Decline of N and P Uptake in the Inner Protection Zone of a Terminal Reservoir during Inter-Basin Water Transfers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
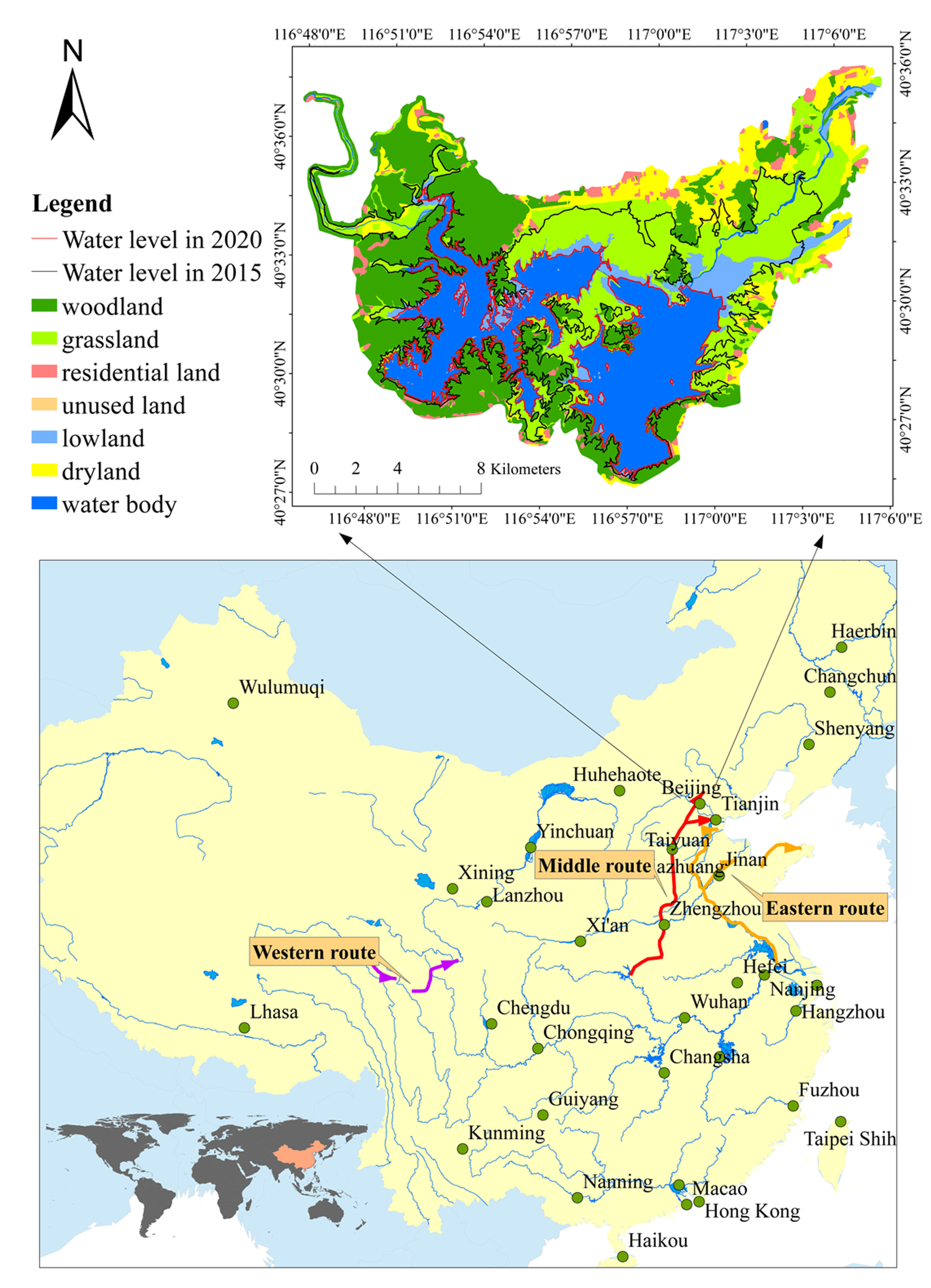
2.1. Study Area
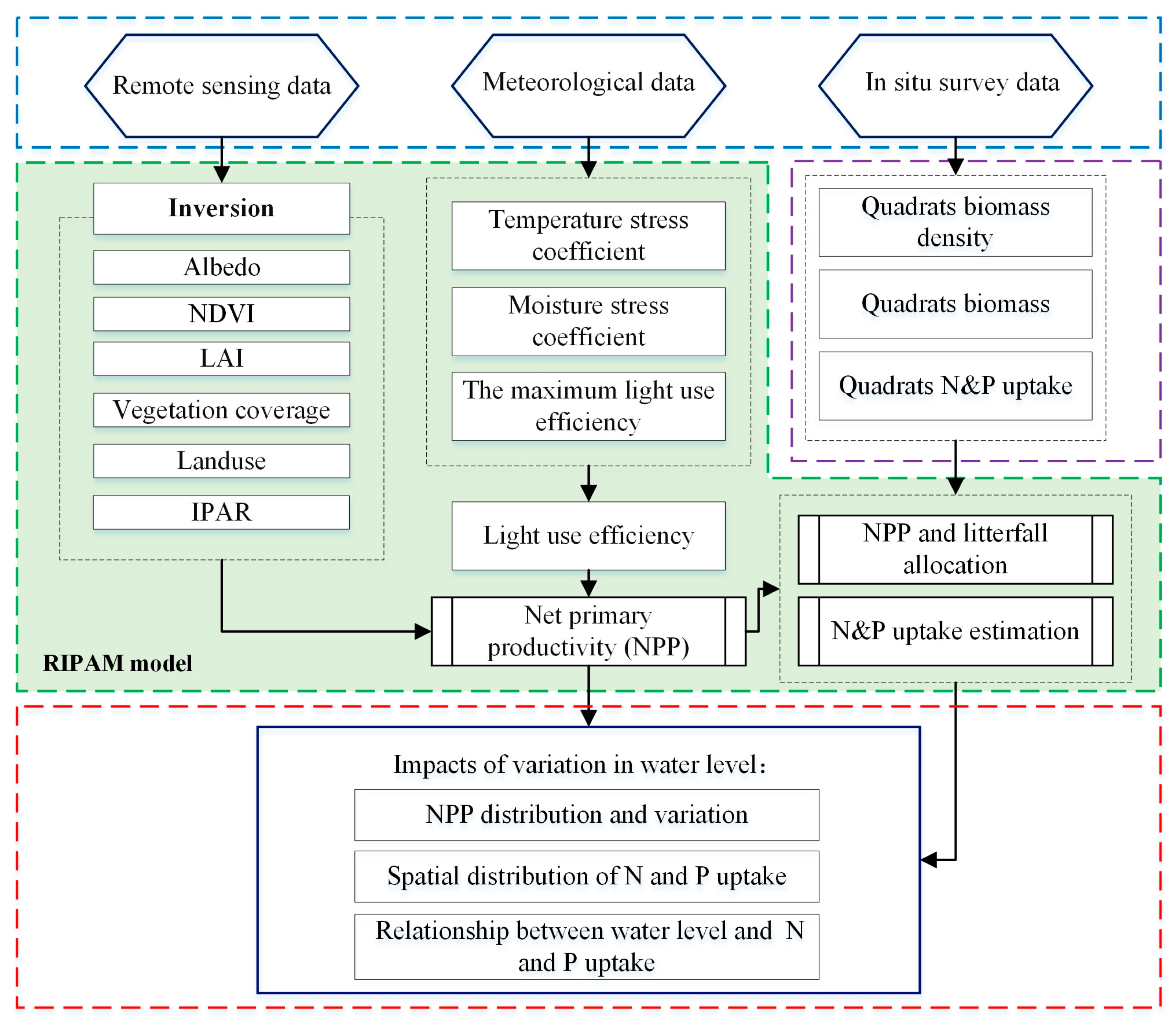
2.2. Simulation of N and P Uptake
2.3. Multi-Source Data for Driving the RIPAM
2.4. In Situ Survey Data for Validation
3. Results
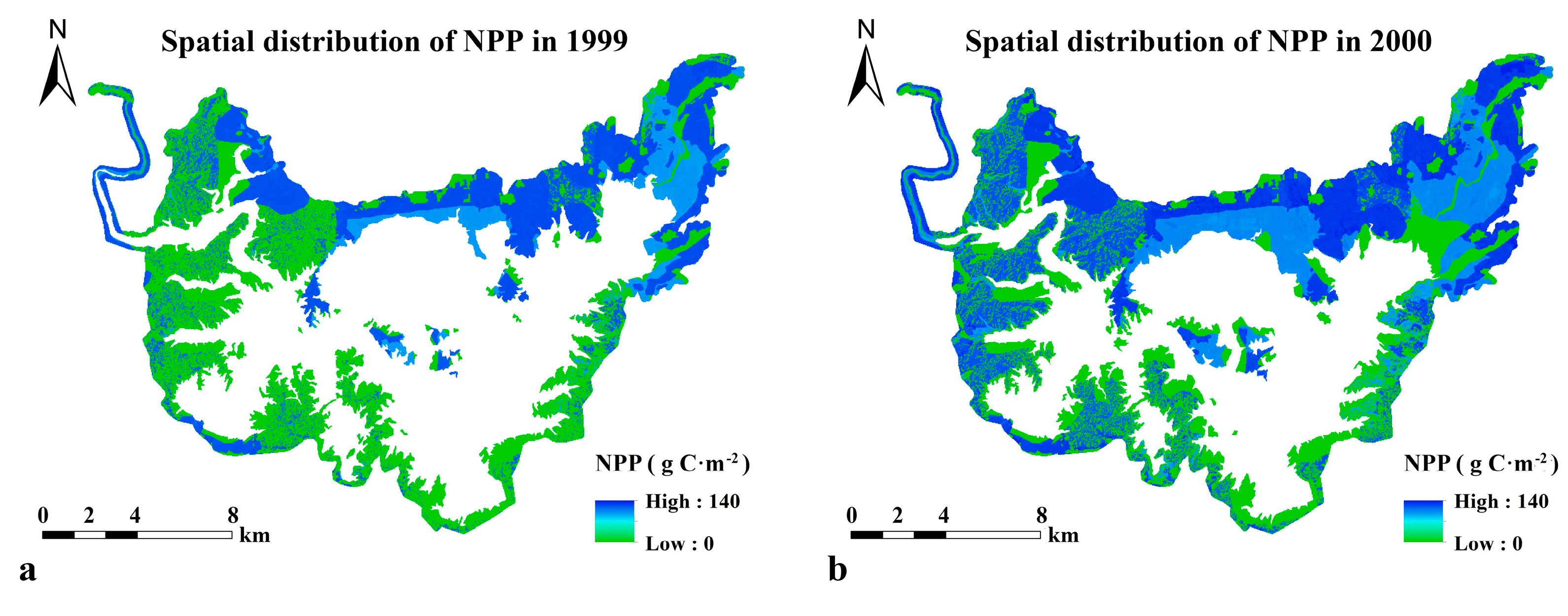
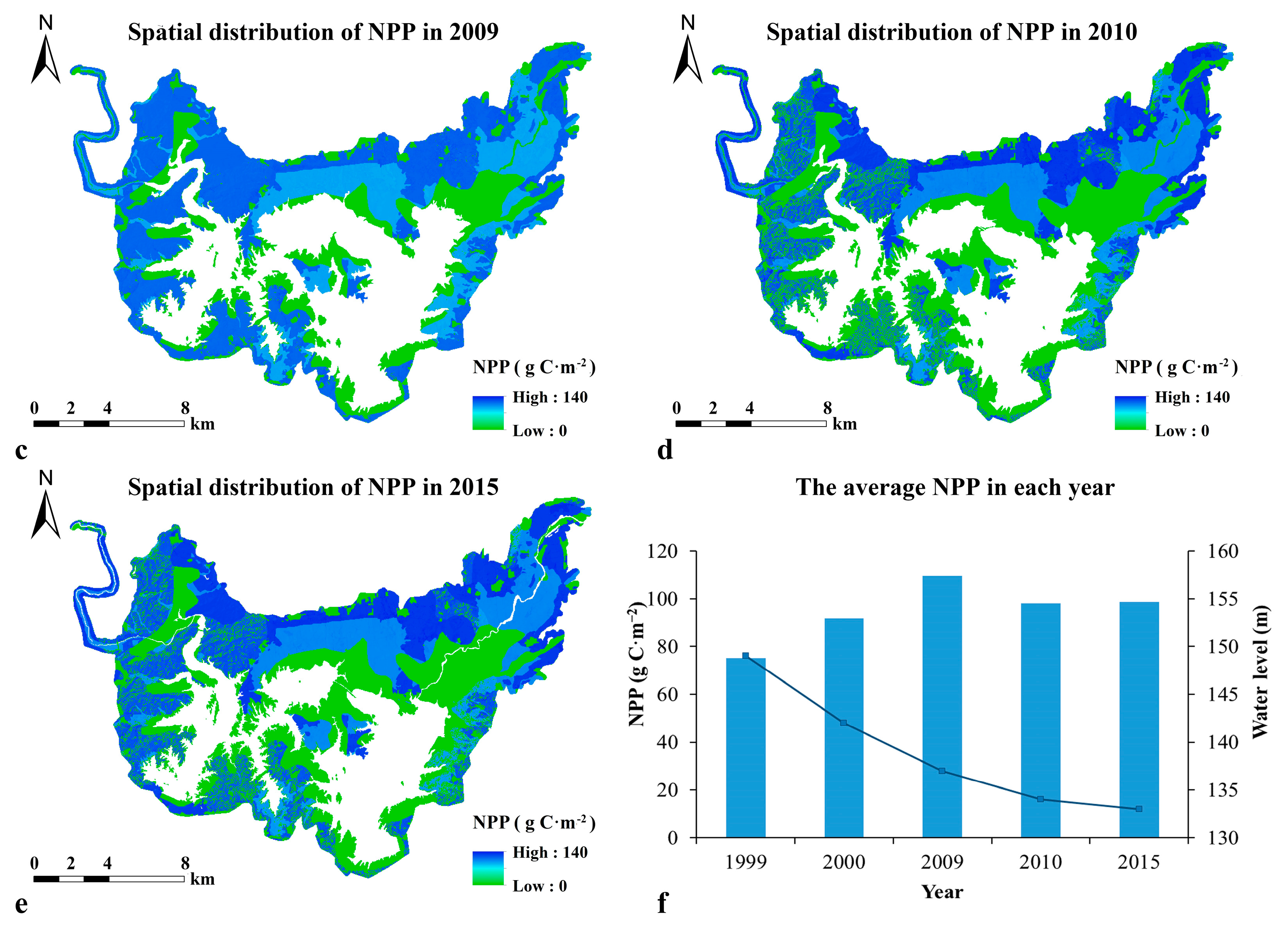
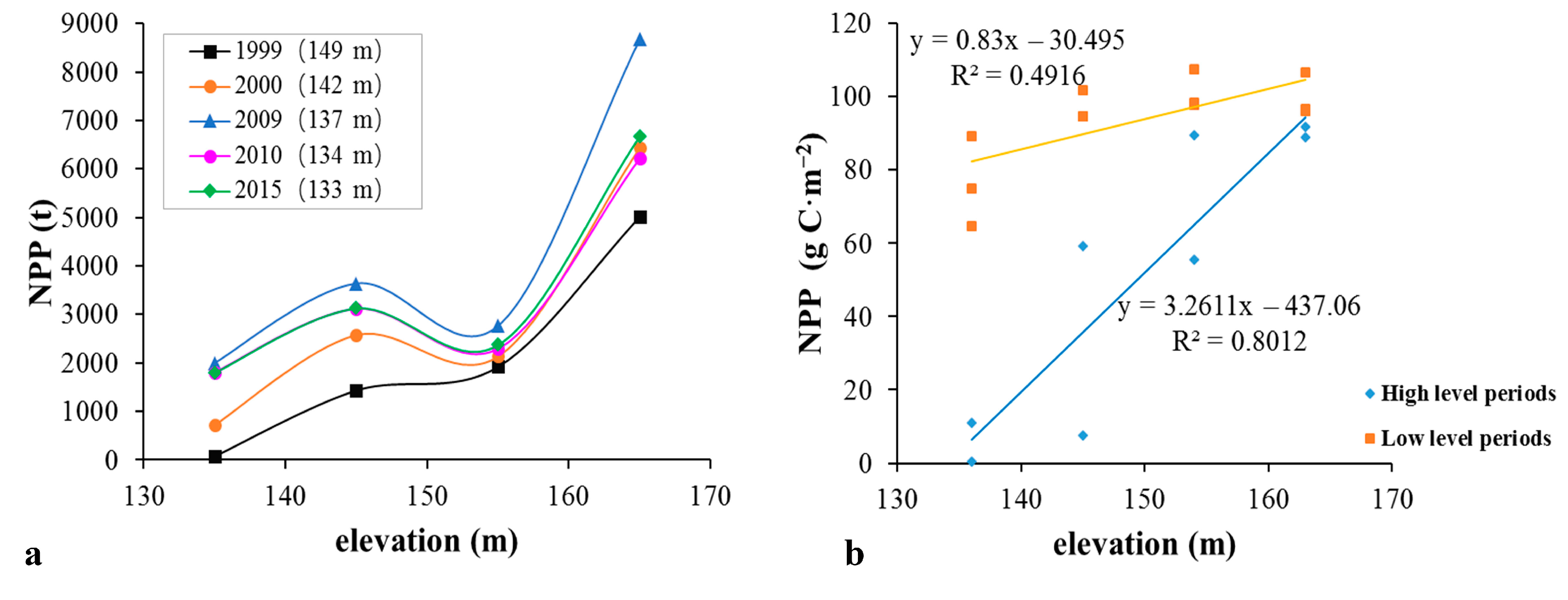
3.1. NPP Distribution and Variation
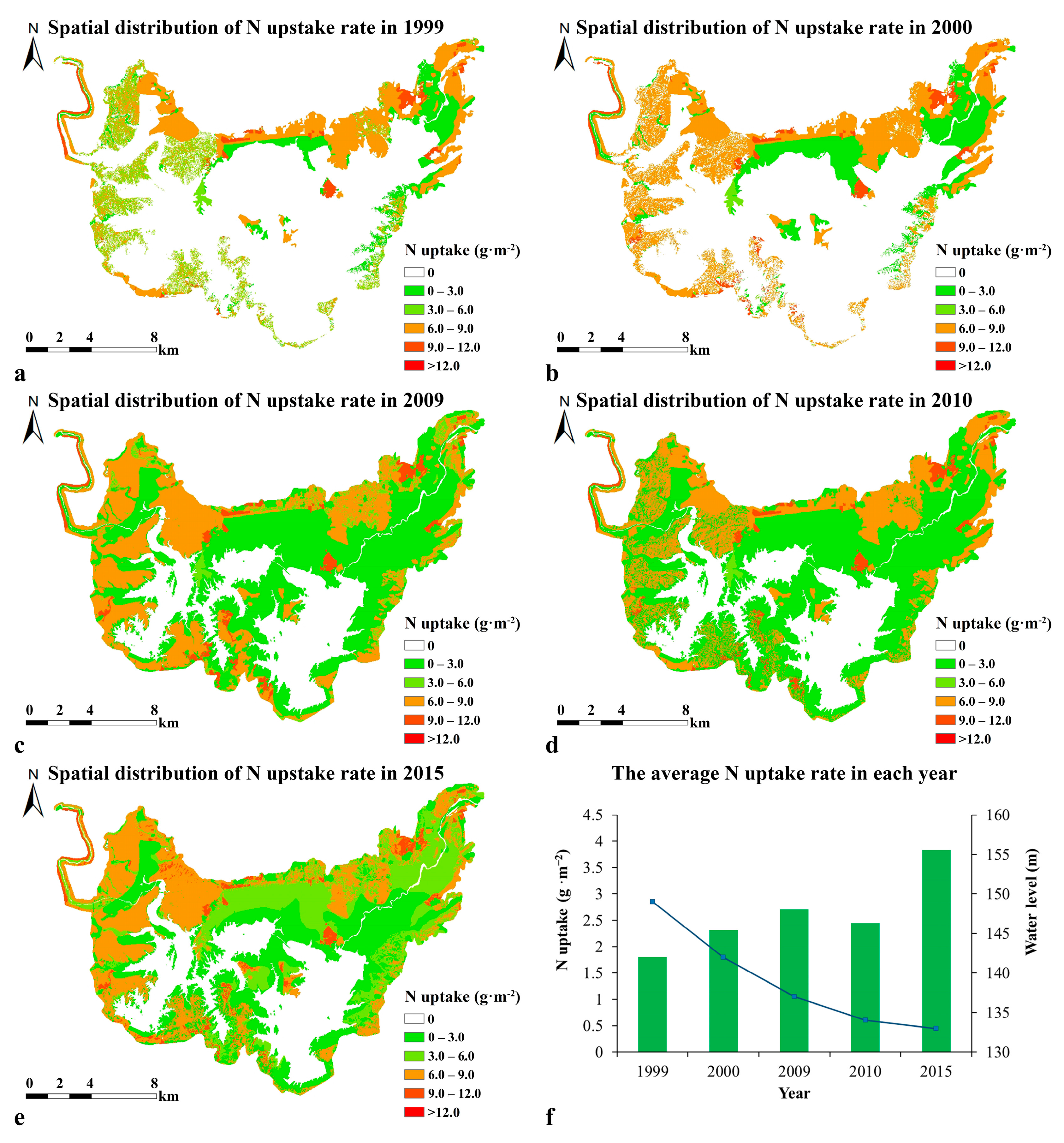
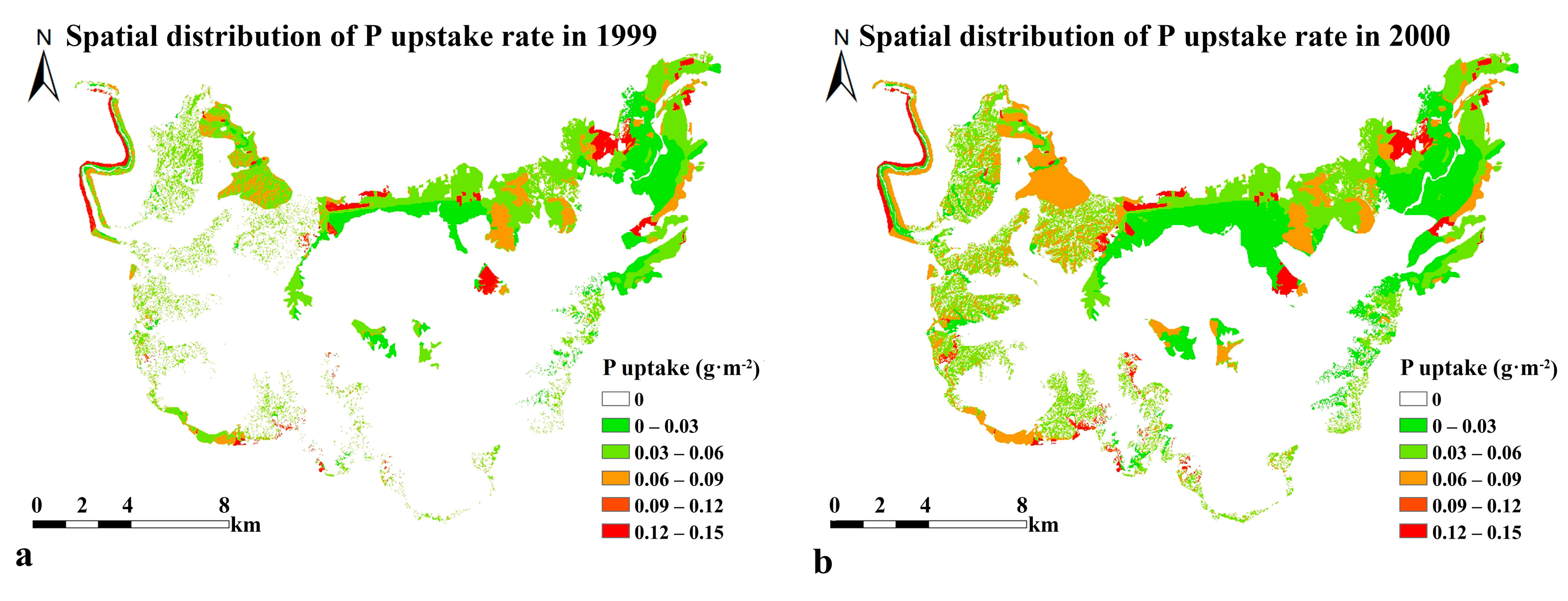
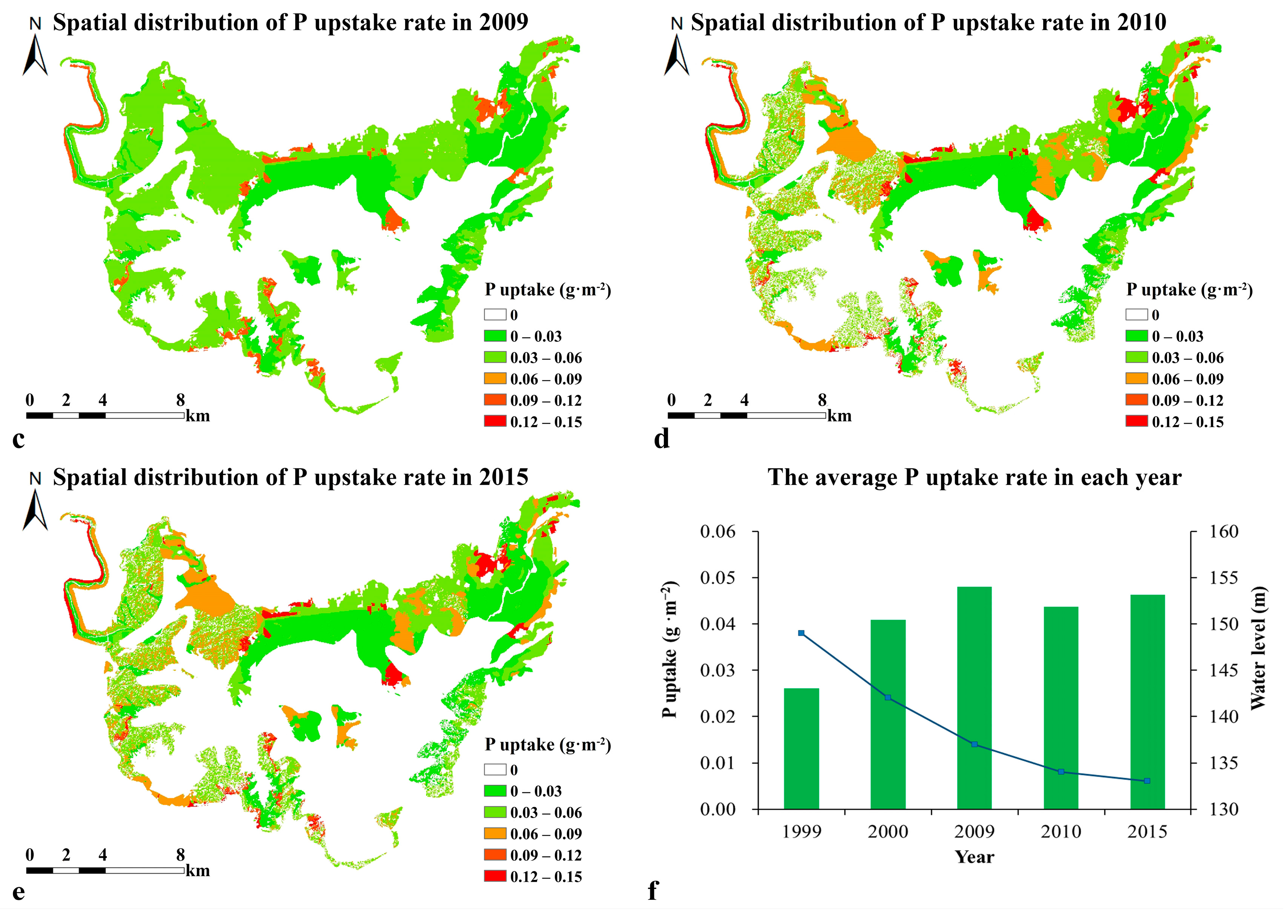
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variation of N and P Uptake
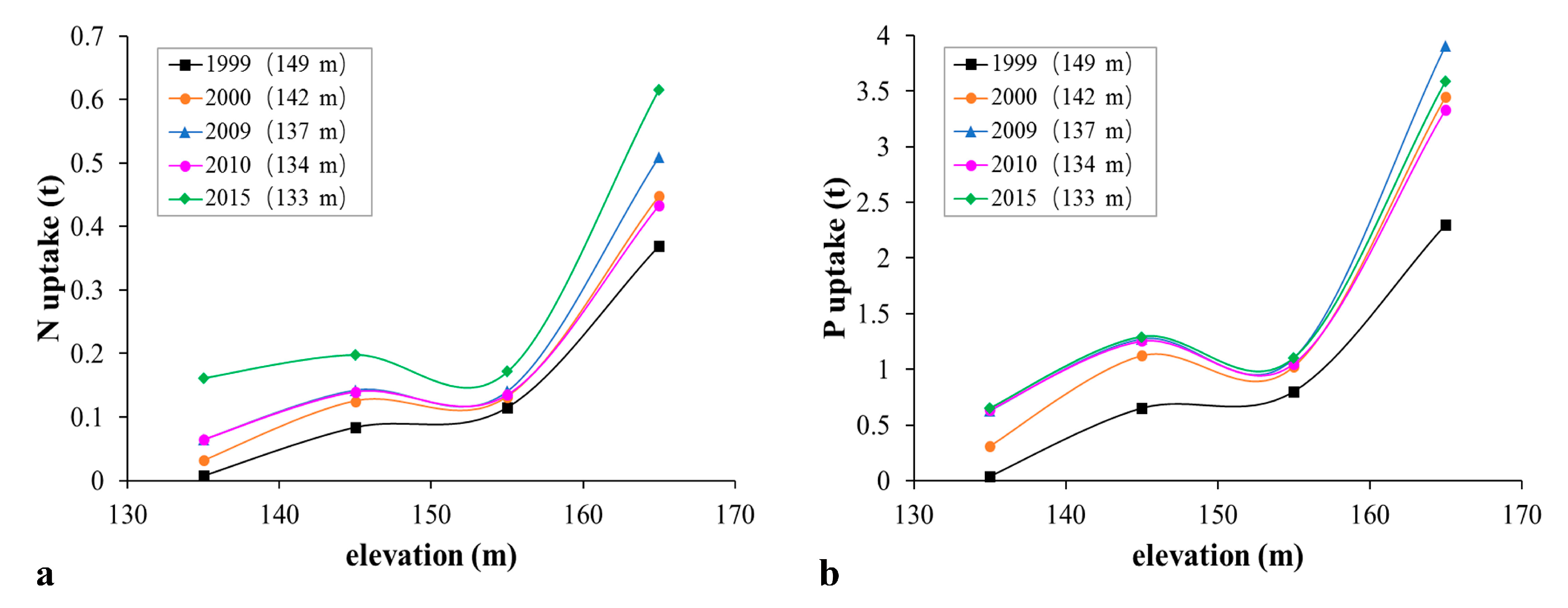
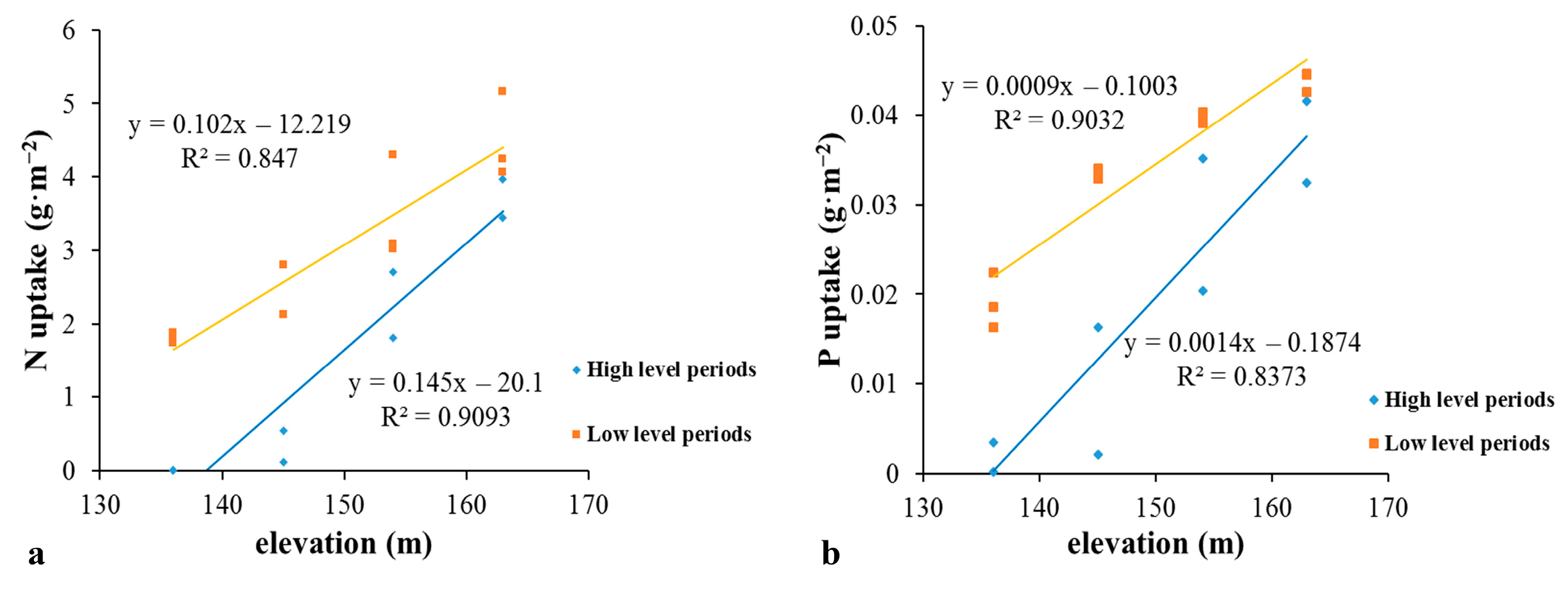
3.3. Negative Relationship between the Water Level and N and P Uptake
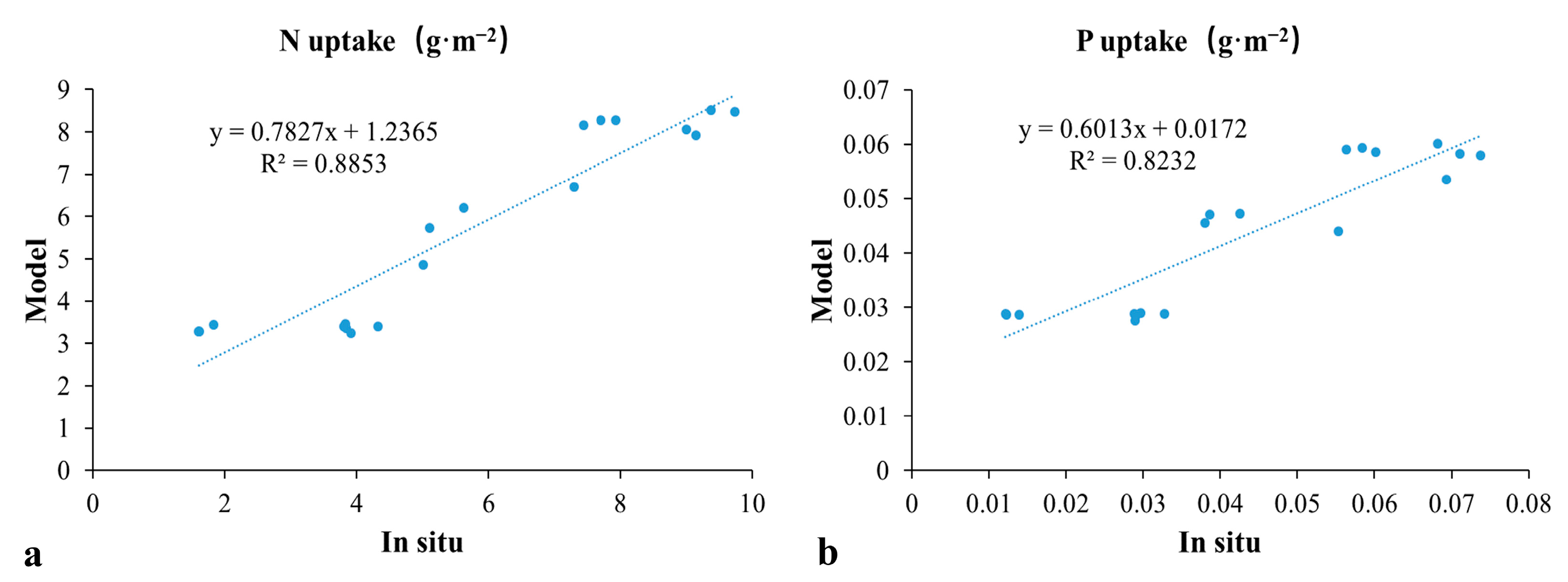
3.4. Validation of N and P Uptake Based on In Situ Survey Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Reason for the Decline of N and P Uptake
4.2. Prediction of the Inner Protection Zone’s Defense for N and P Interception
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantor, L.M. The California state water project-a reassessment. J. Geogr. 1980, 79, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Gastelum, J.R.; Cullom, C. Application of the Colorado River simulation system model to evaluate water shortage conditions in the central Arizona project. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2369–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voropaev, G.; Velikanov, A. Partial southward diversion of Northern and Siberian Rivers. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 1984, 2, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.W. The Role of Water in the Biology of the Antelope Ground Squirrel Citellus Leucurus; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, A.K.; Saxena, A.; Yaduvanshi, M.; Mishra, A.; Bhadauriya, Y.; Thakur, A. Proposed river-linking project of India: A boon or bane to nature. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 1361–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, H. South-to-North water transfer schemes for China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2002, 18, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.R.; Thoms, M.; Meador, M. An assessment of the ecological impacts of inter-basin water transfers, and their threats to river basin integrity and conservation. Aquat. Conserv.-Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 1992, 2, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Chang, L.; Li, F.; Li, T.; Gao, Y. Gully erosion regionalization of black soil area in Northeastern China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ding, H.; Tang, G.; Na, J.; Huang, X.; Xue, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, F. Detection of catchment-scale gully-affected areas using unmanned aerial vehicle (uav) on the Chinese loess plateau. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W. Eco-environmental impact of inter-basin water transfer projects: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 12867–12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Ma, H. A gully erosion assessment model for the Chinese loess plateau based on changes in gully length and area. Catena 2017, 148, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, X. Water pollution risk simulation and prediction in the main canal of the South-to-North water transfer project. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Shan, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, S. Response of extreme hydrological events to climate change in the water source area for the middle route of south-to-north water diversion project. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Qin, L.; Li, X. The potential impact of an inter-basin water transfer project on nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorous) and chlorophyll a of the receiving water system. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q. The South-to-North water transfer project of China: Environmental implications and monitoring strategy1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, G.-M. Influence of south-to-north water diversion on major cones of depression in north China plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 3845–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fang, H. Impacts of climate change on water erosion: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 163, 94–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Himanshu, S.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Singh, V.P. Physically based soil erosion and sediment yield models revisited. Catena 2016, 147, 595–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcher, M.; Bormann, H. On the transferability of the concept of drinking water protection zones from EU to Latin American Countries. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1803–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenčič, M.; Prestor, J.; Kompare, B.; Matoz, H.; Kranjc, S. Integrated approach to delineation of drinking water protection zones. Geologija 2009, 52, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, S.; Butturini, A.; Clement, J.-C.; Burt, T.; Dowrick, D.; Hefting, M.; Matre, V.; Pinay, G.; Postolache, C.; Rzepecki, M. Nitrogen removal by riparian buffers along a European climatic gradient: Patterns and factors of variation. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 0020–0030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, D. Buffer zones and water quality protection: General principles, Buffer zones: Their processes and potential in water protection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Buffer Zones, Harpenden, Hertfordshire, UK, September 1996; pp. 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- Klemas, V. Remote sensing of riparian and wetland buffers: An overview. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 297, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C.; Svedmark, M. Basic principles and ecological consequences of changing water regimes: Riparian plant communities. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Vidon, P.; Jacinthe, P.A.; Fisher, K.; Baker, M. Seasonal and geomorphic controls on n and P removal in riparian zones of the US Midwest. Biogeochemistry 2014, 119, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.-K. Groundwater–surface water interaction in the riparian zone of an incised channel, Walnut Creek, Iowa. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Džubáková, K.; Molnar, P.; Schindler, K.; Trizna, M. Monitoring of riparian vegetation response to flood disturbances using terrestrial photography. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, T.T. Physiological-ecological impacts of flooding on riparian forest ecosystems. Wetlands 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R.; Jia, H. Going against the flow. Science 2006, 313, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Meng, F.; Lu, Y.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C. Ecological assessment of lakeshore wetland rehabilitation on eastern route of south-to-north water transfer project. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2008, 2, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Song, H. Conservation buffer systems for water quality security in south to north water transfer project in China: An approach review. Front. For. China 2009, 4, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Shao, D.; Jiang, Y. Risk evaluation of water shortage in source area of middle route project for south-to-north water transfer in China. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3479–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-S.; Wang, W.; Li, H.-J.; Shen, X.-H.; Xu, Y.-L.; Dai, J.-R. The South-to-North water diversion project: Effect of the water diversion pattern on transmission of oncomelania hupensis, the intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum in China. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, J.; Rogers, S.; Webber, M.; Finlayson, B.; Wang, M. Sustainability: Transfer project cannot meet China’s water needs. Nature 2015, 527, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-S.; Wu, B.-F.; Zhang, L. Dynamic monitoring of soil erosion for upper stream of Miyun reservoir in the last 30 years. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Du, P.; Lang, C. Nutrient concentrations and fluxes in the upper catchment of the Miyun reservoir, China, and potential nutrient reduction strategies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y.; Bai, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, D. Spatial evaluation of phosphorus retention in riparian zones using remote sensing data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1643–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, D. Evaluation of soil nitrogen emissions from riparian zones coupling simple process-oriented models with remote sensing data. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3310–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Zheng, D.; Wu, C.; Mannaerts, C.M. Evaluating nitrogen removal by vegetation uptake using satellite image time series in riparian catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2567–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Gao, Y.; Guo, J. Spatially explicit estimation of soil denitrification rates and land use effects in the riparian buffer zone of the large Guanting reservoir. Geoderma 2009, 150, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, S.D.; Goward, S.N. Global primary production: A remote sensing approach. J. Biogeogr. 1995, 22, 815–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Arp, P.A.; Meng, F.R.; Bourque, C.P.A.; Foster, N.W. A forest nutrient cycling and biomass model (FORNBM) based on year-round, monthly weather conditions, part 1: Assumption, structure and processing. Ecol. Model. 2003, 169, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, P.A.; Oja, T. A forest soil vegetation atmosphere model (ForSVA) 1. Concepts. Ecol. Model. 1997, 95, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-T.; Li, Z.-B.; Wang, S.-S. Spatial scale effect on sediment dynamics in basin-wide floods within a typical agro-watershed: A case study in the hilly loess region of the Chinese loess plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husson, E.; Lindgren, F.; Ecke, F. Assessing biomass and metal contents in riparian vegetation along a pollution gradient using an unmanned aircraft system. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachamba, D.J.; Orka, H.O.; Gobakken, T.; Eid, T.; Mwase, W. Biomass estimation using 3D data from unmanned aerial vehicle imagery in a tropical woodland. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Bai, J.; Zhao, C.; Lou, H.; Zhang, C.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X. The assessment of the changes of biomass and riparian buffer width in the terminal reservoir under the impact of the South-to-North water diversion project in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Burt, T.; Bates, P. Toward a conceptual model of floodplain water table response. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheinhardt, R.; Brinson, M.; Meyer, G.; Miller, K. Integrating forest biomass and distance from channel to develop an indicator of riparian condition. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, A.C. A comparative study on the growth and nitrogen and phosphorus uptake characteristics of 15 wetland species. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 27, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y. Study on the Adjustment and Control Mechanism of Forest to Nonpoint Source Pollution in Beijing Mountain Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 29 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X. Study on the Variation of N, P, K Nutrients Pool of Different Type of Alpine Meadow in Eastern Qilian Mountains. Master’s Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 10 June 2008. [Google Scholar]

| No. | Module Name | Equations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NPP simulation | GLO-PEM model [41] | |
| 2 | NPP allocation | ForNBM model [42] | |
| 3 | Nutrient absorption | ForNBM model [42,43] | |
| 4 | Litterfall decomposition | ForNBM model [42] |
| Data Type | Data Name | Resolution | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meteorological data | Precipitation, wind speed, air pressure, air temperature, daily max/min temperature, relative humidity, sunshine duration, sun radiation, surface temperature | - | National basic weather station (http://data.cma.cn/) |
| Remote sensing data | Digital elevation model (DEM) | 30 m | ASTER-GDEM (http://www.gscloud.cn/) |
| Albedo, NDVI, LAI, land use, vegetation coverage, land surface temperature (LST) | 30 m | Landsat (http://www.gscloud.cn/) | |
| Soil data | Bulk density, soil texture, soil nutrient content (TN, NO3-N, NH4-N), pH | - | Second National Soil Survey field investigations |
| Quadrant ID | Biomass Density (g·m−2) | Quadrant ID | Biomass Density (g·m−2) | Quadrant ID | Biomass Density (g·m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1222.13 | 14 | 172.35 | 27 | 4699.23 |
| 2 | 1114.83 | 15 | 188.35 | 28 | 3139.40 |
| 3 | 773.61 | 16 | 171.57 | 29 | 4275.75 |
| 4 | 1321.03 | 17 | 192.58 | 30 | 13,825.23 |
| 5 | 1375.40 | 18 | 184.78 | 31 | 10,893.78 |
| 6 | 1185.17 | 19 | 177.98 | 32 | 7510.89 |
| 7 | 1332.65 | 20 | 142.32 | 33 | 12,186.66 |
| 8 | 1453.43 | 21 | 5291.21 | 34 | 10,159.57 |
| 9 | 859.52 | 22 | 3275.53 | 35 | 11,741.42 |
| 10 | 1001.63 | 23 | 1796.98 | 36 | 12,123.08 |
| 11 | 1488.09 | 24 | 2043.25 | 37 | 5930.64 |
| 12 | 172.73 | 25 | 1528.09 | 38 | 10,361.92 |
| 13 | 152.52 | 26 | 2679.09 | 39 | 7192.59 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Bai, J.; Zhao, C.; Lou, H.; Wang, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yu, X. Decline of N and P Uptake in the Inner Protection Zone of a Terminal Reservoir during Inter-Basin Water Transfers. Water 2018, 10, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020178
Yang S, Bai J, Zhao C, Lou H, Wang Z, Guan Y, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Yu X. Decline of N and P Uptake in the Inner Protection Zone of a Terminal Reservoir during Inter-Basin Water Transfers. Water. 2018; 10(2):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020178
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shengtian, Juan Bai, Changsen Zhao, Hezhen Lou, Zhiwei Wang, Yabing Guan, Yichi Zhang, Chunbin Zhang, and Xinyi Yu. 2018. "Decline of N and P Uptake in the Inner Protection Zone of a Terminal Reservoir during Inter-Basin Water Transfers" Water 10, no. 2: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020178
APA StyleYang, S., Bai, J., Zhao, C., Lou, H., Wang, Z., Guan, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., & Yu, X. (2018). Decline of N and P Uptake in the Inner Protection Zone of a Terminal Reservoir during Inter-Basin Water Transfers. Water, 10(2), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020178





