Improving PM2.5 Air Quality Model Forecasts in China Using a Bias-Correction Framework
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. PM2.5 Model Forecasts
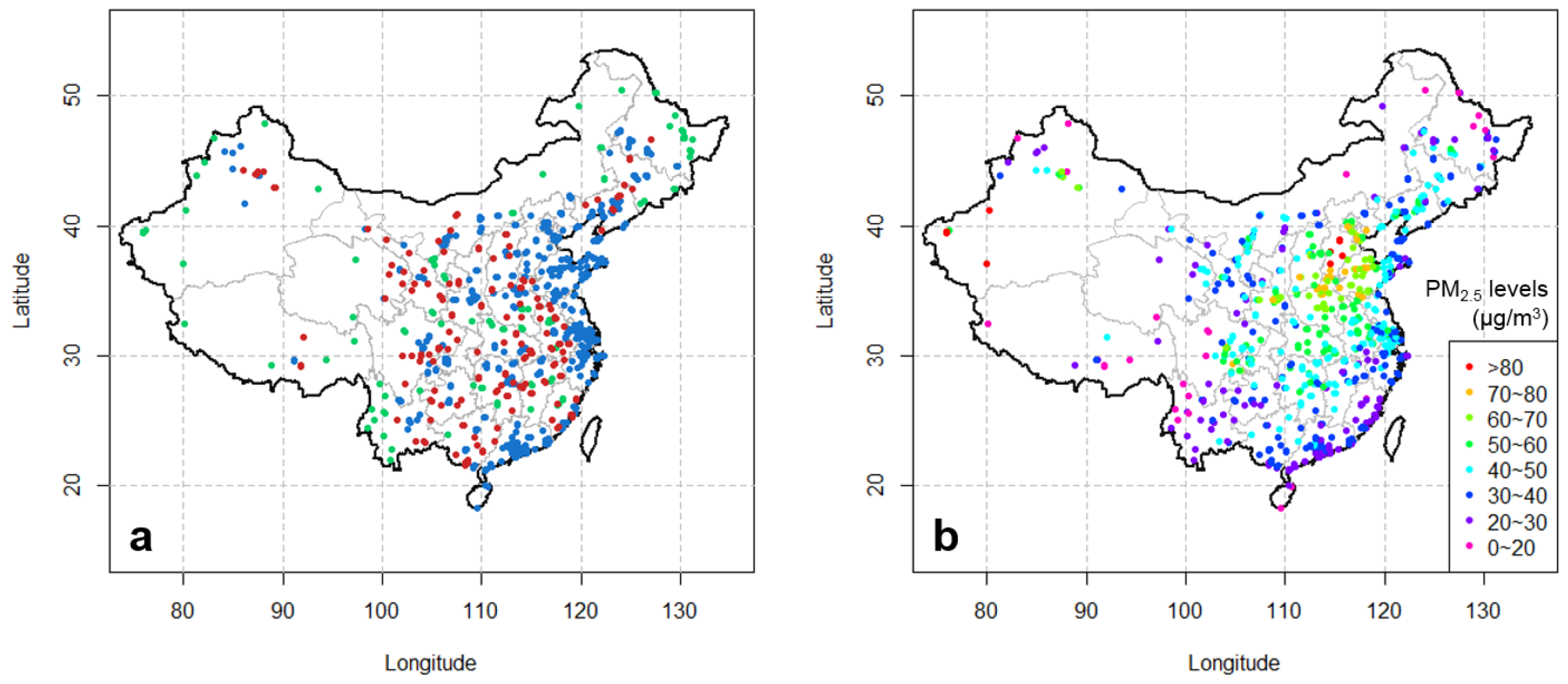
2.2. PM2.5 Observations
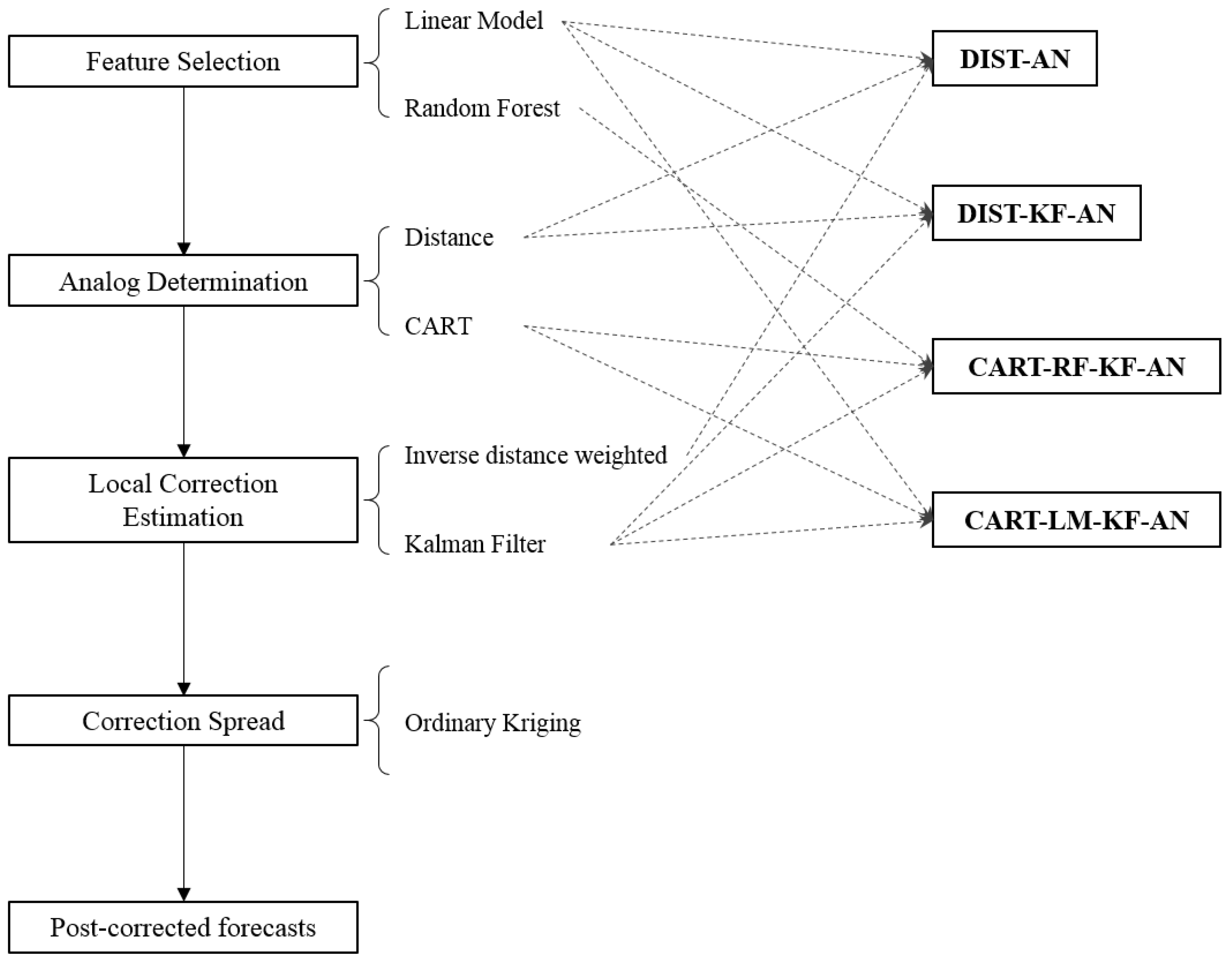
2.3. Bias-Correction Framework
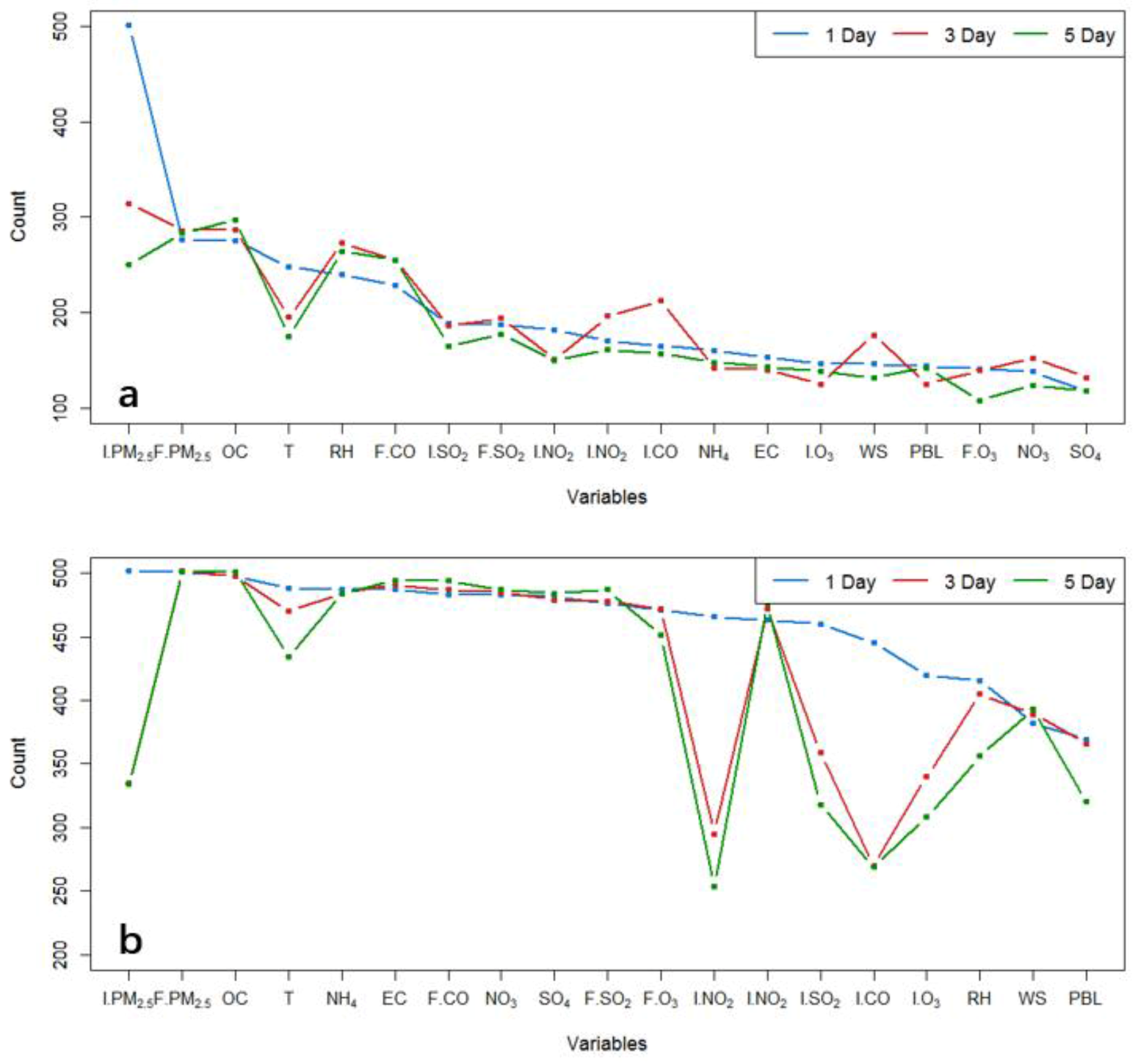
2.3.1. Feature Selection
2.3.2. Analog Determination
2.3.3. Local Correction Estimation
2.3.4. Correction Spread
2.4. Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Performance in Estimating Local Corrections
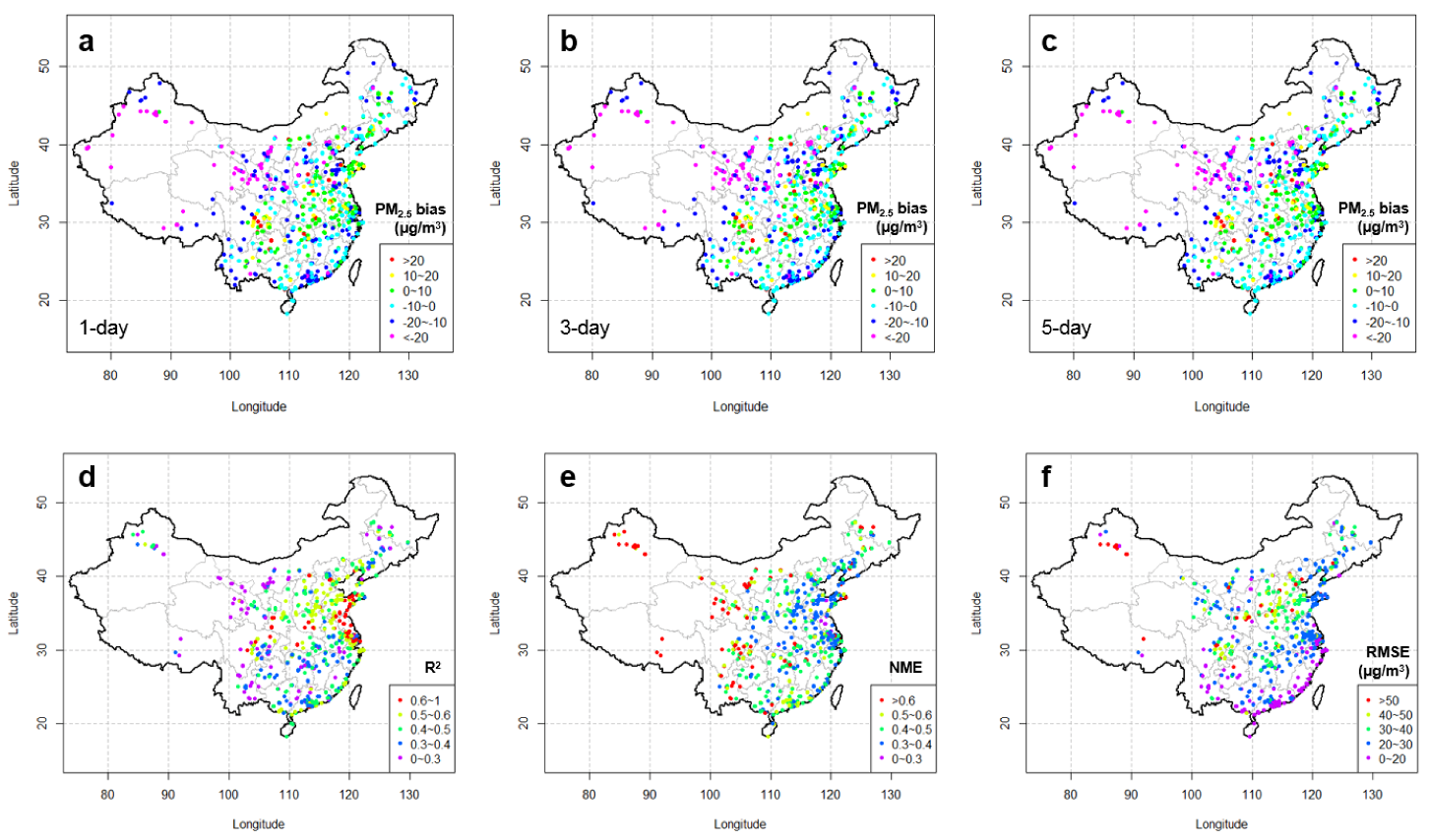
3.2. Performance of the Final Product
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.L.; Cao, F. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in China at a city level. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Wang, Q.g.; Li, H.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qian, X. Mortality effects assessment of ambient PM2.5 pollution in the 74 leading cities of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Saide, P.E.; Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pagowski, M.; Guttikunda, S.K.; Carmichael, G.R. Estimates of health impacts and radiative forcing in winter haze in eastern China through constraints of surface PM2.5 predictions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Odman, M.T.; Chang, M.E.; Russell, A.G. Operational forecasting of source impacts for dynamic air quality management. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 116, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bocquet, M.; Mallet, V.; Seigneur, C.; Baklanov, A. Real-time air quality forecasting, part I: History, techniques, and current status. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 632–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Cobourn, W.G.; Bai, Y. Development of nonlinear empirical models to forecast daily PM2.5 and ozone levels in three large Chinese cities. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, P.; Salini, G. PM2.5 forecasting in a large city: Comparison of three methods. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8219–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, B.; Kang, D.; Mathur, R.; Yu, S.; Schere, K. An operational evaluation of the Eta–CMAQ air quality forecast model. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4894–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bocquet, M.; Mallet, V.; Seigneur, C.; Baklanov, A. Real-time air quality forecasting, part II: State of the science, current research needs, and future prospects. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 656–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.; Schere, K.L. Review of the governing equations, computational algorithms, and other components of the models-3 community multiscale air quality (CMAQ) modeling system. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckeen, S.; Grell, G.; Peckham, S.; Wilczak, J.; Djalalova, I.; Hsie, E.Y.; Frost, G.; Peischl, J.; Schwarz, J.; Spackman, R. An evaluation of real-time air quality forecasts and their urban emissions over eastern texas during the summer of 2006 second texas air quality study field study. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.; Lamb, B.; Frei, C.; Wilson, R.; Bowman, C.; Figueroa-Kaminsky, C.; Otterson, S.; Boyer, M.; Mass, C.; Albright, M.; et al. A numerical daily air quality forecast system for the Pacific Northwest. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otte, T.L.; Pouliot, G.; Pleim, J.E.; Young, J.O.; Schere, K.L.; Wong, D.C.; Lee, P.C.S.; Tsidulko, M.; McQueen, J.T.; Davidson, P.; et al. Linking the Eta model with the community multiscale air quality (CMAQ) modeling system to build a national air quality forecasting system. Weather Forecast. 2005, 20, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.Q.; Xu, J.M.; Xie, Y.; Chang, L.Y.; Gao, W.; Gu, Y.X.; Zhou, J. Numerical air quality forecasting over eastern China: An operational application of WRF-Chem. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 153, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkowski, F.S.; Roselle, S.J. Models-3 community multiscale air quality (CMAQ) model aerosol component 1. Model description. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djalalova, I.; Delle Monache, L.; Wilczak, J. PM2.5 analog forecast and kalman filter post-processing for the community multiscale air quality (CMAQ) model. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 108, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Monache, L.; Nipen, T.; Deng, X.X.; Zhou, Y.M.; Stull, R. Ozone ensemble forecasts: 2. A kalman filter predictor bias correction. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D05308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Mathur, R.; Rao, S.T. Implementation of real-time bias-corrected o-3 and PM2.5 air quality forecast and their performance evaluations during 2008 over the continental united states. In Air Pollution Modeling and its Application XX; Steyn, D.G., Rao, S.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; p. 283. [Google Scholar]
- Djalalova, I.; Wilczak, J.; McKeen, S.; Grell, G.; Peckham, S.; Pagowski, M.; DelleMonache, L.; McQueen, J.; Tang, Y.; Lee, P.; et al. Ensemble and bias-correction techniques for air quality model forecasts of surface o-3 and PM2.5 during the texaqs-ii experiment of 2006. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, K.; Kumar, U.; Lauwaet, D.; Blyth, L.; Lefebvre, W. Kalman filter-based air quality forecast adjustment. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Monache, L.; Djalalova, I.; Wilczak, J. Analog-based postprocessing methods for air quality forecasting. In Air Pollution Modeling and its Application XXIII; Steyn, D.G., Rao, S.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 237–239. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.P.; McQueen, J.; Wilczak, J.; Djalalova, I.; Stajner, I.; Shafran, P.; Allured, D.; Lee, P.; Pan, L.; Tong, D.; et al. Improving NOAA NAQFC PM2.5 predictions with a bias correction approach. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Monache, L.; Nipen, T.; Liu, Y.; Roux, G.; Stull, R. Kalman filter and analog schemes to postprocess numerical weather predictions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 3554–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolman, B.K.; Reid, I.M. Bias correction and overall performance of a VHF spaced antenna boundary layer profiler for operational weather forecasting. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2014, 118, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckeen, S.; Wilczak, J.; Grell, G.; Djalalova, I.; Peckham, S.; Hsie, E.Y.; Gong, W.; Bouchet, V.; Menard, S.; Moffet, R. Assessment of an ensemble of seven real-time ozone forecasts over eastern north america during the summer of 2004. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 3003–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monache, L.D.; Grell, G.A.; Mckeen, S.; Wilczak, J.; Pagowski, M.O.; Peckham, S.; Stull, R.; Mchenry, J.; Mcqueen, J. A kalman-filter bias correction of ozone deterministic, ensemble-averaged, and probabilistic forecasts. Tellus 2006, 60b. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczak, J.; Mckeen, S.; Djalalova, I.; Grell, G.; Peckham, S.; Gong, W.; Bouchet, V.; Moffet, R.; Mchenry, J.; Mcqueen, J. Bias-corrected ensemble and probabilistic forecasts of surface ozone over eastern North America during the summer of 2004. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 111, 6443–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Mathur, R.; Rao, S.T. Real-time bias-adjusted O3 and PM2.5 air quality index forecasts and their performance evaluations over the continental united states. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, J.L.; Özkaynak, H. Simultaneous statistical bias correction of multiple PM2.5 species from a regional photochemical grid model. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, L.S.; Agnew, P.; Moseley, S.; Ordonez, C.; Savage, N.H.; Tilbee, M. Application of a statistical post-processing technique to a gridded, operational, air quality forecast. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silibello, C.; Bolignano, A.; Sozzi, R.; Gariazzo, C. Application of a chemical transport model and optimized data assimilation methods to improve air quality assessment. Air. Qual. Atmos. Health 2014, 7, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 2; No. NCAR/TN-468+ STR; Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology Division, National Center For Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2005.
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Fu, L.X.; He, K.B.; Wang, S.X.; Hao, J.M.; Chen, J.C.; Li, C.Y. The impact of transportation control measures on emission reductions during the 2008 olympic games in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Urban Air Quality Real-Time Publishing Platform. Available online: http://106.37.208.233:20035 (accessed on 14 January 2017).
- Malik, M.B. Applied linear regression. Technometrics 2005, 47, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.W.; Quirk, F.H.; Baveystock, C.M.; Littlejohns, P. A self-complete measure of health status for chronic airflow limitation. The st. George’s respiratory questionnaire. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992, 145, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Lin, C.J. Combining svms with various feature selection strategies. In Feature Extraction; Guyon, I., Nikravesh, M., Gunn, S., Zadeh, L.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 3, pp. 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; The R Team: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.; Stone, C.J. Classification and regression trees. Biometrics 1984, 40, 358. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Sun, D.; He, F.; Zhang, W.; Guan, X. Land use/cover classification with classification and regression tree applied to MODIS imagery. J. Appl. Sci. 2013, 13, 3070–3773. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Pourtaghi, Z.S.; Al-Katheeri, M.M. Landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest, boosted regression tree, classification and regression tree, and general linear models and comparison of their performance at Wadi Tayyah Basin, asir region, Saudi Arabia. Landslides 2016, 13, 839–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, M.; Nestler, I.; Huwe, B. Gis-based regionalization of soil profiles with classification and regression trees (CART). J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sci. 2002, 165, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’Ath, G.; Fabricius, K.E. Classification and regression trees: A powerful yet simple technique for the analysis of complex ecological data. Ecology 2000, 81, 3178–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Duin, R.P.W.; Mao, J. Statistical pattern recognition: A review. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 2000, 22, 4–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Mathur, R.; Rao, S.T.; Yu, S. Bias adjustment techniques for improving ozone air quality forecasts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 113, 2036–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. Kriging: A method of interpolation for geographical information systems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1990, 4, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Mathur, R.; Rao, S.T. Assessment of bias-adjusted PM2.5 air quality forecasts over the continental united states during 2007. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2009, 2, 309–320. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, B.N.; Lamsal, L.N.; Thompson, A.M.; Yoshida, Y.; Lu, Z.F.; Streets, D.G.; Hurwitz, M.M.; Pickering, K.E. A space-based, high-resolution view of notable changes in urban NOX pollution around the world (2005–2014). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 976–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; McLinden, C.A.; Li, C.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Marchenko, S.V.; Swartz, W.H.; Bucsela, E.J.; Joiner, J.; Duncan, B.N.; et al. Aura omi observations of regional SO2 and NO2 pollution changes from 2005 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4605–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.J.; Hao, J.M.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.M.; Hu, J.N.; Walsh, M.P.; Wallington, T.J.; Zhang, K.M.; Stevanovic, S. On-road vehicle emissions and their control in China: A review and outlook. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
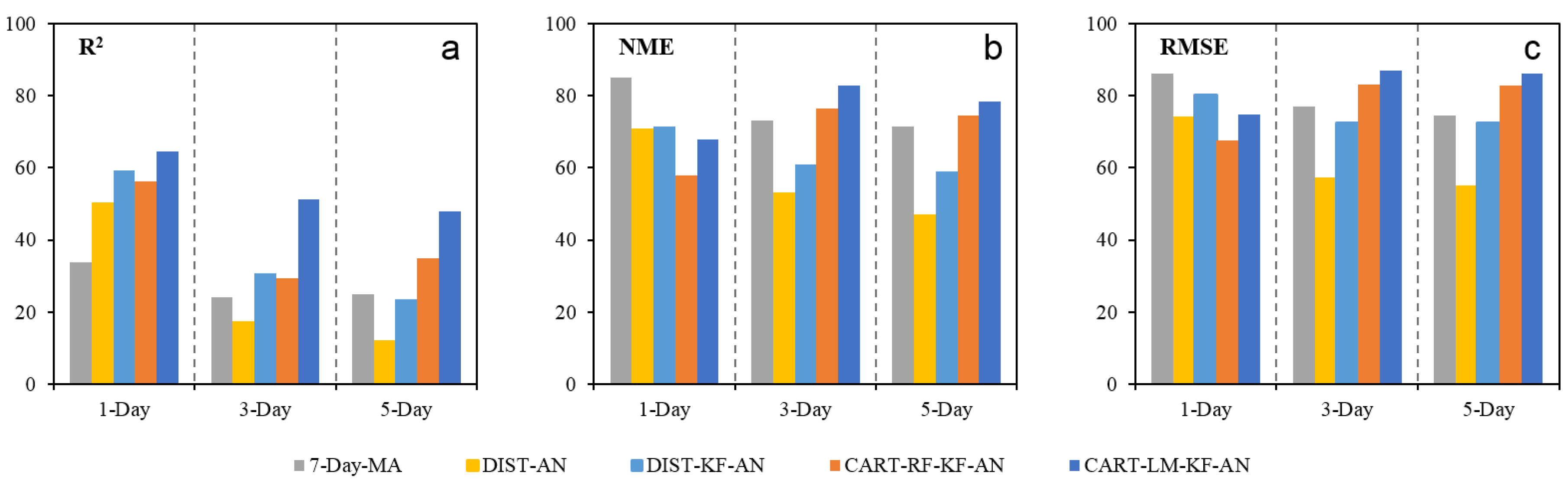
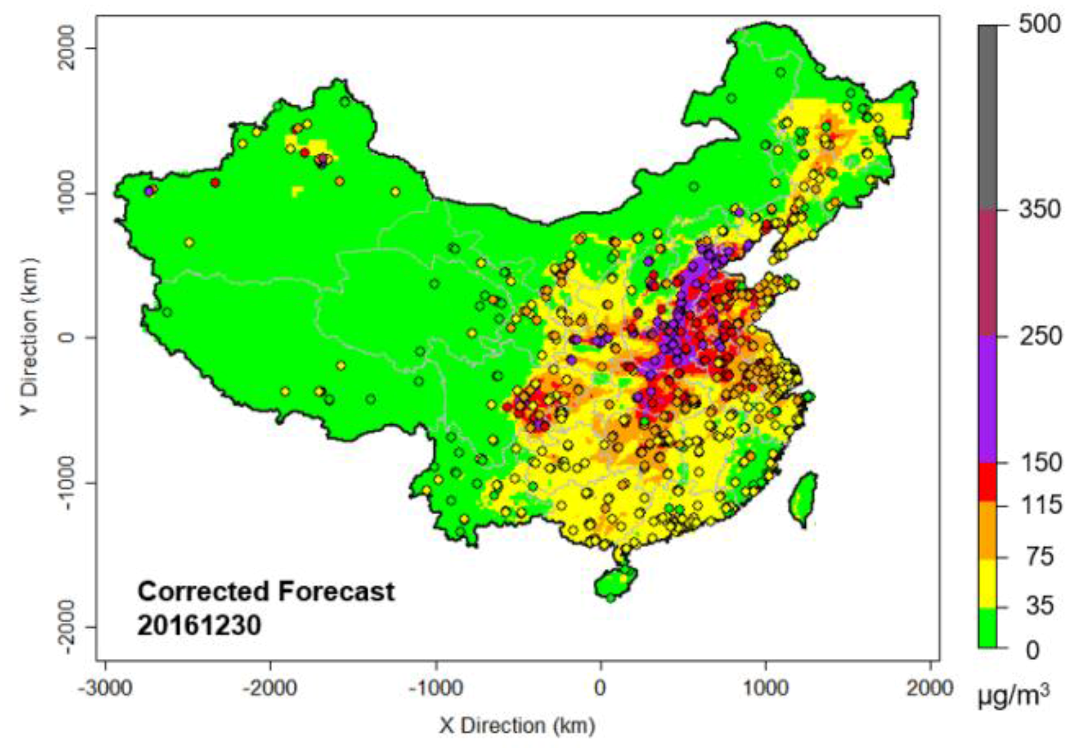
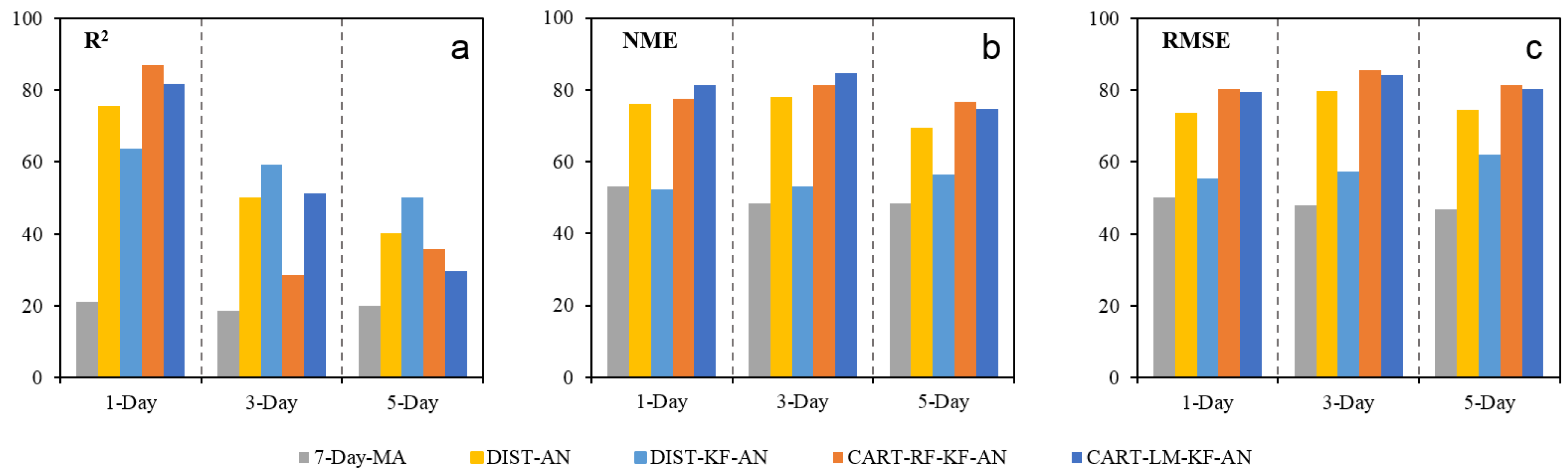
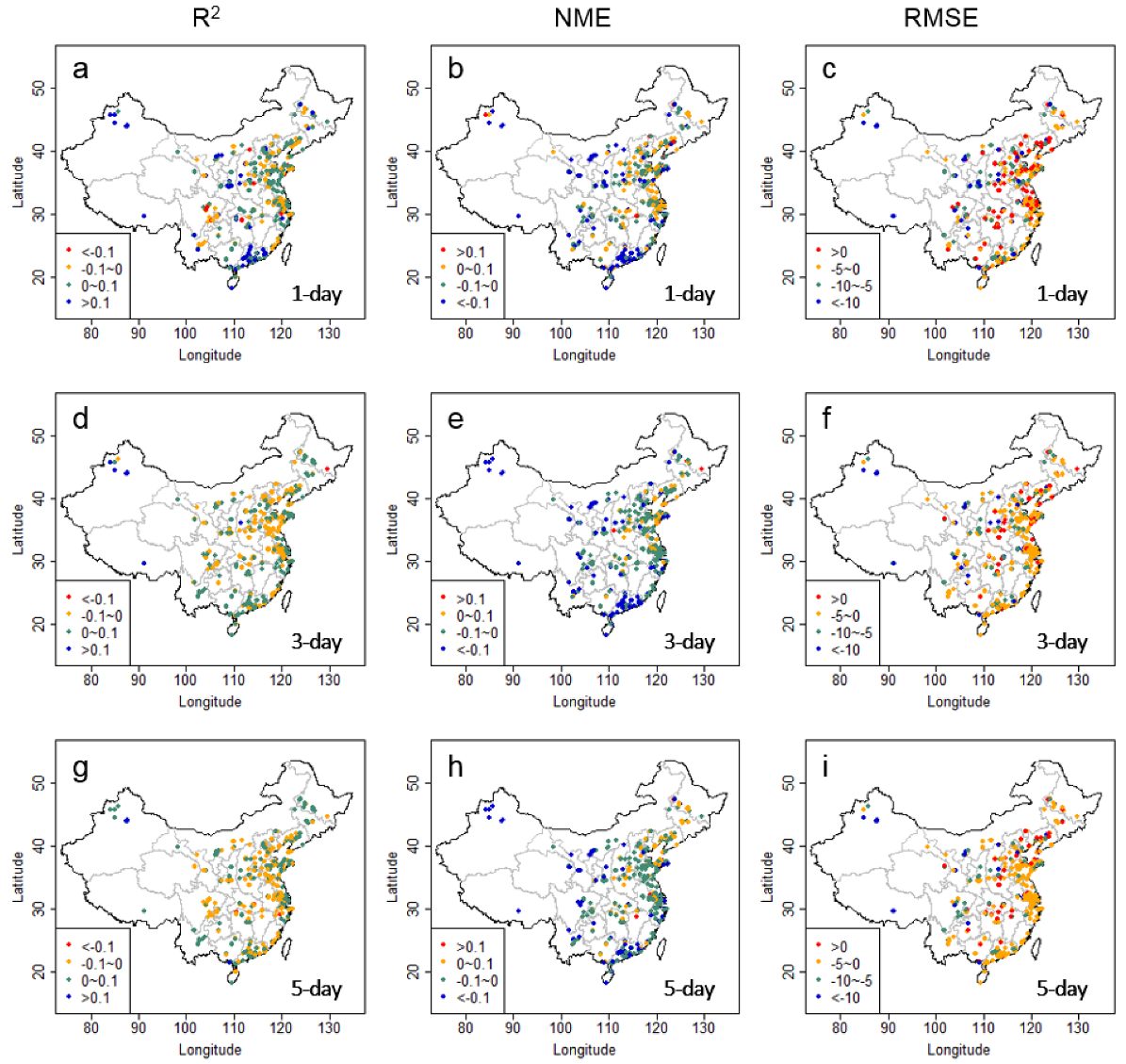
| Lead Time | Metrics | Raw | 7-Day-MA | DIST-AN | DIST-KF-AN | CART-RF-KF-AN | CART-LM-KF-AN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 day | R2 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.49 |
| NME | 0.49 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.41 | |
| RMSE | 32.2 | 27.0 | 27.0 | 27.2 | 29.7 | 27.5 | |
| 3 day | R2 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.39 |
| NME | 0.50 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.43 | |
| RMSE | 31.4 | 27.8 | 29.0 | 28.0 | 28.2 | 27.5 | |
| 5 day | R2 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.34 |
| NME | 0.51 | 0.46 | 0.49 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.45 | |
| RMSE | 32.4 | 29.1 | 30.3 | 28.8 | 29.5 | 28.7 |
| Lead Time | Metrics | 7-Day-MA | DIST-AN | DIST-KF-AN | CART-RF-KF-AN | CART-LM-KF-AN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 day | R2 | −2.7 | 0.3 | 3.1 | 3.5 | 6.1 |
| NME | −19.3 | −18.3 | −17.3 | −7.4 | −14.7 | |
| RMSE | −16.0 | −16.1 | −15.6 | −7.8 | −14.6 | |
| 3 day | R2 | −8.3 | −13.3 | −4.0 | −1.5 | 0.7 |
| NME | −13.6 | −7.3 | −10.0 | −12.6 | −14.4 | |
| RMSE | −11.6 | −7.5 | −10.9 | −10.1 | −12.5 | |
| 5 day | R2 | −8.9 | −17.7 | −7.0 | −2.0 | −0.3 |
| NME | −11.2 | −4.5 | −8.9 | −10.7 | −12.2 | |
| RMSE | −10.0 | −6.3 | −11.1 | −9.0 | −11.3 |
| Lead Time | Metrics | Raw | 7-Day-MA | DIST-AN | DIST-KF-AN | CART-RF-KF-AN | CART-LM-KF-AN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 day | R2 | 0.38 | 0.33 | 0.40 | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.43 |
| NME | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.41 | |
| RMSE | 28.4 | 27.7 | 25.6 | 27.4 | 24.5 | 24.3 | |
| 3 day | R2 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| NME | 0.49 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.44 | |
| RMSE | 27.7 | 26.8 | 25.3 | 26.6 | 25.8 | 25.6 | |
| 5 day | R2 | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| NME | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.46 | |
| RMSE | 28.3 | 27.6 | 26.1 | 27.1 | 26.5 | 26.5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y. Improving PM2.5 Air Quality Model Forecasts in China Using a Bias-Correction Framework. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8080147
Lyu B, Zhang Y, Hu Y. Improving PM2.5 Air Quality Model Forecasts in China Using a Bias-Correction Framework. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(8):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8080147
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Baolei, Yuzhong Zhang, and Yongtao Hu. 2017. "Improving PM2.5 Air Quality Model Forecasts in China Using a Bias-Correction Framework" Atmosphere 8, no. 8: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8080147
APA StyleLyu, B., Zhang, Y., & Hu, Y. (2017). Improving PM2.5 Air Quality Model Forecasts in China Using a Bias-Correction Framework. Atmosphere, 8(8), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8080147




