Long-Term Measurement for Low-Tropospheric Water Vapor and Aerosol by Raman Lidar in Wuhan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Site and Instrument
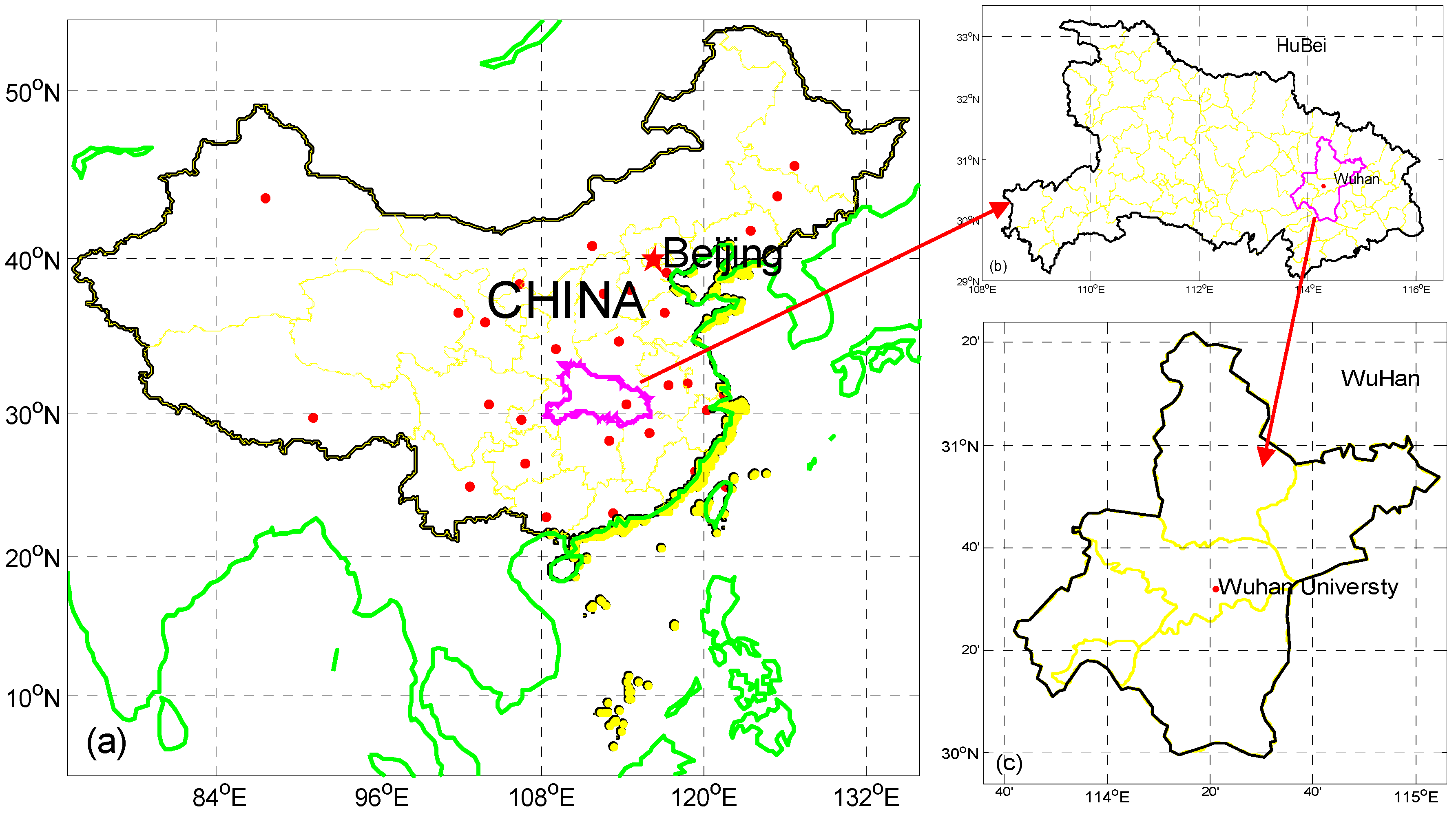
2.1. Site
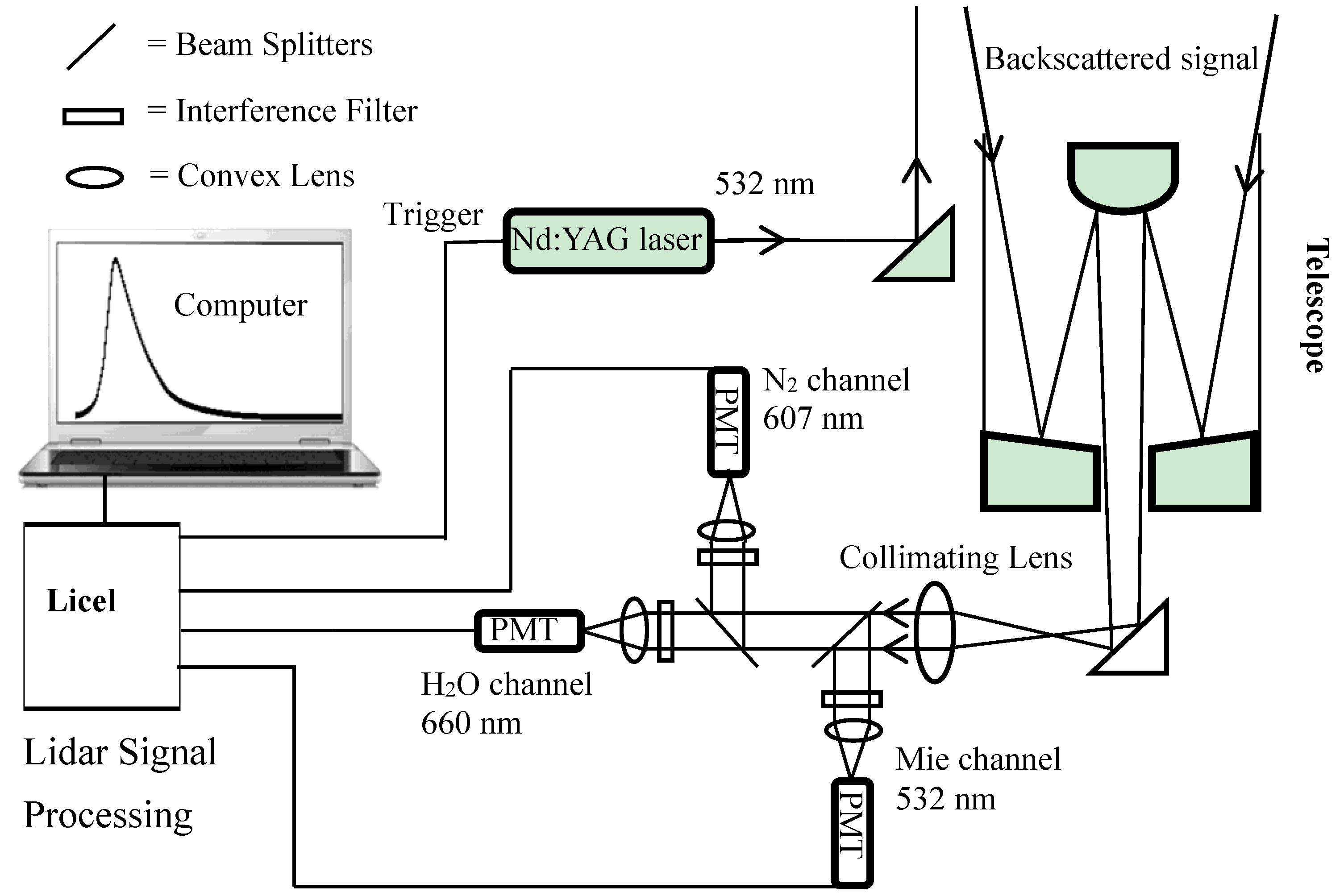
2.2. Instrument and Method
| System | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Laser | Output wavelength | 532 nm |
| Output energy | 200 mJ | |
| Pulse width | ~10 ns | |
| Energy stability | ≤5% | |
| Frequency | 10 Hz | |
| Telescope | Type | Schmidt-Cassegrain |
| Effective aperture | 356 mm | |
| Primary mirror diameter | 370 mm | |
| Focal length | 3556 mm | |
| Detector | PMT Hamamatsu R 7400 | |
| Interference Filter | Mie Channel | |
| CWL | 532 nm | |
| FWHM | 5 ± 1 nm | |
| Out-of-Band Rejection | >10−4 | |
| Minimum Transmission | 50% | |
| Raman Channels | ||
| CWL | 607 nm (660 nm) | |
| FWHM | 3 ± 0.5 nm | |
| Out-of-Band Rejection | >10−4 | |
| Minimum Transmission | 50% | |
| Acquisition System | A/D conversion | 12 bit, 20 MHz |
| PC | 250 MHz | |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Representative Case
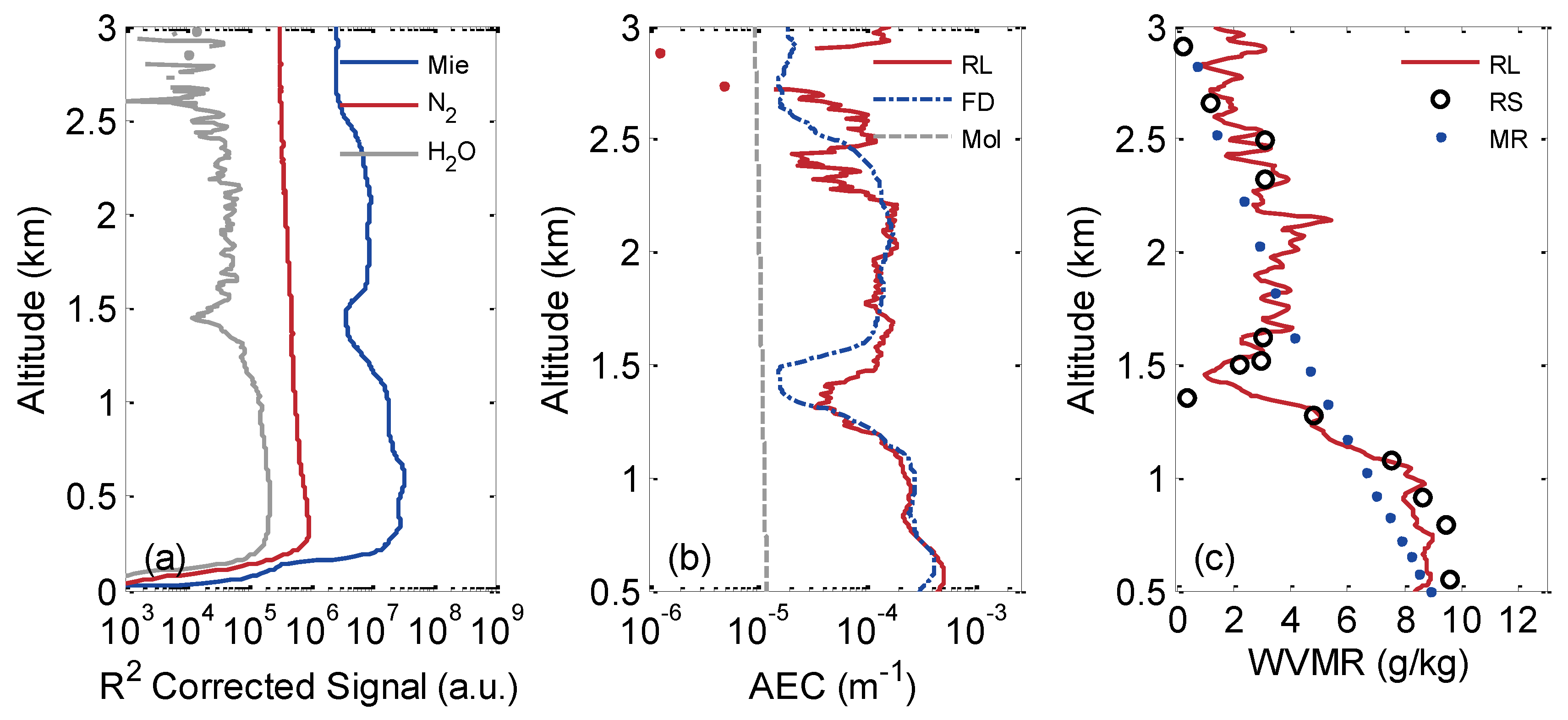
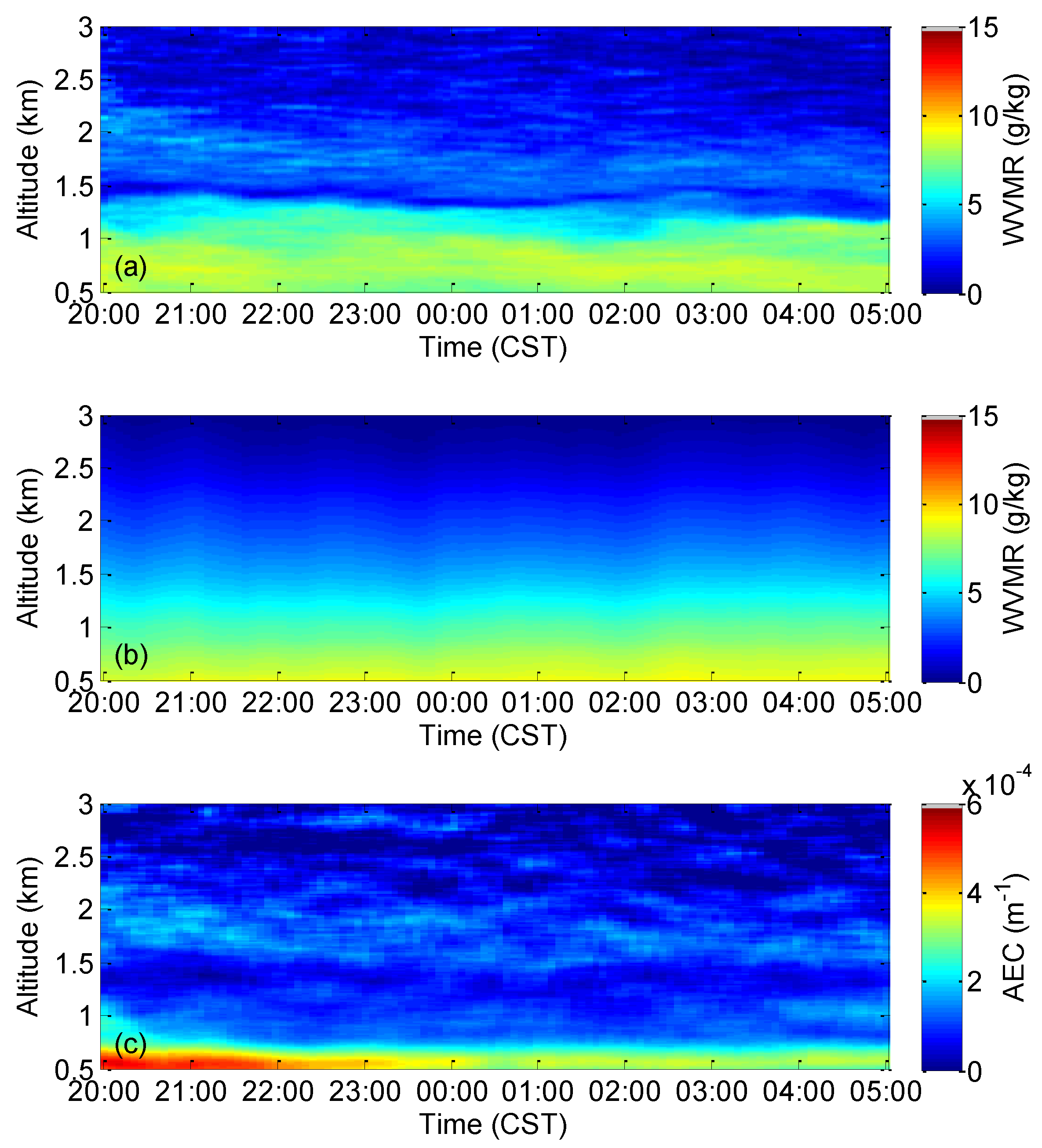
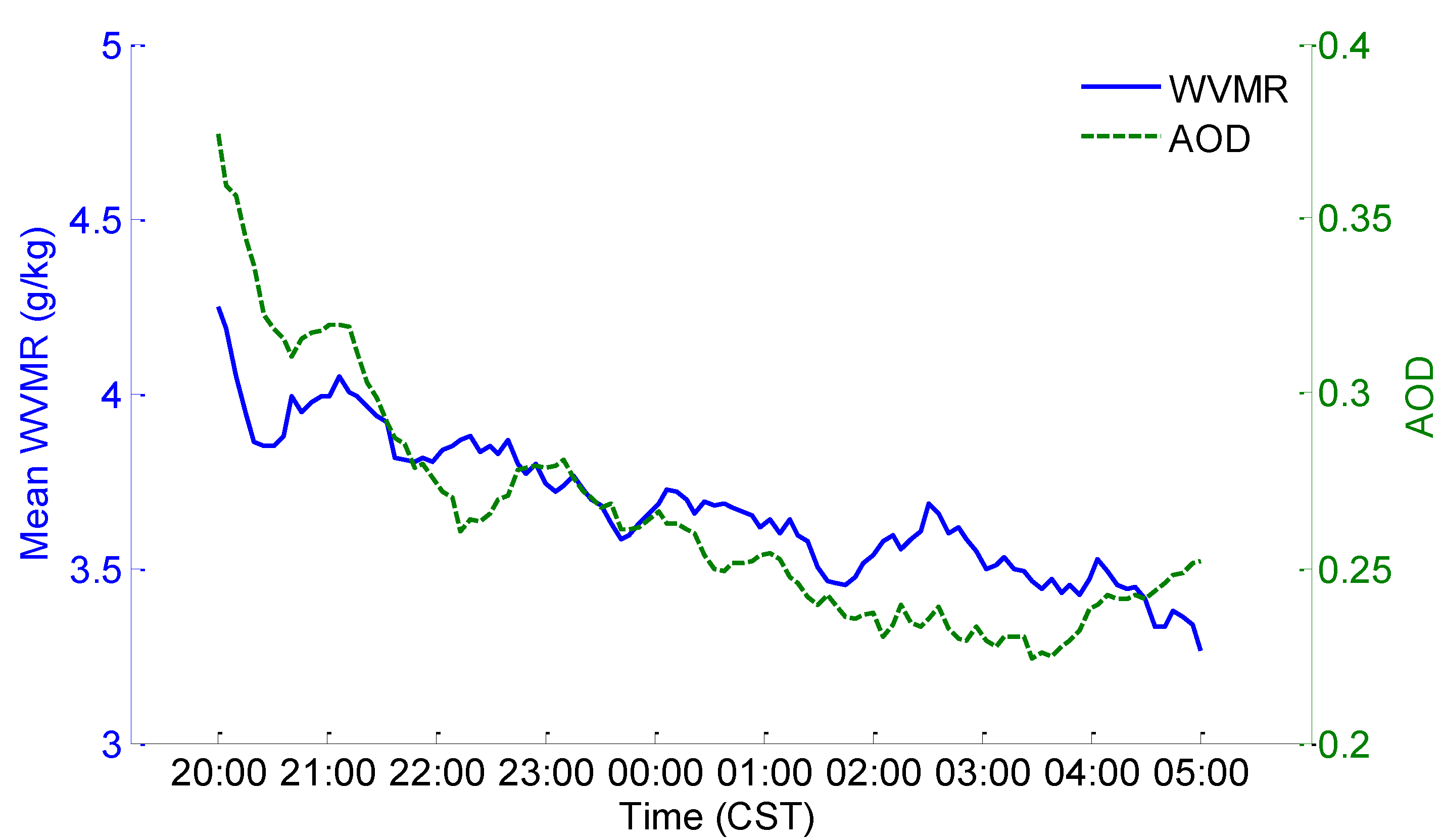
3.2. Long-Term Observation
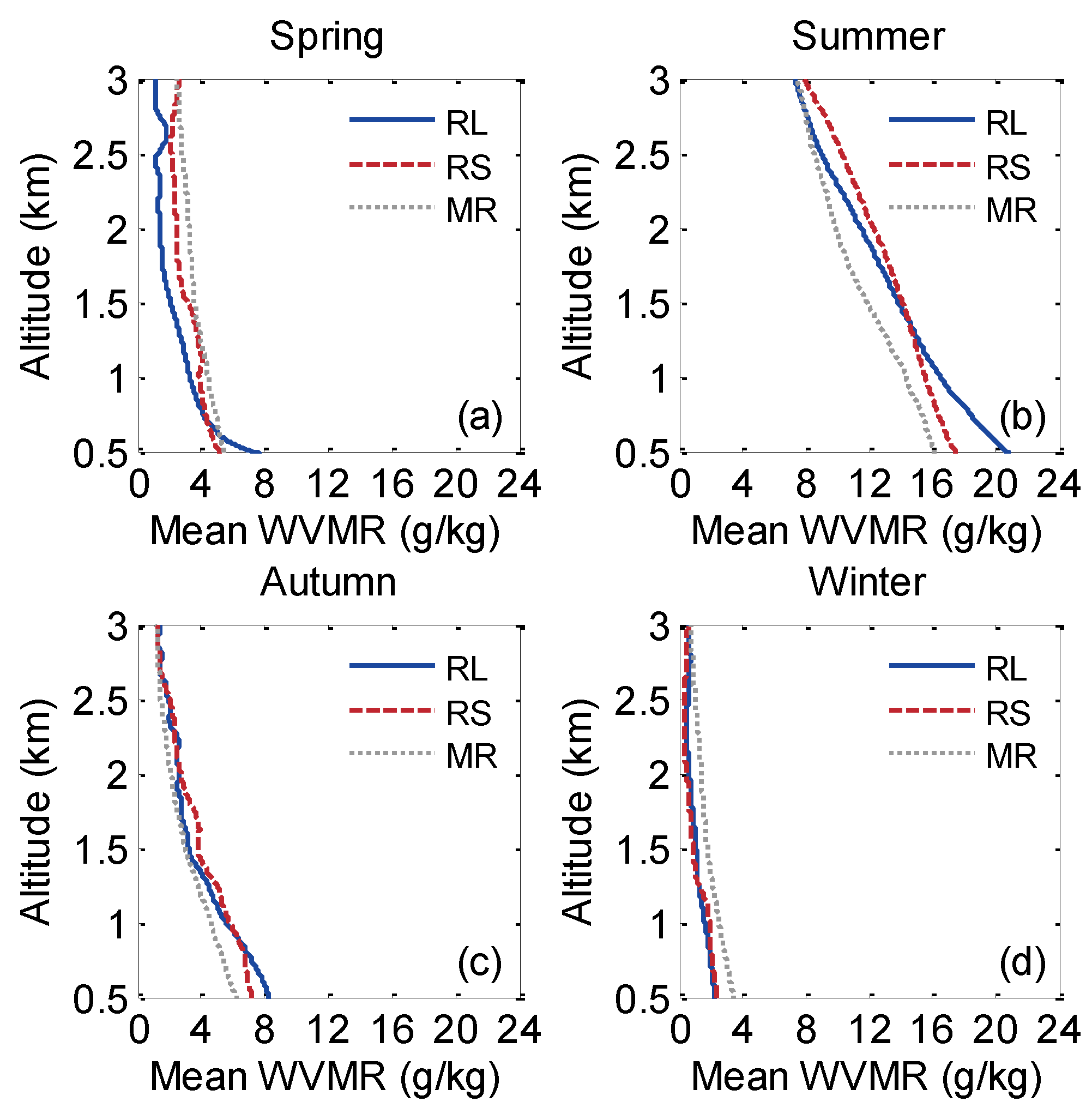

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, W.; Zhang, S.S.; Ma, Y.Y. Aerosol optical properties and determination of aerosol size distribution in wuhan, china. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.Y.; Gong, W.; Zhu, Z.M. Aerosol optical properties of a haze episode in wuhan based on ground-based and satellite observations. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 699–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.; Hales, J.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.A., Jr.; Hansen, J.; Hofmann, D. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, K.-N. Influence of cirrus clouds on weather and climate processes: A global perspective. Mon. Weather Rev. 1986, 114, 1167–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerding, M.; Ritter, C.; Müller, M.; Neuber, R. Tropospheric water vapour soundings by lidar at high arctic latitudes. Atmos. Res. 2004, 71, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harries, J. Atmospheric radiation and atmospheric humidity. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 123, 2173–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Hua, D.X.; Wang, L.; Tang, J.; Mao, J.T.; Kobayashi, T. Observations and analysis of relationship between water vapor and aerosols by using raman lidar. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 51, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. Aerosols, clouds and radiation. Atmos. Environ. Part A General Top. 1991, 25, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.D.; Goldsmith, J. Twenty-Four-Hour raman lidar water vapor measurements during the atmospheric radiation measurement program’s 1996 and 1997 water vapor intensive observation periods. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 1062–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, K.P.; Sinha, A. Sensitivity of the earth’s climate to height-dependent changes in the water vapour mixing ratio. Nature 1991, 354, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yufeng, W.; Fei, G.; Chengxuan, Z.; Qing, Y.; Dengxin, H. Observations of atmospheric water vapor, aerosol, and cloud with a raman lidar. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 114105–114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocke, K.; Kämpfer, N.; Gerber, C.; Mätzler, C. A complete long-term series of integrated water vapour from ground-based microwave radiometers. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiobara, M.; Spinhirne, J.D.; Uchiyama, A.; Asano, S. Optical depth measurements of aerosol, cloud, and water vapor using sun photometers during fire cirrus ifo ii. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 35, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, W.B. Differential absorption and raman lidar for water vapor profile measurements: A review. Opt. Eng. 1991, 30, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitkamp, C. Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere; Springer: Geesthacht, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D.D.; Ferrare, R.; Brasseur, L.H.; Feltz, W.; Tooman, T. Automated retrievals of water vapor and aerosol profiles from an operational raman lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, J.; Mao, F.; Li, J. Measurements for profiles of aerosol extinction coeffcient, backscatter coeffcient, and lidar ratio over wuhan in china with raman/mie lidar. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2010, 8, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Li, J.; Mao, F.; Zhang, J. Comparison of simultaneous signals obtained from a dual-field-of-view lidar and its application to noise reduction based on empirical mode decomposition. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2011, 9, 050101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Gong, W.; Li, C. Anti-Noise algorithm of lidar data retrieval by combining the ensemble kalman filter and the fernald method. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 8286–8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, F.Y.; Gong, W.; Ma, Y.Y. Retrieving the aerosol lidar ratio profile by combining ground- and space-based elastic lidars. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z. Long-Term observations of aerosol optical properties at wuhan, an urban site in central china. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, D.; Melfi, S.; Ferrare, R. Raman lidar system for the measurement of water vapor and aerosols in the earth’s atmosphere. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 3068–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klett, J.D. Stable analytical inversion solution for processing lidar returns. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansmann, A.; Riebesell, M.; Weitkamp, C. Measurement of atmospheric aerosol extinction profiles with a raman lidar. Opt. Lett. 1990, 15, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navas-Guzman, F.; Fernandez-Galvez, J.; Granados-Munoz, M.J.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Tropospheric water vapour and relative humidity profiles from lidar and microwave radiometry. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Gong, W.; Mao, F.; Zhang, J. Long-Term Measurement for Low-Tropospheric Water Vapor and Aerosol by Raman Lidar in Wuhan. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 521-533. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6040521
Wang W, Gong W, Mao F, Zhang J. Long-Term Measurement for Low-Tropospheric Water Vapor and Aerosol by Raman Lidar in Wuhan. Atmosphere. 2015; 6(4):521-533. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6040521
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei, Wei Gong, Feiyue Mao, and Jinye Zhang. 2015. "Long-Term Measurement for Low-Tropospheric Water Vapor and Aerosol by Raman Lidar in Wuhan" Atmosphere 6, no. 4: 521-533. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6040521
APA StyleWang, W., Gong, W., Mao, F., & Zhang, J. (2015). Long-Term Measurement for Low-Tropospheric Water Vapor and Aerosol by Raman Lidar in Wuhan. Atmosphere, 6(4), 521-533. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6040521








