Examining Storage Capacity Loss and Sedimentation Rate of Large Reservoirs in the Central U.S. Great Plains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
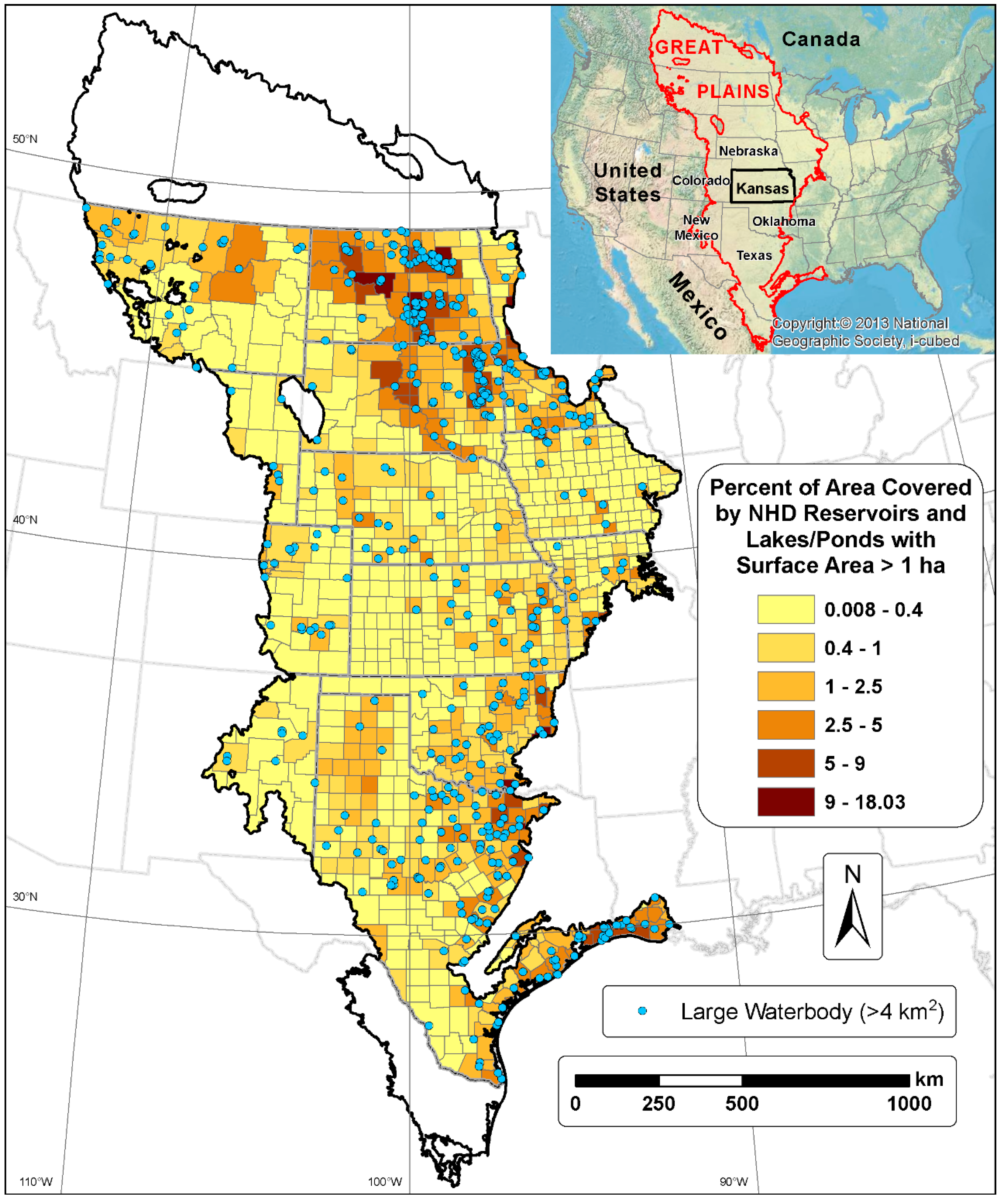
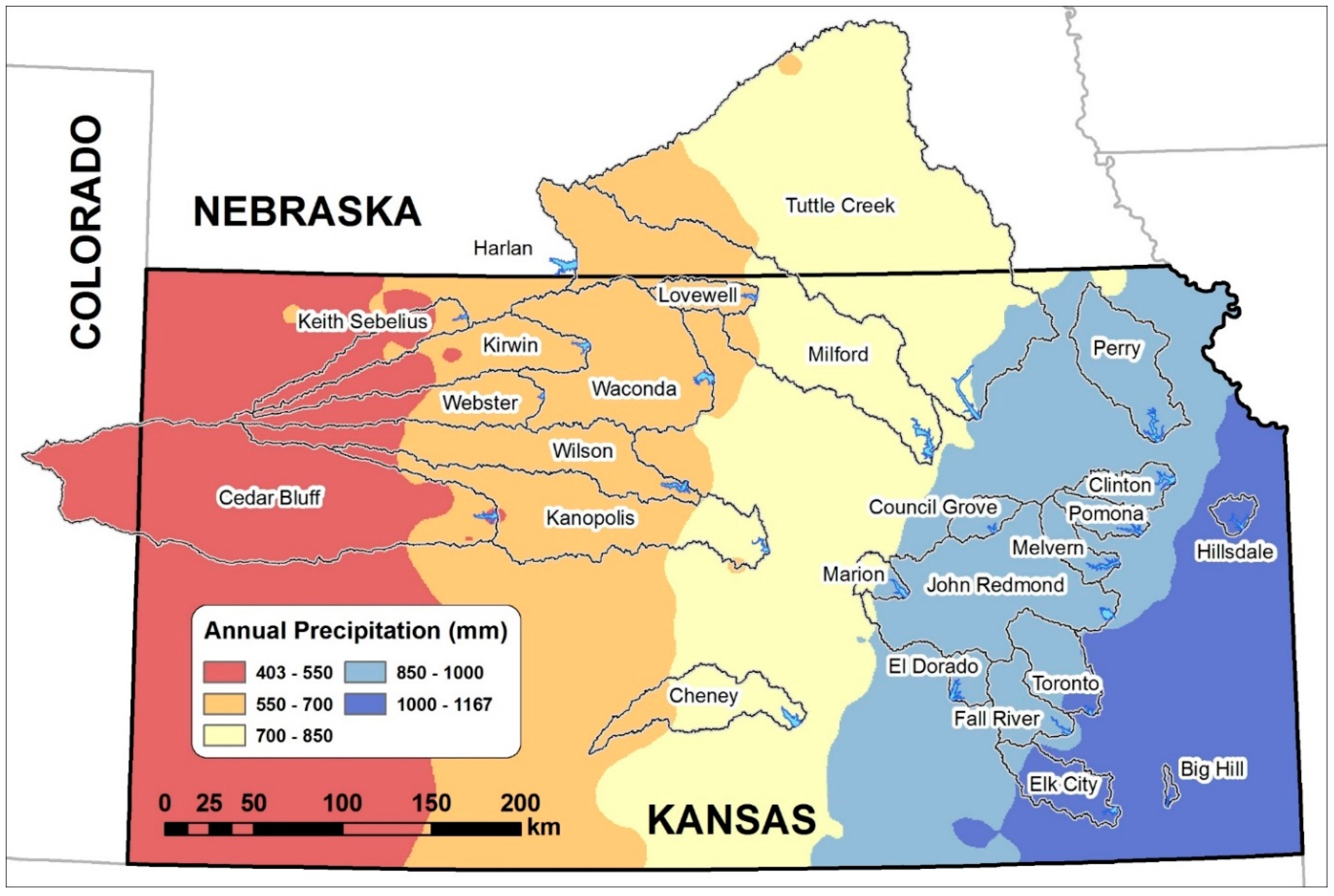
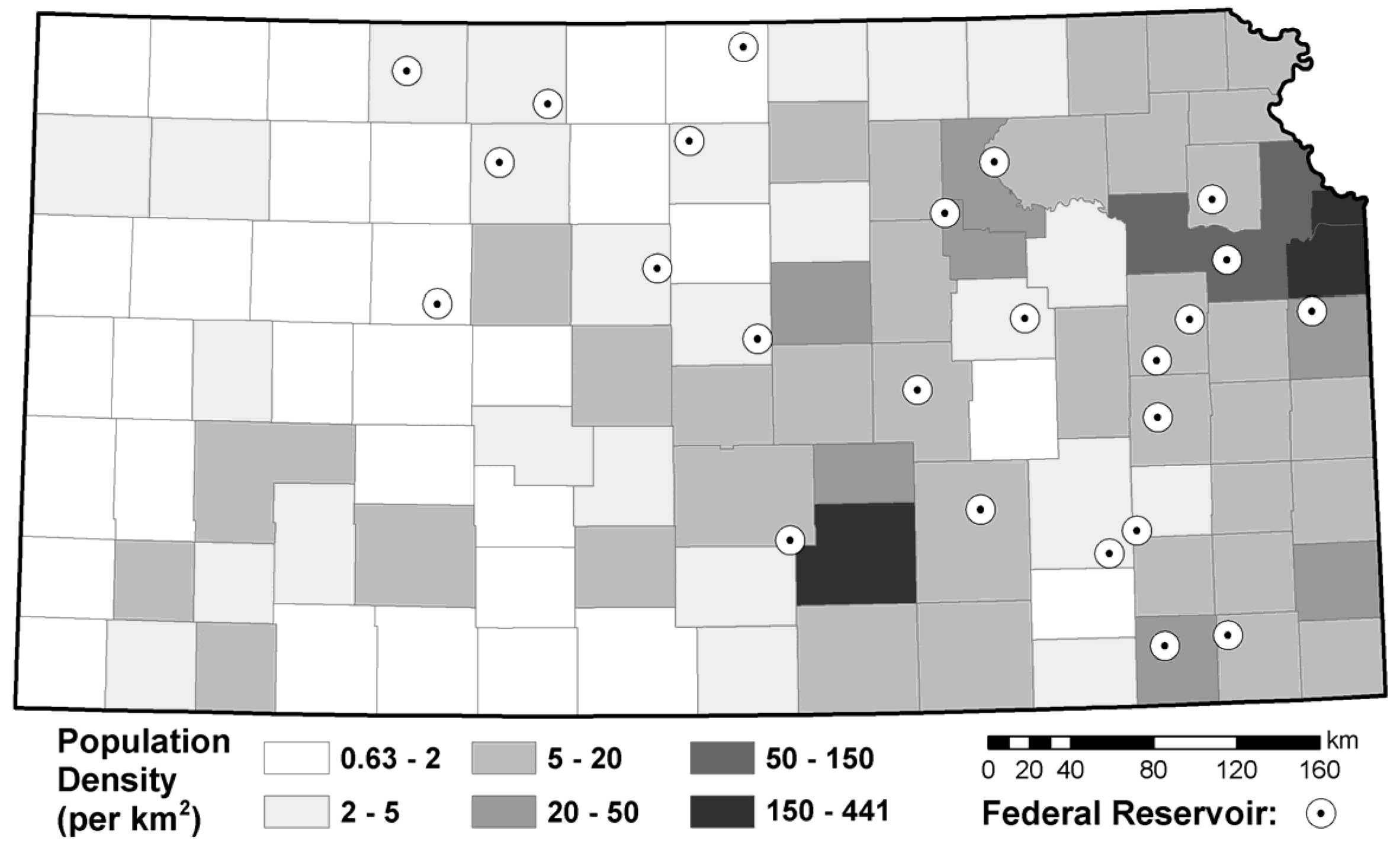
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
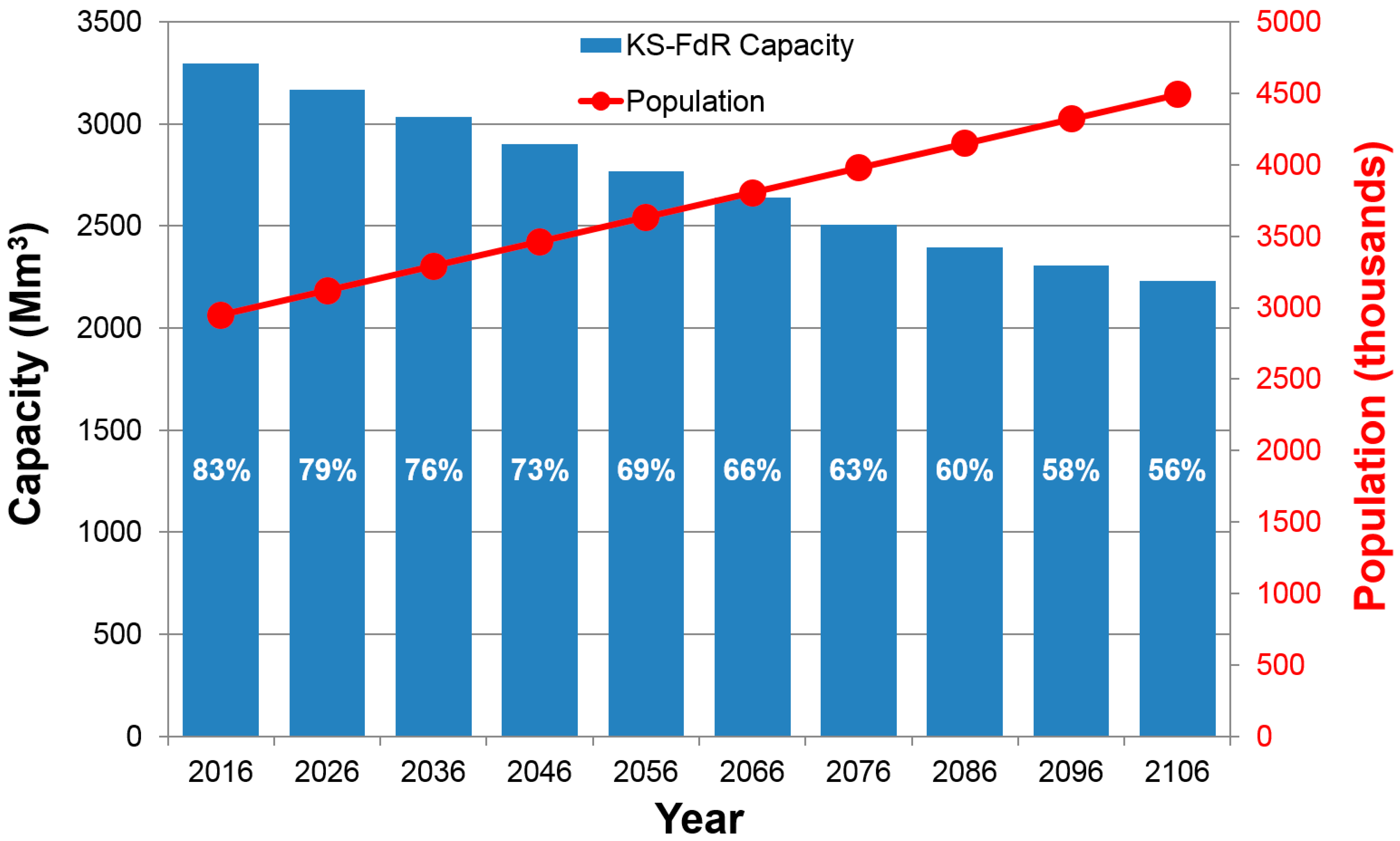
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, N. A History of Dams; Peter Davies: London, UK, 1971; p. 279. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, M.; Lall, U.; Allaire, M.; Devineni, N.; Kwon, H.H.; Pal, I.; Raff, D.; Wegner, D. The Future Role of Dams in the United States of America. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 982–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilt, B.; Braun, Y.; He, D. Social Impacts of Large Dam Projects: A Comparison of International Case Studies and Implications for Best Practice. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, S257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCully, P. Rivers No More: The Environmental Effects of Dams; Zed Books: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shucheng, W. On Dam Construction and Ecological Protection. China Three Gorges Construct. 2004, 6, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, E.; Hildyard, N. The Social and Environmental Effects of Large Dams. Volume 1: Overview; Wadebridge Ecological Centre: Camelford, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, J.S.; Basson, G.R. The Hydraulics of the Impacts of Dam Development on the River Morphology; Water Research Commission: Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Meade, R.H.; Moody, J.A. Causes for the Decline of Suspended-Sediment Discharge in the Mississippi River System, 1940–2007. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryirs, K. (Dis) Connectivity in Catchment Sediment Cascades: A Fresh Look at the Sediment Delivery Problem. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselman, N.E.; Middelkoop, H. Floodplain Sedimentation: Quantities, Patterns and Processes. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1995, 20, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K. Reservoir Sedimentation: Impact, Extent, and Mitigation; International Bank for Reconstruction and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Meade, R.H.; Parker, R.S. Sediment in Rivers of the United States. US Geol. Surv. Water-Suppl. Pap. 1985, 2275, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Huntzinger, T.L. Surface water: A critical resource of the Great Plains. In Conservation of Great Plains Ecosystems: Current Science, Future Options; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 253–273. [Google Scholar]
- Annandale, G. Quenching the Thirst: Sustainable Water Supply and Climate Change; CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform: North Charleston, SC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Noyelles, F.; Jakubauskas, M. Current State, Trend, and Spatial Variability of Sediment in Kansas Reservoirs. In Sedimentation in Our Reservoirs: Causes and Solutions; Kansas State University Agricultural Experiment Station and Cooperative Extension Service: Manhattan, KS, USA, 2008; pp. 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Texas State Historical Association (TSHA). Lakes and Reservoirs. Available online: http://www.texasalmanac.com/topics/environment/lakes-and-reservoirs (accessed on 13 September 2017).
- Vance, B.; Whitley, D.; Mills, O. Lakes of Oklahoma, 2nd ed.; Oklahoma Water Resources Board and Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation: Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 2012; p. 179. [Google Scholar]
- Hurd, B.; Leary, N.; Jones, R.; Smith, J. Relative Regional Vulnerability of Water Resources to Climate Change. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1999, 35, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, M. From Safe Yield to Sustainable Development of Water Resources—The Kansas Experience. J. Hydrol. 2000, 235, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Chen, X. Evaluation of the Impact of Groundwater Irrigation on Streamflow in Nebraska. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.P.; Buddemeier, R.W. Climate Variation: Implications of Long-Term Records and Recent Observations; Kansas Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Milly, P.C.; Dunne, K.A.; Vecchia, A.V. Global Pattern of Trends in Streamflow and Water Availability in a Changing Climate. Nature 2005, 438, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, N.J.; Brown, R.A.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Thomson, A.M. Integrated Assessment of Hadley Centre (HadCM2) Climate Change Projections on Agricultural Productivity and Irrigation Water Supply in the Conterminous United States: I. Climate Change Scenarios and Impacts on Irrigation Water Supply Simulated with the HUMUS Model. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2003, 117, 73–96. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, V.; Hutchinson, S.L.; Harrington, J.A.; Hutchinson, J.M.S. Analysis of Frequency and Magnitude of Extreme Rainfall Events with Potential Impacts on Flooding; a Case Study from the Central United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 3578–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansas Water Office (KWO). Reservoir Information. Available online: https://kwo.ks.gov/reservoirs (accessed on 13 September 2017).
- Martinko, E.; deNoyelles, J.; Bosnak, K.; Jakubauskas, M.; Huggins, D.; Kastens, J.; Shreders, A.; Baker, D.; Blackwood, A.; Campbell, S.; et al. Atlas of Kansas Lakes: A resource for Communities, Policy Makers and Planners; Kansas Biological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, S. Uncertainty in Bathymetric Surveys; U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center, Defense Technical Information Center: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, T.; Mitchell, N.C.; Ramsay, A.T.S. Characterizing Uncertainties for Quantifying Bathymetry Change between Time-Separated Multibeam Echo-Sounder Surveys. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansas Water Office (KWO). John Redmond Dredging Initiative. Available online: http://kwo.ks.gov/projects/john-redmond-dredging (accessed on 13 September 2017).
- USGS National Hydrography Dataset (NHD). United Sates Geological Survey, Department of the Interior. Available online: http://nhd.usgs.gov/data.html (accessed on 20 September 2015).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Western Ecology Division. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/wed/pages/ecoregions.htm (accessed on 20 September 2015).
- Kenny, J.F. Public-Supply Water Use in Kansas, 1990–2012; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2014.
- PRISM Climate Group. PRISM Climate Data. Northwest Alliance for Computational Science & Engineering. Available online: http://prism.oregonstate.edu (accessed on 13 September 2017).
- Rahmani, V.; Hutchinson, S.L.; Hutchinson, J.M.S.; Aavudai, A. Extreme Daily Rainfall Event Distribution Patterns in Kansas. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, V.; Hutchinson, S.L.; Harrington, J.A., Jr.; Hutchinson, J.M.S.; Anandhi, A. Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Distribution and Change-Points for Annual Precipitation in Kansas, USA. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3879–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNoyelles, F.; Kastens, J.H. Reservoir Sedimentation Challenges Kansas. Trans. Kans. Acad. Sci. 2016, 119, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liechti, P.M.; Jakubauskas, M.; deNoyelles, J.; Martinko, E.A. Characterization and Mapping of Sediment Thickness and Pattern in John Redmond Reservoir, Coffey County, Kansas; Applied Science and Technology for Reservoir Assessment Program, Kansas Biological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2014.
- Baker, D.; Everhart, R.; Huggins, D.; Bennett, L.; Blackwood, A. Biological Impairment in Three Kansas Reservoirs and Associated Lotic Ecosystems due to Sediment and Nutrients; Kansas Biological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Institute for Policy & Social Research (IPSR). Kansas Statistical Abstract 2015; Institute for Policy & Social Research: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Census Bureau. State Population Total. U.S. Department of Commerce. Available online: https://www.census.gov/data/tables/2016/demo/popest/state-total.html (accessed on 28 May 2017).
- Jakubauskas, M.; deNoyelles, J.; Martinko, E. Bathymetric Survey of John Redmond Reservoir, Coffey County, Kansas; Kansas Biological Survey, Applied Science and Technology for Reservoir Assessment Program, Kansas Biological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shotbolt, L.A.; Thomas, A.D.; Hutchinson, S.M. The use of Reservoir Sediments as Environmental Archives of Catchment Inputs and Atmospheric Pollution. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2005, 29, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juracek, K.E. Suspended-Sediment Loads and Reservoir Sediment Trap Efficiency for Clinton Lake, Kansas, 2010–2012; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2013.
- Vanoni, V.A. Sedimentation Engineering; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2006; p. 418. [Google Scholar]
- Brune, G.M. Trap Efficiency of Reservoirs. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1953, 34, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, A.; Elsahabi, M.; Ali, K. A Satellite Remote Sensing Approach to Estimate the Lifetime Span of Aswan High Dam Reservoir; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sumi, T.; Okano, M.; Takata, Y. Reservoir Sedimentation Management with Bypass Tunnels in Japan. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on River Sedimentation, Yichang, China, 18–21 October 2004; pp. 1036–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Tate, E.L.; Farquharson, F.A. Simulating Reservoir Management Under the Threat of Sedimentation: The Case of Tarbela Dam on the River Indus. Water Resour. Manag. 2000, 14, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.D.; He, D.M.; Lu, X.X. Sedimentation in the Manwan Reservoir in the Upper Mekong and its Downstream Impacts. Quat. Int. 2008, 186, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, J.C.; Guntner, A.; Bronstert, A. Loss of Reservoir Volume by Sediment Deposition and its Impact on Water Availability in Semiarid Brazil. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glymph, L.M. Summary: Sedimentation of Reservoirs. In Man-Made Lakes: Their Problems and Environmental Effects; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1973; pp. 342–348. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.O.; Vetter, C.P.; Cummings, G.B. Comprehensive Survey of Sedimentation in Lake Mead, 1948–49; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1960.
- Mount, J.F. California Rivers and Streams: The Conflict between Fluvial Process and Land Use; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dendy, F.M.; Champion, W.A.; Wilson, R.B. Reservoir sedimentation surveys in the United States. In Man-Made Lakes: Their Problems and Environmental Effects; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1973; pp. 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Crowder, B.M. Economic Costs of Reservoir Sedimentation: A Regional Approach to Estimating Cropland Erosion Damage. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1987, 42, 194–197. [Google Scholar]
- Homer, C.G.; Dewitz, J.A.; Yang, L.; Jin, S.; Danielson, P.; Xian, G.; Coulston, J.; Herold, N.D.; Wickham, J.D.; Megown, K. Completion of the 2011 National Land Cover Database for the Conterminous United States-Representing a Decade of Land Cover Change Information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Callihan, R.A. Distribution, Proliferation and Significance of Small Impoundments in Kansas; University of Kansas: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Verstraeten, G.; Prosser, I.P.; Fogarty, P. Predicting the Spatial Patterns of Hillslope Sediment Delivery to River Channels in the Murrumbidgee Catchment, Australia. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 440–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doetterl, S.; Van Oost, K.; Six, J. Towards Constraining the Magnitude of Global Agricultural Sediment and Soil Organic Carbon Fluxes. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2012, 37, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbein, W.B.; Schumm, S.A. Yield of Sediment in Relation to Mean Annual Precipitation. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1958, 39, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.L.; Annandale, G.; Hotchkiss, R. Reservoir Sedimentation. In Sedimentation Engineering: Processes, Measurements, Modeling, and Practice; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 579–612. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.L.; Fan, J. Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook: Design and Management of Dams, Reservoirs, and Watersheds for Sustainable Use; McGraw Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, B.N. Life of Reservoir; Central Board of Irrigation and Power: New Delhi, India, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, M. Sedimentation Engineering: Processes, Measurements, Modeling, and Practice; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; p. 1132. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, R.I.; Pemberton, E.L. Reservoir Sedimentation Technical Guidelines for Bureau of Reclamation; US Bureau of Reclamation: Denver, CO, USA, 1982.
- Lajczak, A. Modelling the Long-Term course of Non-Flushed Reservoir Sedimentation and Estimating the Life of Dams. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1996, 21, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansas Water Office (KWO). Surplus Water Available in Water Marketing Program Lakes Calendar Year 2015; Kansas Water Office: Topeka, KS, USA, 2015.
- Kansas Water Office (KWO). Kansas Water Vision. Kansas Water Office. Available online: http://kwo.ks.gov/water-vision-water-plan/water-vision (accessed on 17 January 2018).
- Minear, J.T.; Kondolf, G.M. Estimating Reservoir Sedimentation Rates at Large Spatial and Temporal Scales: A Case Study of California. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renwick, W.H.; Carlson, K.J.; Hayes-Bohanan, J.K. Trends in Recent Reservoir Sedimentation Rates in Southwestern Ohio. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 60, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- National Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). Sediment Delivered to Rivers and Streams from Sheet and Rill Erosion; US Department of Agricutlure: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- National Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). Soil Erosion on Cropland 2007; National Resources Conservation Service (NRCS): Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Renwick, W.H.; Smith, S.V.; Bartley, J.D.; Buddemeier, R.W. The Role of Impoundments in the Sediment Budget of the Conterminous United States. Geomorphology 2005, 71, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, L.J. A Reservoir Sedimentation Survey Information system—RESIS. In Proceedings of the Sixth Federal Interagency Sedimentation Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–14 March 1996; pp. 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubauskas, M.; deNoyelles, J.; Martinko, E.A. Bathymetric and Sediment Survey of Elk City Reservoir, Montgomery County, Kansas; Applied Science and Technology for Reservoir Assessment Program, Kansas Biological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Boyce, R.C. Sediment Routing with Sediment Delivery Ratios; Present and Prospective Technology for Predicting Sediment Yields and Sources, Publ. ARS-S-40; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; pp. 61–65.
- Hrissanthou, V. Computation of Lake or Reservoir Sedimentation in Terms of Soil Erosion. In Sediment Transport in Aquatic Environments; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, L.J.; Hernandez, M.; Nichols, M. Processes Controlling Sediment Yield from Watersheds as Functions of Spatial Scale. Environ. Model. Softw. 1997, 12, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkinshaw, S.J.; Bathurst, J.C. Model Study of the Relationship between Sediment Yield and River Basin Area. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, D.D. Sediment Yields from Small Drainage Areas in Kansas; Kansas Water Resources Board: Topeka, KS, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Gao, Y.; Annandale, G.W.; Morris, G.L.; Jiang, E.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Carling, P.; Fu, K.; Guo, Q. Sustainable Sediment Management in Reservoirs and Regulated Rivers: Experiences from Five Continents. Earth Future 2014, 2, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiss, A.J.; Franca, M.J.; Juez, C.; De Cesare, G. Reservoir Sedimentation. J. Hydraul. Res. 2016, 54, 595–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.W.; Hotchkiss, R.H.; Huffaker, R. Reservoir Sustainability and Sediment Management. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 143, 04016077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Water Supply Storage Reallocation John Redmond Dam and Reservoir, Kansas; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2013.
- United State Army Corps of Engineers. Tuttle Creek Lake Hydrosuction Assessment; United State Army Corps of Engineers: Kansas City, KS, USA, 2017.
- Fox, G.A.; Sheshukov, A.; Cruse, R.; Kolar, R.L.; Guertault, L.; Gesch, K.R.; Dutnell, R.C. Reservoir Sedimentation and Upstream Sediment Sources: Perspectives and Future Research Needs on Streambank and Gully Erosion. Environ. Manag. 2016, 57, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansas Water Office (KWO). Streambank Stabilization Projects. Available online: https://kwo.ks.gov/projects/streambank-stabilization-projects (accessed on 25 October 2017).
- Huggins, D.; Kastens, J.; Baker, D.; Freeman, C. Conversion of Existing Farm Ponds to Wetlands in Agricultural Landscapes for Mitigation, Land Use Treatment and Conservation with a Perspective toward Climate Change; Kansas Biological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kansas Alliance for Wetlands and Streams (KAWS). Flint Hills Stream the Subject of Holistic Watershed Management Plan. Available online: http://www.kaws.org/news/flinthillsstreamthesubjectofholisticwatershedmanagementplan (accessed on 25 October 2017).
- Falinski, K.; Penn, D. Loss of Reservoir Capacity through Sedimentation in Hawai i: Management Implications for the Twenty-First Century. Pac. Sci. 2018, 72, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolak, C.J.; Doyle, M.W. Reservoir Sedimentation and Storage Capacity in the United States: Management Needs for the 21st Century. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 141, 02515001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
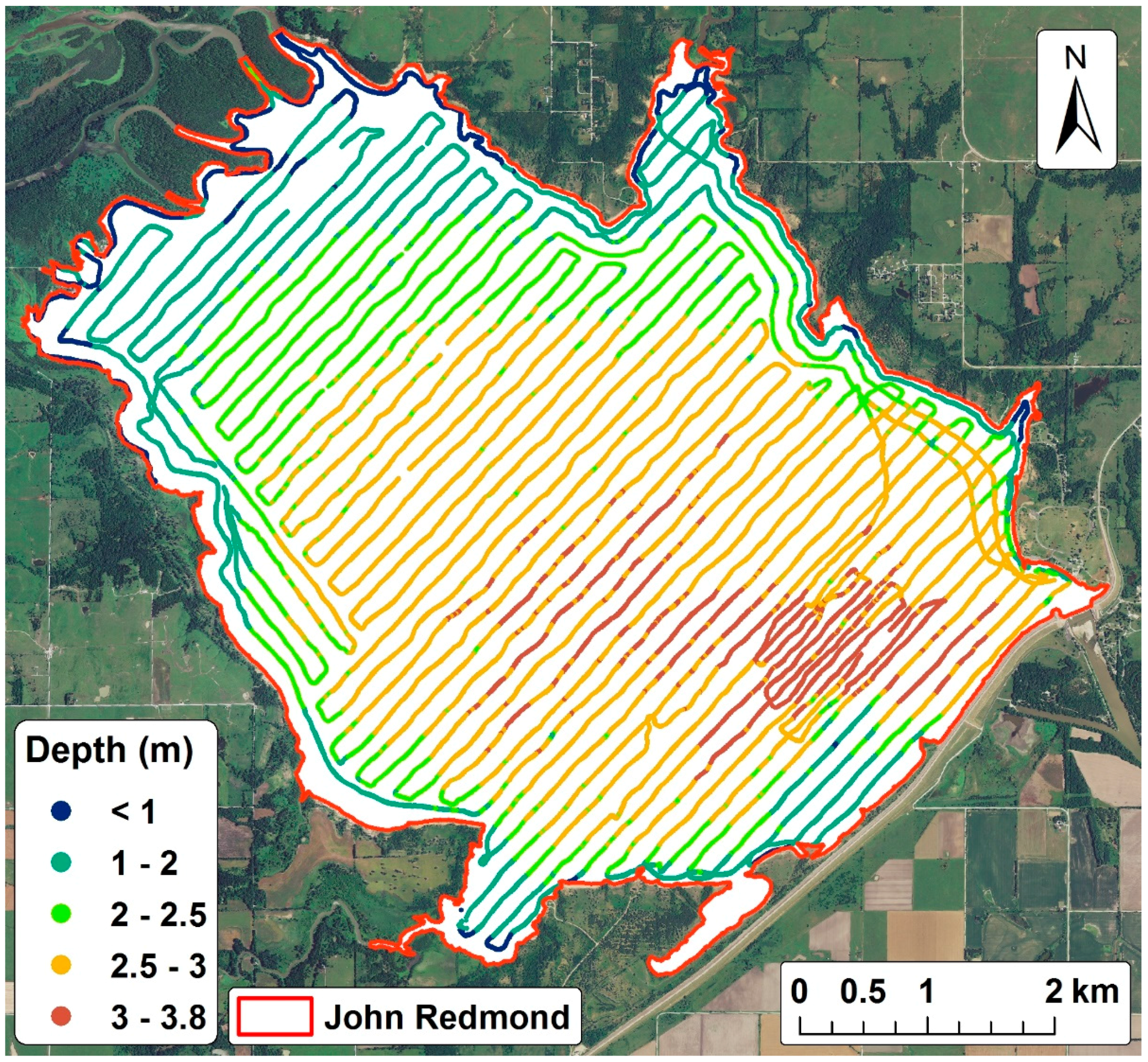
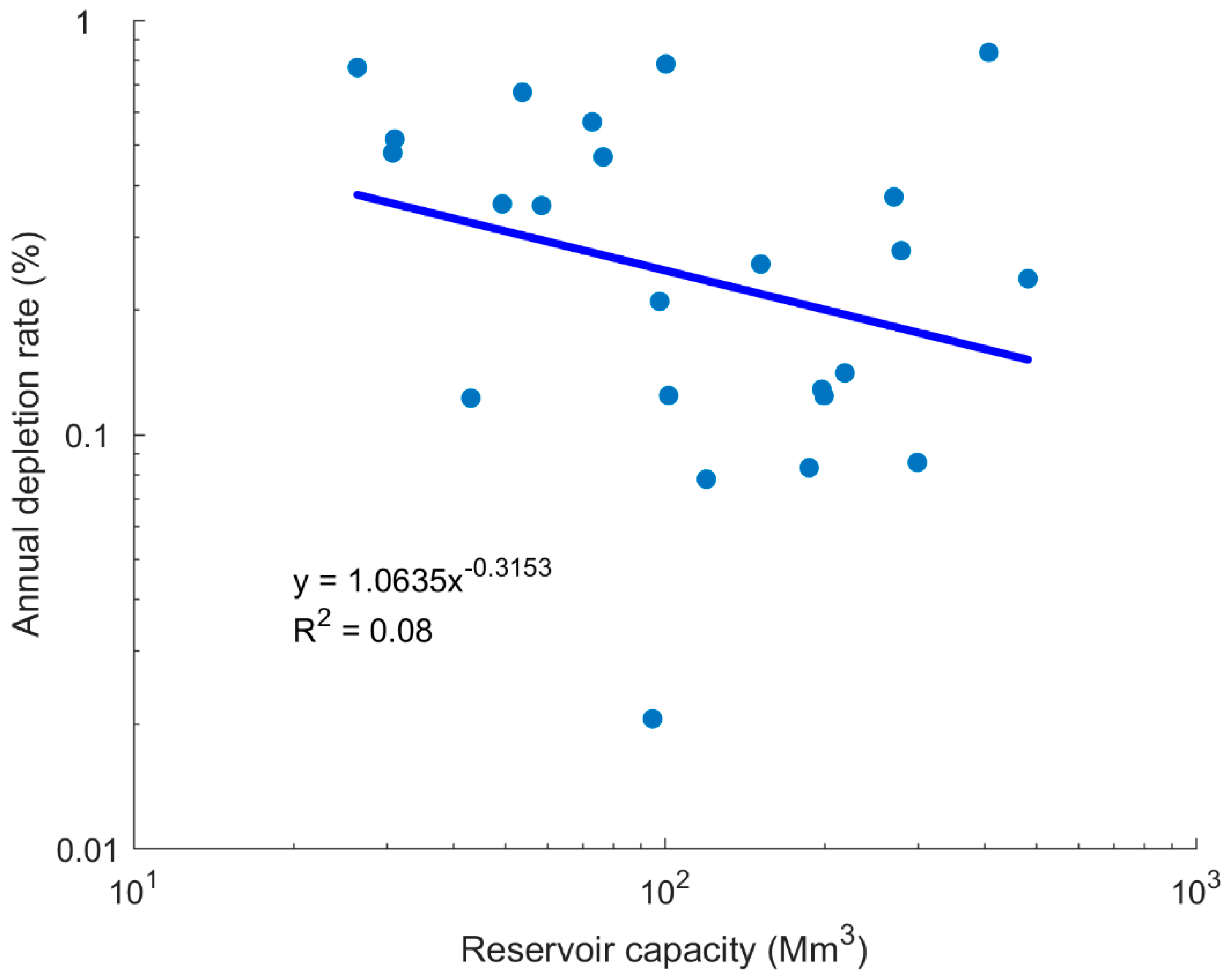
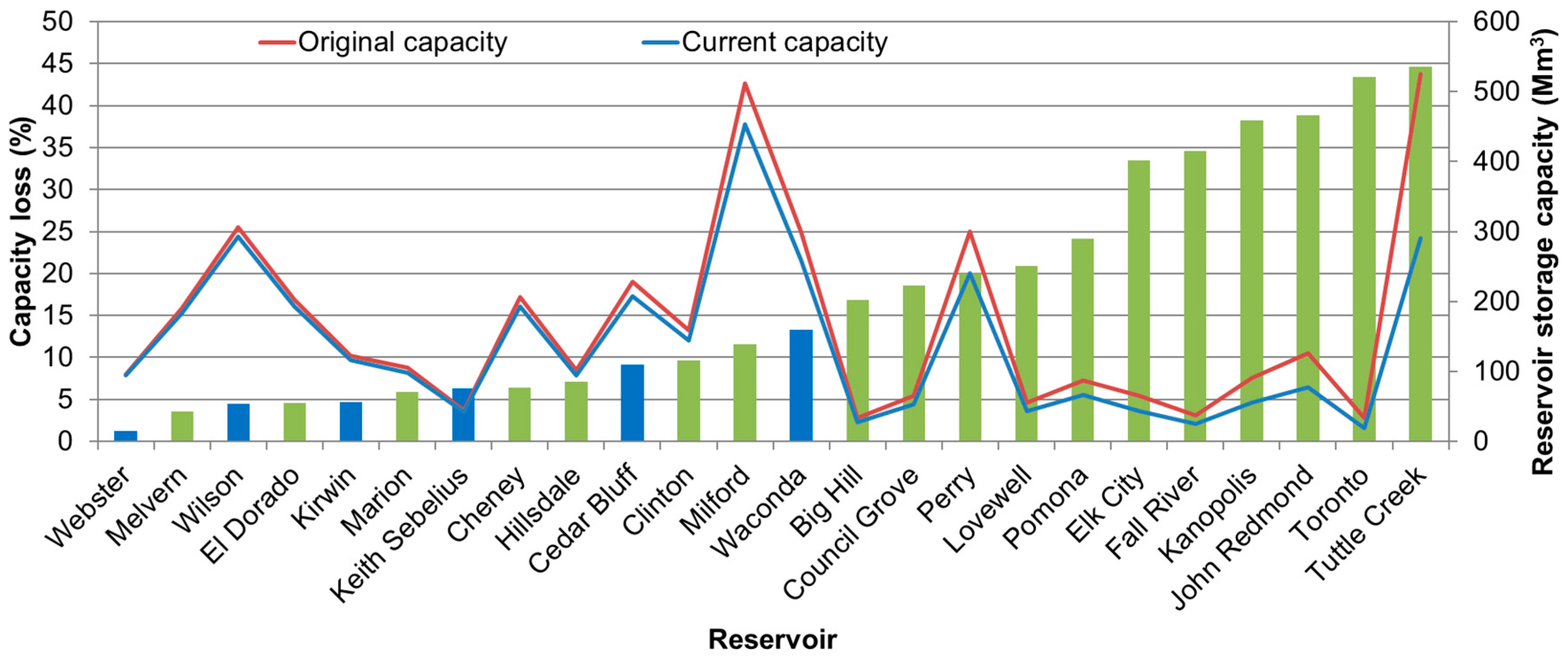
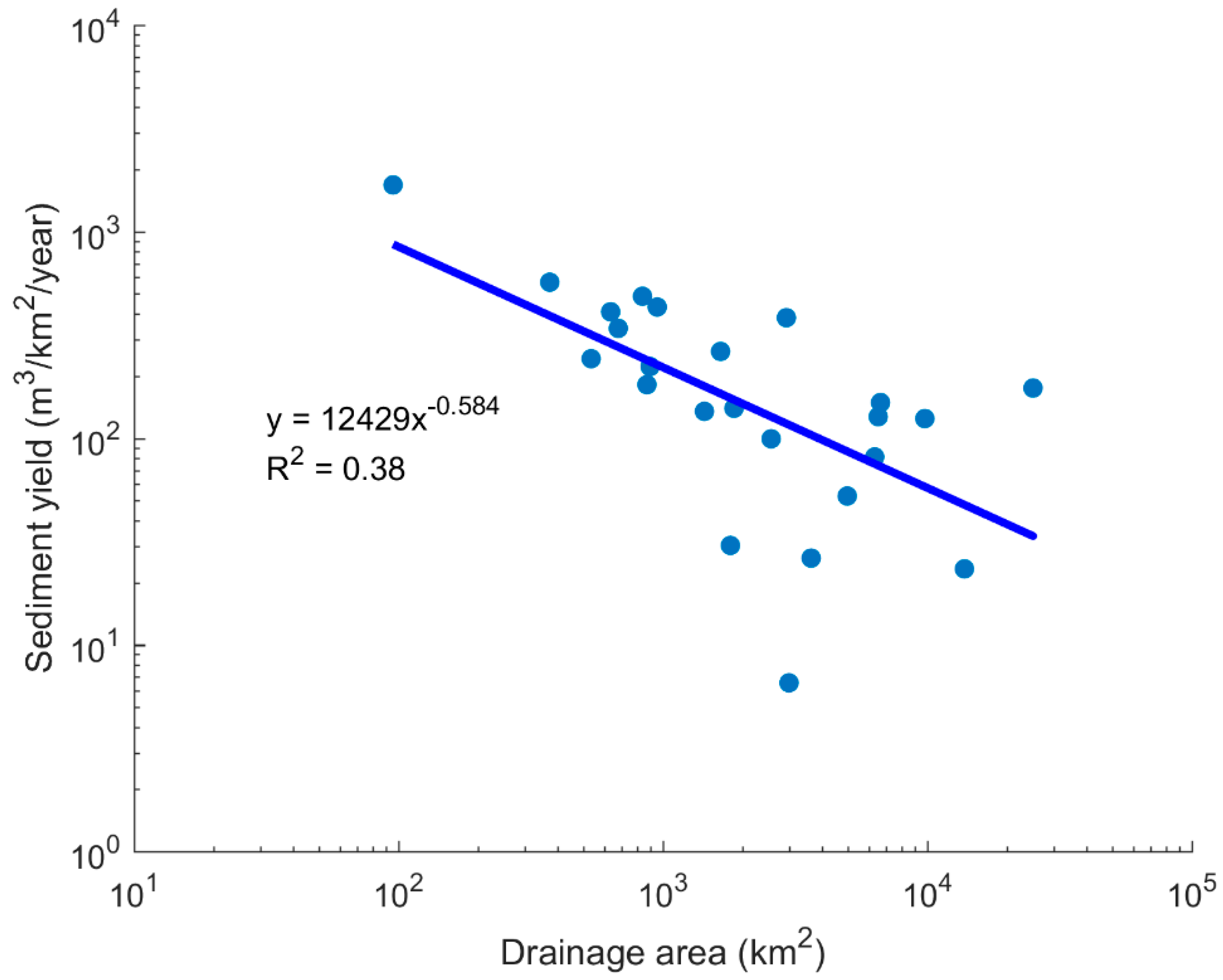
| Reservoir | W (km2) | t0 (year) | V0 (Mm3) | tr (year) | Vr (Mm3) | Vc (Mm3) | Lc (%) | D (%) | Y (m3/km2/year) | t1/2 (year) | Bathymetric Data Source * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Big Hill | 95 | 1980 | 34 | 2010 | 29 | 28 | 17.3 | 0.48 | 1688 | 2085 | USACE |
| Cedar Bluff | 13,794 | 1950 | 229 | 2000 | 213 | 208 | 9.3 | 0.14 | 23 | 2306 | BOR |
| Cheney | 2566 | 1964 | 206 | 1998 | 197 | 193 | 6.5 | 0.12 | 99 | 2368 | USGS |
| Clinton | 950 | 1977 | 159 | 2009 | 146 | 143 | 9.9 | 0.26 | 433 | 2172 | KBS |
| Council Grove | 677 | 1963 | 65 | 2008 | 54 | 52 | 18.9 | 0.36 | 341 | 2104 | KBS |
| El Dorado | 634 | 1979 | 202 | 2004 | 196 | 193 | 4.7 | 0.13 | 410 | 2369 | OWRB |
| Elk City | 1650 | 1965 | 65 | 2008 | 46 | 43 | 34.2 | 0.67 | 263 | 2040 | KBS |
| Fall River | 1433 | 1948 | 37 | 2010 | 26 | 24 | 35.1 | 0.52 | 135 | 2045 | KBS |
| Hillsdale | 372 | 1981 | 101 | 2009 | 95 | 94 | 7.3 | 0.21 | 571 | 2220 | KBS |
| John Redmond | 6642 | 1963 | 126 | 2014 | 78 | 76 | 39.6 | 0.75 | 142 | 2030 | KBS |
| Kanopolis | 6322 | 1948 | 90 | 2007 | 60 | 55 | 38.9 | 0.57 | 81 | 2036 | KBS |
| Keith Sebelius | 1799 | 1964 | 45 | 2000 | 43 | 42 | 6.4 | 0.12 | 30 | 2373 | BOR |
| Kirwin | 3635 | 1955 | 123 | 2013 | 117 | 117 | 4.8 | 0.08 | 26 | 2597 | KBS |
| Lovewell | 894 | 1957 | 55 | 2011 | 44 | 43 | 21.3 | 0.36 | 223 | 2096 | KBS |
| Marion | 535 | 1967 | 105 | 2008 | 99 | 98 | 6.0 | 0.12 | 243 | 2371 | KBS |
| Melvern | 869 | 1972 | 190 | 2009 | 185 | 183 | 3.6 | 0.08 | 182 | 2575 | KBS |
| Milford | 9777 | 1967 | 512 | 2009 | 460 | 452 | 11.8 | 0.24 | 125 | 2177 | USACE |
| Perry | 2924 | 1966 | 300 | 2009 | 247 | 238 | 20.6 | 0.41 | 424 | 2088 | USACE |
| Pomona | 835 | 1963 | 87 | 2009 | 68 | 66 | 24.7 | 0.47 | 488 | 2071 | KBS |
| Toronto | 1854 | 1959 | 34 | 2010 | 20 | 19 | 44.2 | 0.77 | 140 | 2024 | KBS |
| Tuttle Creek | 25,070 | 1962 | 525 | 2009 | 317 | 286 | 45.4 | 0.84 | 175 | 2022 | USACE |
| Waconda | 6518 | 1967 | 299 | 2001 | 271 | 258 | 13.5 | 0.28 | 127 | 2148 | BOR |
| Webster | 2997 | 1956 | 95 | 2011 | 94 | 94 | 1.2 | 0.02 | 7 | 4388 | KBS |
| Wilson | 4976 | 1963 | 306 | 2008 | 294 | 292 | 4.5 | 0.09 | 53 | 2548 | KBS |
| Sum | 97,817 | 3990 | 3298 | ||||||||
| Mean | 4076 | 166 | 137 | 17.9 | 0.34 | 268 | |||||
| Median | 1827 | 114 | 96 | 12.6 | 0.27 | 159 | |||||
| Max | 25,070 | 525 | 452 | 45.4 | 0.84 | 1688 | |||||
| Min | 95 | 34 | 19 | 1.2 | 0.02 | 7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahmani, V.; Kastens, J.H.; DeNoyelles, F.; Jakubauskas, M.E.; Martinko, E.A.; Huggins, D.H.; Gnau, C.; Liechti, P.M.; Campbell, S.W.; Callihan, R.A.; et al. Examining Storage Capacity Loss and Sedimentation Rate of Large Reservoirs in the Central U.S. Great Plains. Water 2018, 10, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020190
Rahmani V, Kastens JH, DeNoyelles F, Jakubauskas ME, Martinko EA, Huggins DH, Gnau C, Liechti PM, Campbell SW, Callihan RA, et al. Examining Storage Capacity Loss and Sedimentation Rate of Large Reservoirs in the Central U.S. Great Plains. Water. 2018; 10(2):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020190
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahmani, Vahid, Jude H. Kastens, Frank DeNoyelles, Mark E. Jakubauskas, Edward A. Martinko, Donald H. Huggins, Christian Gnau, Paul M. Liechti, Scott W. Campbell, Ryan A. Callihan, and et al. 2018. "Examining Storage Capacity Loss and Sedimentation Rate of Large Reservoirs in the Central U.S. Great Plains" Water 10, no. 2: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020190
APA StyleRahmani, V., Kastens, J. H., DeNoyelles, F., Jakubauskas, M. E., Martinko, E. A., Huggins, D. H., Gnau, C., Liechti, P. M., Campbell, S. W., Callihan, R. A., & Blackwood, A. J. (2018). Examining Storage Capacity Loss and Sedimentation Rate of Large Reservoirs in the Central U.S. Great Plains. Water, 10(2), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020190






