Atmospheric Processing and Variability of Biological Ice Nucleating Particles in Precipitation at Opme, France
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Ice Nucleation Assays
2.3. Cell Counts
2.4. Chemical Analyses
2.5. Meteorological Data and Backward Trajectory Plots
2.6. δ18O Measurements
2.7. Data Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
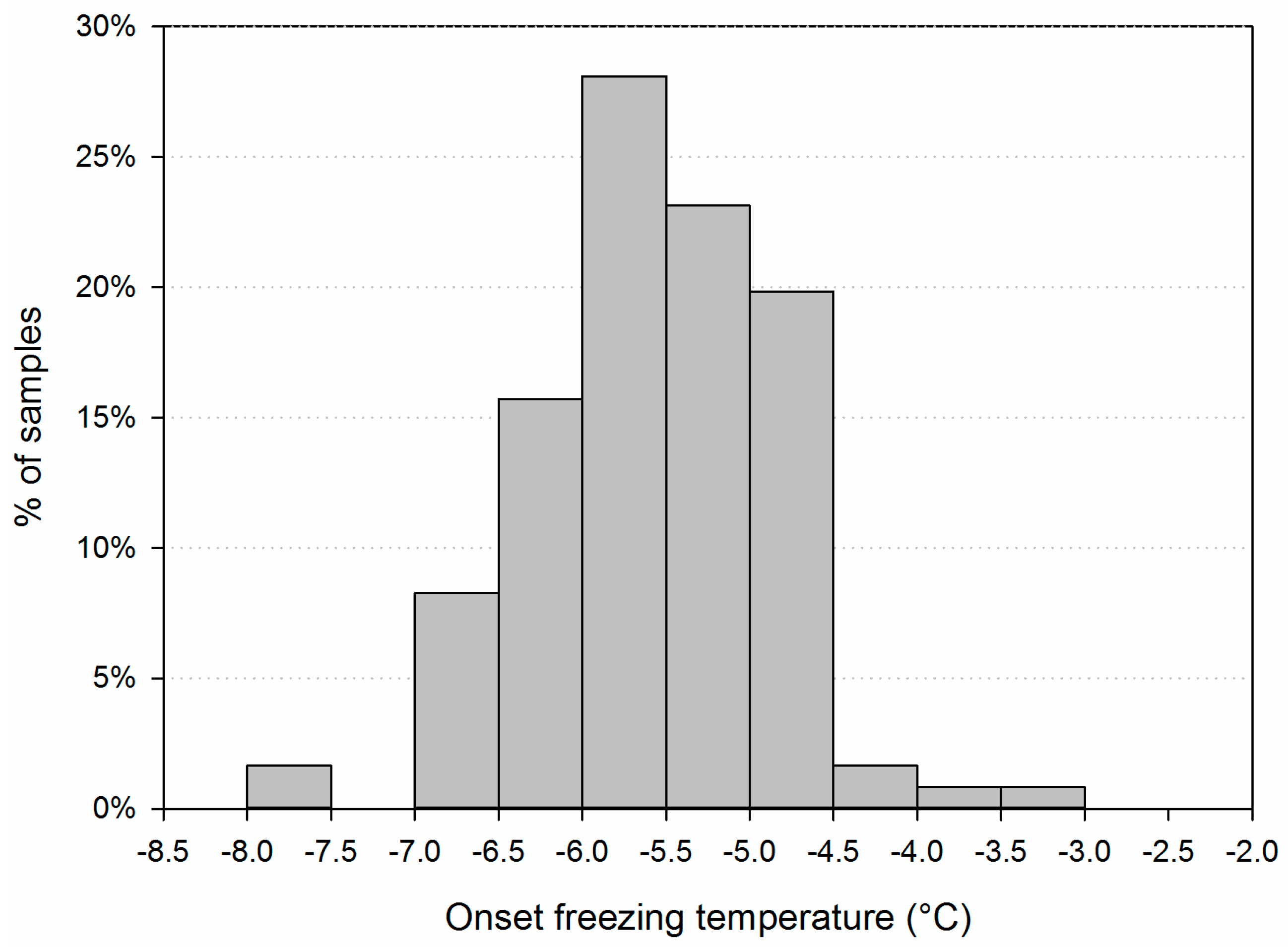
3.1. Main Characteristics of the Samples
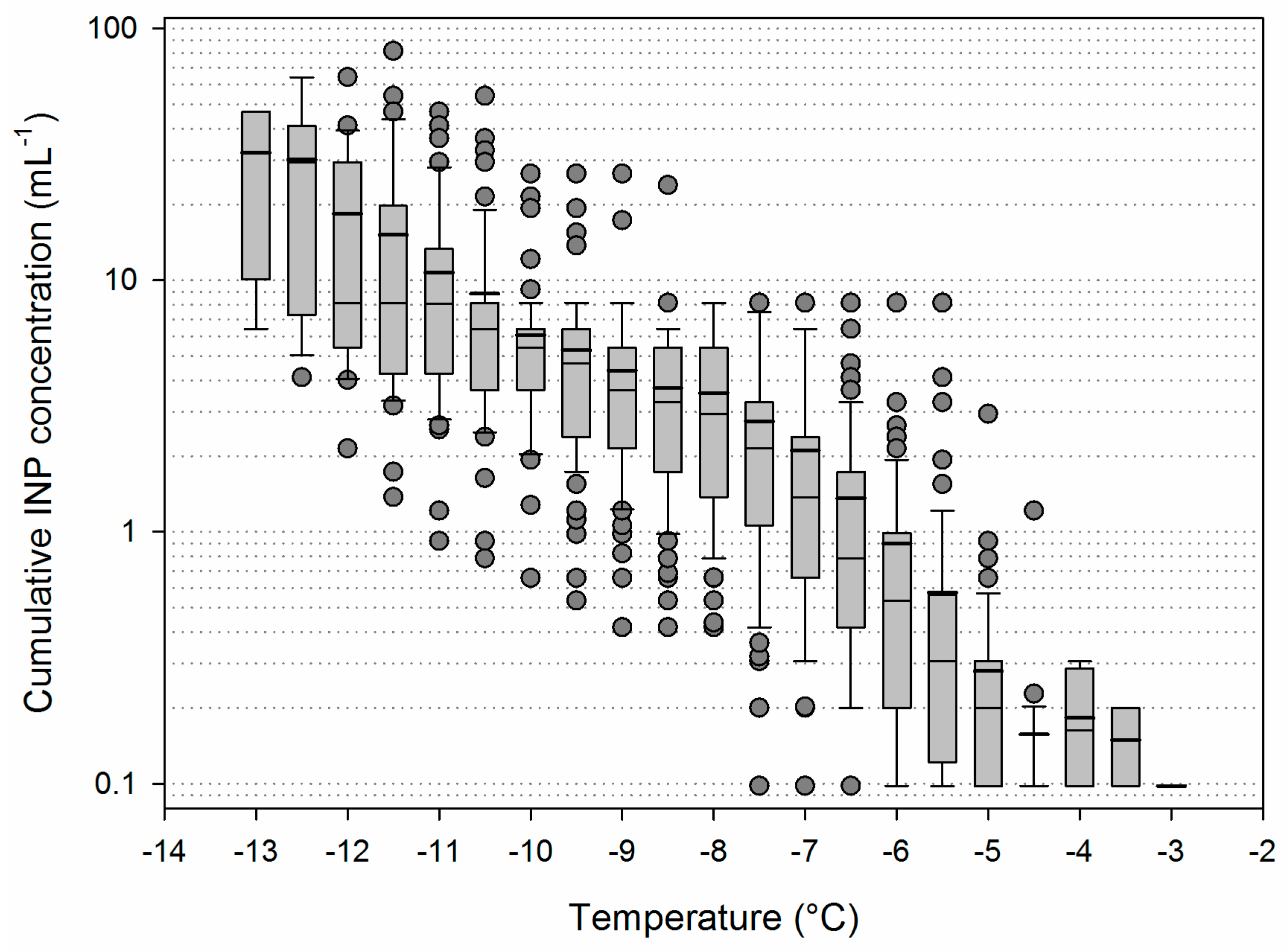
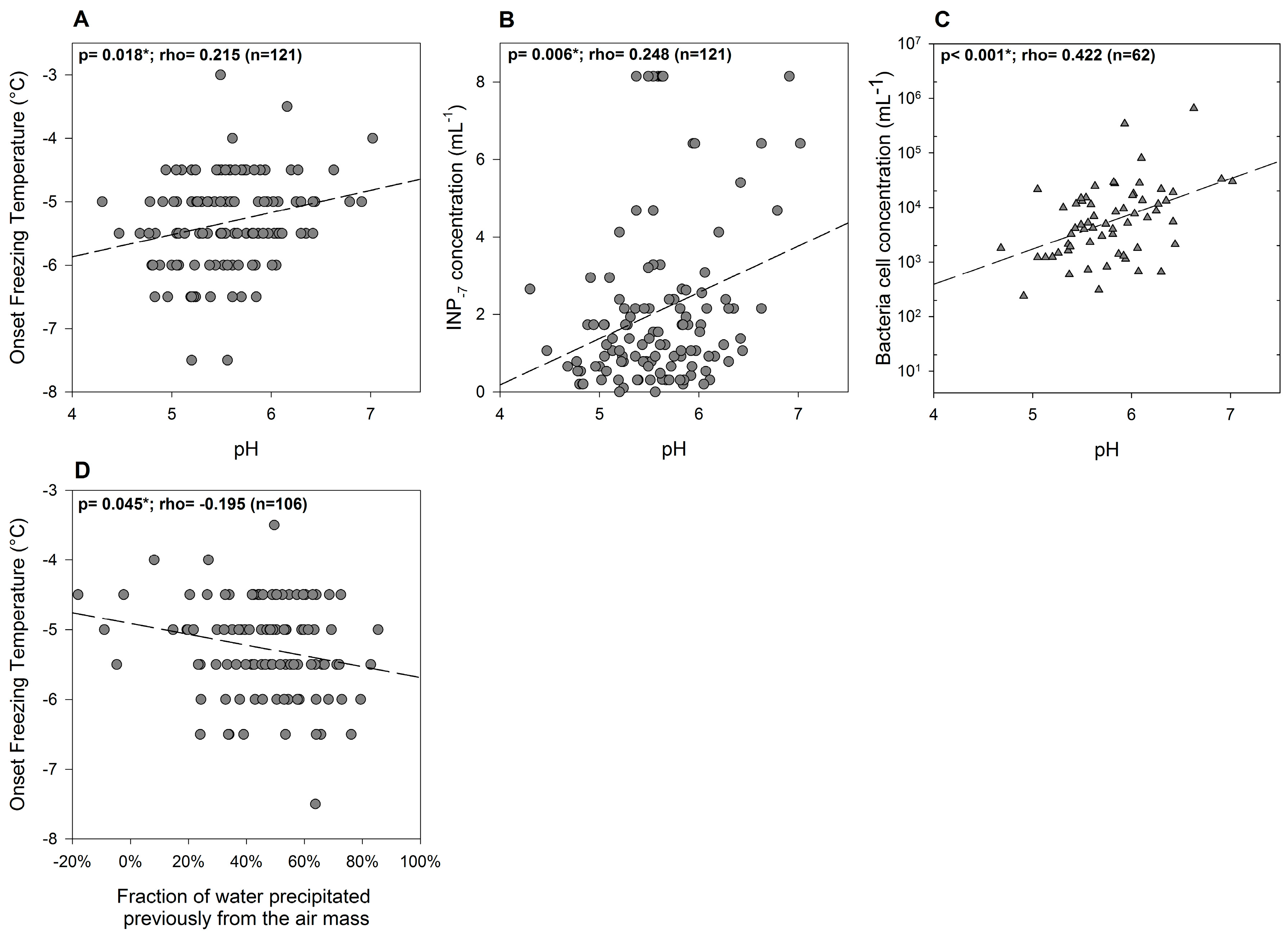
3.2. Variability of INP Concentration and Links with Environmental Variables
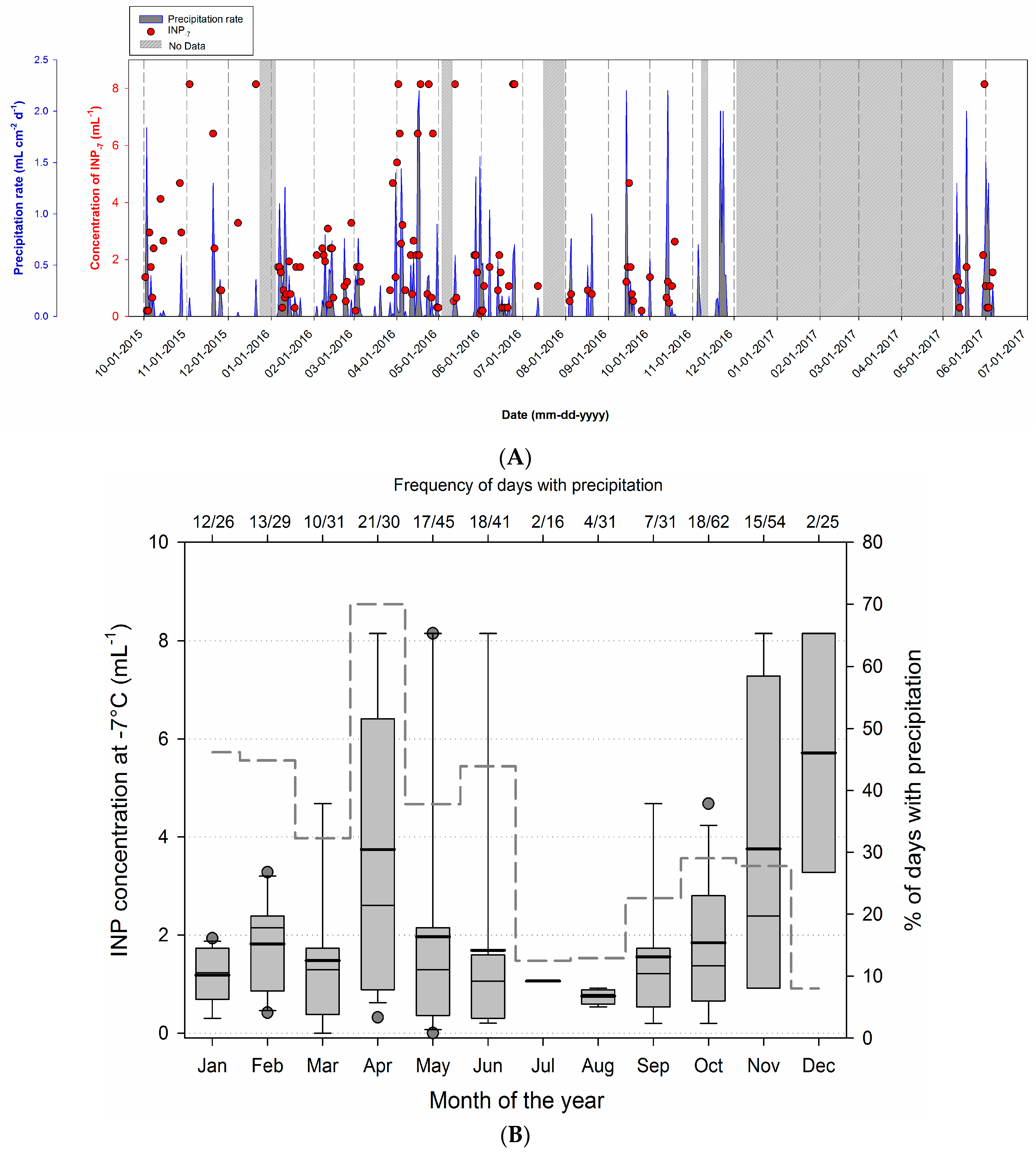
3.3. Temporal Variability
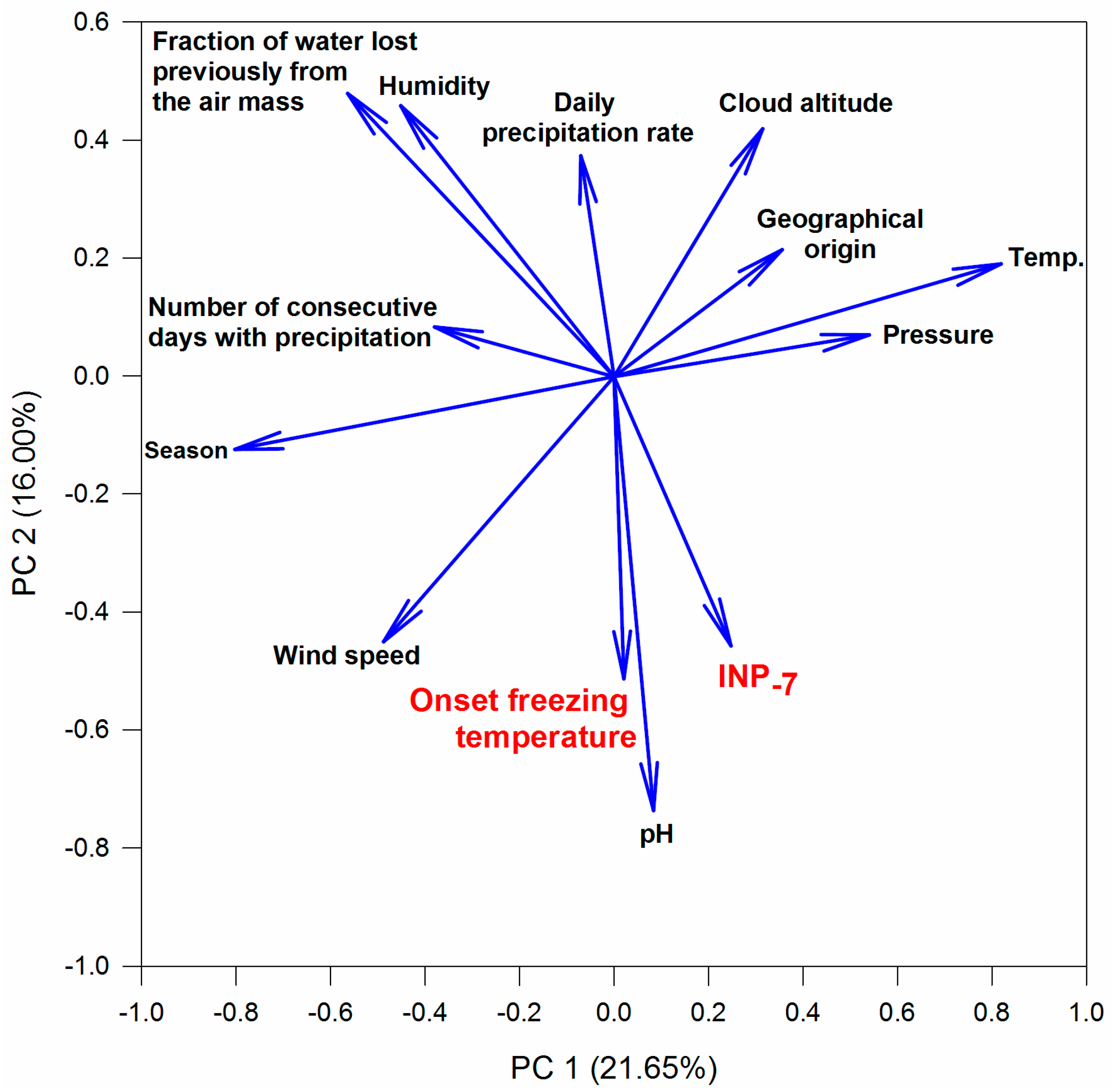
3.4. Relations between INPs, Origin of Air Mass and Precipitation Chemistry
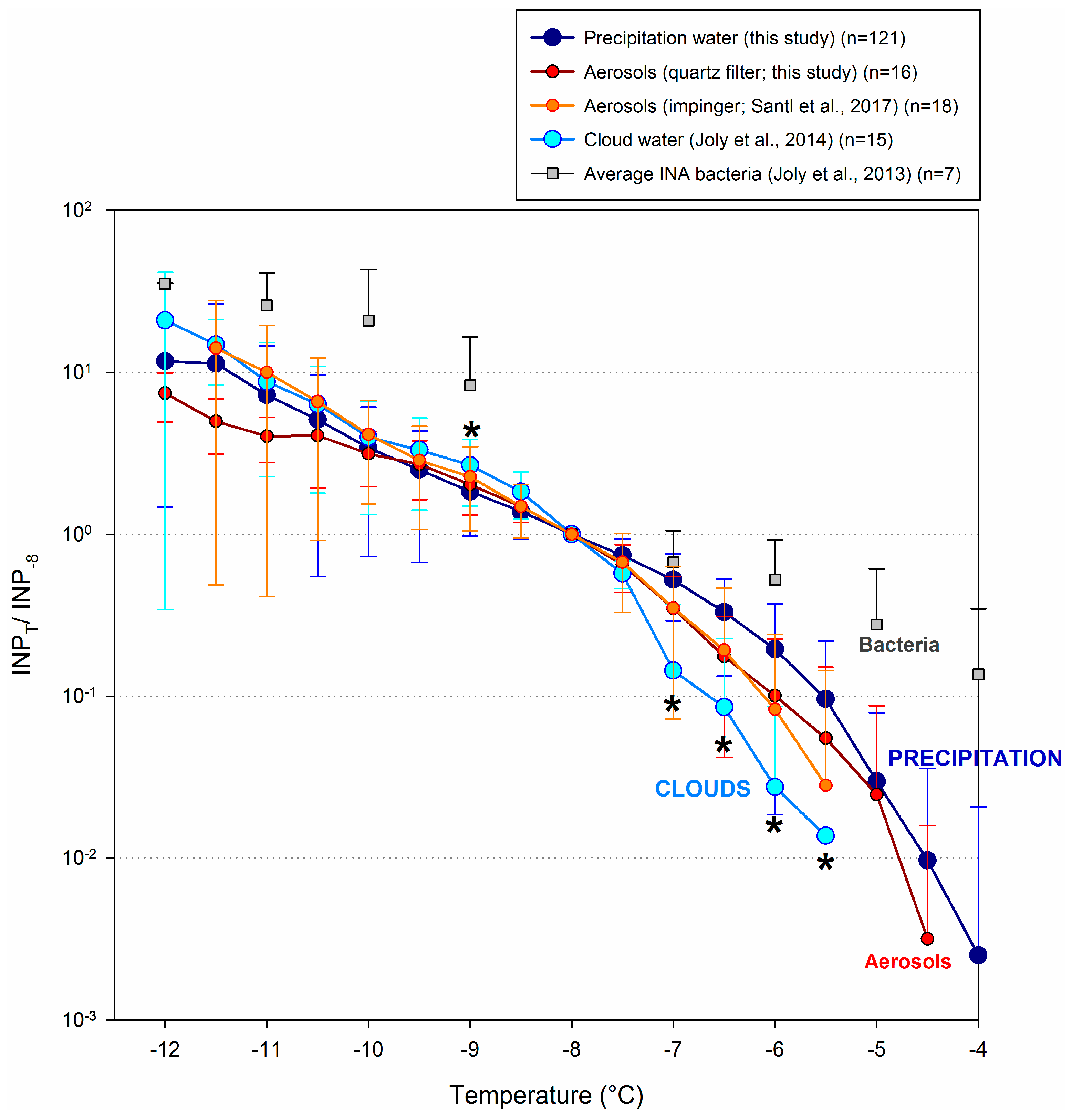
3.5. Comparison with Other Atmospheric Components
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Möhler, O.; DeMott, P.J.; Vali, G.; Levin, Z. Microbiology and atmospheric processes: The role of biological particles in cloud physics. Biogeosciences 2007, 4, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.D.; Murray, B.J.; Woodhouse, M.T.; Whale, T.F.; Baustian, K.J.; Carslaw, K.S.; Dobbie, S.; O’Sullivan, D.; Malkin, T.L. The importance of feldspar for ice nucleation by mineral dust in mixed-phase clouds. Nature 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiranuma, N.; Möhler, O.; Yamashita, K.; Tajiri, T.; Saito, A.; Kiselev, A.; Hoffmann, N.; Hoose, C.; Jantsch, E.; Koop, T.; et al. Ice nucleation by cellulose and its potential contribution to ice formation in clouds. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.C.J.; DeMott, P.J.; Tobo, Y.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Moffett, B.F.; Franc, G.D.; Kreidenweis, S.M. Sources of organic ice nucleating particles in soils. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7195–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conen, F.; Morris, C.E.; Leifeld, J.; Yakutin, M.V.; Alewell, C. Biological residues define the ice nucleation properties of soil dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9643–9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, M.; Amato, P.; Deguillaume, L.; Monier, M.; Hoose, C.; Delort, A.-M. Quantification of ice nuclei active at near 0 °C temperatures in low-altitude clouds at the Puy de Dôme atmospheric station. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8185–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pummer, B.G.; Bauer, H.; Bernardi, J.; Bleicher, S.; Grothe, H. Suspendable macromolecules are responsible for ice nucleation activity of birch and conifer pollen. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoose, C.; Möhler, O. Heterogeneous ice nucleation on atmospheric aerosols: A review of results from laboratory experiments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 9817–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Hill, T.C.J.; Pummer, B.G.; Yordanova, P.; Franc, G.D.; Pöschl, U. Ice nucleation activity in the widespread soil fungus Mortierella alpina. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conen, F.; Eckhardt, S.; Gundersen, H.; Stohl, A.; Yttri, K.E. Rainfall drives atmospheric ice-nucleating particles in the coastal climate of southern Norway. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 11065–11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, M.; Attard, E.; Sancelme, M.; Deguillaume, L.; Guilbaud, C.; Morris, C.E.; Amato, P.; Delort, A.-M. Ice nucleation activity of bacteria isolated from cloud water. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.E.; Sands, D.C.; Vinatzer, B.A.; Glaux, C.; Guilbaud, C.; Buffière, A.; Yan, S.; Dominguez, H.; Thompson, B.M. The life history of the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae is linked to the water cycle. ISME J. 2008, 2, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopelli, E.; Conen, F.; Guilbaud, C.; Zopfi, J.; Alewell, C.; Morris, C.E. Ice nucleators, bacterial cells and Pseudomonas syringae in precipitation at Jungfraujoch. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, L.R.; Galyan, E.L.; Chang-Chien, M.-M.; Caldwell, D.R. Ice Nucleation Induced by Pseudomonas syringae. Appl. Microbiol. 1974, 28, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vali, G.; Christensen, M.; Fresh, R.W.; Galyan, E.L.; Maki, L.R.; Schnell, R.C. Biogenic Ice Nuclei. Part II: Bacterial Sources. J. Atmos. Sci. 1976, 33, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuta, N.; Mason, B.J. Epitaxial growth of ice on organic crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1963, 24, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, R.C.; Vali, G. Atmospheric Ice Nuclei from Decomposing Vegetation. Nature 1972, 236, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christner, B.C.; Morris, C.E.; Foreman, C.M.; Cai, R.; Sands, D.C. Ubiquity of Biological Ice Nucleators in Snowfall. Science 2008, 319, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopelli, E.; Conen, F.; Morris, C.E.; Herrmann, E.; Henne, S.; Steinbacher, M.; Alewell, C. Predicting abundance and variability of ice nucleating particles in precipitation at the high-altitude observatory Jungfraujoch. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 8341–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conen, F.; Rodríguez, S.; Hülin, C.; Henne, S.; Herrmann, E.; Bukowiecki, N.; Alewell, C. Atmospheric ice nuclei at the high-altitude observatory Jungfraujoch, Switzerland. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2015, 67, 25014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, S.M.; Hoose, C.; Pöschl, U.; Lawrence, M.G. Ice nuclei in marine air: Biogenic particles or dust? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 245–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.H.; Si, M.; Li, J.; Chou, C.; Dickie, R.; Toom-Sauntry, D.; Pohlker, C.; Yakobi-Hancock, J.D.; Ladino, L.A.; Jones, K.; et al. Ice nucleating particles at a coastal marine boundary layer site: Correlations with aerosol type and meteorological conditions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12547–12566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, P.J.; Hill, T.C.J.; McCluskey, C.S.; Prather, K.A.; Collins, D.B.; Sullivan, R.C.; Ruppel, M.J.; Mason, R.H.; Irish, V.E.; Lee, T.; et al. Sea spray aerosol as a unique source of ice nucleating particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, 5797–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopelli, E.; Conen, F.; Morris, C.E.; Herrmann, E.; Bukowiecki, N.; Alewell, C. Ice nucleation active particles are efficiently removed by precipitating clouds. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoose, C.; Kristjánsson, J.E.; Burrows, S.M. How important is biological ice nucleation in clouds on a global scale? Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 024009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesartic, A.; Lohmann, U.; Storelvmo, T. Bacteria in the ECHAM5-HAM global climate model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8645–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigg, E.K.; Soubeyrand, S.; Morris, C.E. Persistent after-effects of heavy rain on concentrations of ice nuclei and rainfall suggest a biological cause. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2313–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahyoun, M.; Korsholm, U.S.; Sørensen, J.H.; Šantl-Temkiv, T.; Finster, K.; Gosewinkel, U.; Nielsen, N.W. Impact of bacterial ice nucleating particles on weather predicted by a numerical weather prediction model. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, P.; Ménager, M.; Sancelme, M.; Laj, P.; Mailhot, G.; Delort, A.-M. Microbial population in cloud water at the Puy de Dôme: Implications for the chemistry of clouds. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4143–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaïtilingom, M.; Attard, E.; Gaiani, N.; Sancelme, M.; Deguillaume, L.; Flossmann, A.I.; Amato, P.; Delort, A.-M. Long-term features of cloud microbiology at the puy de Dôme (France). Atmos. Environ. 2012, 56, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, P.; Joly, M.; Besaury, L.; Oudart, A.; Taib, N.; Moné, A.I.; Deguillaume, L.; Delort, A.-M.; Debroas, D. Active microorganisms thrive among extremely diverse communities in cloud water. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šantl-Temkiv, T.; Amato, P.; Gosewinkel, U.; Thyrhaug, R.; Charton, A.; Chicot, B.; Finster, K.; Bratbak, G.; Löndahl, J. High-Flow-Rate Impinger for the Study of Concentration, Viability, Metabolic Activity, and Ice-Nucleation Activity of Airborne Bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11224–11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopelli, E.; Conen, F.; Zimmermann, L.; Alewell, C.; Morris, C.E. Freezing nucleation apparatus puts new slant on study of biological ice nucleators in precipitation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vali, G. Quantitative Evaluation of Experimental Results an the Heterogeneous Freezing Nucleation of Supercooled Liquids. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoni, A.; Laj, P.; Sellegri, K.; Mailhot, G. Cloud chemistry at the Puy de Dôme: Variability and relationships with environmental factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrisford, P.; Dee, D.P.; Poli, P.; Brugge, R.; Fielding, K.; Fuentes, M.; Kållberg, P.W.; Kobayashi, S.; Uppala, S.; Simmons, A. The ERA-Interim Archive Version 2.0; European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, Berkshire, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Clain, G.; Baray, J.-L.; Delmas, R.; Keckhut, P.; Cammas, J.-P. A lagrangian approach to analyse the tropospheric ozone climatology in the tropics: Climatology of stratosphere–troposphere exchange at Reunion Island. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duflot, V.; Dils, B.; Baray, J.L.; De Mazière, M.; Attié, J.L.; Vanhaelewyn, G.; Senten, C.; Vigouroux, C.; Clain, G.; Delmas, R. Analysis of the origin of the distribution of CO in the subtropical southern Indian Ocean in 2007. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D22106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freney, E.; Sellegri Karine, S.K.; Eija, A.; Clemence, R.; Aurelien, C.; Jean-Luc, B.; Aurelie, C.; Maxime, H.; Nadege, M.; Laeticia, B.; et al. Experimental Evidence of the Feeding of the Free Troposphere with Aerosol Particles from the Mixing Layer. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baray, J.-L.; Pointin, Y.; Van Baelen, J.; Lothon, M.; Campistron, B.; Cammas, J.-P.; Masson, O.; Colomb, A.; Hervier, C.; Bezombes, Y.; et al. Case study and climatological analysis of upper tropospheric jet stream and stratosphere-troposphere exchanges using VHF profilers and radionuclide measurements in France. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguillaume, L.; Charbouillot, T.; Joly, M.; Vaïtilingom, M.; Parazols, M.; Marinoni, A.; Amato, P.; Delort, A.-M.; Vinatier, V.; Flossmann, A.; et al. Classification of clouds sampled at the puy de Dôme (France) based on 10 yr of monitoring of their physicochemical properties. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1485–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, T.A.; Marshall, S.J.; Evans, E.C.; Sinclair, K.E. Altitudinal Gradients of Stable Isotopes in Lee-Slope Precipitation in the Canadian Rocky Mountains. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2007, 39, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Ryan, P.; Harper, D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Christner, B.C.; Cai, R.; Morris, C.E.; McCarter, K.S.; Foreman, C.M.; Skidmore, M.L.; Montross, S.N.; Sands, D.C. Geographic, seasonal, and precipitation chemistry influence on the abundance and activity of biological ice nucleators in rain and snow. Proc. National Acad. Sci 2008, 105, 18854–18859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMott, P.J.; Prenni, A.J. New Directions: Need for defining the numbers and sources of biological aerosols acting as ice nuclei. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1944–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petters, M.D.; Wright, T.P. Revisiting ice nucleation from precipitation samples. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2015GL065733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourcier, L.; Masson, O.; Laj, P.; Chausse, P.; Pichon, J.M.; Paulat, P.; Bertrand, G.; Sellegri, K. A new method for assessing the aerosol to rain chemical composition relationships. Atmos. Res. 2012, 118, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, J.A.; Prenni, A.J.; DeMott, P.J.; Pöhlker, C.; Mason, R.H.; Robinson, N.H.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Tobo, Y.; Després, V.R.; Garcia, E.; et al. High concentrations of biological aerosol particles and ice nuclei during and after rain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 6151–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, R.C.; Vali, G. Biogenic ice nuclei: Part I. Terrestrial and marine sources. J. Atmos. Sci. 1976, 33, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, X.; Zhao, T.; An, X.; Zhao, Y.; Quan, J.; Mao, F.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, W.; et al. Are precipitation anomalies associated with aerosol variations over eastern China? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8011–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Jonard, M.; Ponette, Q. Influence of meteorological factors and polluting environment on rain chemistry and wet deposition in a rural area near Chimay, Belgium. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, R.; Powers, C.; Failor, K.; Monteil, C.L.; Vinatzer, B.A.; Schmale, D.G., III. Microbial ice nucleators scavenged from the atmosphere during simulated rain events. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 163, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.C.; Stuart, A.L.; Skamarock, W.C. Numerical simulations of the July 10, 1996, Stratospheric-Tropospheric Experiment: Radiation, Aerosols, and Ozone (STERAO)-Deep Convection experiment storm: Redistribution of soluble tracers. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 12381–12400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Kimura, T.; Magono, C.; Kikuchi, K. Observations of Precipitation Scavenging for Water-Soluble Particles. J. Meteorol. Soci. Jpn. Ser. II 1983, 61, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jaffrezo, J.-L.; Colin, J.-L. Rain-aerosol coupling in urban area: Scavenging ratio measurement and identification of some transfer processes. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1988, 22, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Rodhe, H. Factors controlling the acidity of natural rainwater. Nature 1982, 295, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, E.; Yang, H.; Delort, A.M.; Amato, P.; Poschl, U.; Glaux, C.; Koop, T.; Morris, C.E. Effects of atmospheric conditions on ice nucleation activity of Pseudomonas. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 10667–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muryoi, N.; Kawahara, H.; Obata, H. Properties of a Novel Extracellular Cell-free Ice Nuclei from Ice-nucleating Pseudomonas antarctica IN-74. Bioscience Biotech. Biochem. 2003, 67, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, P.; Joly, M.; Schaupp, C.; Attard, E.; Möhler, O.; Morris, C.E.; Brunet, Y.; Delort, A.-M. Survival and ice nucleation activity of bacteria as aerosols in a cloud simulation chamber. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6455–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Bertram, A.K.; Chou, K.C. Why Do Sulfuric Acid Coatings Influence the Ice Nucleation Properties of Mineral Dust Particles in the Atmosphere? J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, P.; Parazols, M.; Sancelme, M.; Mailhot, G.; Laj, P.; Delort, A.-M. An important oceanic source of micro-organisms for cloud water at the Puy de Dôme (France). Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8253–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giorgio, C.; Krempff, A.; Guiraud, H.; Binder, P.; Tiret, C.; Dumenil, G. Atmospheric pollution by airborne microorganisms in the city of Marseilles. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovallius, A.; Bucht, B.; Roffey, R.; Anäs, P. Three-year investigation of the natural airborne bacterial flora at four localities in sweden. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.-H.; Peng, C.-M. Estimates of the Contribution of Below-cloud Scavenging to the Pollutant Loadings of Rain in Taipei, Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 1999, 10, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellegri, K.; Laj, P.; Marinoni, A.; Dupuy, R.; Legrand, M.; Preunkert, S. Contribution of gaseous and particulate species to droplet solute composition at the Puy de Dôme, France. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 3, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.E.; Georgakopoulos, D.G.; Sands, D.C. Ice nucleation active bacteria and their potential role in precipitation. J. Phys. IV Proc. 2004, 121, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, D.C.; Langhans, V.E.; Scharen, A.L.; De Smet, G. The association between bacteria and rain and possible resultant meteorological implications. J. Hung. Meteorol. Serv. 1982, 86, 148–152. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, D. Suppression of Rain and Snow by Urban and Industrial Air Pollution. Science 2000, 287, 1793–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sampling Duration (h) | Total Volume Collected (mL) | Precipitation Rate (mL cm−2 d−1) (a) | Onset Freezing Temp. (°C) | INP−7 Concentration (mL−1) | Ambient Air Temperature (°C) (b) | Relative Humidity (b) | Pression (hPa) (b) | |||||||
| Min | 24 | 12 | 0.024 | −7.5 | 0.00 | −1.3 | 34.0 | 916 | ||||||
| Max | 24 | 1100 | 2.2 | −3 | 8.15 | 19.9 | 120.8 | 954 | ||||||
| Mean | 24 | 239.7 | 0.5 | −5.3 | 2.08 | 9.2 | 86.9 | 937 | ||||||
| Std error | - | 265.8 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 2.14 | 5.1 | 21.0 | 8 | ||||||
| n | 121 | 121 | 121 | 121 | 121 | 101 | 101 | 101 | ||||||
| Mean Wind Speed (m s−1) (b) | Max Wind Speed (m s−1) (b) | Cells Conc. (mL−1) | 1-fv (c) | pH | Cl− (µM) | NO3− (µM) | SO42− (µM) | PO43− (µM) | Na+ (µM) | NH4+ (µM) | K+ (µM) | Mg2+ (µM) | Ca2+ (µM) | |
| Min | 0.59 | 1.62 | 2.4 × 102 | −0.18 | 4.30 | 1.9 | 3.5 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 1.9 | 7.0 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 6.6 |
| Max | 9.16 | 14.65 | 6.61 × 105 | 0.85 | 7.02 | 32.9 | 36.4 | 21.3 | 3.8 | 13.6 | 60.0 | 16.4 | 3.5 | 33.0 |
| Mean | 3.32 | 6.70 | 2.6 × 104 | 0.5 | 5.59 | 6.3 | 15.3 | 5.0 | 1.3 | 3.9 | 29.9 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 11.2 |
| Std error | 1.70 | 2.64 | 9.3 × 104 | 0.2 | 0.51 | 7.1 | 9.6 | 5.5 | 0.8 | 2.8 | 16.3 | 3.7 | 0.8 | 6.7 |
| n | 84 | 84 | 62 | 106 | 121 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pouzet, G.; Peghaire, E.; Aguès, M.; Baray, J.-L.; Conen, F.; Amato, P. Atmospheric Processing and Variability of Biological Ice Nucleating Particles in Precipitation at Opme, France. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110229
Pouzet G, Peghaire E, Aguès M, Baray J-L, Conen F, Amato P. Atmospheric Processing and Variability of Biological Ice Nucleating Particles in Precipitation at Opme, France. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(11):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110229
Chicago/Turabian StylePouzet, Glwadys, Elodie Peghaire, Maxime Aguès, Jean-Luc Baray, Franz Conen, and Pierre Amato. 2017. "Atmospheric Processing and Variability of Biological Ice Nucleating Particles in Precipitation at Opme, France" Atmosphere 8, no. 11: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110229
APA StylePouzet, G., Peghaire, E., Aguès, M., Baray, J.-L., Conen, F., & Amato, P. (2017). Atmospheric Processing and Variability of Biological Ice Nucleating Particles in Precipitation at Opme, France. Atmosphere, 8(11), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110229






