Numerical Study on the Generation and Transport of Spume Droplets in Wind over Breaking Waves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Methods and Simulation Cases
2.1. Fluid Flow Solver
2.2. Lagrangian Particle-Tracking Method
2.3. Generation of Spume Droplets
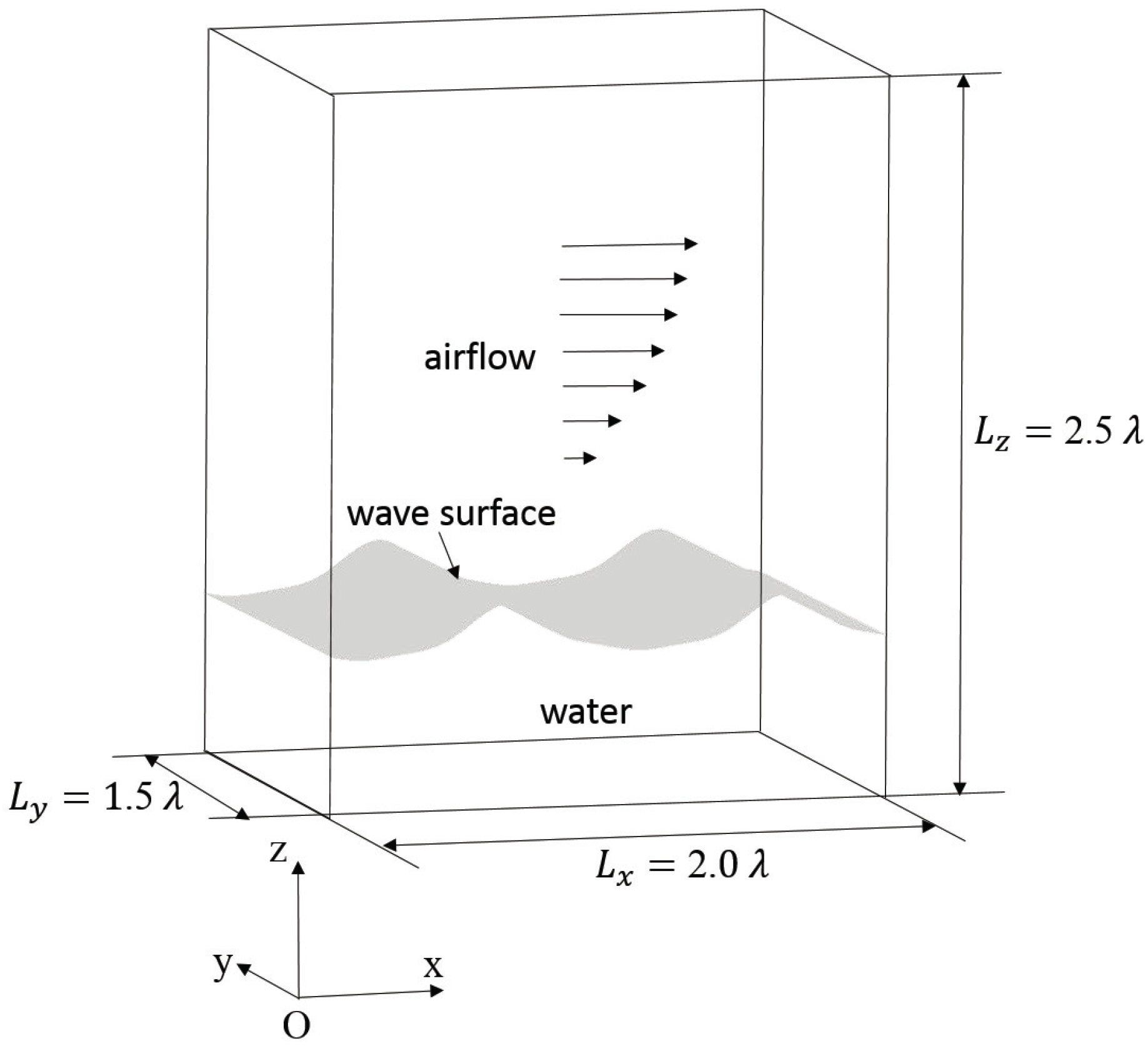
2.4. Simulation Cases and Parameters
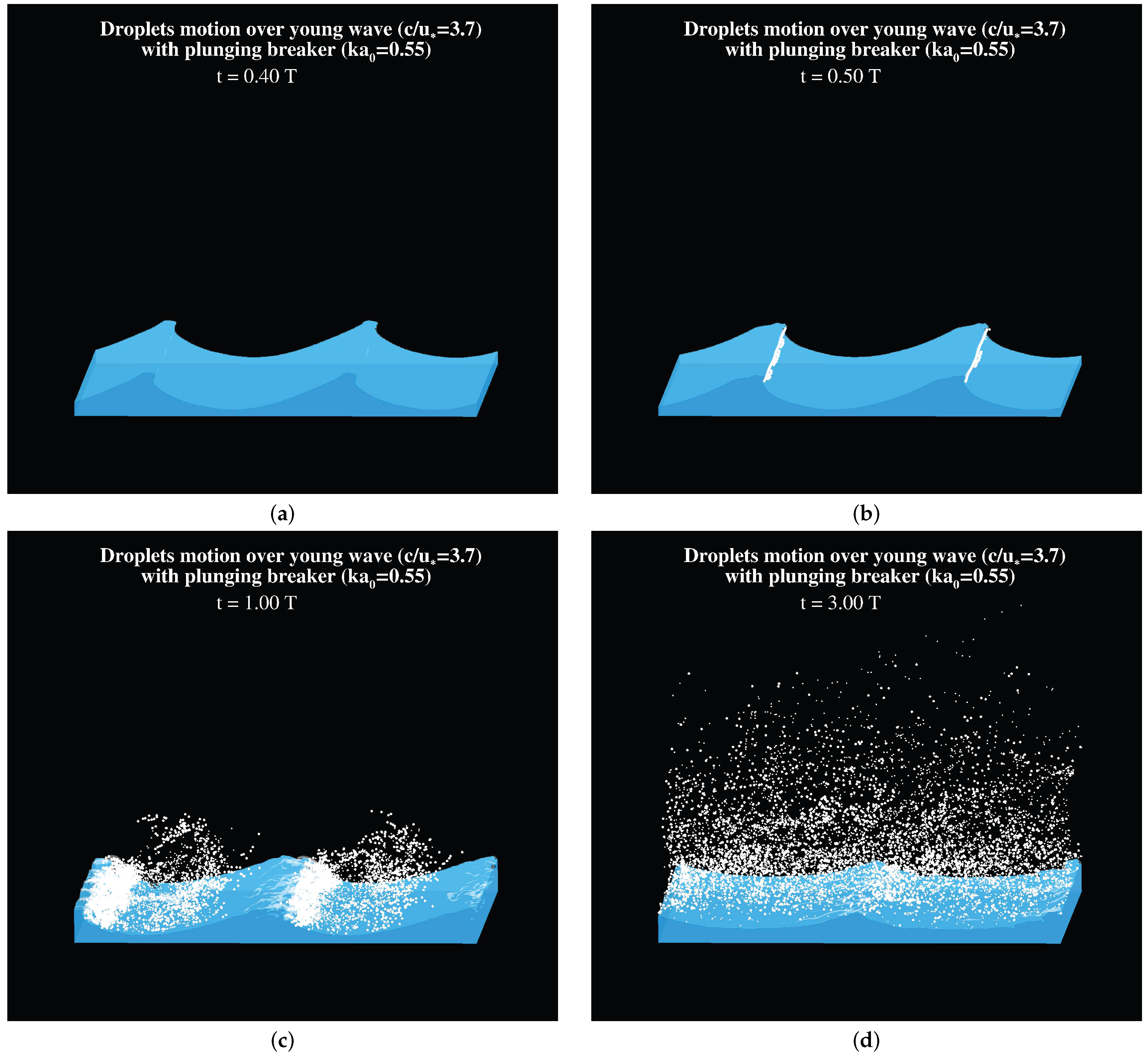
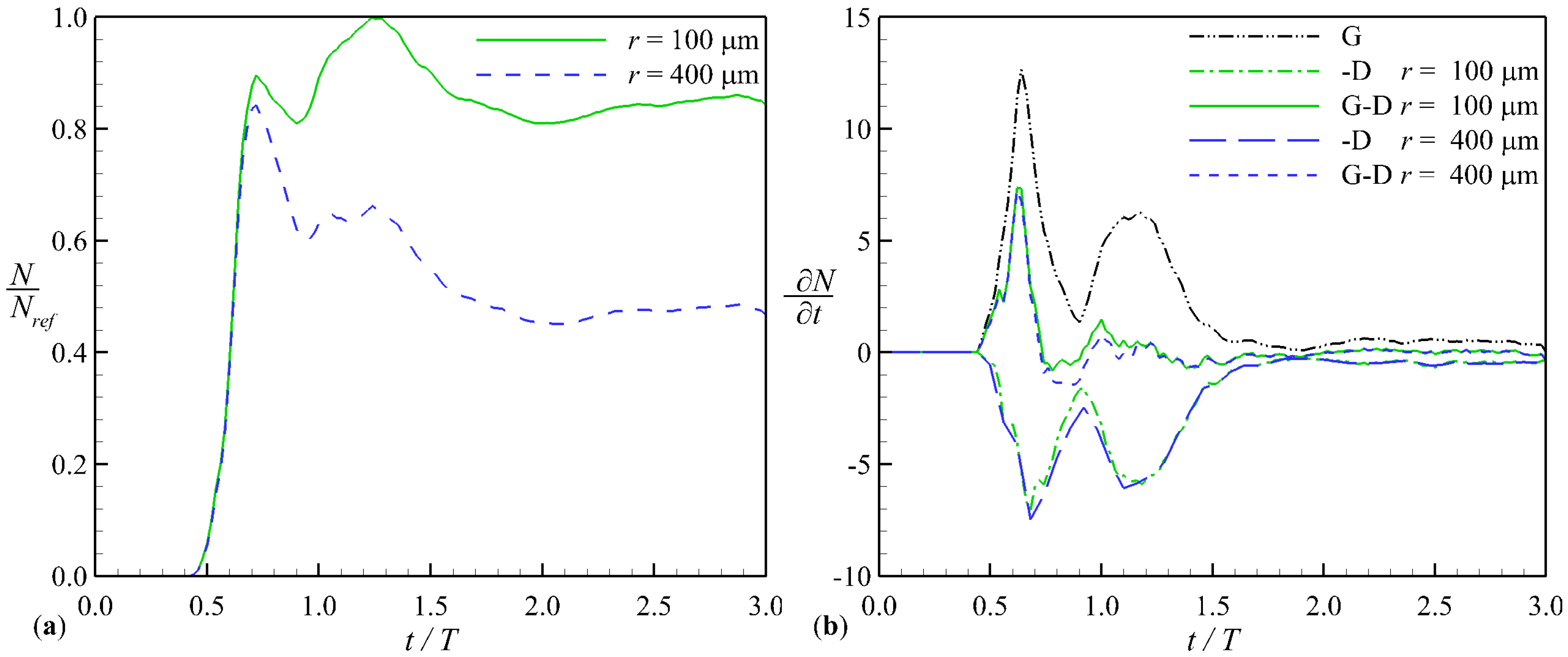
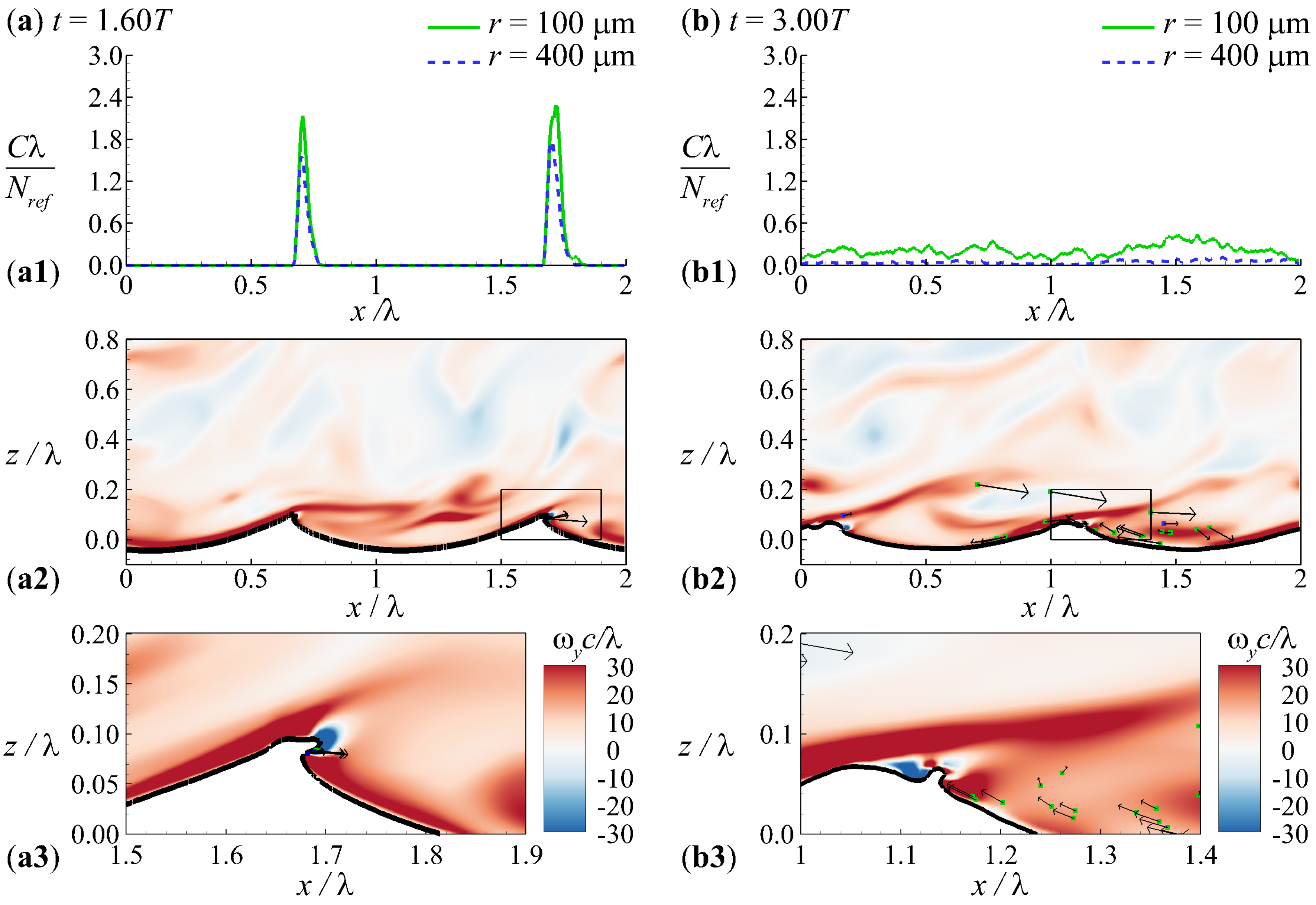
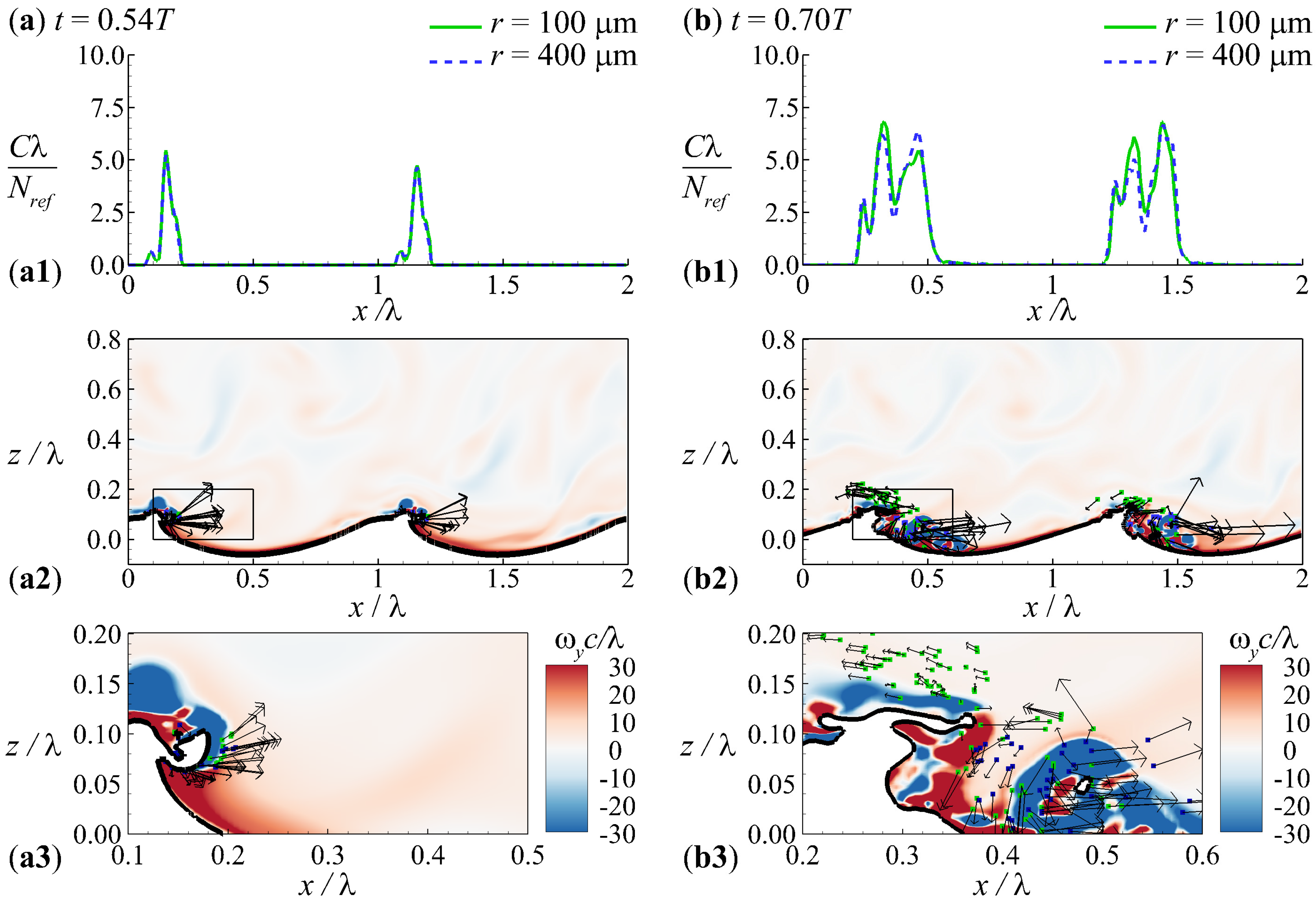
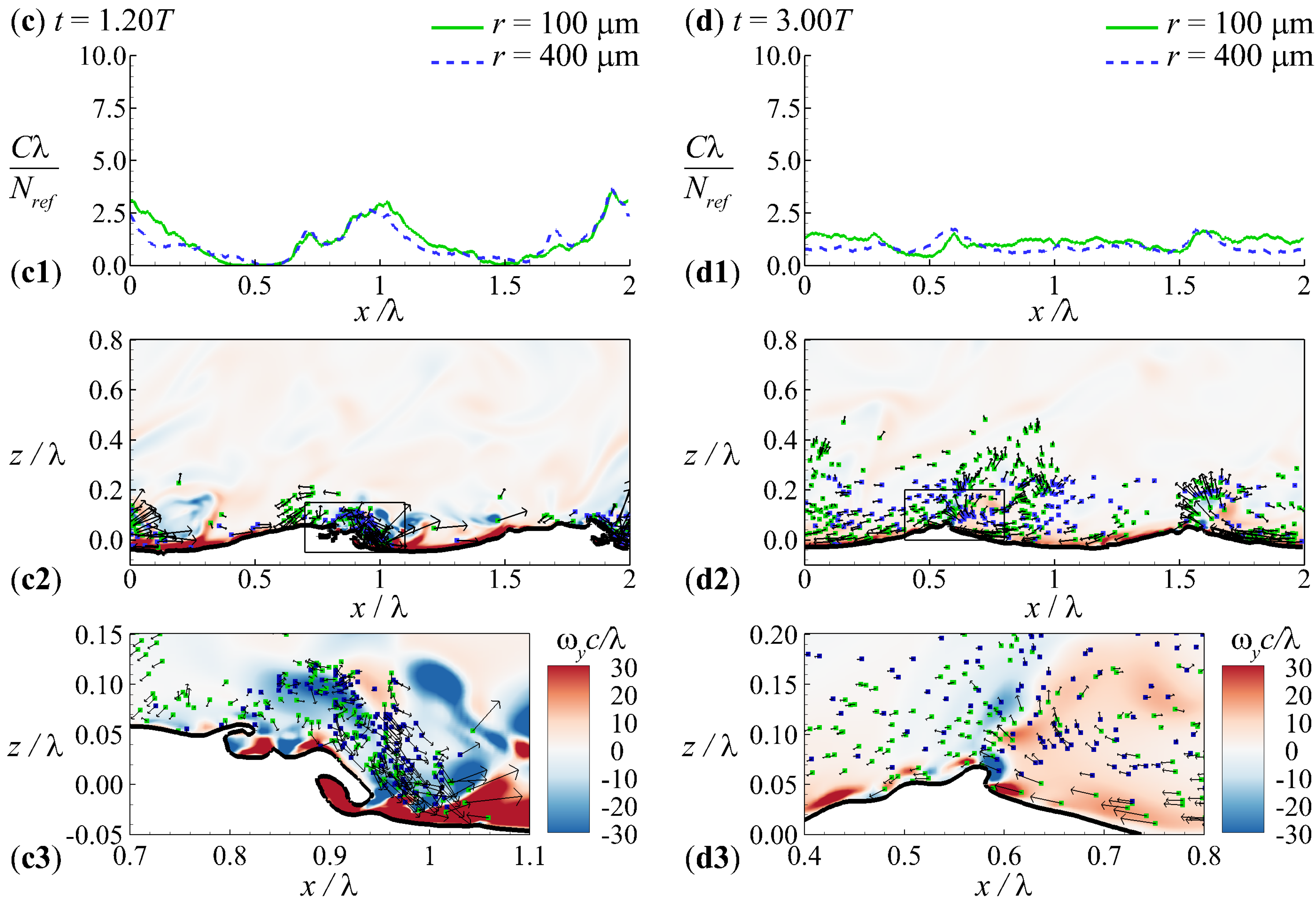
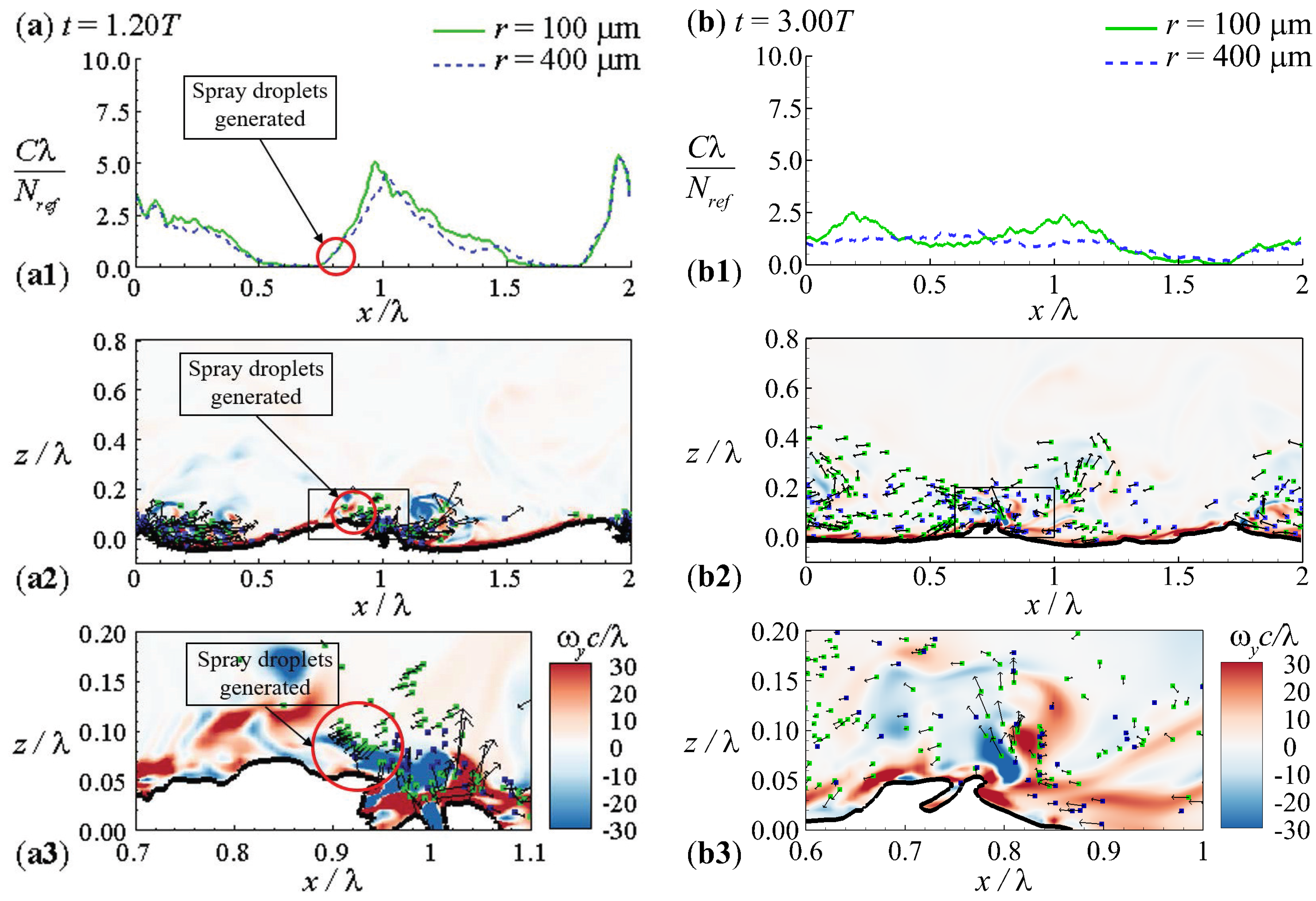
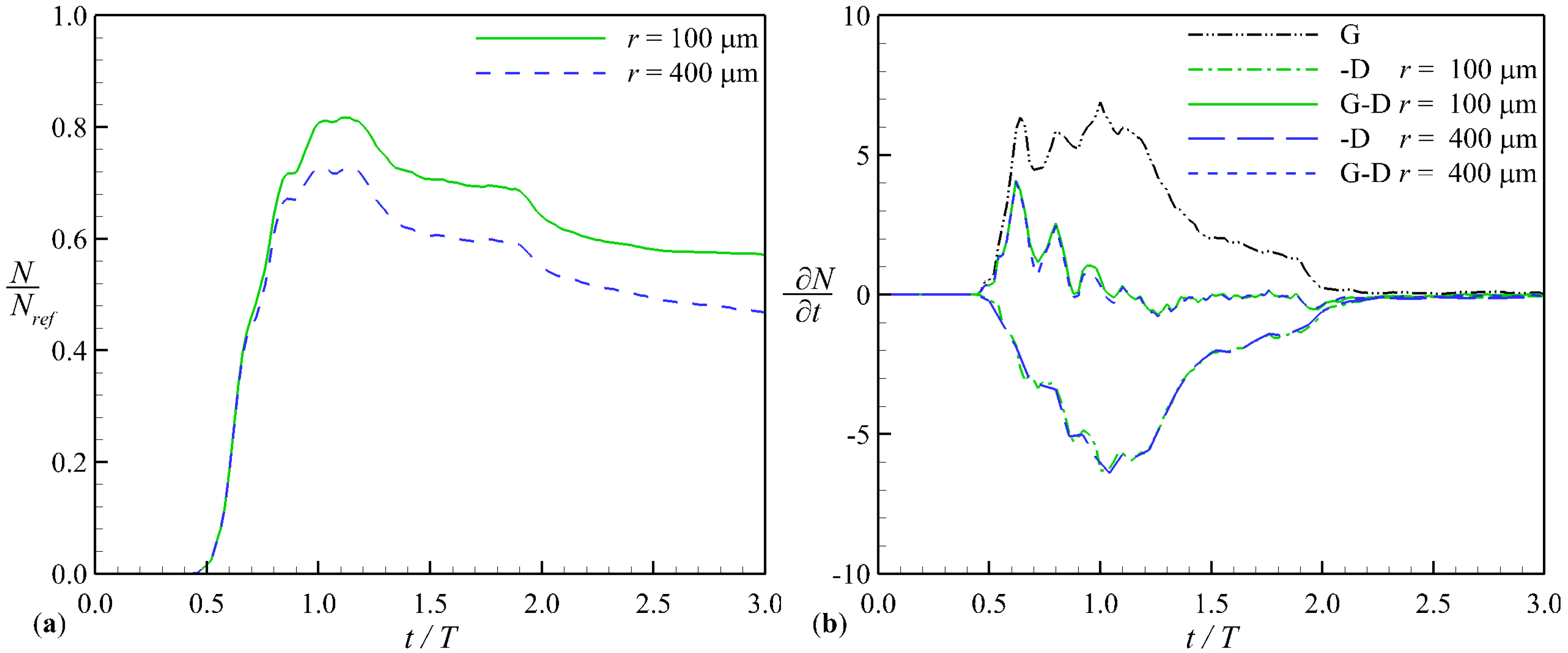
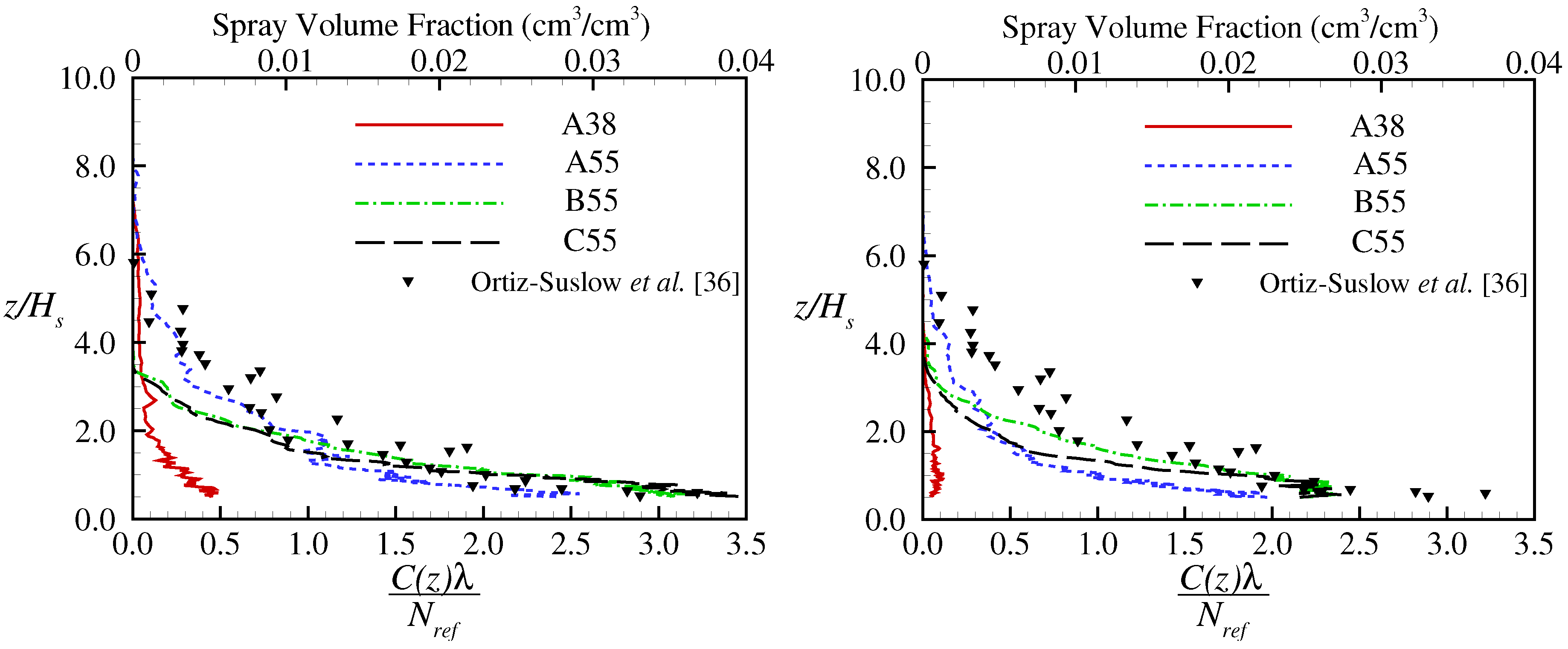
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MABL | Marine atmosphere boundary layer |
| LPT | Lagrangian particle tracking |
| DNS | Direct numerical simulation |
| LS | Level-set |
| VOF | Volume of fluid |
| CLSVOF | Coupled level-set and volume-of-fluid |
| LES | Large eddy simulation |
| SSGF | Sea spray generation function |
References
- Andreas, E.L. Spray stress revisited. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.A.; Veron, F. Impact of sea spray on air-sea fluxes. Part II: Feedback effects. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 2835–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, N.; Toba, Y. Effect of sea-water droplets on evaporation from sea surface. In The Wind-Driven Air-Sea Interface; Banner, M., Ed.; School of Mathematics, University of South Wales: Sydney, Australia, 1999; pp. 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Edson, J.; Paluszkiewicz, T.; Sandgathe, S.; Vincent, L.; Goodman, L.; Curtin, T.; Hollister, J.; Colton, M. Coupled Marine Boundary Layers and Air-Sea Interaction Initiative: Combining Process Studies, Simulations, and Numerical Models (Revision 5.0); Office of Naval Research: Arlington, TX, USA, 1999; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Spiel, D.E. On the birth of film drops from bubbles on seawater surface. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 24907–24918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, C.D.; de Leeuw, G. Marine aerosol production; A review of the current knowledge. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 2007, 365, 1753–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, E.; Coe, H.; Green, D.; de Leeuw, G.; McFiggans, G. Laboratory-generated primary marine aerosol via bubble-bursting and atomization. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C.; Spiel, D.E.; Davidson, K.L. A model of marine aerosol generation via whitecaps and wave disruption. In Oceanic Whitecaps; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kientzler, C.F.; Arons, A.B.; Blanchard, D.C.; Woodcock, A.H. Photographic investigation of the projection of droplets by bubbles bursting at a water surface. Tellus 1954, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntyre, F. Flow patterns in breaking bubbles. J. Geophys. Res. 1972, 77, 5211–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiel, D.E. More on the births of jet drops from bubbles bursting on seawater surfaces. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1997, 102, 5815–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. A review of the sea spray generation function for the open ocean. In Atmosphere-Ocean Interactions; Perrie, W.A., Ed.; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2002; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Production of spume drops by the wind tearing of wave crests: The search for quantification. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1993, 98, 18221–18227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; Edson, J.; Monahan, E.B.; Rouault, M.C.; Smith, S.D. The spray contribution to net evaporation from the sea: A review of recent progress. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1995, 72, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmottant, P.; Villermaux, E. On spray formation. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 498, 73–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veron, F. Ocean Spray. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2015, 47, 507–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preobrazhenskii, L. Estimate of the content of spray drops in the near-water layer of the atmosphere. Fluid Mech. Sov. Res. 1973, 2, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, M. Direct production of droplets from breaking wind-wave—Its observation by a multi-colored overlapping exposure photographing technique. Tellus 1981, 33, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. Sea spray and the turbulent air-sea heat fluxes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1992, 97, 11429–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. A new sea spray generation function for wind speeds up to 32 ms−1. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1998, 28, 2175–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.W.; Kepert, J.D.; Holland, G.J. The effect of sea spray on surface energy transports over the ocean. Glob. Atmos. Ocean Syst. 1994, 2, 121–142. [Google Scholar]
- Veron, F.; Hopkins, C.; Harrison, E.L.; Muelluer, J.A. Sea spray spume droplet production in high wind speeds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L16602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.H.; Park, P.M.; Consterdine, I.E. Marine aerosol concentrations and estimated fluxes over the sea. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 119, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Toba, Y.; Sugioka, K.I.; Komori, S. New sea spray generation function for spume droplets. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.A.; Veron, F. A sea state dependent spume generation function. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.; Zhong, Z. New wave-dependent formulae for sea spray flux at air-sea interface. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2009, 21, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtsev, V.N. On the effect of sea drops on the atmospheric boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovadnevaite, J.; de Leeuw, G.; Ceburnis, D.; Monahan, C.; Partanen, A.I.; Korhonen, H.; O’Dowd, C.D. A sea spray aerosol flux parameterization encapsulating wave state. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1837–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtsev, V.N.; Makin, V.K. Impact of ocean spray on the dynamic of the marine atmospheric boundary layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2011, 140, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastigejev, Y.; Suslov, S.A.; Lin, Y.L. Effect of ocean spray on vertical momentum transport under high-wind conditions. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2011, 141, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastigejev, Y.; Suslov, S.A. E-ϵ model of spray-laden near-sea atmospheric layer in high wind conditions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 742–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Rutgersson, A.; Sahlée, E.; Larsén, X.G. The impact of waves and sea spray on modelling storm track and development. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2015, 67, 27967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Song, J.; Li, S.; Yang, L. The effects of wind-driven waves and ocean spray on the drag coefficient and near-surface wind profiles over the ocean. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastigejev, Y.; Suslov, S.A. Two-temperature nonequilibrium model of a marine boundary layer laden with evaporating ocean spray under high-wind conditions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2016, 46, 3083–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Suslow, D.G.; Haus, B.K.; Mehta, S.; Laxague, N.J. A laboratory study of spray generation in high winds. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016; Volume 35. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Suslow, D.G.; Haus, B.K.; Mehta, S.; Laxague, N.J. Sea spray generation in very high winds. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 3975–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitskaya, Y.; Kandaurov, A.; Ermakova, O.; Kozlov, D.; Sergeev, D.; Zilitinkevich, S. Bag-breakup fragmentation as the dominant mechanism of sea-spray production in high winds. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, D.H.; Sullivan, P.P. Sea surface drag and the role of spray. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.H.; Sullivan, P.P. Momentum transfer in a turbulent, particle-laden Couette flow. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 053304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.H.; Sullivan, P.P. The sea spray contribution to sensible heat flux. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druzhinin, O.A.; Troitskaya, Y.I.; Zilitinkevich, S.S. The study of droplet-laden turbulent airflow over waved water surface by direct numerical simulation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 1789–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banner, M.L.; Peregrine, D.H. Wave breaking in deep water. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1993, 25, 373–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.P.; McWilliams, J.C. Dynamics of winds and currents coupled to surface waves. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2010, 42, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlin, M.; Choi, W.; Tian, Z. Breaking waves in deep and intermediate waters. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2013, 45, 115–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, K.G. Internal wave breaking and dissipation mechanisms on the continental slope/shelf. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, F.H.; Welch, J.E. Numerical calculation of time-dependent viscous incompressible flow of fluid with free surface. Phys. Fluids 1965, 8, 2182–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, H.; Nishimura, S.; Masuko, A. Finite difference simulation of nonlinear waves generated by ships of arbitrary three-dimensional configuration. J. Comput. Phys. 1985, 60, 391–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, H. Finite-difference simulation of breaking waves. J. Comput. Phys. 1986, 65, 179–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osher, S.; Sethian, J.A. Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 1988, 79, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussman, M.; Smereka, P.; Osher, S. A level set approach for computing solutions to incompressible two-phase flow. J. Comput. Phys. 1994, 114, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, Q.; Greaves, D. Numerical simulation of free-surface flow using the level-set method with global mass correction. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2010, 63, 651–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardovelli, R.; Zaleski, S. Direct numerical simulation of free-surface and interfacial flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1999, 31, 567–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.; Hernandez, J.; Gomez, P.; Faura, F. An improved PLIC-VOF method for tracking thin fluid structures in incompressible two-phase flows. J. Comput. Phys. 2005, 208, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weymouth, G.D.; Yue, D.K. Conservative volume-of-fluid method for free-surface simulations on Cartesian-grids. J. Comput. Phys. 2010, 229, 2853–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussman, M.; Puckett, E.G. A coupled level set and volume-of-fluid method for computing 3D and axisymmetric incompressible two-phase flows. J. Comput. Phy. 2000, 162, 301–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zou, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Reeve, D. A novel coupled level set and volume of fluid method for sharp interface capturing on 3D tetrahedral grids. J. Comput. Phys. 2010, 229, 2573–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Numerical Study of Strong Free Surface Flow and Breaking Waves. Ph.D Thesis, The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Kharif, C.; Zaleski, S.; Li, J. Two-dimensional Navier-Stokes simulation of wave breaking. Phys. Fluids 1999, 11, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Sirviente, A.I. A numerical study of breaking waves. Phys. Fluids 2004, 16, 2649–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iafrati, A. Numerical study of the effects of the breaking intensity on wave breaking flows. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 622, 371–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guo, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y.; Dalrymple, R.A.; Shen, L. Idealized numerical simulation of breaking water wave propagating over a viscous mud layer. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 112104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deike, L.; Popinet, S.; Melville, W.K. Capillary effects on wave breaking. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 769, 541–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, P.; Glockner, S. Numerical simulations of three-dimensional plunging breaking waves: Generation and evolution of aerated vortex filaments. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 767, 364–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deike, L.; Melville, W.K.; Popinet, S. Air entrainment and bubble statistics in breaking waves. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 801, 91–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Moin, P. Application of a fractional-step method to incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 1985, 59, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balay, S.; Brown, K.; Eijkhout, V.; Gropp, W.; Kaushik, D.; Knepley, M.; Mcinnes, L.C.; Smith, B.; Zhang, H. PETSc Users Manual; Revision 3.3; Computer Science Division, Argonne National Laboratory: Argonne, IL, USA, 2012.
- Yang, Z.; Lu, X.-H.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Shen, L. Numerical simulation of sediment suspension and transport under plunging breaking waves. Comput. Fluids 2017, 158, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, J.B. Aerosol particle deposition in numerically simulated channel flow. Phys. Fluids 1989, 1, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-H.; Chen, L.-F. The effect of stable stratification and thermophoresis on fine particle deposition in a bounded turbulent flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.H.; Anderson, H.I.; Gillissen, J. Turbulence modulation and drag reduction by spherical particles. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 081702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxey, M.R.; Riley, J.J. Equation of motion for a small rigid sphere in a nonuniform flow. Phys. Fluids 1983, 26, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, R.; Grace, J.R.; Weber, M.E. Bubbles, Drops and Particles; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Elghobashi, S.; Truesdell, G.C. Direct simulation of particle dispersion in a decaying isotropic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1992, 242, 655–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, M.P.; Veron, F. Structure of the airflow above surface waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2016, 46, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, P.; Mahesh, K. Direct numerical simulation: A tool in turbulence research. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1998, 30, 539–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninto, Y.; Garcia, M.H. Experiments on particle turbulence interactions in the near wall region of an open channel flow: Implications for sediment transport. J. Fluid Mech. 1996, 326, 285–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, S.; Shen, L.; Dong, Y. Characteristics of turbulence transport for momentum and heat in particle-laden turbulent vertical channel flows. Acta Mech. Sin. 2017, 33, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dimensional Parameters | ||||||
| Case | ||||||
| A55 | 5 | 0.88 | 3.19 | 0.86 | 25.8 | 1.57 |
| A38 | 0.60 | 2.99 | 0.81 | 24.1 | 1.68 | |
| B55 | 0.88 | 3.19 | 0.27 | 8.1 | 1.57 | |
| C55 | 0.88 | 3.19 | 0.12 | 3.4 | 1.57 | |
| Dimensional Parameters | ||||||
| Case | ||||||
| A55 | 1.205 | 998 | 1.87 | |||
| A38 | 1.76 | |||||
| B55 | 0.59 | |||||
| C55 | 0.26 | |||||
| Dimensionless Parameters | ||||||
| Case | ||||||
| A55 | 3.7 | 0.55 | 180 | |||
| A38 | 3.7 | 0.38 | ||||
| B55 | 12.0 | 0.55 | ||||
| C55 | 27.7 | 0.55 | ||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, S.; Yang, Z.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y.-H.; Shen, L. Numerical Study on the Generation and Transport of Spume Droplets in Wind over Breaking Waves. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120248
Tang S, Yang Z, Liu C, Dong Y-H, Shen L. Numerical Study on the Generation and Transport of Spume Droplets in Wind over Breaking Waves. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(12):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120248
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Shuai, Zixuan Yang, Caixi Liu, Yu-Hong Dong, and Lian Shen. 2017. "Numerical Study on the Generation and Transport of Spume Droplets in Wind over Breaking Waves" Atmosphere 8, no. 12: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120248
APA StyleTang, S., Yang, Z., Liu, C., Dong, Y.-H., & Shen, L. (2017). Numerical Study on the Generation and Transport of Spume Droplets in Wind over Breaking Waves. Atmosphere, 8(12), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120248





