Prediction and Optimization of the Fenton Process for the Treatment of Landfill Leachate Using an Artificial Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Landfill Leachate
2.2. Fenton Process and Optimisation Phase
2.3. Experimental Design and Statistical Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Investigation of the Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Treatment Efficiency
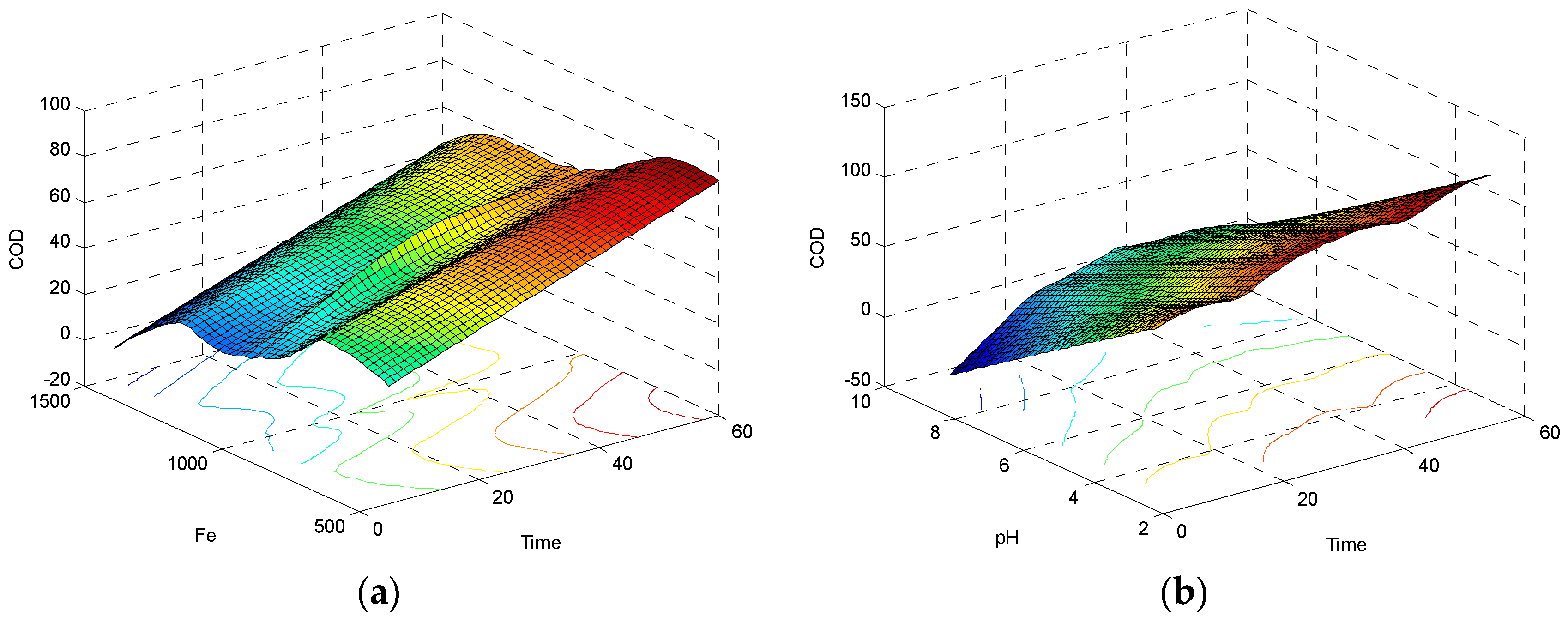
3.1.1. Interactive Effect of Time and Fe2+ Concentration on COD Reduction
3.1.2. Interactive Effect of Contact Time and pH on COD Reduction
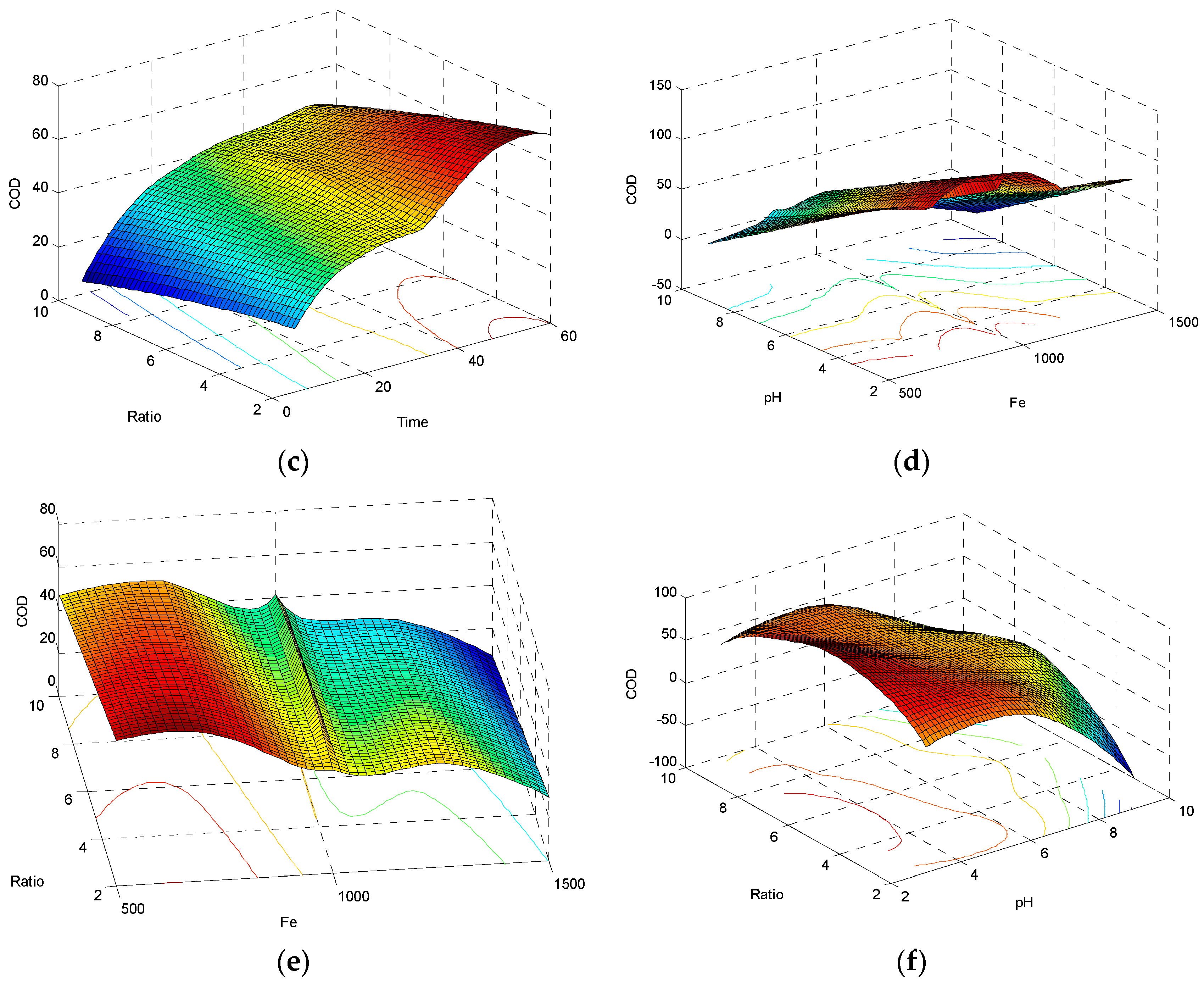
3.1.3. Interactive Effect of Time and H2O2:Fe2+ Ratio on COD Removal
3.1.4. Interactive Effect of Fe2+ Concentration and pH on COD Removal
3.1.5. Interactive Effect of Fe2+ Concentration and Ratio of H2O2:Fe2+ on COD Removal
3.1.6. Interactive Effect of pH and Ratio of H2O2:Fe2+ on COD Reduction
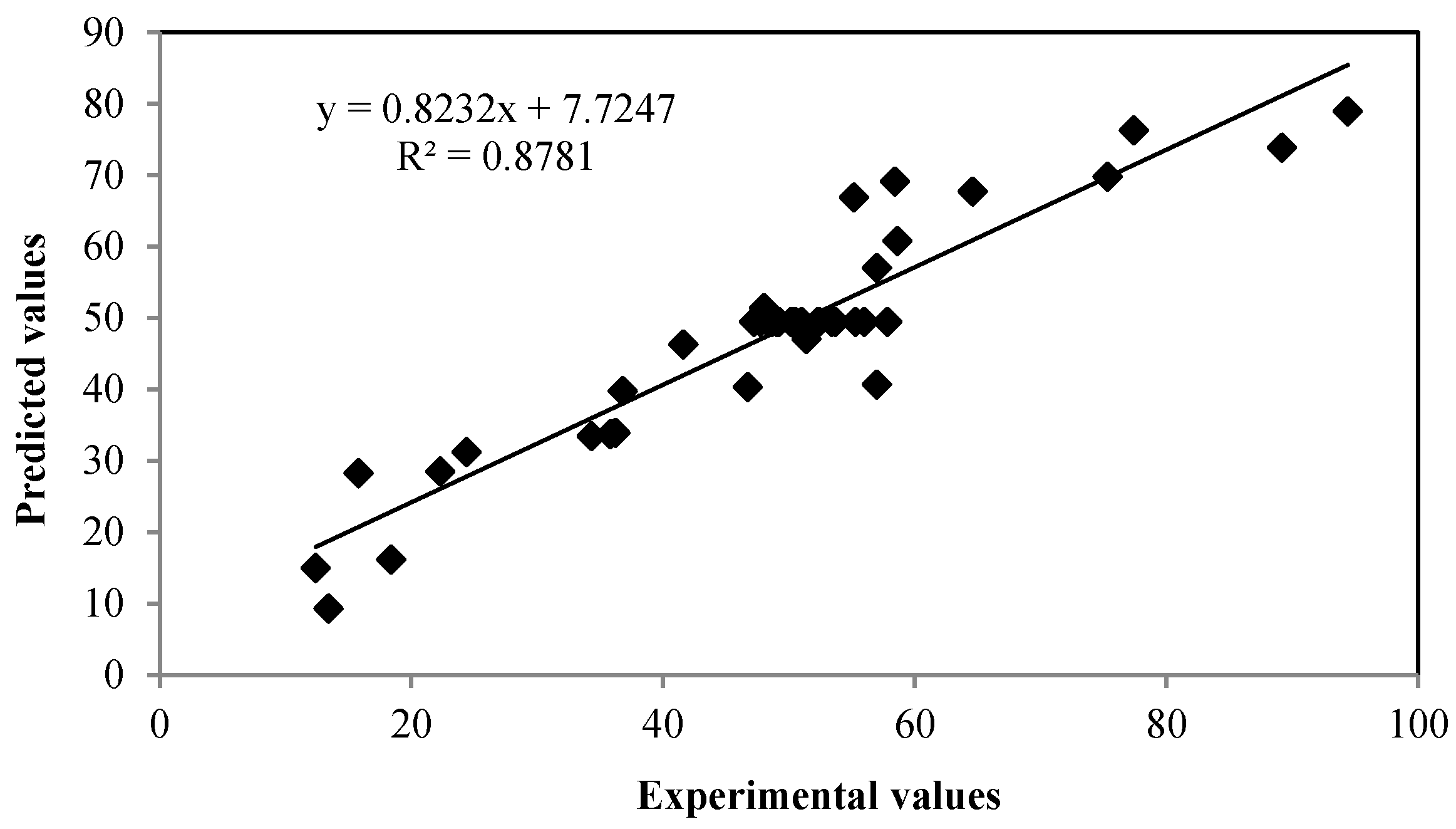
3.2. Response Optimization and Validation of the Experimental Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghiani, G.; Laganà, D.; Manni, E.; Musmanno, R.; Vigo, D. Operations research in solid waste management: A survey of strategic and tactical issues. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 44, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudi, A.M.; Akhlaghi, E.; Chelliapan, S.; Kaboli, A.; Roudi, A.M.; Aslani, H.; Selvam, S.B. Treatment of landfill leachate via advanced oxidation process (AOPs)—A Review. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 260–271. [Google Scholar]
- Sukholthaman, P.; Shirahada, K. Technological challenges for effective development towards sustainable waste management in developing countries: Case study of Bangkok, Thailand. Technol. Soc. 2015, 43, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, A.; Bakhtvar, F.; Jahanshaloo, L.; Sidik, N.A.C.; Bayat, A.E. Malaysia’s stand on municipal solid waste conversion to energy: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabiimam, M.; Dikshit, A.K. Treatment of municipal landfill leachate by oxidants. Am. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Tang, W.Z.; Tachiev, G. Fenton treatment of landfill leachate under different COD loading factors. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J. Optimization of Fenton process for treatment of landfill leachate using response surface methodology. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 6630–6634. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, E.; Yusoff, M.S.; Aziz, H.A.; Adlan, M.N.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Hung, Y.T. The Effectiveness of silica sand in semi-aerobic stabilized landfill leachate treatment. Water 2010, 2, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, S.; Aziz, H.A.; Isa, M.H.; Bashir, M.J.; Mohajeri, L.; Adlan, M.N. Influence of Fenton reagent oxidation on mineralization and decolorization of municipal landfill leachate. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2010, 45, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.E.M.; Gad-Allah, T.A.; Elmolla, E.S.; Badawy, M.I. Heterogeneous Fenton process using iron-containing waste (ICW) for methyl orange degradation: Process performance and modeling. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 4538–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Englehardt, J.D. Treatment of landfill leachate by the Fenton process. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3683–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; MacKay, A. Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the Fenton reaction and related chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S. Trends in the use of Fenton, electro-Fenton and photo-Fenton for the treatment of landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawy, M.; Ali, M. Fenton’s peroxidation and coagulation processes for the treatment of combined industrial and domestic wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajeri, S.; Aziz, H.A.; Isa, M.H.; Zahed, M.A.; Adlan, M.N. Statistical optimization of process parameters for landfill leachate treatment using electro-Fenton technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amor, C.; De Torres-Socías, E.; Peres, J.A.; Maldonado, M.I.; Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Lucas, M.S. Mature landfill leachate treatment by coagulation/flocculation combined with Fenton and solar photo-Fenton processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, A.; Pagano, M.; Volpe, A.; Di Pinto, A.C. Fenton’s pre-treatment of mature landfill leachate. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benatti, C.T.; Tavares, C.R.G.; Guedes, T.A. Optimization of Fenton’s oxidation of chemical laboratory wastewaters using the response surface methodology. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 80, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, A.; Sabour, M.R. Multi-response optimization of Fenton process for applicability assessment in landfill leachate treatment. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2528–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiszniowski, J.; Robert, D.; Surmacz-Gorska, J.; Miksch, K.; Weber, J. Landfill leachate treatment methods: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2006, 4, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y. Physical and oxidative removal of organics during Fenton treatment of mature municipal landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Choi, H.J.; Canazo, P.; Huang, C.P. Multivariate approach to the Fenton process for the treatment of landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadley, S.; Waite, T.D. Fenton Processes—Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water and Wastewater Treatment; Parsons, S., Ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2004; pp. 111–135. ISBN 9781780403076. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, D.; Sree, R.P. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Approach for modeling chromium (VI) Adsorption from aqueous solution using a Borasus Flabellifer coir powder. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 177–192. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, A.L.; Chiavone-Filho, O.; da Silva, S.S.; Foletto, E.L.; Moraes, J.E.; Nascimento, C.A. Application of artificial neural network for modeling of phenol mineralization by photo-Fenton process using a multi-lamp reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Adamowski, J.; Chan, H.F.; Prasher, S.O.; Ozga-Zielinski, B.; Sliusarieva, A. Comparison of multiple linear and nonlinear regression, autoregressive integrated moving average, artificial neural network, and wavelet artificial neural network methods for urban water demand forecasting in Montreal, Canada. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Hu, J.; Cao, R.; Ruan, W.; Wei, X. A review on experimental design for pollutants removal in water treatment with the aid of artificial intelligence. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Jia, B.; Wu, S.; Dai, J.; Tang, D. Comprehensive forecast of urban water-energy demand based on a neural network model. Water 2018, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglarijoo, N.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Bagheri, M.; Ehteshami, M. Assessment of effective parameters in landfill leachate treatment and optimization of the process using neural network, genetic algorithm and response surface methodology. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 106, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabour, M.R.; Amiri, A. Comparative study of ANN and RSM for simultaneous optimization of multiple targets in Fenton treatment of landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2017, 65, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabameri, M.; Javid, A.; Roudbari, A. Artificial neural network (ANN) modeling of cod reduction from landfill leachate by the ultrasonic process. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2017, 43, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Biglarijoo, N.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Ehteshami, M.; Ghaznavi, S.M. Optimization of Fenton process using response surface methodology and analytic hierarchy process for landfill leachate treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 104, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santin-Gusman, M.; Moreno-Andrés, J.; Cisneros-Abad, M.; Aguilar-Ramírez, S. Optimization for fenton process in removal of COD for landfill leachate treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 920–924. [Google Scholar]
- Hamid, K.B.A.; Ishak, M.Y.; Samah, M.A.A. Analysis of municipal solid waste generation and composition at administrative building café in Universiti Putra Malaysia: A case study. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 1969–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Abushammala, M.F.; Basri, N.E.; Elfithri, R.; Younes, M.K.; Irwan, D. Modeling of methane oxidation in landfill cover soil using an artificial neural network. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Fei, C.; Zhang, D.; Tang, F. Degradation of 4-nitrophenol in aqueous medium by electro-Fenton method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 145, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajeri, S.; Aziz, H.A.; Isa, M.H.; Zahed, M.A.; Bashir, M.J.; Adlan, M.N. Application of the central composite design for condition optimization for semi-aerobic landfill leachate treatment using electrochemical oxidation. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, B.G.; Lee, D.S.; Kang, N.; Yoon, J. Characteristics of p-chlorophenol oxidation by Fenton’s reagent. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Reshadat, S.; Yousefi, N. Municipal leachate treatment by Fenton process: Effect of some variable and kinetics. J. Environ. Public Health 2013, 2013, 169682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Test Parameters | Units | Values |
|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 7.5 |
| Temperature | °C | 40 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | mg/L | 10,516 |
| Total Suspended Solid | mg/L | 810 |
| Oil and Grease | mg/L | 9.5 |
| Zinc as Zn | mg/L | 2.48 |
| Iron as Fe | mg/L | 4.8 |
| Chromium as Cr | mg/L | 0.15 |
| Arsenic as As | mg/L | 0.17 |
| Aluminium as Al | mg/L | 20 |
| Barium as Ba | mg/L | 2.75 |
| Formaldehyde | mg/L | 1.9 |
| Ammonia Nitrogen | mg/L | 715 |
| Colour Original pH | ADMI | >500 |
| Colour adjusted to pH 7.0 | ADMI | >500 |
| Run | Time (min.) | Fe2+ Concentration (mg/L) | H2O2 Concentration (mg/L) | pH | H2O2:Fe2+ Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 46.25 | 750 | 3000 | 4.5 | 4 |
| 2 | 46.25 | 1250 | 10,000 | 7.5 | 8 |
| 3 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 4 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 5 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 6 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 7 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 8 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 9 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 10 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 11 | 18.75 | 750 | 3000 | 7.5 | 4 |
| 12 | 18.75 | 750 | 6000 | 4.5 | 8 |
| 13 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 14 | 46.25 | 1250 | 5000 | 4.5 | 4 |
| 15 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 16 | 18.75 | 1250 | 10,000 | 7.5 | 8 |
| 17 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 18 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 19 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 20 | 46.25 | 1250 | 5000 | 7.5 | 4 |
| 21 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 22 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 23 | 46.25 | 1250 | 10,000 | 4.5 | 8 |
| 24 | 18.75 | 1250 | 5000 | 4.5 | 4 |
| 25 | 18.75 | 750 | 6000 | 7.5 | 8 |
| 26 | 18.75 | 1250 | 5000 | 7.5 | 4 |
| 27 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 28 | 46.25 | 750 | 6000 | 7.5 | 8 |
| 29 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 30 | 46.25 | 750 | 6000 | 4.5 | 8 |
| 31 | 18.75 | 1250 | 10,000 | 4.5 | 8 |
| 32 | 32.5 | 1000 | 10,000 | 6 | 6 |
| 33 | 32.5 | 1000 | 10,000 | 6 | 6 |
| 34 | 18.75 | 750 | 3000 | 4.5 | 4 |
| 35 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 36 | 46.25 | 750 | 3000 | 7.5 | 4 |
| 37 | 32.5 | 500 | 3000 | 6 | 6 |
| 38 | 60 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 39 | 32.5 | 1500 | 9000 | 6 | 6 |
| 40 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 3 | 6 |
| 41 | 5 | 1000 | 6000 | 6 | 6 |
| 42 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6000 | 9 | 6 |
| 43 | 32.5 | 1000 | 2000 | 6 | 2 |
| 44 | 32.5 | 1000 | 10,000 | 6 | 10 |
| Parameter | Magnitudes |
|---|---|
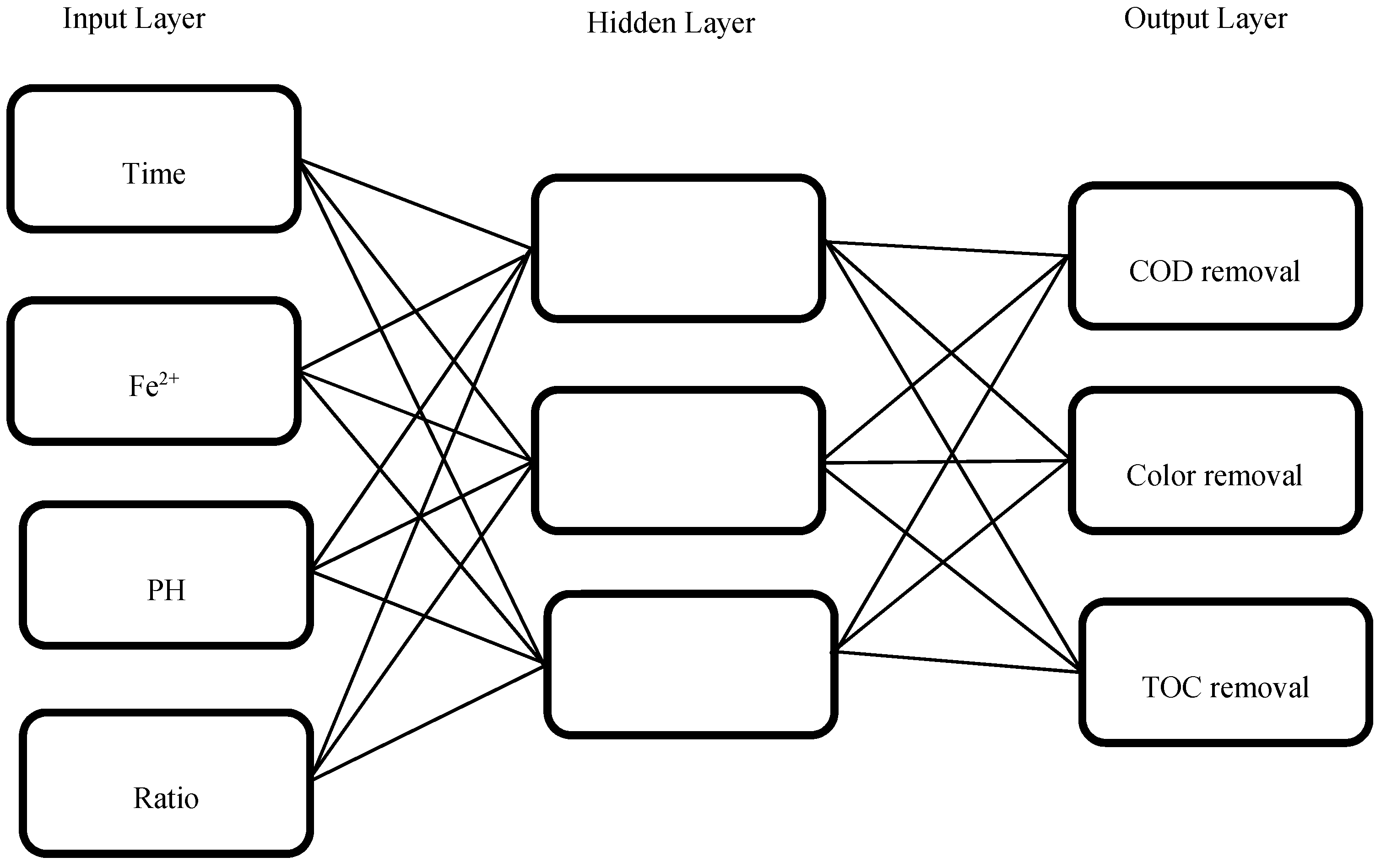
| Number of input nodes | 4 |
| Number of hidden neurons | 3 |
| Number of outputs nodes | 3 |
| Maximum number of epochs | 5000 |
| Learning rate (Ir) | 0.01 |
| Learning rule | Back-propagation |
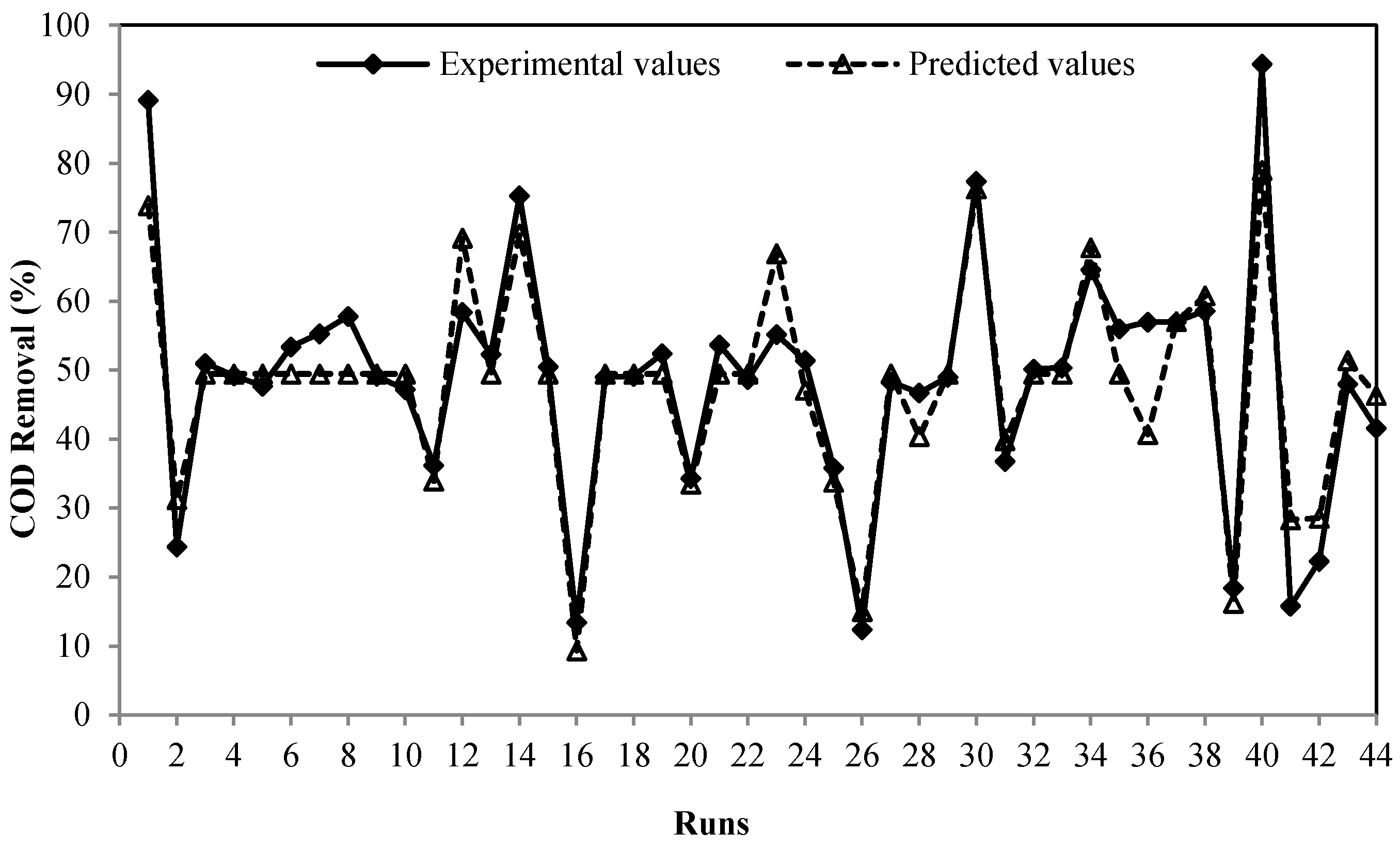
| Run | Time (min.) | Fe2+ Concentration (mg/L) | pH | H2O2:Fe2+ Ratio | Experimental COD Removal % | Predicted COD Removal % | Error % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 46.25 | 750 | 4.5 | 4 | 89.16 | 73.878 | 17.139 |
| 2 | 46.25 | 1250 | 7.5 | 8 | 24.4 | 31.247 | −28.062 |
| 3 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 51 | 49.468 | 3.003 |
| 4 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 49.2 | 49.468 | −0.544 |
| 5 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 47.7 | 49.468 | −3.706 |
| 6 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 53.4 | 49.468 | 7.363 |
| 7 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 55.3 | 49.468 | 10.546 |
| 8 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 57.81 | 49.468 | 14.430 |
| 9 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 49.15 | 49.468 | −0.647 |
| 10 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 47.2 | 49.468 | −4.805 |
| 11 | 18.75 | 750 | 7.5 | 4 | 36.2 | 33.934 | 6.258 |
| 12 | 18.75 | 750 | 4.5 | 8 | 58.4 | 69.144 | −18.398 |
| 13 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 52.3 | 49.468 | 5.414 |
| 14 | 46.25 | 1250 | 4.5 | 4 | 75.3 | 69.790 | 7.316 |
| 15 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 50.5 | 49.468 | 2.043 |
| 16 | 18.75 | 1250 | 7.5 | 8 | 13.4 | 9.331 | 30.365 |
| 17 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 49 | 49.468 | −0.955 |
| 18 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 49.13 | 49.468 | −0.687 |
| 19 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 52.4 | 49.468 | 5.595 |
| 20 | 46.25 | 1250 | 7.5 | 4 | 34.31 | 33.484 | 2.405 |
| 21 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 53.7 | 49.468 | 7.880 |
| 22 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 48.67 | 49.468 | −1.639 |
| 23 | 46.25 | 1250 | 4.5 | 8 | 55.17 | 66.921 | −21.299 |
| 24 | 18.75 | 1250 | 4.5 | 4 | 51.4 | 47.087 | 8.390 |
| 25 | 18.75 | 750 | 7.5 | 8 | 35.8 | 33.766 | 5.681 |
| 26 | 18.75 | 1250 | 7.5 | 4 | 12.4 | 15.035 | −21.256 |
| 27 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 48.3 | 49.468 | −2.418 |
| 28 | 46.25 | 750 | 7.5 | 8 | 46.7 | 40.371 | 13.552 |
| 29 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 49 | 49.468 | −0.9551 |
| 30 | 46.25 | 750 | 4.5 | 8 | 77.41 | 76.310 | 1.420 |
| 31 | 18.75 | 1250 | 4.5 | 8 | 36.79 | 39.777 | −8.121 |
| 32 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 50.15 | 49.468 | 1.359 |
| 33 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 50.36 | 49.468 | 1.77 |
| 34 | 18.75 | 750 | 4.5 | 4 | 64.6 | 67.755 | −4.884 |
| 35 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 56 | 49.468 | 11.664 |
| 36 | 46.25 | 750 | 7.5 | 4 | 57 | 40.696 | 28.602 |
| 37 | 32.5 | 500 | 6 | 6 | 57 | 57.042 | −0.075 |
| 38 | 60 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 58.6 | 60.795 | −3.746 |
| 39 | 32.5 | 1500 | 6 | 6 | 18.4 | 16.230 | 11.790 |
| 40 | 32.5 | 1000 | 3 | 6 | 94.41 | 78.969 | 16.355 |
| 41 | 5 | 1000 | 6 | 6 | 15.8 | 28.303 | −79.135 |
| 42 | 32.5 | 1000 | 9 | 6 | 22.3 | 28.553 | −28.042 |
| 43 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 2 | 48 | 51.403 | −7.089 |
| 44 | 32.5 | 1000 | 6 | 10 | 41.6 | 46.336 | −11.386 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maslahati Roudi, A.; Chelliapan, S.; Wan Mohtar, W.H.M.; Kamyab, H. Prediction and Optimization of the Fenton Process for the Treatment of Landfill Leachate Using an Artificial Neural Network. Water 2018, 10, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050595
Maslahati Roudi A, Chelliapan S, Wan Mohtar WHM, Kamyab H. Prediction and Optimization of the Fenton Process for the Treatment of Landfill Leachate Using an Artificial Neural Network. Water. 2018; 10(5):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050595
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaslahati Roudi, Anita, Shreeshivadasan Chelliapan, Wan Hanna Melini Wan Mohtar, and Hesam Kamyab. 2018. "Prediction and Optimization of the Fenton Process for the Treatment of Landfill Leachate Using an Artificial Neural Network" Water 10, no. 5: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050595
APA StyleMaslahati Roudi, A., Chelliapan, S., Wan Mohtar, W. H. M., & Kamyab, H. (2018). Prediction and Optimization of the Fenton Process for the Treatment of Landfill Leachate Using an Artificial Neural Network. Water, 10(5), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050595






