Chemical Composition of Water Soluble Inorganic Species in Precipitation at Shihwa Basin, Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
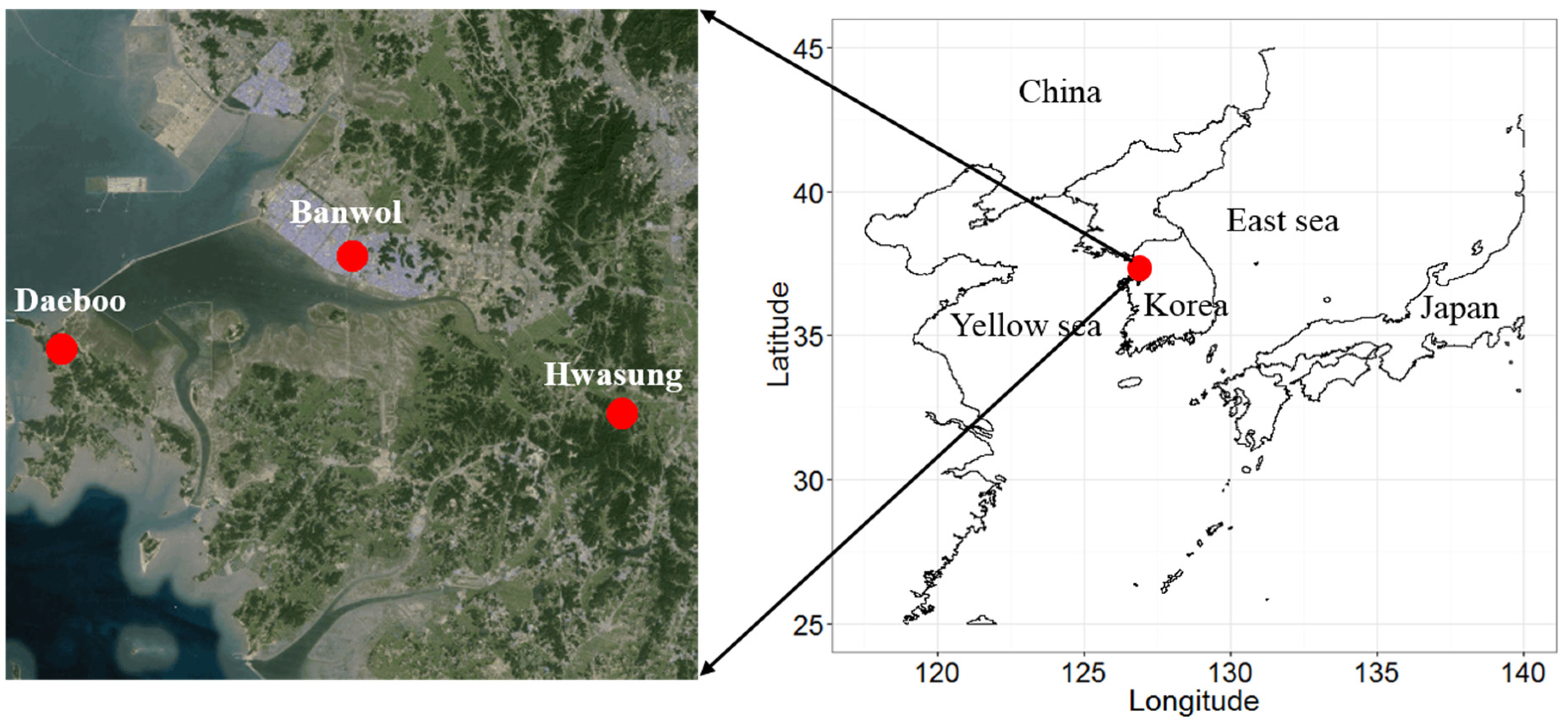
2.1. Sampling Sites
| Shihwa Basin | Latitude | Longitude | Elevation (m) | Land Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hwasung | 37.236 | 126.918 | 31 | Rural and residential |
| Banwol | 37.315 | 126.750 | 56 | Industrial |
| Daeboo | 37.268 | 126.568 | 25 | Agricultural |
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Analysis
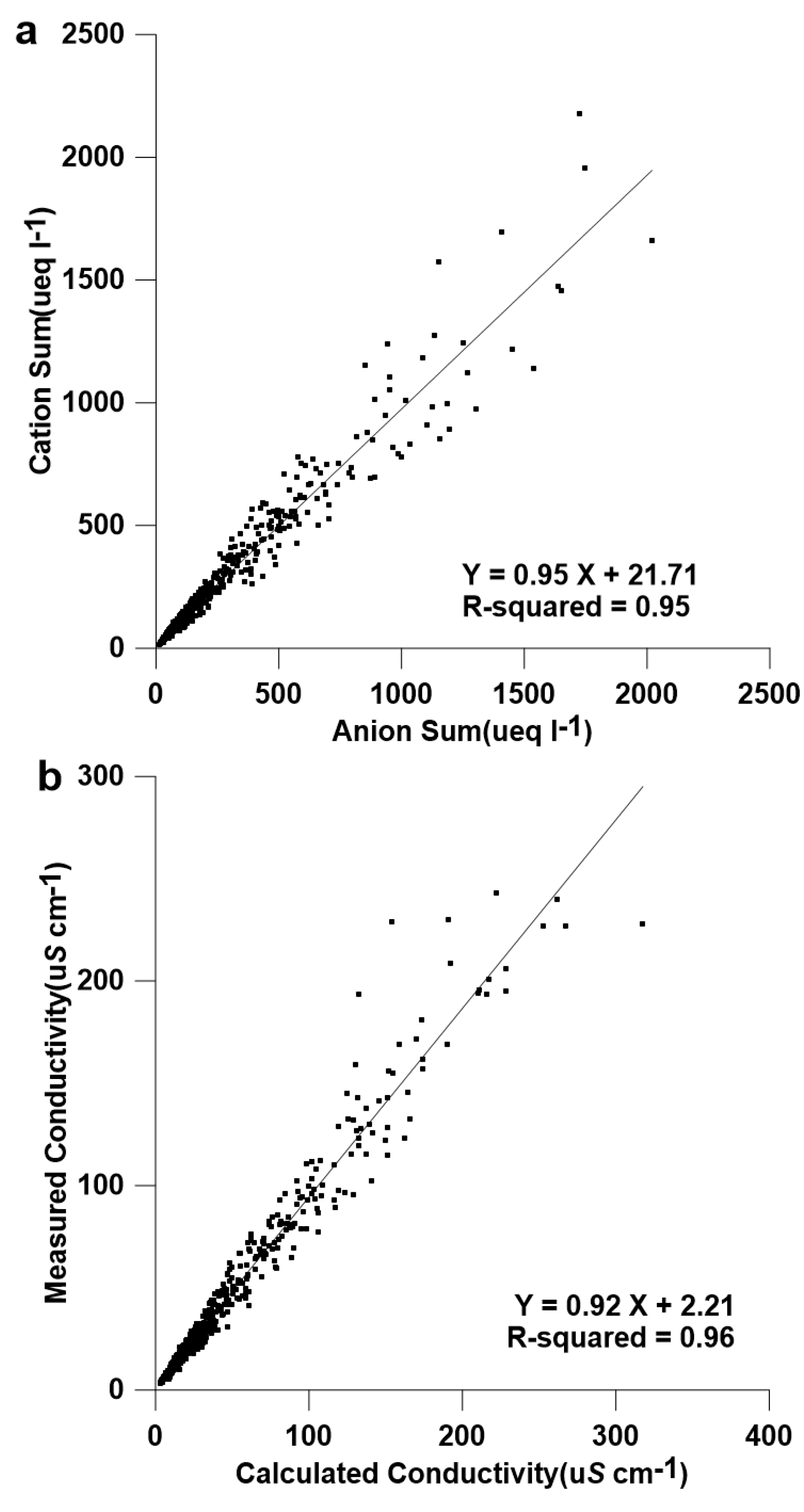
2.4. Quality Assurance
2.5. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF)
3. Results and Discussion
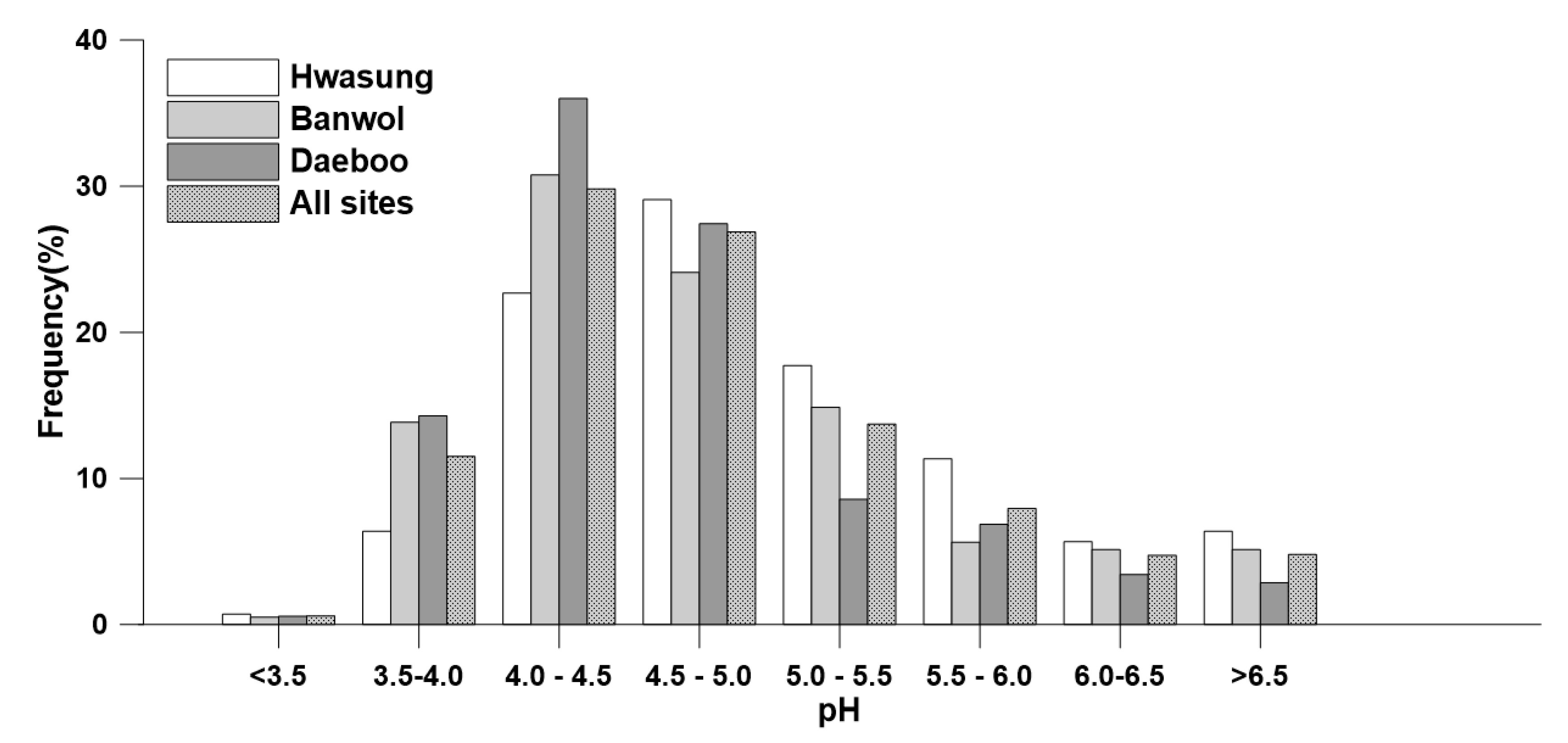
3.1. Acidity
| Station | Parameter | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hwasung | Min | 0.5 | 3.8 | 6.8 | 0.6 | 5.9 | 0.02 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 7.5 |
| Max | 472 | 482 | 1495 | 567 | 1758 | 163 | 297 | 781 | 3.4 | |
| Mean | 45 | 68 | 127 | 33 | 117 | 9 | 15 | 57 | 4.5 | |
| Standard deviation | 82 | 101 | 72 | 79 | 122 | 20 | 32 | 134 | 0.8 | |
| VWM | 13.9 | 19.6 | 45.2 | 9.3 | 43.6 | 3.6 | 4.5 | 13.5 | 4.7 | |
| Banwol | Min | 1.4 | 2.0 | 4.7 | 0.5 | 5.7 | 0.03 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 7.7 |
| Max | 683 | 598 | 839 | 506 | 539 | 308 | 144 | 639 | 3.5 | |
| Mean | 58 | 71.3 | 145 | 34.7 | 116 | 9 | 14 | 65 | 4.3 | |
| Standard deviation | 93 | 83 | 160 | 66 | 104 | 12 | 23 | 108 | 0.8 | |
| VWM | 20 | 23 | 56 | 10 | 51 | 4.4 | 4.6 | 15 | 4.6 | |
| Daeboo | Min | 1.2 | 1.9 | 3.5 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 0.11 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 6.9 |
| Max | 1505 | 594 | 753 | 1434 | 588 | 87 | 320 | 763 | 3.5 | |
| Mean | 70 | 73 | 118 | 59 | 88 | 8.5 | 20 | 61 | 4.4 | |
| Standard deviation | 119 | 89 | 134 | 88 | 89 | 20 | 33 | 115 | 0.7 | |
| VWM | 25 | 22 | 40 | 17 | 40 | 5.1 | 6.6 | 15 | 4.6 |
3.2. Concentration of Inorganic Species
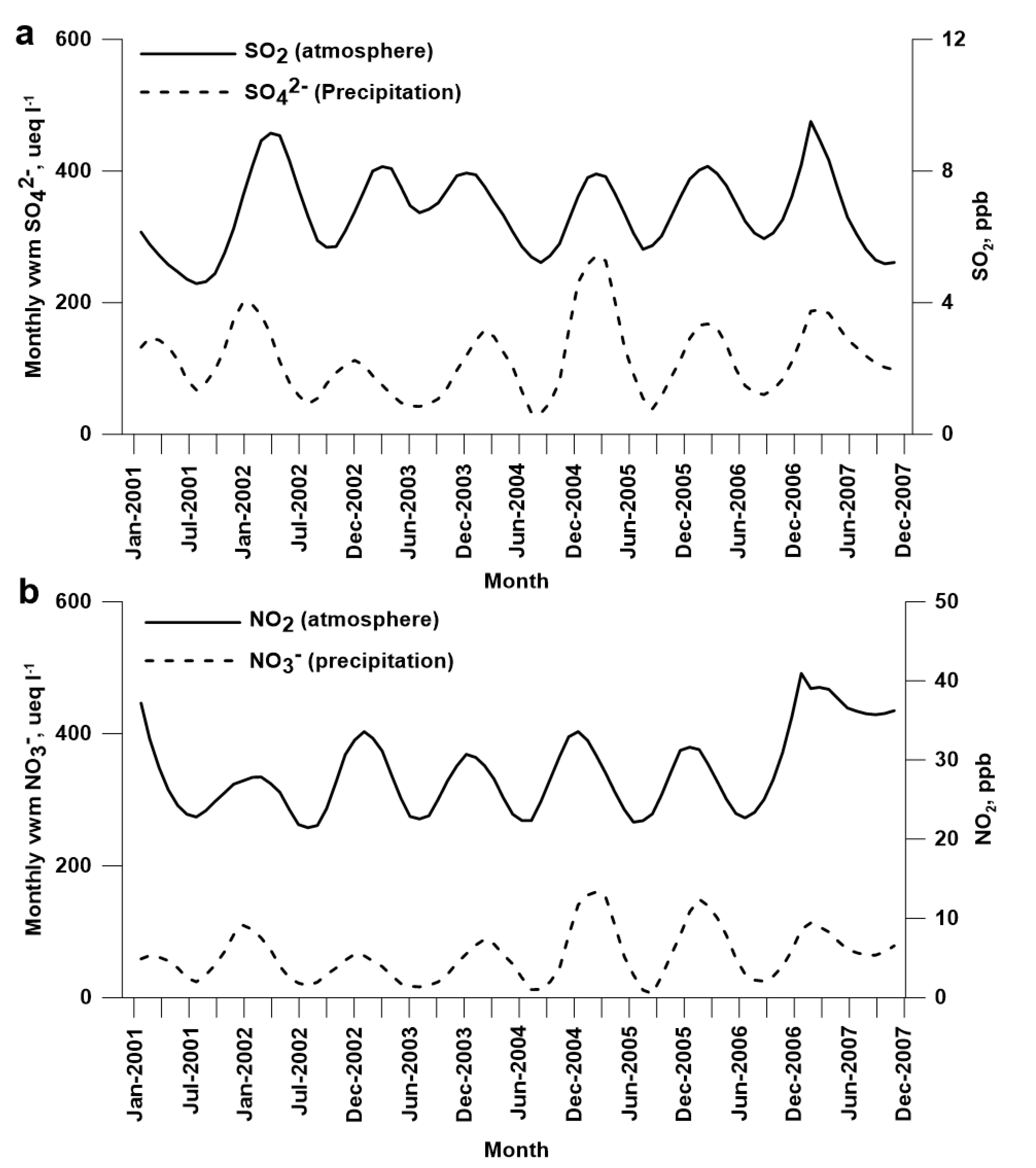
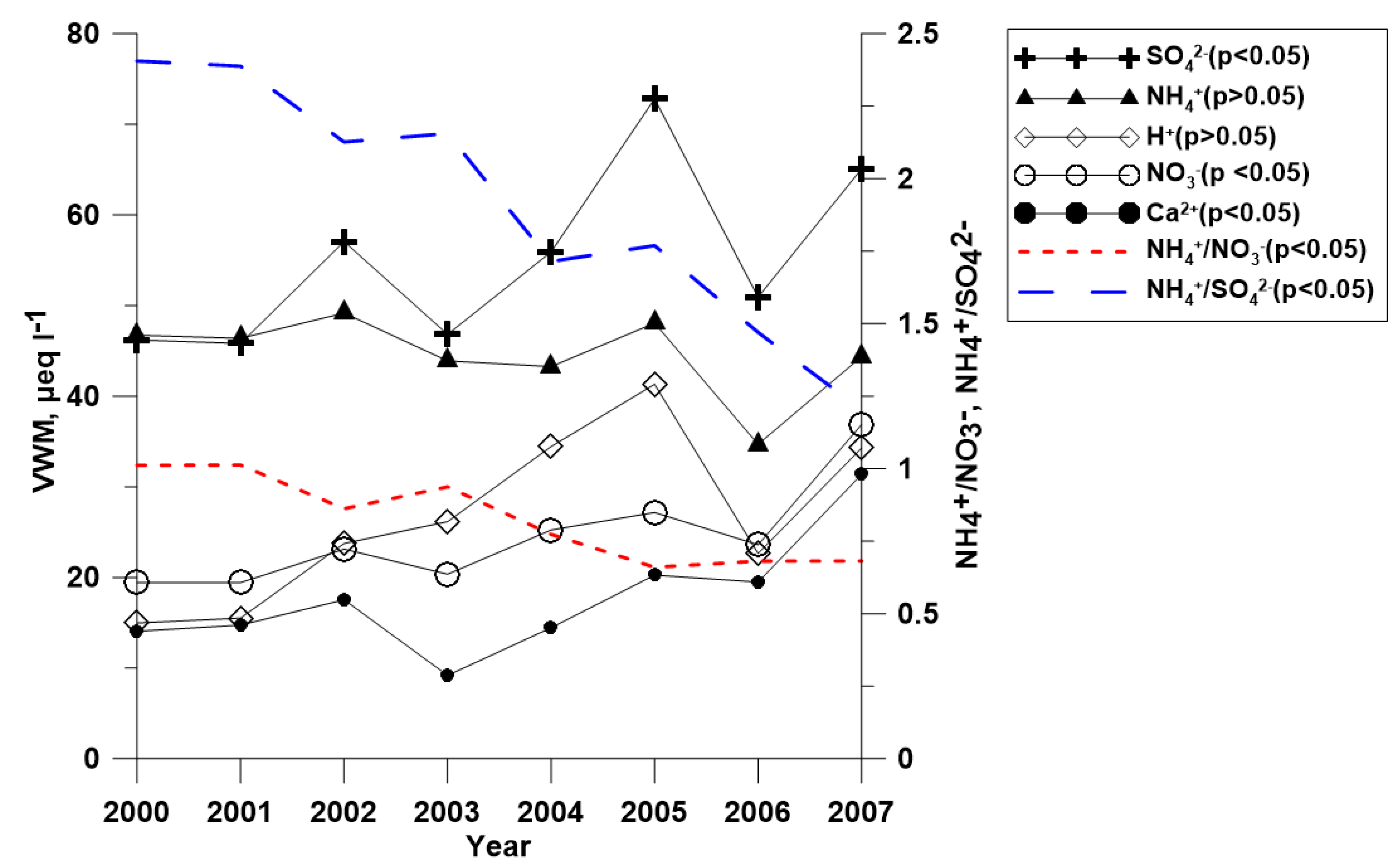
3.3. Temporal Variation

| East Asia | Year(s) | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing a (N China) | 2003 | - | 118 | 380 | - | 211 | - | - | 159 | 6.48 |
| China b (SE China) | 2004 | 9 | 31 | 95 | 6 | 81 | 5 | 3 | 48 | 4.54 |
| Cai Jia Tang c (S China) | 2003 | 11 | 60 | 155 | 7 | 112 | 10 | 10 | 60 | 4.33 |
| Hong Kong d | 1999–2000 | 43 | 27 | 74 | 37 | 22 | 4 | 7 | 16 | 4.20 |
| Singapore e | 1999–2000 | 34 | 22 | 84 | 33 | 19 | 7 | 7 | 16 | 4.20 |
| Japan f (Tokyo) | 1990–2002 | 55 | 31 | 50 | 37 | 40 | 3 | 12 | 25 | 4.52 |
| Jeju g (Korea) | 2000-2007 | 40 | 23 | 22 | 24 | 40 | 21 | 3 | 9 | 5.37 |
| This study | 2000–2007 | 23 | 23 | 54 | 13 | 44 | 4 | 6 | 17 | 4.84 |
3.4. Statistical Analysis
| Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO3− | 0.56 | ||||||
| SO42− | 0.62 | 0.82 | |||||
| Na+ | 0.89 | 0.58 | 0.64 | ||||
| NH4+ | 0.52 | 0.76 | 0.83 | 0.48 | |||
| K+ | 0.66 | 0.43 | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.55 | ||
| Mg2+ | 0.74 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.82 | 0.49 | 0.47 | |
| Ca2+ | 0.63 | 0.71 | 0.82 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 0.80 |
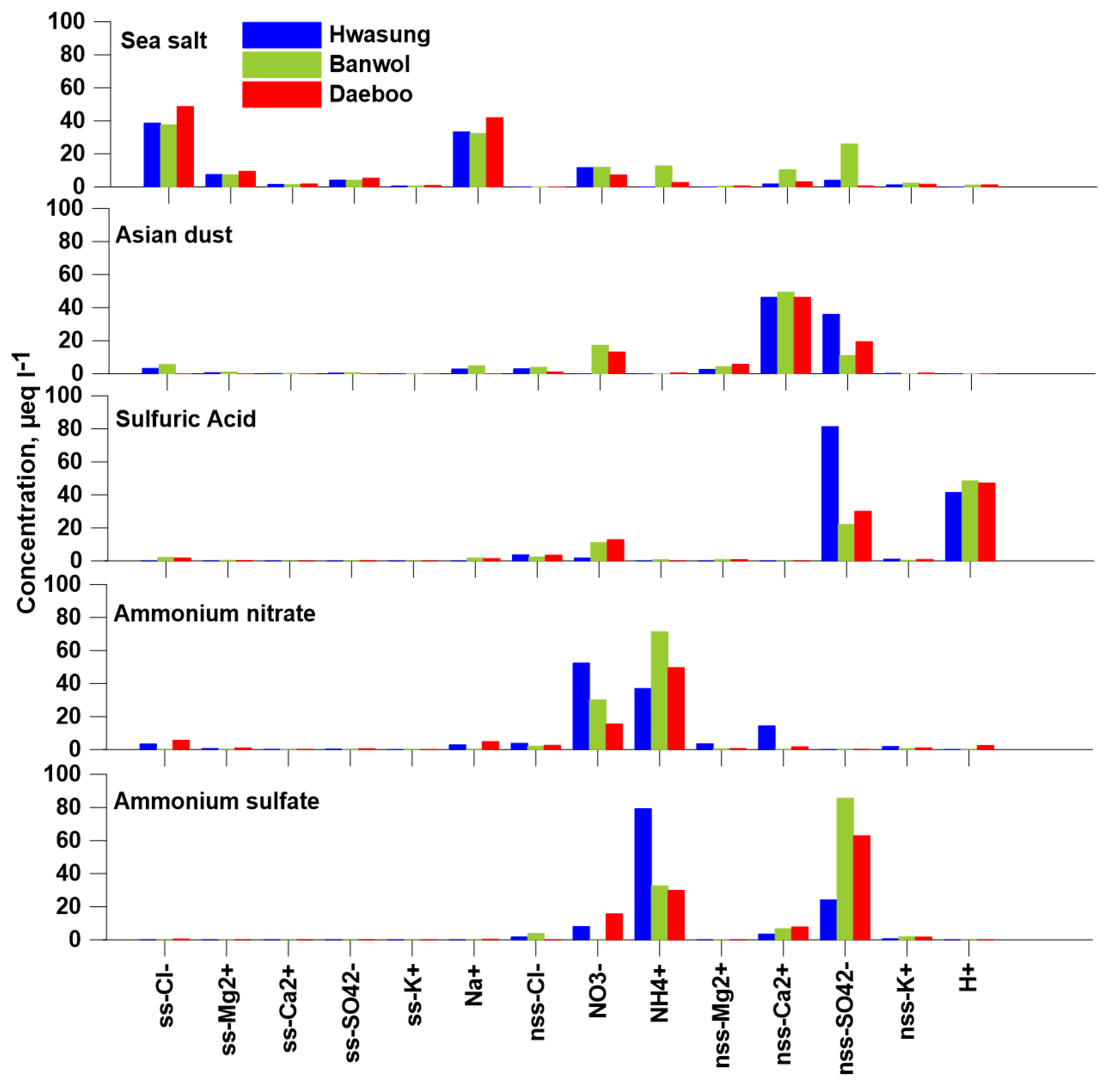
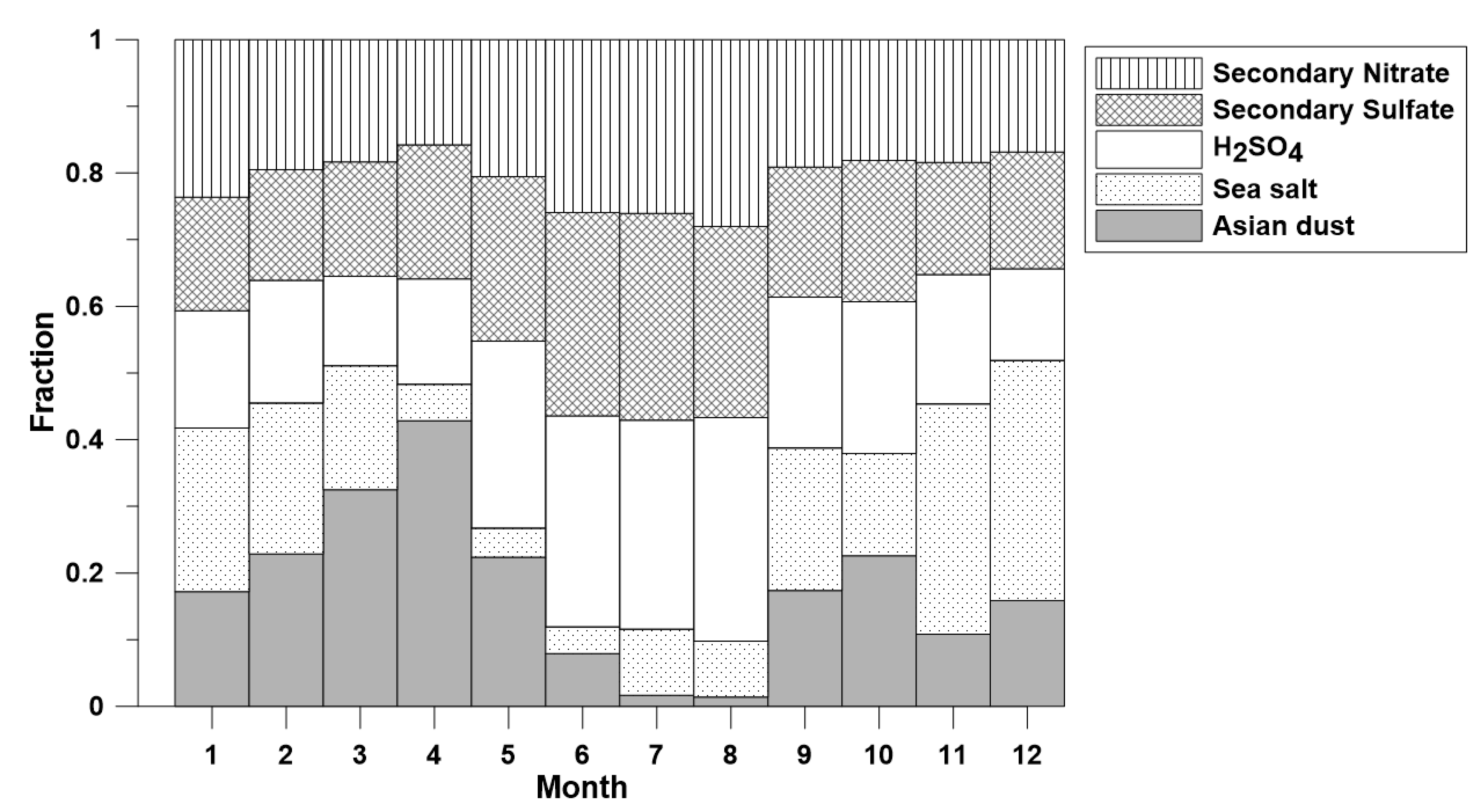
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Draaijers, G.; Erisman, J.; Lövblad, G.; Spranger, T.; Vel, E. Quality and Uncertainty Aspects of Forest Deposition Estimation using Throughfall, Stemflow and Precipitation Measurements; TNO-MEP Report 98/093; TNO Institute of Environmental Sciences, Energy Research and Process Innovation: Apeldoorn, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Duhanyan, N.; Roustan, Y. Below-cloud scavenging by rain of atmospheric gases particulates. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 39, 7201–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Kulshrestha, U.C.; Kumar, N.; Kumari, K.M.; Srivastava, S.S. Characterization of precipitation at Arga. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3405–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, H. Acid deposition chemistry in Asia, Europe, and North America. Progress Nuclear Energy 1998, 32, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoyunlu, B.O.; Tayanç, M. Analyses of wet and bulk deposition in four different regions of Istanbul, Turkey. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3571–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, A.; Costoya, M.; Peña, R.M.; García, S.; Herrero, C. A rainwater quality monitoring network: A preliminary study of the composition of rainwater in Galicia (NW Spain). Chemosphere 2003, 51, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai, K.M.; Wang, S.H.; Taner, P.A.; Lin, N.H. A dual site study of the rainwater chemistry within the western Pacific region. J. Atmos. Chem. 2007, 57, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.A.; Illanes, C.F.; Fornaro, A.; Pedrotti, J.J. Acid rain in downtown São Paulo City, Brazil. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2007, 7, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, A.; Alarcó, M.; Queralt, I. The chemical composition of dust transported in red rains-its contribution to the biogeochemical cycle of a holm oak forest in Catalonia (Spain). Atmos. Environ. 1997, 32, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N. Acidification of the world: Natural and anthropogenic. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 130, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkin, V.N.; Radojevic, M. Acid rain and its mitigation in Asia. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2003, 60, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Yu, J.Z.; Yang, L.; Qin, B. Atmospheric phosphorous in the northern part of Lake Taihu, China. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munger, J.W.; Eisenreich, S. Continental-scale variations in precipitation chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1983, 17, 32A–42A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, C.E.H.; Vincent, K.J.; Campbell, G.W.; Fowler, D.; Smith, R.I. Trends in wet and dry deposition of sulphur in the United Kingdom. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 85, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Iwase, T.; Ueda, H.; Suda, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Dokiya, Y.; Fushimi, K.; Hosoe, M. Long-term trend of chemical constituents in precipitation in Tokyo metropolitan area, Japan, from 1990 to 2002. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 339, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, X.; Li, W. Trends in chemical composition of precipitation in Nanjing, China, during 1992–2003. Atmos. Res. 2005, 73, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, I.; Hara, H. Ionic imbalance due to hydrogen carbonate from Asian dust. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6969–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.; Smith, R.I.; Muller, J.B.A.; Hayman, G.; Vincent, K.J. Changes in the atmospheric deposition of acidifying compounds in the UK between 1986 and 2001. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 137, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicard, P.; Coddeville, P.; Sauvage, S.; Galloo, J.C. Trends in chemical composition of wet-only precipitation at rural French monitoring stations over the 1990–2003 period. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2007, 7, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbieranowski, A.; Aheme, J. Long-term trends in atmospheric reactive nitrogen across Canada: 1899–2007. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5853–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larssen, T.; Seip, H.M.; Semb, A.; Mulder, J.; Muniz, I.P.; Vogt, R.D.; Lydersen, E.; Angell, V.; Dagang, T.; Eilertsen, O. Acid deposition and its effects in China: An overview. Environ. Sci. Policy 1999, 2, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.U.; Kim, J.W. Aerosol size distributions observed at the Seoul National University campus in Korea during the Asian dust and non-Asian dust periods. Atmos. Environ.t 2006, 40, 1772–1730. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, P.; Huang, J.; Li, C.; Zhong, S. The properties of dust aerosol and reducing tendency of the dust storms in northwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5896–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Transport routes and source regions of Asian dust observed in Korea during the past 40 years (1965–2004). Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4778–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xiong, J.; Xu, Y.; Chan, W.H. Acid rain in southwestern China. Atmos. Environ. 1988, 22, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herut, B.; Starinsky, A.; Katz, A.; Rosenfeld, D. Relationship between the acidity and chemical composition of rainwater and climatological conditions along a transition zone between large deserts and Mediterranean climate, Israel. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.; Alagha, O. The chemical composition of rainwater over Büyüqkçekmece Lake, Istanbul. Atmos. Res. 2004, 71, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, J.L. Characteristics of acid rain in Jinyun Mountain, Chongqing, China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2005, 3, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.J.; Noh, H.R.; Kim, B.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Jung, I.U.; Cho, C.R.; Han, J.S. Evaluation of acid deposition in Korea. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 130, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Collettjr, J.L.; Shin, D.Y.; Fujita, S.I.; Kim, H.K. Comparison of the chemical composition of precipitation on the western and eastern coasts of Korea. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 151, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Choi, B.C.; Oh, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Kang, G.U. Acidity and chemical composition of precipitation at background area of the Korean Peninsula (Anmyeon, Uljin, Gosan). J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 22, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.J.; Bu, J.-O.; Kim, W.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Hyeon, D.R.; Kang, C.H. Pollution characteristics of rainwater at Jeju Island during 2009~2010. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 29, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Park, J.S.; Ahn, J.Y.; Oh, J.; Son, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Sung, M.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, S.D.; Hong, Y.D.; et al. The characteristics of long-term variation of acid deposition in Korea. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Anal. 2015, 1, 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.I.; Kim, B.C.; Oh, H.J. Evaluation of lake modification alternatives for Lake Sihwa. Korea Environ. Manag. 2002, 29, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Kim, E.S.; Cho, S.R.; Chung, K.H.; Park, J.K. Distribution and pollution of heavy metals in the environmental samples of the Lake Sihwa. J. Korean Soc. Marine Environ. Eng. 2005, 8, 148–157. [Google Scholar]
- Im, M.S.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Jeon, E.C. Emission characteristics of VOC due to major industrial activities in the Banwol industrial complex. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 22, 325–336. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.; Jang, Y.W.; Arimoto, R.; Uematsu, M.; Lee, G. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition and its impact to Lake Sihwa in South Korea. Geochem. J. 2009, 43, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.J.; Likens, G.E. Weekly and daily precipitation chemistry network comparisons in the eastern U.S.: NADP/NTN vs. MAP3S/AIRMoN. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 3749–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, A.B.; Butler, T.J.; Likens, G.E. Monthly and annual bias in weekly (NADP/NTN) vs. daily (AIRMoN) precipitation chemistry data in the Eastern USA. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5197–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, R.; Lung, F. A critical data analysis and interpretation of the pH, ion loadings and electrical conductivity of rainwater from the territory of Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staelens, J.; Schrijver, A.D.; Avermaet, P.V.; Genouw, G.; Verhoest, N. A comparison of bulk and wet-only deposition at two adjacent sites in Melle (Belgium). Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satsangi, G.S.; Khare, L.P.; Singh, S.P.; Kumari, K.M.; Srivastava, S.S. Composition of rain water at a semi-arid rural site in India. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 3783–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Kulshrestha, U.C.; Sarkar, A.K.; Parashar, D.C. Influence of crustal aerosols on wet deposition at urban and rural sites in India. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 5129–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khashman, O.A. Ionic composition of wet precipitation in the Petra Region, Jordan. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 78, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds, R.L.; Thomas, T.B.; Rhodes, J.J. Canopy and Soil Modification of Precipitation Chemistry in a Temperate Rain Forest. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 3.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; USEPA Office of Research and Development: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gugamstty, B.; Wei, H.; Liu, C.N.; Awasthi, A.; Hsu, S.C.; Tsai, C.J.; Roam, G.D.; Wu, Y.C.; Chen, C.F. Source characterization and apportionment of PM10, PM2.5 and PM0.1 by using positive matrix factorization. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 476–491. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- García, R.; Ma, D.T.; Padilla, H.; Belmont, R.; Azpra, E.; Arcega-Cabrera, F.; Báez, A. Measurement of chemical elements in rain from Rancho Viejo, a rural wooded area in the State of Mexico, Mexico. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6088–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, Z.; Huiwang, G. The characteristics of Asian-dust storms during 2000–2002: From the source to the sea. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 9136–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, S.; Incecik, S.; Atimtay, A.T. Chemical composition of rainwater at EMEP station in Ankara, Turkey. Atmos. Res. 2002, 65, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, P.; Sudheer, A.K.; Sarin, M.M.; Manjunatha, B.R. Chemical characteristics of atmospheric aerosols over southwest coast of India. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7751–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Das, S.N.; Misra, V.N. Chemical composition of rainwater and dustfall at Bhubaneswar in the east coast of India. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5908–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, P.A. Analysis of Hong Kong daily bulk and wet deposition data from 1994 to 1995. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliavacca, D.M.; Teixeira, E.C.; Wiegand, F.; Machado, A.C.M.; Sanchez, J. Atmospheric precipitation and chemical composition of an urban site, Guaíba hydrographic basin, Brazil. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanusi, A.; Wortham, H.; Millet, M.; Mirabel, P. Chemical composition of rainwater in eastern France. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khashman, O.A. Study of chemical composition in wet atmospheric precipitation in Eshidiya area, Jordan. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6175–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, A.; Shingler, T.; Harpold, C.; Feagles, C.W.; Meixner, T.; Brooks, P.D. Aerosol and precipitation chemistry in the southwestern United States: Spatiotemporal trends and interrelationship. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7361–7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayan, U.; Lamb, D. Meteorological indicators of summer precipitation chemistry in central Pennsylvania. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, A.P.; Belmont, R.D.; García, R.M.; Torres, M.C.B.; Padilla, H.G. Rainwater chemical composition at two sites in Central Mexico. Atmos. Res. 2006, 80, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, J.; Rodriguez, S.; Baez, A.P. Chemical composition of bulk precipitation in the metropolitan area of Costa Rica, Central America. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshrestha, U.C.; Kulshrestha, M.J.; Sekar, R.; Sastry, G.S.R.; Vairamani, M. Chemical characteristics of rainwater at an urban site of south-central India. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3019–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acid Deposition Monitoring Network in East Asia (EANET). Data report on the acid deposition in the East Asian region 2001–2012; Network Center for EANET: Nigata-si, Japan, 2013.
- Kang, G.U.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, H.K. An analysis of long-term trends in precipitation acidity of Seoul, Korea. J. Korea Air Pollut. Res. Assoc. 1997, 13, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Safai, P.D.; Rao, P.S.P.; Momin, G.A.; Ali, K.; Chate, D.M.; Praveen, P.S. Chemical composition of precipitation during1984–2002 at Pune, India. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.M. Chemical composition of atmospheric wet depositions from the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Atmos. Res. 2007, 85, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, N.; Sarin, M.M. Chemistry of precipitation events and inter-relationship with ambient aerosols over a semi-arid region. J. Atmos. Chem. 2007, 56, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikawa, M.; Hiraki, T.; Tamaki, M. Comparative field study on precipitation, throughfall, stemflow, fog water, and atmospheric aerosol and gases at urban and rural sites in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, J.L.; Gebhart, K.A.; Schichtel, B.A.; Malm, W.C. Increasing trends in wintertime particulate sulfate and nitrate ion concentrations in the great Plains of the United States (2000–2010). Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aherne, J.; Farrell, E.P. Deposition of sulphur, nitrogen and acidity in precipitation over Ireland: Chemistry, spatial distribution and long-term trends. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, A.; Gutz, I.G.R. Wet deposition and related atmospheric chemistry in the São Paulo metropolis, Brazil, Part 3: Trends in precipitation chemistry during 1983–2003. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5893–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puxbaum, H.; Simeonov, V.; Kalina, M.; Tsakovski, S.; Löffler, H.; Heimburger, G.; Biebl, P.; Weber, A.; Damm, A. Long-term assessment of the wet precipitation chemistry in Austria (1984–1999). Chemosphere 2002, 48, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Wu, F.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y. Chemical compositions of wet precipitation and anthropogenic influences at a developing urban site in southeastern China. Atmos. Res. 2007, 84, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, A.; Belmont, R.; García, R.; Padilla, H.; Torres, M.C. Chemical composition of rainwater collected at a southwest site of Mexico City, Mexico. Atmos. Res. 2007, 86, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, P.; Paatero, P.; Tapper, U.; Järvinen, O. Source identification of bulk wet deposition in Finland by positive matrix factorization. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, K.; Murao, N.; Hara, H. PMF analysis of impacts of SO2 from Miyakejima and Asian continent on precipitation sulfate in Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-M.; Seo, B.-K.; Lee, G.; Kahng, S.-H.; Jang, Y.W. Chemical Composition of Water Soluble Inorganic Species in Precipitation at Shihwa Basin, Korea. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 732-750. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6060732
Park S-M, Seo B-K, Lee G, Kahng S-H, Jang YW. Chemical Composition of Water Soluble Inorganic Species in Precipitation at Shihwa Basin, Korea. Atmosphere. 2015; 6(6):732-750. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6060732
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seung-Myung, Beom-Keun Seo, Gangwoong Lee, Sung-Hyun Kahng, and Yu Woon Jang. 2015. "Chemical Composition of Water Soluble Inorganic Species in Precipitation at Shihwa Basin, Korea" Atmosphere 6, no. 6: 732-750. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6060732
APA StylePark, S.-M., Seo, B.-K., Lee, G., Kahng, S.-H., & Jang, Y. W. (2015). Chemical Composition of Water Soluble Inorganic Species in Precipitation at Shihwa Basin, Korea. Atmosphere, 6(6), 732-750. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6060732






