Efficiency of Flood Control Measures in a Sewer System Located in the Mediterranean Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
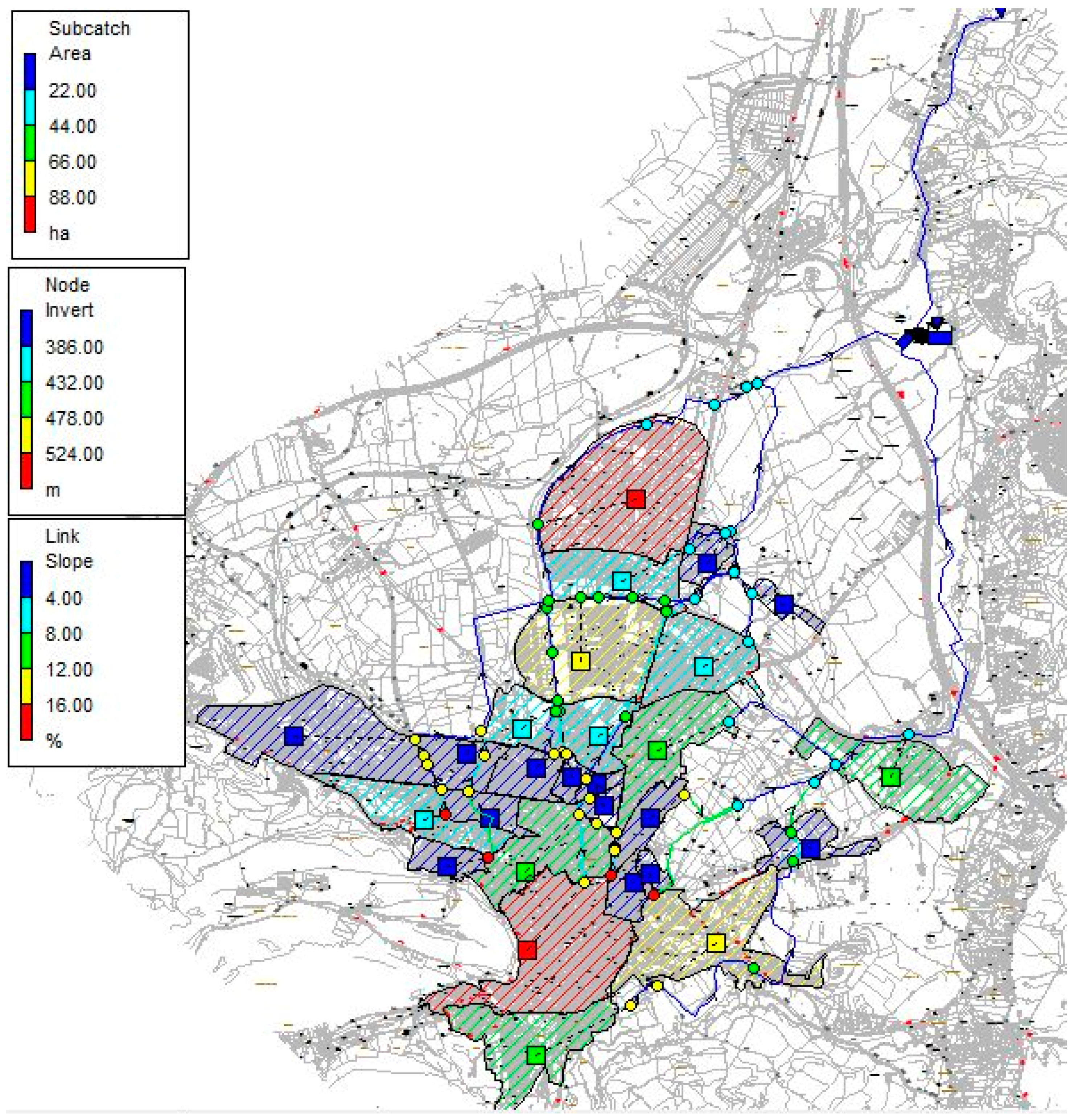
2.1. Study Site
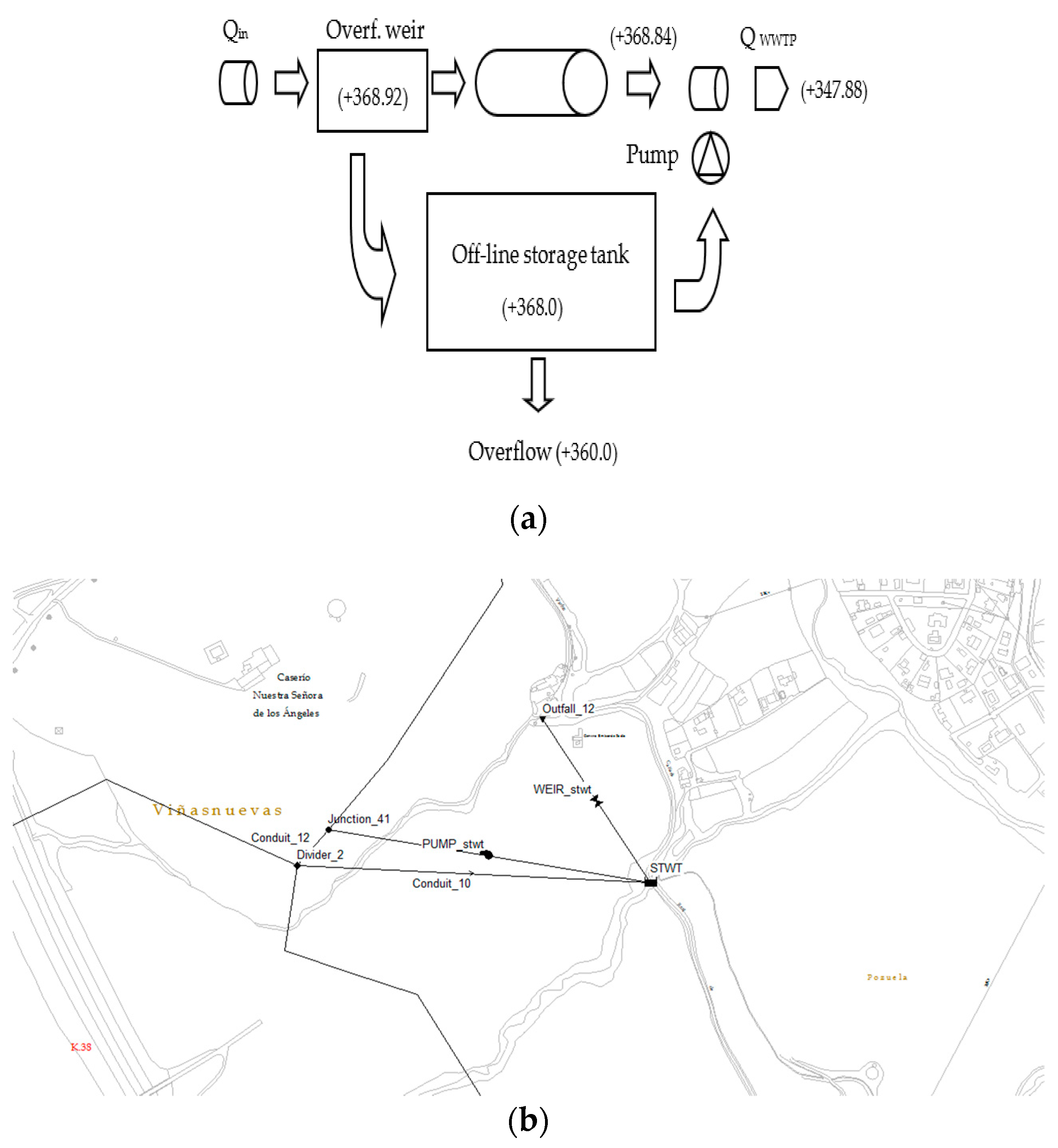
2.2. SWMM Modelling
- The maximum concentration of pollutants in the overflow;
- The duration of overflow/the duration of stormwater runoff;
- The pollutant mass captured/the pollutant mass in the stormwater runoff;
- The volume sent to the wastewater treatment plant/the volume of stormwater runoff;
- The SWDT emptying time.
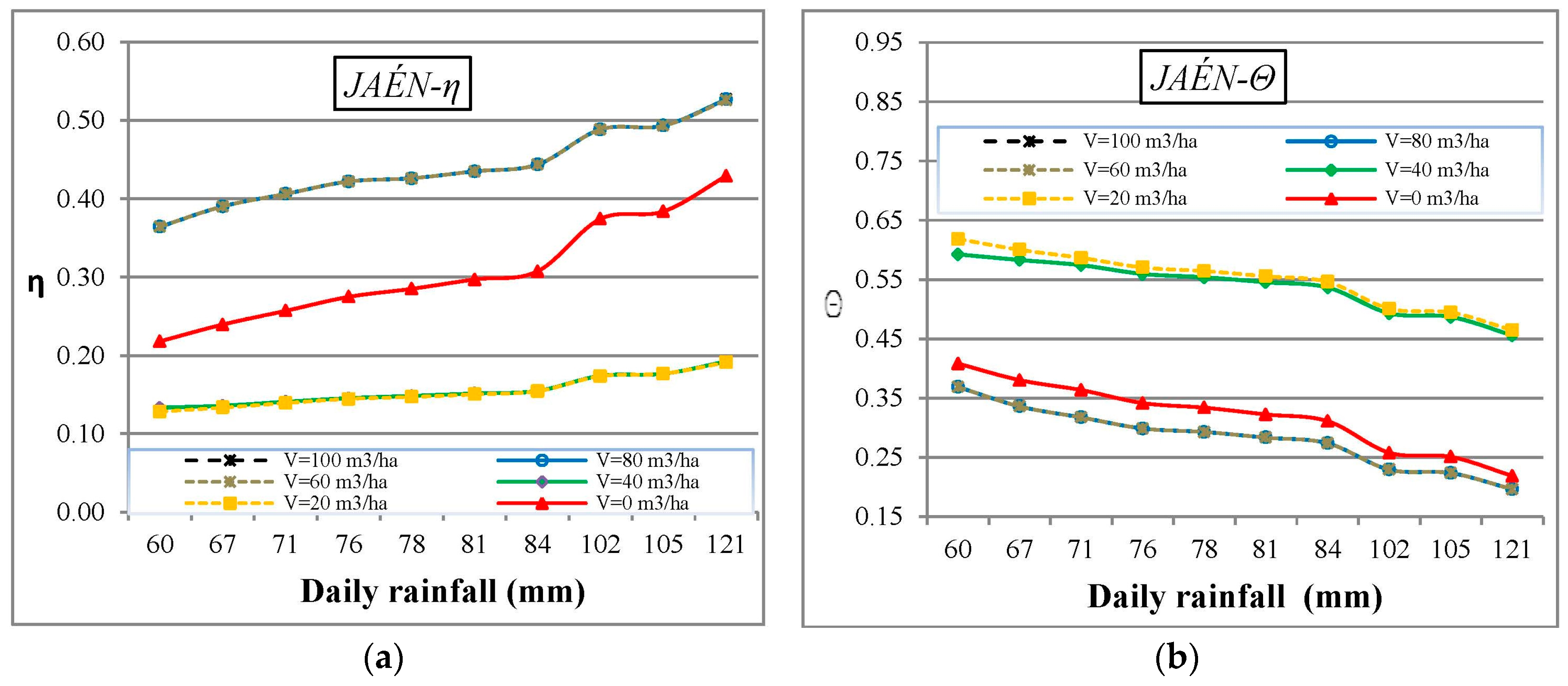
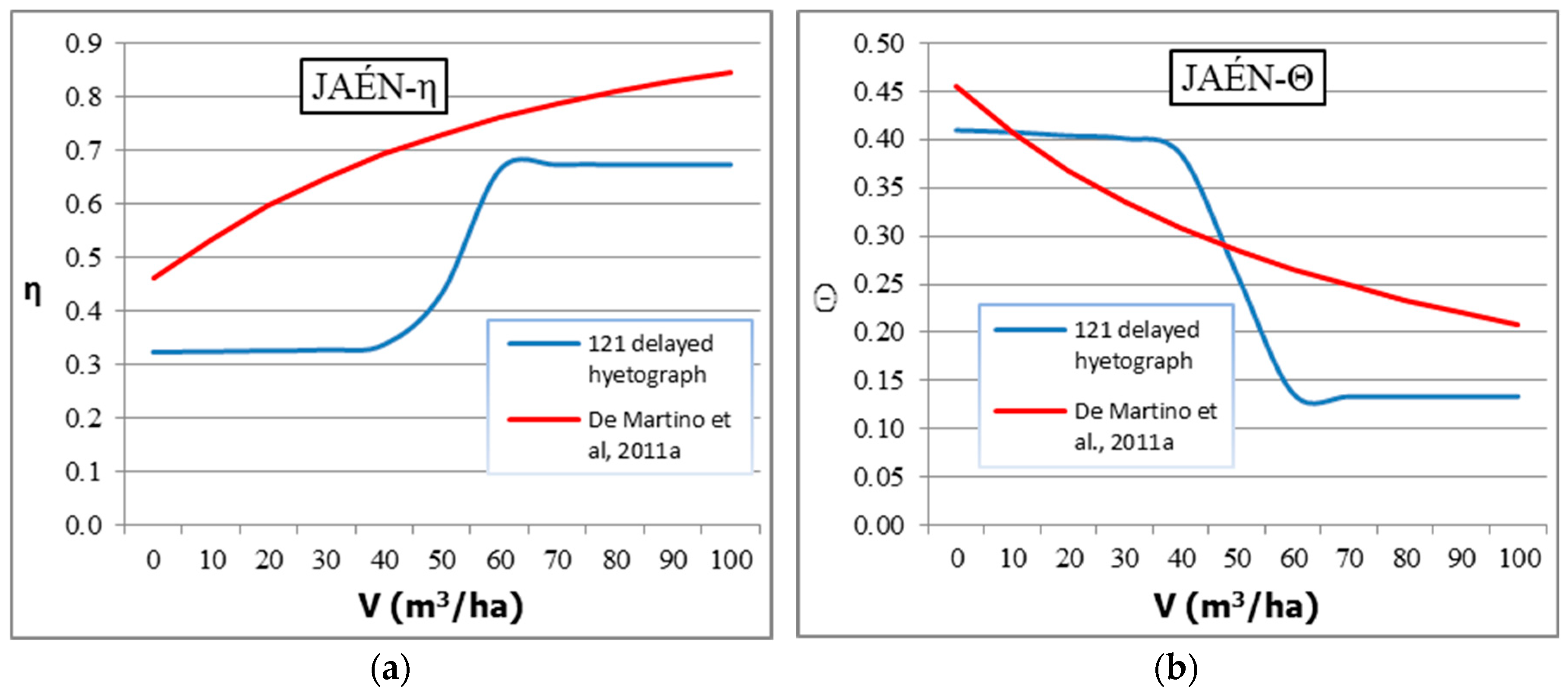
3. Results
Proposed Methodology
4. Discussion
Validation of Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salaverría, M. Las Redes Unitarias de Saneamiento: Criterios de Diseño y Control. 1995. Available online: http://hispagua.cedex.es/documentacion/articulo/58505 (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Osorio, F.; García, P.; Hontoria, E. Técnicas y Gestión de Las Aguas Pluviales; Universidad de Granada: Granada, Spain, 2012; ISBN 97884-15418-86-3. [Google Scholar]
- Barco, J.; Papiri, S.; Stenstrom, M.K. First flush in a combined sewer system. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.-F.; Li, F.; Yan, H. Multi-objective optimal design of detention tanks in the urban stormwater drainage system: LID implementation and analysis. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4635–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, S.; Papiri, S.; Ciaponi, C. Performance of stormwater detention tanks for urban drainage systems in northern Italy. Environ. Manag. 2012, 101, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itsukushima, R.; Ogahara, Y.; Iwanaga, Y.; Sato, T. Investigating the influence of various stormwater runoff control facilities on runoff control efficiency in a small catchment area. Sustainability 2018, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Methodology for Analysis of Detention Basins for Control of Urban Runoff Quality; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
- De Paola, F.; De Martino, F. Stormwater tank performance: Design and management criteria for capture tanks using a continuous simulation and a semi-probabilistic analytical approach. Water 2013, 5, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, P.; Viviani, G. Simulation of the operation of detention tanks. Water Res. 2006, 40, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveri, E.; Viviani, G.; La Loggia, G. Comportamento ed efficienza delle vasche di pioggia. Atti della II Conferenza Nazionale sul Drenaggio Urbano 2001, 279–290. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- De Martino, G.; De Paola, F.; Fontana, N.; Marini, G.; Ranucci, A. Pollution Reduction in Receivers: Stormwater Tanks. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2011, 137, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- De Martino, G.; De Paola, F.; Fontana, N.; Marini, G.; Ranucci, A. Preliminary design of combined sewer overflows and storm water tanks in southern Italy. Irrig. Drain. 2011, 60, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, M.; Geiger, W.F. Characterization of the performance of an off line storage tank. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 34, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Saul, A.J. Specific relationships for the first flush load in combined sewer flows. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.C.Y.; Urbonas, R.B. Runoff capture and delivery curves for stormwater quality control designs. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2002, 128, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochwat, K.; Słyś, D.; Kordana, S. The temporal variability of a rainfall synthetic hyetograph for the dimensioning of stormwater retention tanks in small urban catchments. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolle, H.-J. Mediterranean Climate: Variability and Trends (Regional Climate Studies); Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; ISBN 3540438386. [Google Scholar]
- Goossens, C. Principal component analysis of Mediterranean rainfall. J. Climatol. 1985, 5, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köppen, W. Versuch einer klassifikation der klimate, vorzugsweise nach ihren Beziehungen zur Pflanzenwelt. Geogr. Zeitschrift 1900, 6, 593–611. [Google Scholar]
- Agencia Estatal de Meteorología. Guía Resumida del Clima en España (1981–2010). 2012. Available online: http://www.aemet.es/en/conocermas/recursos_en_linea/publicaciones_y_estudios/publicaciones/detalles/guia_resumida_2010 (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Granata, F.; Gargano, R.; de Marinis, G. Support vector regression for rainfall-runoff modeling in urban drainage: A comparison with the EPA’s storm water management model. Water 2016, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L.A.; Water Supply and Water Resources Division; Office of Research and Development. Storm Water Management Model. User’s Manual Version 5.1; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Grupo Multidisciplinar de Modelación de Fluidos. GMMF-SWMM Modelo de Gestión de Aguas Pluviales 5.0 vE: Manual del Usuario; Universidad Politécnica de Valencia: Valencia, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hogland, W.; Berndtsson, R.; Larson, M. Estimation of quality and pollution load of combined sewer overflow discharge. Göteborg 1984, 841–850. [Google Scholar]
- Lessard, P.; Beron., C.; Briere, F. Estimation of water quality in combined sewers: The Montreal experience. In Proceedings of the 1st International Seminar on Urban Drainage Systems; Southampton, UK, 1982; pp. 367–375. [Google Scholar]
- Verbanck, M.A.; Ashley, R.M.; Bachoc, A. International Workshop on the origin, occurrence and behavior of sediments in sewer systems: Summary of conclusions. Water Res. 1994, 28, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, J.; Boyd, G. Water Pollution Aspects of Street Surface Contamination; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, I.; Imteaz, M.; Gato-Trinidad, S.; Shanableh, A. Development of a catchment water quality model for continuous simulations of pollutants build-up and wash-off. Int. J. Environ. Chem. Ecol. Geol. Geophys. Eng. 2010, 37, 941–948. [Google Scholar]
- Barco, J.; Wong, K.M.; Stenstrom, M.K. Automatic Calibration of the U.S.EPA SWMM Model for a large urban catchment. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 134, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Témez, J.R. Cálculo Hidrometeorológico de Caudales Máximos en Pequeñas Cuencas Naturales. 1978. Available online: https://www.fomento.es/recursos_mfom/0610400.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Anta, J.; Beneyto, M.; Cagiao, J.; Temprano, J.; Piñeiro, J.; González, J.; Suárez, J. Analysis of combined sewer overflow spill frequency/volume in north of Spain. Int. Assoc. Hydraul. Eng. Res. 2007, 32, 458. [Google Scholar]
- Abwasser Technische Verein (ATV). Standards for the Dimensioning and Design of Stormwater Structures in Combined Sewers. 1992. Available online: https://www.dwa.de/dwa/shop/produkte.nsf/4C8CE159B0F5CA13C125753C00334F59/$file/vorschau_ATV-A_128E.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2018).
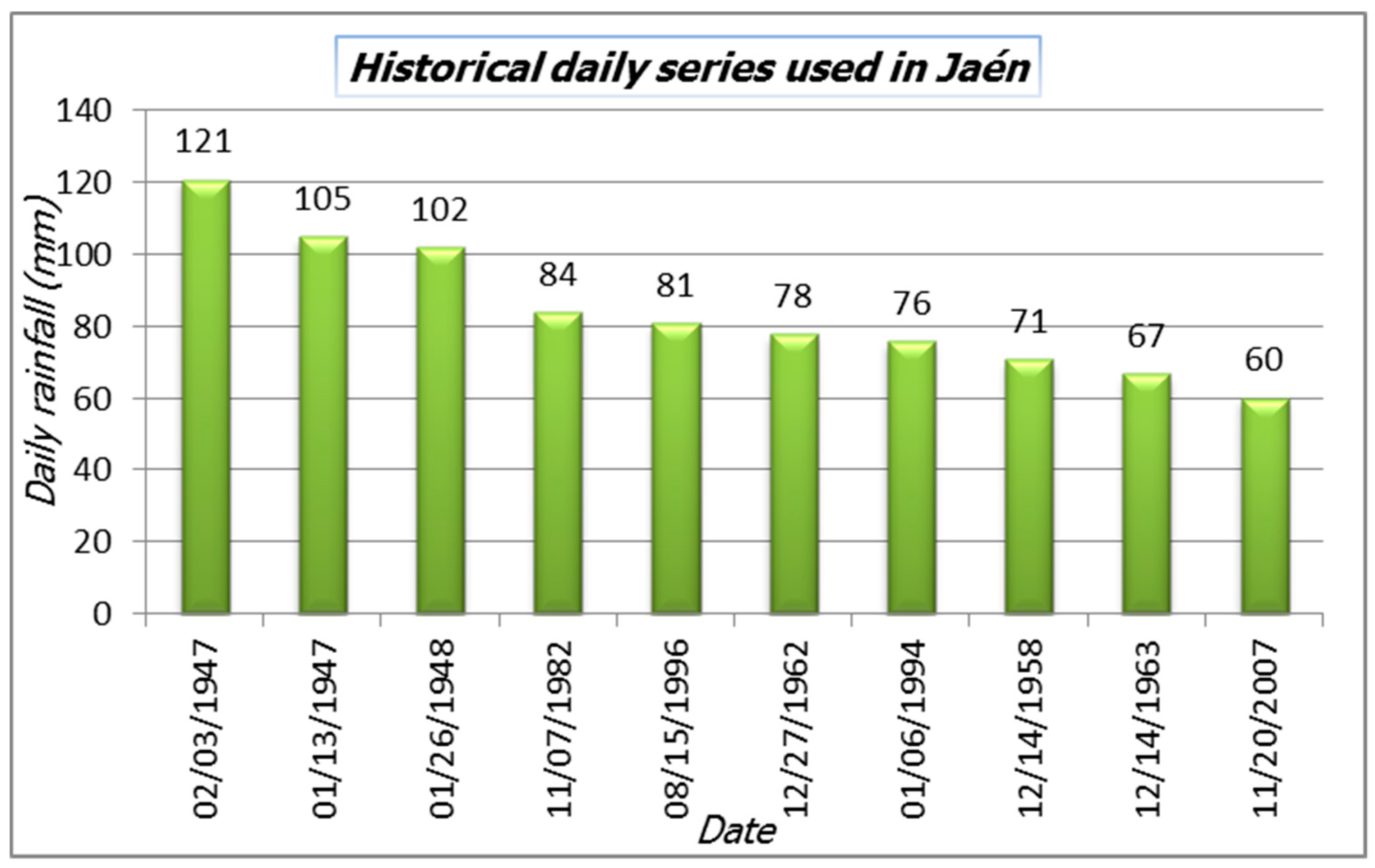
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| signif. | 8.8 | 8.1 | 7.1 | 9.4 | 7.8 | 3 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 4.5 | 8 | 9.6 | 10.3 | 78.6 |
| stormy | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 5.4 |
| Variable | Jaén |
|---|---|
| Number of subcatchments | 27 |
| Subcatchment area (ha) | 1000 |
| Number of nodes | 61 |
| Number of links | 60 |
| Total length of links (m) | 32,632 |
| Number of land uses | 2 |
| Area (Ha) | Width (m) | Slope (%) | Imp Surf. (%) | nimp | nperv | dp-imp (mm) | dp-perv (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 13,218 | 2.53% | 73% | 0.011 | 0.130 | 2 | 5 |
| Impervious Surface | Pervious Surface | |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 60 kg/ha | 30 kg/ha |
| C2 | 26 kg/ha | 8 kg/ha |
| C3 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| E1 | 0.10 | 0.07 |
| E2 | 0.15 | 0.05 |
| Hydrological | |
| Ai: impervious area (ha) | 729.91 |
| Ig: average slope of drained area | 2.679 |
| tc: concentration time (h) | 4.29 |
| Z: impermeability coefficient of the basin | 0.70 |
| hpr: annual rainfall (mm) | 493 |
| JT: mean terrain slope | 0.025 |
| I: design population (inhab) | 111,401 |
| ws: daily average water provision (L/inhab/day) | 250 |
| Qd24: dry weather flow in daily average (L/s) | 322.34 |
| Qc24: commercial wastewater flow (L/s) | 18.92 |
| Qi24: industrial wastewater flow (L/s) | 120.58 |
| Qiw24: sewer infiltration water flow (L/s) | 0.00 |
| Qcw: combined wastewater discharge to the sewage treatment plant (L/s) | 2449.29 |
| x: Number of hours per day with grey water consumption (h) | 8 |
| ac: number of hours per day of commerce work (h) | 12 |
| ai: number of hours per day of industry work (h) | 16 |
| bc: number of days of business work (days) | 300 |
| bi: number of days of industry work (days) | 312 |
| Pollution | |
| w: annual COD load in the basin (kg/ha) | 280.32 |
| Cd24: COD concentration in local domestic wastewater (mg/L) | 600.00 |
| Cc24: COD concentration in local commercial wastewater (mg/L) | 600.00 |
| Ci24: COD concentration in local industrial wastewater (mg/L) | 600.00 |
| Ctp: average COD concentration in the effluent from the WWTP (mg/L) | 70.00 |
| Cdw: dry weather concentration (mg/L) | 600.00 |
| Cr: average COD concentration in runoff waters (mg/L) | 107.00 |
| Results of Applying the ATV A 128 Standard | |
|---|---|
| m: mean mix ratio in overflow water | 16.64 |
| Cr: average COD concentration in runoff water (mg/L) | 81.23 |
| Cd: average COD concentration in dry weather flow (mg/L) | 1229.42 |
| e0: permissible annual overflow rate (%) | 14.72 |
| VS_ATV: specific storage volume (m3/ha net) | 59.67 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hermoso, M.; García-Ruiz, M.J.; Osorio, F. Efficiency of Flood Control Measures in a Sewer System Located in the Mediterranean Basin. Water 2018, 10, 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101437
Hermoso M, García-Ruiz MJ, Osorio F. Efficiency of Flood Control Measures in a Sewer System Located in the Mediterranean Basin. Water. 2018; 10(10):1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101437
Chicago/Turabian StyleHermoso, Martín, María Jesús García-Ruiz, and Francisco Osorio. 2018. "Efficiency of Flood Control Measures in a Sewer System Located in the Mediterranean Basin" Water 10, no. 10: 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101437
APA StyleHermoso, M., García-Ruiz, M. J., & Osorio, F. (2018). Efficiency of Flood Control Measures in a Sewer System Located in the Mediterranean Basin. Water, 10(10), 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101437






