In-Situ Aircraft Measurements of the Vertical Distribution of Black Carbon in the Lower Troposphere of Beijing, China, in the Spring and Summer Time
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Information
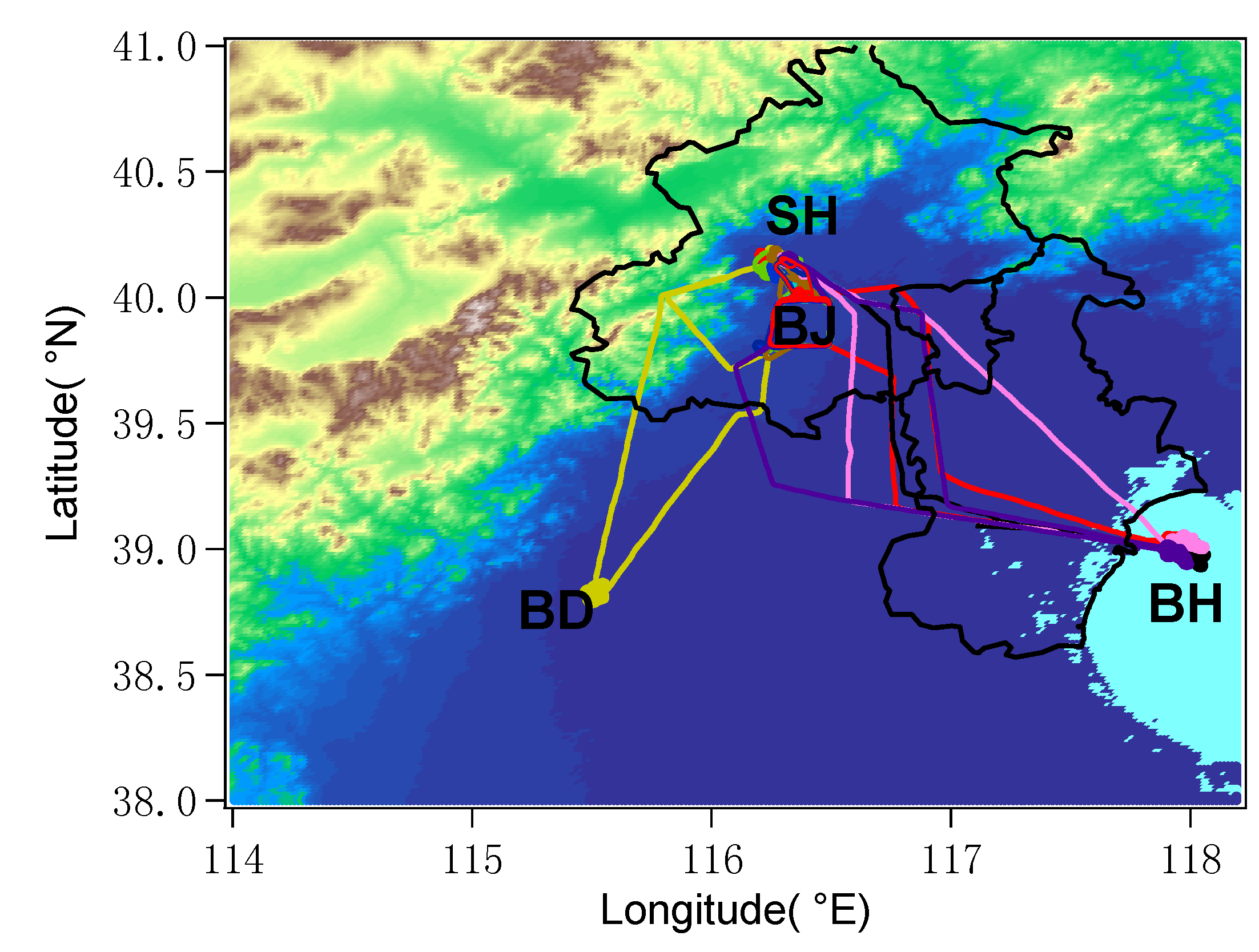
2.1. Flights and Instruments
| Style | Region | Date | Sampling Time (Local Time) | The Direction of Air Mass in the PBL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Beijing City (BJ) | 3 May | 10:20 a.m.–1:50 p.m. | Northwest |
| 19 May | 9:30 a.m.–12:15 p.m. | South and southwest | ||
| 23 May | 9:15 a.m.–12:40 p.m. | Northwest | ||
| 31May | 9:35 a.m.–12:15 p.m. | Southwest | ||
| 11 June | 9:05 a.m.–12:00 p.m. | Northwest | ||
| 16 June | 9:30 a.m.–12:30 p.m. | Northwest | ||
| B | Baoding (BD) | 17 April | 12:24 p.m.–3:29 p.m. | Southwest |
| C | Bohai Sea (BH) | 14 April | 9:50 a.m.–1:20 p.m. | Southwest |
| 25 May | 12:15 p.m.–3:30 p.m. | Southwest | ||
| 9 June | 10:00 a.m.–1:00 p.m. | Southwest | ||
| 15 June | 9:35 a.m.–1:25 p.m. | North |
| Site and Date | Relative Humidity (%) | Average BC Mass Concentration (ng/m3) | Average BC Number Concentration (#/cm3) | The Peak Diameter for BC Mass (nm) | Number Fraction (NF) of Coated Particles (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BJ | 3 May | 10.3 | 461.2 | 282 | 172 | 20.5 |
| 19 May | 73.1 | 4022.8 | 1615 | 193 | 62.2 | |
| 23 May | 16.1 | 236.5 | 137 | 175 | 11 | |
| 11 June | 20.1 | 440.3 | 246 | 179 | 14.7 | |
| 16 June | 30.1 | 482.6 | 289 | 172 | 14.5 | |
| BH | 14 April | 4.4 | 208.7 | 100 | 189 | 43 |
| 25 May | 15.7 | 315.6 | 131 | 197 | 26.5 | |
| 9 June | 43.6 | 617.8 | 223 | 186 | 50.4 | |
| 15 June | 75.4 | 303 | 163 | 172 | 27 | |
| BD | 17 April | 57.6 | 1618.5 | 532 | 206 | 42.2 |
| SH | 14 April | 9.1 | 901.9 | 373 | 185 | 30.7 |
| 17 April | 53.4 | 2670.6 | 991 | 200 | 63.2 | |
| 3 May | 8.6 | 369.2 | 230 | 161 | 20.3 | |
| 23 May | 11 | 190 | 98 | 185 | 13.7 | |
2.2. Single Particle Soot Photometer (SP2)
3. Results and Discussion
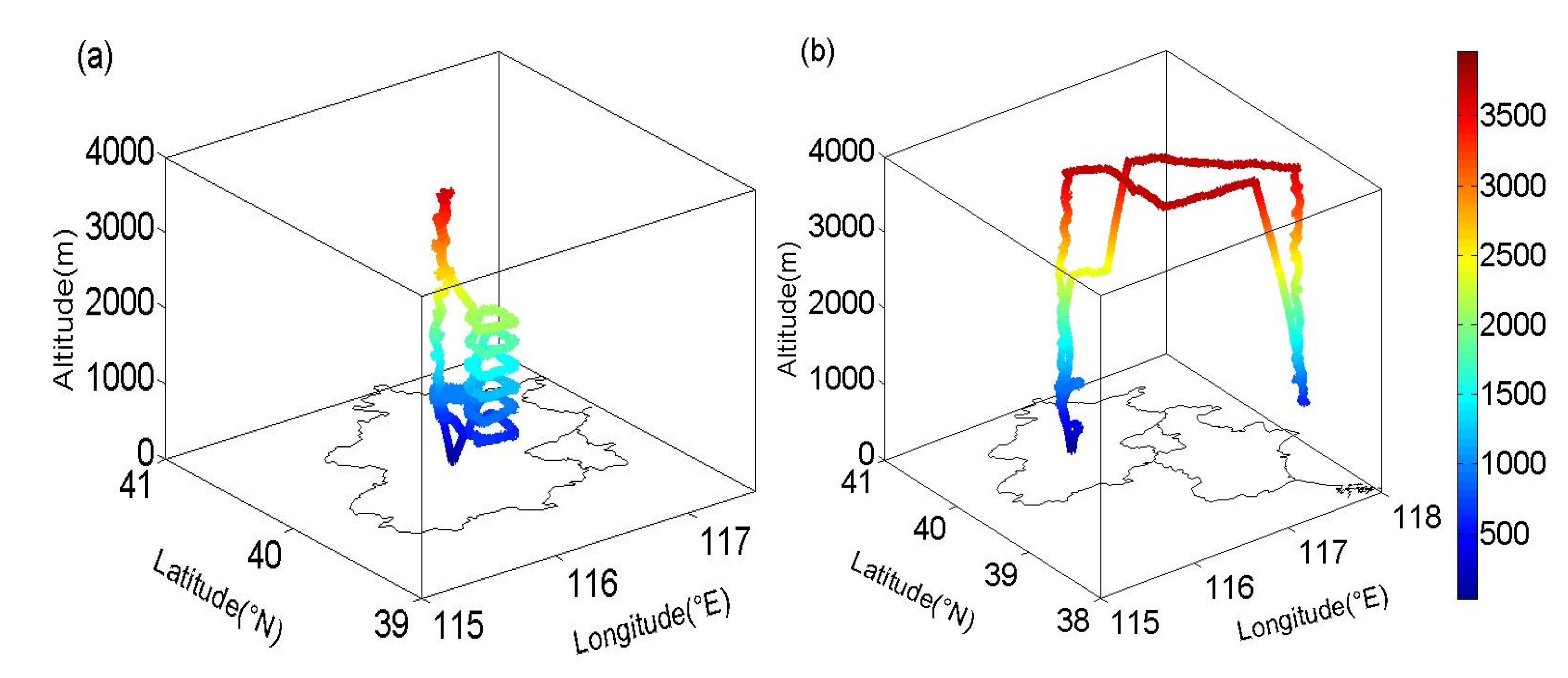
3.1. Vertical Distribution of rBC

| Site | Measurement Period | Pollution Type | Altitude | rBC Mass Concentration (μg/m3) | Peak Mass Diameter (nmin VED) | Number Fraction Of Coated Particles (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Texas, USA | November 2004 | Continental America | <5 km, >10 km | 0.05, 0.008-0.17 | ~178 | ~40 | Schwarz et al., 2006 [7] |
| San Jose, Costa Rica | February 2006 | Tropics | 1–5 km, 17.5–19.5 km | 0.65 | ~200 | 20–70, 75 | Schwarz et al., 2008b [31] |
| Texas, USA | September 2006 | Urban outflow, Biomass burning outflow | Boundary layer | 0.72–0.81, 1.8–3.59 | ~170, ~210 | ~10, ~70 | Schwarz et al., 2008a [30] |
| Nagoya, Japan | March 2004 | Urban outflow | 0.3–4 km | 0.5–1.1 | 182–202 | 35 (±5)–63 (±9) | Moteki et al., 2007 [25] |
| Yellow, East China Seas and the western Pacific Ocean | 18 March–25 April 2009 | Asian outflow | Boundary layer and the free troposphere (<9 km) | 0.185–1.264 | - | - | Oshima et al., 2012 [26] |
| The north of Europe | 23–28 November 2006 | Lower stratosphere | 0.2–2 | 160–240 | - | Baumgardner et al., 2008 [13] | |
| Europe | April and September 2008 | Continental Europe | <3 km | 0.12 ± 0.08 | 154–203 | - | McMeeking et al., 2010 [22] |
| England | April 2008 and June 2009 | Continental Europe | Boundary layer | 0.1–0.6 | - | 3–15, 40–50 | McMeeking et al., 2011 [23] |
| Palmdale, California | 17 June and 24 June 2008 | Biomass burning and Fossil fuels | Boundary layer | 0.513 ± 0.153, 0.243 ± 0.146 | 175 ± 10, 193 ± 16 | - | Sahu et al., 2012 [39] |
| Mexico City, Mexico | March 2006 | Urban outflow | 2.6–5.4 km | 0.24–1.859, 0.375–1.070 | 147–167 | 17 ± 3 | Subramanian et al., 2010 [32] |
| Los Angeles Basin, USA | May 2010 | Urban outflow | Free troposphere | 0.0167 | 161 ± 41 | 76 ± 13 | Metcalf et al., 2012 [33] |
| Beijing, China | May–June 2012 | Urban outflow | Boundary layer | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 180–210 | 31 ± 17% | This study |
3.2. Size Distribution


3.3. Mixing State of rBC Particles

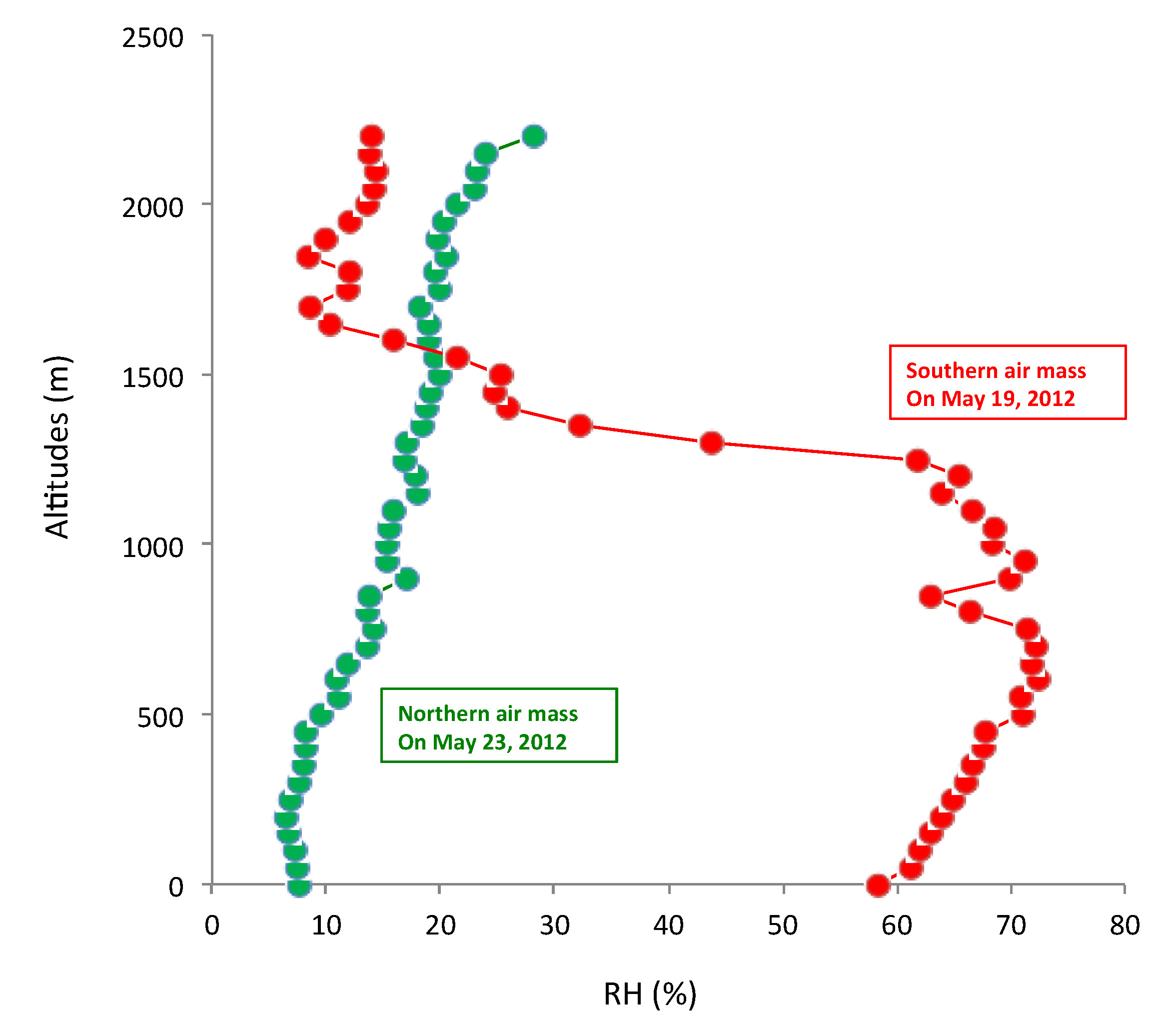
3.4. Effect of Hygroscopic Growth of rBC Particles

4. Summary
- (1)
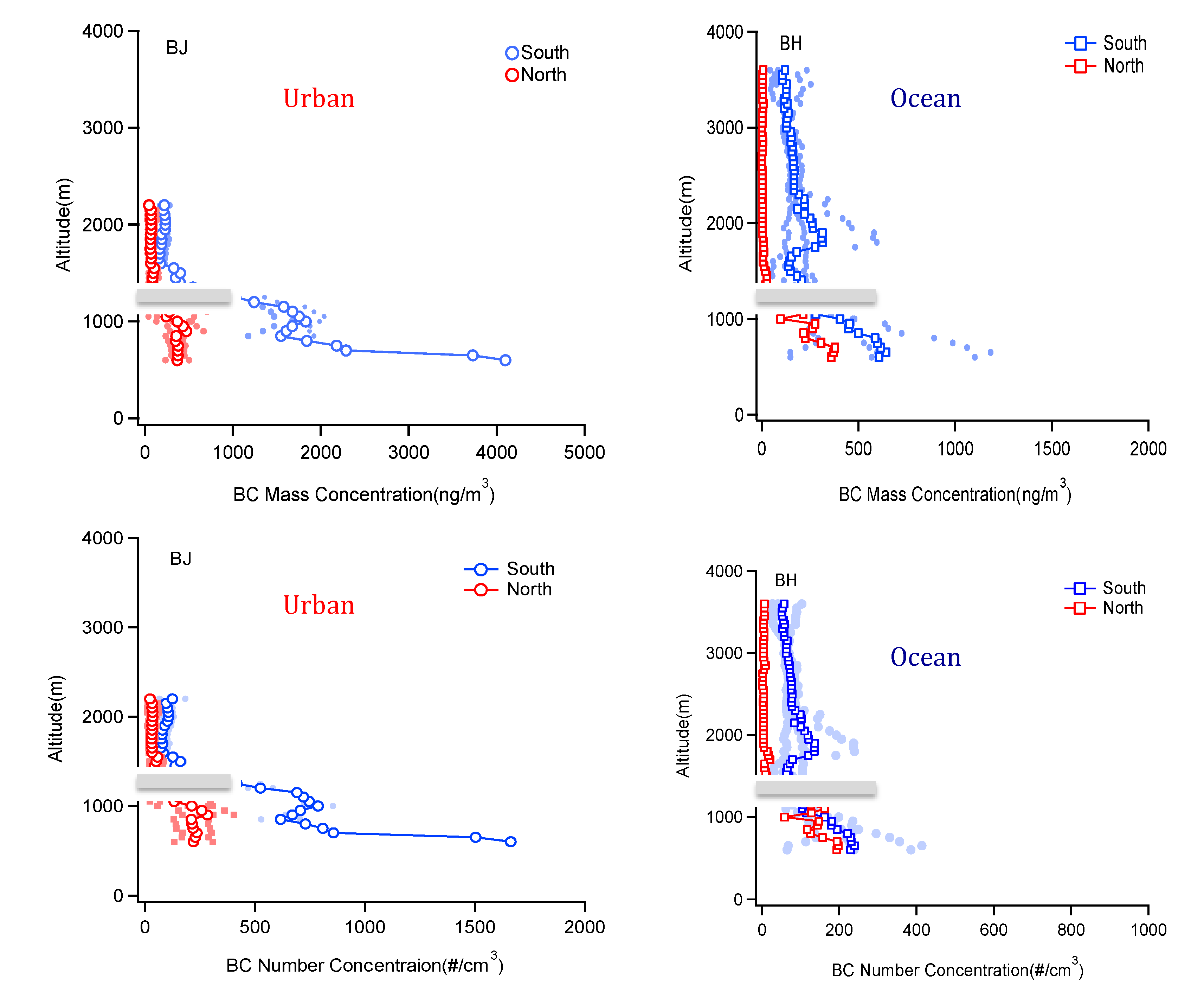
- In the urban area (BJ), the average rBC mass concentration in the PBL was 1128 ng/m3, which was significantly higher than the value (361 ng/m3) in the ocean area (BH).
- (2)
- The vertical distributions had noticeable differences between different air masses in the urban region (BJ) and the remote region (BH). When the air mass originated from the south (the polluted region), the rBC particles were strongly compressed in the PBL, resulting in a large vertical gradient at the top of the PBL. In contrast, when the air mass originated from the north (the clean region), there was a small vertical gradient of rBC particles. This analysis suggests that there was significant regional transport of the rBC particles, which enhanced the air pollution in BJ. Moreover, this transport not only occurred near the surface but also in the middle level of the PBL (around 0.5 to 1 km).
- (3)
- The analysis of the size distributions shows that about 80% of the rBC particles were in the diameter range from 70 to 400 nm, and the mean diameter at the peak rBC concentrations was about 180–210 nm. This suggests that the rBC particles were relatively small (less than 1 μm in diameter).
- (4)
- The “mixing state” of the rBC particles was analyzed to study the coating processes that occurred on the surface of the rBC particles. The results indicate that the air mass conditions strongly affected the number fraction (NF) of the coated particles. Under the southern air mass in BJ, the local air pollution was high at a lower height of the PBL and a higher humidity. As a result, the hygroscopic growth of rBC rapidly occurred, producing high NF values (~65%). The correlation coefficient between the NF and the local relative humidity (RH) was 0.88.
- (5)
- The findings of the rapid hygroscopic growth in BJ under the polluted condition has important implications for studying the rBC budget in the atmosphere. The rapid conversion from hydrophobic to hydrophilic rBC particles results in a shorter lifetime of rBC particles under heavy pollution and a lower residence time of the rBC particles in the atmosphere.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramanathan, V.; Ramana, M.V.; Roberts, G.; Kim, D.; Corrigan, C.; Chung, C.; Winker, D. Warming trends in Asia amplified by brown cloud solar absorption. Nature 2007, 448, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, M.V.; Ramanathan, V.; Feng, Y.; Yoon, S.C.; Kim, S.W.; Carmichael, G.R.; Schauer, J.J. Warming influenced by the ratio of black carbon to sulphate and the black-carbon source. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, X.; Madronich, S.; Walters, S.; Edwards, D.P.; Ginoux, P.; Mahowald, N.; Zhang, R.Y.; Lou, C.; Brasseur, G. Assessment of the global impact of aerosols on tropospheric oxidants. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D03204. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhang, R.; Fan, J.; Tie, X. Impacts of Black Carbon Aerosol on Photolysis Frequenciesand Ozone in the Houston Area. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D23206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, D.; Kok, G.; Raga, G. Warming of the Arctic lower stratosphere by light absorbing particles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L06117. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Gao, R.S.; Fahey, D.W.; Thomson, D.S.; Watts, L.A.; Wilson, J.C.; Reeves, J.M.; Darbeheshti, M.; Baumgardner, D.G.; Kok, G.L.; et al. Single particle measurements of mid-latitude black carbon and light-scattering aerosols from the boundary layer to the lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.S.; Hall, S.R.; Swartz, W.H.; Schwarz, J.P.; Spackman, J.R.; Watts, L.A.; Fahey, D.W.; Aikin, K.C.; Shetter, R.E.; Bui, T.P. Calculations of solar shortwave heating rates due to black carbon and ozone absorption using in situ measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D14203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, W.C.; Nenes, A.; Seinfeld, J.H. Black carbon radiative heating effects on cloud microphysics and implications for aerosol indirect forcing, Extended Köhler theory. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, D21. [Google Scholar]
- Dusek, U.; Reischl, G.P.; Hitzenberger, R. CCN activation of pure and coated carbon black particles. Environ. Sci. 2006, 40, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozic, J.; Mertes, S.; Verheggen, B.; Cziczo, D.J.; Gallavardin, S.J.; Walter, S.; Baltensperger, U.; Weingartner, E. Black carbon enrichment in atmospheric ice particle residuals observed in lower tropospheric mixed phase clouds. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D15209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozic, J.; Verheggen, B.; Mertes, S.; Connolly, P.; Bower, K.; Petzold, A.; Baltensperger, U.; Weingartner, E. Scavenging of black carbon in mixed phase clouds at the high alpine site Jungfraujoch. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgardner, D.; Subramanian, R.; Twohy, C.; Stith, J.; Kok, G. Scavenging of black carbon by ice crystals over the northern Pacific. Geophys. Res .Lett. 2008, 35, L22815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zheng, F.C. Inventory of black carbon and organic carbon emissions from China. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6516–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.W.; He, K.B.; Lei, Y. Black carbon emissions from on-road vehicles in China, 1990–2030. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 51, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerdahl, D.; Wang, X.; Pan, X.C.; Zhang, K.M. Characterization of on-road vehicle emission factors and microenvironmental air quality in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.L.; Wang, Z.A.; Wang, X.Q.; Dong, H.B.; Zhang, W.; Alex, G.; Huang, J.P. Characteristics of urban black carbon concentration around 2008 Beijing Olympic Games. Clim. Environ. Res. 2010, 15, 616–623. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.L.; Kanaya, K.; Wang, Z.F.; Liu, Y.; Pochanart, P.; Akimoto, H.; Sun, Y.L.; Dong, H.B.; Li, J.; Irie, H.; et al. Correlation of black carbon aerosol and carbon monoxide in the high-altitude environment of Mt. Huang in Eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9735–9747. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.D.; Xia, X.H.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Zhang, S.W. Black carbon (rBC) in urban and surrounding rural soils of Beijing, China: Spatial distribution and relationship with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Chemsphere 2011, 82, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.W.; Zhao, J.P.; Chen, J.S.; Xu, Y.; Xu, L.L. Pollution characteristics of organic and elemental carbon in PM2.5 in Xiamen, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.J.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.Y.; Ohara, T.; Hasegawa, S.C.; Li, J.Q.; Yang, L.; Hao, J.M. Black carbon at a roadside site in Beijing: Temporal variations and relationships with carbon monoxide and particle number size distribution. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMeeking, G.R.; Hamburger, T.; Liu, D.; Flynn, M.; Morgan, W.T.; Northway, M.; Highwood, E.J.; Krejci, R.; Allan, J.D.; Minikin, A.; et al. Black carbon measurements in the boundary layer over western and northern Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 9393–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMeeking, G.R.; Morgan, W.T.; Flynn, M.; Highwood, E.J.; Turnbull, K.; Haywood, J.; Coe, H. Black carbon aerosol mixing state, organic aerosols and aerosol optical properties over the United Kingdom. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9037–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMeeking, G.R.; Bart, M.; Chazette, P.; Haywood, J.M.; Hopkins, J.R.; McQuaid, J.B.; Morgan, W.T.; Raut, J.-C.; Ryder, C.L.; Savage, N.; et al. Airborne measurements of trace gases and aerosols over the London metropolitan region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 5163–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moteki, N.; Kondo, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Takegawa, N.; Komazaki, Y.; Kurata, G.; Shirai, T.; Blake, D.R.; Miyakawa, T.; Koike, M. Evolution of mixing state of black carbon particles: Aircraft measurements over the western Pacific in March 2004. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, N.; Kondo, Y.; Moteki, N.; Takegawa, N.; Koike, M.; Kita, K.; Matsui, H.; Kajino, M.; Nakamura, H.; Jung, J.S.; et al. Wet removal of black carbon in Asian outflow: Aerosol Radiative Forcing in East Asia (A-FORCE) aircraft campaign. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D03204. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Kondo, Y.; Moteki, N.; Takegawa, N.; Miyazaki, Y.; Blake, D.R. Evolution of mixing state of black carbon in polluted air from Tokyo. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L16803. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Kondo, Y.; Moteki, N.; Takegawa, N.; Sahu, L.K.; Takami, A.; Hatakeyama, S.; Yonemura, S.; Blake, D.T. Radiative impact of mixing state of black carbon aerosol in Asian outflow. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D24210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, D.; Kok, G.L.; Raga, G.B. On the diurnal variability of particle properties related to light absorbing carbon in Mexico City. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Gao, R.S.; Spackman, J.R.; Watts, L.A.; Thomson, D.S.; Fahey, D.W.; Ryerson, T.B.; Peischl, J.; Holloway, J.S.; Trainer, M.; et al. Measurement of the mixing state, mass, and optical size of individual black carbon particles in urban and biomass burning emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Spackman, J.R.; Fahey, D.W.; Gao, R.S.; Lohmann, U.; Stier, P.; Watts, L.A.; Thomson, D.S.; Lack, D.A.; Pfister, L.; et al. Coatings and their enhancement of black carbon light absorption in the tropical atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D03203. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, R.; Kok, G.L.; Baumgardner, D.; Clarke, A.; Shinozuka, Y.; Campos, T.L.; Heizer, C.G.; Stephens, B.B.; de Foy, B.; Voss, P.B.; et al. Black carbon over Mexico: The effect of atmospheric transport on mixing state, mass absorption cross-section, and rBC/CO ratios. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, A.R.; Craven, J.S.; Ensberg, J.J.; Brioude, J.; Angevine, W.; Sorooshian, A.; Duong, H.T.; Jonsson, H.H.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Black carbon aerosol over the Los Angeles Basin during CalNex. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D00V13. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.F.; Sun, T.L.; Zeng, L.W.; Yu, G.H.; Luan, S.J. Black carbon aerosol characterization in a coastal city in South China using a single particle soot photometer. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 51, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.L.; He, L.Y.; Huang, X.F.; Zeng, L.W.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.H. Characteristics of the size distribution and mixing state of black carbon aerosol in Shenzhen in winter. Chin. Sci. Bull. (Chinese Ver) 2011, 56, 1703–1710. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, X.C.; Tie, X.X.; Huang, M.Y.; Zhao, C.S. Vertical distribution of aerosols under different weather conditions: Analysis of in-situ aircraft measurements in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5526–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Yu, C.; Wu, Y.; Chin, M.; Zhao, Z.C.; Hayasaka, T.; Shi, G.Y. Aerosol trends over China, 1980–2000. Atmos. Res. 2008, 88, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.N.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tie, X.; Cao, J.; Han, S.Q.; Meng, J.W.; Chen, P.F.; Zhao, D.L. Evolution of Planetary Boundary Layer under different weather conditions, and its impact on aerosol concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 11, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, L.K.; Kondo, Y.; Moteki, N.; Takegawa, N.; Zhao, Y.; Cubison, M.J.; Jimenez, J.L.; Vay, S.; Diskin, G.S.; Wisthaler, A.; et al. Emission characteristics of black carbon in anthropogenic and biomass burning plumes over California during ARCTAS-CARB 2008. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D16302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.; Rolph, G. HYSPLIT (HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model Access Via NOAA ARL READY Website; NOAA Air Resources Laboratory: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2003. Available online: http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready/hysplit4.html (accessed on 14 May 2015).
- Tie, X.; Zhang; He, H.; Cao, J.J.; Han, S.Q.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Jia, X.C. A budget analysis on the formation of haze in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 100, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, X.; Madronich, S.; Li, G.H.; Ying, Z.M.; Weinheimer, A.; Apel, E.; Campos, T. Simulation of Mexico City Plumes during the MIRAGE-Mex Field Campaign Using the WRF-Chem Model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 4621–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moteki, N.; Kondo, Y.; Oshima, N.; Koike, M.; Kita, K.; Matsui, H.; Kajino, M. Size dependence of wet removal of black carbon aerosols during transport from the boundary layer to the free troposphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L13802. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, T.C.; Habib, G.; Bergstorm, R.W. Limitations in the enhancement of visible light absorption due to mixing state. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D20211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, X.; Brasseur, G.; Emmons, L.; Horowitz, L.; Kinnison, D. Effects of aerosols on tropospheric oxidants: A global model study. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 22931–22964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Tie, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, H.; Bi, K.; Jin, Y.; Chen, P. In-Situ Aircraft Measurements of the Vertical Distribution of Black Carbon in the Lower Troposphere of Beijing, China, in the Spring and Summer Time. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 713-731. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6050713
Zhao D, Tie X, Gao Y, Zhang Q, Tian H, Bi K, Jin Y, Chen P. In-Situ Aircraft Measurements of the Vertical Distribution of Black Carbon in the Lower Troposphere of Beijing, China, in the Spring and Summer Time. Atmosphere. 2015; 6(5):713-731. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6050713
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Delong, Xuexi Tie, Yang Gao, Qiang Zhang, Haijun Tian, Kai Bi, Yongli Jin, and Pengfei Chen. 2015. "In-Situ Aircraft Measurements of the Vertical Distribution of Black Carbon in the Lower Troposphere of Beijing, China, in the Spring and Summer Time" Atmosphere 6, no. 5: 713-731. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6050713
APA StyleZhao, D., Tie, X., Gao, Y., Zhang, Q., Tian, H., Bi, K., Jin, Y., & Chen, P. (2015). In-Situ Aircraft Measurements of the Vertical Distribution of Black Carbon in the Lower Troposphere of Beijing, China, in the Spring and Summer Time. Atmosphere, 6(5), 713-731. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6050713





