Abstract
Air pollution has impacted people’s lives in urban China, and the analysis of the distribution and driving factors behind air quality has become a current research focus. In this study, the temporal heterogeneity of air quality (AQ) and the dominant air pollutants across the four seasons were analyzed based on the Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test method. Then, the spatial heterogeneity of AQ and the dominant air pollutants across four sites were analyzed based on the Wilcoxon signed-rank test method. Finally, the copula model was introduced to analyze the effect of relative factors on dominant air pollutants. The results show that AQ and dominant air pollutants present significant spatiotemporal heterogeneity in the study area. AQ is worst in winter and best in summer. PM10, O3, and PM2.5 are the dominant air pollutants in spring, summer, and winter, respectively. The average concentration of dominant air pollutants presents significant and diverse daily peaks and troughs across the four sites. The main driving factors are pollutants such as SO2, NO2, and CO, so pollutant emission reduction is the key to improving air quality. Corresponding pollution control measures should account for this heterogeneity in terms of AQ and the dominant air pollutants among different urban zones.
1. Introduction
Urban air pollution has become an issue of global concern [1,2,3,4], particularly in rapidly developing countries like China [5,6,7,8]. According to a World Bank study, 16 of the top 20 most polluting cities in the world are located in China [9,10,11], concentrated in Northern China and Eastern China [8,12,13,14,15,16]. The analysis of urban air pollution and its influencing factors has become the focus of current research recently [8,15,17,18,19].
The dynamics of urban air pollution constitute a comprehensive process which is impacted by factors including the spatiotemporal distribution of pollution sources [5,12,20,21,22], seasonal climate and weather [1,2,23,24,25], urban functional zoning [26,27,28], and topography [14,29,30,31]. Therefore, understanding the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of air pollution distribution, pollution sources, and driving forces is prerequisite to formulating reasonable governing policies and plans for pollution control [20,29].
At the national scale, the concentration of dominant pollutants is higher in northern Chinese cities than in those of Western and South-eastern China, and the number of days with high pollution is greatest in winter and spring and lowest in summer and autumn [12,16,32,33]. The main reasons for the nationwide spatiotemporal heterogeneity in Northern China are that there is more carbon emission in winter [16,32,33] and windblown dust in spring [16,29,30]. On the regional scale, the more heavily polluted of China’s cities are concentrated in specific regions, such as the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region [5,29], Bohai Rim Urban Agglomeration [14], Sichuan Basin [17,30], Yangtze River Delta [8,31], and the Pearl River Delta [8]. The spatiotemporal distributions of pollution are diverse between these regions because of different geomorphic types, pollution sources, and meteorological conditions [1,2,5,12,14,31,32,33].
On the city scale, the dominant air pollutants in Beijing are PM2.5 (PM standing for particulate matter) between January and March, PM10 and PM2.5 in April and May, and O3 in June and August [5,34]. The AQI (Air Quality Index) and PM2.5 concentrations are highest in the south and lowest in the north of the city, while O3 concentrations show the opposite direction pattern [22,35]. The concentration of NO2 and SO2 is higher in urban areas than suburban areas [23]. The main sources of the dominant air pollutants are vehicle emissions in Beijing’s urban areas [5], industrial emissions in the southern and other urban industrial areas. Conversely, there are fewer pollution sources in the northern ecological conservation areas in Beijing [25,35]. In Hangzhou, the concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO are highest in winter because of the stable weather conditions and northerly winds, and lowest in summer because of the clean marine air during the monsoon period. The concentration of O3 is highest during summer and lowest in winter in Hangzhou [36,37]. From the spatial view of air pollutants, the concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, and SO2 are lower in the Xihu tourism region due to its lower vehicular emissions than in other urban regions [36,37]. In Chengdu urban areas, the concentrations of PMs (PM10, PM2.5, and PM1.0) were found to be high for a longer time during the year and generally presented V-shaped distribution with a peak in January and a trough in September, respectively, because of basin topography, low wind, and wet weather [30]. In Guangzhou, the concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 are highest from mid-fall to winter. Industrial emission is the largest contributor, followed by vehicle emissions in the wet season. Both these emissions and transported pollutants play important roles during the dry season [20,38].
Qingdao is located on the Shangdong peninsula in the North China Plain (NCP), and is a part of the Bohai Rim Urban Agglomeration [14,15,39,40,41]. The NCP region suffers from severe haze mainly caused by coal combustion and biomass burning emissions together with SO2 emitted by coal combustion [40,41]. Pollution in the Bohai Rim Urban Agglomeration area presents significant spatiotemporal heterogeneity, AQI and PM2.5 concentrations are higher in the south and lower in the north of the city, and the O3 concentrations display a pattern with the opposite direction, while PM2.5 distribution was high in winter and autumn, but low in spring and summer [14]. Qingdao belongs to the Bohai Rim Urban Agglomeration and is near the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region and the Zibo and Weifang cities on the Shangdong peninsula, where air pollution is an extreme problem [5,29,39]. Air pollution is more severe in Qingdao than in other coastal NCP cities [15]. In addition, the diverse weather, topography, and pollution sources among the different economic functional zones lead to spatiotemporal heterogeneity of air pollution in urban Qingdao [15,42,43,44]. However, systematic studies on the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of air pollution in this area are rare.
Based on the above, the main goal of this study is to systematically analyze the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of air pollution at the zonal spatial scale and the seasonal and hourly temporal scales by taking Qingdao as a study case. First, the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of air quality (AQ) distribution was analyzed based on the Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test method and the Wilcoxon signed-rank test method. In addition, the dominant air pollutants were determined according to the days of dominant air pollution across all four seasons. On this basis, the spatiotemporal distribution of dominant air pollutants was analyzed. Then, the impact of the effect factors on the dominant air pollutants was analyzed using the copula model. Finally, the results and conclusions were compared with those from previous studies, and some suggestions were given for governing policies and plans.
2. Study Area, Materials, and Methodology
2.1. Study Area
Qingdao is a typical coastal tourist city, and air pollution greatly impacts both tourism and the people living there [15,42,43,44]. There are seven administrative zones in the city of Qingdao. Four of these zones, Shibei, Laoshan, Sifang, and Licang, represent downtown, a tourist district, a residential district, and an industrial district, respectively. Population and residential areas are more concentrated in the Shibei and Licang zones; the greening rate is larger in the Laoshan and Licang zones, and there are more polluting enterprises, such as two key state monitored gas-exhausting enterprises, in the Licang zone (Figure 1 and Table 1). South (S) and south-east (S-E) are the prevailing wind directions in spring (March, April, and May) and summer (Jun, July, and August), while north-west (N-W) is the prevailing wind in autumn (September, October, and November) and winter (December, January, and February) (Table 1) [15,42].
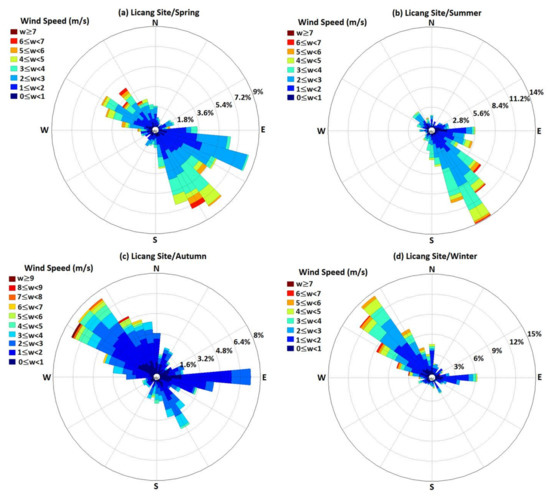
Figure 1.
Wind speed and direction rose charts in winter at the Licang site.

Table 1.
Statistical information of related conditions in the four zones.
Considering the different natural conditions and economic functions in these four zones, we selected four environmental monitoring sites across the four zones, all built by the Qingdao Environmental Monitoring Center Station in this paper. The four meteorological monitoring sites (built by Qingdao Meteorological Bureau) located nearest to environmental monitoring sites were also selected. The names and locations of the environmental monitoring sites are Shibei (120.341389 E, 36.069889 N), Laoshan (120.353989 E, 36.085814 N), Sifang (120.366456 E, 36.104064 N), and Licang (120.385392 E, 36.184747 N). The spatial distribution of these environmental monitoring sites is shown in Figure 2.
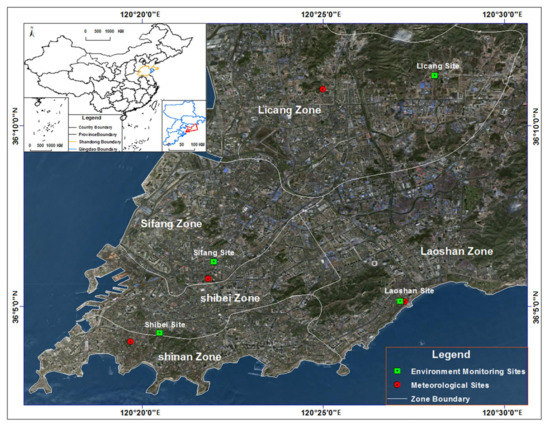
Figure 2.
Maps of study area, monitoring sites, and geomorphic image.
2.2. Materials
Hourly average concentrations of PM10, O3, PM2.5, SO2, NO2, and CO were measured at the four environmental monitoring sites from 1 October 2015, to 30 September 2016. Daily average values of AQI were calculated using the following model [45].
denotes the sub AQI of the pth pollutant; denotes the concentration of the pth pollutant; , and denote the nearest higher and lower concentrations than in Table 1 in the technical specification [45]; and denote the sub AQIs corresponding to and ; denotes the number of pollutants.
Daily AQ scores were sorted into three levels: good, moderate, and polluted, and the daily dominant air pollutants were identified according to the AQ level classification criteria specified in the ambient AQI technical specification [45]. Meteorological data, including hourly averages for temperature, air pressure, wind speed, and humidity at the four meteorological sites in the same period, were obtained from the Qingdao Meteorological Bureau.
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity Analysis Methods
AQ, dominant air pollutants, and meteorological environment each have distinct seasonal and hourly characteristics, so the temporal heterogeneity of the distribution of AQ and dominant air pollutants was studied on seasonal and hourly time scales. The AQI and concentrations of dominant air pollutants can be represented by continuous random variables with unknown probability distributions, and without paired relationship, so the Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test method was suitable for testing the differences between the distributions for AQ and the dominant air pollutants on the season and hourly scales [46,47,48]. The advantages of the Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test method are that it is a nonparametric test method, multiple group samples can be tested together, and the overall levels of samples can be visually compared with box-plots. The testing process is described below [48].
Assume that variable denotes a sample of AQI at sites.
First, the null hypothesis is built as the Equation (3).
denotes the continuous distributions of ; denotes AQI at four sites from the same populations.
Then, the statistic is constructed as Equation (4).
; is the size of the AQI sample at the ith site; is the rank of AQI value in the sample of AQI at the ith site.
Finally, the null hypothesis is tested:
When or , then is rejected.
The null hypothesis H0 means that there is no difference between the distributions of the AQ and the dominant air pollutants in each of the four seasons.
The four environmental monitoring sites each represent different districts, so the spatial heterogeneity of the distributions of AQ and dominant air pollutants among the sites was studied based on the environmental monitoring data. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test method was suitable for testing the differences between their distributions, since AQI and concentrations of dominant air pollutants can be represented by continuous random variables and there are one-to-one correspondence relations between the four monitoring sites [49,50,51]. The advantages of the Wilcoxon signed-rank test method are that it is a nonparametric test method and that it makes full use of the paired difference information in order to reflect the details of the variation between two samples. The testing process is described below [50].
Assume that variable denotes the AQI values at the same time at two sites. Given a random variable , is the mean of , and the median of the population of is .
First, the null hypothesis is built as Equation (6). The null hypothesis means that the AQ and dominant air pollutants are not different between pairs of sites.
Then, the statistic is constructed as Equation (7).
The statistic approximately obeys the standard normal distribution, if .
Finally, the null hypothesis is tested:
When or P( then is rejected, is significance level, and are and quantiles of .
2.3.2. Effect Factors Analysis Methods
The correlation between dominant air pollutants and their effect factors is complex and not linear, so nonlinear models are more appropriate for the effect factors analysis [18,49]. Compared to linear models, the copula model can be applied to analyze nonlinear correlation between variables with the following advantages [52,53,54,55]: (i) The copula model captures abnormal information by visually displaying the tail features of the variable distribution, (ii) the copula model is suitable for variables obeying any type of distribution, and (iii) the copula model is powerful for analyzing the nonlinear correlation between variables. Recently, the copula model was applied with satisfactory results in geoscience, hydrology, finance, and other fields [56,57,58,59,60,61,62]. Therefore, the copula model was introduced to analyze the effect factors on the heterogeneity of dominant air pollutants in this study, and this analysis process is described below.
The diel variation of dominant air pollutants (the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value in one day) was calculated. Consider the diel variation of PM2.5 and the value of precipitation as an example, expressed as and , respectively. The correlation analysis process based on the copula model is as follows. First, the marginal distribution of the random variables and is determined using both the parametric method and the non-parametric method. The parametric method assumes that the random variable obeys some type of distribution with parameters, such as the distribution or normal distribution. In this method, the parameters in the distribution can be estimated by using the sample data, after which the estimated distribution is tested. When it comes to the non-parametric method, either the empirical distribution function of the sample obeys the approximate distribution of the population random variable or the distribution of the population random variable is determined based on kernel density estimation drawn from the sample data. After the marginal distribution () and the marginal distribution () are determined, a suitable copula model can be selected according to the bivariate histogram. Specifically, the bivariate frequency number histogram is drawn first, and then the frequency histogram is drawn on the basis of the frequency number histogram. The Gumbel Copula model can be selected to describe the correlation structure of the data when the bivariate frequency histogram has asymmetric tails, such as cases with a high upper tail and low lower tail. The -Copula model or the bivariate Normal Copula model can be applied when the bivariate frequency histogram has symmetric tails. If the marginal distribution contains unknown parameters, such as when the Gumbel Copula model being applied contains unknown parameters, then the unknown parameters should be estimated. The kernel distribution estimation method can be applied to obtain the marginal distribution of the random variables and , then the copula fit function can be called to estimate the unknown parameters. After the copula parameters are estimated, the copula statistic function is called to obtain the Spearman rank correlation coefficient [58].
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of AQ Distribution
3.1.1. Temporal Heterogeneity of AQ Distribution
The AQI differences at each site were analyzed on a seasonal time-scale. The Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test method is suitable for testing the differences at a significant level of 5% between the seasonal AQI, because there is no paired relationship in the seasonal AQI data at each site and the distribution type and parameters for AQI is unknown. The p-value of the seasonal AQI difference test results was less than 0.05, so the null hypothesis H0 was rejected according to the null hypothesis testing mothed. This indicates that there was significant temporal heterogeneity in terms of the overall level of AQ between the four seasons at each site. The height of the boxes is smaller in summer, and the outlier values are fewer (Figure 3), so it can be inferred that AQI varied less in summer and more in winter. It can be seen that the AQI in summer was less varied and lower on average than in the other three seasons, while the AQI in winter was more varied and higher on average than in the other three seasons. It can be inferred that the AQ was best in summer and worst in winter at each site.
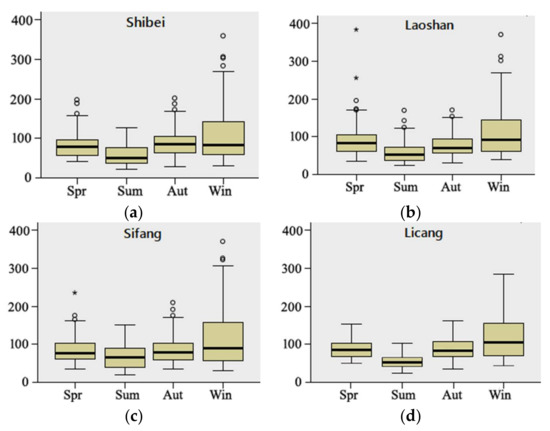
Figure 3.
Box-plot of the Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test for (a) Shibei site; (b) Laoshan site; (c) Sifang; (d) Licang.
To further analyze the temporal heterogeneity of air pollutant distribution, the number of days for each level of AQ and the dominant air pollutants in each season were calculated. Figure 4 shows that AQ level counts at all four sites generally presented significant temporal heterogeneity. The number of days on which AQ ranked as polluted was largest in winter at each site. There were more than 35 polluted days in winter at each site, and the Licang site reached 48. The number of days on which AQ ranked as polluted was smallest in summer at each site. It was less than 15 in summer at all sites, and it dropped as low as 3 at the Laoshan site.
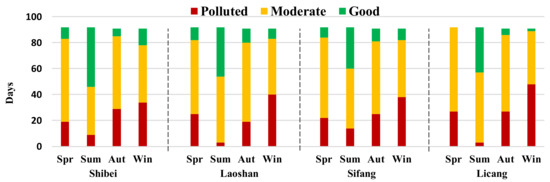
Figure 4.
Chart showing the number of days of each level of air quality (AQ).
3.1.2. Spatial Heterogeneity of AQ Distribution
AQI is a comprehensive evaluation index representing overall levels of urban AQ, so the spatial heterogeneity of overall levels of AQ can be reflected by comparing the differences in AQI between the four monitoring sites. The mean and standard deviation of AQI, as well as the count of days at each AQ level and of the dominant air pollutants were calculated (Table 2). The means and standard deviations of AQI were about 85 and 48.5, respectively, at the Shibei and Laoshan sites, and about 89.5 and 50.5, respectively, at the Sifang and Licang sites, so it can be seen that the overall levels of AQ were coincident between the Laoshan and Shibei sites, as well as between the Sifang and Licang sites. The largest numbers of days on which AQ ranked as good were 74 and 67 at the Shibei and Laoshan sites, and the smallest was 42 at the Licang site, while the largest number of days on which AQ ranked as polluted was 105 at the Licang site, and the smallest was 87 at the Laoshan site. Furthermore, the concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 were significantly higher at the Licang site than at the other three sites (Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). Thus, it can be inferred that air pollution was generally most severe at the Licang site and least severe at the Shibei and Laoshan sites.

Table 2.
Statistical characteristics of AQI (Air Quality Index) and days of dominant air pollutants at the four sites.
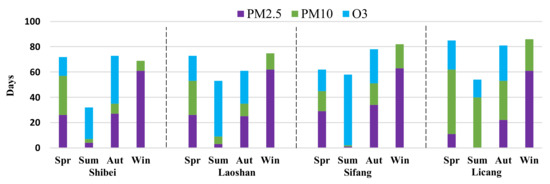
Figure 5.
Chart showing the number of days of the dominant air pollutants.

Figure 6.
Chart of diel variation of concentration of PM10 by hour in spring.

Figure 7.
Chart of diel variation of concentration of PM2.5 by hour in winter.
In order to further analyze the spatial heterogeneity and characteristics of air pollutant distribution at the four sites, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test method was applied to test the differences in AQ at a significant level of 5% between pairs of sites within the space of a year. Only the p value between the Laoshan and Shibei sites was larger than 0.05 (Table 3). According to the null hypothesis testing method, it can be inferred that the AQ was significantly similar at the Laoshan and Shibei sites, and significantly different between the other pairs. So it can be inferred that there is significant spatial heterogeneity between the pairs of sites except the Laoshan–Shibei pair.

Table 3.
Results of AQI difference test among the four sites.
3.2. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Dominant Air Pollutants Distribution
First, the temporal heterogeneity of the dominant air pollutants, in terms of the number of days on which each pollutant was dominant, was examined. The number of days on which PM10 was the dominant air pollutant was larger than 27, which was the largest among all the pollutants in spring, at all three sites, other than the Sifang site (Figure 5). In summer, the number of days on which O3 was the dominant air pollutant was larger than 25, which was the largest among all the pollutants at all three sites, other than the Licang site. The number of days on which PM2.5 was the dominant air pollutant was larger than 61, which was the largest among all the pollutants in winter at each site. The sum of days on which O3 and PM2.5 as the dominant air pollutant was larger than 51, which was the largest among all the pollutants at each site in autumn (Figure 5). In general, the dominant air pollutants were PM10 in spring, O3 in summer, O3 and PM2.5 in autumn, and PM2.5 in winter.
Next, temporal heterogeneity of the diel variation in dominant air pollutant concentration was examined. In Figure 6, the curves show a single peak in the chart of diel variation of the concentration of PM10 at each of the four sites, so PM10 (the dominant air pollutant in spring) appeared to show significant temporal heterogeneity at the hourly scale for each site. At the hourly scale, it reached its minimums between 20:00 and 3:00 (on the next day) and its maximums between 9:00 and 12:00, and the difference was about 25 μg/m3. It can be inferred that human activities, such as construction and vehicle driving in the day-time, impact PM10 diel variation to a certain degree [19,27].
O3 (the dominant air pollutant in summer) showed significant temporal heterogeneity at the hourly scale across all four sites (Figure 8). The concentration of O3 at the four sites varied consistently during the course of a day, and the curves obviously showed trough-and-peak variation patterns; the concentration of O3 was significantly higher in the daytime than at night, and the difference was about 50 μg/m3. It ascended rapidly from 7:00 and reached its peak at 14:00, then gradually descended and finally reached the trough at 7:00 the next day. The rule of diel variation of concentration of O3 reveals that photochemical reactions are an indispensable condition for O3 formation.
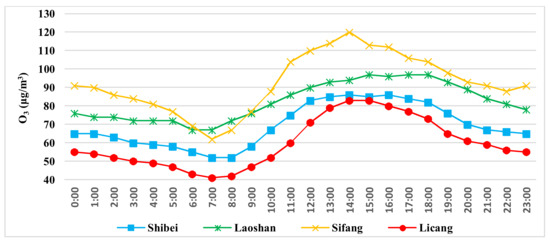
Figure 8.
Chart of diel variation of concentration of O3 by hour in summer.
The dominant air pollutant was PM2.5 at each of the four sites during the winter, and the concentration of PM2.5 reached peaks twice a day. The curves were bimodal, and there was significant temporal heterogeneity in terms of the concentration of PM2.5 across all four sites (Figure 7). The difference in concentration of PM2.5 between the maximum and minimum was about 20 μg/m3, and it ascended rapidly from 5:00 to 7:00 in the morning, reaching its peaks between 11:00 and 12:00 before decreasing quickly and reaching its troughs between 16:00 and 17:00. Then, it increased and reached small peaks between 21:00 to 23:00 before gradually decreasing and reaching small troughs between 5:00 and 7:00 the next day. The time of peaks and troughs is greatly related with urban rush-hours, which indicates that vehicle emission makes some contribution to the formation of PM2.5.
Next, the spatial heterogeneity of dominant air pollutants was analyzed. To determine the dominant air pollutants at each site in each season, the number of days during which each air pollutant was dominant was calculated (Table 4 and Figure 5). The number of days on whichPM10 was the dominant air pollutant at the Licang site was 148, about two times higher than at the other three sites. The number of days on which PM2.5 was the dominant air pollutant was very high at all of the sites, but especially at the Sifang site. The number of days on which O3 was the dominant pollutant was significantly larger at the Laoshan and Sifang sites than at the Shibei and Licang sites (Table 4). In summary, PM10 and PM2.5 were dominant at the Licang site, while PM2.5 and O3 were dominant at the other three sites. Therefore, it can be inferred that industrial dust and construction dust were the main factors causing air pollution in the Licang zone, and it was significantly different in the other three zones.

Table 4.
Statistical characteristics of AQI and days of dominant air pollutants at the four sites.
In order to further identify the distribution characteristics of the three dominant air pollutants, the spatial heterogeneity was tested with hourly concentrations of the three dominant air pollutants among the four sites. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test method is suitable for testing these differences, because the concentrations of the three dominant air pollutants have a one-to-one correspondence by time among the sites. Therefore, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test method was applied to test the difference at the significant level of 5%.
For the Wilcoxon signed-rank test of the concentration of PM10 between the pairs of sites in spring, all of the p-values were smaller than 0.05 except in the case of the Shifang-Shibei pair (Table 5). Thus, it can be deduced that there was significant spatial heterogeneity in the concentrations of PM10 between all of the remaining pairs of sites. For the Wilcoxon signed-rank test of the concentration of O3 between the pairs of sites in summer, all of the p-values were less than 0.05 (Table 5). This indicates that there was significant spatial heterogeneity in the concentrations of O3 in summer across all four sites. For the Wilcoxon signed-rank test of the concentration of PM2.5 between the pairs of sites in winter, all of the p-values were smaller than 0.05, except in the case of the Laoshan-Shibei pair (Table 5). Thus, it can be inferred that there was significant spatial heterogeneity in PM2.5 concentration between the remaining pairs of sites.

Table 5.
Results of PM10, O3, and PM2.5 difference test among the four sites.
Finally, the spatial heterogeneity of the diel variation in concentrations of the pollutants was analyzed. As Figure 6 shows, the difference in the concentration of PM10 between daytime and night-time was lower at the Shibei site than it was at the other sites, and the concentration of PM10 remained near its midday high for a longer time at the Shibei site than it did at the other sites. At the Laoshan site, the concentration of PM10 stayed low at night for a longer time, the initial ascension time was later, and the peak time was later than at the other sites. The difference in the concentration of PM10 between daytime and night was higher at the Sifang site than at other sites, and the lengths of ascension time and descent time were nearly equal at the Sifang site. At the Licang site, the concentration of PM10 was significantly higher, the initial rise was earlier, and the peak time was earlier than at the other sites.
The concentration of O3 was lowest at the Licang site, and highest at the Sifang site (Figure 8). There was roughly a 10 μg/m3 difference in the concentration of O3 among the four sites. The curves in Figure 8 show that the variation trend in the concentration of O3 in summer was nearly the same at all four sites, so there was no spatial heterogeneity in terms of the fluctuation of the concentration of O3 in summer between the sites. Combining Table 5 and Figure 8, it can be deduced that there was a strong correlation between the concentration of PM10 and the intensity of sunlight and temperature. Sunlight intensity and temperature were both very low at night, and the concentration of O3 was correspondingly very low. The atmospheric photochemical reactions gradually increased with the increase in the intensity of solar radiation. As the secondary pollution product of photochemical reactions, the concentration of O3 increased rapidly. After the concentration of O3 reached its peak, it decreased with the decrease of sunshine intensity and temperature.
The curves in Figure 7 show that the variation trend in the concentration of PM2.5 in winter was nearly the same at all four sites, but the fluctuation of it was not obvious in the morning at the Laoshan site. The concentration of PM2.5 was slightly higher at the Licang and Sifang sites, and slightly lower at the Shibei and Laoshan sites.
3.3. The Effect of the Relevant Factors on the Dominant Air Pollutants
The non-parametric method was applied to fit the marginal distribution, because the air pollution data and meteorological data did not obey the normal distribution or the distribution. The appropriate copula function models were selected based on the characteristics of the binary frequency histograms and binary probability density functions, while the binary cumulative distribution functions of the copula model were fitted respectively. For example, the binary frequency histogram and the graph of the binary probability density function between O3 and temperature at the Licang site is shown as Figure 9a,b. According to the histogram, the Clayton Copula model is suitable for the correlation analysis between them.

Figure 9.
(a) The binary frequency histogram and (b) the graph of the binary probability density function. (Note: U denotes marginal distribution of temperature; V denotes marginal distribution of O3).
The Spearman rank correlation coefficient calculated with the copula models are shown in Table 6. The main driving factors of diel variations of the dominant air pollutants at the four sites were generally other pollutants such as SO2, NO2, and CO, while the meteorological factors play diverse roles (Table 6). However, the effects also showed significant diversity between factors. In detail, the diel variation of wind speed had little effect on the diel variation of PM10 at each site, and other factors had certain effects on the diel variation of PM10 at the Shibei and Sifang sites. The diel variation of NO2 had little effect on the diel variation of PM10, and other factors had certain effects on the diel variation of PM10 at the Laoshan site and the Licang site. Humidity had a great effect on the diel variation of O3 at each site. The diel variation of wind speed had a great effect on the diel variation of O3 at Licang site, but little effect at the other three sites. The diel variation of NO2 had little effect on the diel variation of O3 at the Laoshan site, but a great effect at the other three sites; the diel variation of CO had a greater effect on the diel variation of O3 at the Sifang site than at the other three sites. The diel variations of wind speed and humidity had little effect on PM2.5 at all sites, but other factors had greater effects.

Table 6.
The correlation between dominant air pollutants and the effect factors at the four sites.
4. Discussion
In recent years air pollution has become a serious issue which threatens people’s health generally and the economic development in urban Qingdao [42,43,44] particularly. Comprehensive understanding of the distribution characteristics of pollutants is significant and is indispensable for air pollution control [15]. Therefore, the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of the pollutants distribution and the effect factors in Qingdao urban zones were systematically analyzed by introducing the Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, and the copula model in this study.
4.1. Temporal Heterogeneity of AQ and Dominant Air Pollutants
AQI is a very important indicator for assessing AQ in urban areas [63], and we used it to analyze the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of AQ at four sites in the Qingdao urban area. The number of days in each AQ level (Figure 4) and AQI test results (Figure 3) show that AQ was best in summer and worst in winter in the Qingdao urban zones. Similar seasonal heterogeneity in AQ existed in most NCP cities because there are generally more emissions from coal combustion and biomass burning in winter [40,41]. For example, air pollution mainly occurred in winter and spring, and it was generally attributed to local primary emissions (e.g., coal combustion and vehicular, domestic, and industrial emissions) in winter in Qingdao [15,64]. The AQI was largest in winter (January and February) and smallest in autumn (September) in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region [5]. The AQ was worst in spring and best in summer, and it subsequently became more serious in autumn and winter in Beijing [34].
In this study area, PM10, O3, and PM2.5 were identified as the dominant air pollutants in spring, summer, and winter respectively by counting the number of days during which each pollutant was dominant. More wind and less precipitation lead to PM10 diffusing less and staying longer in the air, which results in PM10 becoming the dominant air pollutant in spring. The stronger photochemical effect, lusher vegetation, and higher temperature are the main reasons that O3 was the dominant air pollutant in summer. The burning of carbon for heat in winter raises the concentration of PM2.5, which leads to its being the dominant air pollutant. There were consistent results in previous studies: e.g., the dominant air pollutant was PM10 [64], and PM2.5 was the dominant pollutant contributing to pollution in winter in Qingdao [15,42]. In the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, the dominant air pollutant was PM2.5 in the periods from January to March, July, and from September to December, while PM10 and PM2.5 were the dominant air pollutants in April and May and O3 was dominant in June and August [5]. PM2.5 pollution was much more severe in winter than in other seasons on the Shangdong peninsula [39]. In the entire NCP, PM10 and PM2.5 were highest in winter and lowest in summer [31], while O3 showed the opposite seasonal trend [65].
On an hourly scale, the diel variation of the dominant air pollutants presented significant temporal heterogeneity at each site. The average concentration of PM10 reached peaks between 9:00 and 12:00 and troughs between 20:00 and 3:00 the next day in spring. This resulted from the positive correlation between PM10 and temperature, and a negative correlation between PM10 and pressure and humidity (Table 6). Temperature gradually increased, and pressure and humidity gradually decreased during the daytime; temperature gradually decreased, and pressure and humidity gradually increased at night. The case was slightly different in urban Beijing, where the concentration of PM10 reached peaks at 11:00 and maintained a high level until 22:00 before reaching troughs at 3:00. This was mainly because of the combined actions of traffic emission, fuel and coal combustion, photochemical activity, and dust particles [31,66].
In this study area, the average concentration of O3 reached daily troughs at 7:00 and peaks at 14:00 in summer. This was because O3 was a photochemical product of precursors such as NO2, CO, and SO2, and the concentration of O3 significantly increased with the increase of light intensity while its dissipation process was relatively slow. The diel variation in concentration of O3 in Beijing and the Zhejiang province is similar to that in Qingdao [31,67]. In the Pearl River Delta, the O3 concentrations exhibited broad maximums in the afternoon and minimums at night and in the early morning at Wan Qing Sha in Guangzhou, while they are much lower during morning hours and in the evening at Tung Chung in Hong Kong. The former were affected by regional transport, and the latter were affected by strong titration of O3 by freshly emitted NO [68].
The average concentration of PM2.5 reached daily peaks between 11:00 and 12:00 and troughs between 16:00 and 17:00, before increasing and reaching small peaks between 21:00 and 23:00 in winter. This was because the movement of fine particles was closely related to human activities [6], and the masses driving in rush hours accelerated the fine particle movement in the morning and the evening, which caused PM2.5 to form two peaks at midday and midnight. According to the correlation between PM2.5 and temperature, PM2 mainly resulted from the precursors such as NO2, CO, and SO2 (Table 6). PM2.5 was the primary pollutant in winter; the concentration peaked at noon [15]. The average concentration of PM2.5 reached troughs at 14:00 and peaks at 20:00 in Beijing, and there was only one peak during a day [31,66].
4.2. Spatial Heterogeneity of AQ and Dominant Air Pollutants
According to the number of AQI ranks (Table 2) and AQI test results (Table 3), AQ presented significant spatial heterogeneity. It was best at the Shibei and Laoshan sites and worst at the Licang site. This was mainly because the Shibei zone is an administrative zone with fewer pollution sources, the Laoshan site is a tourist zone with the highest greening rate, and the Licang zone is an industrial zone with more polluting enterprises (Table 1). There have been similar reports on how AQ is impacted by different pollution sources in urban Qingdao and other cities. Ship emissions were especially harmful to AQ in summer in urban areas near the Qingdao Port region [43], and AQ was severely impacted by traffic emissions near the Yangkou tunnel, Qingdao [44]. AQI was higher south of Beijing because of the heavy industries nearby, and lower in the north because of large areas of forest vegetation [22]. The annual AQI was higher in the western parts and central area than in the tourist area in Shenzhen [69]. Land use and industrial structures affected AQ and pollutant distributions in urban Shenzhen. Higher NO2 was attributed to greater traffic or indoor combustion emissions in the west, higher SO2 was caused by industrial coal combustion in the east, and lower CO resulted from tourism protection in tourist areas [69].
The dominant air pollutants also presented significant spatial heterogeneity at the four sites. PM10 concentration was higher and the number of days of PM10 dominance was larger at the Licang site than at the other three sites throughout the year, especially in spring and summer (Figure 5 and Figure 6). This was because there was some industrial dust and construction dust [19,27], as well as more wind at the Licang site in spring and summer (Figure 1) [42]. The Licang site is located in the northern foothills of Laoshan Mountain, and the dust transport from the north is also another important reason for this difference. The other three sites are closer to beaches (Figure 1), and the eastern or southern coastal winds are strong, which are a predominant reason for lower PM10 concentration there. PM10 was one of the major pollutants affecting air quality in China in every season [31,33]. PM10 pollution was mainly attributed to coal combustion and biomass burning in autumn and winter, photochemical reactions in summer, and crustal matter in spring in Xi’an China [70]. The PM10 concentration was larger in urban areas than in suburban areas in Fuzhou, and the discrepancy was significant between them [71].
The concentration and the number of days of O3 dominance were significantly higher and larger at the Sifang site than the other three sites (Figure 5 and Figure 8), and the correlation between the diel variations of O3 and CO was significantly greater at the Sifang site than at the other three sites (Table 6). This indicated that CO emissions were the important impacting factors for the higher concentration and dominance of O3 at this site [67]. Residential and commercial land use is dominant in the Sifang zone, with high population density and heavy traffic. Emissions of CO, NOx, and VOCs (volatile organic compounds) are significantly higher from civil facilities (e.g., garages, gas stations, paint factories, and urban traffic) which are more common in the Sifang zone than in the other three zones. This is the main reason for higher O3 concentration at the Sifang site. O3 concentration was highest in the northern and northern-central regions in Beijing because of photochemical effect, dry weather conditions, and forest vegetation [22].
PM2.5 concentrations were not significantly different among the four sites (Figure 5 and Figure 7), though they were slightly higher at the Licang and Sifang sites. This was mainly because of high concentrations of PMs, SO2, and NO2 due to emissions from thermal power plants and the steel industry at the Licang site and high concentrations of NOx, PMs, and SO2 due to traffic emissions and coal combustion at the Sifang site. With the prevailing N-W and W-N winds in winter, PM2.5 transportation from high PM2.5 areas in the western portions of the Shangdong peninsula and the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region was an important source in Licang and Sifang zones. [5,14,15,39,40,41]. Further analyzing the spatiotemporal distribution of AQ and air pollutants with the transport factor combining wind direction, land use, and topology is a future research objective.
5. Conclusions
The spatiotemporal heterogeneity of pollution distribution can be systematically analyzed by using a method based on the Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test and the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. The copula model can be effectively used to catch the abnormal information about AQ, dominant air pollutants, and relevant factors, and analyze the nonlinear correlation between them. The methods explored in this study can be applied to the spatiotemporal heterogeneity analysis of pollutant distribution in other regions.
We found that there was significant spatiotemporal heterogeneity between the distributions of AQ and dominant air pollutants at the four sites in this study. From the temporal view, AQ was best in summer and worst in winter at each site, while PM10, O3, and PM2.5 were the dominant air pollutants in spring, summer, and winter respectively at each site. The concentration of PM10 peaked at noon and reached its trough in the early morning. The concentration of O3 peaked in the early morning and reached its trough at noon. The concentration of PM2.5 presented a double peak at high noon and early night and reached its trough in the evening.
On a spatial scale, air quality was best at the Shibei and Laoshan sites, and worst at the Licang site. The concentration of PM10 was highest at the Licang site; this was mainly because of building dust from rural reconstruction, industrial dust from steel plants, and strong coastal wind. There were more polluting enterprises (Table 1), e.g., thermal power plants and steel plants in the Licang zone, and the industrial emissions contained NO2 and CO which resulted in the concentration of PM2.5 being highest at the Licang site [67]. High CO concentration caused by traffic emission and coal combustion [21] was the important impacting factor for the highest O3 concentration at the Sifang site. The high PM2.5 concentration was also attributed to the high concentrations of CO and SO2 from traffic emission and coal combustion at the Sifang site. In contrast, the environment was well protected at the tourist areas in the Shibei and Laoshan zones. According to the significant spatiotemporal heterogeneity of air pollutant distribution, urban functional zoning has a great impact on the distribution of air pollution in urban Qingdao.
Through the driving force analysis, we found SO2, NO2, and CO played the main roles in the dominant air pollutants, although the meteorological factors activated certain diverse driving forces. So we argue that pollutant emission reduction is a key for resolving urban air pollution issues. We propose the following recommendations based on the above conclusions. The spatiotemporal heterogeneity should be taken into account when landscape and functional zone are designed [27]. Construction dust should be strongly controlled with gauze in the Licang zone, especially in spring and summer in the Licang zone. The polluting enterprises should be updated, relocated, or shut down to reduce industrial emissions. The new thermal heating measures should be taken to replace coal combustion in winter [20,72], especially in the Sifang zone. Vehicle use should be limited according to the single and double number of the license plate number and weekday to reduce the PM2.5 concentration in the entire urban Qingdao as that in urban Beijing [29].
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to the editor and reviewers for their meaningful comments and helpful suggestions. This study was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFC1405004), the Open Research was funded by the Key Laboratory of Satellite Mapping Technology and Application, National Administration of Surveying (No. KLMSTA-201605), the Young Teachers’ Growth Plan in Shandong Province, and the Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (No. J14LH05). We are grateful to the data providers (Qingdao Environmental Monitoring Center Station and Qingdao Meteorological Observation) for data sources in the paper.
Author Contributions
Xiangwei Zhao, Qian Gao, Xingyuan Xiao, and Bo Ai conceived and designed the research. Xiangwei Zhao, Qian Gao, Meng Sun, and Yunchuan Xue performed the experiments and analyzed the data; Meng Sun and Yunchuan Xue contributed materials and analysis tools; Xiangwei Zhao, Qian Gao, and Ruijin Ma wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Unal, Y.S.; Toros, H.; Deniz, A.; Incecik, S. Influence of meteorological factors and emission sources on spatial and temporal variations of PM10 concentrations in Istanbul metropolitan area. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5504–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, L.; Lacressonnière, G.; Gauss, M.; Engardt, M.; Andersson, C.; Josse, B.; Marécal, V.; Nyiri, A.; Sobolowski, S.; Siour, G.; et al. The impact of meteorological forcings on gas phase air pollutants over Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 119, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, G.; Toscano, P.; Crisci, A.; Di Lonardo, S.; Tartaglia, M.; Vagnoli, C.; Zaldei, A.; Gioli, B. Influence of road traffic, residential heating and meteorological conditions on PM10 concentrations during air pollution critical episodes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 19027–19038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.N.; Wang, Y.H.; Park, T.W.; Deng, Y. Quantifying the relationship between extreme air pollution events and extreme weather events. Atmos. Res. 2017, 188, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Xue, J.J.; Zhang, J.Z. Analysis of Spatial-temporal Distribution Characteristics and Main Cause of Air Pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in 2014. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 39, 34–42, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bao, C.Z.; Chai, P.F.; Lin, H.B.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ye, Z.H.; Gu, M.J.; Lu, H.C.; Shen, P.; Jin, M.J.; Wang, J.B.; et al. Association of PM2.5 pollution with the pattern of human activity: A case study of a developed city in Eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 66, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.Y.; Jia, H.L. Particulate matter and gaseous pollution in three megacities over China: Situation and implication. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 476–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.G.; Gu, J.; Wang, H.W.; Yao, T.; Wu, Z.Z. Uncovering the culprits of air pollution: Evidence from China’s economic sectors and regional heterogeneities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.; Yardley, J. As China Roars, Pollution Reaches Deadly Extremes. The New York Times, 26 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, R.; Galinato, G.I.; Fiscal, A.I. spending and the environment: Theory and empirics. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2011, 62, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.L.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.Z. Multifractal behavior of an air pollutant time series and the relevance to the predictability. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, L.; Luo, R. Spatiotemporal variations of PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations between 31 Chinese cities and their relationships with SO2, NO2, CO and O3. Particuology 2015, 20, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Chen, H.P. Understanding the recent trend of haze pollution in eastern China: Roles of climate change. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4205–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Fang, C.L. Spatial-temporal characteristics and determinants of PM2.5 in the Bohai Rim Urban Agglomeration. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.Y.; Yan, D.Y.; Xu, S.H.; Huang, M.L.; Wang, X.X.; Xie, S.D. Characteristics and source distribution of air pollution in winter in Qingdao, eastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, E.R.; Zhang, T.T.; Hu, H. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Air Pollution in Chinese Cities. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, S.; Luo, B.; Zhai, C. Characteristics and origins of carbon aceousaerosol in the Sichuan Basin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ni, Z.W.; Ni, L.P. Multifractal detrended cross-correlation analysis between PM2.5 and meteorological factors. Physica A 2015, 438, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Dai, S.; Ye, X.Y. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of industrial pollution in China. China Econ. Rev. 2016, 40, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qian, J.; Ou, C.Q.; Zhou, Y.X.; Guo, C.; Guo, Y. Spatial and temporal analysis of Air Pollution Index and its timescale-dependent relationship with meteorological factors in Guangzhou, China, 2001–2011. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 190, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Yao, E.J.; Yang, Y. Impact analysis of traffic-related air pollution based on real-time traffic and basic meteorological information. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 183, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.J.; Cao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.Z.; Hong, T.; Fan, H.L. Spatial and temporal characteristics of air quality and air pollutants in 2013 in Beijing. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 23, 13996–14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Gong, D.Y.; Quan, W.J.; Zhao, X.J.; Ma, Z.Q.; Kim, S.J. Evolution of surface O3 and PM2.5 concentrations and their relationships with meteorological conditions over the last decade in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 108, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.H.; Li, C.L.; Si, Y.L. A detrended cross-correlation analysis of meteorological and API data in Nanjing, China. Physica A 2015, 419, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.F.; Li, X.; Wang, C. PM2.5 Spatiotemporal Variations and the Relationship with Meteorological Factors during 2013–2014 in Beijing, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobedo, F.J.; Nowak, D.J. Spatial heterogeneity and air pollution removal by an urban forest. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 90, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Huang, Z.J.; Ye, X.Y. Spatial heterogeneity of economic development and industrial pollution in urban China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nami, P.; Jahanbakhsh, P.; Fathalipour, A. The Role and Heterogeneity of Visual Pollution on the Quality of Urban Landscape Using GIS; Case Study: Historical Garden in City of Maraqeh. Open J. Geol. 2016, 6, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, X.F.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.Y. Impact of emission control on PM2.5 and the chemical composition change in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei during the APEC summit 2014, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 4509–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Q.L.; Zhao, H.J.; Wang, L.; Tao, R. Variations in PM10, PM2.5 and PM1.0 in an Urban Area of the Sichuan Basin and Their Relation to Meteorological Factors. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, Y.G.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, H.L. Spatial and temporal variability of PM2.5 and PM10 over the North China Plain and the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Ying, Q.; Hu, J.L.; Zhang, H.L. Spatial and temporal variations of six criteria air pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities in China during 2013–2014. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Cui, L.L.; Li, J.L.; Zhao, A.; Fu, H.B.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.W.; Kong, L.D.; Chen, J.M. Spatial and temporal variation of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants in China during 2014–2016. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 161, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.J.; Qiao, Z.; Xu, X.L. Characteristics of particulate matter (PM10) and its relationship with meteorological factors during 2001-2012 in Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batterman, S.; Xu, L.Z.; Chen, F.; Chen, F.; Zhong, X.F. Characteristics of PM2.5 concentrations across Beijing during 2013–2015. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 145, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Wang, S.S.; Li, Y.; Gong, H.; Han, J.Y.; Wu, Z.L.; Yao, S.L.; Zhang, X.M.; Tang, X.J.; Jiang, B.Q. Seasonal variations and source apportionment of atmospheric PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a mixed multi-function area of Hangzhou, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16195–16205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Zhou, X.Y.; Singh, R.P.; Wu, Y.Z.; Ye, Y.M.; Wu, C.F. The Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollutants and Their Relationship with Land-Use Patterns in Hangzhou City, China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.Y.; Chen, W.H.; Dai, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.M.; He, K.B. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in Guangzhou combining observation data analysis and chemical transport model simulation. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 116, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Christakos, G. Spatiotemporal Characterization of Ambient PM2.5 Concentrations in Shandong Province (China). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13431–13438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.Y.; Zhao, C.S.; Ran, L.; Deng, Z.Z.; Liu, P.F.; Ma, N.; Lin, W.L.; Xu, X.B.; Yan, P.; He, X.; et al. Characteristics of pollutants and their correlation to meteorological conditions at a suburban site in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4353–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.Z.; Wang, Z.F.; Lin, W.L.; Xu, X.B.; Li, J.; Ji, D.S.; Ma, Z.Q. Air pollution over the North China Plain and its implication of regional transport: A new sight from the observed evidences. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.D.; Zhou, X.H.; Wang, L.P.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.Z.; Wang, W.X. PM2.5 Characteristics in Qingdao and across Coastal Cities in China. Atmosphere 2016, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Wang, X.T.; Nelson, P.; Li, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, Y.H.; Lang, J.L.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, X.R. Ship emission inventory and its impact on the PM2.5 air pollution in Qingdao Port, North China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.C.; Qu, J.H.; Yang, G.S. On-road measurements of pollutant concentration profiles inside Yangkou tunnel, Qingdao, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 39, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection. Technical Regulation on Ambient Air Quality Index; HJ633-2102; Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, February 2012.
- Vargha, A.; Delaney, H.D. The Kruskal-Wallis test and stochastic homogeneity. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 1998, 23, 170–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruxton, G.D.; Beauchamp, G. Some suggestions about appropriate use of the Kruskal–Wallis test. Anim. Behav. 2008, 76, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertagova, E.; Ostertag, O.; Kovac, J. Methodology and Application of the Kruskal-Wallis Test. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 611, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, D.W. An efficient alternative to the Wilcoxon signed-ranks test for paired nonnormal data. J. Gen. Psychol. 1996, 123, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.M.; Hesamian, G. A generalization of the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and its applications. Stat. Pap. 2013, 54, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, I.K. An algorithm for computing the exact distribution of the Wilcoxon signed-rank statistic. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 2017, 46, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredricks, G.A.; Nelsen, R.B. On the relationship between Spearman’s rho and Kendall’s tau for pairs of continuous random variables. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2007, 137, 2143–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genest, C.; Rémillard, B.; Beaudoin, D. Goodness-of-fit tests for copulas: A review and a power study. Insurance 2009, 44, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudt, A. Tail risk, systemic risk and Copulas. Casualty Actuar. Soc. Forum 2010, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Pourkhanali, A.; Kim, J.M.; Tafakori, L. Measuring systemic risk using vine–copula. Econ. Model. 2016, 53, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.W.; Gao, Q.; Yue, Y.J.; Duan, L.; Pan, S. A System Analysis on Steppe Sustainability and Its Driving Forces—A Case Study in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, K.J.; Rigobon, R. No contagion, only interdependence: Measuring stock market comovements. J. Financ. 2002, 57, 2223–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, G.; Michele, C.D. On the Use of Copulas in Hydrology: Theory and Practice. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2007, 12, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchak, A.; Bardossy, A.; Habib, E. Conditional simulation of remotely sensed rainfall data using a non–Gaussian v–transformed copula. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musafer, G.N.; Thompson, M.H.; Kozan, E. Copula–based spatial modelling of geometallurgical variables. In Proceedings of the Second AUSIMM International Geometallurgy Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 30 September–2 October 2013; pp. 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, B.; Meissner, D.; Lisniak, D. Predictive Uncertainty Estimation of Hydrological Multi–Model Ensembles Using Pair–Copula Construction. Water 2016, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, F.; Tercan, A.E. Coal resource estimation using Gaussian copula. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 175, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Goyal, P. Forecasting of air quality in Delhi using principal component regression technique. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2011, 2, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Guo, L.N.; Ma, Y.; Yu, S.B. Relationship between air quality and meteorological conditions from 2006 to 2012 in Qingdao. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2015, 31, 37–43, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ji, D.; Hsu, S.; Gao, X. Spatial-temporal variations in surface ozone in Northern China as observed during 2009–2010 and possible implications for future air quality control strategies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2757–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Xu, X.F.; Xu, H.H. Comparison analysis of variation characteristics of SO2, NOx, O3 and PM2.5 between rural and urban areas, Beijing. Environmentalscienc 2008, 29, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Zang, L.; Chen, J.Y.; Xu, D.; Yao, D.F.; Zhao, M.R. Characteristics of ambient ozone (O3) pollution and health risks in Zhejiang Province. Environ. Sci Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27436–27444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.R.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.M.; Saunders, S.M.; Lam, S.H.M.; Jiang, F.; Wang, T.J.; Ding, A.J.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, K.F. On the relationship between ozone and its precursors in the Pearl River Delta: application of an observation-based model (OBM). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.S.; Zhang, F.Y.; Shi, Y.; Pilot, E.; Lin, L.Y.; Fu, Y.B.; Krafft, T.; Wang, W.Y. Spatiotemporal characteristics and health effects of air pollutants in Shenzhen. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 7, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.X.; Cao, J.J.; Zhang, L.M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.J.; Han, Y.M.; Zhu, C.S.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Liu, S.X. Day-night differences and seasonal variations of chemical species in PM10 over Xi’an, northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 3697–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.L.; Chen, X.Q.; Chen, J.S.; Zhang, F.W.; He, C.; Du, K.; Wang, Y. Characterization of PM10 atmospheric aerosol at urban and urban background sites in Fuzhou city, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.R.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.L.; Wu, F.K.; Gao, W.K.; Wang, Y.S. Seasonal and diel variation in particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) at an urban site of Beijing: Analyses from a 9-year study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).