Opportunities and Limits of Using Meteorological Reanalysis Data for Simulating Seasonal to Sub-Daily Water Temperature Dynamics in a Large Shallow Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
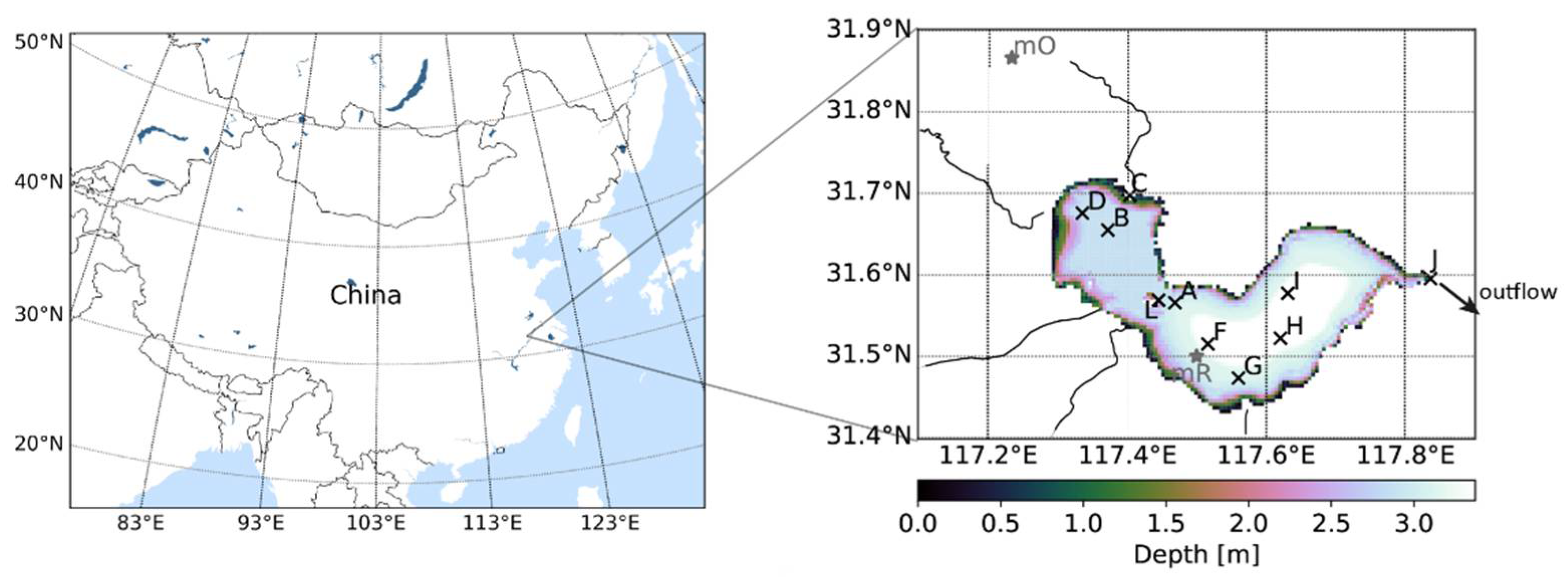
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Lake Model
2.3. Atmospheric Forcing Data
2.4. In-Lake Measurements
2.5. Analysis
3. Results
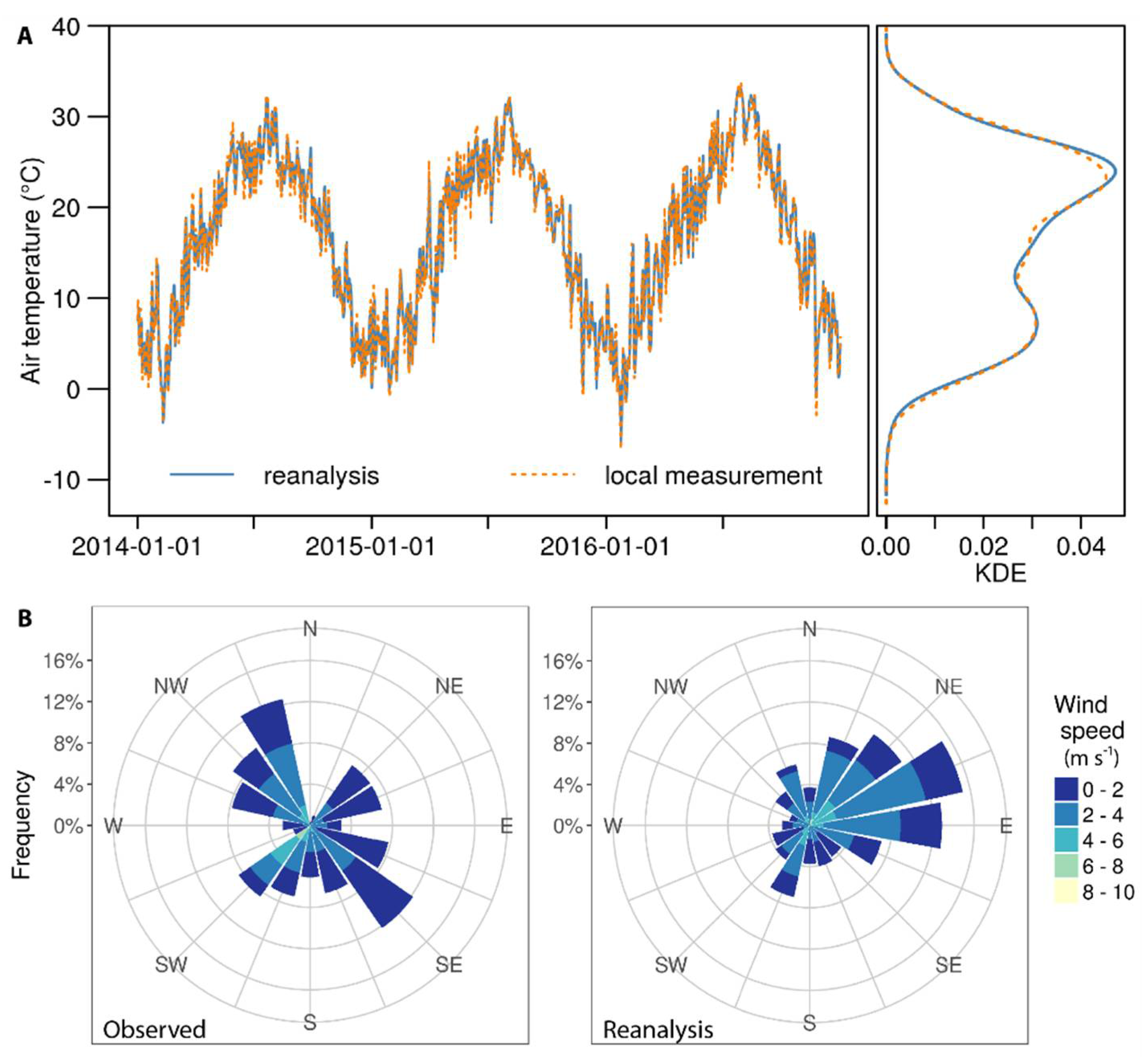
3.1. Meteorological Data
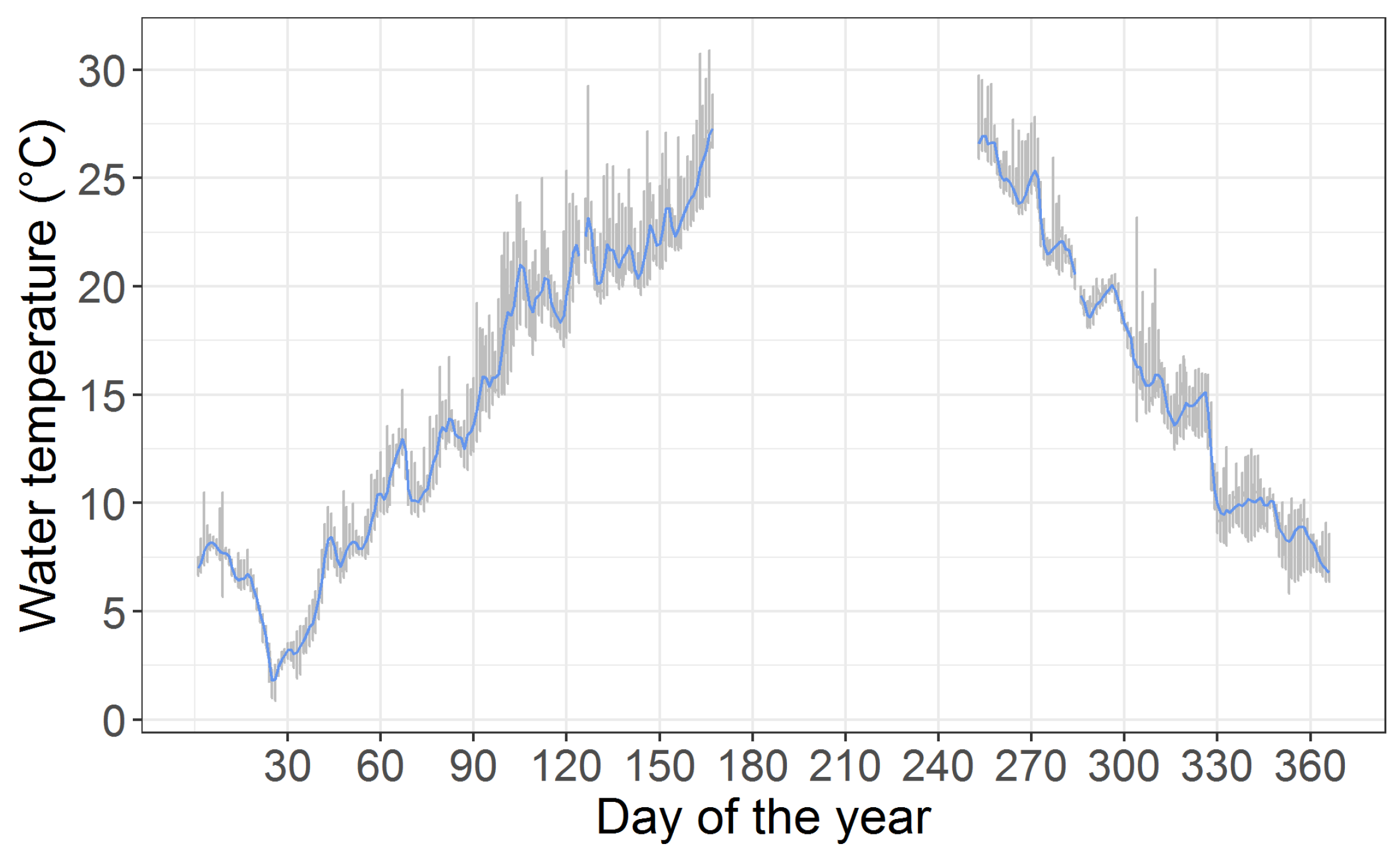
3.2. Field Observations
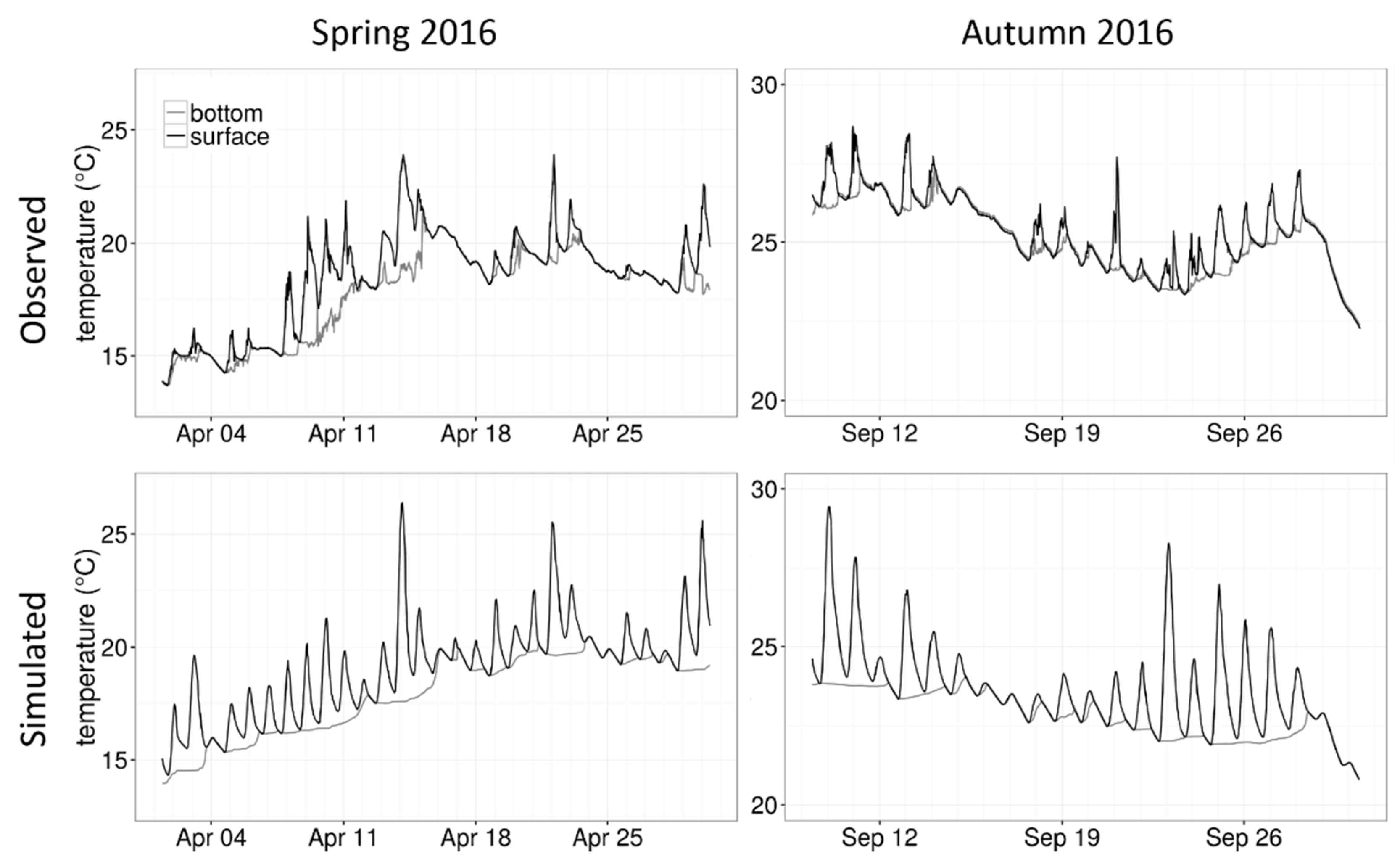
3.3. Simulation Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Applicability of Reanalysis Data in Hydrodynamic Lake Simulations
4.2. Water Temperature Data
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheffer, M. Ecology of Shallow Lakes, 1st ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Messager, M.L.; Lehner, B.; Grill, G.; Nedeva, I.; Schmitt, O. Estimating the volume and age of water stored in global lakes using a geo-statistical approach. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toffolon, M.; Piccolroaz, S.; Majone, B.; Soja, A.; Peeters, F.; Schmid, M.; Wüest, A. Prediction of surface temperature in lakes with different morphology using air temperature. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 2185–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Jones, I.D.; Maberly, S.C.; French, J.R.; Livingstone, D.M.; Monteith, D.T.; Simpson, G.L.; Thackeray, S.J.; Andersen, M.R.; Battarbee, R.W.; et al. Diel Surface Temperature Range Scales with Lake Size. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolway, R.I.; Meinson, P.; Nõges, P.; Jones, I.D.; Laas, A. Atmospheric stilling leads to prolonged thermal stratification in a large shallow polymictic lake. Clim. Chang. 2017, 141, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 1993, 32, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigosi, A.; Carey, C.C.; Ibelings, B.W.; Brookes, J.D. The interaction between climate warming and eutrophication to promote cyanobacteria is dependent on trophic state and varies among taxa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.V.M.; Los, H.F.J.; van der Molen, D.T.; Mooij, W.M. Fuzzy modeling of cyanobacterial surface waterblooms: Validation with NOAA-AVHRR satellite images. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 1456–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Cardoso, L.; da Motta Marques, D. Hydrodynamics-driven plankton community in a shallow lake. Aquat. Ecol. 2007, 43, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Feng, T.; Wang, P.; Hou, J.; Qian, J. Understanding the transport feature of bloom-forming Microcystis in a large shallow lake: A new combined hydrodynamic and spatially explicit agent-based modelling approach. Ecol. Model. 2017, 343, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocaniov, S.A.; Scavia, D. Temporal and spatial dynamics of large lake hypoxia: Integrating statistical and three-dimensional dynamic models to enhance lake management criteria. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 4247–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Liu, J.; Deng, J.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y. Meteorological and hydrological conditions driving the formation and disappearance of black blooms, an ecological disaster phenomena of eutrophication and algal blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of constituent retrieval in optically deep and complex waters from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnhöfer, K.; Oppelt, N. Remote sensing for lake research and monitoring—Recent advances. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 64, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilioli, E. Preface. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.; Kutser, T.; Hunter, P.D. Remote sensing of inland waters: Challenges, progress and future directions Remote Sensing of Environment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R. Ecology’s remote-sensing revolution. Nature 2018, 556, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooij, W.M.; Trolle, D.; Jeppesen, E.; Arhonditsis, G.; Belolipetsky, P.V.; Chitamwebwa, D.B.R.; Degermendzhy, A.G.; DeAngelis, D.L.; De Senerpont Domis, L.N.; Downing, A.S.; et al. Challenges and opportunities for integrating lake ecosystem modelling approaches. Aquat. Ecol. 2010, 44, 633–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, J.C. Modeling the oceanic general circulation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1996, 28, 215–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, B.R.; Imberger, J.; Saggio, A.; Winters, K.B. Modeling basin-scale internal waves in a stratified lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1603–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, F.J.; Schladow, S.G. Quantitative Comparison of Models for Barotropic Response of Homogeneous Basins. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 128, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appt, J.; Imberger, J.; Kobus, H. Basin-scale motion in stratified Upper Lake Constance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocaniov, S.A.; Ullmann, C.; Rinke, K.; Lamb, K.G.; Boehrer, B. Internal waves and mixing in a stratified reservoir: Insights from three-dimensional modeling. Limnologica 2014, 49, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, G.; Cantelli, A.; Monti, P.; Leuzzi, G. A modeling approach to identify the effective forcing exerted by wind on a prealpine lake surrounded by a complex topography. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 4036–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaghi, S.; Hondzo, M. Evaluation and application of a three-dimensional water quality model in a shallow lake with complex morphometry. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 1512–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, E.; Guyennon, N.; Hamilton, D.; Valsecchi, L.; Manfredi, E.C.; Viviano, G.; Salerno, F.; Tartari, G.; Copetti, D. Coupling high-resolution measurements to a three-dimensional lake model to assess the spatial and temporal dynamics of the cyanobacterium Planktothrix rubescens in a medium-sized lake. Hydrobiologia 2012, 698, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffolon, M.; Serafini, M. Effects of artificial hypolimnetic oxygenation in a shallow lake. Part 2: Numerical modelling. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 114, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Carey, C.C.; Little, J.C.; Lofton, M.E.; McClure, R.P.; Lei, C. Effectiveness of a bubble-plume mixing system for managing phytoplankton in lakes and reservoirs. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 113, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, L.F.; Smith, R.E.; Romero, J.R.; Hecky, R.E. Lake Erie hypoxia simulations with ELCOM-CAEDYM. In Proceedings of the 3rd Biennial Meeting of the International Environmental Modelling and Software Society, Burlington, VT, USA, 9–13 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, K.-R.; Ji, Z.-G. Application and Validation of Three-Dimensional Model in a Shallow Lake. J. Waterway Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2005, 131, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G. Forecasting short-term cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Taihu, China, using a coupled hydrodynamic–algal biomass model. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Li, Y.; Acharya, K. Modeling the effects of external nutrient reductions on algal blooms in hyper-eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.B.; de Jager, V.C.; Janse, J.H.; Kong, X.; Liu, S.; Ye, Q.; Mooij, W.M. Spatial identification of critical nutrient loads of large shallow lakes: Implications for Lake Taihu (China). Water Res. 2017, 119, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W. A review of the models for Lake Taihu and their application in lake environmental management. Ecol. Model. 2016, 319, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, M.D.; Anderson, E.J.; Wynne, T.T.; Stumpf, R.P.; Fanslow, D.L.; Kijanka, K.; Vanderploeg, H.A.; Strickler, J.R.; Davis, T.W. Vertical distribution of buoyant Microcystis blooms in a Lagrangian particle tracking model for short-term forecasts in Lake Erie. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 5296–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtermann, P.L.; Burchard, H.; Graewe, U.; Klingbeil, K.; Umlauf, L. Deep-water dynamics and boundary mixing in a nontidal stratified basin: A modeling study of the Baltic Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 1465–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingbeil, K.; Lemarié, F.; Debreu, L.; Burchard, H. The numerics of hydrostatic structured-grid coastal ocean models: State of the art and future perspectives. Ocean Model. 2018, 125, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umlauf, L.; Lemmin, U. Interbasin exchange and mixing in the hypolimnion of a large lake: The role of long internal waves. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becherer, J.K.; Umlauf, L. Boundary mixing in lakes: 1. Modeling the effect of shear-induced convection. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116, C10017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräwe, U.; Holtermann, P.; Klingbeil, K.; Burchard, H. Advantages of vertically adaptive coordinates in numerical models of stratified shelf seas. Ocean Model. 2015, 92, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingbeil, K.; Burchard, H. Implementation of a direct nonhydrostatic pressure gradient discretisation into a layered ocean model. Ocean Model. 2013, 65, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umlauf, L.; Burchard, H. Second-order turbulence closure models for geophysical boundary layers: A review of recent work. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 795–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtermann, P.; Burchard, H.; Jennerjahn, T. Hydrodynamics of the Segara Anakan lagoon. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2009, 9, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 2; National Center For Atmospheric Research, Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology Division: Boulder, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, F.; Mearns, L.O. Approaches to the simulation of regional climate change: A review. Rev. Geophys. 1991, 29, 191–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.L.; Gao, S.B. Impact of different reanalysis data on WRF dynamical downscaling over China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 200, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehlík, J.; Bárdossy, A. Multivariate stochastic downscaling model for generating daily precipitation series based on atmospheric circulation. J. Hydrol. 2002, 256, 120–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrisford, P.; Dee, D.P.; Poli, P.; Brugge, R.; Fielding, K.; Fuentes, M.; Kållberg, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A. The ERA-Interim Archive; ERA Report Series, No. 2; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Layden, A.; MacCallum, S.N.; Merchant, C.J. Determining lake surface water temperatures worldwide using a tuned one-dimensional lake model (Flake, v1). Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 2167–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Lorke, A.; Wüest, A.; Halbwachs, M.; Tanyileke, G. Development and sensitivity analysis of a model for assessing stratification and safety of Lake Nyos during artificial degassing. Ocean Dyn. 2003, 53, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Piccolroaz, S.; Toffolon, M. Deep water renewal in Lake Baikal: A model for long-term analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 6717–6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Schwab, D.J.; Hu, S. An investigation of the thermal response to meteorological forcing in a hydrodynamic model of Lake Superior. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 5233–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wei, L.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.; Kong, F. Spatial and seasonal shifts in bloom-forming cyanobacteria in Lake Chaohu: Patterns and driving factors. Phycol. Res. 2016, 64, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-R.; Meng, W.; Jin, X.-C.; Zheng, B.-H.; Zhang, L.; Xi, H.-Y. Ecological security problems of the major key lakes in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3825–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, M.; Duan, H.; Loiselle, S.; Xu, J. Fourteen-Year Record (2000–2013) of the Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Floating Algae Blooms in Lake Chaohu, Observed from Time Series of MODIS Images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10523–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, K.; Chen, C.; Bilke, L.; Liao, Z.; Rinke, K.; Frassl, M.; Yue, T.; Kolditz, O. Virtual geographic environments for water pollution control. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 11, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Yin, B. Eutrophication of Lake Waters in China: Cost, Causes, and Control. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; He, Q.; Yang, B.; He, W.; Xu, F.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Kuiper, J.J.; van Gerven, L.P.A.; Qin, N.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Hydrological regulation drives regime shifts: Evidence from paleolimnology and ecosystem modeling of a large shallow Chinese lake. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yan, R.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, L. Modeling the impacts of water transfer on water transport pattern in Lake Chao, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingbeil, K.; Mohammadi-Aragh, M.; Gräwe, U.; Burchard, H. Quantification of spurious dissipation and mixing—Discrete variance decay in a Finite-Volume framework. Ocean Model. 2014, 81, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Liu, Q.-Q. Numerical study of hydrodynamic process in Chaohu Lake. J. Hydrodyn. 2015, 27, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idso, S.B.; Jackson, R.D. Thermal radiation from the atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1969, 74, 5397–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipsey, M.R.; Bruce, L.C.; Hamilton, D.P. GLM-General Lake Model: Model Overview and User Information; The University of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, N.; Eber, L.; Laurs, R.; Renner, J.; Saur, J. Heat Exchange between Ocean and Atmosphere in the Eastern North Pacific for 1961–71; US Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1974.
- Kondo, J. Air-sea bulk transfer coefficients in diabatic conditions. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1975, 9, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Pre-classification improves relationships between water clarity, light attenuation, and suspended particulates in turbid inland waters. Hydrobiologia 2013, 711, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, N.; Wendler, G.; Curtis, J. The Urban Heat Island Effect at Fairbanks, Alaska. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1999, 64, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menne, M.J.; Durre, I.; Vose, R.S.; Gleason, B.E.; Houston, T.G. An Overview of the Global Historical Climatology Network-Daily Database. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerimoglu, O.; Rinke, K. Stratification dynamics in a shallow reservoir under different hydro-meteorological scenarios and operational strategies. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 7518–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.R.; Sand-Jensen, K.; Woolway, I.R.; Jones, I.D. Profound daily vertical stratification and mixing in a small, shallow, wind-exposed lake with submerged macrophytes. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 79, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Clouds and Aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Balsamo, G.; Salgado, R.; Dutra, E.; Boussetta, S.; Stockdale, T.; Potes, M. On the contribution of lakes in predicting near-surface temperature in a global weather forecasting model. Tellus A 2012, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivapalan, M. Prediction in ungauged basins: A grand challenge for theoretical hydrology. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 3163–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrachowitz, M.; Savenije, H.; Blöschl, G.; McDonnell, J.; Sivapalan, M.; Pomeroy, J.; Arheimer, B.; Blume, T.; Clark, M.; Ehret, U.; et al. A decade of Predictions in Ungauged Basins (PUB)—A review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1198–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Tao, M.; Loiselle, S.A.; Zhao, W.; Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Tang, X. MODIS observations of cyanobacterial risks in a eutrophic lake: Implications for long-term safety evaluation in drinking-water source. Water Res. 2017, 122, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, G.; Shang, J. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Eutrophication in Western Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 130, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hupfer, M.; Lewandowski, J. Oxygen Controls the Phosphorus Release from Lake Sediments—A Long-Lasting Paradigm in Limnology. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2008, 93, 415–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, J.; Bolding, K. A general framework for aquatic biogeochemical models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 61, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on April 2017).
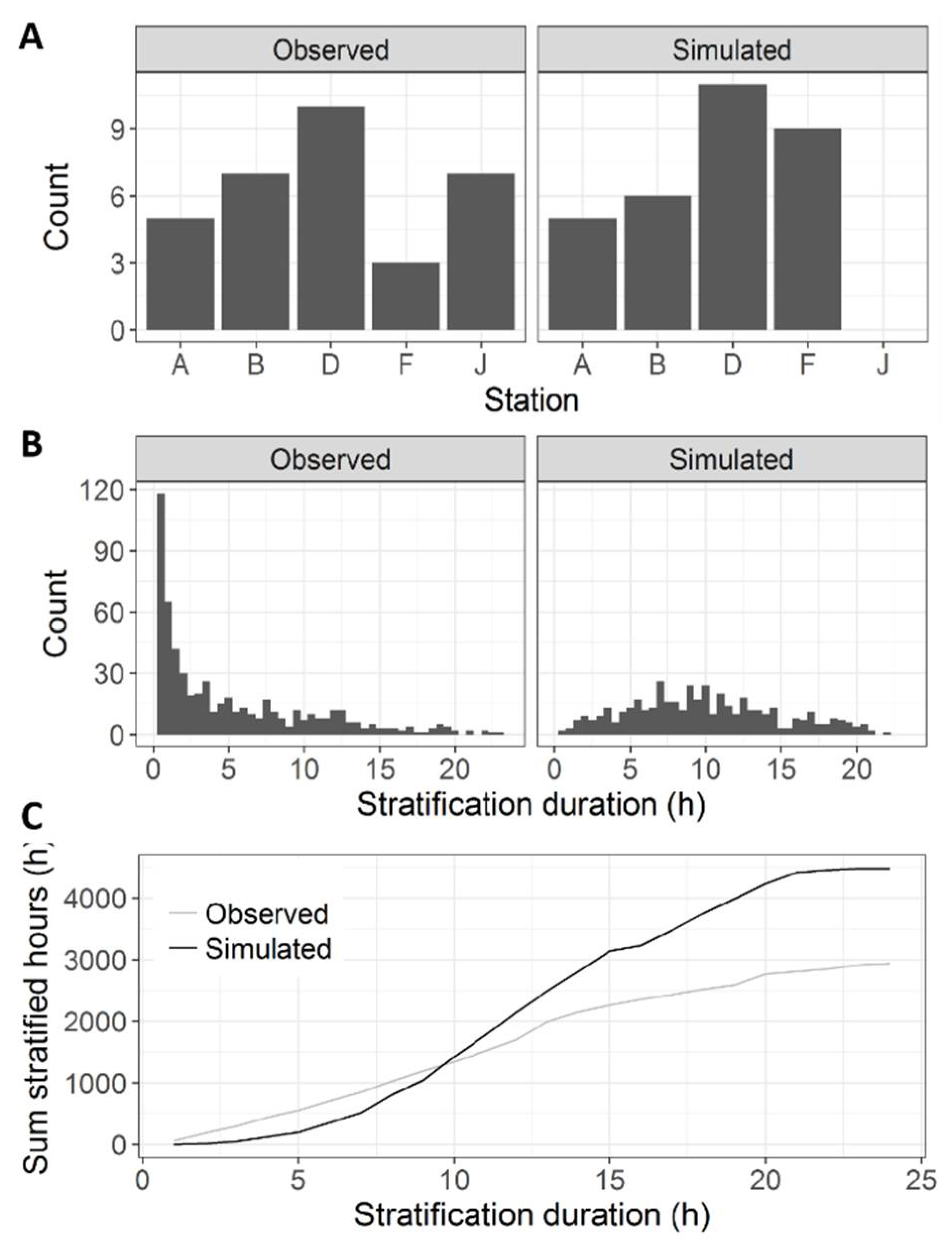
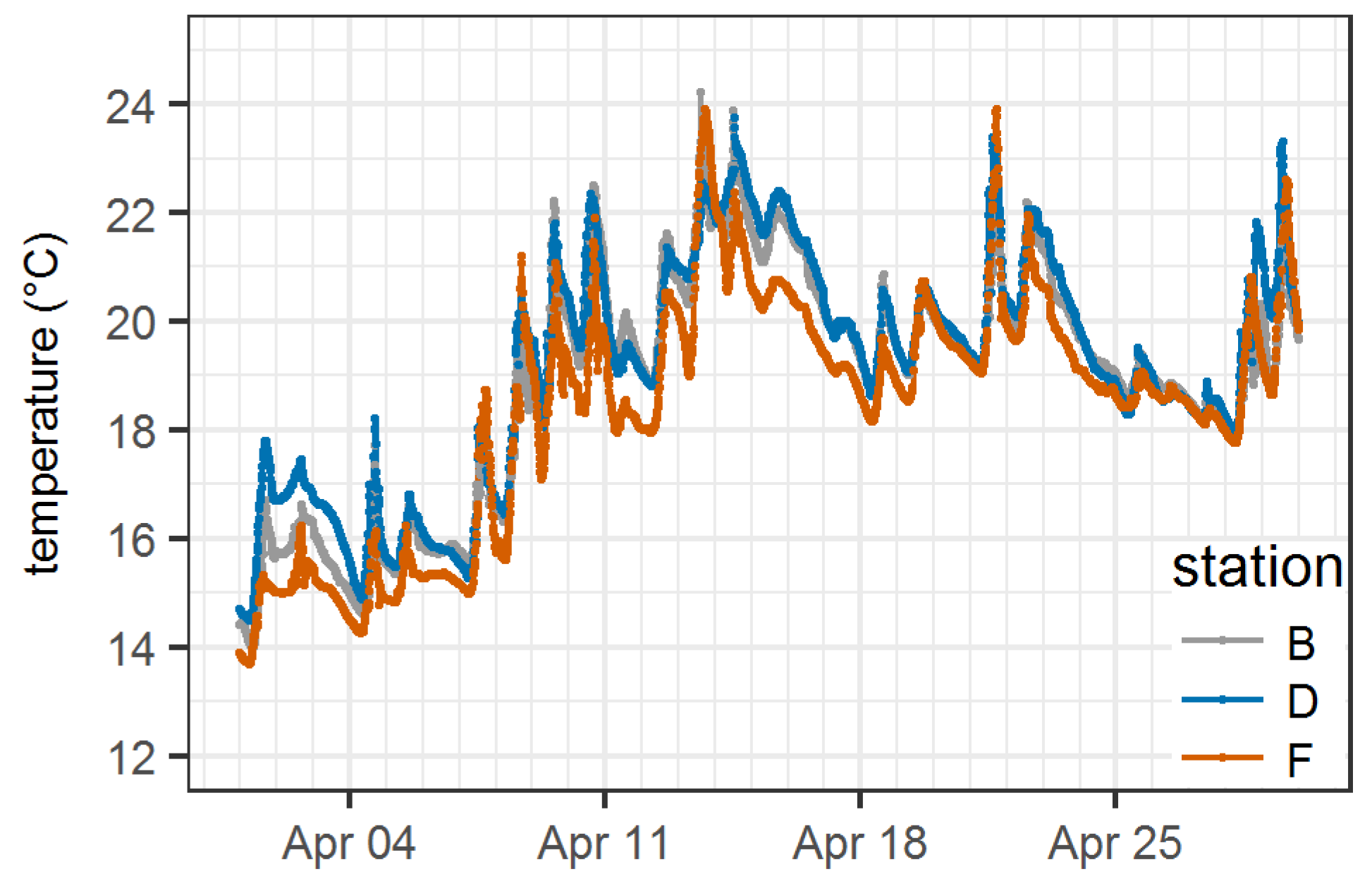
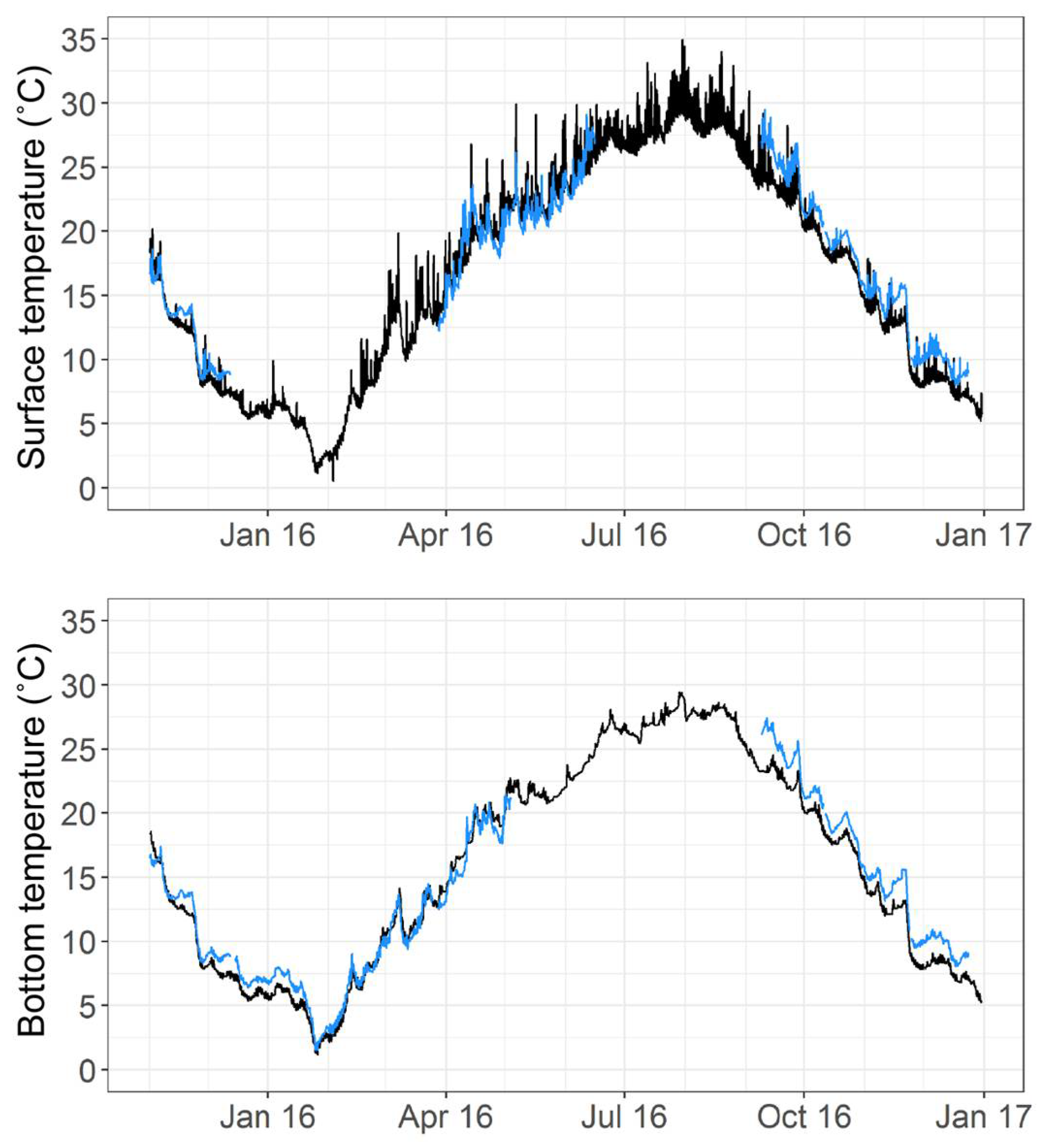
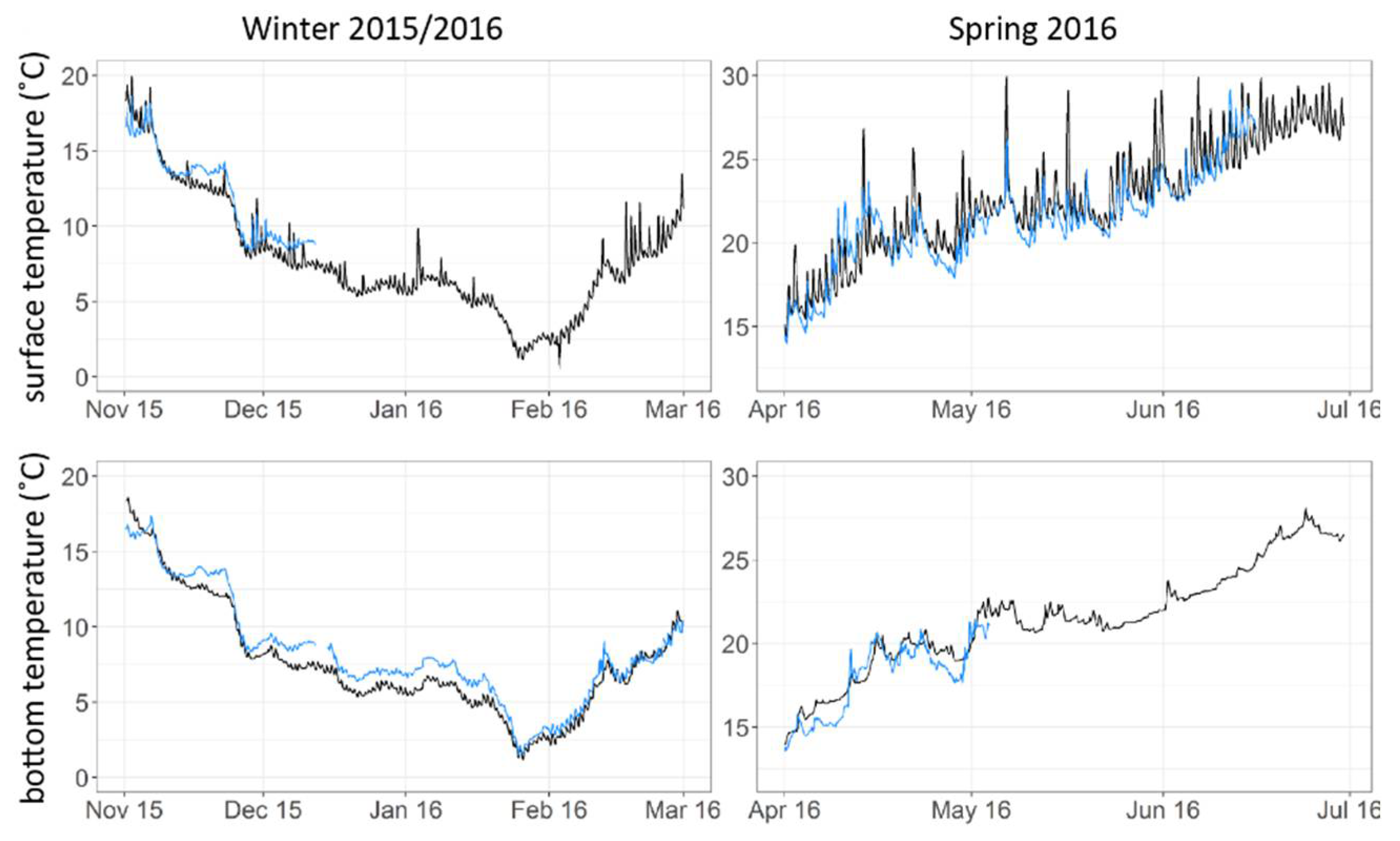
| Station | Total | Time Stratified | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed | Observed | Simulated | Simulated–Observed | ||||
| (h) | (h) | (%) | (h) | (%) | (h) | (%) | |
| A | 4685 | 648 | 13.83 | 1270 | 27.11 | 622 | 13.28 |
| B | 3565 | 924 | 25.92 | 1166 | 32.71 | 242 | 6.79 |
| D | 4572 | 1263 | 27.62 | 1783 | 39.00 | 520 | 11.37 |
| F | 3694 | 710 | 19.22 | 1702 | 46.07 | 992 | 26.85 |
| J | 4558 | 943 | 20.69 | 804 | 17.64 | −139 | −3.05 |
| average | 4215 | 898 | 21.46 | 1345 | 32.51 | 447 | 11.05 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frassl, M.A.; Boehrer, B.; Holtermann, P.L.; Hu, W.; Klingbeil, K.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, J.; Rinke, K. Opportunities and Limits of Using Meteorological Reanalysis Data for Simulating Seasonal to Sub-Daily Water Temperature Dynamics in a Large Shallow Lake. Water 2018, 10, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050594
Frassl MA, Boehrer B, Holtermann PL, Hu W, Klingbeil K, Peng Z, Zhu J, Rinke K. Opportunities and Limits of Using Meteorological Reanalysis Data for Simulating Seasonal to Sub-Daily Water Temperature Dynamics in a Large Shallow Lake. Water. 2018; 10(5):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050594
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrassl, Marieke A., Bertram Boehrer, Peter L. Holtermann, Weiping Hu, Knut Klingbeil, Zhaoliang Peng, Jinge Zhu, and Karsten Rinke. 2018. "Opportunities and Limits of Using Meteorological Reanalysis Data for Simulating Seasonal to Sub-Daily Water Temperature Dynamics in a Large Shallow Lake" Water 10, no. 5: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050594
APA StyleFrassl, M. A., Boehrer, B., Holtermann, P. L., Hu, W., Klingbeil, K., Peng, Z., Zhu, J., & Rinke, K. (2018). Opportunities and Limits of Using Meteorological Reanalysis Data for Simulating Seasonal to Sub-Daily Water Temperature Dynamics in a Large Shallow Lake. Water, 10(5), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050594





