Abstract
The management of water quality is an important part of natural resource governance. Assurance of water quality therefore requires formulation of the regulatory framework and institutional process. Water quality-related problems and their management are mainly recognized as local responsibilities in Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM). The politics of environmental policy-making should consider the political economic dynamics and socio-ecological patterns. Decentralization by providing more power to the local level and moving to a new spatial management system that is based on water basins are the two strong entreaties in the new water governance paradigm. Transitional countries facing rapid institutional adjustment, restructuring of regulations, and political-economic changes are encountering these demands internally and externally in their policy formulations. In this context, this study critically examines the case of Georgia, a transitional country. In particular, the focus is on how local governance entities can be empowered and what obstacles water quality governance encounters in Georgia. Qualitative research design is the main research method implemented in this study. The key findings from the research analysis are as follows: the existing regulations and governance system do not facilitate the active engagement of local entities in water quality governance. The application of new water polices may fail again if a top-down governance model is put in place that only creates a narrow space for local governance entities to effectively govern water quality.
1. Introduction
Access to improved water quality is a challenging factor for drinking water, as well as water used in the food production process. Many communities are unable to access or have limited access to good quality water. According to the United Nation Water Policy Brief about water quality in 2011, human-induced water pollution is the major source of water contamination. The stress of poor water quality diminishes or even abolishes the functions of ecosystems [1] and causes acute and chronic health impacts on human wellbeing [2]. The complexity of water pollution makes the politics of water quality a challenging governance issue [3].
The main issues to be dealt with in water quality management are macro (large scale and sectoral level) and micro (personal and individual level) water pollution [3,4], waste water management [5,6], drinking water quality management [7,8], sanitation [9] and water quality in food production and processing [10]. Though water quality management has been developed as a technically-oriented discipline, the scope, objectives, strategies, standards, criteria, and monitoring are frequently related to economic, social, and political spheres that connect stakeholders who are within and outside of the water sector [11,12,13]. The complex environmental factors cannot be analyzed without considerable scrutiny of the interactions within socio-ecological systems [14,15,16]. The deeply-rooted societal values and political-economic dynamics play a vital role in water quality management [11]. Thus, the politics of environmental policy-making should consider the political economic dynamics and socio-ecological patterns [17,18]. The challenge lies in bringing together the international and national dialogues to reach a common goal and then harmonizing the legal and policy systems with the institutionalization process for protecting water resources as part of a process which is contested by and competing with political and economic interests [19,20].
In the last decades, policy development at the global level, including important international treaties and the involvement of international governance bodies, has aimed to advance a sustainable governance framework for improved water quality. Also, various countries have passed laws and regulations to establish legislative frameworks for water quality management that are governed by national ministerial bodies in most cases [21]. By studying legal and policy development in various countries, it becomes clear that water quality governance (WQG) oscillates between different types of governance systems. Protecting water sources, mitigating water pollution, maintaining and monitoring the water quality standards, and implementing enforcement directives (e.g., pollution fees) are the key governance factors to observe in order to determine which governance system is being utilized, who has the authority, and where the nodes of power lay for each WQG element [20,22,23].
Given the nature of water quality issues, the local governance bodies are the essential governance level [24]. The local level is the most vulnerable to water quality problems, as well as the most proximate level to address these problems [3,11,25]. The water pollution control laws and the drinking water quality regulations in some countries mention that the local governance units are responsible for maintaining the water quality [26,27] or that the policy implementation or application of water quality management is a local-scale topic [3,11]. In most transitional countries, local governance entities are not well-recognized in WQG and responsibilities are bound to more centralized governance systems [23,28]. The central governance entities are the only or key stakeholder in the water governance process [29,30,31]. In the new water governance paradigm, two key components are decentralization and basin-oriented management. These demands create a new spatial organization for governance, give more power to the local level, and provide the opportunity for the active participation of citizens [11]. Transitional countries undergoing rapid institutional adjustments, restructuring of regulations, and political-economic changes are encountering these demands internally and externally in their policy formulations [30,32,33]. In this context, this study critically examines the case of Georgia, a transitional country. By discussing the “notion of the local” and politics in policy formulation, this study scrutinizes how local governance entities can be empowered and what obstacles water quality governance encounter in Georgia.
Georgia is currently transforming their water laws and policies, as well as the institutional system, into an integrated management system with respect to Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM) and the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD). The new water policy discussion proposes the river basin as the scale of water resource management by replacing current administrative systems in water management [34,35]. Water quality is also a strong focus in the new Water Law corresponding to the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD) guidelines. By shifting to a new water governance system, novel institutional setups and policy implementation processes become necessary. The IWRM proposes river basin councils as the governance bodies that represent stakeholders from different levels and sectors [33,36]. The role of local governance has varied case by case with the establishment of the river basin councils [37,38,39]. The structure of the paper is as follows: the next section builds a theoretical framework of the governance systems in natural resource management and then traces the role of local governance within WQG by comparing several policy implementations and their dynamics. The following sections discuss the development and the dynamics in the water laws and water policy implementation in Georgia. After this discussion, the research paper concludes with a summary of the main arguments and potential areas for further research.
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Governance Systems in Natural Resource Management
The general discourse in this field defines natural resource management (NRM) as the application of scientific ecological knowledge to resource management [40]. The main themes of this discourse focus on regulations, procedures, and technologies [40,41]. However, the power relationships between competing actors involved with natural resources across all levels and scales in the different governance and management structures also determine the success of sustainable development [19,40]. Natural resources are governed in order to meet competing socioeconomic demands, while also giving priority to environmental sustainability. The appropriate level or scale for governance or the governance system is open policy questions in NRM [42,43,44]. Based on the literature, political-jurisdictional space governance, stakeholders’ approaches, and biophysical-space oriented approaches are the three governance systems in natural resource governance. Within these approaches, there are different characteristics that reflect vivid trade-offs (Table 1). However, a sharp separation between these approaches is not evident in real-world applications.

Table 1.
Governance systems in natural resource management.
The water basin can be utilized as the primary geo-spatial unit for WQG. From the river basin to stream and stream segments, the water basins can be divided to manage water quality issues [61]. Before concrete policy discussions on IWRM, river-basin organizations, authorities, or committees can be assigned as the unit of governance in WQG issues [61,62,63]. The federal government of the USA introduced a management system based on river basins in the form of coordinated governance through the 1965 Water Resources Planning Act [62]. This act proposed to instate river-basin regional commissions to replace regional-interagency committees. With the 1964 Water Law, France introduced a basin committee system for each of the six water basins to govern the water resources. The water quality standard was one of the main outcomes of this law that increased the power of the central government in water quality regulation and planning [39]. In the UK, due to the lack of active involvement, as well as negligence and financial difficulties faced by local authorities regarding sewage management and other water quality issues, the central government brought about institutional reform via the 1963 Water Resources Act and 1973 Water Act by shifting some powers to the Regional Water Authorities (RWA) that were based on watershed or catchment area [37,38]. This new law introduced 10 catchment-based water authorities to integrate water resource management [64]. This institutional restructuring can be identified as a new spatial scale integrated into local-level sewage, water quality, and water supply management. RWA, as a technocratic institution, could positively take part in the water quality improvement [38].
The EU WFD proposed and implemented the river basin management to manage European surface water. The EU WFD points out that “decisions should be taken as close as possible to the locations where water is affected or used” [65]. Collaborative and integrated management plans to advance WQG are supported by the river basin water management concept in the EU WFD [66]. In Germany, river basin management is the driving principle of the water resource management and is working with all stakeholders to achieve a “good status” of all water sources in the river basins [67,68]. All governance actors across national, regional, and local levels are cooperating with the management committees to manage water resources based on the river basin system in Germany [68,69]. River basin authorities act as the main institutional body to govern water resources in each basin with cooperation of the central, regional, and local governments in Spain [13,70,71]. Based on the 1985 Water Law in Spain, river basin authorities are independent governance bodies with functional autonomy. Water resource management in Spain is also based on a decentralized system [72]. Regional water agencies at the basin level hold the responsibility to control and monitor water quality and water resource planning and development [70,72]. Agreement as well as competing interests can be observed among stakeholders in river basin management in Spain. Stakeholders of the Water Council of Ebro Basin include a diverse range of members from the ministerial level, river basin authority, different autonomous regions, local administrative bodies, water use associations, agricultural associations, environmental organizations, business associations, labor organizations, and a representative of the recreational users [73]. However, there are conflicts of interest among stakeholders in some river basins. In the Guadalquivir River Basin, for example, the regional government and river basin authority must handle the competing and conflicting interests of communities using large-scale irrigation and other water users [17]. Thus, a lack of cooperation regarding WQG between river basin management authorities and other governance entities can be observed.
2.2. Notion of the “Local” in Water Quality Governance (WQG)
The term “local” is defined relative to the policy discourse of the level of governance and management [74,75], the scale of governance and management [76], or the fragmentation of institutions [77]. In addition, the locality is identified as the geo-spatial domain in which the collective consciousness and socio-spatial identities are embedded [78]. The local government is mainly based on one single-agency system, whereas local governance is a broad concept based on the principle of plurality [77] that facilitates an inclusive local participatory framework [79] and a platform to cooperate, deliberate, and negotiate among stakeholders concerning policy implementation in diverse matters such as political, economic, social, and environmental fields [80]. The local community, government bodies, and economic stakeholders are included as the entities of local governance. However, this sector-oriented identity can overlap in real-world applications. The community members can be economic stakeholders, as well as active members in the local government bodies. Thus, strict segmentation between the categories is not observed.
Water quality-related problems have been mainly recognized as locally-centered matters [3,11], though water pollution is not only generated by local activities [26]. Since local governance is an inclusive governance concept [77], the local level is the ideal governance domain because it gives space for active community participation in the WQG process, which leads to real integration among all stakeholders [11]. In traditional WQG, the local government agencies were the main or only responsible, authorized body to implement water quality standards and monitor the situation, though standards and monitoring principles were adopted by high level political authorities. Currently, local authorities provide water delivery functions as the service delivery institutes [81] and enforce regulations [3] such as by charging pollution fees.
In the UK, in a pioneer example of WQG, local authorities were given the power and responsibility to govern water pollution at the ground level by coordinating the industries and local citizens. During the industrial revolution, the UK was one of the countries that encountered severe water pollution problems in rivers and tributaries, including the general drinking water supply, which caused high mortality due to waterborne diseases such as typhoid and cholera [38,82]. The Metropolis Water Act of 1852 and 1871 (amendments), the Rivers Pollution Prevention Act of 1876, the Public Health Act of 1875, and the Sewage Utilization Act of 1865 and 1867 delivered considerable power to local authorities to examine the sources of pollution, charge penalties, and oblige cooperation among each adjacent local authority to minimize the water pollution and manage sewage [27,38,83]. With the advancement of each act, weaknesses were identified and local authorities were empowered [84]. In the USA, monitoring water quality and enforcing water pollution control were tasks handled directly at the local level, and then gradually fell under the jurisdiction of the state and governance bodies before the Clean Water Act of 1972 [85,86]. The local governments and companies were proximate responsible authorities to address household waste issues [85]. When the water pollution issues spread across watersheds and beyond the local government jurisdiction, state governments gradually took responsibility [86]. Drinking WQG in France is mainly based on local government authorities [26]. Corresponding to the financial capacities, the local, political tension between stakeholders (e.g., farmers and companies) could influence the actions taken by local government bodies in WQG [26]. In the EU WFD, the policy implementation in water resource management is identified as the responsibility of the local government. In river basin management plans, local governments should be able to address their local demands and issues regarding water management [87]. In Germany, local government entities are empowered to govern the local issues that can and should be managed at the lowest level under the Basic Law (Grundgesetz) as part of the right to self-government [69] and principle of subsidiarity [88]. The municipal codes (Gemeindeordnungen) also acknowledge the local governments’ rights regarding their local environment and services. Water quality is part of their local responsibilities. Local government institutes can cooperate with other local governments by initiating a water management association (Wasserverbände) [69]. Under the EU WFD, this close cooperation among local authorities is encouraged. Municipalities cooperate through inter-municipal associations for water services (Zweckverbände) to address common water resource management issues [87]. However, critics claim that water resource management in some parts of Germany takes a “top-down” approach. For example, Lower Saxony Watershed Partnerships demonstrates a “top-down” approach that limits participation of the local community, while allowing more involvement from the regional and local official authorities [47]. With the 1985 Water Law, local government authorities in Spain were given the power and responsibility to distribute safe water as an essential public utility and to maintain wastewater treatment systems at the local level. Water quality treatments are conducted with the coordination of the central government [70].
The responsibilities of local government agencies in WQG have been gradually curbed and abated for multiple reasons in some countries. The weakness of decentralized policies, the policy and power tension between central and local government authorities, fiscal and economic policies of the central government, NRM policies of the central government (including new spatial changes in water resource management, such as water basin-oriented management systems), unclear and complex division of power and responsibilities between different political levels [47], and inconsistencies in the water policies have been observed as some reasons for the power shift away from local authorities. The aim of IWRM and river-basin management system is to proximate and cooperate the local level governance entities into the water governance process. In the case of WQG, it has been a centralized governance duty and applied as a franchised duty of local authorities or private companies.
2.3. Water Quality Governance (WQG) Elements
The vibrant and enforceable obligations of the governments to provide clean water, citizens’ rights to clean water, and ecologically-sound approaches to protect water quality were identified as important factors for an ideal WQG regime by Bruce Pandy [13]. Though WQG is only one unit of natural resource governance, few governance elements that compose the total concept of WQG can be analyzed. In this research study, we categorize WQG elements into three main groups: standardization, mitigation and protection, and enforcement (Figure 1). Each element represents a set of different qualities with connectivity to other elements. Water quality monitoring is the task of observing the status of the water sources according to quality standards and norms. The detailed information that is analyzed through the monitoring assists in rational decision-making in water quality management, pollution control, permitting as well as delivering penalties, and protecting water sources [89]. Setting water quality standards and norms determines the institutional setup that will be required and divulges the vision and commitment of a country’s political system, as well as the international pressure for adapting such principles [90]. Moreover, the setting of quality standards is in the large pool of policy-making processes governed by the administrative feasibility, technical capacity, and political consequences of a country [13]. Unidentified water pollution causes that are based upon the precautionary principles should be considered in setting water quality standards to avoid all possible contaminants in the future [13,91]. As part of the water quality standards, the quality guidelines and thresholds for biological, hydromorphological, and physico-chemical quality must be set. In the mitigation of short and long-term pollution, the setting of regulations and the waste management systems are the other areas to be examined [92]. By catalyzing these elements, researchers and policy-makers may be able to further examine which points need to be attained, which actors need to be involved, what kind of government model should be adapted, and identify problems or trade-offs for each step of management. In conducting an analytical investigation of the total processes at work in WQG, the institutionalization process, political dynamics, and socioeconomic demands should be critically scrutinized.
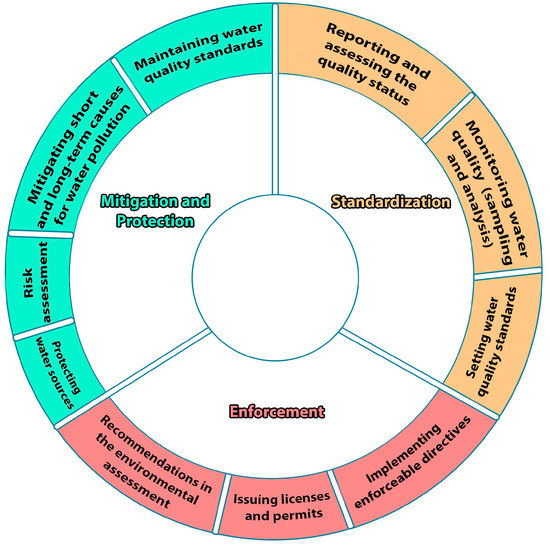
Figure 1.
Water quality governance (WQG) elements (Authors’ illustration).
3. Research Methods
This research study is part of a collaborative research project that investigates the multiple impacts of water quality on food security in the Republic of Georgia. Georgia is considered a transitional economy country [93] that is passing rapid legal and institutional changes, political reforms, and economic alterations. For example, a recent statement from the government presents some structural changes at the ministerial level and to governance components [94]. Countries with transitional economies are undergoing these changes with complex political dynamics within a short time period, with ramifications for their environmental policy management [29,30,32]. The natural resource governance was highly centralized before separation from the Soviet Union and the pressure on natural resources was high due to industrial development, which brought negative impacts including environmental pollution [32]. The regional and global political effects, as well as the immediate political and historical influences, can be observed in many contemporary policy and governance sectors of Georgia.
Qualitative research design is the main research method in this study. Legal documents, including laws and regulations, agreements and treaties, government policy documents and reports published by international organizations, government agencies, and research institutes, have been observed according to the weight and credibility of the sources. In-depth expert interviews (N = 39) were conducted with representatives from government institutes, research foundations, international organizations, non-governmental organizations, local government authorities, and civil organizations (Table 2). The expert interviews were independent of each other in terms of the questions and area of the subject field. The experts were selected based on the nature of the research questions. There were also qualitative interviews with local farmers, mainly in the Kvemo Kartli Region, Georgia. There were 20 group discussions (N = 21) and 50 individual interviews (N = 37). The interview questions were slightly altered based on factors related to location and position, but were always fixed according to the main thematic areas of the research. These qualitative, in-depth interviews allowed the interviewees’ detailed opinions and experiences to be captured without a strict template. The interviews were conducted from 2015 to 2017. The gathered data from the legal and policy documents, as well as interviews, were analyzed with the content analysis approach to scrutinize the related information by comparison and in-text analysis of each interview [95,96].

Table 2.
Interview partners in the field study (2015–2017).
4. Results
4.1. Current Status of Water Usage and Water Pollution in Georgia
The demand for water is accelerating due to socioeconomic development in the country. However, the agricultural water demand is still high in Georgia compared to other sectors. Water withdrawal for agriculture and irrigation in Georgia was 611.8 million m3 in 2016. This was about 46 percent of the total water withdrawal. In the same year, the industrial sector extracted 262.4 million m3 from natural water bodies (26 percent of the total water withdrawal), while 340.8 million m3 was used by households (28 percent of the total water withdrawal) (Figure 2) [97].
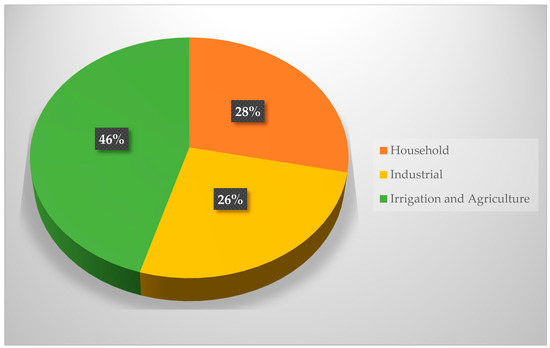
Figure 2.
Water withdrawals by sectors in Georgia (2016). Source: National Statistics Office of Georgia [97].
Water quality degradation is one of the major outcomes of environmental pollution in Georgia [35,98]. Water quality of all water sources has decreased due to alarming pollution that indicates severe water pollution at a level above the world average [96,98]. Hotspots have been identified where the water quality has become a major NRM issue and leads to a domino effect in Georgia [99]. Among them, industrial activities are one of main reason to water contamination in Georgia [100,101]. The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) “Environmental Performance Reviews 2016” pointed out the untreated wastewater discharge from the urban areas, Chiatura manganese mines, copper (JSC RMG Copper) and gold mines in Bolnisi area, coal mines in Tkibuli area, factories in Batumi, and the Batumi Oil Refinery, as well as eutrophication in the Black Sea, as alarming contributors to water pollution [102]. Untreated wastewater discharge from the urban areas is the biggest polluter of surface water, with about 70% of wastewater flowing into tributaries and rivers without treatment [103]. Based on data from the National Statistics Office of Georgia, untreated water discharge to the surface water bodies is relatively high compared to treated wastewater discharge. In 2016, a drastic decrease in the amount of untreated wastewater was recorded; however, this is merely due to a new data calculation approach excluding water used for hydroelectricity generation (Figure 3) [97]. Due to the mismanagement of wastewater treatment plants in municipalities, drinking water is contaminated by leaking pipes and cross-contamination of stored water [104,105].
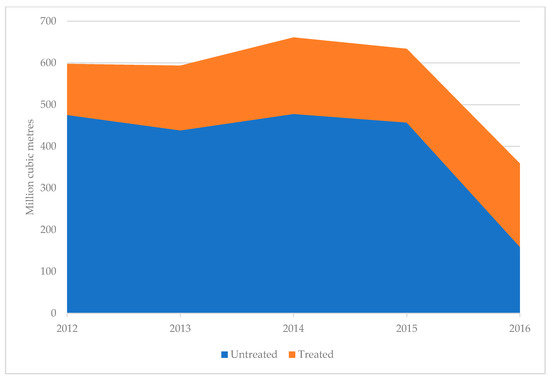
Figure 3.
Wastewater discharge into surface waters, 2012–2016. Source: National Statistics Office of Georgia [97].
Industrial water pollution in Georgia causes severe health and ecological impacts. Due to the weakness of the existing law and unwillingness of some industries to participate in sustainable NRM in Georgia, the polluter pays principle is dysfunctional [38]. Also, the threat to the local labor market is another reason to reverse tough political actions against such industries [99]. The self-monitoring of outflow is irregular and small industries do not have the technical facilities required to treat wastewater [104]. Unsustainable agricultural activities are other causes for water quality degradation in Georgia. The farming practices in Georgia have been identified as unsustainable and ecologically harmful. The intensive application of chemical fertilizers and pesticides and the mismanagement of natural resources, such as soil, water, and forest, induce long-term effects on climate conditions in the region [106,107]. Felix-Henningsen et al. [108] investigated the impacts of toxic sulphidic heavy metals (Copper, Zinc and Cadmium) on the food system due to soil contamination. They argued that water tables have been contaminated due to the run-off from agricultural lands [108]. Systemic monitoring for such nonpoint source contamination has not yet been developed in Georgia [35,105]. Thus, water quality is a key governance theme in water resource management in Georgia.
4.2. Implementation of Water Quality Governance (WQG) in the Contemporary System
Water resource management is currently based on the Law of Georgia on Water 1997. Parallel to this law, there are other laws that directly and indirectly govern water resources in different ways that create inconsistency and fragmentation in the water policy implementation in Georgia [34,109]. In existing laws, water quality is a key emphasis. Table 3 analyzes the existing regulations within each law related to water quality, their model of WQG, and their spatiality.

Table 3.
Existing laws related to WQG and their political dynamics.
Beyond the above-mentioned laws and orders, there are more that directly facilitate other functions in water resource management. They do not, however, explicitly mention water quality. For example, the Law of Georgia on Land Melioration 1997 determines the water sources to be used and responsibilities of hydro-technical constructions for the amelioration of water bodies for agricultural irrigation [110]. During Soviet occupation, the Ministry of Amelioration and Water Economy was one of the core ministries governing the water economy and oversaw the development of irrigation systems to support booming agricultural production. Georgian Amelioration is a state-owned company which has its own regional branches. They mainly focus on the construction of irrigation canals and maintenance of the existing canals, and have no responsibilities regarding water quality management [110].
The legal fortification for the water quality standardization and mitigation and protection is seemingly well-covered by other laws emphasizing various aspects of the issue. There are a few points in the legislation dealing with the enforcement of WQG. However, the critiques of these laws address two main issues: (1) the gap between legislative expectations and the implementation or enforcement of these regulations; (2) internal contradictions in the laws. WQG is primarily the responsibility of the national-level ministries in Georgia. Based on the interview data and the study of the current management system, most WQG elements for law-making and implementation are centralized at national-level institutes (Table 4). The different responsibilities regarding WQG vary within each ministerial level, and little integration exists across ministerial levels (i.e., vertical cooperation) [102]. The Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection of Georgia (MENRP) acts as the key institution for WQG. The Department of Environmental Pollution Monitoring under the National Environmental Agency has been the main responsible body in Georgia for water quality since 2006. They conduct sampling in pre-selected sample sites on a monthly basis, as well as two times per month in hotspots. In 2016, there was a total of 150 sites across the whole country. The monitoring process, laboratory analysis by their two regional offices (Batumi and Kutaisi), and assessment of the water quality status for the whole of Georgia (including surface, ground and marine water sources) are the main duties of the department. The Department on Environmental Supervision will be informed of any alarming water pollution in order to conduct the necessary action against the polluters or prevent the action by working with the responsible stakeholders. The Department of Geology conducts the groundwater quantity analysis, while the Department of Hydrometeorology collects the surface water quantity data [111]. The Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Affairs is responsible for setting the water quality standards for all water sources [34,104]. The minimum level of water system surveillance to ensure drinking water quality is officiated by the Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Affairs. The drinking water quality standards were established in 2001 by following WHO guidelines and former Soviet Russian norms [104,112]. The Ministry of Agriculture of Georgia is also responsible for drinking water quality monitoring and supervision [34] (NPD, 2013). Neither the Ministry of Agriculture of Georgia nor their extension service offices conduct water quality measurements in the irrigation channels. At the practical level, it is unclear who should conduct the quality testing of irrigation channels or if anyone is responsible for the monitoring [113,114]. Concerning the water supply and waste management in municipalities, this is mainly governed by the Ministry of Regional Development and Infrastructure with the Municipal Development Fund and the Georgian National Energy and Water Supply Regulatory Commission. Their actions to maintain drinking water quality are vital [104]. The institutional setup in the WQG is totally centralized [103].

Table 4.
Current distribution of water quality governance (WQG) elements in Georgia.
The other critique is the internal contradictions of laws. For example, the 2004 Tax Code and the Law of Georgia on Licenses and Permits 2005 obliterate some key environmental pollution taxes and certain conditions to obtain permits in matters of natural resource usage that negatively influence water resources management [34]. Industries do not need to obtain a license or permission for surface water extraction and discharge of wastewater, only for the groundwater extraction. As a result, there is no legal mechanism or institutional setup to terminate such environmentally harmful activities [105]. Thus, the National Environmental Agency can only conduct monitoring of the condition and seek voluntary cooperation from industries for sustainable natural resource usage. Overall, there is a lack of consolidated mechanisms for water quality management in Georgia [111].
4.3. Role of Local Authorities in Water Quality Governance (WQG)
According to the new demarcation based on the 2016 ordinance, there are five self-governing cities, including Tbilisi, Porti, Batumi, Rustavi, and Kutaisi, with more than 50,000 inhabitants, and 59 municipalities that combine rural areas and a city as a local government unit in Georgia. The mayor and the council members (Sakrebulo) are directly elected. Apart from this election, there are limited opportunities for the active participation of the community in the local government in Georgia [115,116].
Local government institutions function as service delivery institutes in water resource management in Georgia. Drinking water distribution is the main responsibility of the local authorities. Local authorities either join with private water supply companies, as in Tbilisi, or with a government-owned company [117]. Centralized water is supplied to 95 percent of residents in urban areas and 35 percent in rural areas [104]. The local government agencies are not really empowered by law to be involved in general water resource management, though limited power is granted to manage their local natural resources. Based on Article 16 of the Law on Local Self-Government Code 2014, local governments are also responsible for performing small restorations of local water canals. The critics say that the definition of local water is not clear in the Law on Local Self-Government Code or in the existing Water Law. This gap in the law is a practical issue in the rural municipalities who use spring water sources for drinking water. As municipalities are responsible, along with the local water supply companies, for delivering drinking water to the area, they need to obtain the authority from the National Environmental Agency [117,118]. The interviewees from the local government offices admitted that most of decisions are made by the central government. The interviewees felt that, following cooperation with the national government, the local government should have the power and authority to govern their own natural resources. Local authorities are keen to have their own regulation capacity for decisions regarding their local resources [118]. Due to a lack of technical staff, the local government is unable to maintain the public services efficiently. The reserved budgetary portion may a limited amount to train staff or limit building technical capacity at the local level (Table 5). This financial constraint leads to either limited and regular training facilities or a lack of technical staff. Overall, local governments currently fully depend on the central government, and face financial and administrative limitations [119].

Table 5.
Human resources and financial capacity of local government.
4.4. Drafted Water Law—Integration and River Basin Management
The key issues for contemporary water policies in Georgia are the complexity and malfunction of the water resource management in the institutionalization process and implementation; the limited power and authority of local officials; and missing legislation to address key water management issues, such as concrete water pollution prevention tools, a combination of water protection requirements, and restrictions for unsustainable land use and other spatial development [104,105].
Water resource management in Georgia is in a transformation period. Discussion regarding a new water management system commenced in 2005 [109]. The international discussion about IWRM and the river basin management approach have been gradually introduced to the Georgian water community through several projects aided by international organizations, such as the EU, UNDP, IBRD, GEF, and USAID, as well as other donor countries. In these policy dialogues, water quality is a key nodal point as water pollution from several industrial and municipal sources causes many negative impacts in Georgian society [103,120]. Water quality is a key focus of the Kura (Mtkvari) Ara(k)s River Basin Project of the UNDP and GEF, which addresses a transboundary river basin between Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. For Georgia, updating the water quality standards [121] and harmonization of institutions and governance processes are recommended [103].
The new drafted Water Law of Georgia on Water Resources Management is being discussed and revised in a multi-stage process. In 2011, the Memorandum of Understanding on the implementation of the National Policy Dialogue (NPD) on IWRM was signed by the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection of Georgia and the UNECE. The concept of the new Water Law was approved by the NPD Steering Committee and the first draft of the “Law on Water Resources Management” was formulated in 2013. EU WFD guidelines and their obligations are a mandatory part within the cooperation between the EU and Georgia based on the EU-Georgia Association Agreement signed in 2014 by both parties [34,105]. This agreement aims to harmonize Georgian environmental governance and policy with EU legislation in accordance with a time schedule [122]. Specifically, there is a roadmap for Georgian legal and policy implementations for environmental and climate action to approximate those of the EU. This is part of the EU-Georgia Association Agreement in the fields of environment and climate action. In this Road Map, water quality and water resource management is one of the identified sectors that also set a timeline to draft new laws and by-laws [123]. The new draft has to be approved by the Georgian parliament before September 2018 [124]. The drafted law should be enriched by an integrated water management plan, river basin management system, and a detailed plan for water resources management. Establishing a new institutional and regulatory framework has been identified as the main structural advancement of the prospective water law [125]. By referring to the draft, changes in the water laws and policies can be grouped into three categories, including:
4.4.1. Governance and Institutional Changes
The lack of stakeholder integration is one cause of ineffective water resource management in Georgia [110]. By shifting away from sectoral water resource management, the new water governance will be based on the integrated water governance system. Chapter I, Article 5 in the drafted law elaborates on the concept of integrated protection and sustainable use of water resources at the national, regional, and local level, with mutual cooperation among all water users [125]. According to this definition, new water policy institutionalization expects to have vertical and horizontal coordination. Harmonized vertical coordination between ministerial levels is one priority of the new law which is missing from the present water governance. The river basin system will be the spatial basis for IWRM implementation and institutions under the new law. As the umbrella governance unit, the Intersectional Committee for Protection and Use of Water Resources will be officiated by combining all line-ministries, namely the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection of Georgia, Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Affairs, Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Economy and Sustainable Development, and Ministry of Finance, as well as other stakeholders including local government authorities. The main responsibility of this committee will be the coordination of policy in the field of water resources management. Other ministerial-level government units are still being discussed [124].
WQG will be a main thematic area in the Intersectional Committee, and the duties of the National Environmental Agency regarding water quality management will be more organized and coordinated with other ministries, as well as the River Basin Management Unit. Under the coordination of the MENRP and the Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Affairs, local government authorities will gain special competencies regarding the protection and use of water resources. Along with the above-mentioned ministries, local municipalities with the River Basin Management Units under MENRP will be responsible for the protection and use of water resources [125]. One of the main focuses in the WQG is monitoring. In the future, there will be a more constructive plan for water quality monitoring by advancing the monitoring points and a joint institutional arrangement between the National Environmental Agency and the Ministry of Agriculture to monitor the agricultural water discharge to surface and groundwater sources. However, there is not yet an exact and finalized institutional structure. This kind of inter-institutional arrangement will be settled after implementing the new law. Also, transboundary cooperation will be a thematic area in water resource governance, and water quality, in particular, will be a key topic in this regional cooperation [124].
4.4.2. Spatial Reconfiguration
River basin-oriented water resource management is one of the main goals of the new water law. This spatial change of water management can be observed as the main policy revolution in the water governance paradigm shift in Georgia. There will be a special application of this concept in Georgia, going beyond the classical river basin spatial scale by applying river basin districts. Based on the drafted law, a river basin district is “the area of land and sea, made up of one or more neighboring river basins together with their associated ground waters and coastal waters which is identified as the main unit for integrated management of river basins” [125]. There will be six river basin districts (Figure 4), namely the Alazani-Iori Basin District, Mtkvari Basin District, Khrami-Debeda Basin District, Enguri-Rioni Basin District, Chorokhi-Kintrishi Basin District, and Bzipi-Kodori Basin District [125]. Each river basin will have a River Basin Council after the feasibility study by the authorities. Based on the drafted law, the main goal of the council is to “ensure cooperation between the governmental and non-governmental entities with the view of protection and wise use of water resources within appropriate basin district” [125]. Thus, the functions of the River Basin Councils will include providing consultations, proposals and coordination of the stakeholders during the elaboration and implementation of River Basin Management Plans [103,124]. Hence, the River Basin Council acts as a consultation mechanism to manage water resources. The council will consist of representatives from the central government, local government, and other stakeholders in the district. For the management of water resources, there will be River Basin Management Units under the MENRP body consisting of authorities who are directly involved in the water resource management [126]. Based on the drafted law, the committees of each district will create a river basin district managing plan with consultation from the Ministry of Environment and will proceed to the central government for approval and implementation. According to this plan, WQG will be concerned with anthropogenic effects and risk assessment in the region, and will get information from local representatives (Chapter VI, Article 32) and through public hearings (Chapter VI, Article 34) [125]. Regional units of the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection (river basin management services) will probably be established, but this question is still under discussion [124]. The reasons for having river basin districts rather than river basins are convenience in the administrative functions, less financial costs, and better integration in water management [124].
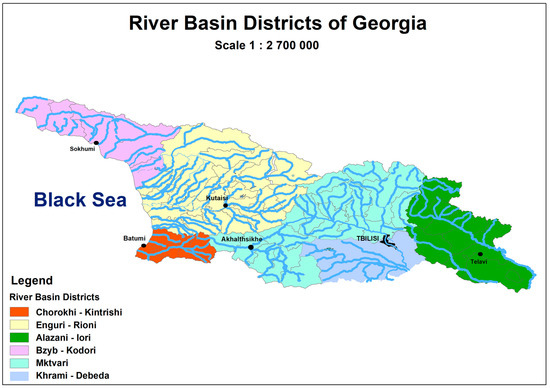
Figure 4.
Borders of the River Basin Districts (based on Approval of the Boundaries of Basin Territorial Entities of River Basin Manage [125]; authors were given permission to rework the original map).
4.4.3. Regulation Changes
The regulations of the drafted Law of Georgia on Water Resources Management have been advanced based on the comprehensive regulations of the EU WFD. By adapting the EU WFD into a national natural resource management system, considerable changes to institutions are an obvious consequence [119]. The guiding framework and legal norms upon which the new regulations are modelled [34] include Directive 2000/60/EC establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy, Directive 2007/60/EC on the assessment and management of flood risks, Directive 91/271/EEC on urban waste water treatment, Directive 76/160/EEC on bathing water, Council Directive 91/271/EEC on urban wastewater treatment, Directive 91/676/EEC on nitrates, Directive 2008/98/EC on waste, Directive 98/83/EC on the quality of water intended for human consumption, Directive 2006/11/EC on pollution caused by certain dangerous substances discharged into the aquatic environment of the Community, Directive 2006/44/EC on the quality of fresh waters, Directive 2008/105/EC on environmental quality standards, Directive 2010/75/EU on integrated pollution prevention and control, Directive 91/676/EC on protection of waters against pollution caused by nitrates from agricultural sources, Directive 76/769/EEC on marketing and use of certain dangerous substances and preparations, Directive 91/414/EEC on plant protection products, and Directive 98/8/EC on Biocidal Products Directive concerning the protection of waters against pollution caused by nitrates from agricultural sources. Water quality management within the EU WFD plays a key role. Ecological standards are well detailed for all water bodies, including their normative definitions and status. By following the EU WFD, the drafted law will advance their quality norms and monitoring with biological, hydromorphological and physico-chemical quality categories [111]. According to the drafted law, surface water requirements will be developed and reviewed within the river basin management plan every six years. In addition, the water quality data repository will be open to the public [125]. Under the regulation framework in the drafted law, there will be programs for maintaining and improving water quality [124]. These programs will aim to take integrated action to search for the cause of water contamination and alleviate or stop the emission factors, as well as advance the regulations in order to maintain the high quality status measures and reach the EU water quality objectives (Article 31) [125].
5. Discussion
5.1. Shifting Passive Members to Active Members: Enhancement of Local Governance Entities in WQG
There is a tendency for most responsibilities in WQG to accumulate with the authorities in the central government. If the agencies at the legislative and implementation levels are not well identified in the total governance process, the role and contribution of local government authorities in WQG can be ambiguous. By sharing the responsibilities and providing opportunities to engage in the different steps of WQG, local government authorities will be active members of the total water resource management in Georgia. Thus, the drafted law and the following policy developments in Georgia need to consider good practices already implemented elsewhere. In Germany, local level authorities, including the local technical agencies (Wasserwirtschaftsämter), are responsible for monitoring, permitting, and licensing, as well as other enforcement actions, to maintain water quality locally [69].
As far as establishing the standardization of water quality, which involves monitoring water quality, reporting, and assessing the quality status, a consideration of local knowledge in sampling is highly recommended by the World Meteorological Organization in their technical report “Planning of Water-quality Monitoring Systems” [126]. Establishment of sampling stations, the close observation of water quality, and the frequency of reporting should all be determined at the local level [89]. Insufficient parameters and locations for monitoring water quality, an inadequate quality control system, and lack of trained staff are some of key challenges that have been identified in Georgia [127]. In the new water policies, organization of water quality monitoring is going to be based on the EU standards [128]. There is an essential importance to establish a mechanism to convert monitoring data into a statement about the status of water bodies as a fundamental factor in a solid water quality assessment, which is missing in the current WQG [129]. Such standardization of the water quality needs to be independent from the negative policy-bias that may misguide the norms and objective of water quality standards. Regarding such a mechanism, local governance entities are an inevitable stakeholder with regards to local knowledge, proximity to the issue, and institutional flexibility. In addition, the local government authorities in Georgia admitted that, although the setting of national standards is the responsibility of the national level, updating the quality parameters and monitoring the status should be the responsibility of the local authorities. The officers from the Department of Environmental Pollution Monitoring could gain active support from the local authorities in this regard and could improve the technical capacity by training local staff to conduct water quality monitoring [111]. Such facilitation and capacity building at the local level are not only meant to empower a few technical staff with the local authorities, but also to empower the local communities. Local participation in monitoring the conditions of natural resources could enhance people’s awareness of their local natural resources and participation in ensuring sustainable use [130]. Local public hearings or a body to handle complaints at the local government level is one of the demands of the local communities [131]. Moreover, local governments could prepare a report on the status of water quality in the area and be a part of the preparation of a comprehensive quality guideline and thresholds for biological, hydromorphological and physico-chemical quality for identified and unidentified pollution threats based upon the precautionary principles in coordination with the watershed management bodies [132]. Certain analyses must still be conducted in the central laboratory due to the complexity of the tests and equipment availability. The central government agencies, connected to the local level by their regional offices, can obtain active support from the local governments under such a system of mutual cooperation in Georgia.
Local-level governance entities cannot be detached from the mitigation and protection WQG elements, including maintaining water quality standards, protecting water sources, mitigating causes of short- and long-term water pollution, and risk assessment. Finding the appropriate, lowest level of governance is proposed as a guiding principle to manage water pollution based on the nature of the issue [133]. In the case of water contamination or any other water degradation issue, addressing the problem at the governance authority in the same geographical location may achieve effective results. Thus, local government is the ideal spatial governance unit to oversee and take immediate action on the issue [134]. Though currently there is limited or no opportunity for the local governance authorities to actively take part in the mitigation of water contamination and protection of water sources in the region, local government agencies expect to have more chances under the new law [117,118]. This instigates a proximate relationship with the local communities and industries, and creates the opportunity to cooperate on NRM in a sustainable manner [52]. In particular, the local authorities, as the main, responsible institutes for water delivery and wastewater treatment in Georgia, should also be responsible for maintaining water quality. In contrast, the centralization process abates the competencies of the local governments. Though the water supply and waste management are tasks of the local government authorities under the Law on Local Self-Government Code, the actual situation is peculiar. Water supply is centralized in most municipalities and sewage systems are malfunctioning in most rural municipalities. The financial capacity is limited to develop their own systems due to the curtailing of tax revenues for the local authorities [117,118,119]. If funding was available, updating and installing wastewater treatment facilities would be priorities [104,105]. Coordination among adjacent local government institutes and other stakeholders, like the inter-municipal associations (Zweckverbände) in Germany [87], is essential in regulating nonpoint source water pollution because the contamination locally may have been generated in another area [135]. Thus, vertical coordination at the local level is missing among municipalities in Georgia and, thus, needs to be strengthened. In the drafted law, risk assessment that includes the identification, assessment, and forecasting of risks (Chapter II, Article 6, G) [125] will be centrally performed at the ministerial level. Local governance entities have the potential to be active stakeholders in risk assessments in their local region and network with the WQG system.
In terms of the enforcement elements in WQG, the active engagement of local government authorities is vital in implementing enforce directives including charging penalties for water contamination, issuing licenses and permits, and recommendations in the environmental impact assessment. Setting a regulatory framework and an appropriate institutional arrangement are essential to controlling water pollution [91]. Increasing the ability for involvement in local environmental matters, such as by implementing regulations at the local level, has a positive effect on local concern for natural resource management [53,130]. Otherwise, natural resource management may be incompatible with the local context [136,137]. Water pollution taxes and penalties for water contamination are strong economic instruments that can be given to the local authorities [138]. Georgian local government institutions anticipate the implementation of a local tax system [119]. Giving the authority to govern their water sources locally with the coordination of the central government would be a cost-effective outcome for the environmental governance system. Even in the mega-scale projects that require permits from the national government, the active participation of the local government is crucial in the surveillance of the process and the environment impact assessment. The local government, as the closer authority to the use of natural resources in the region, must have the necessary power to intervene in any type of misuse of local water sources by industry or agricultural enterprises. Otherwise, poor conduct cannot be directly addressed based on local concerns. This also brings multiple benefits to the local communities, as well as the national interest [118]. To be part of the WQG, the competences of local communities should be considered in the governance process. These applications will be a part of the water governance process that is beyond the legal framework. However, the legal framework should be flexible enough to allow the expanded participation of local communities and this engagement should be supported by capacity-building at the local level.
Logically, the demands for empowerment of the local governance in WQG require legal facilitation through the Local Self-government Law. In that regard, the National Association of Local Authorities of Georgia (NALAG) points out considerable changes and clear definitions in the Local Self-government Law that are in agreement with the prospective water law. Otherwise, the gap between application and expectations will perpetuate the passive role of local governance in the total water resource management in Georgia [117]. With active engagement opportunities, WQG could be carried out by a system of network-governance [139,140] that is entrusted with and feels responsibility for local governance stakeholders by being a partner in the governance process.
5.2. Oscillation or Harmonization: Water Quality Governance (WQG) between Political-Jurisdictional Space Governance and Ecosystem-Based Governance
The drafted law can be identified as a revolutionary attempt to alter the total governance system in Georgia. This law will establish the River Basin District water management system as the new type of natural resource governance model, utilizing an ecosystem-based approach. As previously discussed, there will be a new institutionalization process and regulatory framework to facilitate this new governance model. By shifting governance to a new spatial scale and configuration of water resource management, a modernization of the governance system in Georgia, accompanied by effective and sustainable water management, is anticipated. In addition, there has been a long-term demand for the proper decentralization and devolution of political power to the local governance level [119,141]. This political dynamic also needs to be taken into account in the revision of the NRM in Georgia.
In the existing system, there is strong, sectoral-based water governance. In sectoral-based water governance and management, top-down governance leads to diminished social participation and formulates a hierarchical policy implementation culture and institutional setup [142,143]. The river basin management system demands a concrete river basin management plan and governance system, including a governing body that stakeholders can engage with to join in the decision-making process and an administrative body with technical functions, including monitoring water sources, cooperation and coordination among stakeholders, distribution of water, disaster management, and ecosystem protection [144,145,146]. The water basin system could encourage solidarity among locals to protect their water sources. In France, catchment-based water governance also impacted agricultural systems, resulting in more sustainable practices such as organic and low-input farming methods [26]. If the new law and by-laws do not correctly understand this mechanism and the governance power again moves towards the central government, then the positive expectations and outcomes of this new spatial governance system cannot be obtained. The river basin district council will be a body with consultation tasks with the MENRP. However, the realization of the IWRM within the river basin district system is an important objective. Thus, the establishment and enablement of the management unit is a vital task. However, attaining sufficient financial support may be a challenging obstacle to the establishment of river basin management units for each river basin district [103].
By analyzing the governance elements of WQG in Georgia within the existing system and possible changes in the new water management paradigm, it becomes evident that the key is avoiding a shift back to sector-oriented management in the long-term or a deceptive application of IWRM. In a deceptive application of IWRM, national agencies only maneuver to inter-agency representations and officiate special delegations to the national level from the local government level [11]. These delegations could be a symbolic representation of the local level, rather than creating the truly inclusive engagement of stakeholders in local governance. In Georgia, there is strong political compulsion towards a centrally-oriented governance system. There are still chances to develop a “top-down” governance system and an institutionalization process under the political-jurisdictional space governance approach. How far the ecosystem-based governance system will go in formulating a new type of democratic regulation, institutional system, and productive decentralization within such a spatial governance model will depend on the practices and authentic contribution of each stakeholder. Thus, the proposed Intersectional Committee for Protection and Use of Water Resources or River Basin District Committees should act beyond their role as inter-agency representatives and their delegation activities. The active integration of stakeholders is compulsory for the success of the total IWRM application. Integration is not a neutral process. It is a political process in the plural society [19,147,148]. The interaction of cross-sectoral stakeholders for the achievement of a common goal is manifested in the integration process of the IWRM [143]. With the new water law and the policy changes in Georgia, the governance system for NRM will consolidate with vivid governance characteristics of political-jurisdictional space governance, Ecosystem-based approaches, and Stakeholders’ approaches. WQG is one of the good thematic areas in total water resource management that allows the policymakers to clearly identify the steps of how national-level stakeholders and local governance entities in the River Basin system can be active partners in an integrated manner. A plurality of society in Georgia that connects with a multiplicity of stakeholders, legal pluralism, and multi-functionality [149] needs to be envisaged in a process of long-term application of the drafted law and the new water governance system in Georgia.
5.3. Obstacles and Chances for Efficient Water Quality Management
Hindrances have been identified that negatively affect efficient WQG. However, in the larger context of water resource governance, some specific obstacles may be concealed [23]. Critical obstacles for obtaining effective and efficient water quality management include lacunae in the legal rights to have improved water; low priority on the government agenda or not having a solid national strategic plan for water management; lack of coordination among institutions or “disintegrated” water resources management; neglect and poor management; lack of funds and other resources; the role of the government authorities themselves as large-scale water polluters; little advancement in terms of knowledge; lack of public interest; and the space for corruptions [12,13]. As discussed, water quality is the main theme in water resource management in Georgia, but efficient and effective water quality management cannot be reached due to the gap between legislative expectations and the implementation and outcomes of water quality regulations, as well as the internal contradictions of the laws. This leads to continued detrimental activities by polluters that cause water contamination [103]. Local authorities are mute due to the lack of power to prevent local-scale pollution [117,118]. In other cases, there is currently only a narrow opportunity to engage local communities in governance. Under current power and responsibilities, the local government rather acts as the technical and administrative body. Some local community members admit the gap between the local authority and people’s roles, particularly in local matters of water pollution or other water quality issues. The lobbying power of local communities can be an important factor to mitigate, report, and examine water pollution activities at the local level [11,53]. Hence, public councils, local community meetings, a petition system, and public hearings at the local level could be tools to activate people’s participation in Georgia.
More international cooperation and adjacent work with EU members are vital to advance the technology and knowledge. Currently, Georgia is a strong partner in the European Neighborhood Instrument, which assists by strengthening environmental governance in Georgia. Capacity-building at the local level is the task of national-level stakeholders (i.e., government and NGOs). Local authorities would like to have local staff with technical capacities in water quality monitoring, control, and analysis. Moreover, the cooperation between the Amelioration Institute and entities in water quality management need to be strengthened, as the water supply and allocation are intertwined with water quality. These are the future institutional arrangements that await the new water governance policy paradigm shift in Georgia.
6. Conclusions
This research study identified the thematic areas and demands at the local level that assist in empowering local governance entities for efficient WQG in Georgia. During the ongoing paradigm shift in the water resource management system, Georgia has to prudently enact a new water law and by-laws by considering the challenges of implementing decentralization and a new spatiality in water governance. In this paper, WQG elements were categorized as means of Standardization, Mitigation and Protection, and Enforcement, which provided a framework for an analytical review of the existing institutions and regulation system, as well as the prospective water policy system. As the local level is the proximate governance level regarding the consequences of water quality issues and the domain for active civic engagement, empowerment of the local governance entities could bring financial, administrative, and socioeconomic advantages to Georgia. Rather than creating discordance in governance, river basin district councils and stakeholders in local governance should cooperate by respecting each other’s responsibilities and finding opportunities to bring about effective water resource management. Otherwise, the inconsistencies and overlap of functions and responsibilities could once again lead to the mismanagement of water resources. In this study, we identified that the political economic dynamics and socio-ecological patterns are important factors in the politics of environmental policy-making. The empowerment of local governance in WQG should fit into the river basin management system as a new spatial reconfiguration in Georgia. Overall, the new water law should consider the deeply-rooted societal values and political-economic dynamics in Georgia as a country in a paradigm shift in water quality governance and a transitional political economic context. Further research is required to deeply examine local communities’ understanding of water quality, as well as the hindrances and potential to improve people’s participation in WQG in Georgia.
Acknowledgments
This research was facilitated by the Department of Organic Food Quality and Food Culture at the University of Kassel, Germany and the School of Agricultural and Nature Science, Agricultural University of Georgia with the financial support from the Verein zur Förderung einer natur- und sozialverträglichen Ernährungs- und Landschaftskultur e.V in Germany. Extensive support from the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection and Ministry of Agriculture of Georgia is highly appreciated. We extend our gratitude to all interviewees in the field who dedicated their time and allowed us to participate in their meetings. Without their unconditional support, it would have been impossible to complete this field research study. The costs of this open access publication were covered by Open-Access-Publikationsfonds from the University of Kassel which is financed by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Library of University of Kassel. Special thanks go to Isabel Greenberg for the language editing. Last but not least, we would like to thank the anonymous reviewers of the Journal Water for their critical and constructive comments.
Author Contributions
Sisira S. Withanachchi, Ilia Kunchulia, Giorgi Ghambashidze, Teo Urushadze and Angelika Ploeger conceived and designed the experiments; Sisira S. Withanachchi, Ilia Kunchulia, Giorgi Ghambashidze, Teo Urushadze and Angelika Ploeger contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. All authors contributed equally to this research work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- WWAP (World Water Assessment Programme). The United Nations World Water Development Report 4: Managing Water under Uncertainty and Risk; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: 2017 Update and SDG Baselines; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, D.L. Water Politics: Governing Our Most Precious Resource: 2017; Polity Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Metz, F.; Ingold, K. Sustainable wastewater management: Is it possible to regulate micro-pollution in the future by learning from the past? A policy analysis. Sustainability 2014, 6, 1992–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Parween, M.; Ramanathan, A.L.; Raju, N.J. Waste water management and water quality of river Yamuna in the megacity of Delhi. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 2109–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, H. Abwasser—Rohstoff statt Reststoff. In Themenheft Forschung Ausgabe 8/2012 Wasser und Umwelt; Universität Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 2012; pp. 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme, UNEP. Global Drinking Water Quality Index Development and Sensitivity Analysis Report; Water Programme Office: Burlington, ON, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, M.; Alzua, M.L.; Osbert, N.; Pickering, A.J. Community-level sanitation coverage is more strongly associated with child growth and household drinking water quality than access to a private toilet in rural Mali. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7219–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, R.M.; Bartram, J.; Carr, R. Water in food production and processing: Quantity and quality concerns. Food Control 2003, 14, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.; Vanderklein, E.L. Water Quality: Management of a Natural Resource; Blackwell Science: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Tortajada, C.; Islam, S. Governance in urban water quality and water disasters: A focus on Asia. Water Int. 2011, 36, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardy, B. Seven deadly sins of Canadian water law. J. Environ. Law Pract. 2004, 13, 89–108. [Google Scholar]
- Berkes, F.; Colding, J.; Folke, C. Introduction. In Navigating Social-Ecological Systems: Building Resilience for Complexity and Change; Berkes, F., Colding, J., Folke, C., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pahl-Wostl, C. The implications of complexity for integrated resources management. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. A general framework for analyzing sustainability of social-ecological systems. Science 2009, 325, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.; Blomquist, W. Policy, politics, and water management in the Guadalquivir River Basin, Spain. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, M.E. Environmental Policy and Politics, 6th ed.; Pearson Education, Inc.: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, V.S.; McDonald, G.T.; Mollinga, P.P. Critical review of integrated water resources management: Moving beyond polarised discourse. Nat. Resour. Forum 2009, 33, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Thiers, P.; Netusil, N.R.; Yeakley, J.A.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M.; Singh, S. Relationships between environmental governance and water quality in a growing metropolitan area of the Pacific Northwest, USA. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Water. Compendium of Water Quality Regulatory Frameworks: Which Water for Which Use? UN-Water: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wardropper, C.B.; Chang, C.; Rissman, A.R. Fragmented water quality governance: Constraints to spatial targeting for nutrient reduction in a Midwestern USA watershed. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 137, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, G.L.; Amjad, U.; Dalcanale, F.; Bartram, J.; Bentley, M.E. Drinking water quality governance: A comparative case study of Brazil, Ecuador, and Malawi. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 48, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulazzaky, M.A. Challenges of Integrated Water Resources Management in Indonesia. Water 2014, 6, 2000–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.-L. Perspectives of complexity in water governance: Local experiences of global trends. Water Altern. 2013, 6, 487–505. [Google Scholar]
- Roussary, A. The reorganisation of drinking water quality governance in France. Responsibility- based governance and objective-driven policy setting in question. Rev. Agric. Environ. Stud. 2014, 95, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentmann, F.; Taylor, V. From users to consumers: Water politics in nineteenth century London. In The Making of the Consumer: Knowledge, Power and Identity in the Modern World; Berg Publishers: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 53–79. [Google Scholar]
- Novotny, V.; Somlyódy, L. Water quality management: Western experiences and challenges for central and eastern European countries. In Remediation and Management of Degraded River Basins; Novotny, V., Somlyódy, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Horlemann, L.; Dombrowsky, I. Institutionalising IWRM in developing and transition countries: The case of Mongolia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 65, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withanachchi, S.S.; Houdret, A.; Nergui, S.; Gonzalez, E.E.; Tsogtbayar, A.; Ploeger, A. (Re)Configuration of Water Resources Management in Mongolia: A Critical Geopolitical Analysis; International Center for Development and Decent Work (ICDD) Working Papers: Kassel, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dombrowsky, I.; Hageman, N.; Houdret, A. The river basin as a new scale for water governance in transition countries? A comparative study of Mongolia and Ukraine. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4705–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zylicz, T. Environmental policy in economies in transition. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1999, 25, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Houdret, A.; Dombrowsky, I.; Horlemann, L. The institutionalization of River Basin Management as politics of scale–Insights from Mongolia. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NPD. Results and Lessons Learnt from Georgian National Policy Dialogue on Integrated Water Resources Management under European Union Water Initiative. Georgia- National Water Policy Dialogue on Integrated Water Resources Management. 2013. Available online: https://www.unece.org/index.php?id=35041 (accessed on 4 January 2018).
- EPIRB. Facilitating the Reform of Economic Instruments for Water Management in Georgia Revised Final Report OECD; OECD: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Molle, F.; Chu, T.H. Implementing Integrated River Basin Management: Lessons from the Red River Basin, Vietnam; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, D.J.; Sewell, W.D. Evolving water institutions in England and Wales: An assessment of two decades of experience. NRJ 1988, 28, 751–785. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, D.W.M.; Horan, N.J. Institutional developments, standards and river quality: A UK history and some lessons for Industrialising countries. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 33, 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Laster, L.E. Catchment basin management of water. In Environmental Challenges; Kluwer Academic Publisher & Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 437–446. [Google Scholar]
- Rist, S.; Chidambaranathan, M.; Escobar, C.; Wiesmann, U.; Zimmermann, A. Moving from sustainable management to sustainable governance of natural resources: The role of social learning processes in rural India, Bolivia and Mali. J. Rural Stud. 2007, 23, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.J.; Coleman, K.J. The multidimensionality of trust: Applications in collaborative natural resource management. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2015, 28, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl-Wostl, C. Transitions towards adaptive management of water facing climate and global change. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, M.; Davidson, J.; Curtis, A.; Stratford, E.; Griffith, R. Governance principles for natural resource management. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2010, 23, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termeer, C.J.A.M.; Dewulf, A.; van Lieshout, M. Disentangling scale approaches in governance research: Comparing monocentric, multilevel, and adaptive governance. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 29. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol15/iss4/art29/ (accessed on 1 August 2017). [CrossRef]
- Meadowcroft, J. Politics and scale: Some implications for environmental governance. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2002, 61, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualini, E. Towards a Multi-Level Polity? Regionalisation and the ‘Europeanisation’ of Regional Policy. In European Territorial Governance; Zonneveld, W., de Vries, J., Janssen-Jansen, L., Eds.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 135–156. [Google Scholar]
- Koontz, T.M.; Newig, J. From planning to implementation: Top-down and bottom-up approaches for collaborative watershed management. Policy Stud. J. 2014, 42, 416–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, D. Governance and the commons in a multi-level world. IJC 2008, 2, 7–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, K. Climate governance in the European Union multilevel system: The role of cities. In Multilevel Environmental Governance: Managing Water and Climate Change in Europe and North America; Weibust, I., Meadowcroft, J., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2014; pp. 111–130. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, T.; Newig, J. Multilevel water governance and problems of scale: Setting the stage for a broader debate. Environ. Manag. 2010, 46, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markelova, H.; Mwangi, E. Multilevel governance and cross-scale coordination for natural resource management: Lessons from current research. In The Wealth of the Commons: A World beyond Market and State; Bollier, D., Helfrich, S., Eds.; Levellers Press: Amherst, MA, USA, 2012; Available online: http://wealthofthecommons.org/essay/multilevel-governance-and-cross-scale-coordination-natural-resource-management-lessons-current (accessed on 19 October 2017)ISBN 978-1937146146.
- Larson, A.M.; Soto, F. Decentralization of natural resource governance regimes. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2008, 33, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. Governing the Commons: The Evolution of Institutions for Collective Action; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, G. Nesting, subsidiarity, and community-based environmental governance beyond the local scale. IJC 2008, 2, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, E.; Adger, W.N. Does adaptive management of natural resources enhance resilience to climate change? Ecol. Soc. 2004, 9. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol9/iss2/art10/ (accessed on 15 October 2017). [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.; Arnold, G.; Tomás, S.V. A review of design principles for community-based natural resource management. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol15/iss4/art38/ (accessed on 15 August 2017). [CrossRef]
- Moss, T. Spatiality of the Commons. IJC 2014, 8, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaffee, S.L. Three faces of ecosystem management. Conserv. Biol. 1999, 13, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, P.; Campbell, B.; Medina, G.; Usongo, L. Landscape-scale approaches for integrated natural resource management in tropical forest landscapes. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 30. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol11/iss2/art30/ (accessed on 15 October 2017). [CrossRef]
- Görg, C. Landscape governance: The “politics of scale” and the “natural” conditions of places. Geoforum 2007, 38, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlager, E.; Blomquist, W. Embracing Watershed Politics; University Press of Colorado: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Grigg, N.S. Integrated water resources management: Balancing views and improving practice. Water Int. 2008, 33, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molle, F. River-basin planning and management: The social life of a concept. Geoforum 2009, 40, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OFWAT; Defra. The development of the water industry in England and Wales Economic Regulator of the Water Sector in England and Wales (OFWAT) and Department for Environment Food & Rural Affairs (Defra), 2006. Available online: http://www.ofwat.gov.uk/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/rpt_com_devwatindust270106.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2017).
- EU Commission. Water framework directive 2000/60/EC of the European parliament and of the council. OJEU 2000, 327, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, M. The European water framework directive: An approach to integrated river basin management. Eur. Water Manag. 2002, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Arle, J.; Mohaupt, V.; Kirst, I. Monitoring of surface waters in Germany under the water framework directive—A review of approaches, methods and results. Water 2016, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaupt, V.; Richter, S.; Völker, J.; Borchardt, D. Bewirtschaftungspläne zur Wasserrahmenrichtlinie in Deutschland: Resultate und Schlussfolgerungen. Nat. Landsch. 2012, 4, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kampa, E.; Kranz, N.; Hansen, W.; Madeira, N.; Vorwerk, A. Public Participation in River Basin Management in Germany; Work Package 4 HarmoniCOP Project; Ecologic Institute: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Maestu, J.; Tabara, D.; Sauri, D. Public participation in river basin management in Spain-Reflecting changes in external and self-created context. Working Package 4 HarmoniCOP Project 2003. Available online: http://www.harmonicop.uni-osnabrueck.de/_files/_down/Spain.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2018).
- Ballester, A.; Mott Lacroix, K.E. Public participation in water planning in the Ebro River Basin (Spain) and Tucson Basin (U.S., Arizona): Impact on water policy and adaptive capacity building. Water 2016, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielsa, J.; Cazcarro, I. Implementing integrated water resources management in the Ebro River Basin: From theory to facts. Sustainability 2015, 7, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, R.G.; Margelí, M.O. The Ebro River Basin Authority and the 2014 Basin Plan, 2014. Available online: http://www.globalwaterforum.org/2014/09/16/the-ebro-river-basin-authority-and-the-2014-basin-plan/ (accessed on 4 January 2018).
- Pohlmann, A. Local climate change governance. In Global Transformations towards a Low Carbon Society; University of Hamburg/KlimaCampus: Hamburg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, M.A.; Baiocchi, G. Deliberative democracy and local governance: Towards a new agenda. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2006, 30, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, D.; Adger, W.N.; Berkes, F.; Garden, P.; Lebel, L.; Olsson, P.; Young, O. Scale and cross-scale dynamics: Governance and information in a multilevel world. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol11/iss2/art8/ (accessed on 10 November 2017). [CrossRef]
- Andrew, C.; Goldsmith, M. From local government to local governance—And beyond? Int. Political Sci. Rev. 1998, 19, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paasi, A. Deconstructing regions: Notes on the scales of spatial life. Environ. Plan. 1991, 23, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, N.; Caulfield, J.; Nickson, A.; Olowu, D.; Wollmann, H. Local Governance Reform in Global Perspective. Urban and Regional Research International; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitter, P.C. Democracy in Europe and Europe’s democratization. J. Democr. 2003, 14, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, P.; Hall, A.W. Effective Water Governance; Global Water Partnership Technical Committee: Stockholm, Sweden, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shadwell, A. The London Water Supply; Longmans, Green and Company: London, UK, 1899; Available online: https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=hvd.32044091981860;view=1up;seq=9 (accessed on 10 November 2017).
- Glen, A. The Rivers Pollution Prevention Act, 1876, 39 & 40 Vict. c. 75: With Introduction, Notes, and Index; Knight & Co.: London, UK, 1876; Available online: https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=hvd.hwglxk;view=1up;seq=22;size=150 (accessed on 10 November 2017).
- Hassan, J. A History of Water in Modern England and Wales; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, D.H. Water pollution control in the United States: Policies, planning and criteria. J. Contemp. Water Res. Educ. 1994, 94, 4–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hines, N.W. History of the 1972 clean water act: The story behind how the 1972 act became the capstone on a decade of extraordinary environmental reform. George. Wash. J. Energy Environ. Law 2013, 4, 80–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, R.; Anton, B.; Schraffl, F. Local Governments and Integrated Water Resources Management in the Rhine River Basin in Germany; Report for the LoGo Water Project; International Training Centre: Freiburg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bröhmer, J. Subsidiarity and the German Constitution. In Global Perspectives on Subsidiarity; Evans, M., Zimmermann, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 129–156. [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä, A.; Meybeck, M. Designing a Monitoing Programme. In Water Quality Monitoring: A Practical Guide to the Design of Freshwater Quality Studies and Monitoring Programme; Bartram, J., Balance, R., Eds.; Published on Behalf of UNDP & WHO Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1996; pp. 35–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chave, P.A. Legal and regulatory instruments. In Water Pollution Control: A Guide to the Use of Water Quality Management Principles; Helmer, R., Hespanhol, I., Eds.; E&FN Spon for WHO and UNEP: London, UK, 1997; pp. 125–161. [Google Scholar]
- Helmer, R.; Hespanhol, I. Water Pollution Control: A Guide to the Use of Water Quality Management Principles; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Alaerts, G.J. Institutional arrangement. In Water Pollution Control: A Guide to the Use of Water Quality Management Principles; Helmer, R., Hespanhol, I., Eds.; E&FN Spon for WHO and UNEP: London, UK, 1997; pp. 219–242. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. United Nations World Economic Situation and Prospects; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Georgia (13 November 2017) Special Statement by the Prime Minister of Georgia. Available online: http://gov.ge/index.php?lang_id=ENG&sec_id=463&info_id=62772 (accessed on 14 November 2017).
- Hsieh, H.; Shannon, S.E. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual. Health Res. 2005, 15, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondracki, N.L.; Wellman, N.S. Content analysis: Review of methods and their applications in nutrition education. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2002, 34, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Statistics Office of Georgia. Natural Resources of Georgia and Environmental Protection—Statistical Publication 2016. National Statistic Office of Georgia, 2017. Available online: http://geostat.ge/cms/site_images/_files/english/agriculture/Environment_2016.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2017).
- Lomsadze, Z.; Makharadze, K.; Tsitskishvili, M.; Pirtskhalava, R. Water resources of Kakheti and ecological problems. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CENN—Caucasus Environmental NGO Network (Tbilisi, Georgia). Personal Communication, 2016.
- Lomsadze, Z.; Makharadze, K.; Pirtskhalava, R. The ecological problems of rivers of Georgia (the Caspian Sea Basin). Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2016, 14, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avkopashvili, G.; Avkopashvili, M.; Gongadze, A.; Tsulukidze, M.; Shengelia, E. Determination of Cu, Zn and Cd in soil, water and food products in the vicinity of RMG gold and cupper mine, Kazreti, Georgia. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017, 15, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNECE. Environmental Performance Reviews 2016, Third Review; Environmental Performance Reviews Series No. 43; UNECE: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP/GEF Kura Aras Project/EaP GREEN Activities in Georgia (Global Environment Facility, Washington, DC, USA). Personal communication, 2017.
- Melua, D. Municipal Water and Wastewater Sector in Georgia; NISPAcee: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UNECE. Water Policy Reforms in Eastern Europe, the Caucasus and Central Asia Achievements of the European Union Water Initiative 2006–2016; UNECE: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ölund Wingqvist, G. Georgia Environmental and Climate Change Policy Brief; Department of Economics, Sweden; University of Gothenburg, 2009; Available online: http://sidaenvironmenthelpdesk.se/wordpress3/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/Georgia-EnvCC-Policy-Brief-Draft-090130.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2017).
- World Bank. Integrating Environment into Agriculture and Forestry Progress and Prospects in Eastern Europe and Central Asia: Volume II: Georgia; Europe and Central Asia Region Sustainable Development Department World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Felix-Henningsen, P.; Urushadze, T.; Steffens, D.; Kalandadze, B.; Narimanidze, E. Uptake of heavy metals by food crops from highly-polluted chernozem-like soils in an irrigation district south of Tbilisi eastern Georgia. Agron. Res. 2010, 8, 781–795. [Google Scholar]
- Green Alternative. Management and Protection of Water Resources in Georgia; Green Alternative: Tbilisi, Georgia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Georgian Amelioration (Tbilisi, Georgia). Personal communication, 2016.
- National Environmental Agency (Tbilisi, Georgia). Personal communication, 2016.
- Betsiashvili, M.; Ubilava, M. Water quality and wastewater treatment systems. In Dangerous Pollutants (Xenobiotics) in Urban Water Cycle; Hlavinek, P., Bonacci, B., Marsalek, J., Mahrikova, I., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Marneuli Extension Service, Representing the Ministry of Agriculture (Marneuli, Georgia). Personal Communication, 2017.
- Bolnisi Regional Office of Amelioration, Upper Kvemo Kartlie Regional Office (Kvemo Kartli, Georgia). Personal communication, 2017.
- Jamaspishvili, T. Community participation in local budgeting in Georgia. In Speaking out: Case Studies on How Poor People Influence Decision-Making; van der Gaag, N., Rowlands, J., Eds.; Oxfam: Oxford, UK, 2009; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Parliament of Georgia. National Budget of Georgia in 2015, 2016, 2017 and 2018; Parliament of Georgia: Kutaisi, Georgia, 2017.
- National Association of Local Authorities of Georgia (NALAG) (Tbilisi, Georgia). Personal communication, 2017.
- Governors (Gamgebeli) and Representative Councils (Sakrebulo) Members from Bolnisi (Daminisi, Georgia). Personal communication, 2016.
- Bolkvadze, T.; Kandelaki, K.; Losaberidze, D.; Chikovani, T. Local Self-Government in Georgia 1991–2014; The International Centre for Civic Culture: Tbilisi, Georgia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Caucasus Institute for Peace, Democracy and Development (Tbilisi, Georgia). Personal communication, 2017.
- Abu, E.A.; Arabidze, M.; Avazova, M.; Minasyan, S. Water Quality Hot-Spots Desk Study for the Kura Ara(k)s River Basin. UNDP/GEF Project. Reducing Transboundary Degradation in the Kura Ara(k)s River Basin; Tbilisi, Georgia; Baku, Azerbaijan; Yervan, Armenia, UNDP/GEF; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- USAID. White Paper on Water Allocation Planning Framework USAID Governing for Growth (g4g) in Georgia; USAID: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Particip, J.; Gogaladze, K. Roadmaps for EU Approximation in the Environmental and Climate Action Fields; Ministry of Environment Protection and Agriculture of Georgia: Tbilisi, Georgia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection of Georgia (Tbilisi, Georgia). Personal communication, 2017.
- Draft Law of Georgia on Water Resources Management, 2015.
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Planning of Water-Quality Monitoring Systems Technical Report Series; No. 3; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Javakhishvili, M. Policies, Data Collection, Strengths and Challenges Related to Water Quality in Georgia, 13th Joint Task Force on Environment Statistics and Indicators 29 June 2017 Geneva. Available online: https://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/stats/documents/ece/ces/ge.33/2017/mtg2/7_2_JTF-UNSD_Pilot_Water_Quality-29_June_2017_Georgia.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2017).
- Makarova, M. New Water Legislation in Georgia Review of Progress—Presentation. Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection of Georgia and UNECE: Tbilisi, Georgia, 11 April 2017. Available online: https://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/env/documents/2017/WAT/04Apr_11_5SC/GE_5SC_Makarova_EN.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2017).
- Adeishvili, M.; Gugushvili, T.; Gujaraidze, K.; Macharashvili, I. Environmental Policy, Institutional and Regulatory Gap Analysis; Green Alternative: Tbilisi, Georgia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen, F.; Burgess, N.D.; Balmford, A.; Donald, P.F.; Funder, M.; Jones, J.P.; Alviola, P.; Balete, D.S.; Blomley, T.; Brashares, J.; et al. Local participation in natural resource monitoring: A characterization of approaches. Conserv. Biol. 2009, 23, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Interviews with Local Community May and September 2016. Personal communication, 2016.
- Ardizone, K.A.; Wyckoff, M.A. Filling the Gaps: Environmental Protection Options for Local Governments; Michigan Department of Environmental Quality: Lansing, MI, USA, 2003.
- Larsen, H.; Ipsen, N.H.; Ulmgren, L. Policy and Principles. In Water Pollution Control: A Guide to the Use of Water Quality Management Principles; Helmer, R., Hespanhol, I., Eds.; E&FN Spon for WHO and UNEP: London, UK, 1997; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, K.H. Local Government Has an Important Role for Water Quality Protection: Part 1. 29 May 2015. Available online: http://msue.anr.msu.edu/news/local_government_has_an_important_role_for_water_quality_protection (accessed on 18 November 2017).
- Mandelker, D.R. Controlling nonpoint source water pollution: Can it be done. Chic.-Kent Law Rev. 1989, 65, 479–502. [Google Scholar]
- Holley, C. Environmental Regulation and Governance. In Regulatory Theory: Foundations and Applications; Drahos, P., Ed.; Australian National University: Canberra, Australia, 2017; p. 741. [Google Scholar]
- Holley, C.; Sinclair, D. Compliance and Enforcement of Water Licenses in NSW: Limitations in Law, Policy and Institutions. AJNRLP 2012, 15, 149–189. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, M.S. Economic Instruments and Clean Water: Why Institutions and Policy Design Matter. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Paris, OECD, 2001. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/gov/regulatory-policy/1910825.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- Robins, G.; Bates, L.; Pattison, P. Network governance and environmental management: Conflict and cooperation. Public Adm. 2011, 89, 1293–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingfelder, J. Wicked Water Problems: Can Network Governance Deliver? Integrated Water Management Case Studies from New Zealand and Oregon. Ph.D. Thesis, Portland State University, Portland, OR, USA, June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Skorupska, A.; Zasztowt, K. Georgia’s Local Government Reform: How to Escape from the Soviet Past (and How Poland Can Help). Policy Pap-PISM 2014, 4. Available online: https://www.pism.pl/files/?id_plik=16394 (accessed on 14 November 2017).
- Agarwal, A.; delos Angeles, M.S.S.; Bhatia, R.; Chéret, I.; Davila-Poblete, S.; Falkenmark, M.; Gonzalez-Villarreal, F.; Jonch-Clausen, T.; Ait Kadi, M.; Kindler, J.; et al. Integrated Water Resources Management; Global Water Partnership/Technical Advisory Committee (GWP/TAC) Background Papers, No. 4; Global Water Partnership: Stockholm, Sweden, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, K.; Mollard, E. Introduction: Social Participation in Water Governance and Management. In Social Participation in Water Governance and Management: Critical and Global Perspective; Earthscan: London, UK, 2010; pp. xx–xxviii. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, N. Integrated river basin management: A case for collaboration. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2004, 2, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, M.; Wester, P.; Molle, F. Managing River Basin: Institutional Perspective. In Irrigation and River Basin Management: Options for Governance and Institutions; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka; CABI Publication: Oxon, UK, 2005; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Molle, F. Planning and Managing Water Resources at the River-Basin Level: Emergence and Evolution of a Concept; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Withanachchi, S.S. An Analysis of Politics of Scale in Water Governance and Management in Mongolia. Master’s Thesis, University of Kassel, Kassel, Germany, July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, J.A.; IWRM. The New Sanctioned Discourse? In Integrated Water Resources Management: Global Theory, Emerging Practice and Local Needs. Water in South Asia Volume 1; Sage Publication: New Delhi, India, 2006; pp. 38–63. [Google Scholar]
- Mollinga, P.P.; Meinzen-Dick, R.S.; Merrey, D.J. Politics, Plurality and Problemsheds: A Strategic Approach for Reform of Agricultural Water Resources Management. Dev. Policy Rev. 2007, 25, 699–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).