Analyzing the Impacts of Climate Variability and Land Surface Changes on the Annual Water–Energy Balance in the Weihe River Basin of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
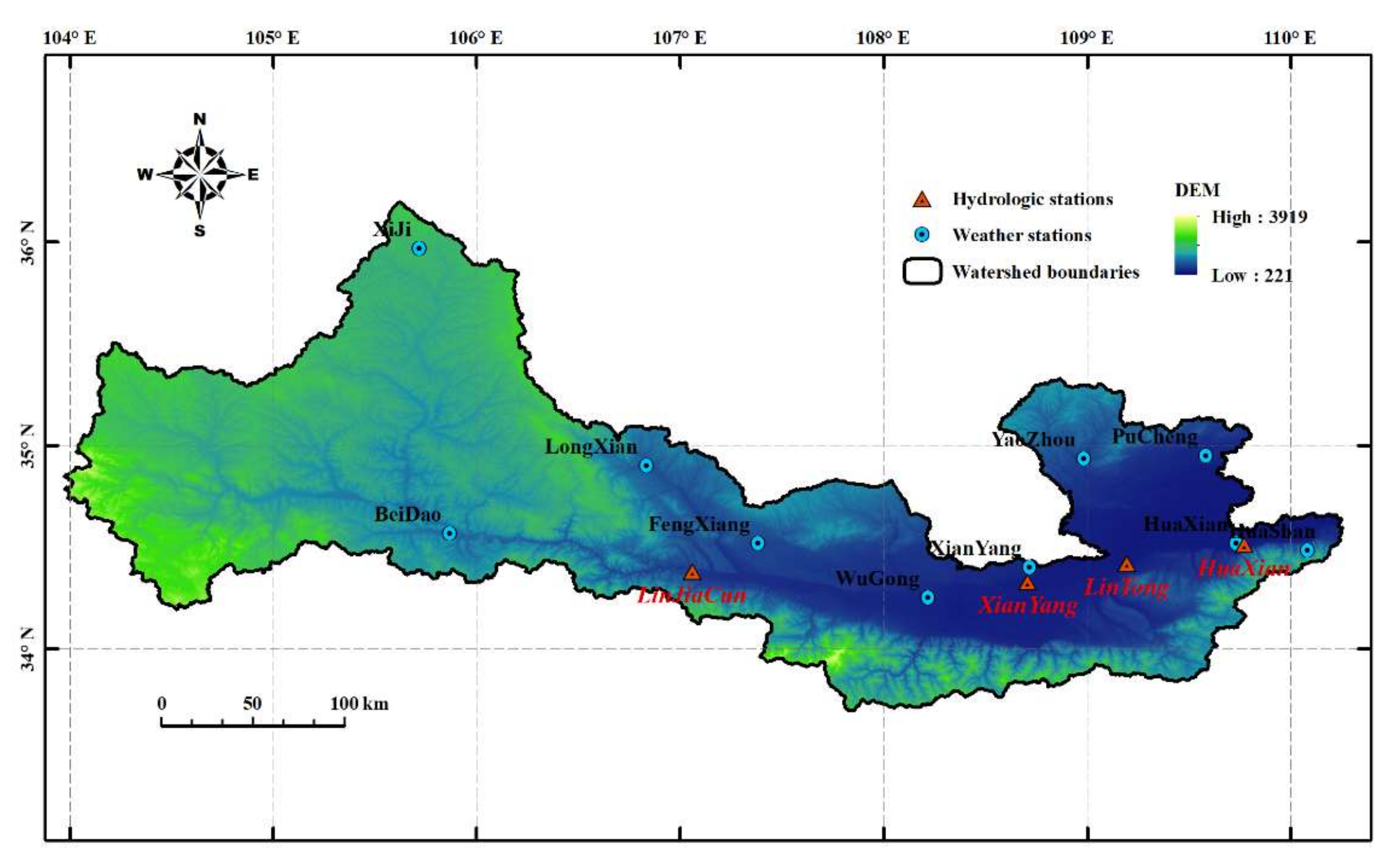
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Trend Analysis and Breakpoint Test
2.3.2. Budyko Framework
2.3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
2.3.4. Contribution Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Long-Term Hydrometeorological Variables
3.2. Elasticity Coefficients on Runoff
3.3. Attribution Analysis of Runoff Reduction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, W. Impacts of climate change and human activities on the surface runoff in the Tarim River Basin over the last fifty years. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 22, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.J.; Foster, P.N.; Prentice, I.C. Evaluation of global continental hydrology as simulated by the land-surface processes and exchanges Dynamic Global Vegetation Model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Rustomji, P.; Hairsine, P. Responses of streamflow to changes in climate and land use/cover in the Loess Plateau, China. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, R.; Liu, C.; Sato, Y.; Fukushima, Y. Responses of streamflow to climate and land surface change in the headwaters of the Yellow River Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dore, M.H. Climate change and changes in global precipitation patterns: What do we know? Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Sun, F.; Liu, Z.; Cong, Z.; Ni, G.; Lei, Z. Analyzing spatial and temporal variability of annual water-energy balance in nonhumid regions of China using the Budyko hypothesis. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, D.; Li, J.; Qin, D. Assessing the impact of climate variability and human activities on streamflow from the Wuding River Basin in China. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 3485–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Tian, P.; Mu, X.; Jiao, J.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Quantifying the impact of climate variability and human activities on streamflow in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Kharrazi, A.; Li, J.; Avtar, R. Agricultural water policy reforms in China: A representative look at Zhangye City, Gansu Province, China. Environ Monit Assess. 2018, 190, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Podlasly, C.; Ren, Y.; Feger, K.; Wang, Y.; Schwӓrzel, K. Separating the effects of changes in land management and climatic conditions on long-term streamflow trends analyzed for a small catchment in the Loess Plateau region, NW China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; McVicar, T.R.; Guo, J.; Tang, Y.; Yao, A. Isolating the impacts of climate change and land use change on decadal streamflow variation: Assessing three complementary approaches. J. Hydrol. 2013, 507, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. Variation in annual runoff of the Wudinghe River as influenced by climate change and human activity. Q. Int. 2011, 244, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Jiang, S.; Sun, F.; Jia, Y.; Niu, C.; Yue, W. Quantitative contribution of climate change and human activities to runoff changes in the Wei River basin, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bronstert, A.; Niehoff, D.; Bürger, G. Effects of climate and land-use change on storm runoff generation: Present knowledge and modelling capabilities. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankarasubramanian, A.; Vogel, R.M.; Limbrunner, J.F. Climate elasticity of streamflow in the United States. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhang, L.; Tong, L.; Su, X. Analysis of impacts of climate variability and human activity on streamflow for a river basin in arid region of northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, F.; Chen, Y.; Dixon, R.N.M. Estimating effects of plantation expansion and climate variability on streamflow for catchment in Australia. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, D.; Jin, C.; Wang, A.; Wu, J.; Yuan, F. Analysis of impacts of climate variability and human activity on streamflow for a river basin in northeast China. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.M.; Wilson, I.; Daly, C. Regional regression models of annual streamflow for the United States. J. Irrig. Drain Eng. 1999, 125, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zou, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wu, X. Quantifying the anthropogenic and climate contributions to changes in water discharge and sediment load into the sea: A case study of the Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaake, J.C. From climate to flow. In Climate Change and U.S. Water Resources; Waggoner, P.E., Ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 177–206. [Google Scholar]
- Budyko, M.I. Climate and Life; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Dooge, J.C. Sensitivity of runoff to climate change: A Hortonian approach. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 73, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Dunne, K.A. Macroscale water fluxes 2. Water and energy supply control of their interannual variability. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoo, Y.; Sivapalan, M.; Oki, T. Investigating the roles of climate seasonality and landscape characteristics on mean annual and monthly water balances. J. Hydrol. 2008, 357, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Liang, W.; Jiang, X. Determing the hydrological responses to climate variability and land use/cover change in the Loess Plateau with the Budyko framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onstad, C.A.; Jamieson, D.G. Modeling the effect of land use modifications on runoff. Water Resour. Res. 1970, 6, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpa, D.; Nunes, J.P.; Santos, J.; Sampaio, E.; Jacinto, R.; Veiga, S.; Lima, J.C.; Mpreira, M.; Corte-Real, J.; Keizer, J.J.; et al. Impacts of climate and land use changes on the hydrological and erosion processes of two contrasting Mediterranean catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buendia, C.; Bussi, G.; Tuset, J.; Vericat, D.; Sabater, S.; Palau, A.; Batalla, R.J. Effects of afforestation on runoff and sediment load in an upland Mediterranean catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 540, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Hou, T.; Horton, R.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, W.; Fu, X. The streamflow estimation using the Xinan jiang rainfall runoff model and dual state-parameter estimation method. J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shao, Q.; Yang, T.; Peng, S.; Xing, W.; Sun, F.; Luo, Y. Quantitative assessment of the impact of climate variability and human activities on runoff changes: A case study in four catchments of the Haihe River Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 1158–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xu, Z.; Hui, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Q. Instream flow requirements for sediment transport in the lower Weihe River. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3547–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Hou, B.; Chang, J.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Y. Spatial-temporal change in precipitation patterns based on the cloud model across the Wei river basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 120, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, S.; Chang, J.; Leng, G. Spatial–temporal changes in potential evaporation patterns based on the Cloud model and their possible causes. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess 2017, 31, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Leng, G.; Luan, J.; Song, X.; Wei, X.; Li, X. Identification of the non-stationarity of extreme precipitation events and correlations with large-scale ocean-atmospheric circulation patterns: A case study in the Wei River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric test against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Measures; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Pettitt, A. A nonparametric approach to the change-point problem. Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.P. The calculation of the evaporation from land surface. Sci. Atmos. Sin. 1981, 5, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Meybeck, M.; He, D.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L. Spatial and temporal analysis of water chemistry records (1958–2000) in the Huanghe (Yellow River) basin. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Saito, Y.; Liu, P.; Sun, X. Interannual and seasonal variation of the Huanghe (Yellow River) water discharge over the past 50 years: Connections to impacts from ENSO events and dams. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 50, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Qi, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, D.; Lv, H. The regional variation in climate elasticity and climate contribution to runoff across China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, K. Effects of watershed topography, soils, land use and climate on baseflow in humid regions: A review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2011, 35, 465–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, R.J.; Roderick, M.L.; McVicar, T.R. On the importance of including vegetation dynamics in Budyko’s hydrological model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2006, 3, 1517–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Pan, M.; Cong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wood, E. Vegetation control on water and energy balance within the Budyko framework. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Vegetation dynamics and climate seasonality jointly control the interannual catchment water balance in the Loess plateau under the Budyko framework. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Bai, D.; Wang, F.; Fu, B.; Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Long, D.; Feng, M. Quantifying the impacts of climate change and ecological restoration on streamflow changes based on a Budyko hydrological model in China’s Loess Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 6500–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Zhang, L.; McVicar, T.; Chille, B.; Gau, P. Analysis of the impact of conservation measures on stream flow regime in catchments of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.; Nichols, M.; McClaran, M.; Nearing, M. Effect of check dams on runoff, sediment yield, and retention on small semiarid watersheds. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 69, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Podlasly, C.; Feger, K.; Wang, Y.; Schwaerzel, K. Different land management measures and climate change impacts on the runoff—A simple empirical method derived in a mesoscale catchment on the Loess Plateau. J. Arid Environ. 2015, 120, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Xu, Z.; Wu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, F. Identification of streamflow response to climate change and human activities in the Wei river basin, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urcola, H.; Elverdin, J.; Mosciaro, M.; Albaladejo, C.; Manchado, J.; Giussepucci, J. Climate change impacts on rural societies: Stakeholders perceptions and adaptation strategies in Buenos Aires, Argentina. In Innovation & Sustainable Development in Agriculture & Food; FRA: Montpellier, France, 2010; pp. 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Georgakakos, K.; Graham, N.; Cheng, F.; Spencer, C.; Shamir, E.; Georgakakos, A.; Yao, H.; Kistenmacher, M. Value of adaptive water resources management in northern California under climatic variability and change: Dynamic hydroclimatology. J. Hydrol. 2012, 412–413, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LJC | XY | LT | HX | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period I 1961–1992 | Period II 1993–2014 | Whole | Period I 1961–1992 | Period II 1993–2014 | Whole | Period I 1961–1989 | Period II 1990–2014 | Whole | Period I 1961–1992 | Period II 1993–2014 | Whole | ||
| R (mm yr−1) | Average | 25.2128 | 10.4614 | 19.203 | 47.4119 | 23.6098 | 37.7147 | 77.511 | 49.6476 | 64.6113 | 77.5528 | 45.9295 | 64.6693 |
| Slope | −0.40782 * | 0.14971 | −0.45334 ** | −0.85665 * | 0.94667 ** | −0.708 ** | −0.99952 | 0.68827 | −0.75 ** | −0.96486 | 1.3153 * | −0.83407 ** | |
| P (mm yr−1) | Average | 543.6715 | 508.4231 | 529.311 | 576.6696 | 531.1751 | 558.1348 | 574.4519 | 535.9655 | 556.6342 | 606.7371 | 551.992 | 584.4335 |
| Slope | 0.26493 | 4.375 | −0.66121 | −0.23257 | 6.8705 * | −0.76634 | −0.30765 | 3.8812 | −0.49851 | −0.53298 | 6.001 * | −1.0773 | |
| ET0 (mm yr−1) | Average | 952.904 | 976.4785 | 962.5085 | 976.0936 | 968.8985 | 973.1623 | 988.01 | 995.2711 | 991.3716 | 1020.1251 | 1013.678 | 1017.4987 |
| Slope | −2.6822 * | 1.2068 | 0.23939 | −4.4722 ** | −0.40235 | −1.2491 * | −3.2497 * | 1.9376 | −0.054167 | −4.3096 ** | −1.6731 | −1.175 * | |
| Station | ω | Period | εET0 | εP | εω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LJC | 2.94 | Whole | −2.62 | 3.62 | −2.60 |
| 1961–1992 | −2.58 | 3.58 | −2.49 | ||
| 1993–2014 | −2.66 | 3.66 | −2.77 | ||
| XY | 3.10 | Whole | −2.74 | 3.74 | −2.59 |
| 1961–1992 | −2.71 | 3.71 | −2.49 | ||
| 1993–2014 | −2.78 | 3.78 | −2.74 | ||
| LT | 2.47 | Whole | −2.11 | 3.11 | −2.25 |
| 1961–1989 | −2.08 | 3.08 | −2.16 | ||
| 1990–2014 | −2.14 | 3.14 | −2.35 | ||
| HX | 2.92 | Whole | −2.56 | 3.56 | −2.47 |
| 1961–1992 | −2.53 | 3.53 | −2.36 | ||
| 1993–2014 | −2.61 | 3.61 | −2.64 |
| Station | Period | RC_(P) (%) | RC_(ET0) (%) | RC_(ω) (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LJC | Period I | 1961–1992 | 9.38 | 39.05 | 51.58 |
| Period II | 1993–2014 | 50.51 | 5.27 | 44.22 | |
| Whole | 1961–2014 | 51.76 | 7.46 | 40.78 | |
| XY | Period I | 1961–1992 | 5.6 | 46.46 | 47.94 |
| Period II | 1993–2014 | 47.72 | 1.13 | 51.15 | |
| Whole | 1961–2014 | 37.58 | 25.74 | 36.68 | |
| LT | Period I | 1961–1989 | 12.07 | 50.07 | 37.87 |
| Period II | 1990–2014 | 52.31 | 9.59 | 38.1 | |
| Whole | 1961–2014 | 47.61 | 1.97 | 50.42 | |
| HX | Period I | 1961–1989 | 14.22 | 49.02 | 36.76 |
| Period II | 1993–2014 | 43.51 | 4.77 | 51.71 | |
| Whole | 1961–2014 | 53.32 | 24.02 | 22.66 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, W.; Song, J.; Bai, H.; He, Y.; Yu, M.; Wang, H.; Cheng, D. Analyzing the Impacts of Climate Variability and Land Surface Changes on the Annual Water–Energy Balance in the Weihe River Basin of China. Water 2018, 10, 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121792
Deng W, Song J, Bai H, He Y, Yu M, Wang H, Cheng D. Analyzing the Impacts of Climate Variability and Land Surface Changes on the Annual Water–Energy Balance in the Weihe River Basin of China. Water. 2018; 10(12):1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121792
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Wenjia, Jinxi Song, Hua Bai, Yi He, Miao Yu, Huiyuan Wang, and Dandong Cheng. 2018. "Analyzing the Impacts of Climate Variability and Land Surface Changes on the Annual Water–Energy Balance in the Weihe River Basin of China" Water 10, no. 12: 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121792
APA StyleDeng, W., Song, J., Bai, H., He, Y., Yu, M., Wang, H., & Cheng, D. (2018). Analyzing the Impacts of Climate Variability and Land Surface Changes on the Annual Water–Energy Balance in the Weihe River Basin of China. Water, 10(12), 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121792





