Coupled Thermally-Enhanced Bioremediation and Renewable Energy Storage System: Conceptual Framework and Modeling Investigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Bioremediation of Contaminated Soil and Groundwater
1.2. Renewable Energy Storage
1.3. Coupled Bioremediation and Renewable Energy Storage System
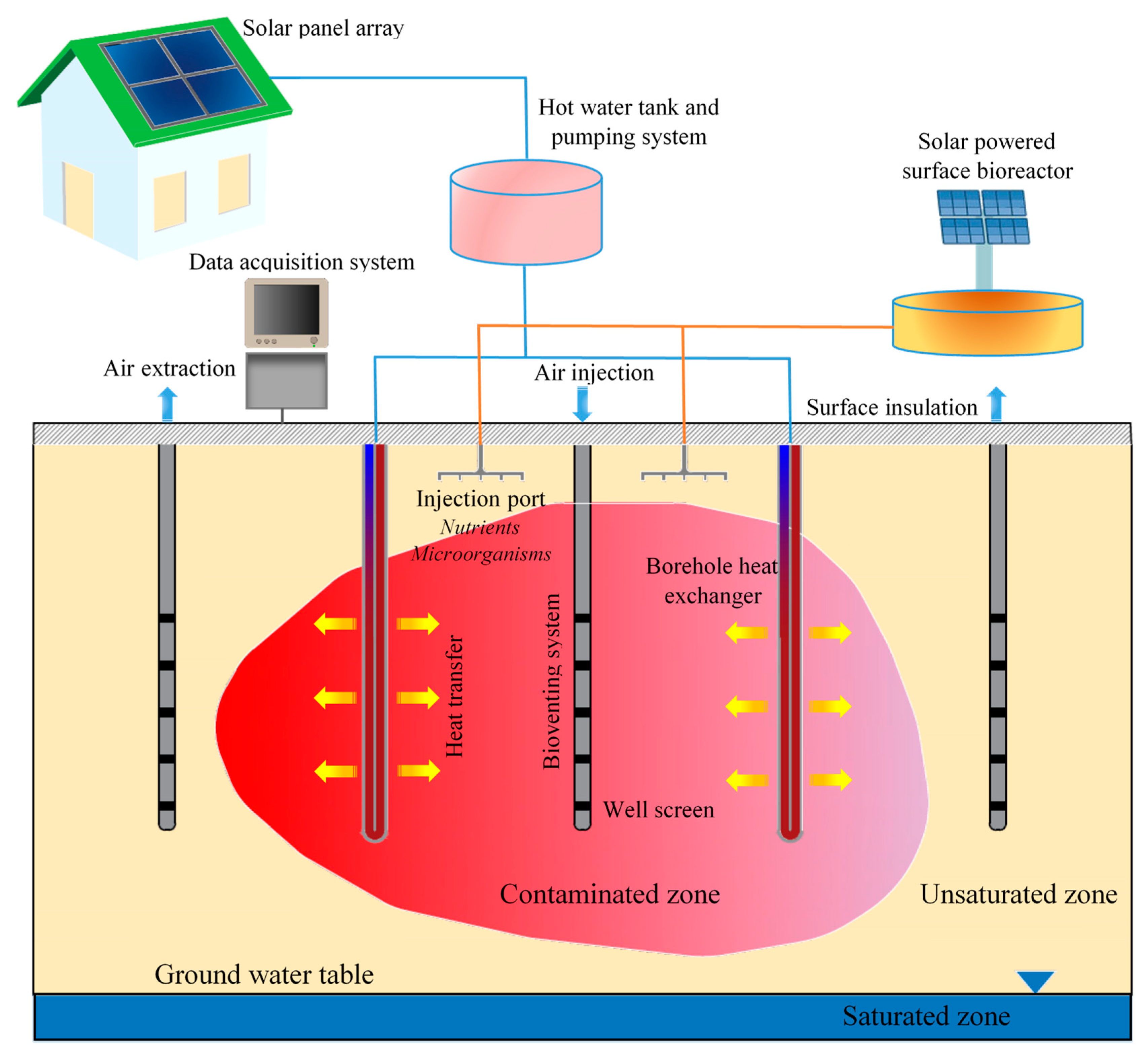
2. System Characteristics
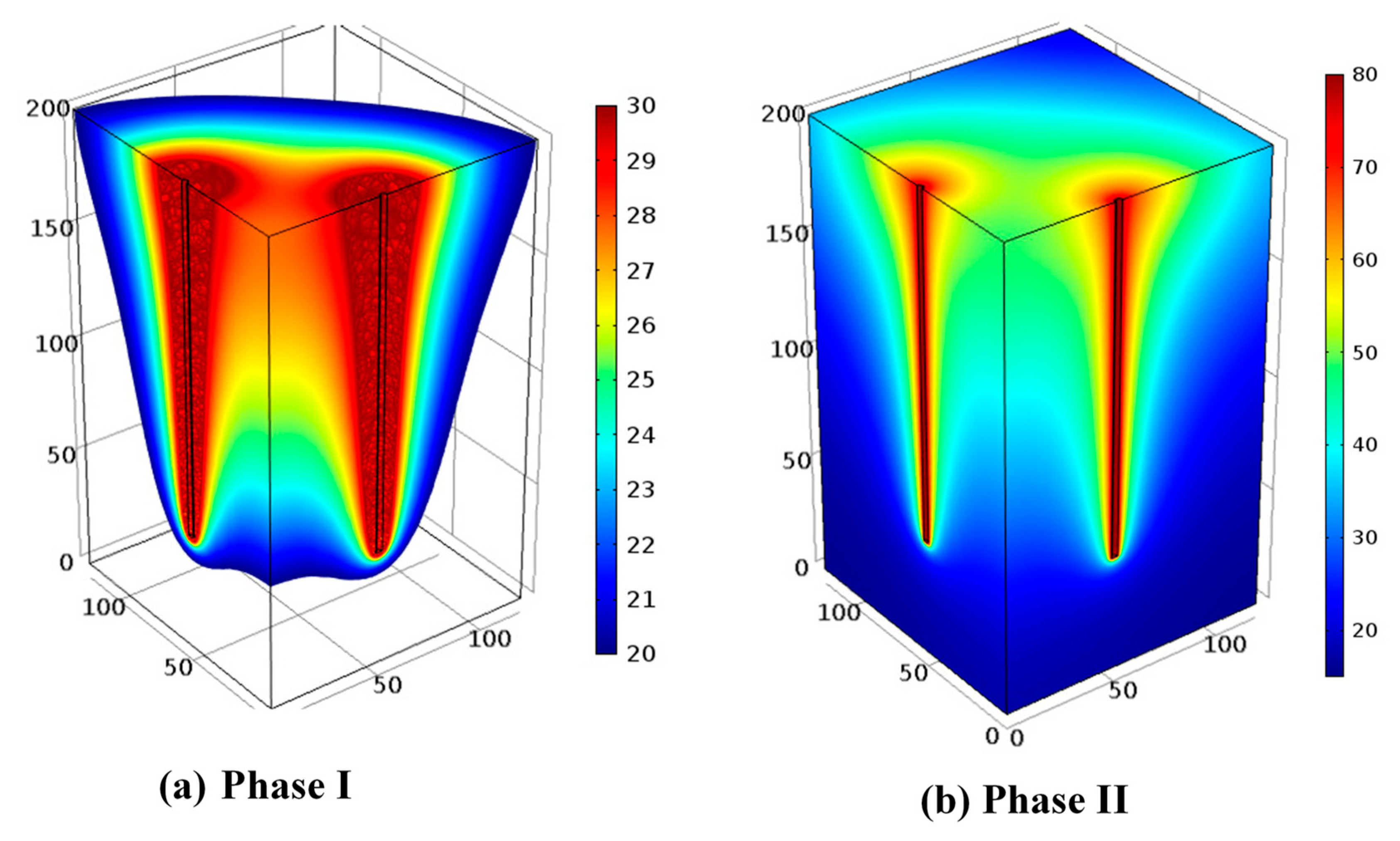
- Elevated temperatures in the soil domain during the bioremediation period (phase I) enhance contaminant attenuation rates: As discussed earlier, temperature can play an important role in increasing the efficacy and rates of bioremediation. In this system, the injected heat can compensate for diurnal and seasonal variations in the soil temperature profile, allowing for more consistent and longer heating periods and thus a shorter remediation time.
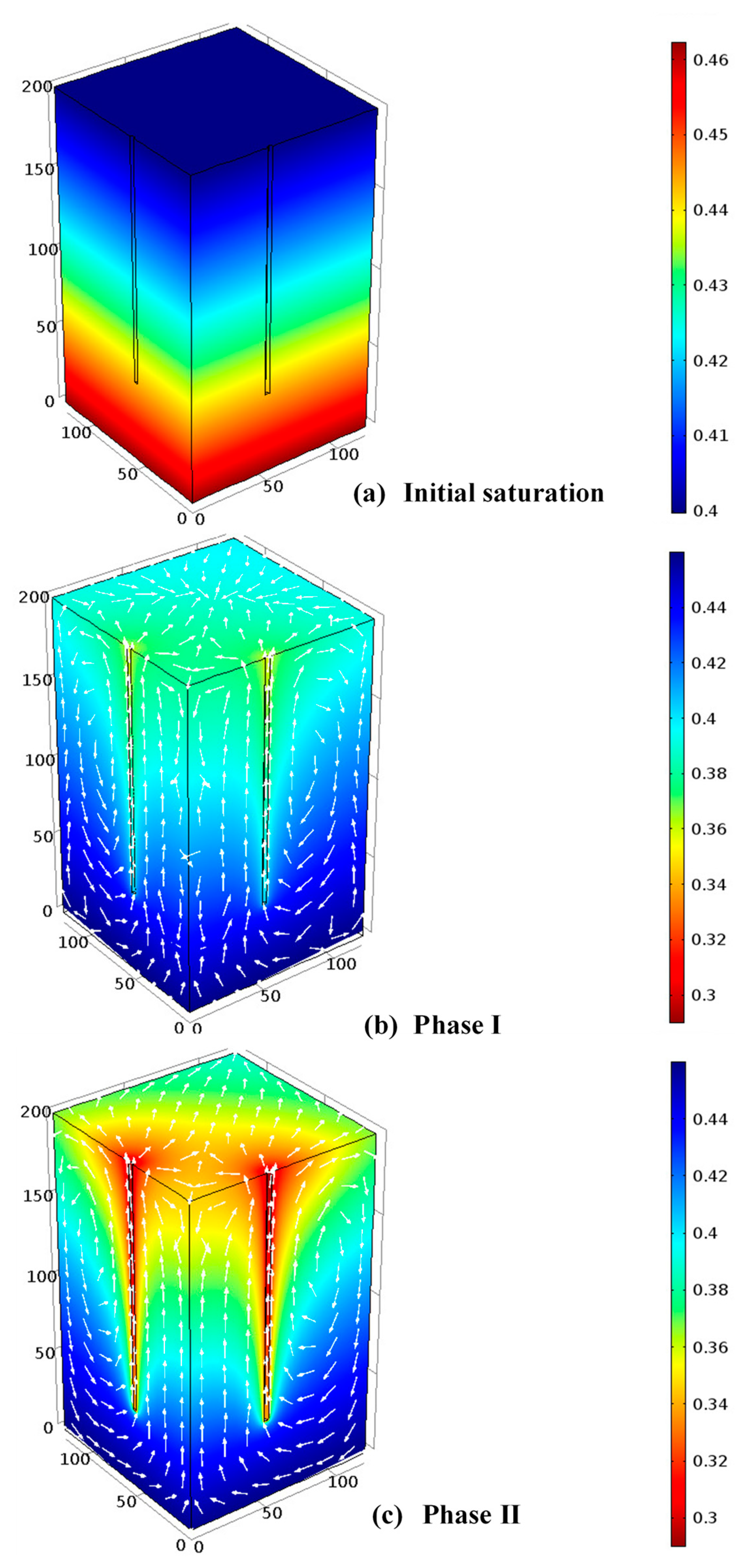
- Uniform distribution of nutrients/oxygen through moisture redistribution increases biostimulation in unsaturated zone: As discussed in Section 4, moisture movement occurs in the presence of thermal gradients. The moisture circulation in both the liquid and vapor forms/phases can help redistribute oxygen and nutrients that are delivered from injection wells, allowing for the increase in contact between microorganisms and contaminant throughout the domain. This is important as in bioremediation injection wells, the injected nutrients/biomass is consumed very quickly and in the vicinity of wells. Thus, nutrients/biomass is rarely distributed far from the injection wells.
- Minimal disruption of the site: Installing borehole heat exchangers does not require any excavation and can be done with minimal disturbance of the soil. This is also known to be one of the important advantages of traditional and thermally enhanced bioremediation as well [22].
- Applicable to both populated and rural areas: Enhanced bioremediation/energy storage systems can be implemented in domestic areas (e.g., under building foundations), and remote/rural locations.
- Renewable energy consumption: Except for the initial installation costs and routine maintenance, there is minimal energy cost associated with this system, resulting in a considerably cheaper remediation technique than traditional thermal remediation systems.
- Environmentally friendly: This method links a remediation initiative with a clean and renewable energy storage system. The clean-up has minimal impact to the environment while implementing a sustainable system that allows the long-term use of the renewable energy system. Historically, bioremediation and renewable energy alternatives are well accepted with the public.
- The proposed method can be implemented in colder environments above freezing point where natural attenuation rates are unacceptably slow. Temperature will enhance the movement of contaminants through the soil which could increase bioavailability.
- In this method, the elevated soil temperature is considerably lower and easier to control compared to, for instance, electrical resistance or radio frequency methods. Therefore, the potential adverse effect of high temperatures (e.g., mobilizing contaminants, sterilizing microorganism, etc.) is minimal.
- Long-term energy storage: When the remediation goals are achieved, the system can still be used to store renewable energy without any additional investment or modification.
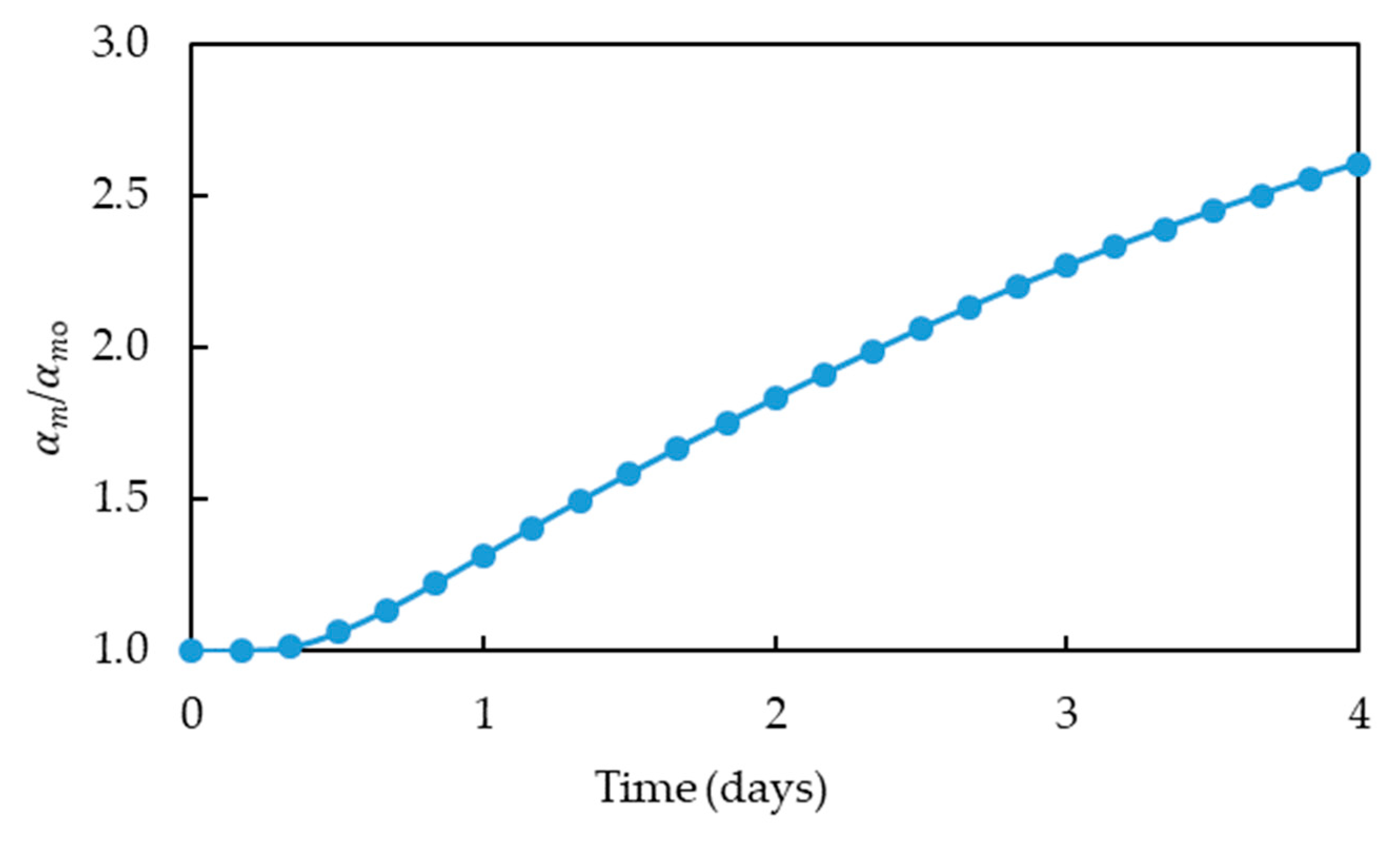
- Higher energy storage efficiency during phase II: Continuous heating of soil domain during phase (I) without a cooling period in the wintertime will likely increase the efficiency during energy storage phase. Although the transition may involve a cooling phase for the central regions of the contaminated domain (only in case of using thermophilic bacteria), it is expected that the surrounding soil will still have a slightly higher temperature than background temperature. Therefore, it results in a lower temperature gradient between core of the system and the surrounding soil, thus, decreasing the heat loss from the system.
- The system has limited footprint, and it is not expected to have an extensive environmental impact in upper soil layers.
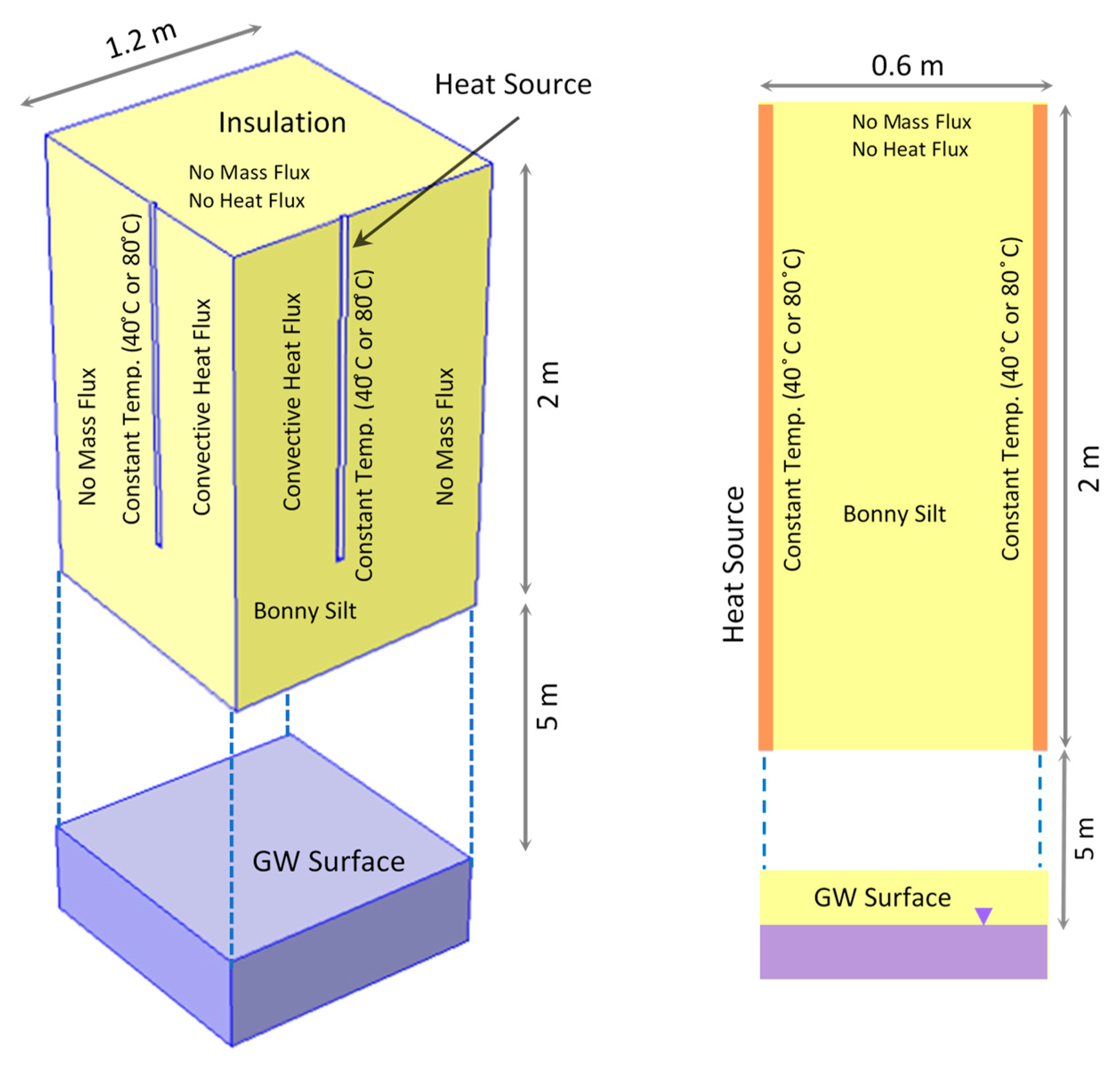
3. Numerical Modeling
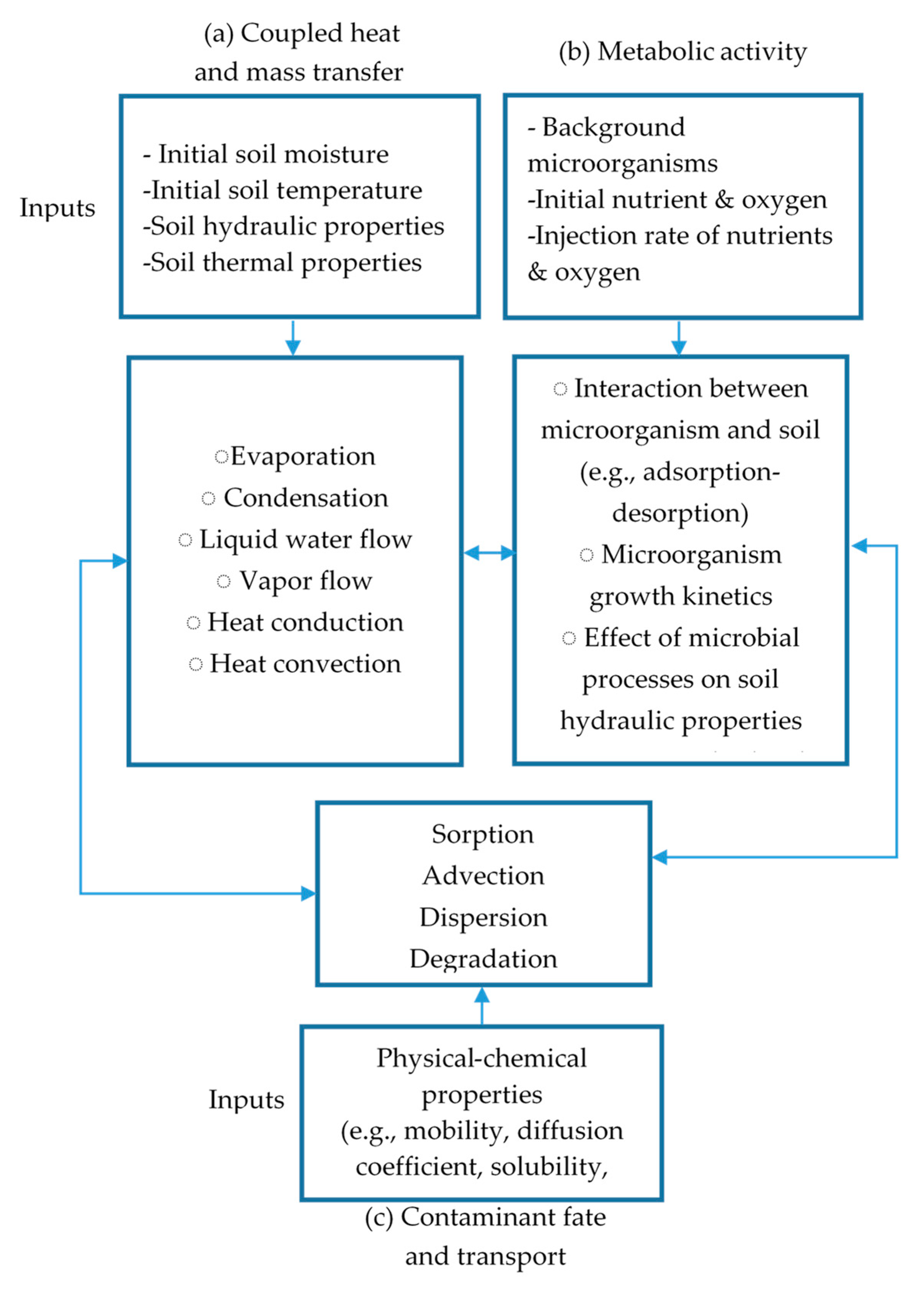
3.1. Simulation of Heat and Mass Transfer
3.2. Simulation of Bioremediation Process
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| d50 (mm) | Porosity | Residual Volumetric Water Content (m/m) | Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity, Ks, (m·s−1) | van Genuchten Parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha (kPa−1) | n | ||||
| 0.039 | 0.430 | 0.030 | 1.3 × 10−6 | 0.0863 | 1.58 |
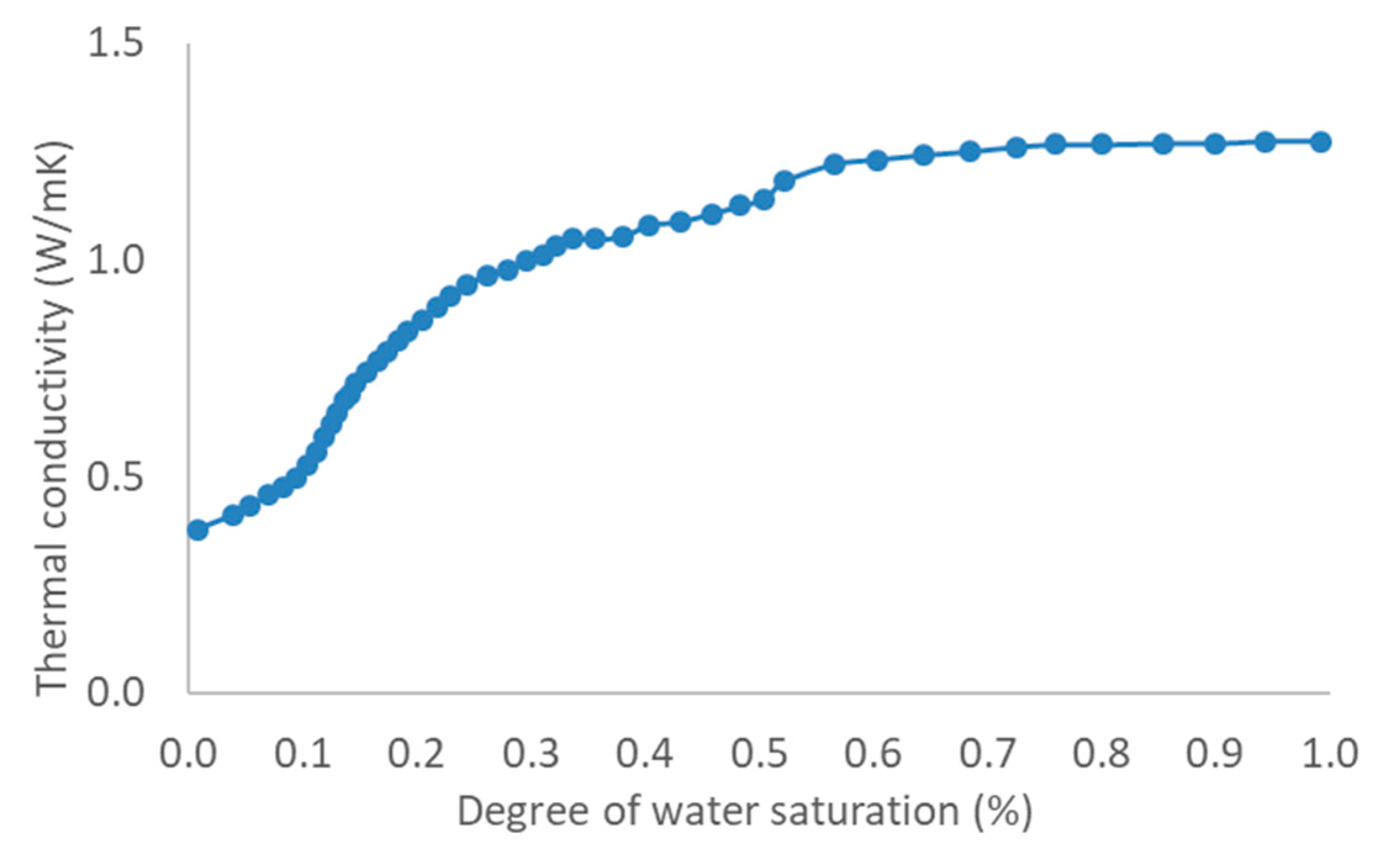
References
- Balba, M.T.; Al-Awadhi, N.; Al-Daher, R. Bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil: Microbiological methods for feasibility assessment and field evaluation. J. Microbiol. Methods 1998, 32, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Suetsugu, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Fujihara, A.; Suyama, K. Enhancing bioremediation of oil-contaminated soils by controlling nutrient dispersion using dual characteristics of soil pore structure. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Allen, A.S.; Schimel, J.P.; Holden, P.A. Controls on microbial CO2 production: A comparison of surface and subsurface soil horizons. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The diversity and biogeography f soil bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzmann, P.D.; Robertson, W.J.; Zappia, L.R.; Davis, G.B. The role of microbial populations in the containment of aromatichydrocarbons in the subsurface. Biodegradation 2002, 13, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, J.L.; Sims, R.C.; DuPont, R.R.; Matthews, E.; Russell, H.H. In-Situ Bioremediation of Contaminated Unsaturated Subsurface Soils; Ann Arbor Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, R.C.; Sorensen, D.L.; Sims, J.; McLean, J.E.; Mahmood, R.; Dupont, R.R. Review of In-Place Treatment Techniques for Contaminated Surface Soils—Volume 2: Background Information for In-Situ Treatment; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Huddleston, R.L.; Bleckmann, C.A.; Wolfe, J.R. Land treatment—Biological degradation processes. In Land Treatment: A Hazardous Waste Management Alternative; Loehr, R.C., Malina, J.F., Jr., Eds.; Center for Research in Water Recourses, University of Texas: Austin, TX, USA, 1986; pp. 41–62. [Google Scholar]
- Rochkind, M.L.; Blackburn, J.W.; Sayler, G.S. Microbial Decomposition of Chlorinated Aromatic Compounds; National Technical Information Service: Springfield, VA, USA, 1986; pp. 2–86.
- Paul, E.A.; Clark, F.E. Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Academic Press, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, P. What are high-temperature bacteria doing in cold environments? Trends Microbiol. 2002, 10, 120–121. [Google Scholar]
- Perfumo, A.; Banat, I.M.; Marchant, R. The use of thermophilic bacteria in accelerated hydrocarbon bioremediation. In Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions VI: Including Oil Spill Studies; Brebbia, C.A., Ed.; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2006; pp. 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Marchant, R.; Sharkey, F.H.; Banat, I.M.; Rahman, T.J.; Perfumo, A. The degradation of n-hexadecane in soil by thermophilic geobacilli. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 56, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lugowsky, A.J.; Palamteer, G.A.; Boose, T.R.; Merriman, J.E. Biodegradation Process for Detoxifying Liquid Streams. U.S. Patent 5,656,169, 12 August 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Markl, H.; Antranikian, G.; Becker, P.; Markossian, S. Aerobic Biodegradation of Aromatic Compounds Having Low Water Solubility Using Bacillus Thermoleovorans Strain DSM 10561. U.S. Patent 5,965,431, 12 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Feitkenhauer, H.; Müller, R.; MAuml, H. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and long chain alkanes at 6070 C by Thermus and Bacillus spp. Biodegradation 2003, 14, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margesin, R.; Schinner, F. Biodegradation and bioremediation of hydrocarbons in extreme environments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 56, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietikäinen, J.; Pettersson, M.; Bååth, E. Comparison of temperature effects on soil respiration and bacterial and fungal growth rates. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 52, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.T.; Jia, Z.; Wang, D.; Chiu, C.Y. Effects of temperature on the composition and diversity of bacterial communities in bamboo soils at different elevations. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 4879–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dijkstra, P.; Thomas, S.C.; Heinrich, P.L.; Koch, G.W.; Schwartz, E.; Hungate, B.A. Effect of temperature on metabolic activity of intact microbial communities: Evidence for altered metabolic pathway activity but not for increased maintenance respiration and reduced carbon use efficiency. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, R.M.; Al-Kharusi, S.; Al-Hinai, M. Effect of biostimulation, temperature and salinity on respiration activities and bacterial community composition in an oil polluted desert soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 98, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathy, R. Factors limiting bioremediation technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 74, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanscartier, D.; Zeeb, B.; Koch, I.; Reimer, K. Bioremediation of diesel-contaminated soil by heated and humidified biopile system in cold climates. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2009, 55, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosegi, J.M.; Minsker, B.S.; Dougherty, D.E. Feasibility study of thermal in-situ bioremediation. J. Environ. Eng. 2000, 126, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfumo, A.; Banat, I.M.; Marchant, R.; Vezzulli, L. Thermally enhanced approaches for bioremediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendry, M.J.; Mendoza, C.A.; Kirkland, R.A.; Lawrence, J.R. Quantification of transient CO2 production in a sandy unsaturated zone. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraishi, A.; Yamanaka, Y.; Narihiro, T. Seasonal microbial community dynamics in a flowerpot-using personal composting system for disposal of household biowaste. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 46, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouillard, B.M.; Mikkelson, K.M.; Bokman, C.M.; Berryman, E.M.; Sharp, J.O. Extent of localized tree mortality influences soil biogeochemical response in a beetle-infested coniferous forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchee, R.E.; Smith, L.A. In-Situ Thermal Technologies for Site Remediation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, T.; Senior, C.L.; Burns, E.G.; Bell, M.D. Solar-powered soil vapor extraction for removal of dense non-aqueous phase organics from soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2000, 35, 795–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, A.J.; Hayden, N.J.; Rizzo, D.M. Low-temperature soil heating using renewable energy. J. Environ. Eng. 2006, 132, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, J.S.; Ge, S.; Reed, A.; Lu, N.; Smits, K. Soil-borehole thermal energy storage systems for district heating. In Proceedings of the European Geothermal Congress, Pisa, Italy, 3–7 June 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, A.; Smits, K.M.; Cihan, A.; Massey, J.; McCartney, J.M. Impact of coupled heat transfer and water flow on soil borehole thermal energy storage (SBTES) systems: Experimental and modeling investigation. Geothermics 2015, 57, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moradi, A.; Smits, K.M.; Lu, N.; McCartney, J.S. Heat transfer in unsaturated soil with application to borehole thermal energy storage. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.T.; Jackson, K.J.; Duba, A.G.; Chen, C.I. In Situ Thermally Enhanced Biodegradation of Petroleum Fuel Hydrocarbons and Halogenated Organic Solvents. U.S. Patent 5,753,122, 19 May 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bear, J.; Bensabat, J.; Nir, A. Heat and mass transfer in unsaturated porous media at a hot boundary: I. One-dimensional analytical model. Transp. Porous Med. 1991, 6, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeppel, R.E.; Hinchee, R.E.; Arthur, M.F. Bioventing soils contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1991, 8, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchee, R.E. Bioventing of Petroleum Hydrocarbons. In Handbook of Bioremediations; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Test Method for Evaluating Total Recoverable Petroleum Hydrocarbon, Method 418.1 (Spectrophotometric, Infrared); Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). How to Evaluate Alternative Cleanup Technologies for Underground Storage Tank Sites. A guide for Corrective Action Reviewers; EPA 510-R-04-002; Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Rees, S.J.; He, M. A three-dimensional numerical model of borehole heat exchanger heat transfer and fluid flow. Geothermics 2013, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, H.; Diao, N.; Fang, Z. Efficiency of vertical geothermal heat exchangers in the ground source heat pump system. J. Ther. Sci. 2003, 12, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.M.; Ginn, T.R. Modeling microbial processes in porous media. Hydrogeol. J. 2000, 8, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsi, I.; Fasano, A. A general model for bioremediation processes of contaminated soils. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Sci. Appl. Math. 2009, 1, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapatwala, K.D.; Babu, G.R.V.; Vijaya, O.K.; Armstead, E.; Palumbo, A.V.; Zhang, C.; Phelps, T.J. Effect of temperature and yeast extract on microbial respiration of sediments from a shallow coastal subsurface and vadose zone. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1996, 57, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, B.D.; Keller, C.K.; Johnstone, D.L. In-situ measurement of microbial activity and controls on microbial CO2 production in the unsaturated zone. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Or, D.; Smets, B.F.; Wraith, J.M.; Dechesne, A.; Friedman, S.P. Physical constraints affecting bacterial habitats and activity in unsaturated porous media—A review. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 1505–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Environmental Factor | Optimum Range * |
|---|---|
| Soil moisture | 25–85% of soil porosity |
| Oxygen | Aerobes > 0.2 mg/L and Anaerobes thrive in the absence of oxygen |
| Redox potential | Aerobes > 50 mV and Anaerobes < 50 mV |
| pH | 5.5–8.5 |
| Nutrients | Sufficient for microbial growth |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moradi, A.; M. Smits, K.; O. Sharp, J. Coupled Thermally-Enhanced Bioremediation and Renewable Energy Storage System: Conceptual Framework and Modeling Investigation. Water 2018, 10, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101288
Moradi A, M. Smits K, O. Sharp J. Coupled Thermally-Enhanced Bioremediation and Renewable Energy Storage System: Conceptual Framework and Modeling Investigation. Water. 2018; 10(10):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101288
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoradi, Ali, Kathleen M. Smits, and Jonathan O. Sharp. 2018. "Coupled Thermally-Enhanced Bioremediation and Renewable Energy Storage System: Conceptual Framework and Modeling Investigation" Water 10, no. 10: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101288
APA StyleMoradi, A., M. Smits, K., & O. Sharp, J. (2018). Coupled Thermally-Enhanced Bioremediation and Renewable Energy Storage System: Conceptual Framework and Modeling Investigation. Water, 10(10), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101288





