Horizontal Electric Field in the Vicinity of Structures Hit by Lightning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Considerations
2.1. Effect of Placing the Channel Base on the Top of the Structure
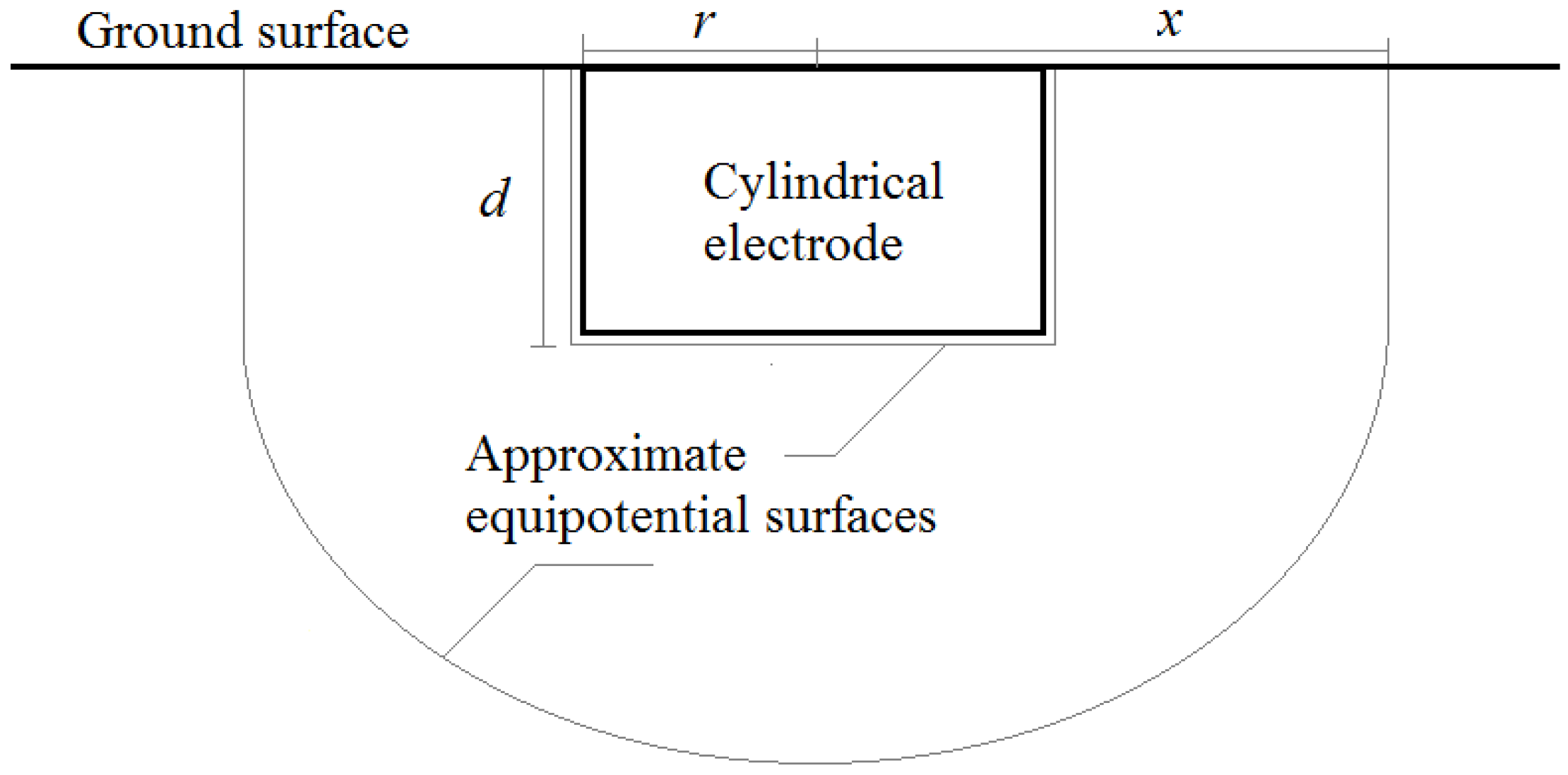
2.2. Effect of the Structure Foundation
3. Model Validation
3.1. Reference Data
3.2. Horizontal Electric Field Calculation
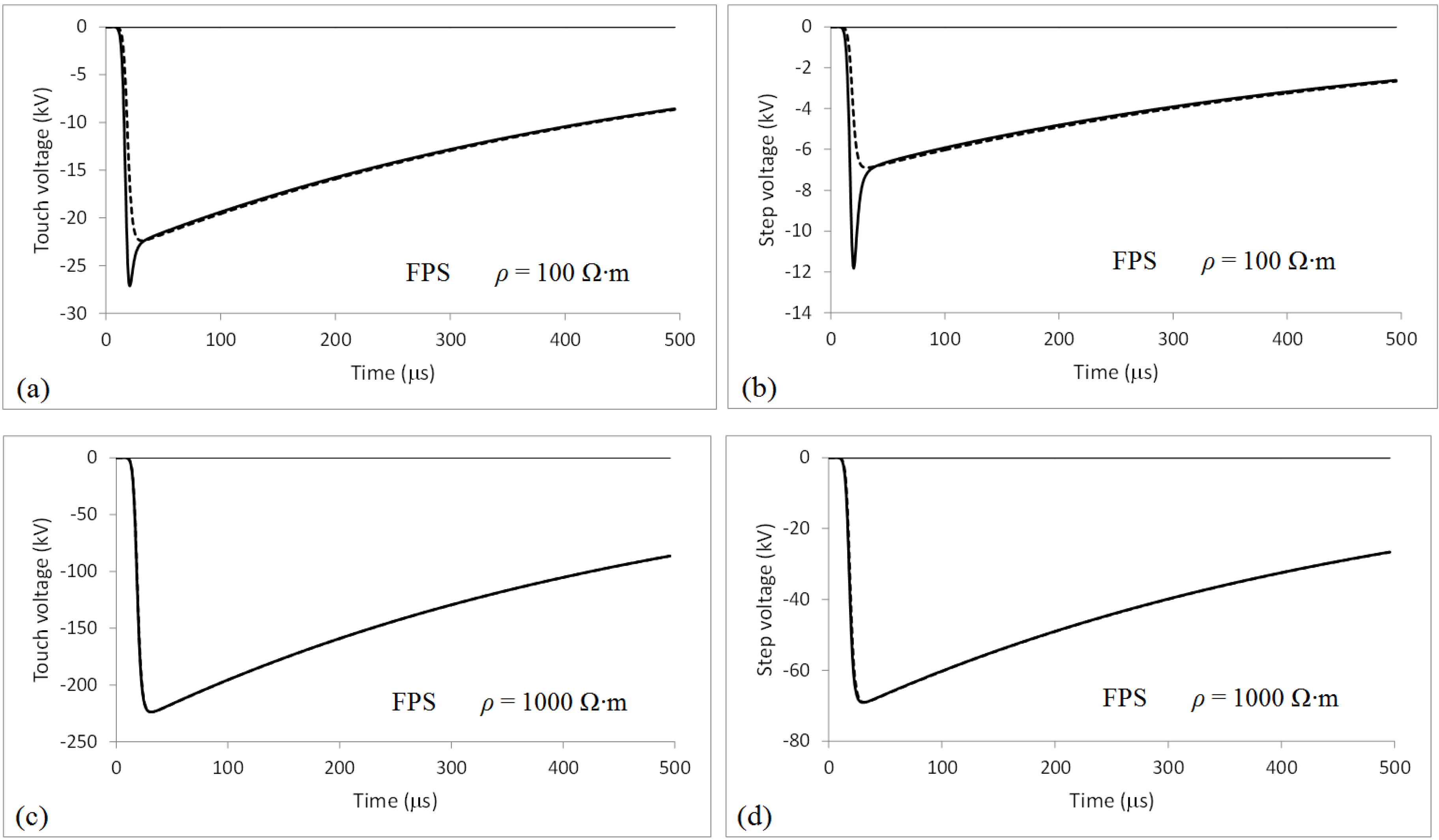
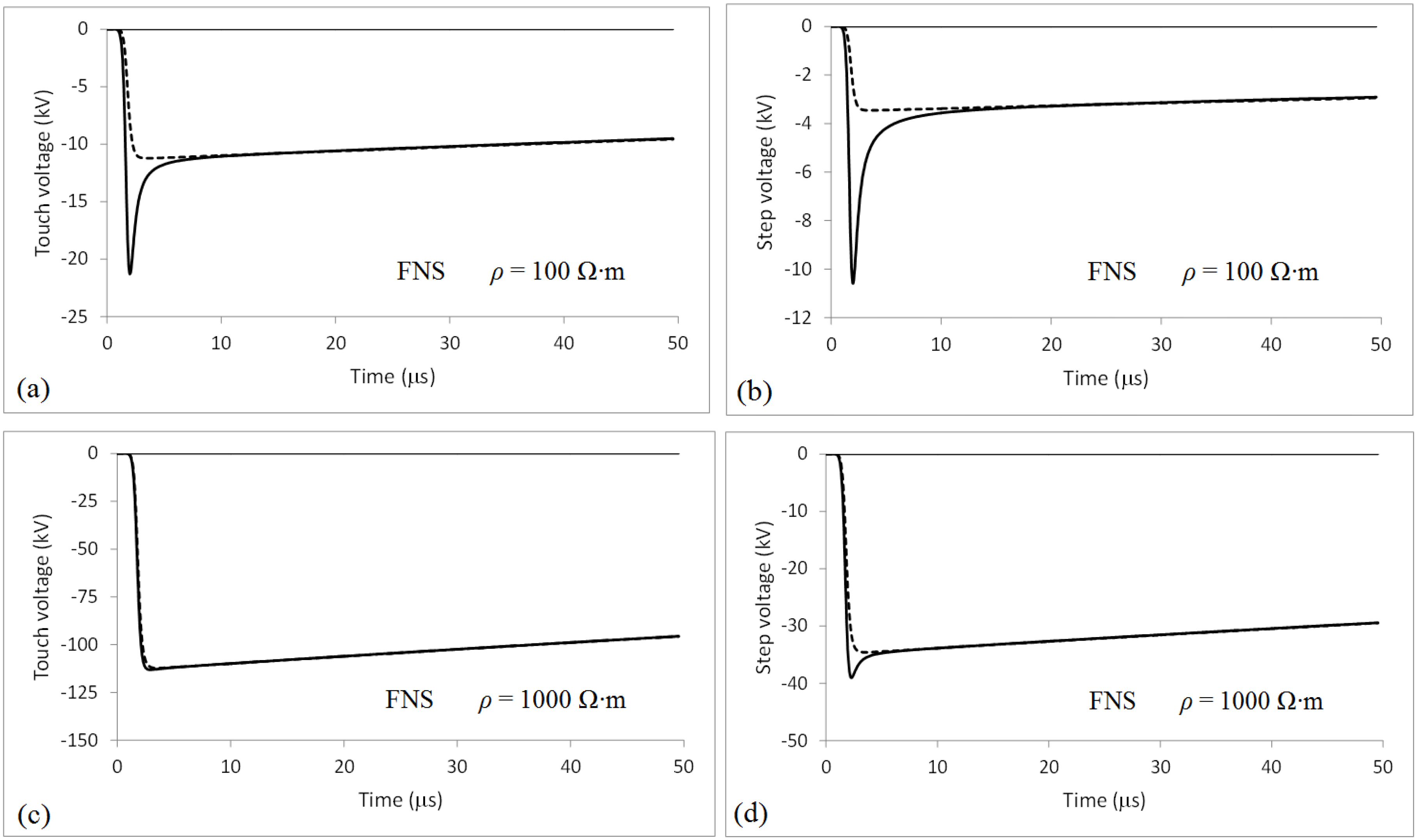
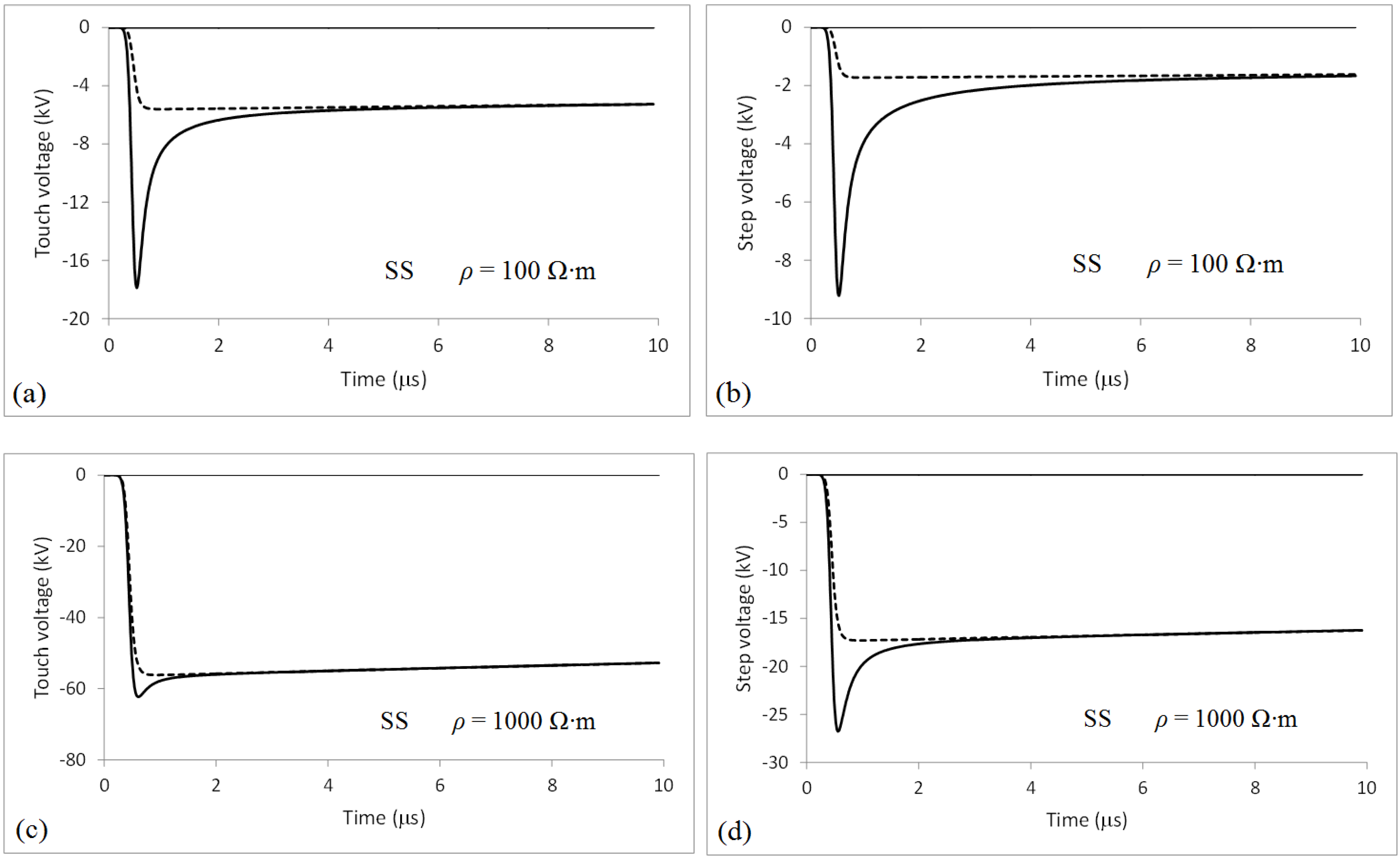
4. Touch and Step Voltages
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEC-62305–3. Protection against Lightning—Part 3: Physical Damage to Structures and Life Hazard; IEC: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, Y.; Rakov, V.A. Influence of strike object grounding on close lightning electric fields. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, A. Uber die Ausbreitung der Wellen in der drahtlosen Telegraphie. Ann. d. Phys. 1909, 28, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, A. Partial Differential Equations in Physics—Lectures on Theoretical Physics VI—Chapter VI: Problems of Radio; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Zeddam, A.; Degauque, P. Current and voltage induced on a telecommunication cable by a lightning stroke. Electromagnetics 1987, 7, 541–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, F.; Procopio, R.; Rossi, M.; Rachidi, F.; Nucci, C.A. An algorithm for the exact evaluation of the underground lightning electromagnetic fields. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, F.; Procopio, R.; Rossi, M. Lightning return stroke current radiation in presence of a conducting ground: 1. Theory and numerical evaluation of the electromagnetic fields. J. Geophys. Res. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, F.; Procopio, R.; Rossi, M.; Rachidi, F.; Nucci, C.A. Lightning return stroke current radiation in presence of a conducting ground: 2. Validity assessment of simplified approaches. J. Geophys. Res. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, F.; Procopio, R.; Rossi, M.; Rachidi, F. Influence of frequency dependent soil electrical parameters on the evaluation of lightning electromagnetic fields in air and underground. J. Geophys. Res. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, F.; Procopio, R.; Rossi, M.; Shoory, A.; Rachidi, F. Lightning electromagnetic radiation over a stratified conducting ground−Part I: Formulation and numerical evaluation of the electromagnetic fields. J. Geophys. Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoory, A.; Rachidi, F.; Delfino, F.; Procopio, R.; Rossi, M. Lightning electromagnetic radiation over a stratified conducting ground−Part II: Validity of simplified approaches. J. Geophys. Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, V. Horizontal fields generated by return strokes. Radio Sci. 1992, 27, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, M. An approximate formula for the calculation of the horizontal electric field from lightning at close, intermediate and long range. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 1996, 38, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachidi, F.; Rubinstein, M.; Zweiacker, P.; Ianoz, M.; Braendli, P.; Kaelin, A. Indirect lightning effects on short overhead lines. Int. Symp. Electromagn. Comp. 1998, 98, 345–349. [Google Scholar]
- Borghetti, A.; Nucci, C.A.; Paolone, M. An improved procedure for the assessment of overhead line indirect lightning performance and its comparison with the IEEE STD. 1410 Method. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2007, 22, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, V. Horizontal electric field above and underground produced by lightning flashes. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2010, 52, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, C.F.; Paulino, J.O.P. An approximate time domain formula for the calculation of the horizontal electric field from lightning. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2007, 49, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, J.O.S.; Barbosa, C.F.; Lopes, I.J.S.; Boaventura, W.C. Assessment and analysis of indirect lightning performance of overhead lines. Electri. Power Sys. Res. 2015, 118, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, J.O.S.; Barbosa, C.F.; Lopes, I.J.S.; Boaventura, W.C.; Miranda, G.C. Indirect lightning performance of aerial distribution lines considering the induced-voltage waveform. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2015, 57, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligaris, C.; Delfino, F.; Procopio, R. Cooray-Rubinstein formula for the evaluation of lightning radial electric fields: Derivation and implementation in the time domain. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2008, 50, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, F.; Girdinio, P.; Procopio, R.; Rossi, M.; Rachidi, F. Time-domain implementation of Cooray–Rubinstein Formula via convolution integral and rational approximation. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2011, 53, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, A.; Rachidi, F.; Verolino, L. A new formulation of the Cooray–Rubinstein expression in time domain. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2015, 57, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, C.F.; Paulino, J.O.S. A time-domain formula for the horizontal electric field at the earth surface in the vicinity of lightning. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2010, 52, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, V. Horizontal electric field at ground level in the vicinity of lightning return stroke channels evaluated using Sommerfeld’s integrals. In Processing of the 29th International Conference on Lightning Protection, Uppsala, Sweden, 23–26 June 2008.
- Paulino, J.O.S.; Barbosa, C.F.; Lopes, I.J.S.; Miranda, G.C. Time-domain analysis of rocket-triggered lightning-induced surges on an overhead line. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2009, 51, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, J.O.S.; Barbosa, C.F.; Boaventura, W.C. Effect of the surface impedance on the induced voltages in overhead lines from nearby lightning. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2011, 53, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, J.O.S.; Barbosa, C.F.; Boaventura, W.C. Lightning-induced current in a cable buried in the first layer of a two-layer ground. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2014, 56, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC-62305–1. Protection against Lightning−Part 1: General Principles; IEC: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Uman, M.A.; McLain, D.K. Magnetic field of lightning return stroke. J. Geophys. Res. 1969, 74, 6899–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusck, S. Induced lightning overvoltages on power transmission lines with special reference to the overvoltage protection of low voltage networks. Trans. Royal Inst. Tech. 1958, 120, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Cooray, V.; Cooray, G. The deep physics hidden within the field expressions of the radiation fields of lightning return strokes. Atmosphere 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallén, E. Lösung zweir potentialprobleme der elektrostatic. Arkif. Matematik. Astronomi. Och Fysik. 1929, 21, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Dwight, H.B. Calculation of resistances to ground. Trans. AIEE 1936, 55, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, C.F. On the vertical ground rod resistance with special reference to thick rods. In Proceedings of International Conference on Grounding and Earthing, Porto de Galinhas, Brazil, 10–16 June 2016.
- Heidler, F.; Manhardt, M.; Stimper, K. Upward positive lightning measured at the Peissenberg Tower, Germany. Int. Symp. Light. Prot., SIPDA 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidler, F. Analitsche blitzstromfunktion zur LEMP-berechnung. In Proceedings of 18th International Conference Lightning Protection, Munich, Germany, 2–9 August 1985.
- Greenwood, A. Electrical Transients in Power Systems—Section 2.6: Duhamel’s Integral - Response of A Circuit to An Arbitrary Stimulus; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, Y.; Rakov, V.A. Voltages induced on an overhead wire by lightning strikes to a nearby tall grounded object. IEEE Trans. Elect. Compat. 2006, 48, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachidi, F.; Janischewskyj, W.; Hussein, A.M.; Nucci, C.A.; Guerrieri, S.; Kordi, B.; Chang, J.S. Current and electromagnetic field associated with lightning return strokes to tall towers. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2001, 43, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakov, V.A. Transient response of a tall object to lightning. IEEE Trans. Elect. Comp. 2001, 43, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Component | Delay (μs) | I (kA) | τ1 (μs) | τ2 (μs) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.53 | 11.4 | 0.07 | 1.35 | 2 |
| 2 | 0.53 | 4.60 | 2.3 | 12 | 2 |
| 3 | 1.60 | 1.90 | 0.08 | 0.33 | 2 |
| 4 | 2.67 | 0.38 | 0.08 | 0.33 | 2 |
| Component | Delay (μs) | I (kA) | τ1 (μs) | τ2 (μs) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.53 | 10.3 | 0.07 | 1.50 | 2 |
| 2 | 0.53 | 4.30 | 2.1 | 25 | 2 |
| 3 | 1.60 | 2.20 | 0.08 | 0.40 | 2 |
| 4 | 2.67 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0.40 | 2 |
| Voltage | Resistivity (Ω∙m) | First Positive Stroke | First Negative Stroke | Subsequent Stroke |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Touch | 100 | 27 | 21 | 18 |
| 1000 | 224 | 113 | 62 | |
| Step | 100 | 12 | 11 | 9 |
| 1000 | 69 | 39 | 27 |
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbosa, C.F. Horizontal Electric Field in the Vicinity of Structures Hit by Lightning. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7090115
Barbosa CF. Horizontal Electric Field in the Vicinity of Structures Hit by Lightning. Atmosphere. 2016; 7(9):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7090115
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbosa, Celio Fonseca. 2016. "Horizontal Electric Field in the Vicinity of Structures Hit by Lightning" Atmosphere 7, no. 9: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7090115
APA StyleBarbosa, C. F. (2016). Horizontal Electric Field in the Vicinity of Structures Hit by Lightning. Atmosphere, 7(9), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7090115





