Evaluating the Relationship between Field Aerodynamic Roughness and the MODIS BRDF, NDVI, and Wind Speed over Grassland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
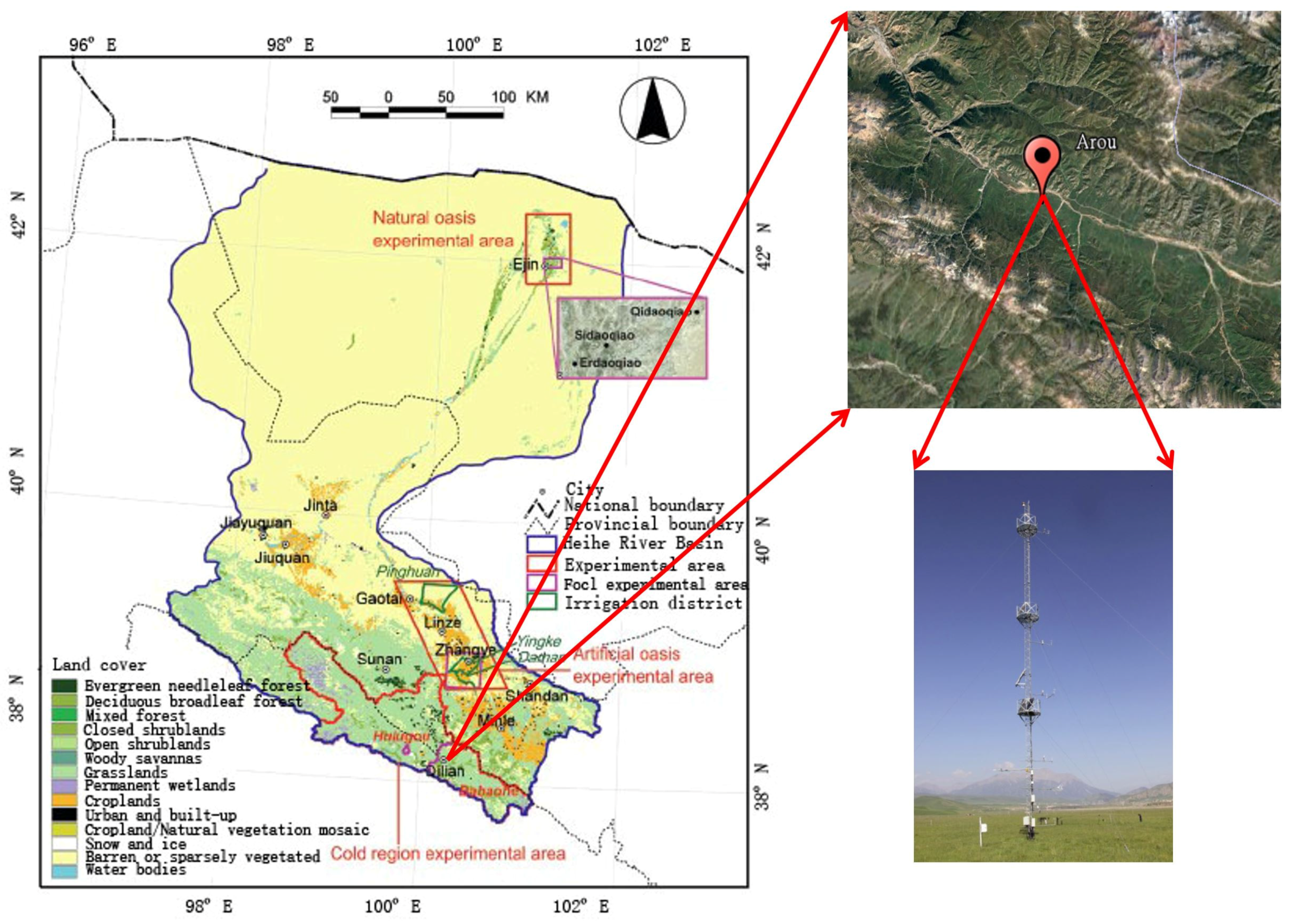
2. Research Site and Experiments
3. Methodology
3.1. Remote Sensing Index
3.1.1. MODIS BRDF_R Index
3.1.2. NDVI
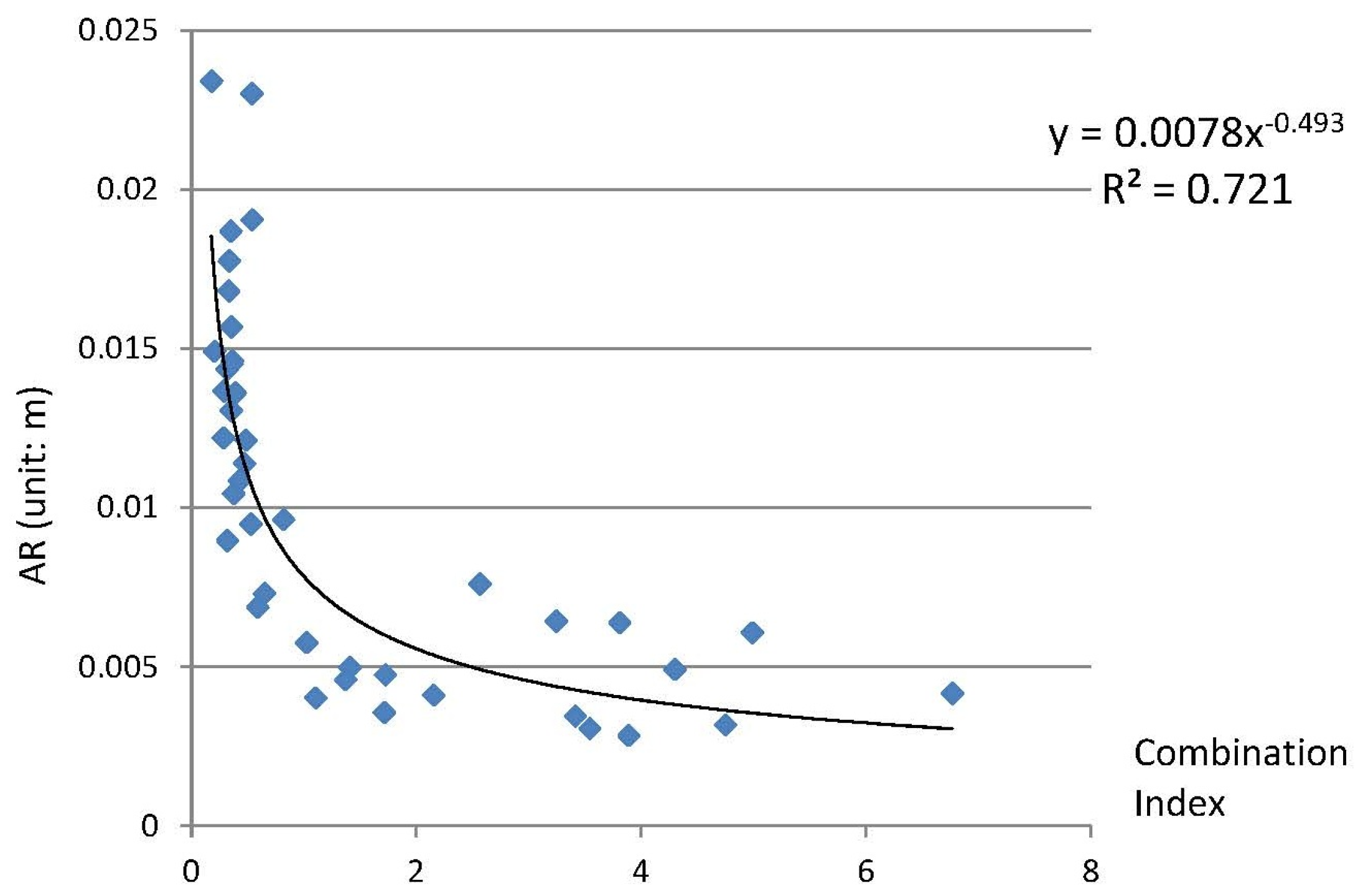
3.1.3. Combination Index
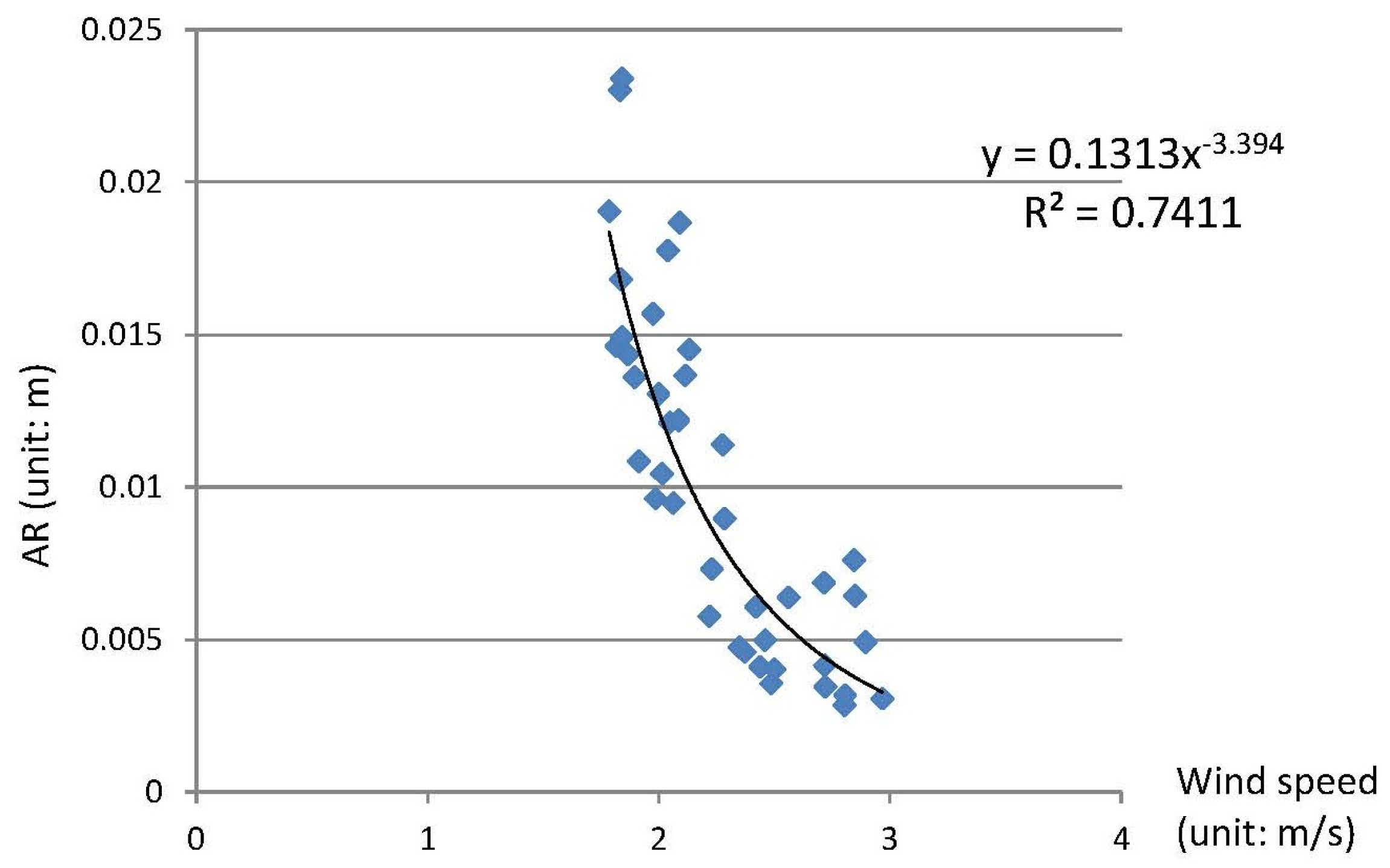
3.2. Field Aerodynamic Roughness Calculation
4. Results and Analysis
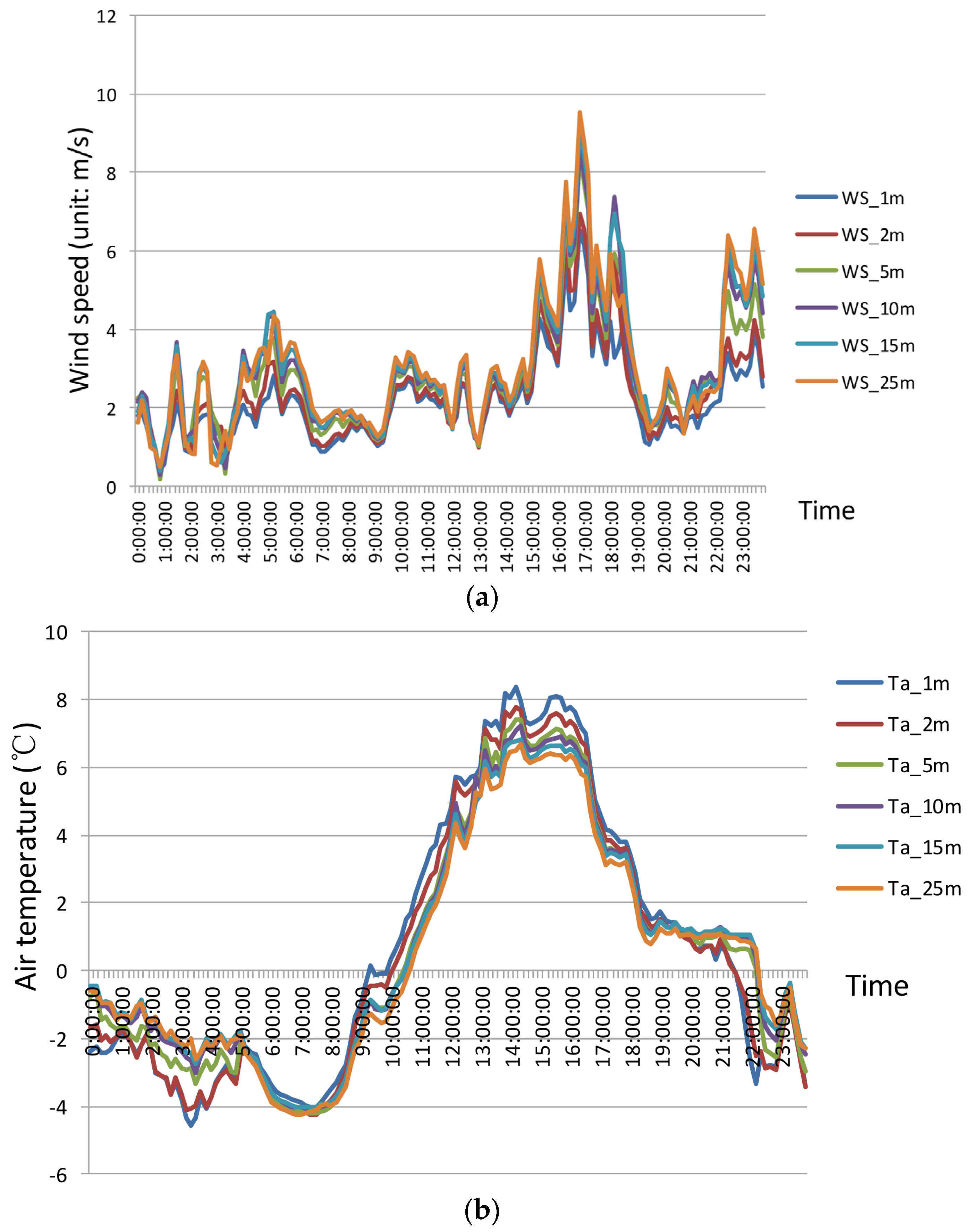
4.1. Consistency Analysis of the Observed Data
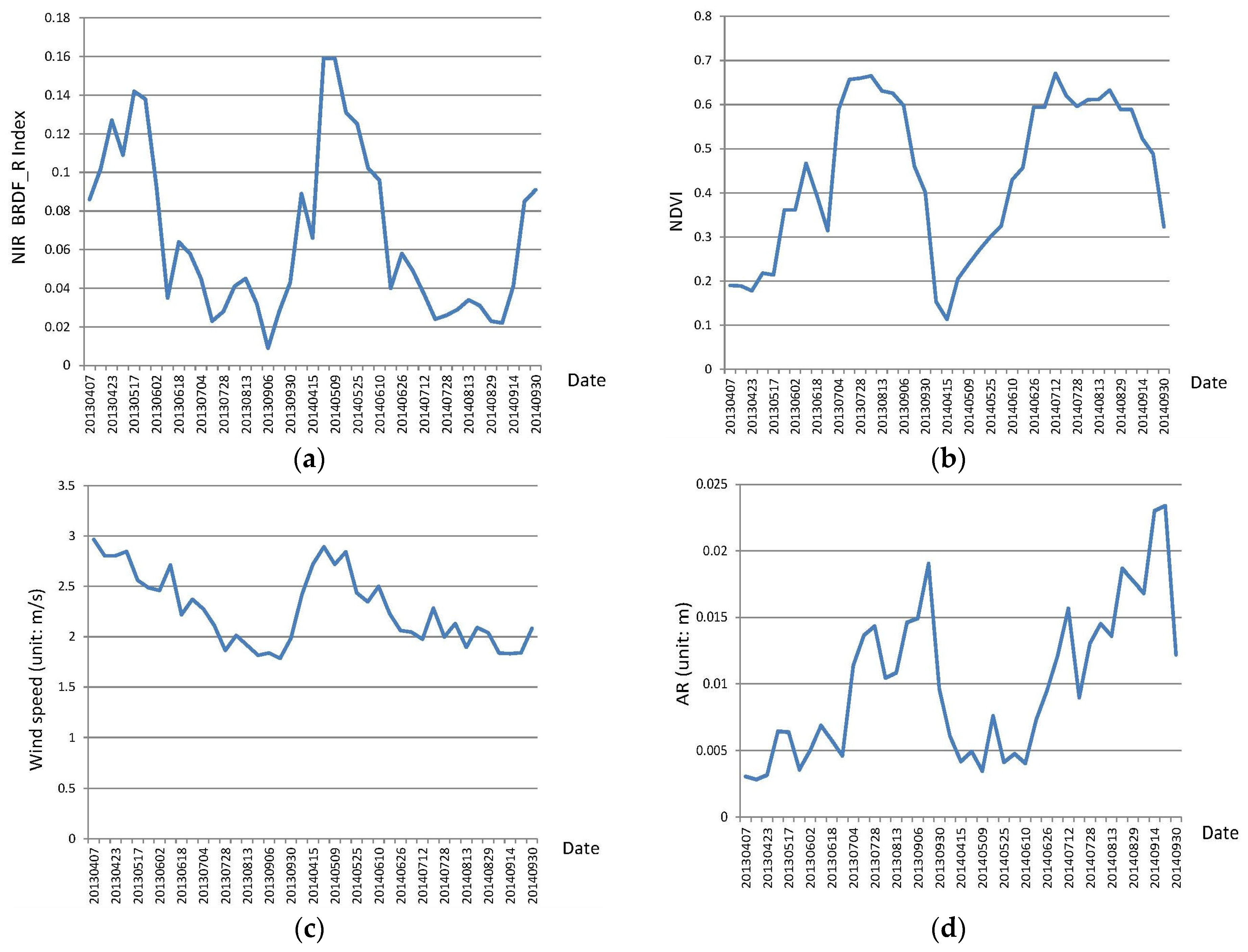
4.2. Change Trend Analysis of the Indicators
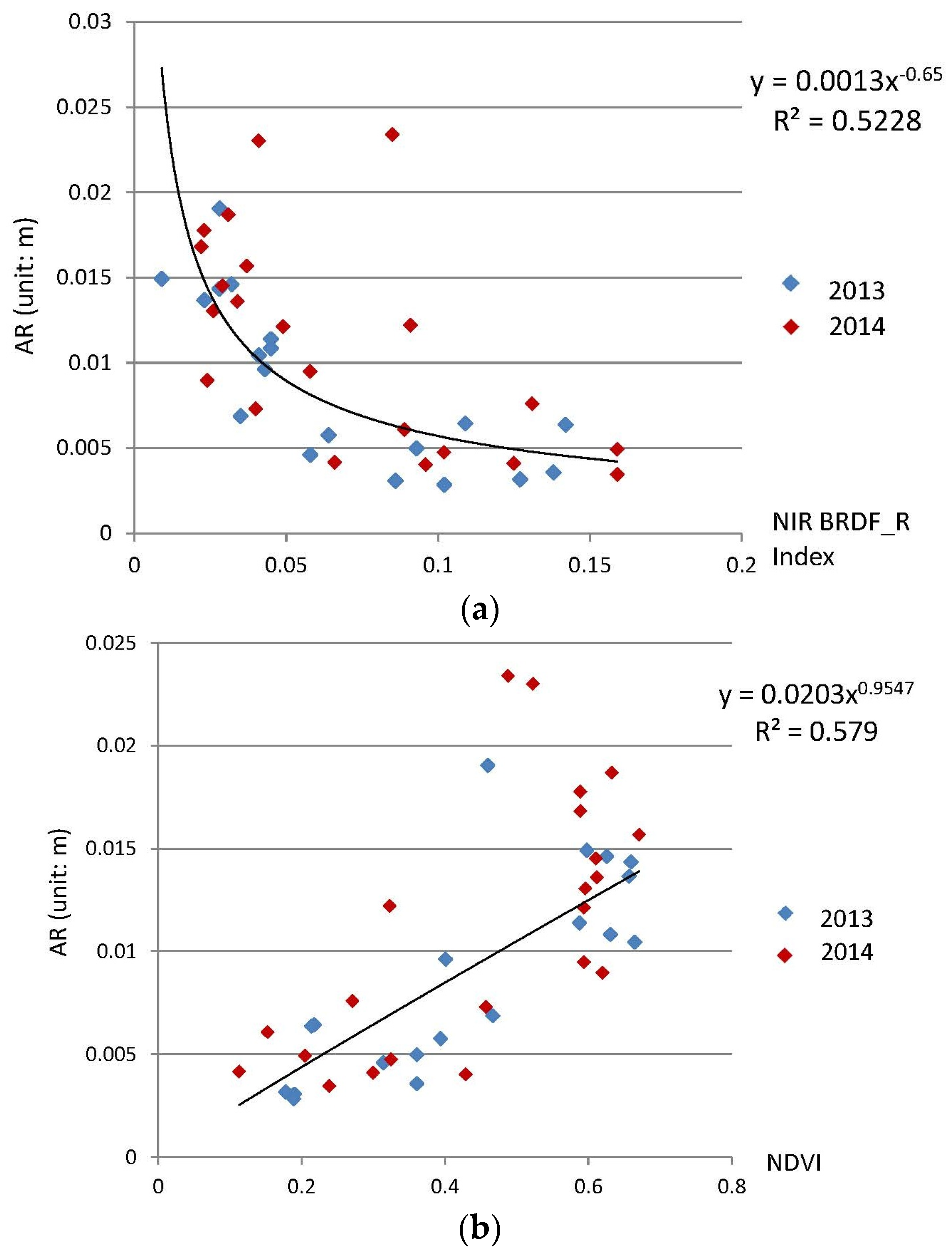
4.3. Relationship Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blumberg, D.G.; Greeley, R. Field studies of aerodynamic roughness length. J. Arid Environ. 1993, 25, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marticorena, B.; Kardous, M.; Bergametti, G.; Callot, Y.; Chazette, P.; Khatteli, H.; Hegarat-Mascle, S.L.; Maille, M.; Rajot, J.L. Surface and aerodynamic roughness in arid and semiarid areas and their relation to radar backscatter coefficient. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, R.; Lancaster, N.; Sullivan, R.J.; Saunders, R.S.; Theilig, E.; Wall, S.; Dobrovolskis, A.; White, B.R.; Iversen, J.D. A relationship between radar backscatter and aerodynamic roughness: Preliminary results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1988, 15, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, R.; Blumberg, D.G.; McHone, J.F.; Dobrovolskis, A.; Iversen, J.D.; Lancaster, N.; Rasmussen, K.R.; Wall, S.D.; White, B.R. Applications of spaceborne radar laboratory data to the study of Aeolian processes. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 10971–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, D.J.; Clow, G.D.; Tigges, R.K.; Reynolds, R.L., Jr.; Chavez, P.S. Comparison of aerodynamically and model-derived roughness lengths (Z0) over diverse surfaces, central Mojave Desert, California, USA. Geomorphology 2004, 63, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL)—1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.T.; Jia, L.; Hutjes, R.; Menenti, M. Estimation of aerodynamic roughness length over oasis in the Heihe River Basin by utilizing Remote Sensing and ground data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3690–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Li, Z.Y.; Tol, C.V.; Su, Z.; Li, X.; He, Q.S.; Bao, Y.F.; Chen, E.X.; Li, L.H. Estimating zero-plane displacement height and aerodynamic roughness length using synthesis of LiDAR and SPOT-5 data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2330–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, J.; Faivre, R. Aerodynamic roughness length estimation from very high-resolution imaging LIDAR observations over the Heihe Basin in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2661–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.O.; Bréon, F.M. Towards a generalized approach for correction of the BRDF effect in MODIS directional reflectances. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujean, J.L.; Leroy, M.; Deschamps, P.Y. A bidirectional model of the Earth’s surface for the correction of remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 20455–20468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.F.; Xing, Q.; Yan, N.N.; Zhu, W.W.; Zhuang, Q.F. A linear relationship between temporal multiband MODIS BRDF and aerodynamic roughness in HiWATER wind gradient data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 507–511. [Google Scholar]
- Stull, R.B. Meteorology for Scientists and Engineers, 2nd ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.M.; Tsukamoto, O.; Wang, J.M.; Ishikawa, H.; Tamagawa, I. Analysis of aerodynamic and thermodynamic parameters on the grassy marshland surface of Tibetan Plateau. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2002, 12, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Koike, T.; Yang, D. Surface flux parameterization in the Tibetan Plateau. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2003, 116, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, W.B.; Chris, H.H. Estimating aerodynamic roughness (Z0) in mixed grassland prairie with airborne LiDAR. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 37, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.D.; Liu, S.M.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.G.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.H.; Wang, W.Z.; Qi, Y.; et al. Heihe Watershed Allied Telemetry Experimental Research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, S.M.; Liu, Q.H.; Ma, M.G.; Xiao, Q.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Wang, W.Z.; Qi, Y.; Guo, J.W.; et al. Implementation Plan of the Heihe Watershed Allied Telemetry Experimental Research (HiWATER); Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Lanzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Zhu, Z.L.; Jia, Z.Z.; Zhu, M.J. Measurements of evapotranspiration from eddy-covariance systems and large aperture scintillometers in the Hai River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 487, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Wang, W.Z.; Bai, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.M. A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.F.; Yan, N.N.; Xiong, J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Zhu, W.W.; Stein, A. Validation of ETWatch using field measurements at diverse landscapes: A case study in Hai Basin of China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 43, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Ju, W.M.; Sun, X.M.; Wen, X.F. Significant decrease of uncertainties in sensible heat flux simulation using temporally variable aerodynamic roughness in two typical forest ecosystems of China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2012, 51, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Sun, X.M.; Zhu, Z.L.; Zhang, R.H.; Tian, J.; Liu, Y.F.; Guan, D.X.; Yuan, G.F. Surface roughness length dynamic over several different surfaces and its effects on modeling fluxes. Sci. China Ser. D 2006, 49, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Instrument | Observation Height |
|---|---|---|
| Air temperature and humidity | HMP45C, Vaisala, Vaisala Oyj, Vanha Nurmijärventie 21, 01670 Vantaa, Finland; AV-14TH, Avalon, 35-1802 River Drive South, Jersey City, NJ 07310, USA | 1 m; 2 m; 5 m; 10 m; 15 m; 25 m |
| Wind speed and direction | 03002, R.M. Young, 2801 Aero Park Drive Traverse City, Michigan 49686 USA; Windsonic, Gill, Saltmarsh Park, 67 Gosport Street, Lymington, Hampshire, UK | |
| Air pressure | Model 278, Setra, 159 Swanson Rd. Boxborough, MA 01719, USA; PTB210, Vaisala, Vaisala Oyj, Vanha Nurmijärventie 21, 01670 Vantaa, Finland |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, Q.; Wu, B.; Yan, N.; Yu, M.; Zhu, W. Evaluating the Relationship between Field Aerodynamic Roughness and the MODIS BRDF, NDVI, and Wind Speed over Grassland. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8010016
Xing Q, Wu B, Yan N, Yu M, Zhu W. Evaluating the Relationship between Field Aerodynamic Roughness and the MODIS BRDF, NDVI, and Wind Speed over Grassland. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Qiang, Bingfang Wu, Nana Yan, Mingzhao Yu, and Weiwei Zhu. 2017. "Evaluating the Relationship between Field Aerodynamic Roughness and the MODIS BRDF, NDVI, and Wind Speed over Grassland" Atmosphere 8, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8010016
APA StyleXing, Q., Wu, B., Yan, N., Yu, M., & Zhu, W. (2017). Evaluating the Relationship between Field Aerodynamic Roughness and the MODIS BRDF, NDVI, and Wind Speed over Grassland. Atmosphere, 8(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8010016








