Gaseous Products of Incense Coil Combustion Extracted by Passive Solid Phase Microextraction Samplers
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Methods
2.1. Theory of Gaseous Compound Extraction via a Needle Trap Sampler
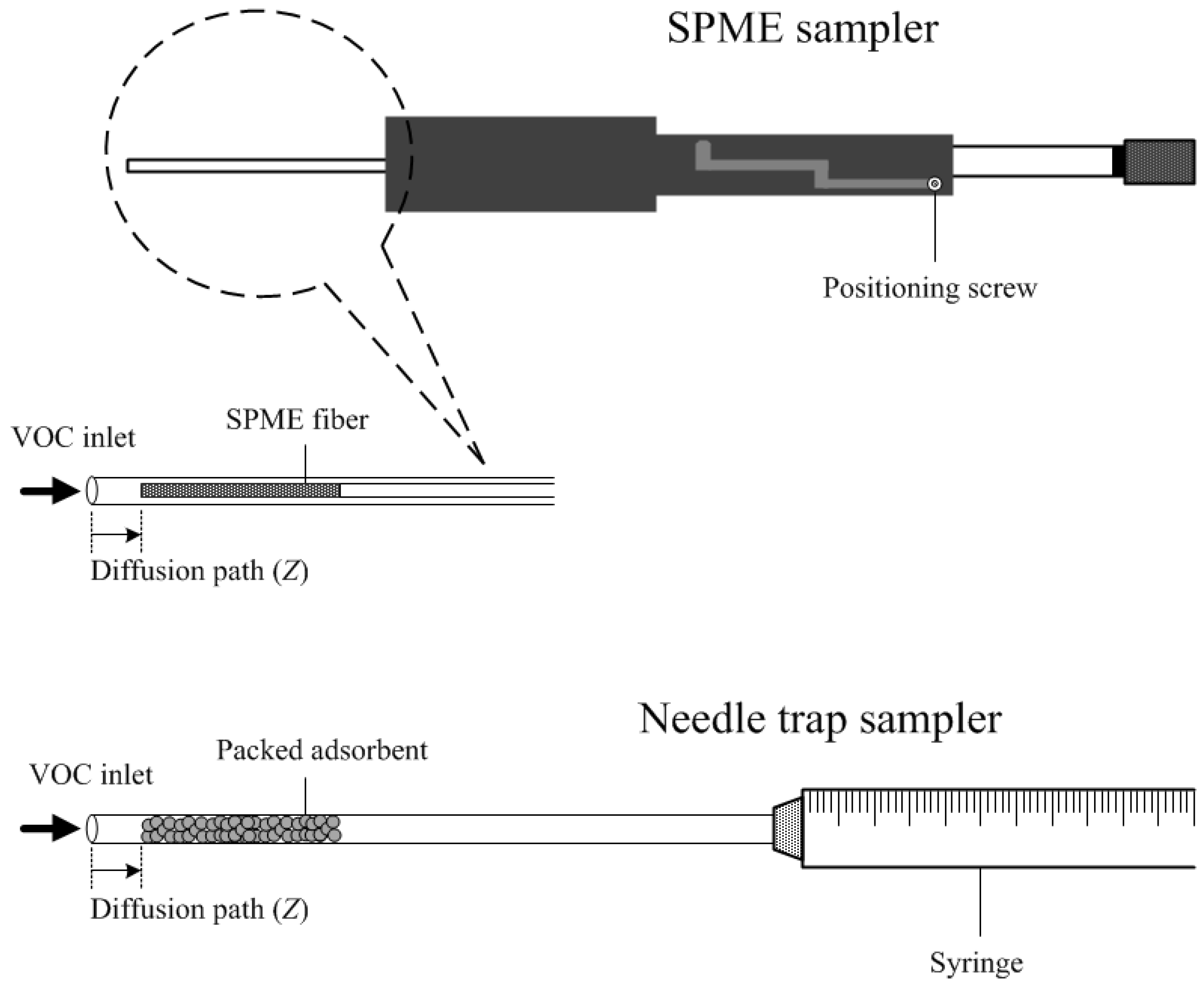
2.2. Chemicals, Materials and Equipment
2.3. Preparation of Needle Trap Sampler
2.4. Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Sampling and Analytical Products from Burning Sandalwood Incense Coils
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. VOC Combustion Products of Sandalwood Incense Coils
| Chemicals | Concentration (ppbv) a,b | Concentration (µg/m3) c |
|---|---|---|
| Alkane Compounds | ||
| Propane | 131.84 (41.20) | 258.8 |
| 1,3-Butadiene | 460.16 (57.52) | 1108.2 |
| trans-2-Butene | 42.88 (5.40) | 107.1 |
| cis-2-Butene | 40.78 (4.50) | 101.9 |
| Aromatic Compounds | ||
| Benzene | 1.12 (0.20) | 3.9 |
| Toluene | 21.12 (2.60) | 86.6 |
| Ethylbenzene | 31.76 (3.22) | 150.1 |
| m/p-Xylene | 4.48 (0.41) | 21.2 |
| o-Xylene | 4.50 (0.20) | 21.3 |
| Styrene | 4.08 (0.51) | 18.9 |
| Chlorinated Compounds | ||
| Chloromethane | 188.24 (23.53) | 423.2 |
| Dichloromethane | 33.12 (5.20) | 125.2 |
| Other Oxyganated Compounds | ||
| Methanol | 54.24 (4.60) | 77.4 |
| Acetone | 76.56 (9.57) | 198.0 |
| Vinyl acetate | 28.64 (1.20) | 109.8 |
3.2. Qualification Tests of Flow Rates and BTEX Extraction Rates for NTS
| Test Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Sampling flow rate of NTS (mean values, mL/min) a | |
| Hollow needle | 790 (RSD = 4.88%) |
| NTS packed with 60–80 mesh DVB adsorbents | 64.2 (RSD = 4.79%) |
| NTS packed with 100–120 mesh DVB adsorbents | 47.1 (RSD = 4.98%) |
| VOC extraction rates (mean values, ng BTEX/min) b,c,d | |
| 60–80 mesh DVB NTS | |
| Benzene | 2.22 (RSD = 3.73%) |
| Toluene | 3.29 (RSD = 4.66%) |
| Ethylbenzene | 4.58 (RSD = 4.37%) |
| o-Xylene | 6.13 (RSD = 4.90%) |
| 100–120 mesh DVB NTS | |
| Benzene | 4.58 (RSD = 4.36%) |
| Toluene | 5.55 (RSD = 3.00%) |
| Ethylbenzene | 7.19 (RSD = 4.63%) |
| o-Xylene | 8.58 (RSD = 4.08%) |
| 100 μm PDMS-SPME fiber sampler | |
| Benzene | 1.56 (RSD = 0.9%) |
| Toluene | 3.14 (RSD = 1.0%) |
| Ethylbenzene | 4.52 (RSD = 1.6%) |
| o-Xylene | 5.33 (RSD = 2.8%) |
3.3. Sampling Products from Incense Coils by SPME Fiber and NTS Samplers
 ,
,  and
and  respectively indicate the integral area extracted by 60–80 mesh, 100–120 mesh NTS and SPME fibers via GC-GID analysis.
respectively indicate the integral area extracted by 60–80 mesh, 100–120 mesh NTS and SPME fibers via GC-GID analysis.
 ,
,  and
and  respectively indicate the integral area extracted by 60–80 mesh, 100–120 mesh NTS and SPME fibers via GC-GID analysis.
respectively indicate the integral area extracted by 60–80 mesh, 100–120 mesh NTS and SPME fibers via GC-GID analysis.


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, T.-T. The air pollution of burning incense sticks and its health hazards and control strategy. Environ. Protect. Source 2014, 197. Available online: http://www.fengtay.org.tw/paper.asp?page=2014&num=1373&num2=231 (accessed on 21 October 2014). (In Chinese)[Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, K.F.; Kang, Y.M. Characteristics of emissions of air pollutants from burning of incense in temples, Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 377, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.-T.; Lin, S.-T.; Lin, T.-S.; Hong, W.-L. Characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon emissions in the particulate phase from burning incenses with various atomic hydrogen/carbon ratios. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, S.-C.; Tsai, Y.-I.; Khajornsak, S. Emission identification and health risk potential of allergy-causing fragrant substances in PM2.5 from incense burning. Build. Environ. 2015, 87, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navasumrit, P.; Arayasiri, M.; Hiang, O.M.T.; Leechawengwongs, M.; Promvijit, J.; Choonvisase, S.; Chantchaemsai, S.; Nakngam, N.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, M. Potential health effects of exposure to carcinogenic compounds in incense smoke in temple workers. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2008, 173, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.-T.; Chen, S.-J.; Huang, K.-L.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lee, W.-J.; Chang-Chien, G.-P.; Tsai, J.-H.; Lee, J.-T.; Chiu, C.-H. Characteritization of, and health risks from, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans from incense burned in a temple. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4870–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.; Sexton, K.G.; Yeatts, K.B. Hazard assessment of United Arab Emirates (UAE) incense smoke. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Lee, H.-W.; Tseng, H.-H. The formation of incense smoke. J. Aerosol Sci. 2007, 38, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, H.; Pawliszyn, J. Evolution of solid phase microextraction technology. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 885, 153–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-H.; Zhan, W.; Pawliszyn, J. Extraction of gaseous VOCsusing passive needle trap samplers. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.-H.; Zhan, W.; Pawliszyn, J. Gaseous and particle-bound VOC products of combustion extracted by needle trap samplers. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2013, 60, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-H.; Jiang, J.-R.; Lin, C.; Liou, J.-J.; Wu, Z.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Yang, Z.-Y. Preparation of needle trap samplers to extract air compounds from indoor electric-vaporizing sources. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2014, 64, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-H.; Lai, C.-H. Sampling gaseous compounds from essential oils evaporation by solid phase microextraction devices. Atm. Environ. 2014, 99, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, H.; Zhan, W.; Pawliszyn, J. Fundamentals and applications of needle trap devices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 677, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lung, S.-C.; Hu, S.-C. Generation rates and emission factors of particulate matter and particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of incense sticks. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Education and Information Division. NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/ (accessed on 24 March 2015).
- Chromatography Products for Analysis & Purification. In SUPELCO Catalogue; Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013.
- NIOSH. Manual of Analytical Methods, 4th ed.; National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH): Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gałuszka, A.; Konieczka, P.; Migaszewski, Z.M.; Namieśnik, J. Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, W.-H.; Lai, C.-H.; Tzeng, W.-J.; Her, C.; Hsu, Y.-H. Gaseous Products of Incense Coil Combustion Extracted by Passive Solid Phase Microextraction Samplers. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 822-833. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6060822
Cheng W-H, Lai C-H, Tzeng W-J, Her C, Hsu Y-H. Gaseous Products of Incense Coil Combustion Extracted by Passive Solid Phase Microextraction Samplers. Atmosphere. 2015; 6(6):822-833. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6060822
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Wen-Hsi, Chin-Hsing Lai, Wen-Jiunn Tzeng, Chyn Her, and Ya-Han Hsu. 2015. "Gaseous Products of Incense Coil Combustion Extracted by Passive Solid Phase Microextraction Samplers" Atmosphere 6, no. 6: 822-833. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6060822
APA StyleCheng, W.-H., Lai, C.-H., Tzeng, W.-J., Her, C., & Hsu, Y.-H. (2015). Gaseous Products of Incense Coil Combustion Extracted by Passive Solid Phase Microextraction Samplers. Atmosphere, 6(6), 822-833. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6060822







