Extreme Sea Ice Loss over the Arctic: An Analysis Based on Anomalous Moisture Transport
Abstract
:1. Introduction
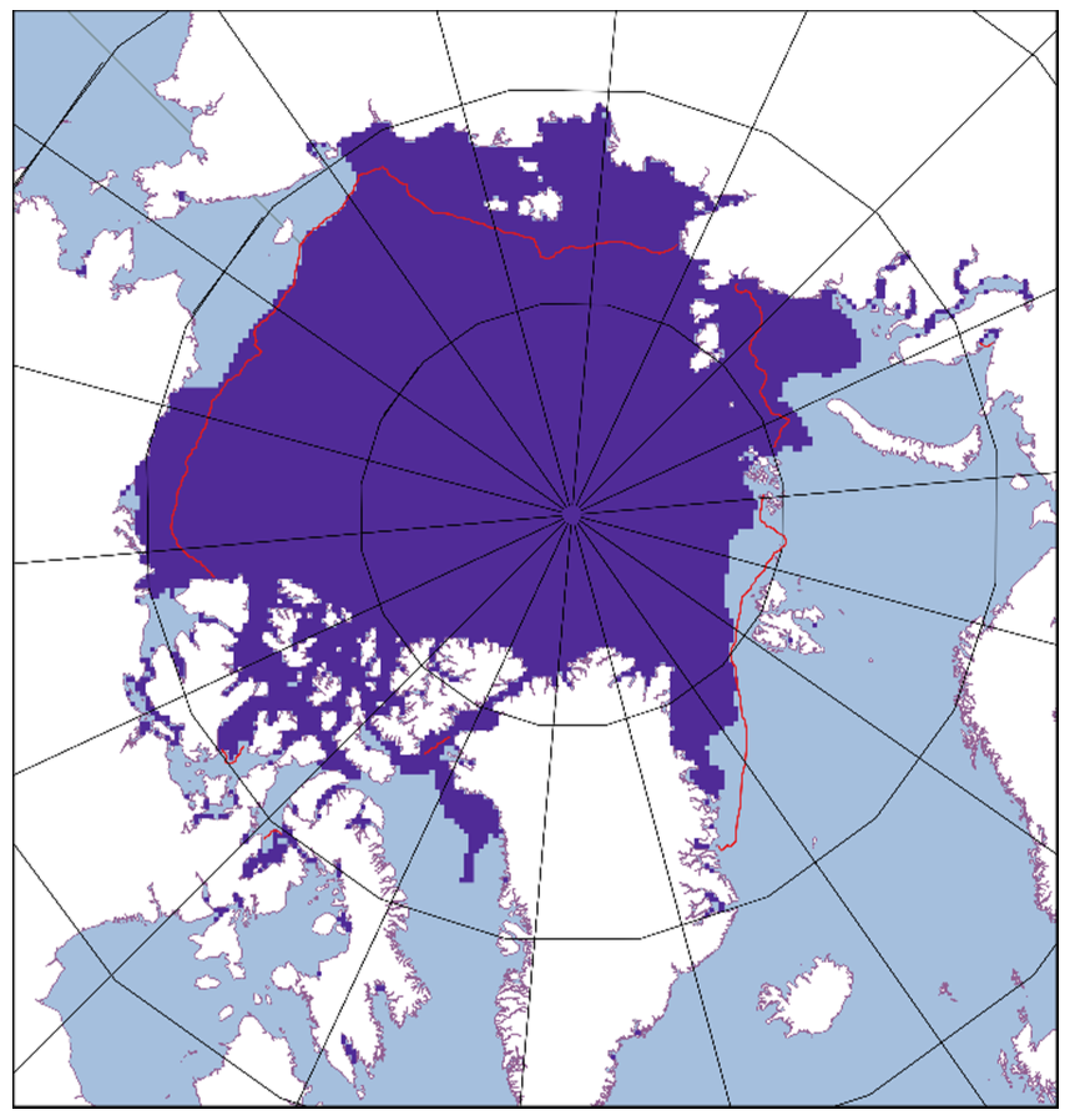
2. Experiments
3. Results
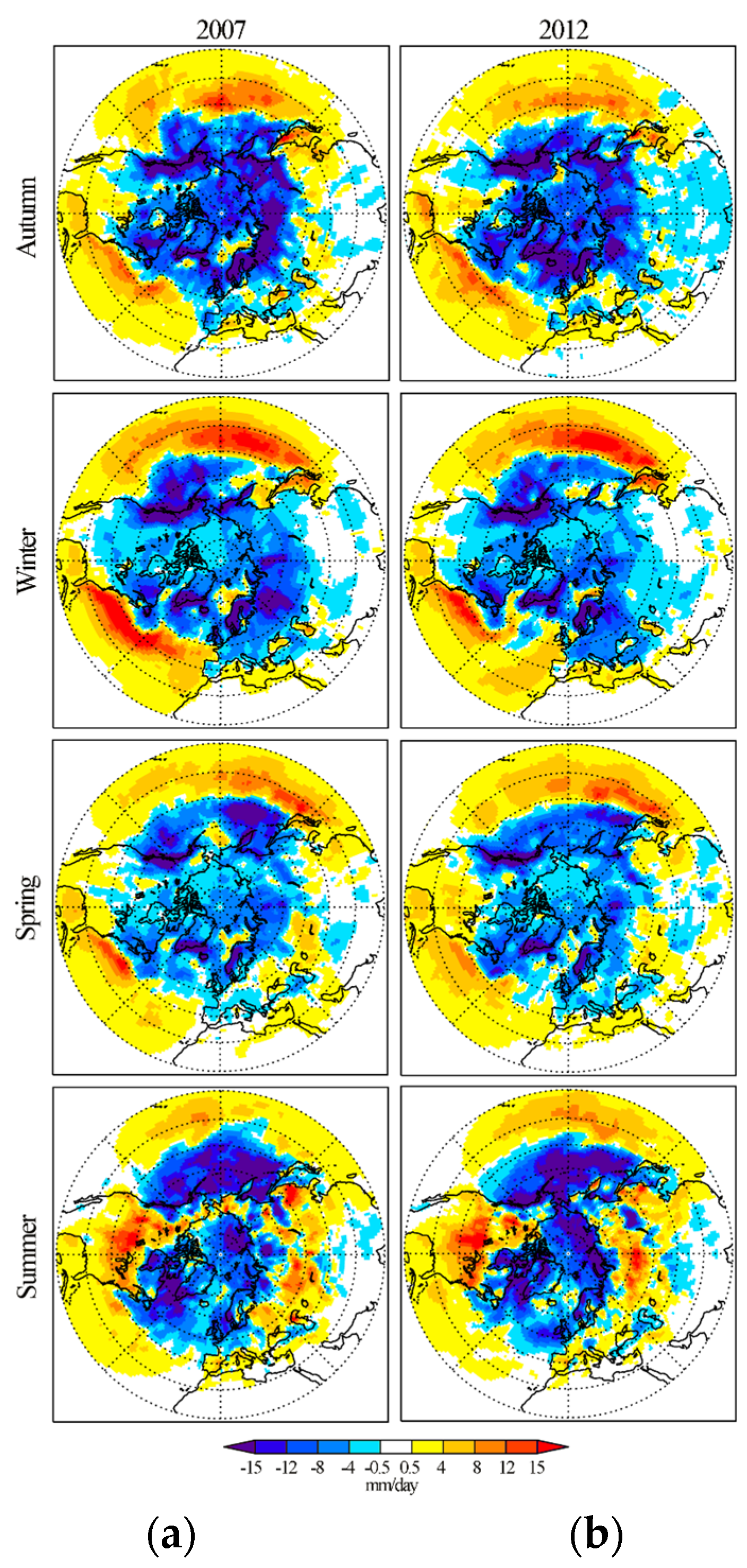
3.1. Changes in Moisture Sources
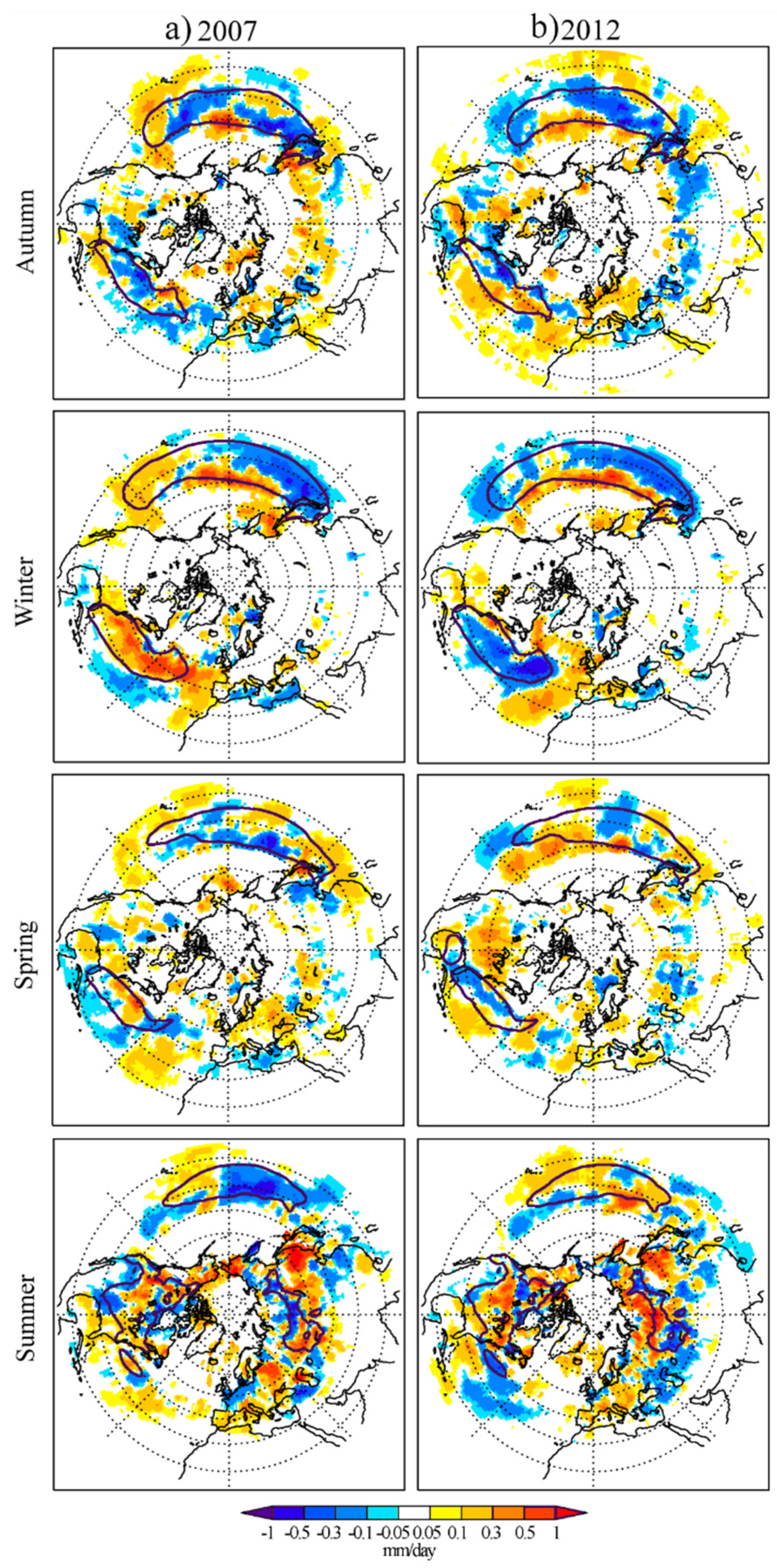
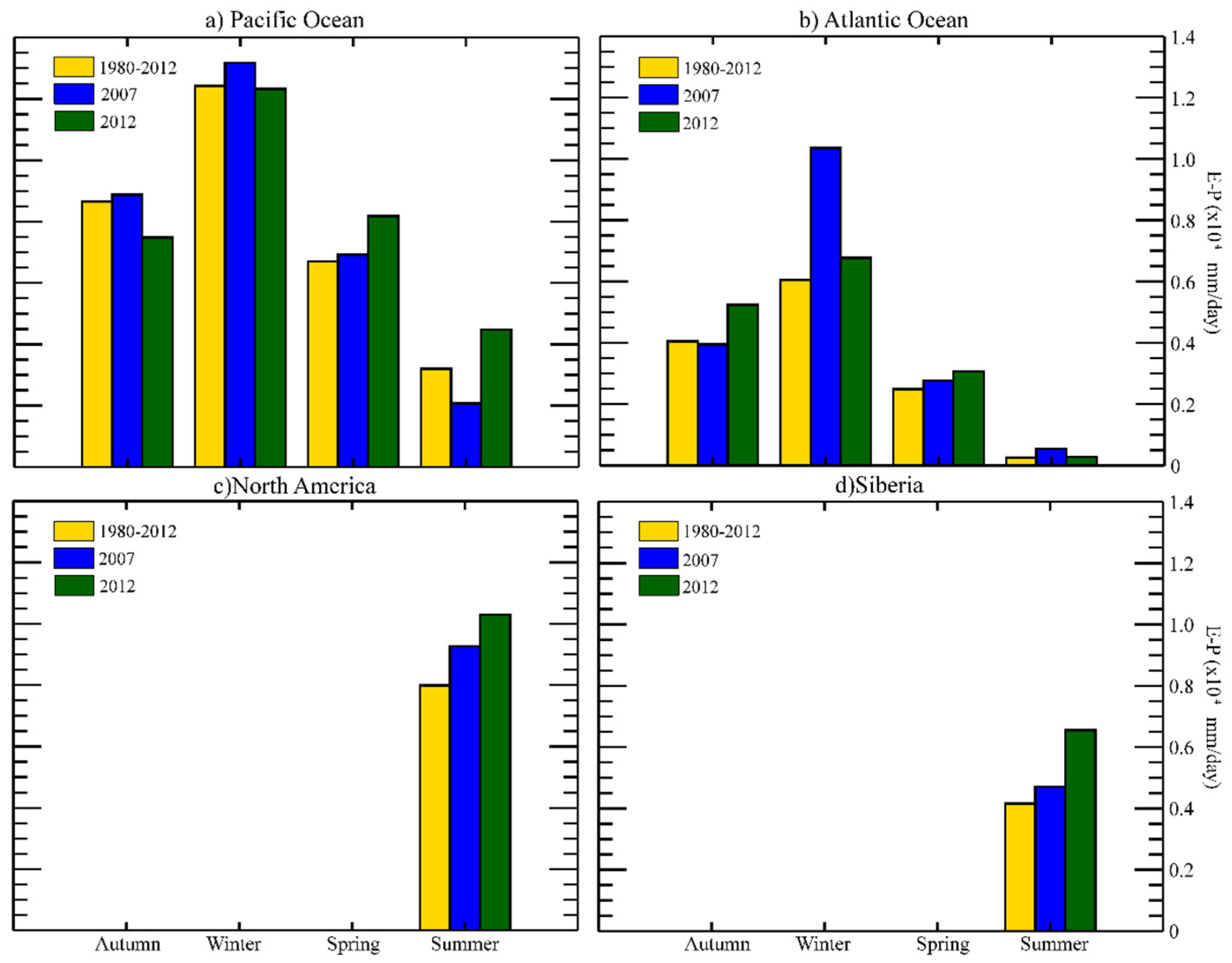
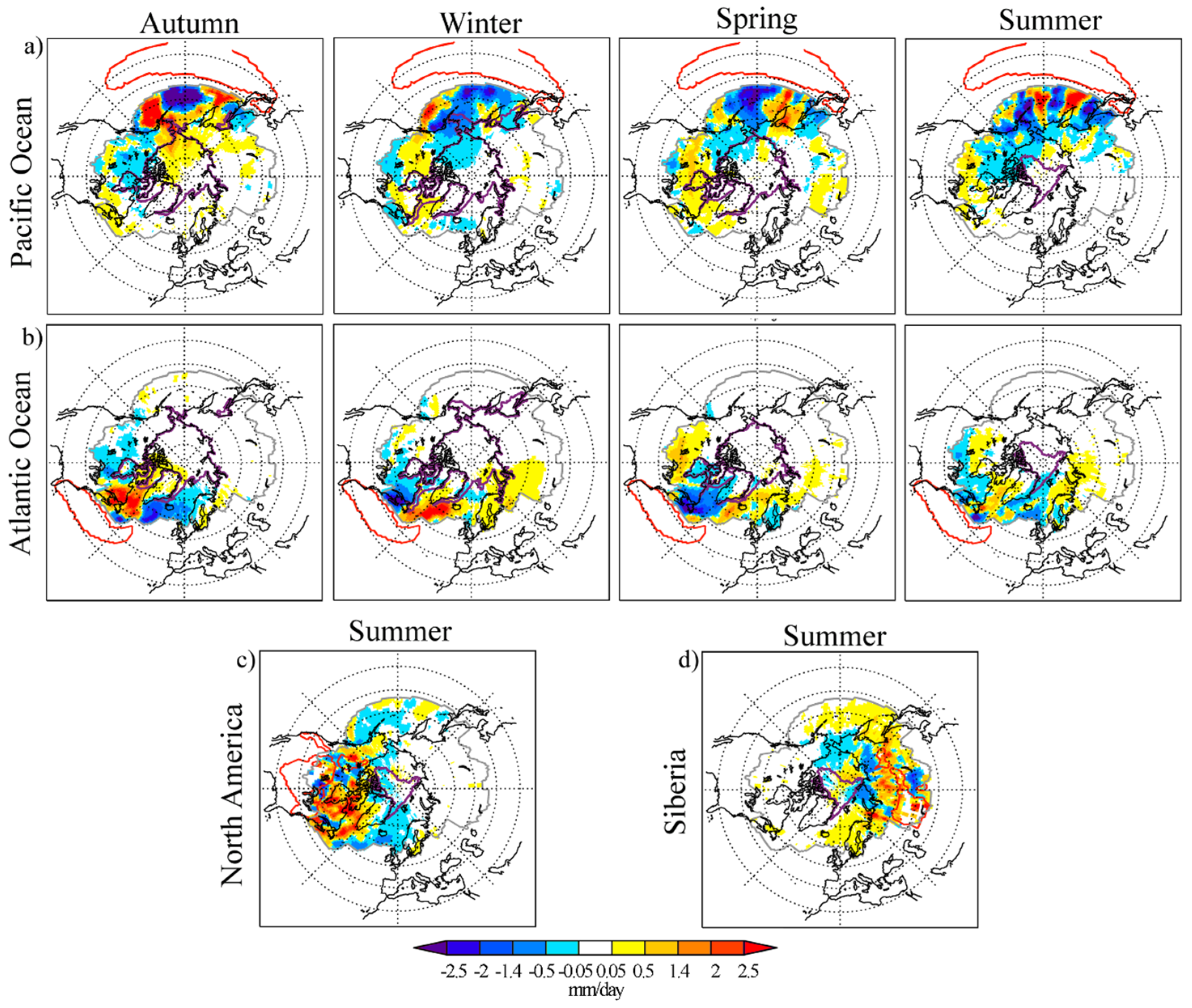
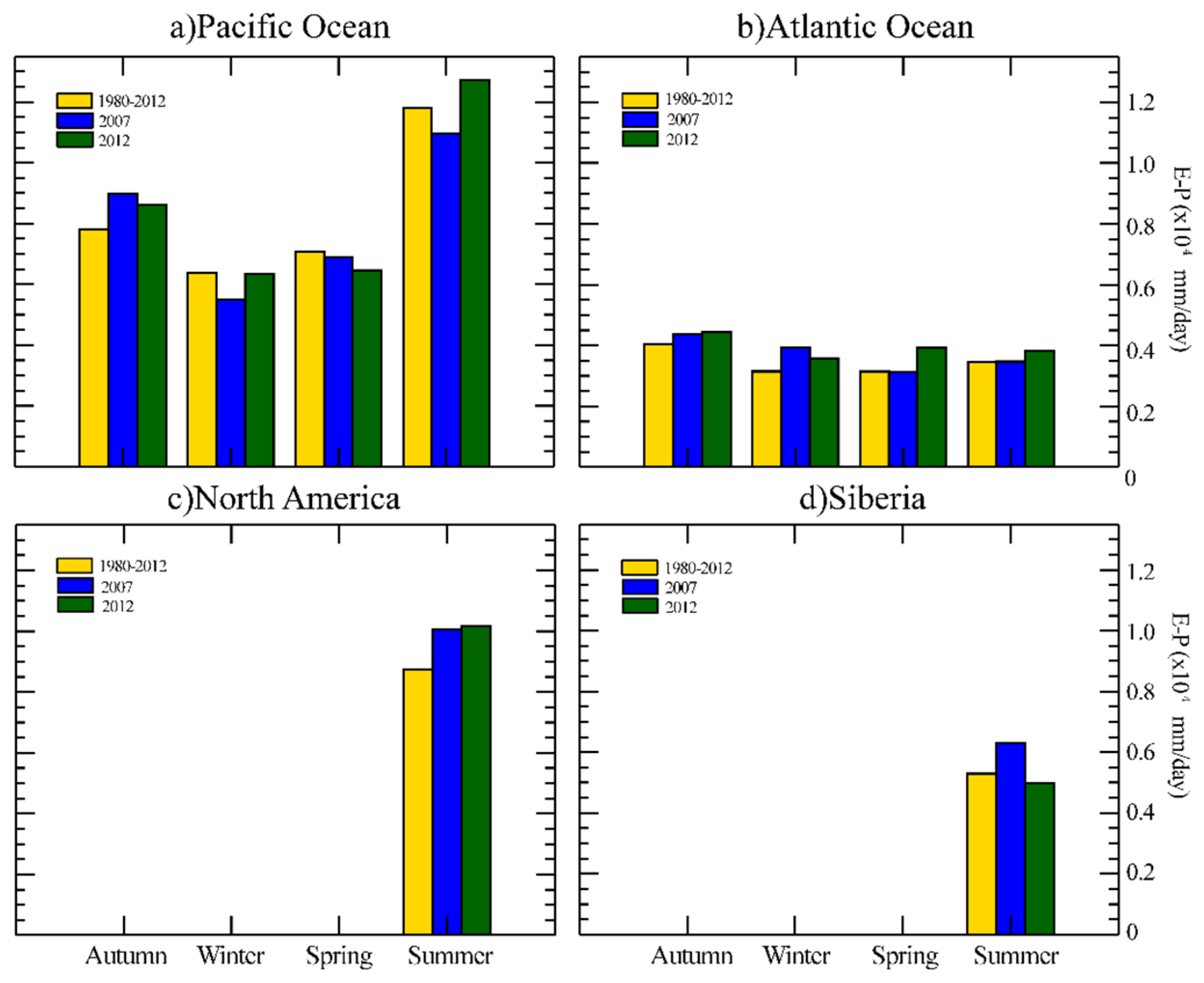
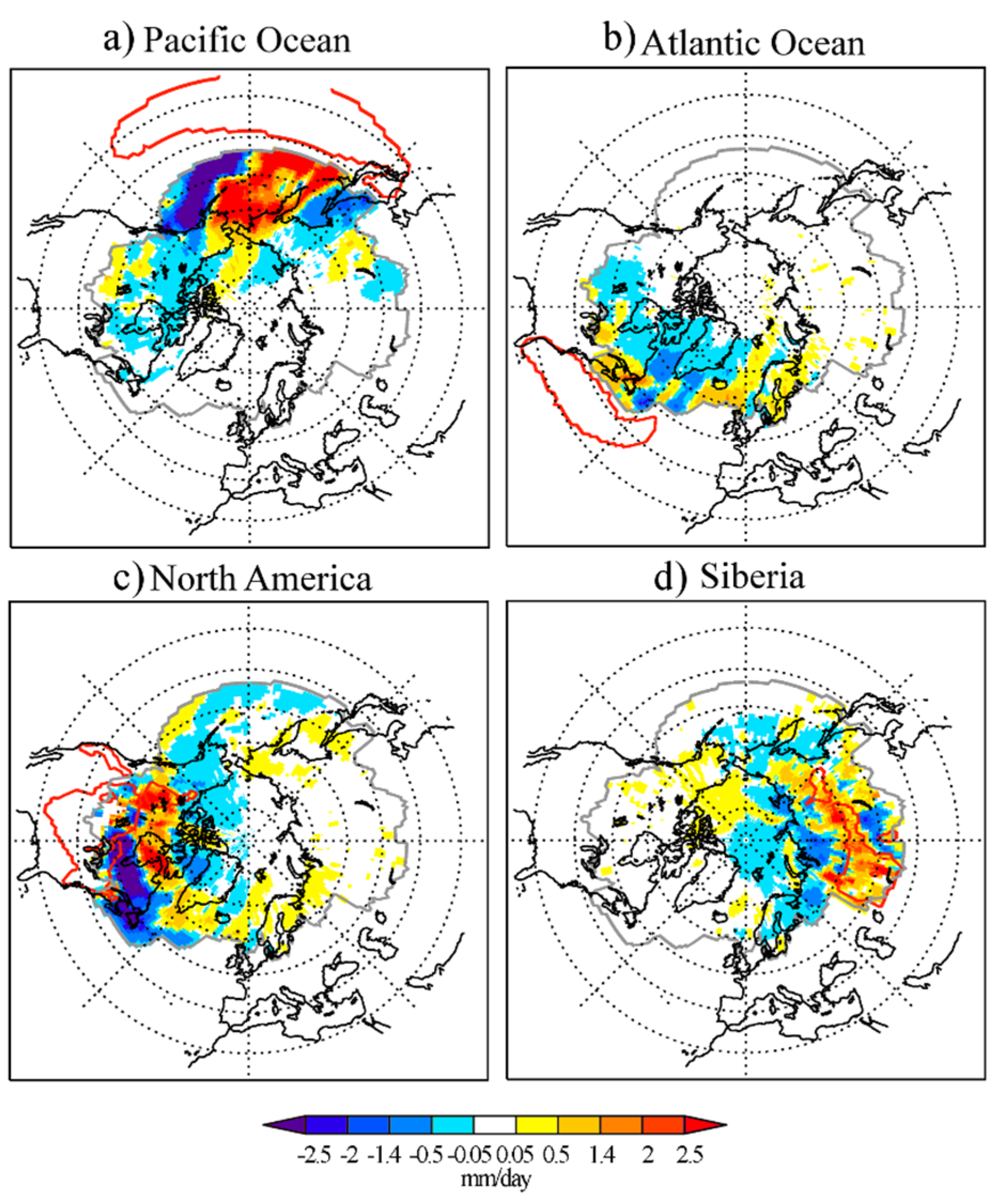
3.2. Anomalous Moisture Contribution from Each Moisture Source
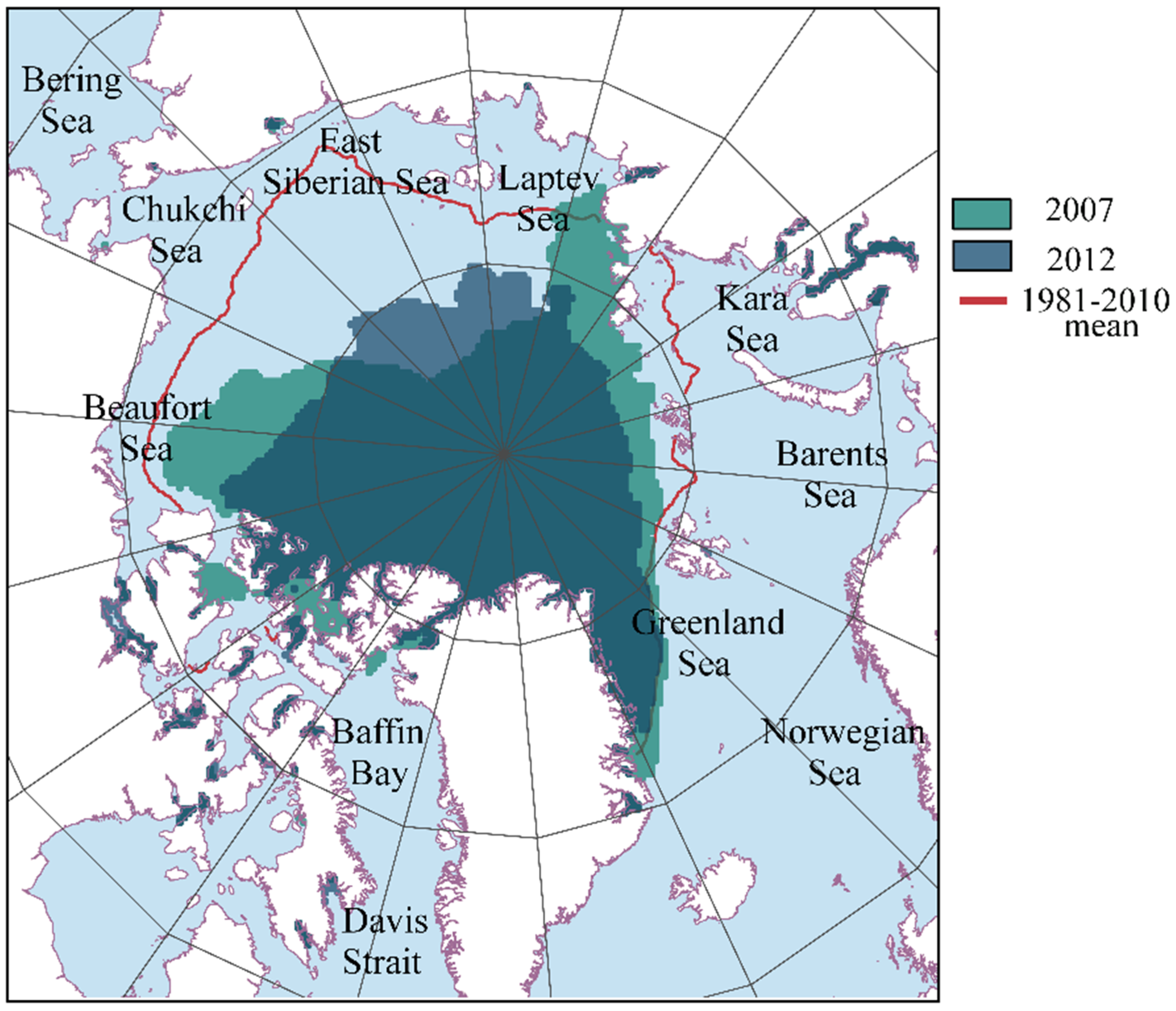
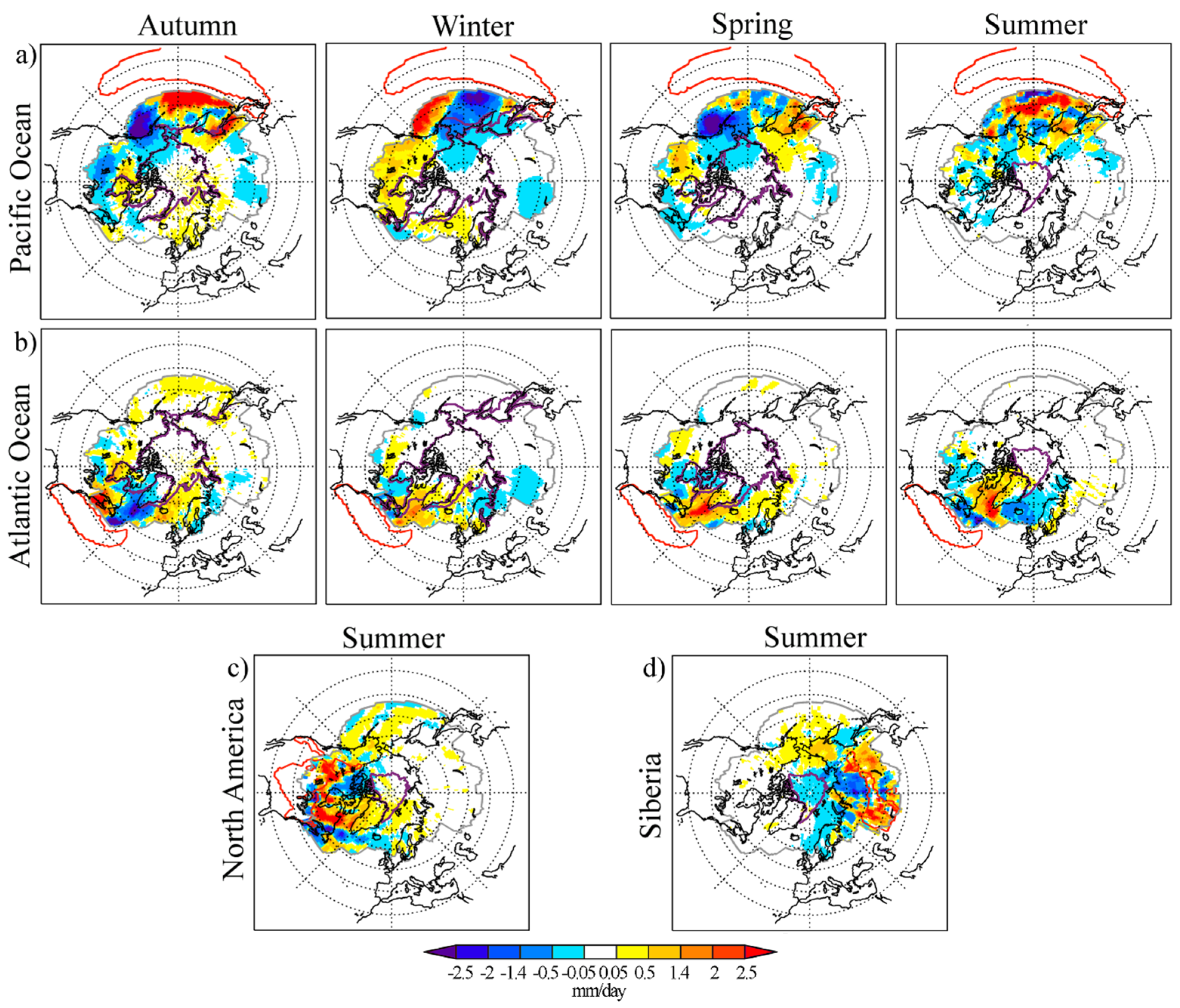
3.3. Contrasting Analysis: Maximum September Sea Ice Extent
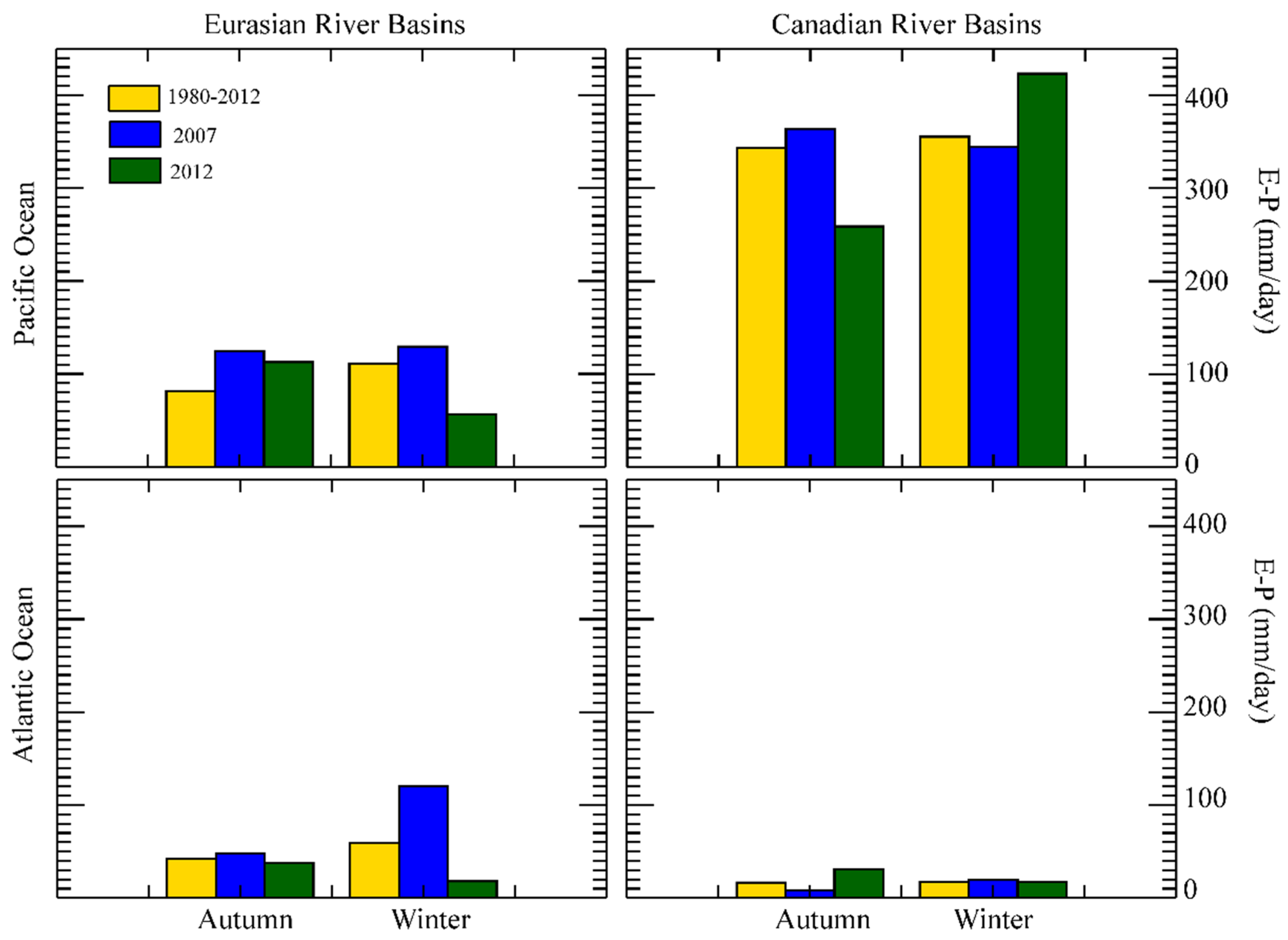
3.4. River Basins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stroeve, J.C.; Kattsov, V.; Barrett, A.; Serreze, M.; Pavlova, T.; Holland, M.; Meier, W.N. Trends in Arctic sea ice extent from CMIP5, CMIP3, and observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L16502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.; Holland, M.M.; Meier, W.; Scambos, T.; Serreze, M. Arctic sea ice decline: Faster than forecast. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L09501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C.; Parkinson, C.L.; Gersten, R.; Stock, L. Accelerated decline in the Arctic sea-ice cover. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L01703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, C.L.; DiGirolamo, N.E. New visualizations highlight new information on the contrasting Arctic and Antarctic sea-ice trends since the late 1970s. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 183, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.M.; Bitz, C.M.; Tremblay, B. Future abrupt reductions in the summer Arctic sea ice. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L23503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.M.; Stott, P.A.; Cresswell, D.J.; Rayner, N.A.; Gordon, C.; Sexton, D.M.H. Recent and future changes in Arctic sea ice simulated by the HadCM3 AOGCM. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxon, S.W.; Giles, K.A.; Ridout, A.L.; Wingham, D.J.; Willatt, R.; Cullen, R.; Kwok, R.; Schweiger, A.; Zhang, J.; Haas, C.; et al. CryoSat-2 estimates of Arctic sea ice thickness and volume. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Parkinson, C.L. Arctic sea ice variability and trends, 1979–2010. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, W.N.; Gerland, S.; Granskog, M.A.; Key, J.R.; Haas, C.; Hovelsrud, G.K.; Kovacs, K.; Makshtas, A.; Michel, C.; Perovich, D.; et al. Sea ice. In AMAP (2011) Snow, Water, Ice and Permafrost in the Arctic (SWIPA): Climate Change and the Cryosphere; Arctic Monitoring and Assesment Programme (AMAP): Oslo, Norway, 2011; Chapter 9. [Google Scholar]
- Serreze, M.C.; Holland, M.M.; Stroeve, J. Perspectives on the Arctic’s Shrinking Sea-Ice Cover. Science 2007, 315, 1533–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloersen, P.; Campbell, W.J.; Cavalieri, D.J.; Comiso, J.C.; Parkinson, C.L.; Zwalley, H.J. Satellite passive microwave observations and analysis of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice, 1978–1987. Ann. Glaciol. 1993, 17, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson, C.L.; Cavalieri, D.J.; Gloersen, P.; Zwally, H.J.; Comiso, J.C. Arctic sea ice extents, areas, and trends, 1978–1996. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 20837–20856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, C.L. Global Sea Ice Coverage from Satellite Data: Annual Cycle and 35-Yr Trends. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 9377–9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.; Serreze, M.C.; Holland, M.M.; Kay, J.E.; Malik, J.; Barrett, A.P. The Arctic’s rapidly shrinking sea ice cover: A research synthesis. Clim. Chang. 2012, 110, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screen, J.A.; Simmonds, I. The central role of diminishing sea ice in recent Arctic temperature amplification. Nature 2010, 464, 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopec, B.G.; Feng, X.; Michel, F.A.; Posmentier, E.S. Influence of sea ice on Arctic precipitation. Proc. Natl. Aacd. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Francis, J.A. Cold winter extremes in northern continents linked to Arctic sea ice loss. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 014036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screen, J.A. Influence of Arctic sea ice on European summer precipitation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihma, T. Effects of Arctic Sea Ice Decline on Weather and Climate: A Review. Surv. Geophys. 2014, 35, 1175–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetterer, F.; Knowles, K.; Meier, W.; Savoie, M. Sea Ice Index; National Snow and Ice Data Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Polyakov, I.V.; Walsh, J.E.; Kwok, R. Recent changes in the Arctic multiyear sea ice coverage and its likely causes. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 96, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, S.V.; Rigor, I.G.; Perovich, D.K.; Clemente-Colón, P.; Weatherly, J.W.; Neumann, G. Rapid reduction of Arctic perennial sea ice. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L19504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslanik, J.; Fowler, C.; Stroeve, J.; Drobot, S.; Zwally, J.; Yi, D.; Emery, W. A younger, thinner Arctic ice cover: Increased potential for rapid, extensive sea-ice loss. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L24501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummelin, A.; Ilicak, M.; Li, C.; Smedsrud, L.H. Consequences of future increased Arctic runoff on Arctic Ocean stratification, circulation, and sea ice cover. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 617–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauch, D.; Hölemann, J.A.; Nikulina, A.; Wegner, C.; Janout, M.A.; Timokhov, L.A.; Kassens, H. Correlation of river water and local sea-ice melting on the Laptev Sea shelf (Siberian Arctic). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, S.V.; Hall, D.K.; Rigor, I.G.; Li, P.; Neumann, G. Effects of Mackenzie River discharge and bathymetry on sea ice in the Beaufort Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, I.; Keay, K. Extraordinary September Arctic sea ice reductions and their relationships with storm behavior over 1979–2008. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L19715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, M.; Hodges, K.I.; Atkinson, D.E.; Bader, J. Sea-ice anomalies in the Sea of Okhotsk and the relationship with storm tracks in the Northern Hemisphere during winter. Tellus A 2011, 63, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francis, J.A.; Hunter, E. New insight into the disappearing Arctic Sea ice. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union AGU 2006, 87, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.A.; Hunter, E. Changes in the fabric of the Arctic’s greenhouse blanket. Environ. Res. Lett. 2007, 2, 045011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortin, J.; Svensson, G.; Graversen, R.G.; Kapsch, M.L.; Stroeve, J.C.; Boisvert, L.N. Melt onset over Arctic sea ice controlled by atmospheric moisture transport. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 6636–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Polyakov, I.; Gerdes, R.; Inoue, J.; Wu, P. Enhanced poleward moisture transport and amplified northern high-latitude wetting trend. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Holmes, R.M.; McClelland, J.W.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Lammers, R.B.; Shiklomanov, A.I.; Shiklomanov, I.A.; Rahmstorf, S. Increasing river discharge to the Arctic Ocean. Science 2002, 98, 2171–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, J.W.; Déry, S.J.; Peterson, B.J.; Holmes, R.M.; Wood, E.F. A pan-arctic evaluation of changes in river discharge during the latter half of the 20th century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L06715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitefield, J.; Winsor, P.; McClelland, J.; Menemenlis, D. A new river discharge and river temperature climatology data set for the pan-Arctic region. Ocean Model. 2015, 88, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Dominguez, F.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Drumond, A.; Reason, C.; Taschetto, A.S.; Ramos, A.M.; Kumar, R.; Marengo, J. Major Mechanisms of Atmospheric Moisture Transport and Their Role in Extreme Precipitation Events. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2016, 41, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; James, P.A. A Lagrangian Analysis of the Atmospheric Branch of the Global Water Cycle. Part I: Method Description, Validation, and Demonstration for the August 2002 Flooding in Central Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 656–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; James, P.A. A Lagrangian Analysis of the Atmospheric Branch of the Global Water Cycle. Part II: Moisture Transports between Earth’s Ocean Basins and River Catchments. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirmeyer, P.A.; Brubaker, K.L. Characterization of the Global Hydrologic Cycle from a Back-Trajectory Analysis of Atmospheric Water Vapor. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R.; Drumond, A.; Castillo, R.; Trigo, R.M. Influence of the intensification of the major oceanic moisture sources on continental precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Stohl, A.; Trigo, R.M.; Domínguez, F.; Yoshimura, K.; Yu, L.; Drumond, A.; Durán-Quesada, A.M.; Nieto, R. Oceanic and Terrestrial Sources of Continental Precipitation. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; Cassano, J.; Döscher, R.; Hinzman, L.; Holland, M.; Mitsudera, H.; Sumi, A.; Walsh, J.E.; Alessa, L.; Alexeev, V.; et al. A Science Plan for Regional Arctic System Modeling: A Report to the National Science Foundation from the International Arctic Science Community; International Arctic Research Center (IARC): University of Alaska, Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Vicente, S.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I. Where does the Iberian Peninsula moisture come from? An answer based on a Largrangian approach. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Stohl, A. On the origin of continental precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numagati, A. Origin and recycling processes of precipitation water over the Eurasian continent: Experiments using an atmospheric general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 1957–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, M.; Nieto, R.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L. Moisture transport into the Arctic: Source-receptor relationships and the roles of atmospheric circulation and evaporation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsch, M.L.; Graversen, R.G.; Tjernström, M. Springtime atmospheric energy transport and the control of Arctic summer sea-ice extent. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Vázquez, M.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M. Atmospheric moisture transport: The bridge between ocean evaporation and Arctic ice melting. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2015, 6, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiklomanov, A.I.; Lammers, R.B. Record Russian river discharge in 2007 and the limits of analysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, C.L.; Comiso, J.C. On the 2012 record low Arctic sea ice cover: Combined impact of preconditioning and an August storm. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lindsay, R.; Schweiger, A.; Steele, M. The impact of an intense summer cyclone on 2012 Arctic sea ice retreat. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, I.; Rudeva, I. The great Arctic cyclone of August 2012. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L23709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorteberg, A.; Walsh, J.E. Seasonal cyclone variability at 70°N and its impact on moisture transport into the Arctic. Tellus A 2008, 60, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Walsh, J.E.; Zhang, J.; Bhatt, U.S.; Ikeda, M. Climatology and interannual variability of Arctic cyclone activity: 1948–2002. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2300–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisvert, L.N.; Petty, A.A.; Stroeve, J.C. The Impact of the Extreme Winter 2015/16 Arctic Cyclone on the Barents–Kara Seas. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 4279–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez, M.; Nieto, R.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L. Extreme Sea Ice Loss over the Arctic: An Analysis Based on Anomalous Moisture Transport. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8020032
Vázquez M, Nieto R, Drumond A, Gimeno L. Extreme Sea Ice Loss over the Arctic: An Analysis Based on Anomalous Moisture Transport. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(2):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8020032
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez, Marta, Raquel Nieto, Anita Drumond, and Luis Gimeno. 2017. "Extreme Sea Ice Loss over the Arctic: An Analysis Based on Anomalous Moisture Transport" Atmosphere 8, no. 2: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8020032
APA StyleVázquez, M., Nieto, R., Drumond, A., & Gimeno, L. (2017). Extreme Sea Ice Loss over the Arctic: An Analysis Based on Anomalous Moisture Transport. Atmosphere, 8(2), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8020032








