The Fingerprint of Climate Change and Urbanization in South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
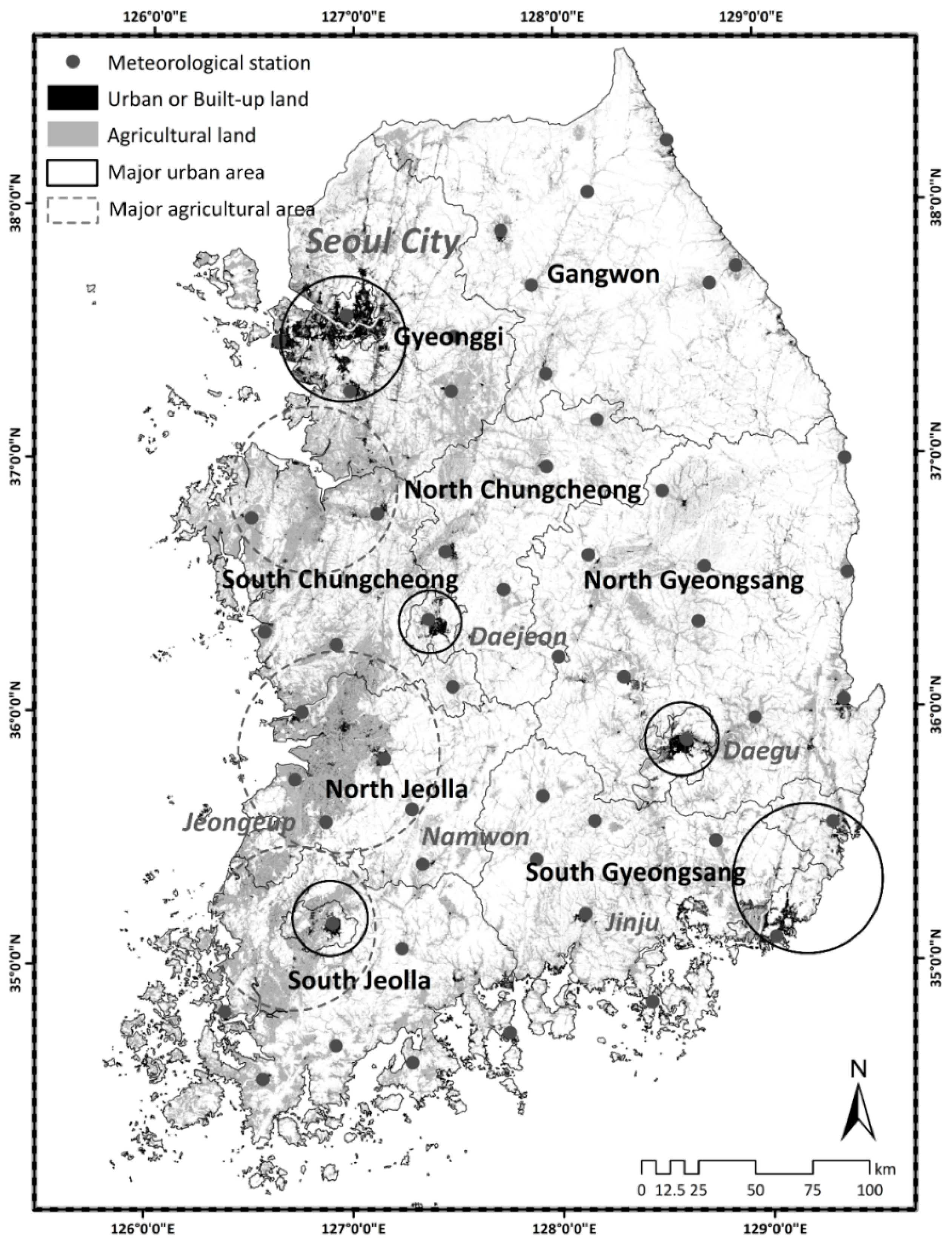
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Meteorological Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis of Climate
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Annual Climate Changes
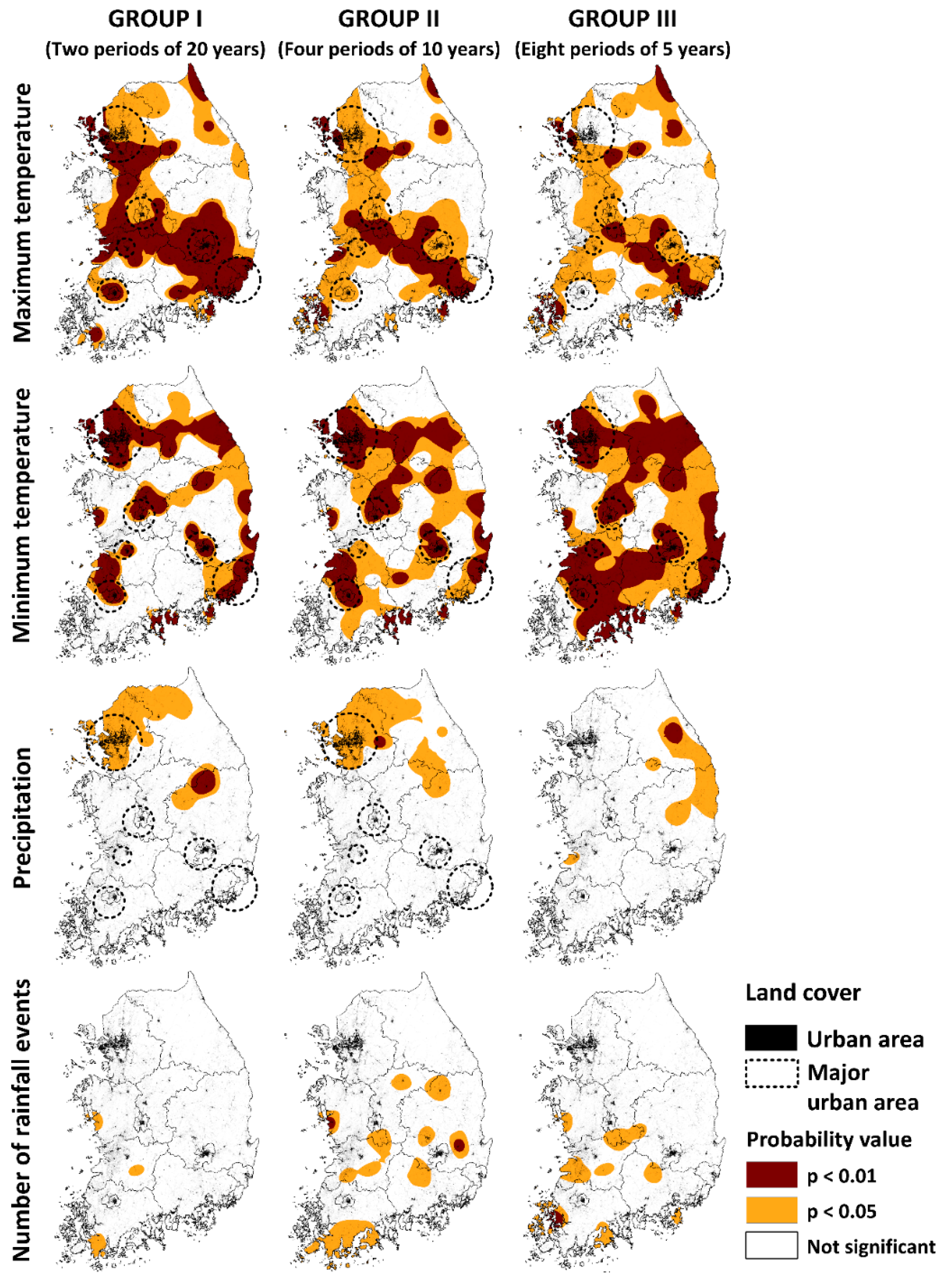
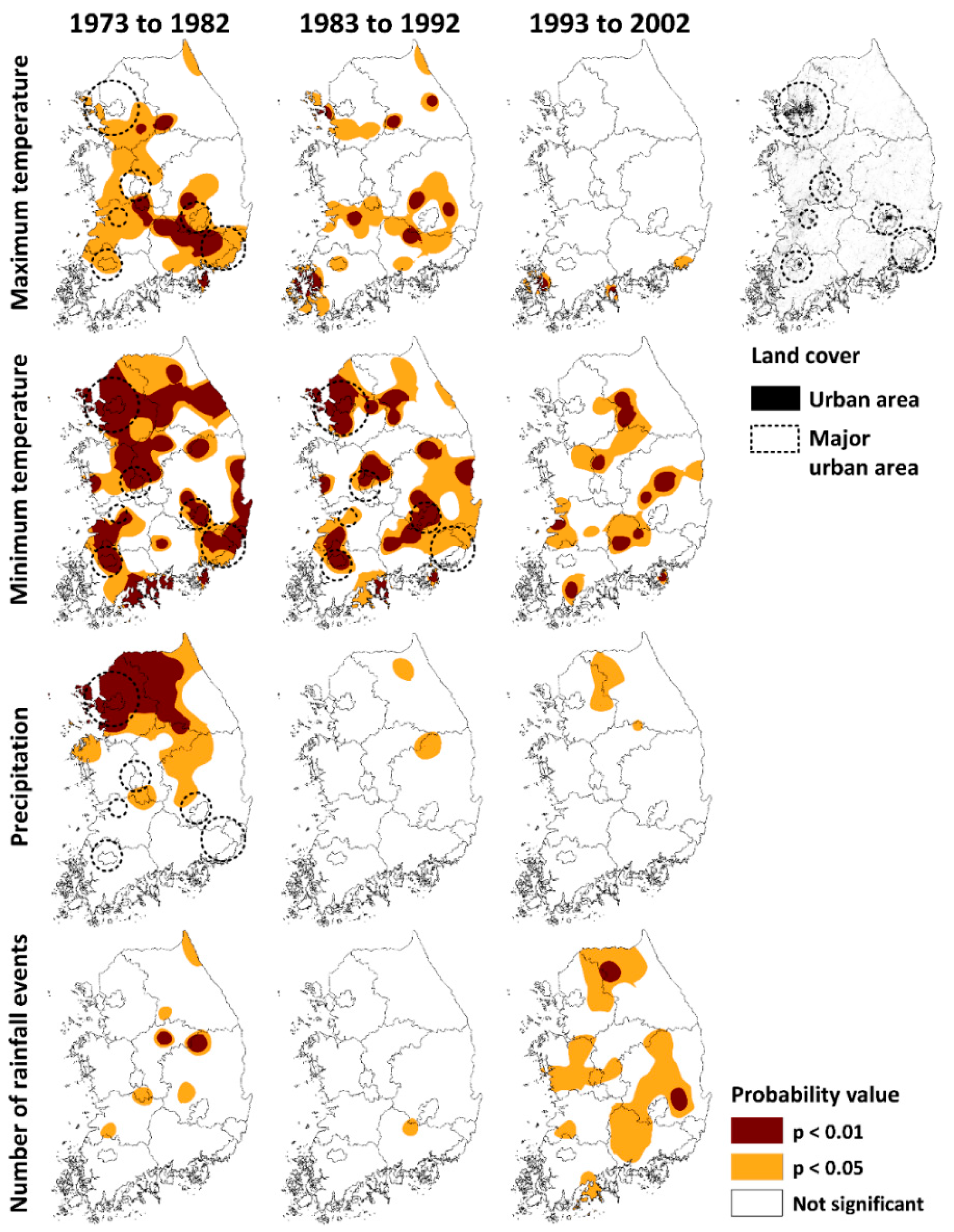
3.2. Timing and Location of Annual Climate Changes
3.3. Analysis of Monthly Climate Changes
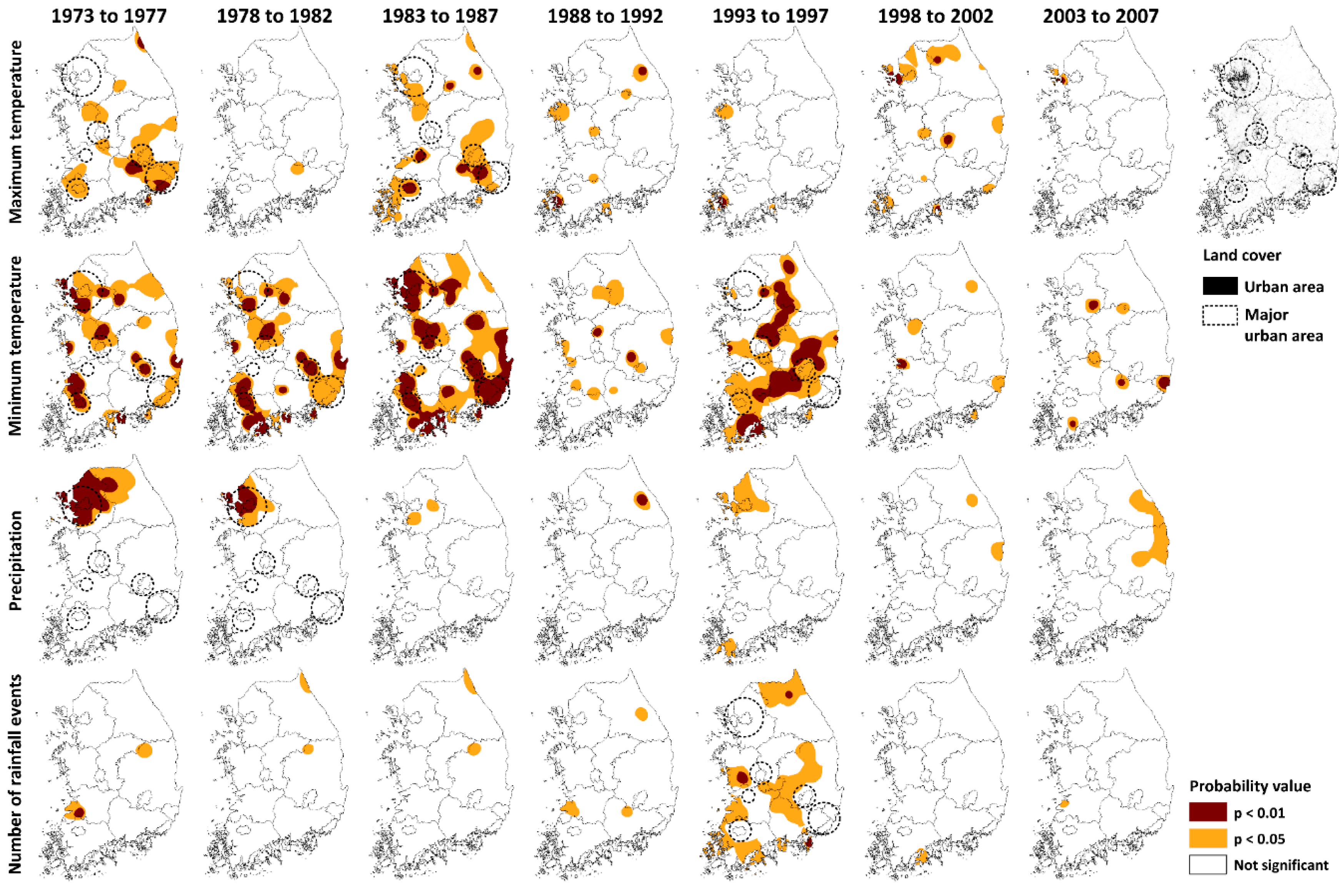
3.4. Timing and Location of Monthly Climate Changes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mann, M.E.; Bradley, R.S.; Hughes, M.K. Global-scale temperature patterns and climate forcing over the past six centuries. Nature 1998, 392, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; New, M.; Parker, D.E.; Martin, S.; Rigor, I.G. Surface air temperature and its changes over the past 150 years. Rev. Geophys. 1999, 37, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hu, Q. Changes in the agro-meteorological indicators in the contiguous United States: 1951–2000. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2004, 78, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.X.; Brauning, A.; Thomas, A.; Li, J.B.; Cao, K.F. Spatial and temporal temperature trends on the Yunnan Plateau (Southwest China) during 1961–2004. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 2078–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhou, Y. Urbanization effect on trends of extreme temperature indices of national stations over Mainland China, 1961–2008. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2340–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Hulme, M. Calculating regional climatic time series for temperature and precipitation: Methods and illustrations. Int. J. Climatol. 1996, 16, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheneider, S.H. Detecting climatic change signals: Are there any “fingerprints”? Science 1994, 263, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegerl, G.C.; von Storch, H.; Hasselmann, K. Detecting greenhouse-gas-induced climate change with an optimal fingerprint method. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 2281–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Knight, R.W.; Easterling, D.R.; Quayle, R.G. Indices of climate change for the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, E.; Gao, X. Climate change impacts on extreme events in the United States: An uncertainty analysis. Clim. Chang. 2015, 131, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, M.; Jones, P.D.; Sigro, J.; Saladie, O.; Aguilar, E.; Moberg, A.; Della-Marta, P.M.; Lister, D.; Walther, A.; Lopez, D. Temporal and spatial temperature variability and change over Spain during 1850–2005. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Ho, C.H.; Kim, J.; Song, C.K. Assessment of the changes in extreme vulnerability over East Asia due to global warming. Clim. Chang. 2012, 113, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Evans, J.L.; Groisman, P.Y.; Karl, T.R.; Kunkel, K.E.; Ambenje, P. Observed variability and trends in extreme climate events: A brief review. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Jones, P.D.; Ambenje, P.; Bojariu, R.; Easterling, D.; Klein Tank, A.; Parker, D.; Rahimzadeh, F.; Renwick, J.A.; Rusticucci, M.; et al. Observations: Surface and Atmospheric Climate Change. In Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Available online: http://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1/ (accessed on 2 July 2018).
- Baigorria, G.A.; Jones, J.W. GiST: A stochastic model for generating spatially and temporally correlated daily rainfall data. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 5990–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.S.; Yuan, F. Trends in extreme temperatures in relation to urbanization in the Twin Cities metropolitan area, Minnesota. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 669–679. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Guo, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. The effects of urbanization on temperature trends in different economic periods and geographical environments in northwestern China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 116, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Diaz, H.F.; Kukla, G. Urbanization: Its detection and effect in the United States climate record. J. Clim. 1988, 1, 1099–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujibe, F. Detection of urban warming in recent temperature trends in Japan. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.P.; Best, M.J.; Betts, R.A. Climate change in cities due to global warming and urban effects. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L09705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Ho, C.H.; Kim, J.; Gong, D.Y.; Park, R.J. The impact of aerosols on the summer rainfall frequency in China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.S.; Yoon, M.B.; Kim, H.S. On climate variations and changes observed in South Korea. Clim. Chang. 2004, 66, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Kim, D.W.; Byun, H.R. The regime shift in the early 1980s of spring precipitation in Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Kang, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, M.K. Changes in the extreme daily rainfall in South Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 2290–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, E.S.; Jung, I.W.; Bae, D.H. The temporal and spatial structures of recent and future trends in extreme indices over Korea from a regional climate projection. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Choi, Y.E.; Oh, J.H.; Lim, G.H. Recent trends in temperature and precipitation over South Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Ahn, M.H.; Lee, H.S. A sudden change in summer rainfall characteristics in Korea during the late 1970s. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.H.; Hong, E.H.; Choi, J.Y. Has climate change already affected the spatial distribution and temporal trends of reference evapotranspiration in South Korea? Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 150, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.H.; Hong, E.M.; Baigorria, G.A. How climate change has affected the spatio-temporal patterns of precipitation and temperature at various time scales in North Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigorria, G.A.; Jones, I.W.; O’Brien, J.J. Understanding rainfall spatial variability in southeast USA at different timescales. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastwirth, J.L.; Gel, Y.R.; Miao, W. The impact of Levene’s test of equality of variances on statistical theory and practice. Stat. Sci. 2009, 24, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levene, H. Robust Test for Equality of Variances. In Contributions to Probability and Statistics: Essays in Honour of Harold Hotelling; Olkin, I., Ghurye, S.G., Hoeffding, W., Madow, W.G., Mann, H.B., Eds.; Stanford University Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 1955, 11, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, S.; Charles, C.; Degre, A. Geostatistical interpolation of daily rainfall at catchment scale: The use of several variogram models in the Ourthe and Ambleve catchment, Belguim. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2259–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, D.S. A Two-Dimensional Interpolation Function for Irregularly-Spaced Data. In Proceedings of the 1968 ACM National Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–29 August 1968; pp. 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.Y.; Baik, J.J.; Lee, H. Urban impacts on precipitation. Asia Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 50, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGaetano, A.T.; Allen, R.J. Trends in twentieth-century temperature extremes across the United States. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 3188–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, J. Urban heat island effect on annual mean temperature during the last 50 years in China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2004, 79, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, U.; Choi, J.; Yun, J.I. Urbanization effect on the observed change in mean monthly temperatures between 1951–1980 and 1971–2000 in Korea. Clim. Chang. 2004, 66, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Regions | Maximum Temperature (°C) | Minimum Temperature (°C) | Precipitation (mm) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1973 to 1982 | 1983 to 1992 | 1993 to 2002 | 2003 to 2012 | 1973 to 1982 | 1983 to 1992 | 1993 to 2002 | 2003 to 2012 | 1973 to 1982 | 1983 to 1992 | 1993 to 2002 | 2003 to 2012 | ||
| Urban areas | Seoul | 16.75 | 16.80 (+0.05) | 17.02 (+0.27) | 17.45 (+0.70) | 7.94 | 8.22 (+0.28) | 8.89 (+0.95) | 9.02 (+1.08) | 1135 | 1416 (+281) | 1446 (+311) | 1640 (+505) |
| Daejeon | 17.67 | 18.11 (+0.44) | 18.13 (+0.46) | 18.61 (+0.94) | 7.23 | 7.72 (+0.49) | 8.02 (+0.79) | 8.44 (+1.21) | 1247 | 1354 (+107) | 1401 (+154) | 1475 (+228) | |
| Daegu | 18.97 | 19.32 (+0.35) | 19.67 (+0.70) | 19.75 (+0.78) | 8.55 | 9.06 (+0.51) | 9.74 (+1.19) | 10.09 (+1.54) | 968 | 1050 (+82) | 1089 (+121) | 1133 (+165) | |
| Agriculture areas | Jeongeup | 18.19 | 18.82 (+0.63) | 18.83 (+0.64) | 18.90 (+0.71) | 7.54 | 7.85 (+0.31) | 8.16 (+0.62) | 8.27 (+0.73) | 1264 | 1265 (+1) | 1312 (+48) | 1372 (+108) |
| Namwon | 18.82 | 19.13 (+0.31) | 19.06 (+0.24) | 19.24 (+0.42) | 6.40 | 6.67 (+0.27) | 6.42 (+0.02) | 6.69 (+0.29) | 1282 | 1367 (+85) | 1339 (+57) | 1432 (+150) | |
| Jinju | 19.10 | 19.19 (+0.09) | 19.72 (+0.62) | 19.78 (+0.68) | 7.57 | 7.61 (+0.04) | 7.70 (+0.13) | 7.97 (+0.40) | 1460 | 1521 (+61) | 1497 (+37) | 1589 (+129) | |
| Regions | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | 1966 | 1970 | 1975 | 1980 | 1985 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban areas | Seoul | 37.57 | 126.97 | 3.793 | 5.525 (146%) | 6.879 (181%) | 8.351 (220%) | 9.626 (254%) | 10.603 (280%) | 10.217 (269%) | 9.854 (260%) | 9.763 (257%) | 9.631 (254%) | 9.904 (261%) |
| Daejeon | 36.37 | 127.37 | 0.315 | 0.414 (131%) | 0.506 (161%) | 0.651 (207%) | 0.866 (275%) | 1.050 (333%) | 1.272 (404%) | 1.368 (434%) | 1.443 (458%) | 1.502 (477%) | 1.538 (488%) | |
| Daegu | 35.89 | 128.62 | 0.845 | 1.081 (128%) | 1.309 (155%) | 1.604 (190%) | 2.028 (240%) | 2.228 (264%) | 2.445 (289%) | 2.474 (293%) | 2.456 (291%) | 2.432 (288%) | 2.466 (292%) | |
| Agriculture areas | Jeongeup | 35.56 | 126.87 | 0.278 | 0.259 (93%) | 0.248 (89%) | 0.221 (79%) | 0.200 (72%) | 0.185 (67%) | 0.139 (50%) | 0.129 (46%) | 0.115 (41%) | 0.109 (39%) | 0.111 (40%) |
| Namwon | 35.41 | 127.33 | - | - | - | - | 0.061 | 0.063 (103%) | 0.104 (170%) | 0.095 (156%) | 0.086 (141%) | 0.078 (128%) | 0.080 (131%) | |
| Jinju | 35.16 | 128.04 | 0.254 | 0.254 (100%) | 0.271 (107%) | 0.303 (119%) | 0.311 (122%) | 0.329 (130%) | 0.330 (130%) | 0.339 (133%) | 0.336 (132%) | 0.335 (132%) | 0.350 (138%) | |
| Month | Maximum Temperature (°C) | Minimum Temperature (°C) | Precipitation (mm) | Number of Rainfall Events | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1973 to 1982 | 1983 to 1992 | 1993 to 2002 | 1973 to 1982 | 1983 to 1992 | 1993 to 2002 | 1973 to 1982 | 1983 to 1992 | 1993 to 2002 | 1973 to 1982 | 1983 to 1992 | 1993 to 2002 | |
| January | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | 2 | 2 | - | 31 | 7 | 20 | 24 |
| February | 33 | 24 | - | 20 | 2 | - | 2 | - | - | 2 | 15 | 17 |
| March | 6 | 9 | 6 | 35 | 4 | 2 | - | - | - | 6 | - | 4 |
| April | 2 | 4 | 4 | 22 | 20 | - | - | - | - | 2 | 7 | 17 |
| May | 30 | 20 | 9 | 70 | 65 | 22 | - | 11 | 7 | - | 9 | 2 |
| June | 35 | 20 | 15 | 54 | 41 | 26 | - | - | - | - | 2 | - |
| July | - | - | 7 | - | 6 | - | 33 | 7 | 46 | 11 | 6 | 57 |
| August | 4 | - | - | 33 | 13 | 4 | - | 11 | - | 13 | 22 | - |
| September | 20 | 28 | 2 | 83 | 31 | 48 | 6 | - | - | 33 | - | 52 |
| October | 6 | 26 | 6 | 48 | 41 | - | 22 | - | 28 | 19 | - | 19 |
| November | 43 | 6 | - | 33 | 31 | 6 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| December | - | 6 | 6 | - | - | 2 | 6 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Meteorological Elements | Month | 1973 to 1982 | 1983 to 1992 | 1993 to 2002 | 2003 to 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation (mm, stand deviation in parentheses) | January | 26.7 (9.4) | 32.5 (9.3) | 33.3 (12.0) | 19.7 (7.5) |
| July | 238.2 (41.5) | 300.8 (57.2) | 240.3 (53.7) | 377.1 (73.6) | |
| October | 57.5 (16.0) | 50.8 (20.9) | 67.7 (16.0) | 38.9 (12.7) | |
| Number of rainfall events (days, stand deviation in parentheses) | January | 6.4 (1.8) | 6.7 (1.9) | 7.0 (2.0) | 5.2 (1.8) |
| July | 13.5 (1.0) | 14.4 (1.3) | 12.5 (1.2) | 16.1 (1.3) | |
| October | 6.5 (0.7) | 5.6 (0.9) | 6.1 (0.8) | 4.7 (0.8) |
| Month | Maximum Temperature (°C) | Minimum Temperature (°C) | Precipitation (mm) | Number of Rainfall Events | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | |
| January | - | - | - | 7 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 9 | - | 7 | 2 | - | 4 | - | - | - | 13 | - | 2 | 11 | 4 | 20 | 4 | 30 | 2 |
| February | - | - | 20 | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | 6 | 11 | - | - |
| March | - | - | 2 | 2 | - | 15 | - | 30 | 17 | 19 | - | 9 | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | 9 | - |
| April | - | - | 2 | 2 | - | 7 | - | 17 | 11 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 | - | 57 | - | - | - | 4 | - | - | 6 | 4 | - | 4 | 26 | - | - |
| May | 59 | - | 4 | 22 | 22 | 2 | 4 | 48 | 56 | 35 | 39 | 39 | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | - | - | 2 | 4 | - | 7 | - | - | 4 | - |
| June | 33 | 9 | 4 | 15 | 11 | 7 | - | 57 | 13 | 31 | 7 | 17 | 17 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| July | - | - | 13 | 7 | - | 6 | 13 | 2 | - | 30 | 11 | 4 | 11 | 11 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 4 | - | 6 | 2 | 15 | 4 | - |
| August | - | 4 | - | 2 | - | 4 | - | 2 | 9 | - | 13 | - | 4 | - | 2 | - | 2 | 15 | - | - | 2 | 9 | 2 | - | 31 | - | - | - |
| September | 4 | 48 | 33 | 24 | 2 | 6 | 11 | 9 | 94 | 7 | 20 | 93 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 4 | - | - | 2 | - | 6 | 37 | 2 | 9 |
| October | 2 | - | 4 | 4 | 6 | 7 | - | 15 | 46 | 4 | 56 | 28 | - | - | 6 | - | 9 | 37 | - | 15 | - | 13 | - | 15 | - | - | 26 | - |
| November | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | 6 | 2 | 4 | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | 2 | 2 |
| December | - | 2 | - | 59 | 7 | 17 | - | - | - | - | 39 | 2 | 7 | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | 4 | - | - | - | - | 13 | 7 | 6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, W.-H.; Baigorria, G.A.; Hong, E.-M.; Kim, T.; Choi, Y.-S.; Feng, S. The Fingerprint of Climate Change and Urbanization in South Korea. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9070273
Nam W-H, Baigorria GA, Hong E-M, Kim T, Choi Y-S, Feng S. The Fingerprint of Climate Change and Urbanization in South Korea. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(7):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9070273
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Won-Ho, Guillermo A. Baigorria, Eun-Mi Hong, Taegon Kim, Yong-Sang Choi, and Song Feng. 2018. "The Fingerprint of Climate Change and Urbanization in South Korea" Atmosphere 9, no. 7: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9070273
APA StyleNam, W.-H., Baigorria, G. A., Hong, E.-M., Kim, T., Choi, Y.-S., & Feng, S. (2018). The Fingerprint of Climate Change and Urbanization in South Korea. Atmosphere, 9(7), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9070273






