Abstract
Several long-term monitoring of aerosol datasets from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on board Terra/Aqua, Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR), Sea-Viewing Wide Field-of-View Sensor (SeaWiFS) were used to derive the dust aerosol optical depth (DOD) in Central Asia based on the Angstrom exponent parameter and/or the particle shape. All sensors agree very well on the interannual variability of DOD. The seasonal analysis of DOD and dust occurrences identified the largest dust loading and the most frequent dust occurrence in the spring and summer, respectively. No significant trend was found during the research period in terms of both DOD and the dust occurrence. Further analysis of Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation (CALIPSO) aerosol products on a case-by-case basis in most dust months of 2007 suggested that the vertical structure is varying in terms of the extension and the dust loading from one event to another, although dust particles of most episodes have similar physical characteristics (particle shape and size). Our analysis on the vertical structure of dust plumes, the layer-integrated color ratio and depolarization ratio indicates a varied climate effect (e.g., the direct radiative impact) by mineral dust, dependent on the event being observed in Central Asia.
1. Introduction
Mineral dust is one of the most abundant aerosols on the Earth. Mineral dust may affect the climate system by interacting with the atmospheric radiation [1], with the ecosystems [2], and with the cloud microphysics [3]. Accurately quantifying these effects by mineral dust, however, is still one of the major scientific problems at both global and regional scales. Once lifting into the atmosphere, dust aerosols experience a variety of physical and chemical processes. The crucial factors for exploring these issues include accurately quantifying the dust loading in the fine mode (for estimating the direct radiative effect) and in the coarse mode (for studies on its role in the cloud formation, as well as the radiative effects), measuring chemical compositions, determining transport pathways and the deposition intensity (e.g., for studies on the iron supply to the ecosystem), and studying vertical structures (for radiative and cloud microphysical effects). Thus, studies on the dust occurrence and the vertical structure are of great importance to understand the role of dust in the human–climate–environment system.
Numerous publications documented the dust occurrence in Africa and East Asian deserts, two main dust sources, but few studies exist addressing this issue in Central Asia. Central Asia consists of five countries: Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan. Mineral dust in Central Asia is mainly found along the “dust belt” from the eastern Caspian Sea, through the Ustyurt Plateau and the Aral Kum Deserts to Balqash Lake [4]. The Aral Kum is a newly formed dust source caused by the desiccation of the Aral Sea. Approximately tons of dust are blown out of the desert annually [5], rendering it to be one of the most important dust sources worldwide. Dust particles from this region can be carried thousands of kilometers to northern Iran, as revealed by images from the Advanced very-high-resolution radiometer (AVHRR) [6]. Only a small fraction of dust occurrence can have a long-range transport, one branch northeastward into the north of Mongolia (a frequency of 9%) and the other into the Central Russia (a frequency of 13%) during spring seasons [7]. Existing publications suggest that the dust occurrence in this region has contributed to the surface heating of the Aral Sea, the energetic cyclone activity, and the cold wave intrusions during warm seasons [8]. Thus, monitoring and documenting the dust occurrence characteristic and intensity, dust sources, and its transport are urgently needed from both environmental and climatic perspectives so that governments of these regions can make appropriate decisions to prevent dust adverse impacts. Most available studies that address the development of dust storms in Central Asia [6], e.g., in Turkmenistan [9] and the Aral Sea Basin [10], are limited by the short period of observations (less than a decade) and/or the amount of available data on the deposition, visibility, and absorbing index (AI). Furthermore, to gain the dust occurrence in the atmosphere indirectly from the dust deposition measurement is very difficult due to the lack of transport information. Analysis of Indoitu et al. [6] also suffered from the height-dependence problem of the AI products [11], although the dependence might not be that strong in this region due to small AI values. In addition to the very short period (2005–2008), contributions from non-dust absorbing aerosols such as biomass burning, which produces AI almost as high as dust plumes, are not excluded.
Satellite remote sensed Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) is the most useful information available to characterize dust activities over source regions, especially in Central Asia where few ground-based observations are available and modeling dust emissions are still challenging on both daily and monthly basis [4]. The use of satellite sensing AOD has been increasing in the last decade to quantify aerosols over a specific region or around the globe [12,13]. Evaluation works [14,15] have shown that the Multi-angle Imaging Spectro-Radiometer (MISR) AOD is in general consistent with ground-based observations, within 20% of the AOD in desert areas, although it is substantially underestimated for cases with AOD > 0.5 in China [16]. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) AOD is also well correlated with the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) measurements in general around the globe [17]. Here, aerosol products from several satellite sensors, MODIS on board Terra and Aqua, Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI), MISR, and Sea-Viewing Wide Field-of-View Sensor (SeaWiFS), are analyzed. MODIS aerosol product provides a useful tool to monitor the dust occurrence and to evaluate the model performance of simulating dust from regional to global scales, although it overpassed a specific site once per day. The L2 aerosol product has a very high spatial resolution (10 km × 10 km), which is helpful to quantify dust characteristics. In 2004, Hsu et al. [18] extended the retrieval of AOD at 550 nm from the dark target (ocean and dense vegetation-covered land surfaces) to the relative bright surface types such as bare soil types, taking advantage of the multiple radiances (especially at 412 nm) measured by the MODIS sensor. Based on the newly developed product, Ginoux et al. [19] designed a simple algorithm by calculating the dust frequency of occurrence (FOO) to try to identify the anthropogenic and nature dust sources. OMI Aerosol Index (AI) along with its predecessor, TOMS (TOtal Ozone Mapping Spectrometer) AI, is another commonly used satellite remote sensing product to obtain the information on dust aerosols and their sources [20,21,22], although it has a rough spatial resolution (averaged 100 km and 50 km at nadir, horizontally) and it is sensitive to the aerosol layer height [11]. In addition, the use of the Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) offers an opportunity to measure the vertical distribution of aerosols. For example, using the CALIPSO and surface measurements, Huang et al. [23] found that dust aerosols originating from the source regions of the Taklimakan and Gobi Deserts may undergo long-range transport via upper tropospheric westerly jets where dust might impose a long-lasting impact on the climate due to the extended lifetime. Utilizing the CALIPSO lidar data, Liu et al. [24] examined a long-distance transport across the Atlantic Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico for a dust storm case in North Africa on 17 August 2006.
The goal of this study is to characterize the spatial, inter-annual, and seasonal variations of dust aerosol properties in Central Asia based on satellite retrievals over a long-term period (2000–2016). We further confirm results from the existing literature and show whether there are significant differences among aforementioned sensors on these issues. To fulfill this goal, MODIS, Level 2, Collection 6 swath data were used with a horizontal resolution of 10 km × 10 km at the nadir, including spectral AOD, the fraction of AOD from particles in the fine mode to total AOD, and the Angstrom parameter over the entire area of Central Asia for 2000–2016. For MISR, Level 2 swath data were utilized with the horizontal resolution of 17.6 km × 17.6 km, covering a period from 2003 to 2016. For SeaWiFS, the swath data of Level 2 from 2000 to 2010 were used. This work is among the first systematical dust climatology studies over Central Asia, employing the prevailing long-term satellite datasets. The radiative effect of dust is highly dependent on the vertical structure of dust layers [25,26,27]. The vertical distribution, especially relative to the cloud, is vital for estimating the impact of mineral dust on the cloud microphysics, as well as the dust radiative impact. Numerous observations with both in-situ measurements and satellite remote sensing (lidar) have been performed to study the vertical dust profiles in East Asia [23], North Africa [28], and Mediterranean [29] moving toward the Atlantic [30,31,32] and the Pacific Ocean [33]. However, there are no studies available, to the best of our knowledge, that examine dust over the Central Asia region. Thus, this paper also presents the dust radiative properties using the CALIPSO instrument (Vertical Feature Mas and the total backscatter coefficient at 532 nm) based on several dust storm cases, e.g., the ones that occurred on 7 May 2007. Our analysis also includes one of the important East Asia dust sources, the Taklimakan Desert, for a comparison purpose.
2. The Study Domain
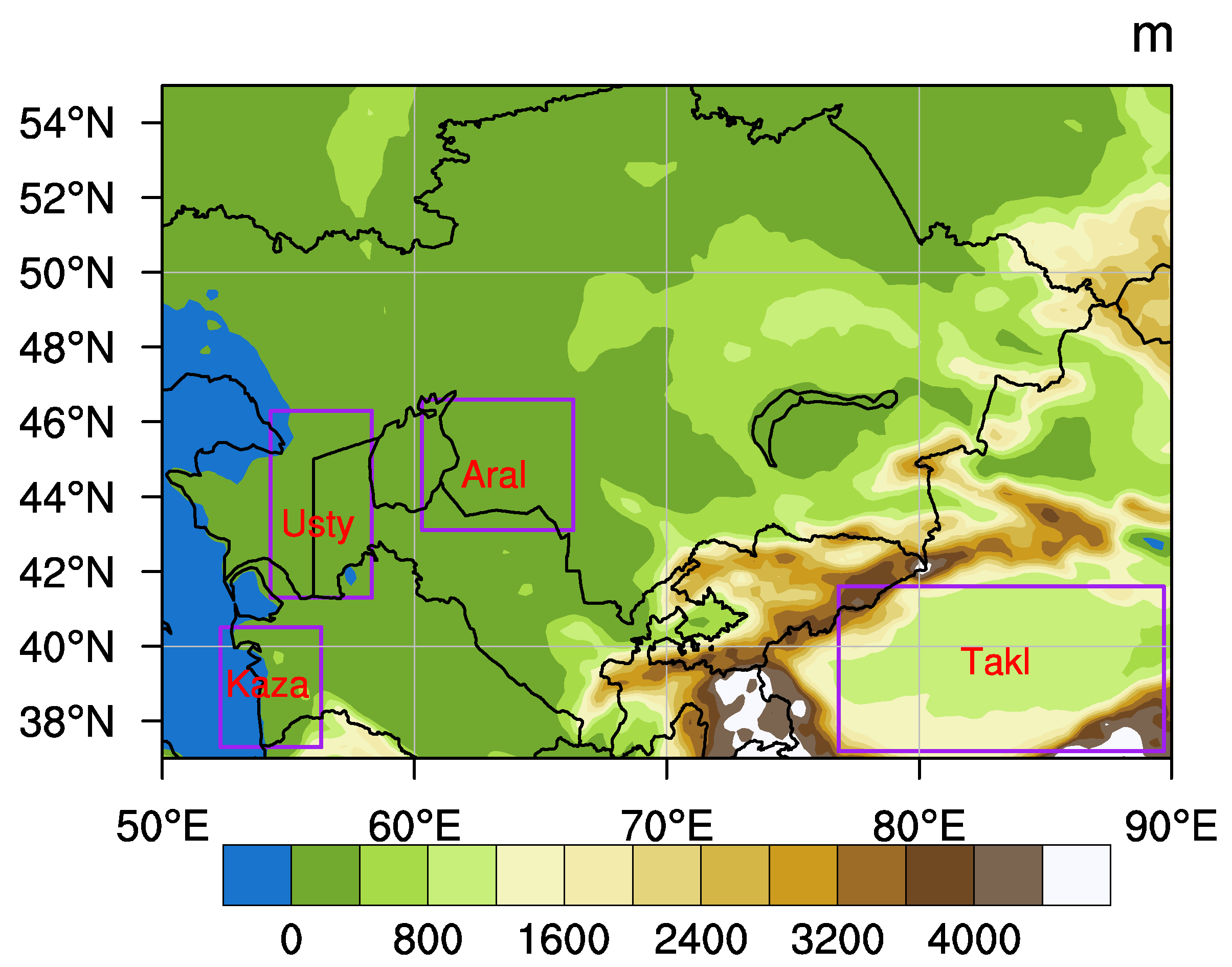
Our study domain is the Central Asia region (Figure 1) that is bounded by western China to the east, southern Kazakhstan to the north, the Caspian Sea to the west, and the mountain range in Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan to the south. The annual amount of rainfall ranges (maximum in the spring) and is less than 100 mm in most desert regions (e.g., Kara Kum, Kyzyl Kum, and Betpak-Dala) [34]. It has a distinct climate contract between northern and southern parts: cold and dry continental climate in the north (mean annual temperatures: °C), but hot and dry Mediterranean climate in the south (mean annual temperatures: °C) [34]. Deserts in Central Asia are different from other regions such as North Africa where few human activities occur. Humans play an important role in the formation of deserts in Central Asia. The retreating of the Aral Sea began in the 1960s due to a combination effect of agricultural activities, an expansion of the irrigated area (increasing by 40.6% from 1918 to 1960), and regional climate changes [34]. Particularly, during the first decade of the 21st century, the retreating of the Aral Sea was accelerating (the desiccation process has been successfully captured by the MODIS true color images). Thus, the exposed bottom becomes the so-called Aral Kum Desert, covering more than 57,500 by August 2011 [34]. It has become a powerful source of dust and salt emissions. For instance, an estimation based on the WRF-Chem (Weather Research and Forecasting coupled with Chemistry) model indicates that this area contributed approximately 12% of the total dust emissions of this area by mass in April during 2000–2014 [4]. An “ideal” dust storm that occurred over this area occurred during 7–9 May 2007 (lasting three days) due to a cyclone system. This event was also successfully captured by the MODIS true color image, as shown in Figure 5 of Li and Sokolik (2018) [35] and the AVHRR image [6]. More details about the land cover and land use map and changes are readily available in Figure 3 of Li and Sokolik (2018) [35] and in Figure 2 of Li and Sokolik (2017) [4].
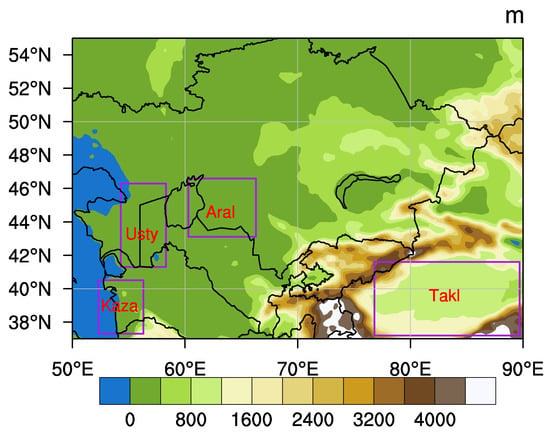
Figure 1.
The research domain, Central Asia and its topography (shading area, unit: m). Purple boxes represent four sub-regions where statistical analysis was applied. We use Kaza to refer to the area surrounding Kazandzhik and use Usty, Aral, and Takl to refer to the Ustyurt Plateau, the Aral Kum Desert, and the Taklimakan Desert, respectively.
3. Data
3.1. MODIS AOD
MODIS was launched in 1999 in the Terra constellation. MODIS AOD over bright regions is obtained by best fitting the reflectance database based on its geo-location to the simulated lookup table consisting of observation angles, surface reflectances, AOD, and aerosol radiative properties at deep blue (412 nm), 490 nm, and 670 nm (Deep Blue Algorithm) for each retrieval pixel [18] (Hsu et al., 2004). The pixel AOD is then averaged over a 10 km × 10 km cell (at nadir) to obtain the released product (Level 2 Collection 6 MODIS AOD), swath granules consisting of approximately 1500 × 2000 such cells (swath width: 2300 km). To produce AOD statistics, we remap these granules onto 20 km × 20 km regular grids and averaged all granules from the same grid to form a daily value. Although the MODIS AOD has a regular gridded data (Level 3), the spatial resolution of this dataset is too rough () to use for regional studies. During the data processing, we avoid remapping onto a much finer grid because the interpolation algorithm would lead to an additional error. The remapping and averaging method is repeated for every day for nine months (March–November) from 2000 to 2016. For simplicity, we use “annual” to refer to these nine months for all aerosol products hereafter without any further statement.
The Deep Blue Algorithm screens out pixels with cloud contaminations. The main uncertainties of the AOD retrievals are due to the cloud processing, measured surface reflectances, and some assumptions on the complex refractive indices, the particle shape, the vertical profile, and the particle size distribution. The spherical assumption leads to an error as large as 40% in the phase function calculation [36]. It would likely reduce the number of retrieved pixels yielding an underestimation of AOD. Because most dust occurrence in Central Asia is due to high-pressure systems and only some associated with cyclones, the cloud-contamination is not a great problem. The sensitivity test on the vertical profile shows that an error of 2 km in the altitude results in the AOD of 25% at 412 nm and 5% at 490 nm [18]. The vertical extension of the dust layer in Central Asia is within 3 km for the most dust occurrence (see further discussions of this issue in Section 5 based on the CALIPSO product). Thus, the error associated with the vertical profile assumption in the algorithm is negligible for Central Asia and the overall uncertainty of retrieving AOD using this algorithm should be less than the reported value at 550 nm.
3.2. SeaWiFS AOD
SeaWiFS has a spatial footprint of approximately , resulting from the averaging of 33 pixel, each with . Its sampling time is from the noon to the early afternoon in between Terra and Aqua satellites. The aerosol products of Version 003, Level 3 gridded composite at a spatial resolution of are used here. The over-land AOD retrieval from this product is also based on the Deep Blue Algorithm, as used by MODIS over-land AOD dataset. This dataset provides AOD at the commonly-used reference wavelength of 550 nm with a valid range of 0–5 from an arithmetic mean of data with the confidence flag equal to 3, directly available through the parameter “aerosol_optical_thickness_550_land”. The basic principle for the AOD retrieval over land is the same as MODIS, but has two distinguishing developments. Firstly, SeaWiFS has been expanded to include the vegetated surfaces in addition to the bright arid land. Secondly, it employs a more sophisticated handling with the surface reflectance dataset based on the stratified Lambertian-equivalent reflectivity (LER) for a specific location by the viewing geometry to account for surface bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) effects. The AOD dataset used here spans from 2000 to 2010, although SeaWiFS was in operation between September 1997 and December 2010, as the MODIS AOD dataset has been available since 2000.
3.3. MISR AOD
MISR is another instrument observing the Earth on the Terra platform orbiting the polar at an altitude of 705 km. It uses nine cameras (having 36 channels in total) that are fixed at particular view zenith angles () paired in a symmetrical arrangement. The swath widths of these cameras are approximately 413 km and 378 km for the eight off-nadir and nadir ones, respectively. The aerosol properties are retrieved based on the laterally homogeneousness assumption with the region and minimizations of the difference between observed radiances and pre-computed model radiances via the use of a look-up table (LUT). The aerosol model used by the MISR retrieval procedure contains eight different single composition particle types, called components, which are modeled using lognormal size distributions. All components other than dust are assumed to be spherical for the convenient use of the Mie theory to compute the scattering properties. The discrete dipole approximation and the T-matrix technique are used instead for dust components. Combinations of the eight components forming 74 distinct mixtures, and thus 74 aerosol models, are used to simulate the aerosol compositions in the troposphere.
3.4. OMI AAI
The Aura/Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) onboard the NASA EOS Aura spacecraft does not provide AOD at or close to the wavelength 550 nm. Thus, the daily Level 3 global gridded absorbing aerosol index (AAI) product derived from OMI observations are used to distinguish absorbing aerosol types such as biomass burning and dust from non-absorbing aerosols (e.g., sea-salt particles, or sulfates). OMI AAI has also been a widely used medium to obtain dust spatial and temporal distributions by many other peer-reviewed journal articles (e.g., Indoitu et al. [6]). The measurement of the Earth reflectance by OMI is in the visible and ultraviolet spectral bands around the globe. Distinguishing absorbing aerosols from non-absorbing ones is based on their spectral contrast in the near-UV region, where ozone absorption is very small. For instance, the absorbing aerosol tends to have large positive AAI, while the non-absorbing aerosol shows near-zero or negative AAI. More details about the near-UV aerosol index retrieval algorithm are described in Torres et al. [37]. The product has a spatial resolution varying from at nadir to along the scanning edges and it has been available since 2005. It is well known that the OMI has undergone an instrumental problem, the so-called “row anomaly”, since 2007, and this has affected almost half of the 60 rows in a cross-track direction with unpredictable patterns around the globe, depending on seasons and latitudes up to present (see more details at http://www.knmi.nl/omi/research/product/rowanomaly-background.php). Furthermore, no technique is available to differentiate mineral dust from biomass burning based on solely AAI. Thus, we only use AAI data for 2005–2007 as an auxiliary tool to characterize the spatial distribution of absorbing aerosols in the first section of our results.
3.5. CALIPSO Data
The CALIPSO data have been available since 2006, as the CALIPSO was launched on 28 April of this year along with the CALIPSO Sun-synchronous satellite in the A-Train constellation. The instrument operates at the dual wavelength (532 and 1064 nm) with the altitude of 702 km during both day and night of the satellite orbit. Three products from the CALIPSO are utilized in the present study: the vertical feature mask (version 3.0.1 and 3.02 level 2), AOD, and the total backscatter coefficient at 532 nm. The former product provides a feature classification between aerosols and clouds, with the spatial resolution varying with respect to the altitude and from horizontal to vertical directions. Horizontally, the spatial resolutions are , 1 km, and 5 km for three atmospheric layers, ground to, , and , respectively. In contrast, the product has much higher vertical resolutions: up to 30 m, 60 m, and 180 m in the three layers, respectively. The CALIPSO vertical feature mask is able to distinguish six types of aerosols (e.g., dust, polluted dust, smoke, etc.) from clouds using a set of algorithms (the cloud-aerosol discrimination algorithm), based on five-dimensional probability distribution functions of the mean attenuated backscatter coefficient at 532 nm, volume color ratio, depolarization, latitude, and layer-center height.
The CALIPSO detects dust aerosols using the volume depolarization ratio (the perpendicular to parallel component of received lidar signals) at 532 nm with a threshold value of 0.2 [38]. All normally defined dust events by horizontal visibility would likely be detected using this threshold value since it corresponds to the dust occurrence with a horizontal visibility exceeding 30 km and a particulate depolarization ratio of 0.35 and a lidar ratio of 45 sr [23]. However, this is not 100% true. Firstly, the current CAD algorithm can still misclassify some dense dust layers as cirrus cloud when they present at high altitudes and/or high latitudes, although it has been improved significantly compared to earlier versions. However, this issue is not a problem because, firstly, Central Asia does not situate at high latitudes. This paper is to identify the dust aerosol feature based on the feature type along with the quality assurance. We just keep the “dust” and “polluted dust” feature, but consider all other aerosol features (e.g., “smoke”) that we are not interested in as “others”. Because dust mixed with other aerosols for very few episodes in Central Asia, disregarding other dust-like features would not yield significant errors.
4. Methodology
The level 2, collection 6 aerosol products from the MODIS contain a parameter, Angstrom exponent (AE hereafter), which is retrieved between 412 and 470 nm and is inversely related to the particle size, in general, ranging from to in dusty environment and higher in polluted regions [39]. Dust aerosols (the effective radius in coarse mode:) are much larger than smoke in sizes. Thus, the Angstrom exponent could be used to distinguish dust particles from aerosols such as smoke and urban pollution. Schepanski et al. [40] used 0.6 (the threshold value and hereafter refer as AEt) to screen out fine-mode particles (aged dust, some anthropogenic dust and other types of aerosols in small sizes), while Ginoux et al. [39] employed a much smaller value, 0, as the threshold. In a recent publication, Xu [41] set the threshold to be a moderate value, 0.6. For Central Asia, no previous studies are available as our reference. Therefore, a series of AEt values (0.5, 0.7, and 1.0) were used to make conclusions more robust, following Ciren et al. [42]. We refer to and 0.7 as Criteria 1 and 2, respectively. The value 1.0 is the largest AEt found in the publication [42] to our best knowledge to screen out fine-mode aerosols together with a second condition of . We refer to this method as Criterion 3. was also utilized in this study to show influence of the threshold selection on the spatial-temporal variability of derived dust aerosol optical depth (DOD hereafter) and dust occurrences. Some publications (e.g., by Ginoux et al. [19]) also include the single scattering albedo as a criterion to exclude the possible influence of sea salts for coastal areas. However, our calculations by comparing results of DOD with and without adding this variable to the three criteria have shown that this influence is negligible in the study region. This is because our results are based on statistical methods (long-term/huge-area averaging and significant tests) and mineral dust is the dominant aerosol over the considered region. Thus, we derived DOD based on AEt and/or AODt without including the single scattering albedo. Because of this dominance near desert regions and the non-spherical shape of mineral dust, MISR AOD for non-spherical particles is regarded as DOD in this region.
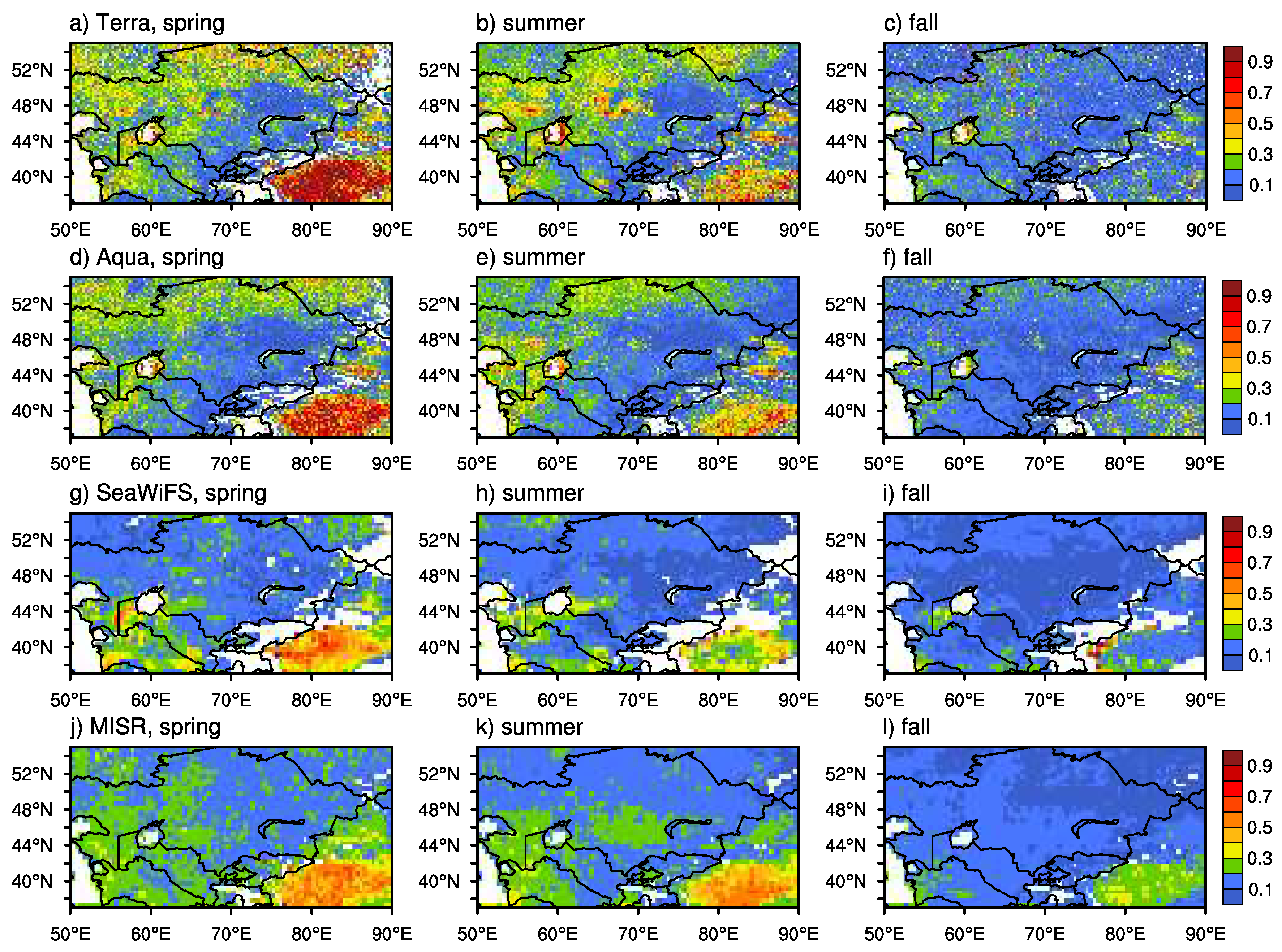
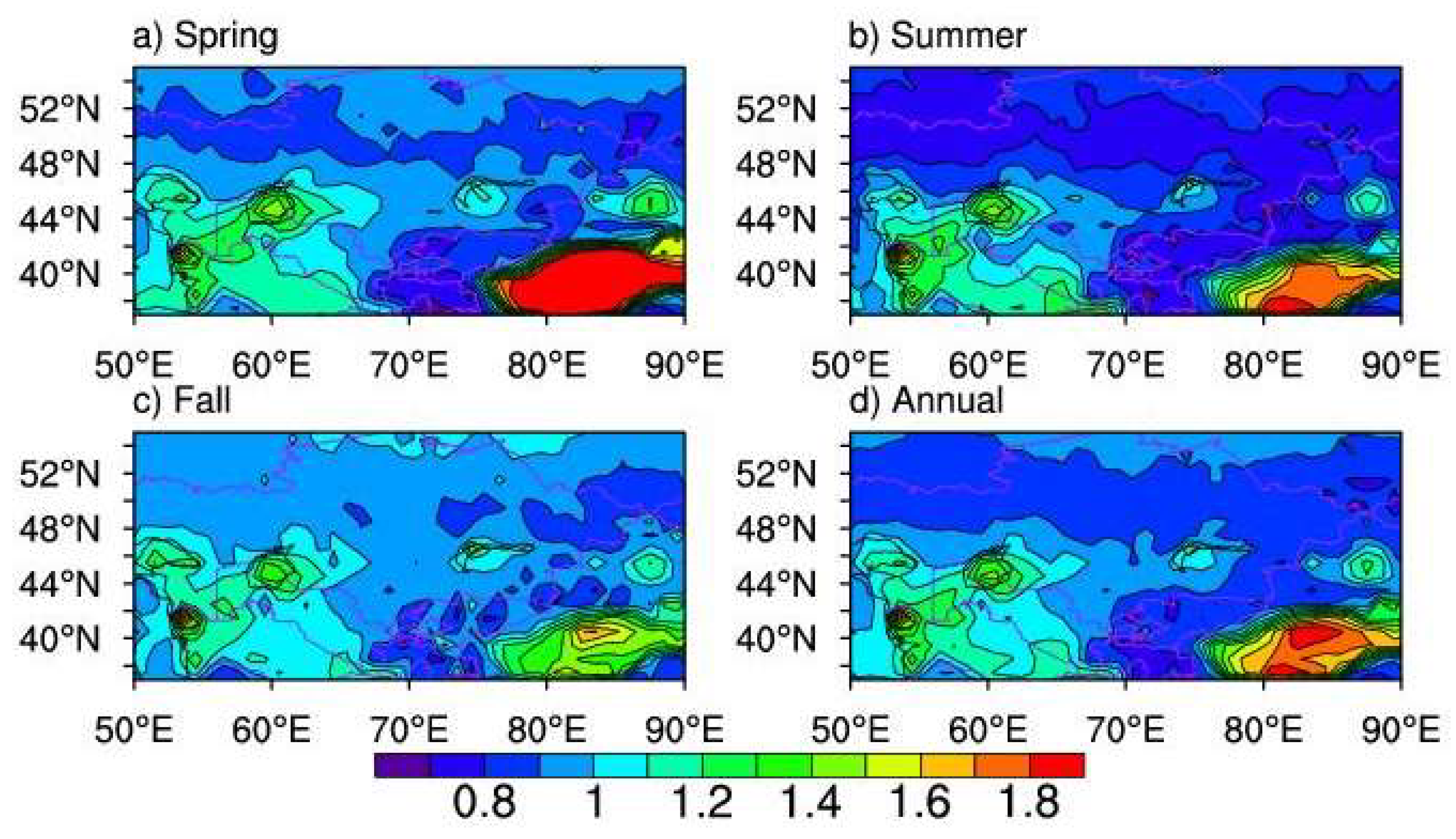
Figure 2 shows the seasonal mean AOD from Terra, Aqua, SeaWiFS, and MISR of the period 2003–2007 based on which the dust aerosols are obtained. Pixels with all quality flags were used from Terra and Aqua. The analysis periods for SeaWiFS and Terra are 2000–2010 and 2000–2016, respectively. For MISR and MODIS onboard Aqua, it is 2003–2016. All satellites agree well over the dust source regions surrounding the Aral Sea basin. It is evident that Terra and Aqua show larger seasonal-mean AOD over the Taklimakan Desert in spring and summer periods. The best estimation for dust AOD is also utilized with quality flags of 2 or 3. MODIS onboard Aqua and Terra has a similar sampling rate, much larger than SeaWiFS and MISR do. Particularly, the pixel amounts for MISR is smaller than for other satellites by approximately 2 orders of magnitude due to its narrow swath width. Retrievals are rarely available over the water mask, e.g., the Caspian Sea and the Aral Sea (Figure 3).
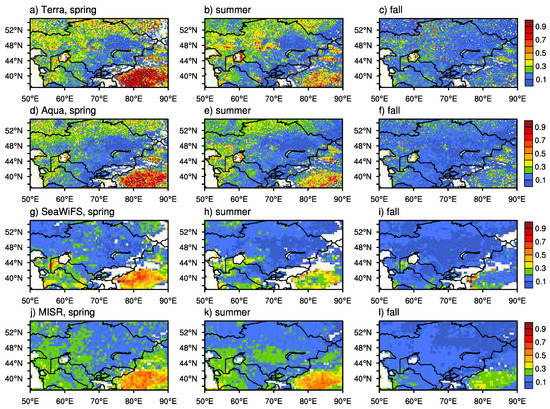
Figure 2.
Seasonal distribution of AOD (unitless) from MODIS onboard the Terra (a, b, and c) and Aqua (d, e, and f) satellites, SeaWiFS (g, h, and i), and from MISR (j, k, and l) for MAM, JJA, and SON of the 2003–2007 period.
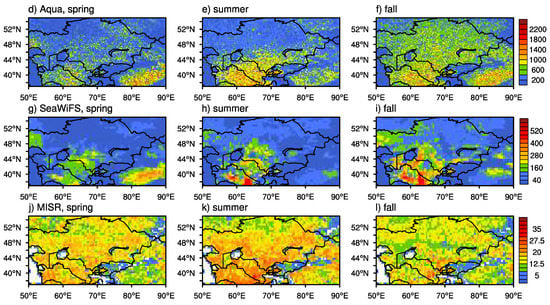
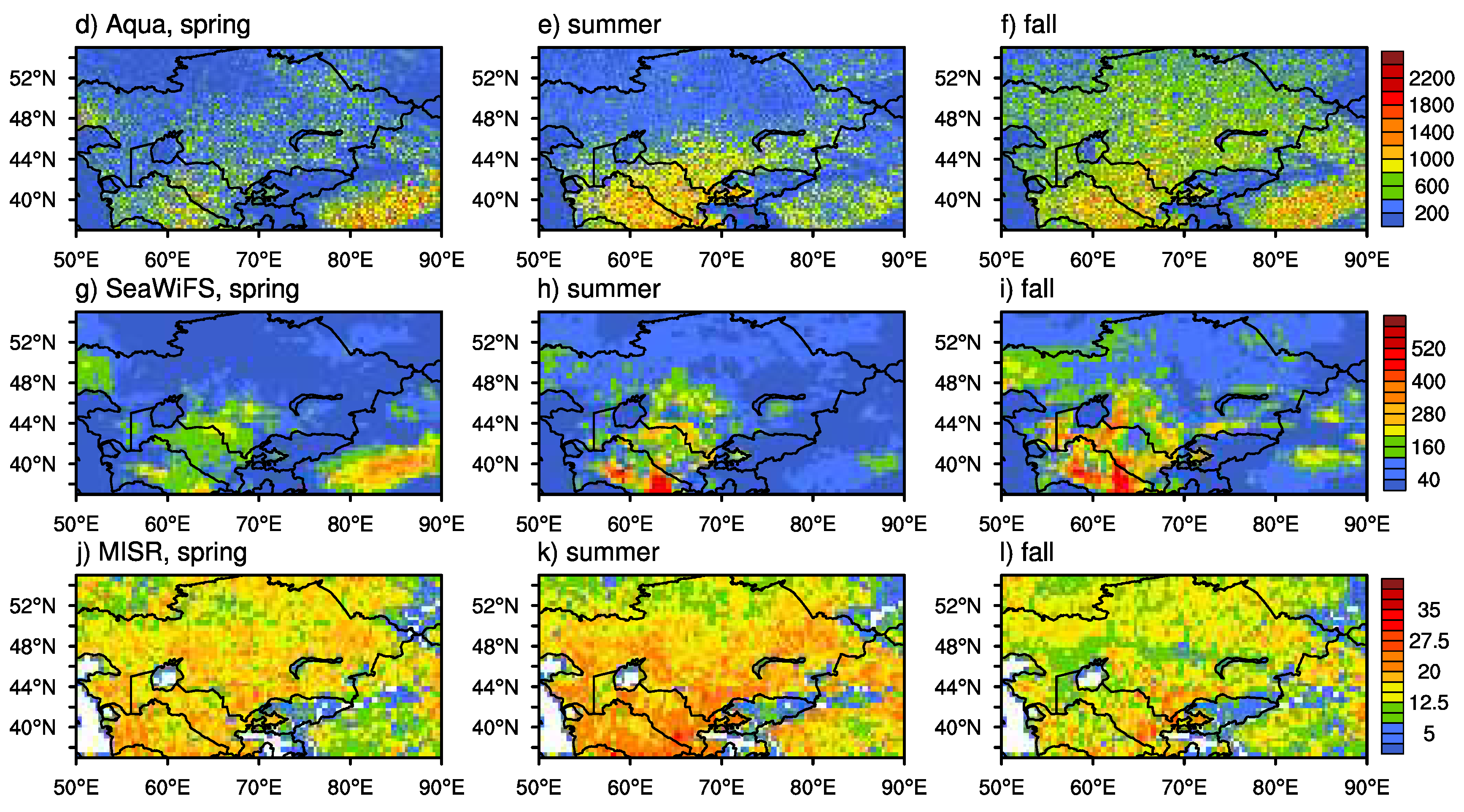
Figure 3.
Seasonal mean sampling numbers across Central Asia for MODIS onboard the Aqua satellite (d, e, and f), SeaWiFS (g, h, and i), and from MISR (j, k, and l) during the 2003–2007 period.
5. Results
5.1. The Variability of DOD
5.1.1. Spatial Distributions
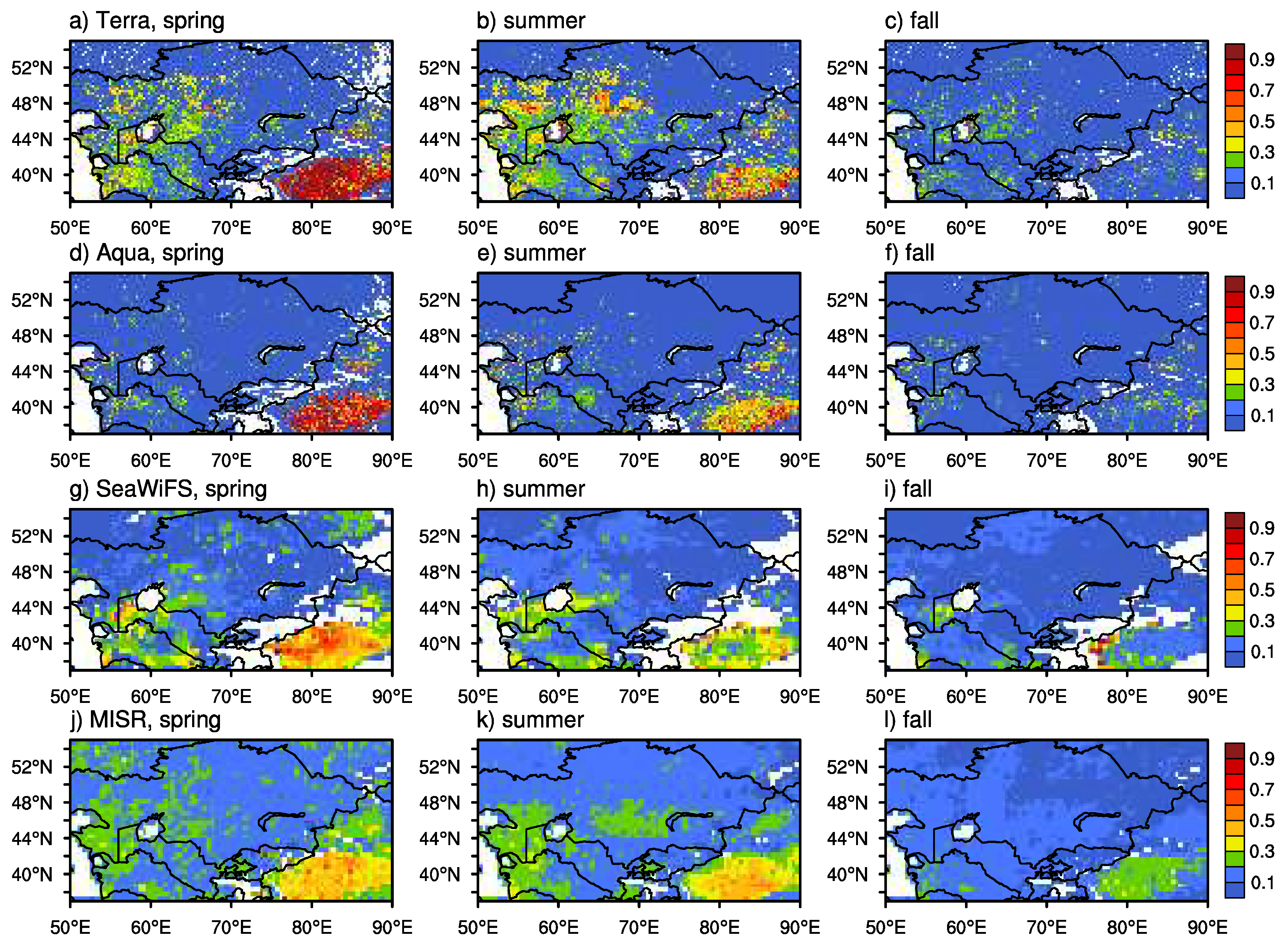
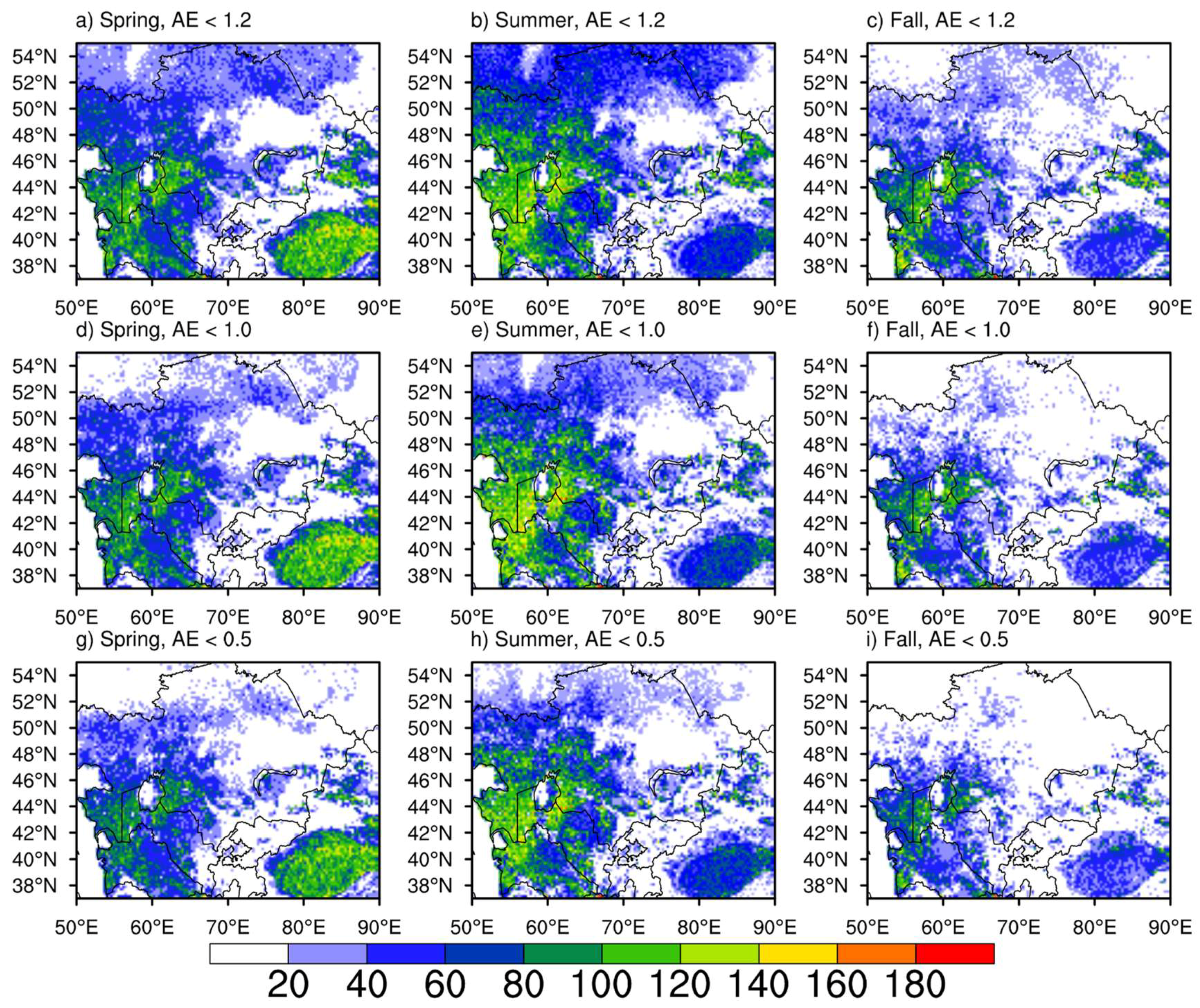
Figure 4 shows the mean DOD at the 0.55 μm band from the MISR, SeaWiFS, and MODIS onboard Terra and Aqua for spring, summer, and fall seasons of the same period (2003–2007). DOD values from SeaWiFS and MODIS are derived following Criterion 1. Despite obviously different coverage areas of DOD > 0.3 with respect to seasons, most sensors show high DOD (>0.5) over the Taklimakan Desert, the Ustyurt Plateau, western Turkmenistan, and the Turan Lowland. Only MODIS onboard Terra provides very high DOD (>0.7) over central and western Kazakhstan and the Aral Sea Basin. No retrievals are available from SeaWiFS and MISR over the latter region, as the land algorithms masked out the water pixels. Because of the complex topography, a very limited number of retrievals are made over land patches surrounding Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. Available data show very small DOD (<0.2) in this area during the considered three seasons. In the spring and summer, the seasonal mean DOD from Terra is higher than from Aqua and both are higher than from SeaWiFS and MISR, in particular, over the Taklimakan Desert. It is very likely that MISR greatly underestimated DOD over the Taklimakan Desert, the Ustyurt Plateau, the eastern Kara Kum Desert near the boundary of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan. In the fall, however, MISR shows higher DOD over the central part of the Taklimakan Desert.
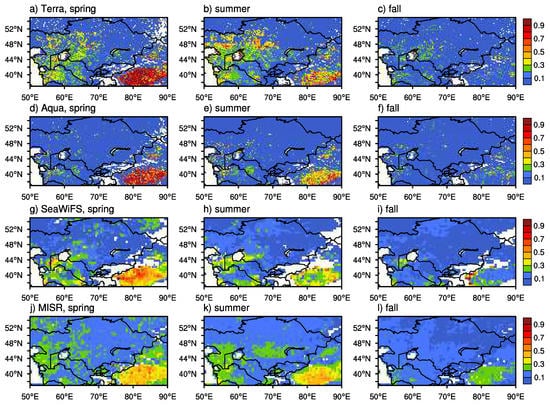
Figure 4.
Seasonal mean of DOD in the spring, summer, and fall during the 2003–2007 period from MODIS onboard Terra (a, b, and c)/Aqua (d, e, and f), SeaWiFS (g, h, and i), and MISR (j, k, and l). White indicates no retrievals available.
In comparison to satellite DOD, the seasonal mean AAI from OMI shows five significant high centers over the Taklimakan Desert, southeast of the Bekdash, the Aral Sea Basin, Urumqi in China, and the Balkhash Lake in decreasing order, as shown in Figure 5. Locations of these centers and areas with AAI higher than 1.2 change only a little bit among the three seasons. The spatial distribution of AI is very similar to the one obtained by Indoitu et al. [6], although a different period is considered here. As indicated by the shading area with AI greater than 1, dust particles originating from the Aral Kum Desert could be transported hundreds of kilometers away to the east, which is also consistent with their findings. Large patches with high AI (>1.0) can be found in Turkmenistan, western Uzbekistan, southwestern Kazakhstan, and western China, surrounding the high-AI centers. The eastern Kara Kum Desert is not that active as suggested by the derived DOD from MODIS and SeaWiFS, very likely due to a smaller vertical extension of dust plumes in this area.

Figure 5.
Seasonal mean of AAI for 2003–2007: (a–d) spring, summer, fall, and the averaging of these three seasons, respectively.
As shown in Figure 4, generally, the seasonal variation of DOD over the western deserts is much smaller than over the Taklimakan Desert, but for some hot spots such as the eastern Aral Sea basin they are persistently active through all three seasons with DOD around 0.6. These aspects are also supported by seasonal mean OMI AAI (Figure 5), which identifies a much smaller aerosol loading in western Central Asia than in the Taklimakan Desert and similar hot spots with AAI over this basin consistently over 1.0. The seasonal variation of OMI AAI, however, is not as obvious as is suggested by MODIS-derived DOD, particularly over the western Central Asia deserts. This likely provides the evidence that OMI AAI is insensitive to absorbing aerosols in the low-level atmosphere within the boundary layer, which is typically around 2–3 km in this region (details in the vertical dust plume extension are discussed in Section 5.3). The small variation, thus, indicates either that most dust particles associated with dust storms present within the low-level atmosphere in the spring or that more present above the boundary layer in the summer and fall such that the OMI can readily capture them. Further study on the vertical structure of dust plumes with respect to seasons is needed to find out the reason of causing these features in OMI AAI.
5.1.2. The Inter-Annual Variability
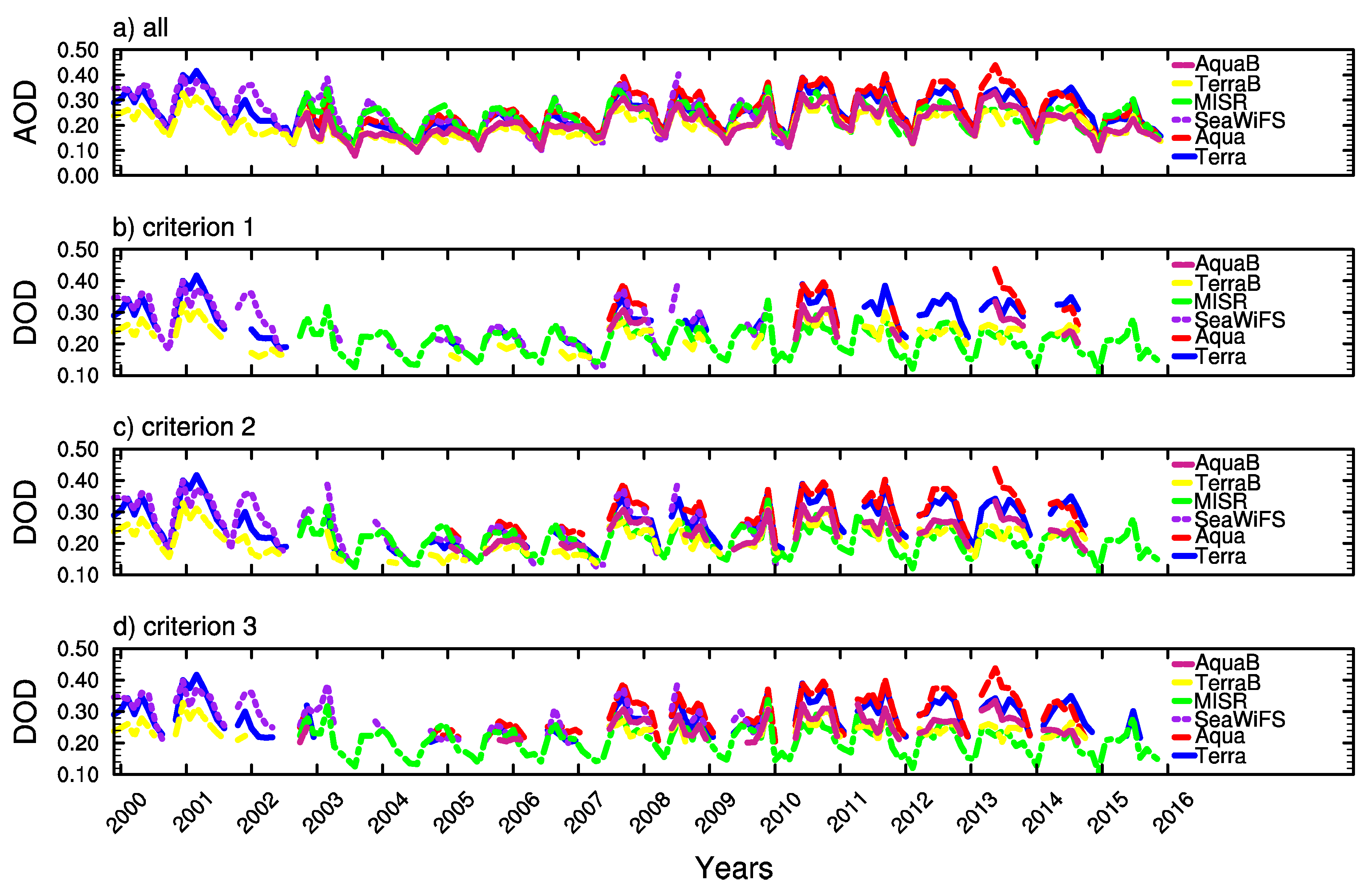
Figure 6 shows the interannual variability of AOD and DOD that obtained with three criteria over the western part of Central Asia from Terra, Aqua, SeaWiFS, and MISR. AODs from different satellites agree very well in terms of annual variability, which is significant during the research period. AOD is limited within 0.1–0.4. High AOD was registered in 2001, 2003, 2007–2014. Extremely high AODs are found in 2009 and 2011, which are evidently greater than in any other years during the research period. AOD with quality flags equal to 2 or 3 is smaller than with all flags for both Aqua and Terra satellites, except in some years (e.g., 2009).
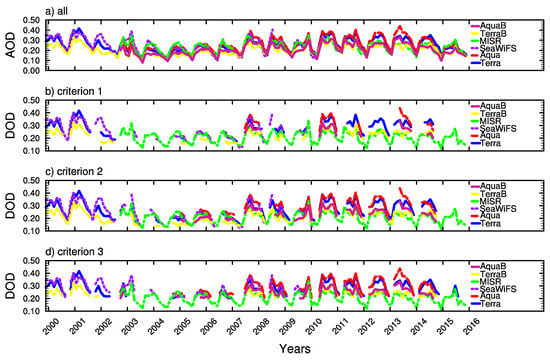
Figure 6.
Interannual variability of AOD (a); and dust AOD with the three criteria given in Table 1 (b–d) for the 2000–2016 (Terra), 2003–2016 (MISR), and 2000–2010 (SeaWiFS) periods over western Central Asia. TerraB and AquaB represent best estimate with quality flags = 2 or 3.
It can be noted that Criterion 1 is the most stringent in deriving DOD. Only a small fraction of dust episodes is kept in comparison to the others. According to this criterion and nonzero DOD in at least two satellites retrievals, most dust events occurred during 2000, 2001, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, and 2014. It is likely that 2009, 2011, and 2013 had very intensive dust storms. In fact, based on the measurement taken by Groll et al. [10], the most severe dust storm was registered in September 2009 in Uzbekistan due to very strong surface winds. Limited information is further available on that dust storm case. In contrast, another extreme dust storm that has been well studied [43] was registered in April 2001, lasting for several days after the maximum emission date on 8 April. This event can also be seen in DOD from MODIS onboard the Aqua and Terra satellite. The dry condition and strong surface winds over the dust source regions, Aral Sea basin, the Ustyurt Plateau etc., induced intensive dust emissions. During 2002, 2003, and 2004, very few dust events occurred in general. Thus, the AOD remained low and DOD became zero.
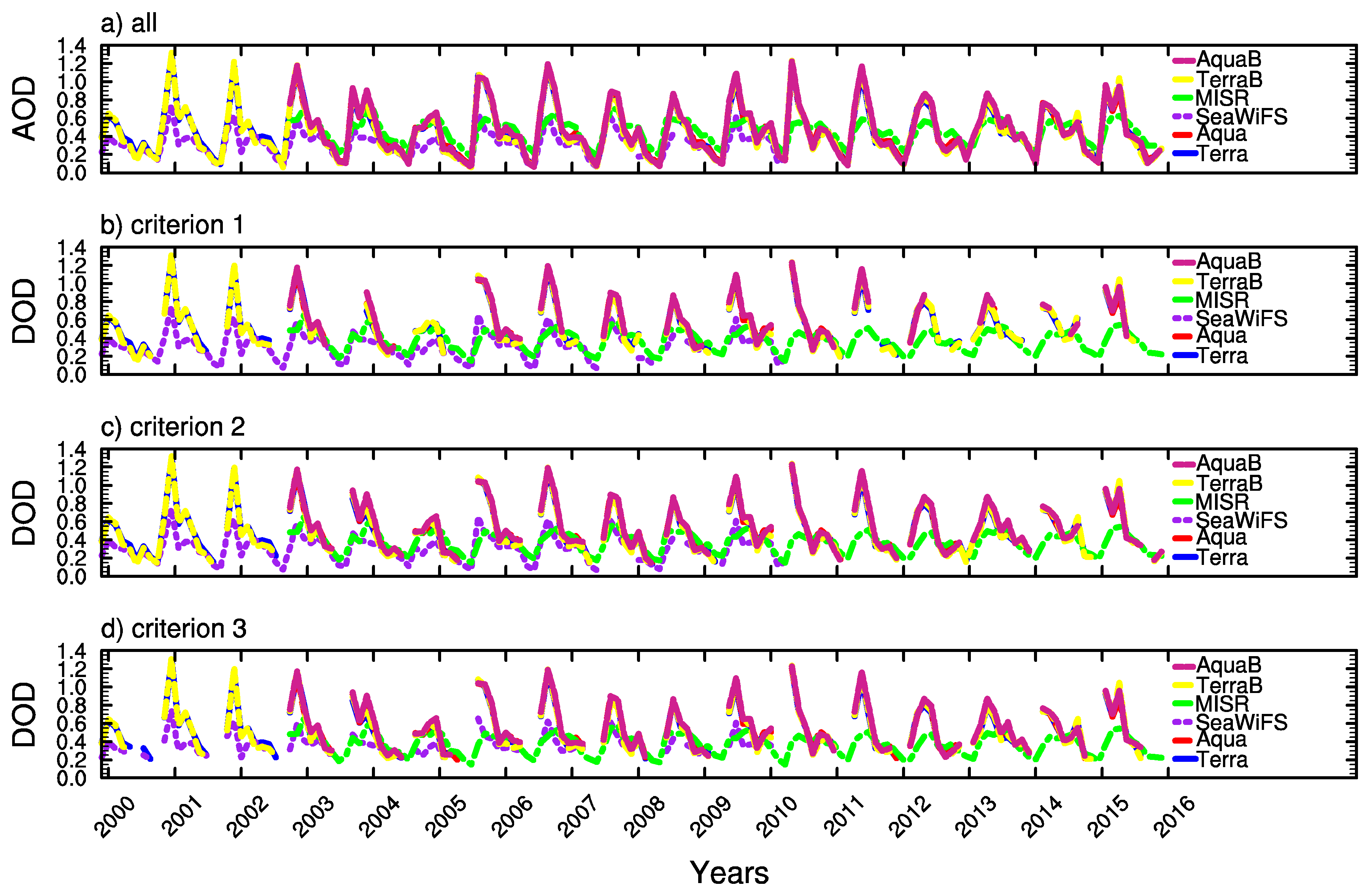
In contrast to the western part of Central Asia, the DOD amplitudes exhibit a significant difference among the four sensors over the Taklimakan Desert (Figure 7). The annual variability of DOD is again similar among the four sensors, but MODIS tends to show higher amplitude than the others do. AOD from Aqua and Terra are perfectly overlapping with each other no matter whether restrictions are placed on pixels according to their quality flags. Dust events are more frequent and intensive in general over the Taklimakan Desert than over the western part of Central Asia. Because aerosols in this region are far dominant by mineral dust, applying different Angstrom exponent thresholds has negligible influence on the annual variability of DOD.
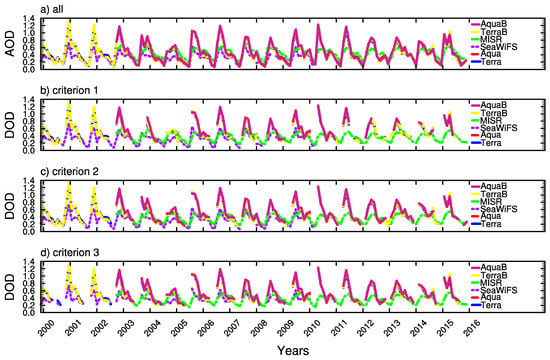
Figure 7.
Same as Figure 6, but for the Taklimakan Desert.
A comparison of AOD and DOD among Aqua, SeaWiFS, MISR, and Terra is done on the daily and monthly basis over the western part of Central Asia and the Taklimakan desert, as illustrated in Figure 6 and Figure 7. Over the Taklimakan Desert, Aqua AOD is very close to that from Terra, but AODs from MISR and SeaWiFS are evidently smaller than from Terra and Aqua on both daily and monthly basis. Over western Central Asia, it is a little bit smaller than the latter one. These statements apply well to both AOD and DOD with all three criteria. In terms of daily AOD/DOD with all quality flags and the best estimation, Aqua is comparable to Terra over the western part of Central Asia. However, the best estimated AOD/DOD from SeaWiFS is larger than from Terra on monthly basis, but the former becomes smaller if all quality flags are applied. DOD derived from the MISR is smaller than from any other satellites over the western part of Central Asia (the Taklimakan Desert) on monthly (daily) basis.
5.1.3. The Seasonal Variability
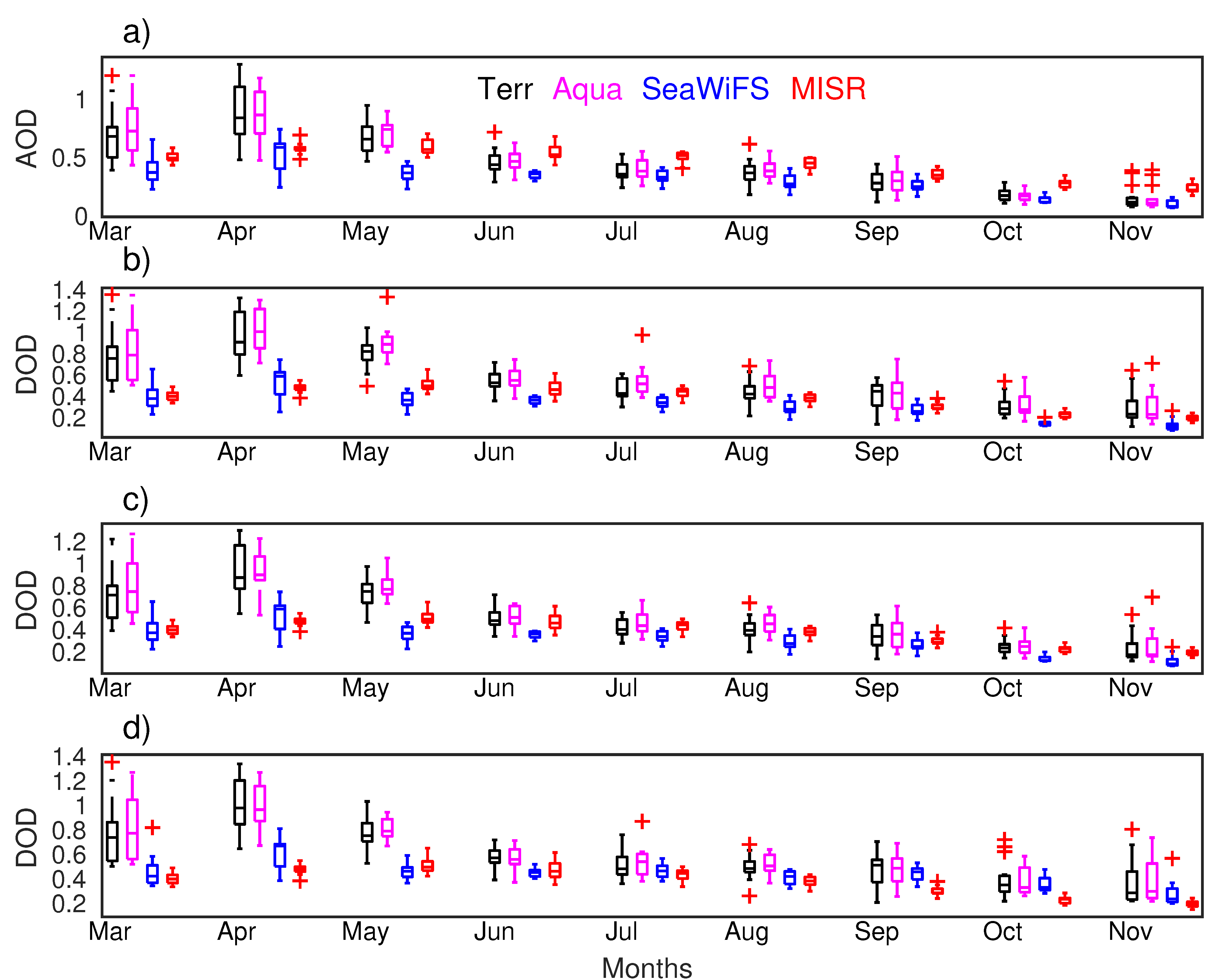
Figure 8 presents the annual distribution of the monthly mean AOD and DOD statistic metrics (minimum, maximum, median, and 5% and 95% quantiles) over the Taklimakan Desert. The associated periods are 2000–2016, 2003–2016, and 2000–2010 for MODIS onboard Terra/Aqua, SeaWiFS, and MISR, respectively. Consistent to the mean values, AOD and DOD from SeaWiFS and MISR are systematically smaller than from MODIS onboard Terra and Aqua in all statistic parameters. Both MODIS and SeaWiFS identify the spring as a season with the highest AOD/DOD, but MISR does not provide a clear seasonal variation with AOD/DOD only slightly higher in May (median: 0.53) than in other months, whatever criterion is utilized. The smallest DOD is seen in October, but the smallest AOD is in November. The month November tends to have more extreme cases with the AOD significantly exceeding the statistic metrics from MODIS aerosol products. With criteria applied to AOD, one can find these extreme cases are absent from the MODIS-derived DOD, yielding a higher value in this month than in October. Similar results could be seen over the western part of Central Asia, but the seasonal variability is not as obvious as over the Taklimakan Desert.
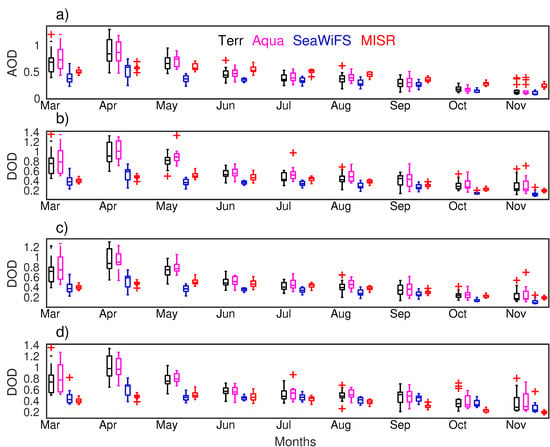
Figure 8.
The statistic metrics of the annual distribution of monthly mean AOD (a); and derived DOD (0.55 μm) with the three criteria (b–d) (corresponding to Criteria 1, 2, and 3, respectively) during the examined period from MODIS, SeaWiFS, and MISR. The red “+” indicates AOD/DOD of extreme cases.
The amount of invalid satellite sampling pixels is not homogenously distributed among the three seasons, which could bias the results obtained from simple means or median values. For instance, much less frequent AOD retrievals are available in the winter due to ice- or snow-covering and in the spring (Figure 3d,g) because of a higher frequency of cloud appearances in comparison to the other seasons. For Central Asia, as the winter is already excluded, the problem does not reside in the ice- or snow-covering, but after applying a threshold to the satellite data such that non-dust aerosols are efficiently excluded, the heterogeneous amount of valid AOD/DOD points still exist among three seasons. To overcome this issue, we applied the one-sided Wilcoxon sum rank test on the null hypothesis of equal median distributions to robustly explore whether there is a statistically significant seasonal variation in the satellite-derived DOD with the best estimation quality flag, as shown in Table 1. Generally, most tests with four different sensors confirm the significantly higher DOD in the spring (MAM) than in the summer (JJA) or fall (SON) at a confidence level of 99% over the Taklimakan Desert and the western Central Asia. This holds for all threshold values selected to remove non-dust particles such as smoke, sea salt, etc., demonstrating that the higher dust amount in the spring is a robust conclusion that presents in the satellite data, as all p-values are very close to zero. Two exceptions are tests constructed on the equality between the spring and summer seasons over the western Central Asia using Criterion 3 based on Terra (p-value = 0.55), Aqua (p-value = 0.096), and SeaWiFS (p-value = 0.0915). Not enough evidence exists to conclude that higher DOD appears in the former season at the 99% test level. As indicated by p-value = 0.001 and 0.00000231, higher AOD is found in the summer rather than in the spring by MODIS onboard both Terra and Aqua, contrary to conclusions by the other sensors.

Table 1.
p-values from the Wilcoxon sum rank test on AOD and DOD that derived using the three criteria, Criterion 1, Criterion 2, and Criterion 3, for the seasonal variation over the western Central Asia (Cen) and the Taklimakan Desert (Tak). The test is made using AOD/DOD with the quality flag 2 or 3; The superscript 1 shows test between MAM and JJA, rather than JJA and MAM (Note the order matters in the Wilcoxon sum rank test). Note for instance, 2.10(−1) stands for .
5.2. Dust Occurrences
It is useful to derive the dust occurrence in addition to presenting AOD and DOD; firstly, for a comparison purpose, since most existing publications are addressing the dust events using the frequency; secondly, for the monitoring purpose; and, finally, because of its severe consequence on the air quality near the source areas. Therefore, based on the dust climatology dataset presented in previous section, we calculated the dust event numbers by applying a threshold constant to MODIS DOD (referred to DODt hereafter). Note, if DOD at a location on a day exceeds the given DODt, we defined it as a dust event. MISR-derived and SeaWiFS-derived DOD were not further utilized because of the limited amount of retrievals and much smaller values and variance in comparison to MODIS-derived one, as found above (Figure 7 and Figure 8). AOD retrievals with all quality flags were used following the recommendation by Baddock et al. [44] to derive the dust occurrence numbers, because the quality flag is not well marked over desert regions where a larger standard deviation is always found [4]. Consistent to Baddock et al. [44], a threshold DODt = 0.2 was also applied in the present study to count the dust occurrence numbers. To avoid the contamination of the use of a threshold constant on the results, a series of threshold values close to 0.2 was applied to the dust event selecting procedure to yield a more robust conclusion.
5.2.1. Spatial Distributions
Figure 9 shows the calculated dust occurrence numbers based on the threshold value of 0.2 using DOD by MODIS onboard Terra during 2000–2016. Obviously, the spatial distribution of the calculated dust occurrence numbers is similar to that of high DOD (>0.2, Figure 4a–c) and AI (>1.0, Figure 5). Persistently active dust activities can be seen over the Taklimakan Desert, the Aral Kum Desert, the Ustyurt Plateau, and western Turkmenistan. The use of different AEt values to remove non-dust aerosols does not change the calculated dust occurrence numbers greatly, particularly over the Taklimakan Desert, where the least sensitivity of the spatial coverage of dust occurrences numbers to AEt is found. An increase of the Angstrom exponent from 1.0 to 1.2 only leads to a slight expansion of the horizontal distribution, pushing the area with the dust occurrence numbers greater than 80 days northward into the northern Kazakhstan.
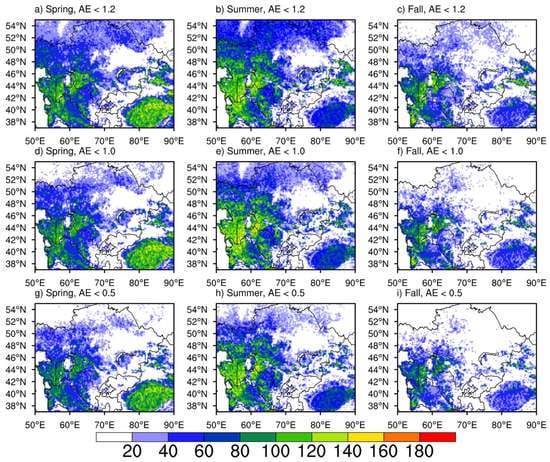
Figure 9.
Spatial distributions of the dust occurrence number during the 2000–2016 period in the spring (a,d,g), summer (b,e,h), and fall (c,f,i) seasons with different Angstrom exponents as the threshold: (a–c) AEt = 1.2; (d–f) AEt = 1.0; and (g–i) AEt = 0.5.
Numbers of the dust occurrence for four sub-regions stratified by four AEt and three DODt values are summarized in Table 2. The least sensitivity of the sub-domain averaged dust occurrence number to both AEt and DODt can be seen over that of the Taklimakan Desert while the largest one is over the Aral Kum Desert. For DODt = 0.2, the use of AEt = 2.0 in comparison to that of 0.5 leads to an increase of the dust occurrence number by approximately 21, 15, and 24 in the spring, summer, and fall, respectively, with the relative percentage slightly larger than 20% over the latter area (the Aral Kum Desert) in contrast to 7, 5, and 11 over the former Desert. However, if a lower DODt is used, e.g., 0.1, the dust occurrence number raise up rapidly from 47, 66, and 29 to 96, 141, and 95 in the spring, summer, and fall, respectively, in comparison to the case of DODt = 0.3, indicating a higher sensitivity of the calculated dust occurrence number to DODt than to AEt over the Aral Kum Desert. Similar results can also be seen in other locations. Although the dust occurrence number could change a lot, if different DODt and/or AEt are applied to the calculation given a fixed location, its rank among the four sub-regions remains unchanged in a specific season. For instance, highest value is found over the Taklimakan in the spring (78–114 days) and over the Ustyurt Plateau in the summer (93–166). It seems that, even though AOD and/or DOD are both smaller, the Ustyurt Plateau has been experiencing a more frequent dust occurrence than the Taklimakan Desert. It continues to be active through all three seasons during the study period (2000–2016), as can be intuitively seen in Figure 9.

Table 2.
Dust occurrence numbers for four sub-regions (Kaza: Kazandzhik; Usty: Ustyurt Plateau; Takl: Taklimakan; Aral: Aral Kum), as labeled by the purple boxes in Figure 1, with three different DOD thresholds (0.1, 0.2, and 0.3) and four Angstrom exponent thresholds (2.0, 1.2, 0.7 and 0.5). The last two Angstrom exponent thresholds correspond to Criterion 2 and Criterion 1, respectively. All quality levels from MODIS/Terra are used. Note numbers in parenthesis of the first three columns represent relative percentages (%) between dust occurrence numbers with AEt = 0.2 and those with AEt = 0.5. Similarly, numbers in parenthesis from column 7 to column 7 represent relative percentages (%) between dust occurrence numbers with DODt = 0.1 and those with DODt = 0.3 for AEt = 0.7.
5.2.2. The Inter-Annual Variability
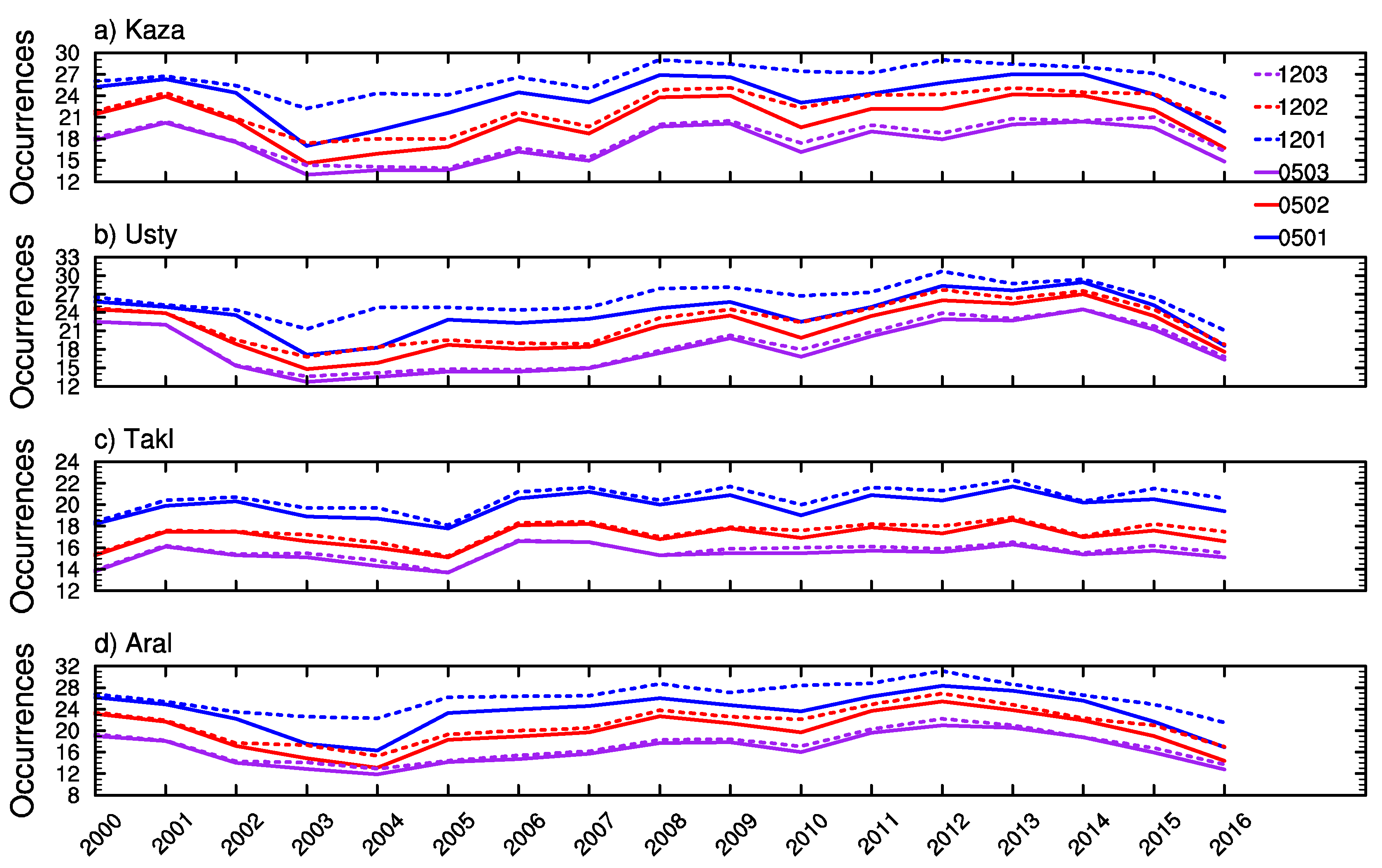
According to Section 5.2.1, the dust occurrence number is monotonically increasing with respect to AEt at a slower rate than with respect to DODt. Therefore, calculations of this part are made on three DODt values (0.1, 0.2, and 0.3) and two AEt values (1.2 and 0.5) only. Figure 10 shows the interannual variability of the dust occurrence calculated over the four sub-regions as labeled in Figure 1 during 2000–2016. The interannual variability of dust occurrences that are derived using different DODt and AEt values is consistent among the four sub-regions, but some differences are distinct between the Taklimakan Desert and the other three sub-regions. The Taklimakan Desert has a lower dust occurrence and year-to-year variation than the others during the research period. We found the dust occurrence is decreasing from 2013 to 2014 over the Taklimakan Desert, but it is increasing over the other three sub-regions. High dust occurrences are found in 2006, 2009, and 2010, which are consistent with the findings of Groll et al. [10], based on the ground measurement on dust depositions in Central Asia. Dust emissions are initiated when the surface wind friction exceeds the local threshold friction velocity. Physically, the threshold friction velocity is determined by the surface soil characteristics such as the soil moisture and the roughness length [35]. Thus, in Central Asia, a combination of the surface wind with surface soil characteristics may explain the dust activities derived from the satellite. Precipitation affects the surface soil and thus dust emissions indirectly via changes in the soil moisture and the vegetation cover. For instance, an increase of the soil moisture and the vegetation cover in rainfall-rich years could effectively suppress dust emissions and vice versa. This explains the low/high dust occurrence in 2003/2006, 2009, and 2010 since a greater/smaller amount of precipitation was found leading to a higher/lower content of the soil moisture and flourish/die-out of green vegetation [45]. The effect of using different AEt and DODt values on the dust occurrence calculation also presents an obvious year-to-year variation, but it is consistent with the finding shown in Section 5.2.1 that dust occurrences are more sensitive to AEt than to DODt, in general, particularly over the Taklimakan Desert. AEt has a greater effect over the Kazadzhik, the Ustyurt Plateau, and the Aral Kum Desert for DODt = 0.1 than for DODt = 0.3, which might provide evidence of the find-mode dominance in the low AOD case. However, it is unfair to set a low bound when deriving DOD, because theoretically to say dust particles can present for all ranges of AOD values.
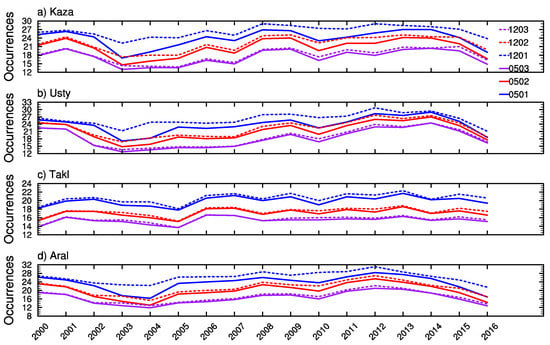
Figure 10.
The inter-annual variability of dust occurrences that obtained by applying two AEt and three DODt values to MODIS/Terra AOD over the four sub-regions ((a) Kaza-Kazandzhik; (b) Usty-Ustyurt Plateau; (c) Takl-Taklimakan; and (d) Aral-Aral Kum) during the 2000–2016 period. The legend labels represent AEt and DODt, for instance, 1203 means AEt = 1.2 and DODt = 0.3.
The trend analysis was also made using a non-parametric statistic method, Mann–Kendall, following Li and Sokolik [4], for the four sub-regions. No assumption on the distribution is required and the outliners have a negligible influence on the test result in this method. Table 3 shows that positive but not statistically significant trends are observed for all targeted regions at a confidence interval of 95%, suggesting a longer time spanning is needed for a more robust result. The largest trend of the dust occurrence during the 2000–2016 period is found over the Ustyurt Plateau approximately 0.22, 0.47, and 0.52 per year for DODt = 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3, respectively, using AEt = 0.5 according to this method. The positive trend based on DODt = 0.3 and AEt = 0.5 is not statistically significant at the confidence level of 95%, but it becomes significant at a just smaller confidence level, 90%. The dust occurrence over the Taklimakan stays stable during this period with the trend very close to 0, whatever DODt and/or AEt are utilized. Consistent to previous sections, the trend over the Taklimakan Desert is less sensitive to AEt than over the other sub-regions.

Table 3.
Trend (per year) and associated p-values with the confidence interval of 0.95 for dust occurrences derived from MODIS/Terra ADO over the four sub-regions during 2000–2016 by a non-parametric test, Mann–Kendall.
5.2.3. The Seasonal Variability
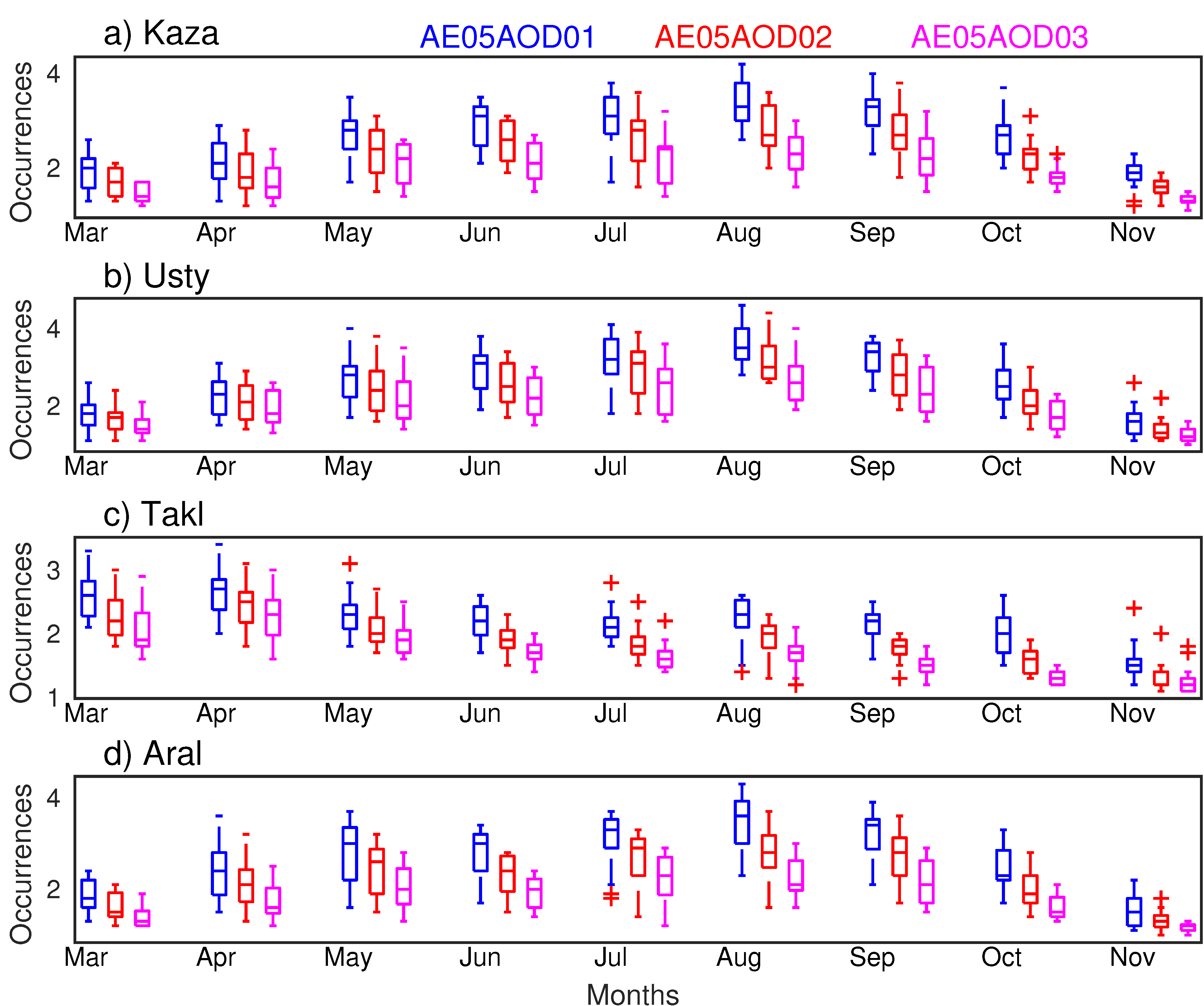
As can be seen in Figure 9, the area with the dust occurrence numbers exceeding 80 days in total within in each season are mainly found over the Taklimakan Desert during the spring season. In summer and fall seasons, the dust occurrences are both lower than 80 days over the whole desert region. It seems that there also exists a season variation of dust occurrences. We then calculated the median, 5% and 95% quantiles, minimum, and maximum of the dust occurrence that derived from three DODt for the four sub-regions, as shown in Figure 11.
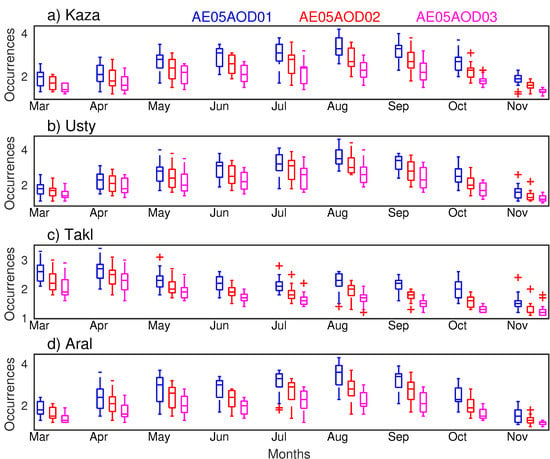
Figure 11.
The statistic metrics of the annual distribution of dust occurrences that derived from MODIS/Terra AOD over the four sub-regions ((a) Kaza, eastern Turkmenistan; (b) Usty, Ustyurt Pleateau; (c) Takl, the Taklimakan Desert; and (d) Aral, the Aral Sea Basin), as labeled in Figure 1, using three DODt (blue: 0.1; red: 0.2, and purple: 0.3). The red “+” indicates AOD/DOD of extreme cases.
The one-sided Wilcoxon Sum Rank test is again applied to the derived dust occurrence based on MODIS/Terra AOD such that a robust conclusion could be achieved. The p-values for the four sub-regions are summarized in Table 4 based on three DODt and two AEt among paired spring, summer, and fall seasons. For the three sub-regions over the western part of Central Asia, all p-values between MAM and JJA are close to 0, indicating the dust occurrence is statistically higher in the summer than in the spring. Similarly, statistically higher dust occurrence in the summer season than in the fall is seen. Comparisons between the spring and fall seasons are distinct over these sub-regions. p-values over the Ustyurt Plateau and the Aral Kum are 0.88 and 0.37, respectively, using DODt = 0.1. It is also the case when different DODt values are used instead. Thus, no evidence is displayed to support that any significant difference of the dust occurrences between the spring and fall seasons exists. The seasonal variation of the dust occurrence is more sensitive to AEt than the seasonal variation of AOD/DOD is, because the p-values over the two sub-regions become greater than 0.95, if AEt = 1.2 is used. The dust occurrence is higher in the spring than in the fall, according to the p-values (0.0139), over the Kazandzhik, using DODt = 0.1, but it becomes insignificant, if a higher DODt is used. Over the Taklimakan Desert, the spring season has the most frequent dust occurrence, followed by the summer and differences among the paired seasons are significant for all thresholds.

Table 4.
p-values from the Wilcoxon sum rank test on the seasonal variation of dust occurrence that derived using several criteria: AEt = 0.5 and AEt = 1.2 against DODt = 0.1, DODt = 0.2, and DODt = 0.3 over the four sub-regions, as shown by boxes in Figure 1. Note for instance, 2.14 stands for .
5.3. Physical Properties and Vertical Profiles of Dust Aerosols
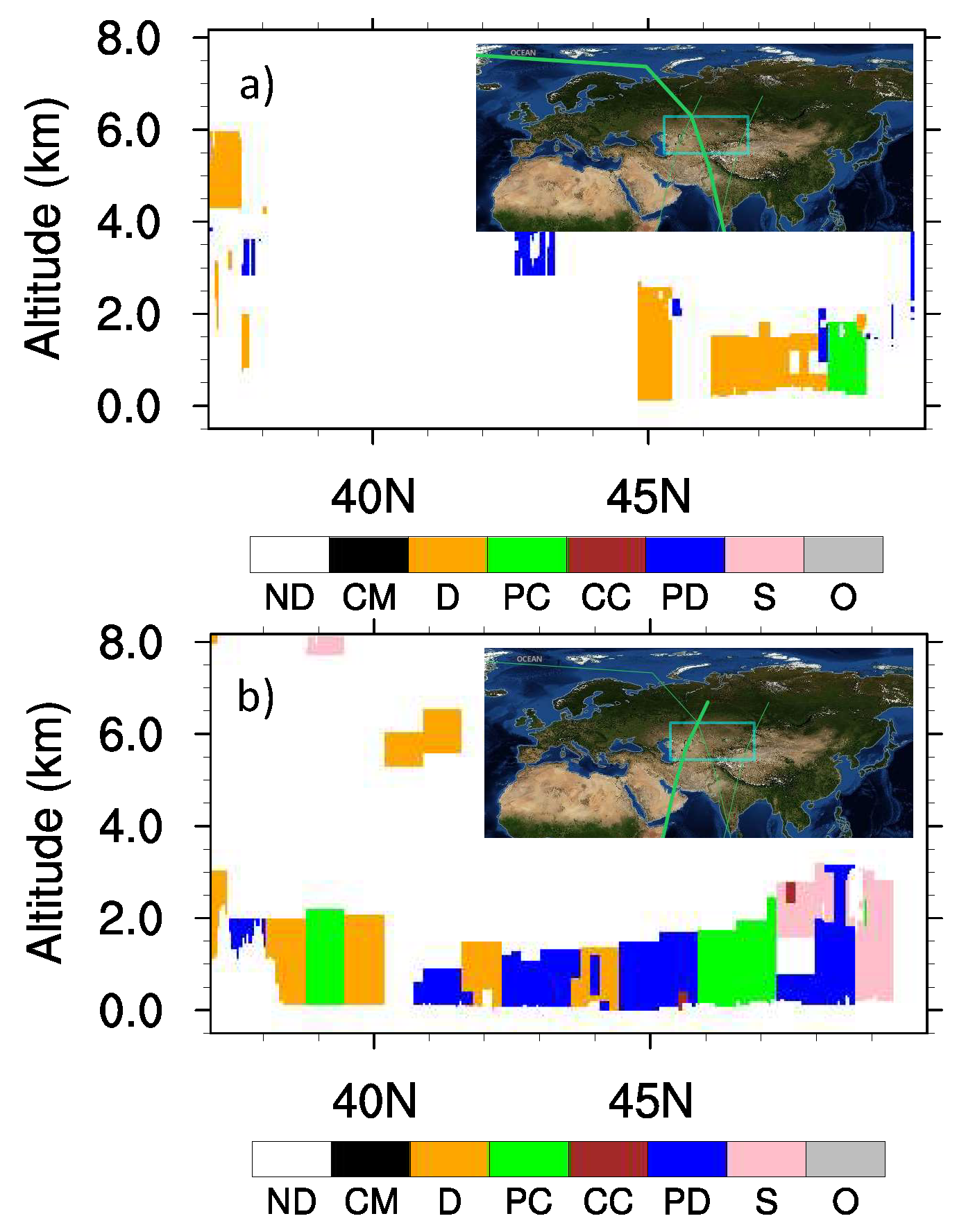
One dust case that occurred on 7 May 2007 was chosen to analyze the dust vertical distribution in Central Asia. A dominant fraction of dust particles was originating from the Aral Kum, according to the model simulation [35]. MODIS onboard the Terra satellite also happened to capture this dust storm, as the retrieved AOD using the deep blue algorithm reached up to 3.5 to the southern edge of the sea basin. Plots of the subtype features of the CALIPSO VFM indicate a limitation of dust vertical extension for this event within the boundary layer not exceeding 3 km (Figure 12). At the early stage of the storm, the retrieval detected freshly pure mineral dust (Figure 12a) which was transformed to polluted dust (Figure 12b). The different subtypes very likely provide evidence of aging processes after main dust storms by taking non-mineral aerosols such as salt, smoke, and hydrogen carbonate. It is possible that mineral dust originally mixed with other compositions such as salt, hydrogen carbonate, and sulfate in the soil. However, the amount of these non-minerals experienced a rapid increase in the dust particles. Razakov and Konsnazarov [46] found that dust deposits close to the Aral Kum desert contain a considerable fraction of sea salts up to 20–30%. The recent chemical analysis [10] with samples taken from stations close to the Aral Kum, however, found a mixing of non-mineral compositions (hydrogen carbonate, sulfate, and chloride). Efforts to quantify differences between compositions of dust aerosols and those of the source soil are needed to ensure their mixing state and to learn about aging processes of the freshly emitted particles.
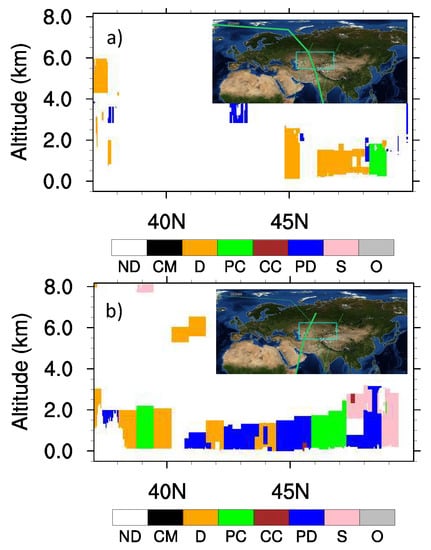
Figure 12.
Vertical Feature Mask (VFM) from CALIPSO for a dust storm occurring during daytime (a) and during nighttime (b) on 7 May 2007 over the Aral Sea Basin. Subplots in both plots show the CALIPSO track, as indicated by green line over Central Asia (the domain is labeled by green boxes). ND: not determined; CM: clean marine; D: dust; PC: polluted continental; CC: clean continental; PD: polluted dust; S: smoke; O: other.
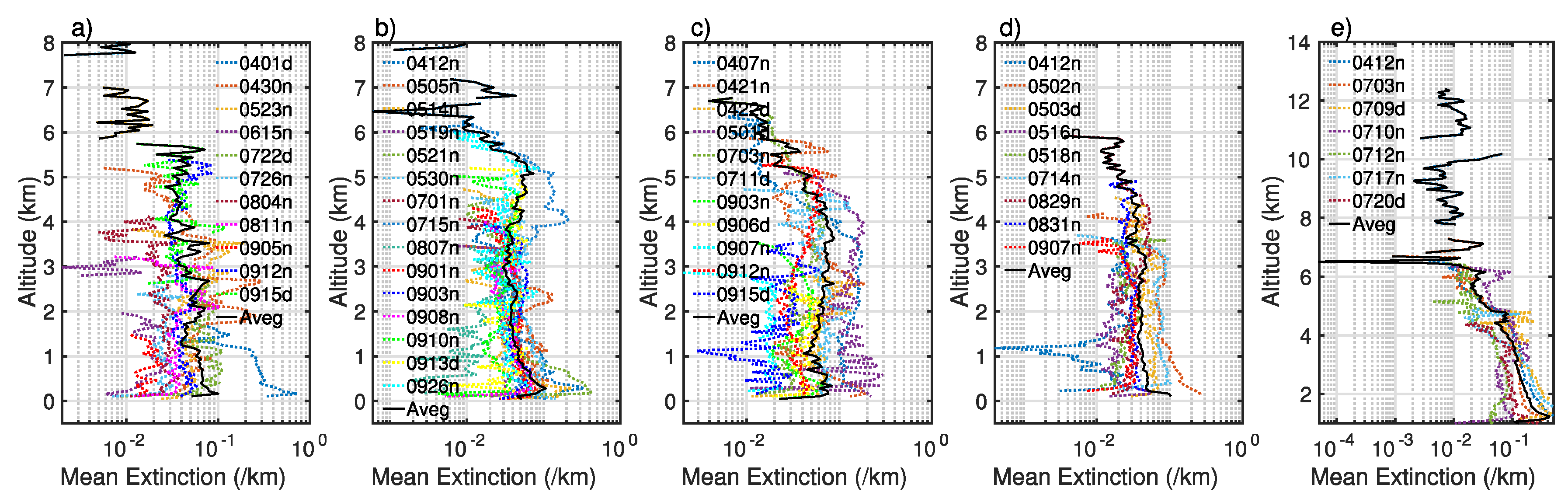
The deployment of lidar makes quantitative analysis available on the aerosol extinction coefficient profile, which is one of the most uncertain factors in modeling the radiative process. Based on the vertical feature mask, we selected several dozen dust events that have been captured by CALIPSO to calculate the mean extinction profile at 532 nm, as shown in Figure 13, along the satellite path covering the main dust source regions including the Aral Kum Desert, the Kyzyl Kum Desert, the Ustyurt Plateau, the Kara Kum Desert, and the Taklimakan Desert in 2007. Of the selected dust events, 66 are over the western part of Central Asia and 17 over the Taklimakan Desert. Approximately 16.8% are found during the day and 38.65% in the summer season. All pixels classified as non-aerosols and/or non-dust aerosols were removed based on the CALIPSO feature and sub-feature types. Note we retained polluted dust, which is classified as a separate subtype from dust by CALIPSO, in the analysis, as it is difficult to distinguish whether the mixing is made in the atmosphere after emissions or originally in the soil. To further control the data quality, we also removed low confident retrievals that have the CAD_score (the cloud-aerosol discrimination score) out of the range from −100 to −20 and the extinction uncertainty exceeding 120%.
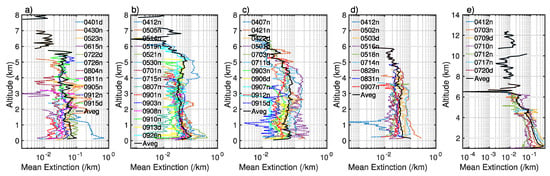
Figure 13.
Aerosol extinction coefficient profiles for selected caces with the height above the sea surface level over the following sub-regions: (a) the Aral Sea Basin; (b) Ustyurt Plateau; (c) the Kara Kum Desert; (d) the Kyzyl Kum Desert; and (e) the Taklimakan Desert. The characters d and n in the legend denote “day” and “night”, respectively.
In general, no evident differences exist among the four sub-regions in the western Central Asia. The Taklimakan Desert has a systematically larger mean extinction and the extinction remains large until the high troposphere. Most dust particles are located at the low-level layer within 2 km from the surface with the extinction decreasing, in general, from the surface to the top boundary layer, but the extinction profile spreads a lot from one event to another, particularly over the Kara Kum Desert. The peaking (0.09) of the extinction profile averaged over these events is seen approximately at 3.6 km, which is quite different from the other source regions where dust plumes peak are very close to the surface. Effective vertical transport can also be seen for some cases via the mean extinction profile, although the maximum value appears near the surface. For instance, on 1 May 2017, the mean extinction reaches up to 0.19around 3.8 km over the central Kara Kum Desert. For the event on 7 April, dust aerosols were lifted up effectively to approximately 5.6 km over the Kara Kum Desert. Another evident characteristic of the mean extinction profile for the later event is the multiple structure with another two minor peaks at layers around 2.6 km and 5 km. According to the selected cases, the dust extinction is weaker in September and April than in May and July for all these source regions with profiles systematically located to the left of the mean line. In addition, non-zero extinctions can only be seen below the 3.5 km in September because the low boundary layer height efficiently inhibited the vertical transport of dust aerosols after emissions. Aerosol signals are frequently influenced by the solar illumination during the daytime [47], so a higher quality threshold is applied for the data processing, resulting in much fewer dust events than during the nighttime. Because of this, the mean extinction during the daytime tends to be, but not always stronger and noisier relative to that during the nighttime.
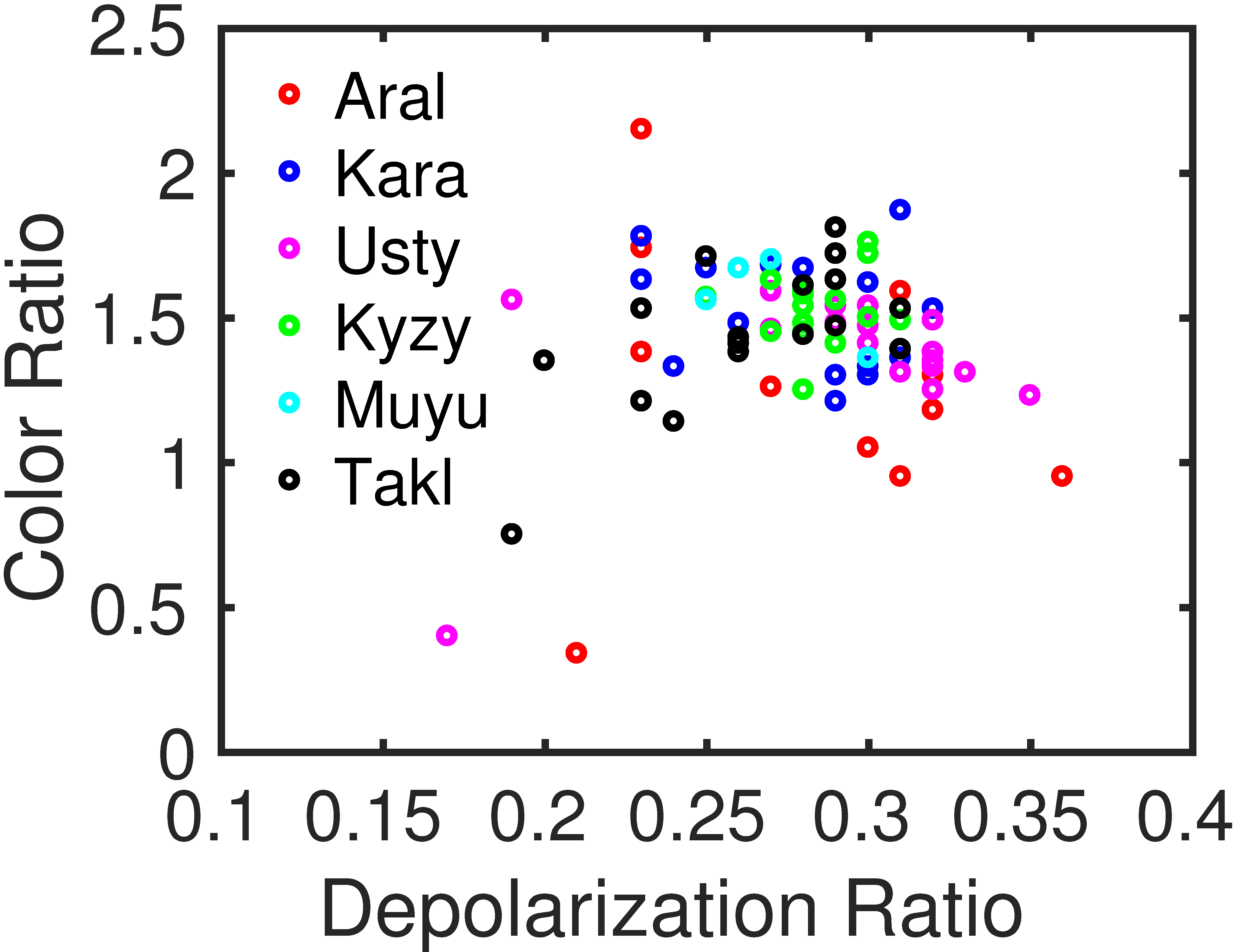
Figure 14 shows scatter plots of the layer-integrated color ratio () against the layer-integrated depolarization ratio (), which are related to the particle shape and size, respectively, and thus are often used to subtype aerosol features in the CALIPSO classification algorithm [38] for the selected dust cases. The depolarization ratio is defined as the ratio between the perpendicular and parallel backscattering at the 532 nm wavelength. The color ratio is defined as the ratio of the backscattering at 1064 nm and 532 nm. We calculated the layer-integrated depolarization and color ratio following Equations (1) and (2), respectively,
where K is the altitude index indicating the top of the dust layer derived from CALIPSO 5 km aerosol layer products; and are the backscattering intensity of perpendicular and parallel components at 532 nm, respectively; and and are the total backscattering intensity at 1064 and 532 nm, respectively.
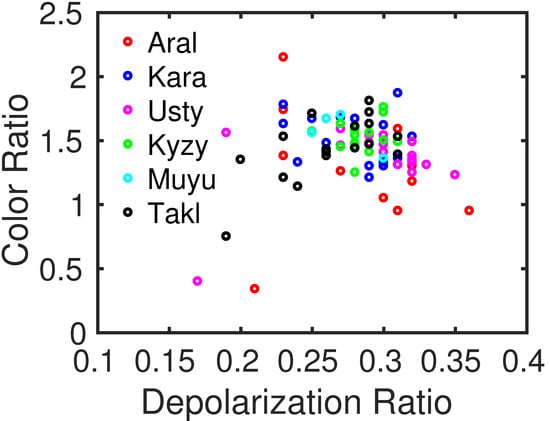
Figure 14.
The scatter plot of the layer-integrated color ratio against the layer-integrated depolarization ratio.
According to the selected cases, dust particles over the western part of Central Asia tend to be coarser than over the Taklimakan Desert. Excluding extreme cases, the layer-integrated color ratio ranges 1.23–2.15 (median: 1.48; mean: 1.49) and 1.14–1.81 (median: 1.46; mean: 1.49) for the western part of Central Asia and the Taklimakan Desert, respectively. Extreme cases were seen on 13 September over the Ustyurt and 15 September over the Aral Sea basin. The layer-integrated color ratio is only 0.4 and 0.34, respectively, which are much smaller comparing with other episodes, indicating finer dust aerosols. These extremely low values can be partly explained by the large dust plume height, as coarse particles are readily deposited onto the ground because of the gravitational settling process and only particles in small sizes can be transported to a higher level. In fact, the layer base heights for these two cases are approximately 2.61 km and 4.49 km, respectively, much larger in comparison to that for other episodes with the plume base close to the surface. A typical dust depolarization ratio is approximately 0.2–0.3, as suggested by Gautam et al. [48]. For Central Asia, the layer-integrated depolarization ratio is greater than 0.2 for most dust episodes except two, one (~0.17) during the nighttime on 13 September over the Ustyurt Plateau and the other one (~0.19) on 15 October over the Taklimakan Desert. The median (mean) for the western part of Central Asia is 0.28 (0.29) a little bit larger than for the Taklimakan Desert 0.26 (0.26). The maximum layer-integrated depolarization ratio reaches up to 0.36, much larger than the threshold value 0.2 used by ground-based lidars to identify clouds [49], for dust episodes that occurred on 15 July and 5 September over the Ustyurt Plateau and the Aral Sea, respectively. Coincidentally, this episode is also the one that has the smallest layer-integrated color ratio, indicating a majority of dust particles with non-spherical shape but in small size.
6. Discussion and Conclusions
In this study, satellite data including four aerosol products from SeaWiFS, MISR, MODIS onboard Terra and Aqua, etc. were analyzed during 2000–2016 to investigate the annual and seasonal variability, the vertical distribution, and physical and optical properties of dust aerosols over Central Asia from the statistic perspective. We also performed sensitivity tests to show the influence of selecting different thresholds on deriving DOD and dust event numbers. Based on the non-parametric algorithm, we demonstrate the seasonal variation of DOD and dust event numbers derived from available satellite observations. DOD was derived from original AOD based on three criteria utilizing the relationship between the particle size and Angstrom exponent. High DOD derived from the four sensors (MODIS onboard Terra and Aqua, SeaWiFS, and MISR) is mainly found over the Taklimakan Desert, the Ustyurt Plateau, the Aral Kum Desert, and the eastern Kara Kum Desert near the boundary of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan, although horizontal extensions surrounding these areas exhibit a clear year-to-year variation. A one-sided Wilcoxon sum rank test on the null hypothesis of equal median distributions among the spring, summer, and fall seasons was performed to explore whether there is a statistically significant seasonal variation in the satellite-derived DOD with the best estimation quality flag.
Our analysis on the seasonal dynamics suggested that both DOD and dust occurrence derived from satellite multi-sensor observations is insensitive to the selection of the AEt (Table 2). This finding, firstly, indicates the dominance of mineral dust in Central Asia and secondly provides evidence that no considerable differences on derived DOD should be yielded, particularly if results are achieved on seasonal basis, with different AEt values utilized by the scientific community [39,40], as aforementioned references [41]. Significantly higher dust activities were found in the spring in terms of both DOD and dust occurrences under all AEt values over the Taklimakan Desert, but for the western part of Central Asia, the spring season had significantly more frequent dust occurrences, whereas the summer season tends to have statistically larger AOD, albeit disagreement appears among different sensors (e.g., MODIS/Terra) (Table 1 and Table 4). It is very likely that the dust event in the summer has a higher intensity, emitting a greater number of particles on average than in the spring. Using in situ measurements on dust depositions, however, Groll et al. [10] found the most dust is deposited during summer months, particularly in June, when the highest dust frequency is also registered. The frequency they calculated is based on a medical indicated threshold value. Our previous analysis (Figure 11 and Table 4) has shown that the distribution of the calculated dust occurrence with respect to months is insensitive to DODt and AEt values that are selected and no evident differences on the distribution are seen over the three sub-regions located in the western part of Central Asia. The disagreement on the month with the maximum dust occurrence (frequency), thus, might not be explained by the different sub-regions and the threshold values that are used. It is reasonable to argue that their measurement mainly contains coarser dust particles (for instance, dust diameter >8), which tends to deposit due to the gravitational settling mechanism during transport. The unevenly distributed deposition explains the difference, although we cannot exclude other possible reasons associated with the retrieval bias.
DOD is a measure of the dust loading in the atmosphere. Most dust aerosols are deposited onto the ground without experiencing long-range transport. Thus, the derived DOD in this region can be regarded as mainly a result of local emissions, albeit some areas such as Kyrgyzstan might be influenced by the transport of dust aerosols from deserts in Middle East [50]. The dust emission process is mainly controlled by the combination of the soil characteristics such as the surface roughness, the soil moisture, the vegetation presence, etc. and regional meteorological conditions, mainly the wind velocity. The deserts in Central Asia are characterized as a continental climate region. Most precipitation and the green vegetation growing are registered in springs associated with the northward migration of the Iranian branch of the Polar front [51]. The average July temperature and maximum temperatures are 32 °C and 52 °C, respectively, in the eastern Kara Kum [51]. The high near-surface temperature and dryness in the summer leading to a reduction of the soil moisture content and the surface covers, which are two main factors that prevent the soil from erosion, very likely contribute to the strong dust emissions [52]. The seasonal surface vegetation dynamics for the Taklimakan Desert is much less evident than for the western part of Central Asia, as can be seen from Figure 3 in the report by Li and Sokolik [4]. Therefore, the seasonal variability of DOD is greatly possible a direct result from changes of the aridity and surface winds induced by the atmospheric patterns such as the Siberian Highs and Arctic anticyclones instead of the surface roughness. The peak of DOD and dust occurrences in the spring from the satellite perspective is also supported by results from Xuan and Sokolik [53] and Laurent et al. [54] over the Taklimakan. The decreasing trend of DOD might be explained by the increase of greenings [55] due to the more abundant CO2 concentration, which can increase the photosynthetic rate and reduce water loss through decreasing the stomatal opening.
The similarity of the spatial and temporal variability only indicates a consistency among different sensors at longer time (e.g., annual) scales. At daily and monthly scales, however, differences of AOD and DOD derived from multiple sensors are evident over the Taklimakan Desert and the western part of Central Asia. MISR and SeaWiFS yield significantly lower DOD in comparison to MODIS onboard Terra/Aqua, particularly over the Taklimakan Desert, as can be clearly seen in Figures S1 and S2 at the 95% confidence level. The reported uncertainties in the aerosol products of MODIS on board Terra/Aqua, and MISR are usually obtained by comparing with ground-based observations. Unfortunately, over the considered sub-regions (Figure 1), no ground-based observations on DOD/AOD are currently available. In addition, it is unsafe to speculate about the retrieval accuracy in the considered areas from the performance of a sensor over other areas, considering the intensive land cover and land use changes in Central Asia that strongly affect the dust emission. Therefore, these uncertainties remain unreliable for these specific areas and we did not include any analysis on them. However, the difference should be “real” because it is always significant at the confidence level of 95% for statistical parameters such as median, mean, minimum, and maximum. The reasons for the significant difference are complex, taking MODIS and MISR as an example. In general, there are not too many coincident samplings of MISR and MODIS on the daily basis. On the monthly basis, however, the coincident sampling could be found over much of the research domain (Figure 2 and Figure 4), although the narrow swath width of MISR leads to a much less sampling volume in the interested domain by MISR than by MODIS (Figure 3). MISR AOD is systematically lower than MODS AOD of collection 6 for AOD greater than 0.2 or 0.3 but higher for low AOD. This phenomenon also appears when MODIS AOD of collection 5 is used instead [56]. Due to a lack of ground-based observations, the bias might exist in all these sensors in this region. In fact, a previous study [57] has found that MISR slightly underestimated AOD over land, whereas MODIS with the dark target algorithm generally overestimated it in comparison to AERONET. The performance of collection 6 with the deep blue algorithm is similar to that of collection 5 over selected AERONET sites and both have larger uncertainties for low and high-AOD conditions [17]. The slight difference in MISR and MODIS spectral bandpasses, with the effective wavelengths of 557.5 and 553.7 nm, respectively, should unlikely cause a significant impact on the AOD retrievals [58]. In addition, MISR set an upper boundary 3 (pixels with AOD greater than 3 are set to 3) to avoid a huge data volume. MISR tends to show lower AOD/DOD in comparison to MODIS for large-size aerosols (mineral dust) (Figure S3). This behavior arises likely due to the different aerosol optical properties from aerosol models that are used by MODIS and MISR. Models with stronger absorption ability need higher DOD to fit the observed radiance at TOA. The difference in AOD/DOD/occurrences arises mainly due to differences in the spatial coverage, the pixel resolution and the retrieval algorithm, for instance the cloud masking, the radiometric calibration, aerosol models, and surface model assumptions that are used to make aerosol retrievals. More comprehensive comparisons between MODIS and MISR retrievals are available in Kahn et al. [58] over both oceans and lands for MODIS aerosol products with the dark target algorithm. Significant efforts on investigating these factors are needed to explain the difference among multiple sensors.
Analysis on the CALIPSO aerosol product for 83 events in 2007 suggest that dust plumes have multiple structures and are mainly distributed from the surface to the 4-km height with a few episodes over the Taklimakan Desert extending to the top troposphere. Slightly coarser dust particles were found over the western part of Central Asia in comparison to the Taklimakan Desert. No significant differences in particle shape and size are found among sub-regions in the western Central Asia area. In contrast, differences of these physical properties and of the vertical extinction profile are evident among the selected events, likely resulting from varied meteorological conditions that generate the dust emission. Dust aerosols uplifted from desert regions greatly enhance the aerosol extinction near the surface to a higher altitude (Figure 13) due to the vertical transport. However, we are not aware of any cases with dust aerosols from western Central Asia that can have a long-range transport possibly because of the blocking of the high topography to the south and east (Figure 1), whereas the long-range transport for the East Asian dust is well known [23,59,60,61]. The weaker mean extinction of dust plume is consistent to smaller AOD/DOD as suggested by multiple passive sensors over the western part of Central Asia than over the Taklimakan Desert region. Dust aerosols near the Taklimakan Desert are much closer to crustal materials. In contrast, polluted dust either internally-mixed with non-mineral materials [10,46] or externally-mixed with smoke is often detected by CALIPSO over the western part of Central Asia and only a few episodes have the dust plume base away from the surface showing a different size distribution with much finer aerosols (Figure 14). The frequent detection of polluted dust might provide a second explanation of the smaller layer-integrated color ratio over the western part of Central Asia, as the CALIPSO algorithm often misclassifies the transported smoke as the polluted dust [62,63]. The vertical extension of dust plume, particularly relative to clouds [26], the size distribution and chemical compositions primarily mineral oxides [35,64] are crucial factors determining the radiative effects. So, the differences on these parameters between the western Central Asia and the Taklimakan Desert might lead to different radiative effects by mineral dust, although the shape and size of detected particles are similar.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/9/8/288/s1, Figure S1: Comparisons of AOD (a,e) and DOD (b–d,f–h) from MISR, SeaWiFS, and MODIS onboard Aqua with those from MODIS onboard Terra over the Taklimakan Desert on daily basis: (b,f) for Criterion 1; (c,g) for Criterion 2; and (d,h) for Criterion 3. Top panels: all quality flags; Bottom panels: the best estimate. The correlation co-efficiencies and root mean square errors for MISR (red), SeaWiFS (blue), and Aqua (purple) are also shown. Dash lines indicate the 1:1 lines. Figure S2: Same as Figure S1, but on monthly basis. Figure S3. Differences AOD between MISR (red)/SeaWiFS (blue)/Aqua (purple) and Terra with all quality flags (a,c) and the best estimation (b,d) against the Angstrom exponent from Terra.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.L. and I.N.S.; Methodology, L.L. and I.N.S.; Visualization, L.L. Investigation, L.L.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, L.L.; and Writing—Review and Editing, L.L. and I.N.S.
Funding
This research was funded by the NASA Goddard Space and Flight Center grant number [3506c69].
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by NASA Radiation Program. The MODIS data were obtained through the NASA Goddard Space and Flight Center Data Center Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System (https://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov). The MISR data are available through the Jet Propulsion Laboratory website (https://www-misr.jpl.nasa.gov). OMI AAI was obtained through this link https://disc.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov. The CALIPSO data used in this study were obtained from the NASA Langley Atmospheric Science Data Center (https://eosweb.larc.nasa.gov/project/calipso). We also acknowledge all anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments that improve the original manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sokolik, I.N.; Toon, O.B. Direct radiative forcing by anthropogenic airborne mineral aerosols. Nature 1996, 381, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickells, T.D.; An, Z.S.; Andersen, K.K.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Cao, J.J.; Boyd, P.W.; Duce, R.A.; Hunter, K.A.; et al. Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate. Science 2005, 308, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, J.D.; Murray, B.J.; Woodhouse, M.T.; Whale, T.F.; Baustian, K.J.; Carslaw, K.S.; Dobbie, S.; O’Sullivan, D.; Malkin, T.L. The importance of feldspar for ice nucleation by mineral dust in mixed-phase clouds. Nature 2013, 500, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Sokolik, I.N. Developing a dust emission procedure for central Asia. Air Soil Water Res. 2017, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiko, T.A.; Zonn, I.S. Irrigation expansion and dynamics of desertification in the circum-aral region of central Asia. Appl. Geogr. 2000, 20, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indoitu, R.; Kozhoridze, G.; Batyrbaeva, M.; Vitkovskaya, I.; Orlovsky, N.; Blumberg, D.; Orlovsky, L. Dust emission and environmental changes in the dried bottom of the Aral Sea. Aeolian Res. 2015, 17, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.X.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, D.W. Temporal variability and potential diffusion characteristics of dust aerosol originating from the Aral Sea basin, central Asia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlovsky, L.; Orlovsky, N.; Durdyev, A. Dust storms in Turkmenistan. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 60, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlovsky, N.; Birnbaum, E.H. The role of haloxylon species for combating desertification in central Asia. Plant Biosyst. 2002, 136, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groll, M.; Opp, C.; Aslanov, I. Spatial and temporal distribution of the dust deposition in central Asia—Results from a long term monitoring program. Aeolian Res. 2013, 9, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Dufresne, J.L. Sensitivity of toms aerosol index to boundary layer height: Implications for detection of mineral aerosol sources. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimas, C.D.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Querol, X.; Vardavas, I. Spatial and temporal variability in aerosol properties over the Mediterranean basin based on 6-year (2000–2006) modis data. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Nastos, P.T.; Kambezidis, H.D. Seasonal variation of columnar aerosol optical properties over athens, greece, based on modis data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martonchik, J.V.; Diner, D.J.; Kahn, R.; Gaitley, B.; Holben, B.N. Comparison of MISR and AERONET aerosol optical depths over desert sites. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.A.; Wang, J. Intercomparison between multi-angle imaging spectroradiometer (MISR) and sunphotometer aerosol optical thickness in dust source regions over china: Implications for satellite aerosol retrievals and radiative forcing calculations. Tellus B 2004, 56, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xia, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Min, M.; Hao, W.; Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Validation of multi-angle imaging spectroradiometer aerosol products in China. Tellus B 2010, 62, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for MODIS collection 6 “deep blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.C.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Aerosol properties over bright-reflecting source regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2004, 42, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Garbuzov, D.; Hsu, N.C. Identification of anthropogenic and natural dust sources using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (modis) deep blue level 2 data. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Ginoux, P.; Torres, O.; Nicholson, S.E.; Gill, T.E. Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the nimbus 7 total ozone mapping spectrometer (toms) absorbing aerosol product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kambezidis, H.D.; Nastos, P.T.; Kosmopoulos, P.G. Study on an intense dust storm over greece. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6884–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepanski, K.; Tegen, I.; Macke, A. Comparison of satellite based observations of Saharan dust source areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Minnis, P.; Chen, B.; Huang, Z.W.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Yi, Y.H.; Ayers, J.K. Long-range transport and vertical structure of asian dust from CALIPSO and surface measurements during PACDEX. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Omar, A.; Vaughan, M.; Hair, J.; Kittaka, C.; Hu, Y.X.; Powell, K.; Trepte, C.; Winker, D.; Hostetler, C.; et al. CALIPSO lidar observations of the optical properties of Saharan dust: A case study of long-range transport. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Radiative forcing by mineral dust aerosols: Sensitivity to key variables. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1998, 103, 31637–31645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano, A.L.; Sokolik, I.N.; Toon, O.B. Radiative heating rates and direct radiative forcing by mineral dust in cloudy atmospheric conditions. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2000, 105, 12207–12219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.; di Sarra, A.; Di Iorio, T.; Fiocco, G. Influence of the vertical profile of Saharan dust on the visible direct radiative forcing. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. 2005, 93, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulet, P.; Mallet, M.; Pont, V.; Pelon, J.; Boone, A. The 7–13 March 2006 dust storm over west Africa: Generation, transport, and vertical stratification. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkikas, A.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Torres, O. Characterization of aerosol episodes in the greater Mediterranean sea area from satellite observations (2000–2007). Atmos. Environ. 2016, 128, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamonou, E.; Chazette, P.; Balis, D.; Dulac, F.; Schneider, X.; Galani, E.; Ancellet, G.; Papayannis, A. Characterization of the vertical structure of saharan dust export to the Mediterranean basin. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1999, 104, 22257–22270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Baars, H.; Tesche, M.; Muller, D.; Althausen, D.; Engelmann, R.; Pauliquevis, T.; Artaxo, P. Dust and smoke transport from africa to south america: Lidar profiling over cape verde and the Amazon rainforest. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.M.; Prospero, J.M.; Zhang, C.D. CALIPSO-derived three-dimensional structure of aerosol over the Atlantic basin and adjacent continents. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6862–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Uno, I.; Yumimoto, K.; Takemura, T.; Shimizu, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Liu, Z. Trans-pacific dust transport: Integrated analysis of NASA/CALIPSO and a global aerosol transport model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 3137–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indoitu, R.; Orlovsky, L.; Orlovsky, N. Dust storms in central Asia: Spatial and temporal variations. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 85, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sokolik, I.N. The dust direct radiative impact and its sensitivity to the land surface state and key minerals in the WRF-Chem-DuMo model: A case study of dust storms in central Asia. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2018, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.I.; Travis, L.D.; Kahn, R.A.; West, R.A. Modeling phase functions for dustlike tropospheric aerosols using a shape mixture of randomly oriented polydisperse spheroids. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1997, 102, 16831–16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Tanskanen, A.; Veihelmann, B.; Ahn, C.; Braak, R.; Bhartia, P.K.; Veefkind, P.; Levelt, P. Aerosols and surface UV products from ozone monitoring instrument observations: An overview. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Kittaka, C.; Vaughan, M.A.; Liu, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.X.; Trepte, C.R.; Rogers, R.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.P.; et al. The calipso automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M.; Gill, T.E.; Hsu, N.C.; Zhao, M. Global-scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on modis deep blue aerosol products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepanski, K.; Tegen, I.; Laurent, B.; Heinold, B.; Macke, A. A new Saharan dust source activation frequency map derived from MSG-SEVIRI IR-channels. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Evaluation of mineral dust aerosol optical depth and related components from the chimere-dust model using satellite remote sensing and ground-based observations. Atmos. Environ. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciren, P.; Kondragunta, S. Dust aerosol index (DAI) algorithm for MODIS. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 4770–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmenova, K.; Sokolik, I.N.; Shao, Y.P.; Marticorena, B.; Bergametti, G. Development of a physically based dust emission module within the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model: Assessment of dust emission parameterizations and input parameters for source regions in central and east Asia. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddock, M.C.; Ginoux, P.; Bullard, J.E.; Gill, T.E. Do MODIS-defined dust sources have a geomorphological signature? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Sokolik, I.N. Dust interannual variability and trend in central Asia from 2000 to 2014 and their climatic linkages. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2015, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razakov, R.M.; Kosnazarov, K.A. Dust and salt transfer from the exposed bed of the Aral Sea and measures to decrease its environmental impact. In NATO ASI Series (Series 2. Environment); Micklin, P.P., Williams, W.D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; Volume 12, pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Winker, D.M.; Tackett, J.L.; Getzewich, B.J.; Liu, Z.; Vaughan, M.A.; Rogers, R.R. The global 3-d distribution of tropospheric aerosols as characterized by CALIOP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3345–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Liu, Z.Y.; Singh, R.P.; Hsu, N.C. Two contrasting dust-dominant periods over India observed from MODIS and CALIPSO data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Matsui, I.; Arao, K.; Uno, I.; Murayama, T.; Kagawa, N.; Aoki, K.; Uchiyama, A.; Yamazaki, A. Continuous observations of Asian dust and other aerosols by polarization lidars in China and Japan during ACE-Asia. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.B.; Sverdlik, L.G.; Imashev, S.A.; Solomon, P.A.; Lantz, J.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Artamonova, M.S.; Carmichael, G.R. Lidar measurements of the vertical distribution of aerosol optical and physical properties over central Asia. Int. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 2013, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioubimtseva, E.; Cole, R.; Adams, J.M.; Kapustin, G. Impacts of climate and land-cover changes in arid lands of central Asia. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 62, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Sokolik, I.N. Seasonal dynamics of threshold friction velocity and dust emission in central Asia. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2015, 120, 1536–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, J.; Sokolik, I.N. Characterization of sources and emission rates of mineral dust in northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4863–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, B.; Marticorena, B.; Bergametti, G.; Mei, F. Modeling mineral dust emissions from chinese and Mongolian deserts. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 52, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beurs, K.M.; Henebry, G.M.; Owsley, B.C.; Sokolik, I. Using multiple remote sensing perspectives to identify and attribute land surface dynamics in central Asia 2001–2013. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A.; Garay, M.J.; Nelson, D.L.; Yau, K.K.; Bull, M.A.; Gaitley, B.J.; Martonchik, J.V.; Levy, R.C. Satellite-derived aerosol optical depth over dark water from MISR and MODIS: Comparisons with aeronet and implications for climatological studies. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, W.A.; Diner, D.J.; Martonchik, J.V.; Bruegge, C.J.; Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J.; Crean, K.A.; Remer, L.A.; Holben, B. Comparison of coincident multiangle imaging spectroradiometer and moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer aerosol optical depths over land and ocean scenes containing aerosol robotic network sites. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A.; Nelson, D.L.; Garay, M.J.; Levy, R.C.; Bull, M.A.; Diner, D.J.; Martonchik, J.V.; Paradise, S.R.; Hansen, E.G.; Remer, L.A. Misr aerosol product attributes and statistical comparisons with modis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2009, 47, 4095–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, I.; Amano, H.; Emori, S.; Kinoshita, K.; Matsui, I.; Sugimoto, N. Trans-pacific yellow sand transport observed in April 1998: A numerical simulation. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2001, 106, 18331–18344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Sugimoto, N.; Murayama, T. Extinction-to-backscatter ratio of Asian dust observed with high-spectral-resolution lidar and raman lidar. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 2760–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, I.; Eguchi, K.; Yumimoto, K.; Takemura, T.; Shimizu, A.; Uematsu, M.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Hara, Y.; Sugimoto, N. Asian dust transported one full circuit around the globe. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.P.; Ferrare, R.A.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.H.; Rogers, R.R.; Hostetler, C.A.; Hair, J.W. Aerosol classification from airborne hsrl and comparisons with the CALIPSO vertical feature mask. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Cordero, L.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. Assessment of calipso attenuated backscatter and aerosol retrievals with a combined ground-based multi-wavelength lidar and sunphotometer measurement. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 84, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolik, I.N.; Toon, O.B. Incorporation of mineralogical composition into models of the radiative properties of mineral aerosol from UV to IR wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1999, 104, 9423–9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).