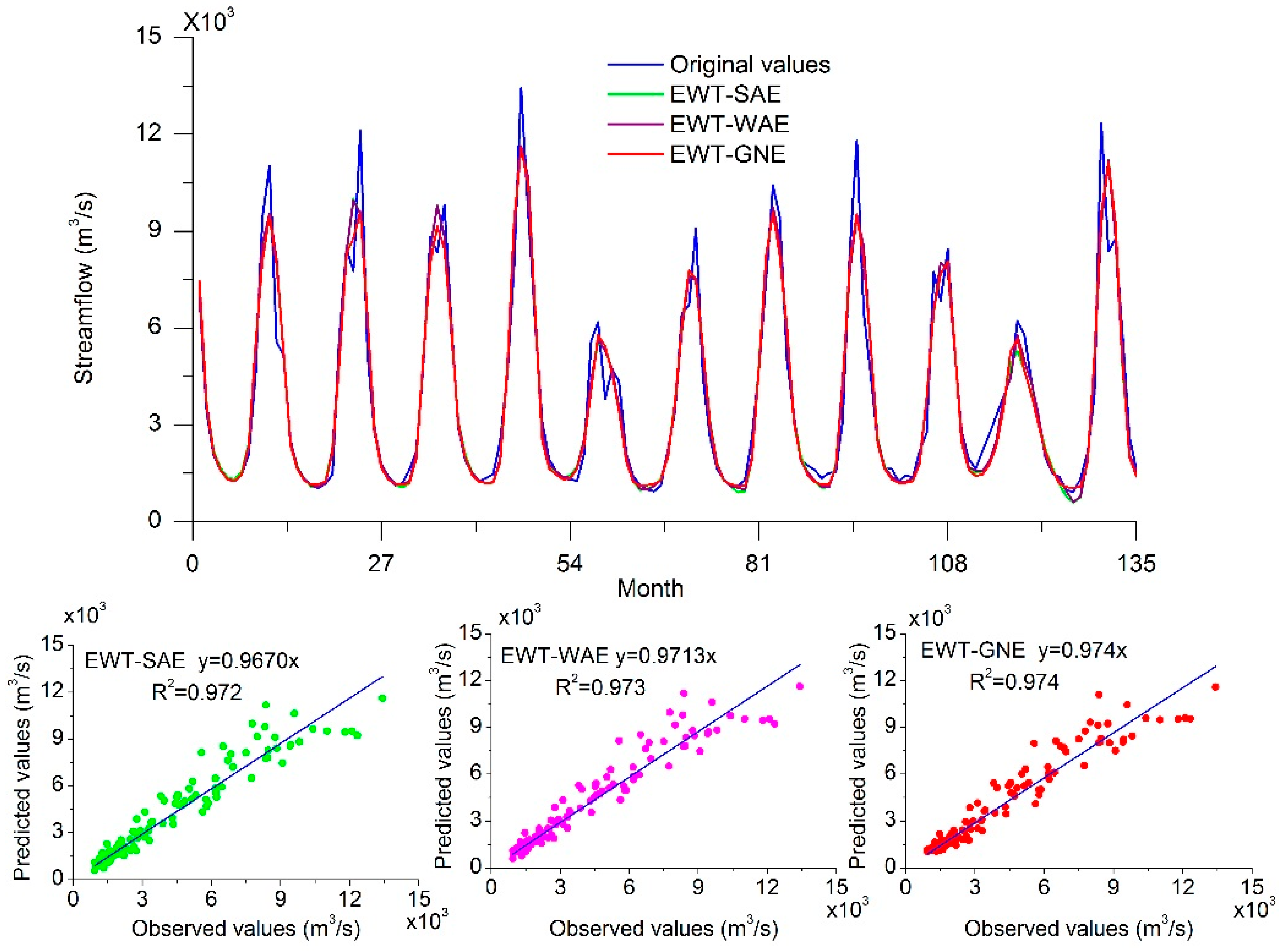
4. Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ge, S.; Yan, H.; Singh, V.P. Mid- and long-term runoff predictions by an improved phase-space reconstruction model. Environ. Res. 2016, 148, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Fu, W. Streamflow forecasting using empirical wavelet transform and artificial neural networks. Water 2017, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.C.; Pai, P.F. Potential assessment of the support vector regression technique in rainfall forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomatine, D.P.; Ostfeld, A. Data-driven modelling: Some past experiences and new approaches. J. Hydroinform. 2008, 10, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumo, D.; Viola, F.; Noto, L.V. Generation of natural runoff monthly series at ungauged sites using a regional regressive model. Water 2016, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumo, D.; Conti, F.L.; Viola, F.; Noto, L.V. An automatic tool for reconstructing monthly time-series of hydro-climatic variables at ungauged basins. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Fu, W.; Peng, T. A compound structure of ELM based on feature selection and parameter optimization using hybrid backtracking search algorithm for wind speed forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 143, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Guo, S.; Zhou, J.; Ye, L. Copula entropy coupled with artificial neural network for rainfall–runoff simulation. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 1755–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.J.; Chen, P.A.; Lu, Y.R.; Huang, E.; Chang, K.Y. Real-time multi-step-ahead water level forecasting by recurrent neural networks for urban flood control. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Moghari, S.M.; Araghinejad, S. Monthly and seasonal drought forecasting using statistical neural networks. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, F.; Yang, Z. Comparative analysis of ANN and SVM models combined with wavelet preprocess for groundwater depth prediction. Water 2017, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Singh, V. Forward prediction of runoff data in data-scarce basins with an improved ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) model. Water 2018, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Chau, K.W.; Qiu, L.; Chen, Y.B. Improving forecasting accuracy of medium and long-term runoff using artificial neural network based on EEMD decomposition. Environ. Res. 2015, 139, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zhou, J.; Ye, L.; Meng, C. Streamflow estimation by support vector machine coupled with different methods of time series decomposition in the upper reaches of Yangtze river, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Kim, S.; Kisi, O.; Singh, V.P. Daily water level forecasting using wavelet decomposition and artificial intelligence techniques. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, J. Empirical wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 3999–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, J. Short-term wind speed prediction using empirical wavelet transform and Gaussian process regression. Energy 2015, 93, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, J. A robust combination approach for short-term wind speed forecasting and analysis—Combination of the ARIMA (Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average), ELM (Extreme Learning Machine), SVM (Support Vector Machine) and LSSVM (Least Square SVM) forecasts using a GPR (Gaussian Process Regression) model. Energy 2015, 93, 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Xi, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X. An EMD-based chaotic least squares support vector machine hybrid model for annual runoff forecasting. Water 2017, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, J.; Qin, H.; Zou, Q.; Li, Q. Monthly streamflow forecasting based on improved support vector machine model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 13073–13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Luo, G.; Teng, Z.; Jia, C. Characterizing cross-scale chaotic behaviors of the runoff time series in an inland river of Central Asia. Quat. Int. 2013, 311, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Lu, W.; Xin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Yu, T. Monthly rainfall forecasting using EEMD-SVR based on phase-space reconstruction. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2311–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumo, D.; Francipane, A.; Conti, F.L.; Arnone, E.; Bitonto, P.; Viola, F.; La Loggia, G.; Noto, L.V. The SESAMO early warning system for rainfall-triggered landslides. J. Hydroinform. 2016, 18, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Suganthan, P.N.; Srikanth, N. Ensemble methods for wind and solar power forecasting—A state-of-the-art review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, R.Ž.; Sretenović, A.A.; Živković, B.D. Ensemble of various neural networks for prediction of heating energy consumption. Energy Build. 2015, 94, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.F.; Chen, L.H. A non-linear rainfall-runoff model using radial basis function network. J. Hydrol. 2004, 289, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Siew, C.K. Extreme learning machine: A new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 July 2004; Volume 982, pp. 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Elman, J.L. Finding structure in time. Cogn. Sci. 1990, 14, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, D.F. A general regression neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1991, 2, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ye, L.; Singh, V.; Asce, F.; Zhou, J.; Guo, S. Determination of input for artificial neural networks for flood forecasting using the copula entropy method. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, N.H.; Crutchfield, J.P.; Farmer, J.D.; Shaw, R.S. Geometry from a time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L. Practical method for determining the minimum embedding dimension of a scalar time series. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1997, 110, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Chau, K.W.; Fan, C. Prediction of rainfall time series using modular artificial neural networks coupled with data-preprocessing techniques. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 146–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstein, M.T.; Collins, J.J.; Luca, C.J.D. A practical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data sets. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1993, 65, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Y. Multi-step ahead wind speed forecasting using a hybrid model based on two-stage decomposition technique and AdaBoost-extreme learning machine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 153, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, C. Daily reservoir inflow forecasting using multiscale deep feature learning with hybrid models. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Models | RBF | EWT-RBF | ELM | EWT-ELM | Elman | EWT-Elman | GNE | EWT-GNE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurons | 20 | 20 | 43 | 35 | 9 | 20 | -- | -- |
| Spread | 1.4 | 1.8 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.045 | 0.029 |
| Models | RMSE (m3/s) | MAE (m3/s) | R | MAPE (%) | Models | RMSE (m3/s) | MAE (m3/s) | R | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBF | 1175.70 | 710.11 | 0.931 | 17.751 | EWT-RBF | 748.72 | 480.94 | 0.973 | 13.508 |
| ELM | 1138.34 | 711.62 | 0.935 | 19.445 | EWT-ELM | 712.07 | 462.07 | 0.975 | 13.046 |
| Elman | 1071.81 | 641.72 | 0.943 | 15.380 | EWT-Elman | 715.71 | 463.51 | 0.975 | 13.551 |
| SAE | 1103.51 | 648.95 | 0.939 | 15.513 | EWT-SAE | 711.13 | 443.49 | 0.975 | 11.362 |
| WAE | 1070.36 | 574.04 | 0.943 | 12.268 | EWT-WAE | 693.70 | 399.46 | 0.976 | 9.204 |
| GNE | 920.53 | 548.81 | 0.958 | 13.055 | EWT-GNE | 613.16 | 385.95 | 0.982 | 10.237 |
| Models | RMSE (m3/s) | MAE (m3/s) | R | MAPE (%) | Models | RMSE (m3/s) | MAE (m3/s) | R | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBF | 1351.04 | 796.64 | 0.898 | 20.342 | EWT-RBF | 854.68 | 574.94 | 0.959 | 17.446 |
| ELM | 1308.82 | 796.89 | 0.903 | 19.350 | EWT-ELM | 833.07 | 554.03 | 0.961 | 15.679 |
| Elman | 1292.60 | 796.78 | 0.906 | 20.045 | EWT-Elman | 821.11 | 543.21 | 0.962 | 14.455 |
| SAE | 1293.75 | 752.28 | 0.906 | 17.159 | EWT-SAE | 820.40 | 538.90 | 0.962 | 13.699 |
| WAE | 1264.56 | 677.82 | 0.910 | 14.016 | EWT-WAE | 796.13 | 481.35 | 0.965 | 11.410 |
| GNE | 1246.47 | 753.16 | 0.913 | 17.602 | EWT-GNE | 790.35 | 527.15 | 0.965 | 13.541 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Peng, T.; Zhang, C.; Sun, N. Data Pre-Analysis and Ensemble of Various Artificial Neural Networks for Monthly Streamflow Forecasting. Water 2018, 10, 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050628
Zhou J, Peng T, Zhang C, Sun N. Data Pre-Analysis and Ensemble of Various Artificial Neural Networks for Monthly Streamflow Forecasting. Water. 2018; 10(5):628. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050628
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jianzhong, Tian Peng, Chu Zhang, and Na Sun. 2018. "Data Pre-Analysis and Ensemble of Various Artificial Neural Networks for Monthly Streamflow Forecasting" Water 10, no. 5: 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050628
APA StyleZhou, J., Peng, T., Zhang, C., & Sun, N. (2018). Data Pre-Analysis and Ensemble of Various Artificial Neural Networks for Monthly Streamflow Forecasting. Water, 10(5), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050628




