Difference in PM2.5 Variations between Urban and Rural Areas over Eastern China from 2001 to 2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Satellite-Derived PM2.5
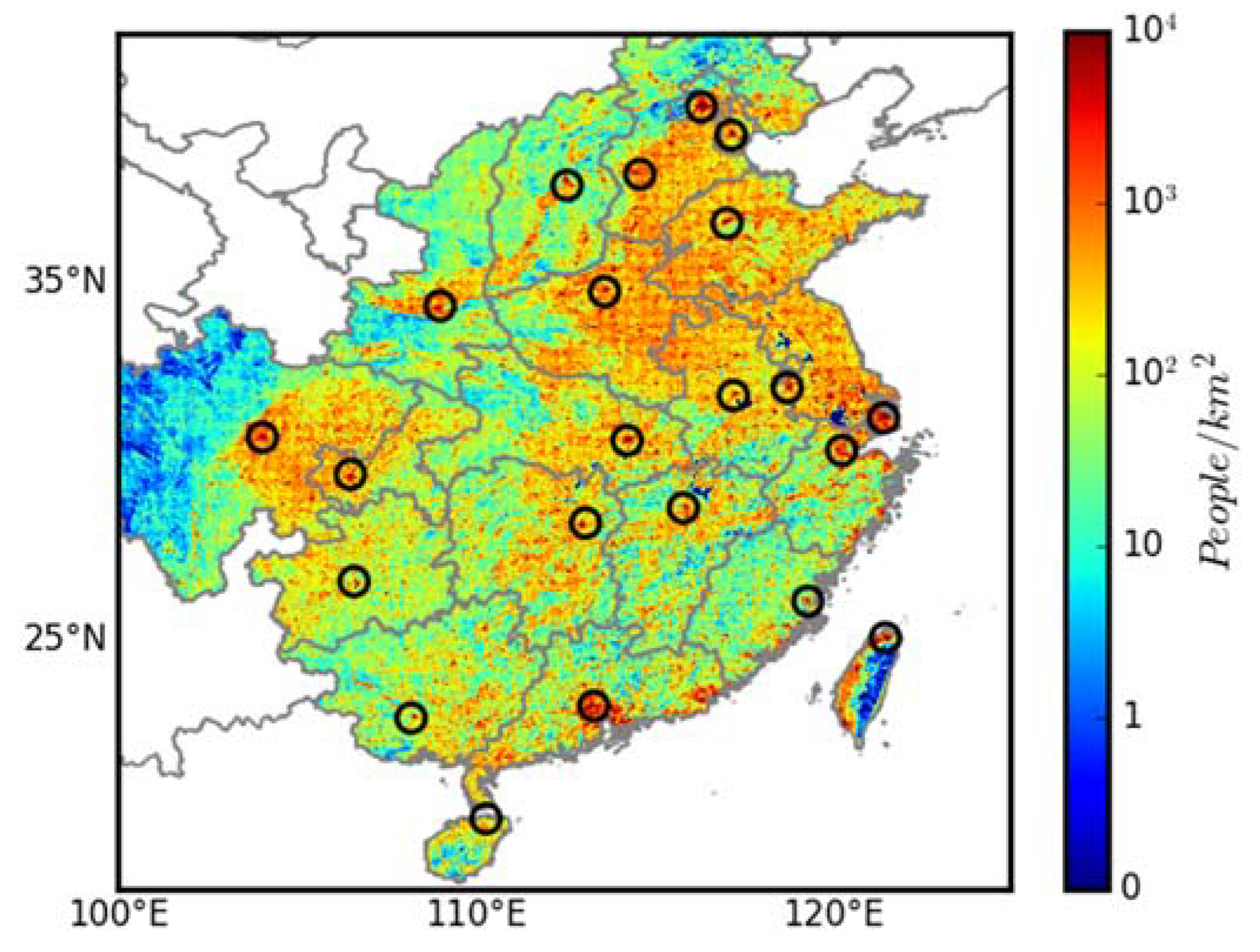
2.3. Urban and Rural Areas
3. Results
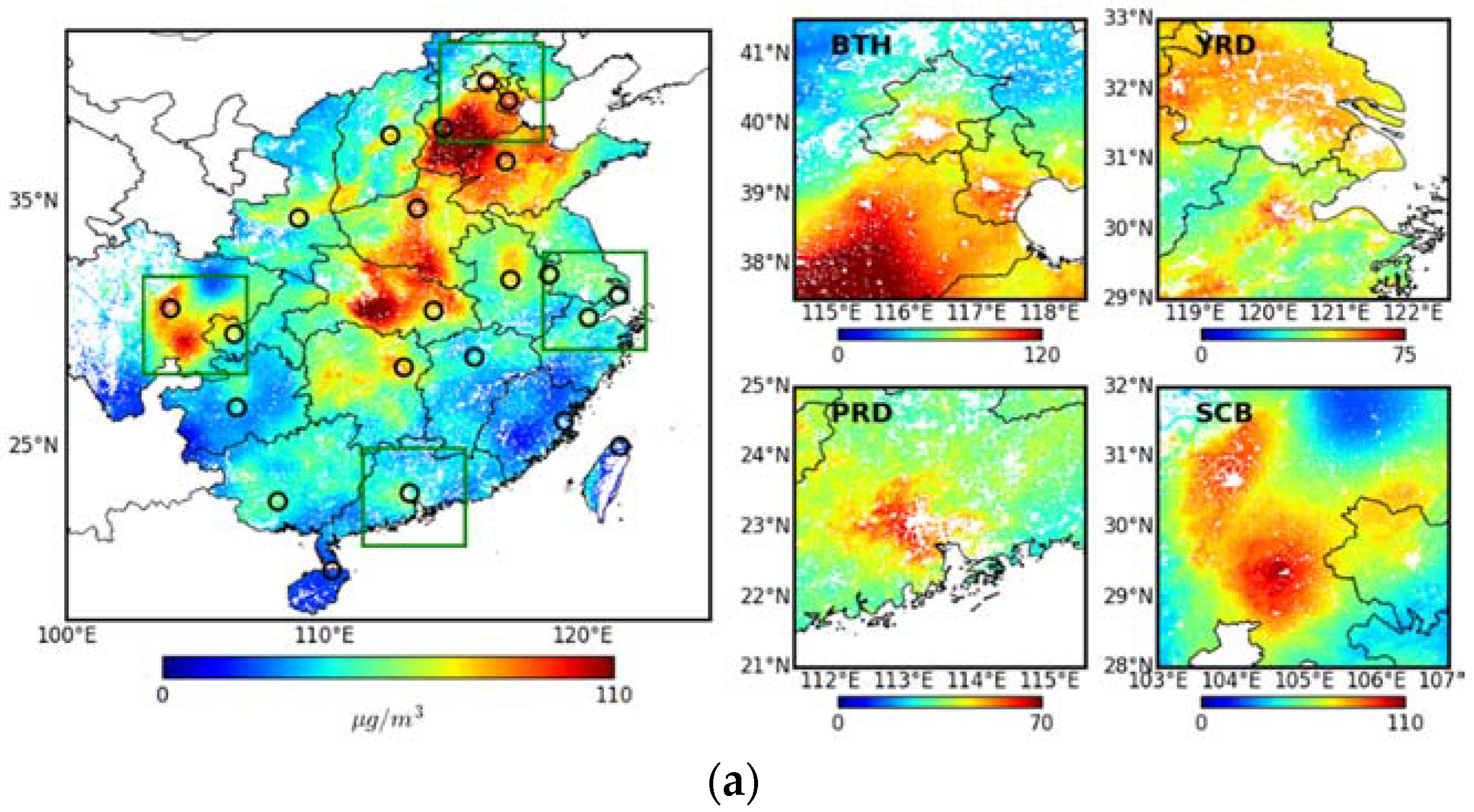
3.1. PM2.5 in Urban and Rural Areas
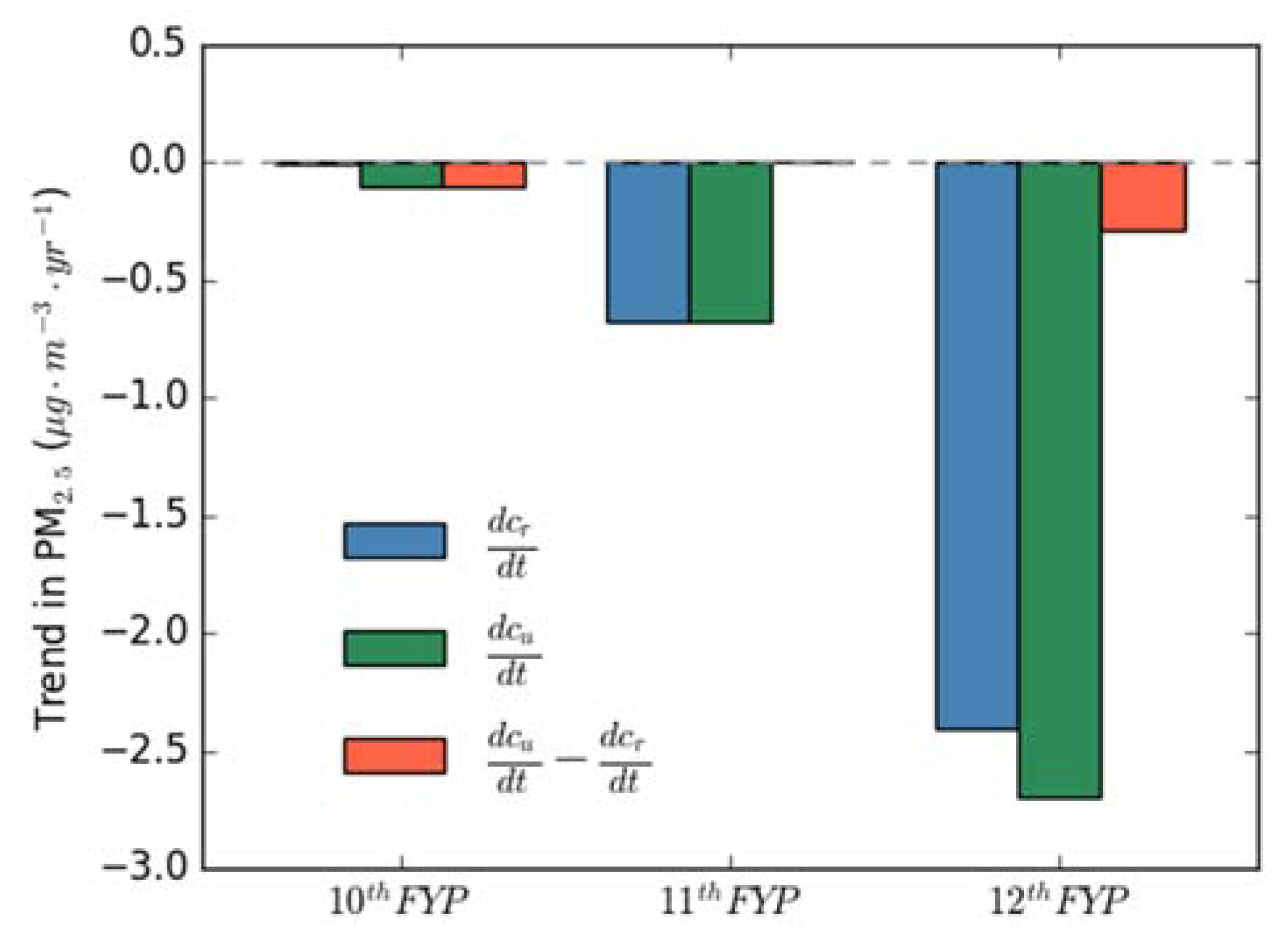
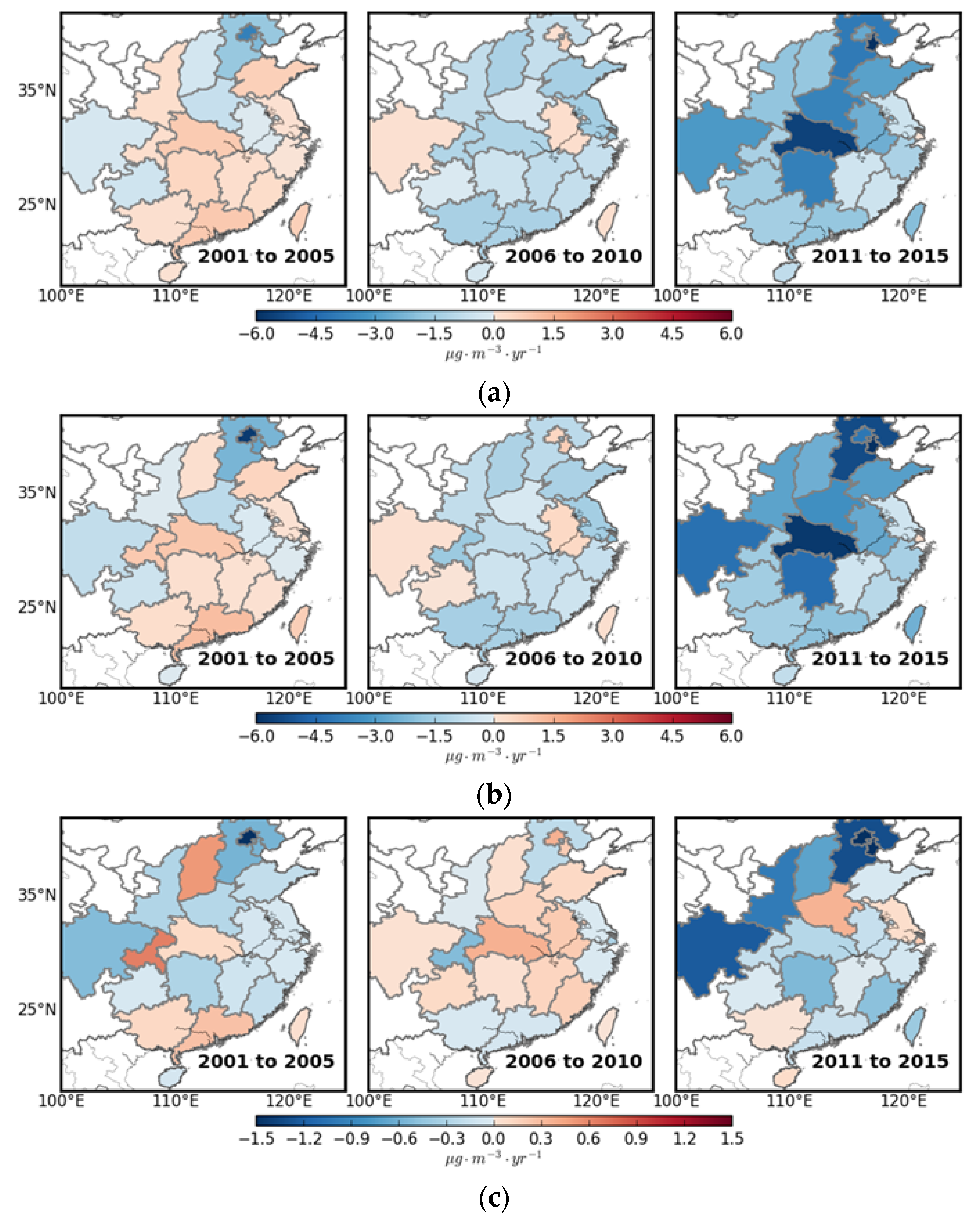
3.2. PM2.5 Trends in Urban and Rural Areas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A.; Xu, X.; Spengler, J.D.; Ware, J.H.; Fay, M.E.; Ferris, B.G., Jr.; Speizer, F.E. An association between air pollution and mortality in six US cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lau, A.K.H.; Lin, C.Q.; Chuang, Y.C.; Chan, J.; Jiang, W.K.; Tam, T.; Yeoh, E.-K.; Chan, T.-C.; et al. Effect of long-term exposure to fine particulate matter on lung function decline and risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Taiwan: A longitudinal, cohort study. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, e114–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yao, T.; Fung, J.C.H.; Lin, C. Estimation of health and economic costs of air pollution over the Pearl River Delta region in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Yao, T.; Fung, J.C.H.; Lau, A.K.H. Assessment of health burden caused by particulate matter in southern China using high-resolution satellite observation. Environ. Int. 2017, 98, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chang, L.-Y.; Lau, A.K.H.; Chan, T.-C.; Chieh Chuang, Y.; Chan, J.; Lin, C.; Kai Jiang, W.; Dear, K.; Zee, B.C.Y.; et al. Satellite-based estimates of long-term exposure to fine particulate matter are associated with C-reactive protein in 30,034 Taiwanese adults. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Chan, T.-C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Lin, C.Q.; Jiang, W.K.; Yeoh, E.; Tam, T.; Woo, K.S.; et al. Long-term Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter, Blood Pressure, and Incident Hypertension in Taiwanese Adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 017008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, J.S.; Marshall, J.D.; Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M. Addressing Global Mortality from Ambient PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8057–8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, R.A.; Muller, R.A. Air Pollution in China: Mapping of Concentrations and Sources. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 in China Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7436–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.B.; Streets, D.G. Primary anthropogenic aerosol emission trends for China, 1990–2005. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 931–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G. Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9839–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nielsen, C.P. The effects of recent control policies on trends in emissions of anthropogenic atmospheric pollutants and CO2 in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 487–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Q.; Liu, G.; Lau, A.K.H.; Li, Y.; Li, C.C.; Fung, J.C.H.; Lao, X.Q. High-resolution satellite remote sensing of provincial PM2.5 trends in China from 2001 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 180, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Q.; Li, Y.; Lau, A.K.H.; Deng, X.J.; Tse, K.T.; Fung, J.C.H.; Li, C.C.; Li, Z.Y.; Lu, X.C.; Zhang, X.G.; et al. Estimation of long-term population exposure to PM2.5 for dense urban areas using 1-km MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 179, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Louie, P.K.K.; Zheng, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yue, D.; Ho, J.W.K.; Lau, A.K.H. Science–policy interplay: Air quality management in the Pearl River Delta region and Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 76, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Liu, W.-L.; Chen, C.-H. Development of a multiple objective planning theory and system for sustainable air quality monitoring networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 354, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, X.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lau, A.K.; Chan, T.-C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Chan, J.; Lin, C.; Guo, C.; Jiang, W.K.; Tam, T.; et al. Exposure to ambient fine particulate matter and semen quality in Taiwan. Occup. Envrion. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.S.; Leung, C.C.; Li, Y.; Poon, C.M.; Yao, S.; Wong, E.L.Y.; Lin, C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Lee, S.S. PM2.5 concentration and elderly tuberculosis: Analysis of spatial and temporal associations. Lancet 2017, 390, S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chan, T.-C.; Guo, C.; Chang, L.; Lin, C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Jiang, W.K.; Ho, K.F.; Tam, T.; Woo, K.S.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient particulate matter (PM2.5) is associated with platelet counts in adults. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Hoek, G.; Chang, L.; Chan, T.-C.; Guo, C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Chan, J.; Lin, C.; Jiang, W.K.; Guo, Y.; et al. Particulate matter air pollution, physical activity and systemic inflammation in Taiwanese adults. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Liao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Li, C.; Fung, J.C.H.; Tse, T.K.T. Assessing Long-Term Trend of Particulate Matter Pollution in the Pearl River Delta Region Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11670–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Q.; Li, C.C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Yuan, Z.B.; Lu, X.C.; Tse, K.T.; Fung, J.C.H.; Li, Y.; Yao, T.; Su, L.; et al. Assessment of satellite-based aerosol optical depth using continuous lidar observation. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Q.; Li, Y.; Lau, A.K.H.; Li, C.C.; Fung, J.C.H. 15-Year PM2.5 Trends in the Pearl River Delta Region and Hong Kong from Satellite Observation. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W. Increasing impact of urban fine particles (PM2.5) on areas surrounding Chinese cities. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Mao, J.; Chu, D.A. Retrieval, validation, and application of the 1-km aerosol optical depth from MODIS measurements over Hong Kong. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Q.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.B.; Lau, A.K.H.; Li, C.C.; Fung, J.C.H. Using satellite remote sensing data to estimate the high-resolution distribution of ground-level PM2.5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Sayer, A.M.; Levy, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Tong, S.; Bi, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Satellite-Based Spatiotemporal Trends in PM2.5 Concentrations: China, 2004–2013. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Boys, B.L. Use of satellite observations for long-term exposure assessment of global concentrations of fine particulate matter. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. OECD Redefining “Urban”: A New Way to Measure Metropolitan Areas; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, F. Research progress in spatialization of population data. Prog. Geogr. 2013, 32, 1692–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Li, L. Impact of urbanization level on urban air quality: A case of fine particles (PM2.5) in Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Li, Y.; Fung, J.C.H.; Li, C.; Lu, X.; Li, Z. Difference in PM2.5 Variations between Urban and Rural Areas over Eastern China from 2001 to 2015. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080312
Lin C, Lau AKH, Li Y, Fung JCH, Li C, Lu X, Li Z. Difference in PM2.5 Variations between Urban and Rural Areas over Eastern China from 2001 to 2015. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(8):312. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080312
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Changqing, Alexis K. H. Lau, Ying Li, Jimmy C. H. Fung, Chengcai Li, Xingcheng Lu, and Zhiyuan Li. 2018. "Difference in PM2.5 Variations between Urban and Rural Areas over Eastern China from 2001 to 2015" Atmosphere 9, no. 8: 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080312
APA StyleLin, C., Lau, A. K. H., Li, Y., Fung, J. C. H., Li, C., Lu, X., & Li, Z. (2018). Difference in PM2.5 Variations between Urban and Rural Areas over Eastern China from 2001 to 2015. Atmosphere, 9(8), 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080312







