Abstract
Aerosol scattering and absorption properties were continuously measured and analyzed at the urban Laboratory for Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing (LIESMARS) site in Wuhan, central China, from 1 December 2009 to 31 March 2014. The mean aerosol scattering coefficient , absorption coefficient , and single scattering albedo (SSA) were 377.54 Mm−1, 119.06 Mm−1, and 0.73, respectively. Both and showed obvious annual variability with large values in winter and small values in summer, principally caused by the annual characteristics of meteorological conditions, especially planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) and local emissions. The SSA showed a slight annual variation. High values of SSA were related to formation of secondary aerosols in winter hazes and aerosol hygroscopic growth in humid summer. The large SSA in June can be attributed to the biomass combustion in Hubei and surrounding provinces. Both and showed double peak phenomena in diurnal variation resulting from the shallow stable PBLH at night and automobile exhaust emission during morning rush hours. The SSA also exhibited a double peak phenomenon related to the proportional variation of black carbon (BC) and light scattering particulates in the day and night. The long-term exploration on quantified aerosol optical properties can help offer scientific basis of introducing timely environmental policies for local government.
1. Introduction
Atmosphere aerosols can alter the climate system through aerosol radiative forcing via two modes: those that directly scatter and absorb sunlight and those that indirectly transform the physical and optical characteristics of clouds by serving as cloud condensation nuclei [1,2,3]. Aerosols in the atmosphere have highly inhomogeneous spatiotemporal distribution and variability [4,5], which create the largest uncertainties among all climate forcing factors [6]. The current effects of aerosols are rarely considered in climate models [7]. Therefore, analysis of aerosol characteristics in various regions worldwide is necessary for understanding their climate effects.
Long-term aerosol observations based on in-situ measurements would improve the precision of parameterizations in models and reduce uncertainties caused by an absence of aerosol information [8,9]. In recent years, comprehensive measurements have been extensively conducted worldwide in such projects as Aerosol Characterization Experiment (ACE); Aerosols, Clouds, and Trace Gases Research Infrastructure (ACTRIS); Tropospheric Aerosol Radiative Forcing Observational Experiment (TARFOX); and Indian Ocean Experiment (INDOEX) [7,10,11,12,13]. Aerosol optical properties and their variations have also been studied at several western stations [14,15,16]. In China, the rapid growth of economic and urbanization construction has led to heavy emissions of anthropogenic pollutants in recent decades. To thoroughly understand the aerosol radiative forcing characteristics in China, numerous surface aerosol experiments have been conducted [17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. However, most of these studies have been conducted in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region [5,15,18,21,22,23], the Pearl River Delta [14,17,24,25], the Yangtze River Delta [26] and the northwest semi-arid areas [27,28,29]. Observations of aerosol scattering and absorption properties in central China are sparse. In addition, few studies have reported long-time continuous measurements of aerosol optical properties with an observation period longer than one year. To understand the exact aerosol radiation effects on the climate in central China, further measurement of the aerosol optical properties in this region is needed.
In this study, we conducted a five-year aerosol experiment to investigate the aerosol scattering coefficients , absorption coefficients , and single scattering albedo (SSA) in Wuhan, Central China, from 1 December 2009 to 31 March 2014, and we analyzed their seasonal and diurnal variations. Section 2 of the paper describes the station information and methods adopted, Section 3 provides the results and discussion, and Section 4 includes brief conclusions.
2. Experiment Area and Methodology
2.1. Site Description and Instrumentation
Our study was conducted at the State Key Laboratory for Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping, and Remote Sensing (LISMARS; 29.97°N, 113.91°E) at the campus of Wuhan University (WHU). Wuhan, a large city in central China and the capital of Hubei Province, is located at the intersection of the Yangtze and Han rivers. The climatic type is subtropical monsoon. The main sources of aerosols in Wuhan are pollutant emissions from transportation and traffic systems, industrial manufacturing, and cooking by using fossil fuels. Aerosol measuring equipment such as a nephelometer and an aethalometer were installed on the top of the four-story lab building. The LIESMARS station is about 200 m from Luoyu Road, a busy highway toward the south. The surrounding zones include residential districts and educational and commercial areas; thus, the experimental site is a typical urban representation of Wuhan city. Figure 1 shows the geographic position of the LIESMARS site.
Figure 1.
Location of the experimental area: (a) location of the Hubei Province in China; (b) location of Wuhan city in Hubei Province; (c) location of the Laboratory for Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing (LIESMARS) site in Wuhan city.
An integrated nephelometer (model 3563) was adopted to obtain the aerosol scattering coefficients. This nephelometer is designed with three wavelengths: 450 nm, 550 nm, and 700 nm. In the process of operation, the instrument was automatically and daily calibrated to zero, and we conducted span checking every three months. In the span checking procedure, standard CO2 was utilized as the span gas [30]. The flow rate of the nephelometer was 30 L∙min−1, and the average sampling time was 1 min. The observation angle was 7°–170° [31]. Correction of truncation error was conducted according to the method mentioned in previous research [32]. During the entire experimental period, the observation errors were mainly from non-Lambert characteristics of the light source, non-idealized wavelengths, and uncertainties in calibration. These errors contributed to approximately 7% error in the data [30,31].
In this research, a seven-wavelength aethalometer (370, 470, 520, 590, 660, 880, and 950 nm; AE-31) was employed to obtain the mass concentration of black carbon (BC) and to retrieve the aerosol absorption coefficients [33]. The aethalometer can measure real-time light attenuation caused by BC particles clustered on a quartz filtration membrane. The BC mass concentration can then be calculated continuously based on the changes in light attenuation [34]. The flow rate of the equipment was 5 L∙min−1 with a 2-min sampling time. A PM2.5 sampling head was installed at the inlet. The inlet was connected to the instrument through a 2.5-m-long tube, the interior of which was coated with Teflon to prevent sample loss. The calibration was done every three months including blank measurements and flow rate calibration to ensure accuracy. We checked the service behavior of the aethalometer daily to ensure the quality of data, which included checking the quartz filtration membrane, filter and the stability of the light source.
In this study, the multichannel microwave radiometer (RPG-HATPRO) was used to obtain the planetary boundary layer height (PBLH). The device is manufactured by Radiometer Physics GmbH (Germany), which is able to provide real-time continuous monitoring of the humidity and temperature profiles in the PBL and troposphere. The frequency range of the V-band (oxygen window) is from 51.6–58 GHz, which is divided into seven temperature channels. The frequency range of the K-band (vapor window) is from 22.24 to 31.4 GHz, which is also divided into seven humidity channels. A profile of the temperature and humidity within 0–10 km range is derived using the neural network algorithm [35]. The profile data is divided into 39 layers of pressure surfaces from 0 to 10 km; the vertical resolution gradually reduces with ascending height. The maximum vertical height resolution is 10 m at low altitude; therefore, the accuracy of low-altitude PBL detection is greater. The temporal resolution is set at 2 min. More detailed information can be found in the relevant literature [36]. The microwave radiometer was installed in September 2010 at the LIESMAR site. Hence, the data set used in this research extended from September 2010 to June 2013. The equipment was not operated continuously during the five-year study period due to maintenance and reconfigurations.
The meteorological datasets in Wuhan were also made available by the China Meteorological Data Sharing Service System. Daily mean wind speed data and precipitation data were collected in this experiment to analyze the influencing factors of the aerosol optical properties. The gases datasets (including SO2, CO and NOx daily observations) were obtained from Wujiashan (WJS) station in Wuhan city.
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Aerosol Optical Properties Calculations
The scattering coefficient of aerosols reflects the aerosol scattering ability. This value can be measured directly by using the integrated nephelometer as previously mentioned. In this study, we mainly used on the 550 nm. The aerosol absorption coefficient can reflect the absorption ability of aerosols and can be calculated indirectly by using the BC mass concentration as the following formula:
where [BC] is the mass concentration of BC, and is the absorption efficiency factor of BC. Schmid et al. measured the absorption efficiency factor in Guangzhou city by utilizing linear regression with a correlation coefficient R2 = 0.92 of (units: Mm−1) measured by using a portable aerosol sensor (PAS) at 532 nm and BC concentrations (units: μg∙m−3) observed by utilizing the aethalometer at the wavelength of 880 nm [24]. The calculated was 8.28 m2∙g−1. In this study, we used the value provided by the manufacturer. From the user manual, the coefficient α is set to 14625/. The aerosol absorption coefficient at the wavelength of 520 nm was adopted in the experiment, because the wavelength was close to 550 nm, which was the wavelength of scattering coefficient used in this study.
The SSA is defined as the value of divided by the extinction coefficient of the particles; the extinction coefficient is the sum of and . The value of SSA can directly reflect the aerosol radiative forcing and a small error in SSA could change the aerosol radiative forcing [37]. When calculating the SSA, and should be revised to a uniform wavelength. We adjusted to 520 nm by using the scattering Ångström exponent at 550 nm and 700 nm from the nephelometer using the following formula:
where is the scattering Ångström exponent, which can be found by the corrected scattering coefficients on 450 nm and 700 nm using the following formula:
Finally, the SSA was calculated to be 520 nm. The details of the specific algorithm used can be found in the previous study [15].
2.2.2. PBLH Detection
PBLH detection using a microwave radiometer is based on the thermodynamic properties of the atmosphere. As PBLHs have greater convectional reactions that develop towards the relatively stable free atmosphere above, the position of the maximum vertical gradient of potential temperature (θ) can be used as the PBLH [38]. In this study, the wavelet curve-fitting method proposed by Sawyer and Li et al. [39] was used to monitor the PBLH. The algorithm defines the PBLH as the position where θ rises rapidly, which lies between the nearly homogeneous mixed layer and the more stable free atmosphere above. Using the thermodynamic profile as a total profile is effective for locating the PBLH and the performance is stable. The detailed process of the algorithm could be seen in the corresponding literature [39]. In the study, we omitted the imperfect values of measurement in the five-year datasets and averaged the data to a 1-h time resolution to reduce the instability of the data originating from equipment noise. All of the local zone time (LZT) utilized in this study is Beijing Time, 8 h ahead of UTC.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overview of Aerosol Scattering and Absorption Properties
Figure 2 shows the temporal variability of daily mean , , and SSA. These extensive parameters showed very large absolute values related to the large number of local anthropogenic emission sources in the urban environment. In Wuhan, the mean values of , , and SSA were 377 Mm−1, 119 Mm−1, and 0.73, respectively. The values of and had large standard deviations reflecting strong fluctuations and large changes in the entire measurement period. A similar performance of aerosol optical parameters was also noted in other urban cities in China [14,22,26,42]. 99th percent of and were extremely large at 1518.65 Mm−1 and 133.66 Mm−1, respectively, which can mainly be attributed to severe haze events occurring in winter. As mentioned in the study of Zhang et al., a severe haze event caused by biomass combustion occurred in Wuhan on 6–14 June 2012. During this haze, the mean and were approximately 5.3 times and 3.4 times that of normal weather, respectively, which explains the hourly mean maximum of and on 11 June 2012 [40].
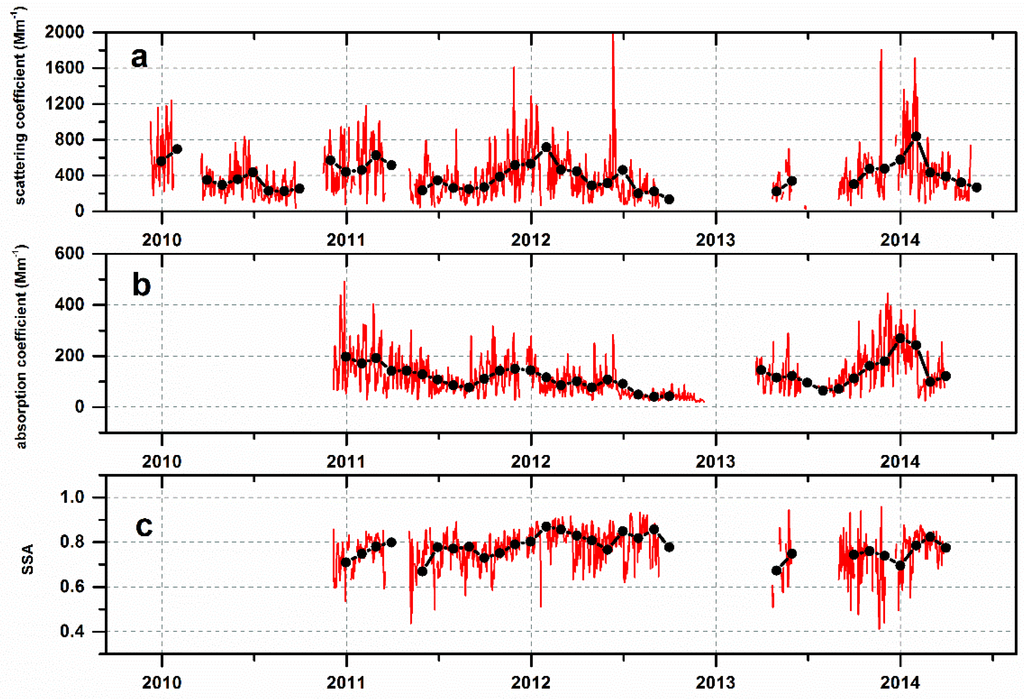
Figure 2.
Entire temporal daily series of aerosol scattering and absorption properties (red line). Black dotted line represents the monthly mean of every parameter: (a) Aerosol scattering coefficients () at three bands; (b) aerosol absorption coefficients () and (c) single scattering albedo (SSA).
Table 1 shows statistical information of aerosol optical parameters such as median, mean, standard deviation and skewness at the LIESMARS site. The skewness represents the degree of asymmetry in the optical parameters. As shown in Table 1, and showed skewness values >1, whereas SSA showed a negative value of skewness. This indicates that the possibilities of and values lower than the mean are higher than those higher than the mean. Thus, the mean was 23% larger than its median, and was 31% greater than its median, which is similar to the results observed at the Shanghai site [26]. The probabilities of SSA values lower than the mean are lower than those higher than the mean, which was similar to the circumstance at the rural MSC station [10]. Figure 3 shows the relative and cumulative frequency distributions of all optical properties determined in the study. The , , and SSA occurred most frequently with a cumulative frequency of 90% in the scope of 0–600 Mm−1, 0–200 Mm−1, and 0.55–0.95, respectively.

Table 1.
Aerosol scattering and absorption properties at the Laboratory for Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing (LIESMARS) site in Wuhan city.
| Hourly base | Counts | Median (50th perc.) | Mean | SD | Skewness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mm−1) | 450 | 25,464 | 414 | 501 | 390 | 1.97 |
| 550 | 25,464 | 306 | 377 | 305 | 2.10 | |
| 700 | 25,464 | 199 | 253 | 215 | 2.14 | |
| (Mm−1) | 520 | 24,262 | 91 | 119 | 92 | 1.84 |
| 520 | 17,061 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.16 | −2.56 | |
| 450–700 | 25,464 | 1.66 | 1.66 | 0.45 | 4.24 |
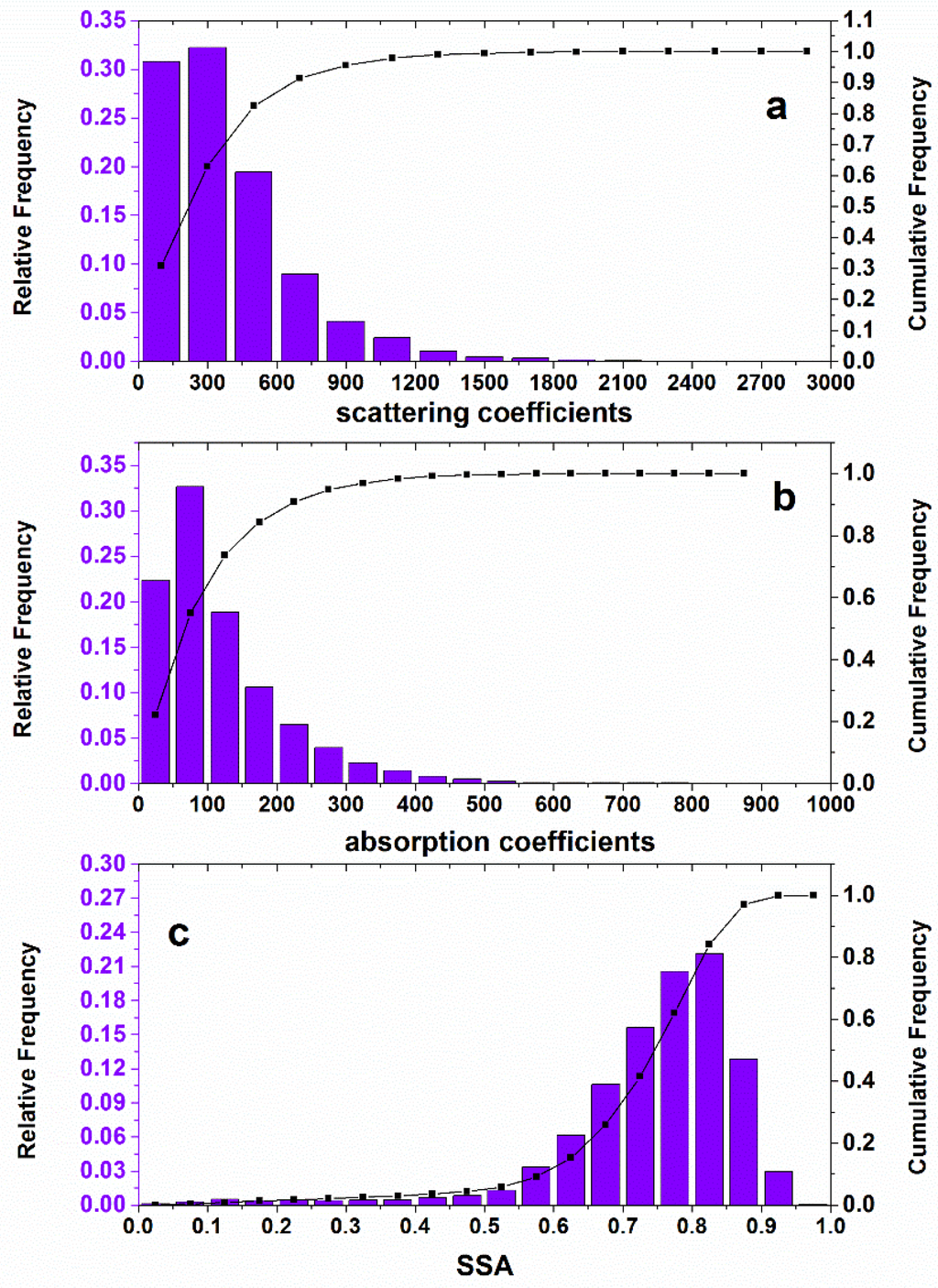
Figure 3.
Relative and cumulative frequency distributions of aerosol optical properties: (a) aerosol scattering coefficients (); (b) aerosol absorption coefficients () and (c) single scattering albedo (SSA).
Table 2 lists the average , , and SSA values observed worldwide in other in situ measurement. The at LIESMARS was lower than that in urban Guangzhou (418 Mm−1) [14]. In Beijing, was 488 Mm−1 in June 1999 [41] and 301 Mm−1 after the implementation of a pollution reduction scheme and the clean energy policy during the Olympic Games in 2008 [22]. The former was larger to that in Wuhan and the latter was lower than that in Wuhan. The in Shanghai was 293 Mm−1, which is lower than that in Wuhan [26]. These results indicated that the degree of contamination and aerosol loadings in urban megacities were high in China including Wuhan city. In some suburban sites in China such as Wuqing (280 Mm−1) [21], Xinken (333 Mm−1) [17], and Changping (263 Mm−1) [22], values were also high. However, values in several rural sites, regional background sites, and Western country sites were much lower than those reported in Wuhan. For example, at the Global Atmosphere Watch (GAW) regional station Shangdianzi (SDZ) in North China, the was 174.6 Mm−1 during 2003–2005 [18] and 182 Mm−1 in another research in 2009 [22]. Both of these values are about a half of that obtained at the LIESMARS site. In Granada, an urban city in Spain, the was only approximately 22% that in Wuhan [16]. Wuhan is a highly industrialized inland megacity in central China, and pollution in this city is caused by anthropogenic emissions from urbanization, industrial activities, and the transportation system. Thus, it is reasonable for to be larger than that in some suburban and rural sites and similar to that at other urban sites in China. The in Wuhan (119 Mm−1) was larger than that in other Chinese urban sites such as Shanghai (66 Mm−1) [26], Beijing (83 Mm−1) [41], and Guangzhou (91 Mm−1) [14]. At the same time, the in Wuhan was larger than that at SDZ (17.5 Mm−1) [18] and Melpitz regional background sites (5.97 Mm−1) [8]. Compared with that in some Western countries, the was lower in Granada (28 Mm−1) [16], MSC (1.5 Mm−1) [10] and BND (4.66 Mm−1) [9]. These situations revealed that the emission of BC in Wuhan was at a high level. The source of BC absorptive aerosol was primarily motor vehicle exhaust and straw-burning in Wuhan.

Table 2.
Aerosol optical properties observed at sites worldwide.
| Site | Type | Period | SSA | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LISMARS (China) | urban | April 2012–March 2014 | 377 (305) | 119 (92) | 0.73 (0.16) | This work |
| BND (USA) | rural | September 1996–September 2000 | 57.0(47.1) | 4.62 (3.82) | 0.906 (0.067) | [9] |
| SGP (USA) | rural | April 1997–September 2000 | 46.7 (42.8) | 2.47 (2.71) | 0.932 (0.051) | [9] |
| WSA (USA) | marine station | November 1994–April 2000 | 40.7 (32.8) | 1.89 (2.26) | 0.953 (0.038) | [9] |
| BRW (USA) | marine station | October 1997–September 2000 | 10.4 (11.1) | 0.38 (0.54) | 0.959 (0.040) | [9] |
| SDZ (China) | regional background | September 2003–January 2005 | 174.6 (189.1) | 17.5(13.4) | 0.88 (0.05) | [18] |
| Melpitz (Germany) | regional background | 2007–2010 | 53.61 (58.64) | 5.97 (5.69) | 0.871 (0.051) | [8] |
| MSC (Spain) | rural | June 2011–June 2013 | 18.9 (20.8) | 1.5 (1.4) | 0.92 (0.03) | [10] |
| Shanghai (China) | urban | December 2010–March 2011 | 293 (206.39) | 66 (46.8) | 0.81 (0.04) | [26] |
| Beijing (China) | urban | June 1999 | 488 (370) | 83 (40) | 0.81 (0.08) | [41] |
| Guangzhou (China) | urban | October 2004–November 2004 | 418 (159) | 91 (60) | 0.826 (0.054) | [14] |
| Wuqing (China) | suburb | March 2009–April 2009 | 280 (253) | 45 (37) | 0.82 (0.05) | [21] |
| Wuqing (China) | suburb | July 2009–August 2009 | 379 (251) | 49 (31) | 0.86 (0.05) | [21] |
| Granada (Spain) | urban | December 2005–February 2006 | 84 (62) | 28 (20) | 0.66 (0.11) | [16] |
| Xinken (China) | regional background | October 2004–November 2004 | 333 (137) | 70 (42) | 0.83 (0.05) | [17] |
| Baolian (China) | urban | August 2008–May 2009 | 301 (307) | [22] | ||
| Changping (China) | suburban | June 2008–January 2009 | 263 (263) | [22] | ||
| SDZ (China) | regional background | June 2008–May 2009 | 182 (201) | [22] | ||
| Linan (China) | regional background | September 1999 | 353 (202) | 23 (14) | [42] | |
| Praia (Cape Verde) | suburb | January 2008–February 2008 | 0.75 (0.07) | [43] |
Standard deviation values are stated within the parentheses.
The mean SSA at the LIESMARS station was 0.73. This value was lower than the value of 0.826 reported in Guangzhou [14], 0.88 at SDZ, 0.81 in summer Beijing [41], 0.82 in spring at the Wuqing site [21], and 0.81 in Shanghai [26]. The low SSA can reflect high loading of absorbing aerosols. The research in Guangzhou indicated that the SSA was low (0.6) when the absorbing aerosols of fresh combustion were dominant in the local region, and the SSA was high (0.9) owing to long-range transport of older pollution in the regional haze [14]. Delene et al. reported that the low SSA is likely to be the result of the advection of pollution aerosols originating from the East Coast of the United States, whereas the high SSA is connected with sea-salt aerosols [9]. In Wuhan, the SSA can be as large as 0.92 when a severe haze episode occurred as a result of long-range aged pollutants from straw-burning [40]. The SSA in Wuhan can be connected with the aerosol sources, age, and environmental conditions.
3.2. Seasonal Variation of Aerosol Scattering and Absorption Properties
A valid aerosol monthly box plot of aerosol optical properties reported at the LISMARS site is shown in Figure 4. All of the aerosol optical parameters revealed remarkable seasonal variations in Wuhan. At the Melpitz site in Germany, the BND, SGP, WSA, and BRW sites in the United States, cycles also can be clearly identified for each aerosol optical parameter [8,9]. As shown in Figure 4, the mean monthly values of and were always larger than the medians, particularly in winter, Ma et al. attributed this phenomenon to the fact that severe pollution events exist more frequently in winter than in summer and that mesoscale or large-scale motion of atmospheric phenomena may lead to a wide range of probability distributions for aerosol optical properties in winter [8]. Similar situations were reported by Delene et al. and Zhao et al., in which the monthly medians and means always differed because of the abnormal distributions of aerosol parameters [9,22].
Annual changes were significant for both and in Figure 4. These values were high in winter and low in summer. The maximum and minimum monthly means of occurred in January (678 Mm−1) and July (186 Mm−1), respectively; those of occurred in December (192 Mm−1) and August (63 Mm−1), respectively. These results are practically same as those recorded at the Melpitz site, where the maximum and minimum monthly means of occurred in January and July, respectively, and those of occurred in January and June, respectively [8]. The and at the BRW site were both larger in winter and very low in summer as well because of the high concentration of submicron particulates including sulfate and sea-salt aerosols in the arctic haze [9]. In Wuhan, as mentioned by Ma et al., the annual cycles of and are mainly dependent on the annual variability of the planetary boundary layer (PBL) height and contaminant emissions [8].
Figure 5a shows the seasonal variations of PBLH in Wuhan. The mean maximum was in August (1349 m) and the mean minimum was in December (643 m). PBLHs were deep in summer (June, July and August) and shallow in winter (December, January and February) in the whole year. In summer months, due to rising ambient temperature, deep and strong convection and turbulence would develop and become vigorous. The vertical mixing effect was enhanced, which resulted in deeper PBLHs. The deeper PBLHs aid in pollutant dilution. Therefore, and in summer were at lower levels with no significant changes. In winter, the temperature was low and the atmospheric convection and fluctuation were relatively weaker, PBLHs were mainly stable and shallow PBLHs. The shallow PBLH were not conducive to evacuation of pollutants and instead favored the accumulation of aerosols. Moreover, air pollution events occur frequently in winter with usually large concentrations of aerosols. In haze, the formation of secondary aerosols through photochemical reactions, aerosol aging, and the hygroscopic effect could enlarge the .
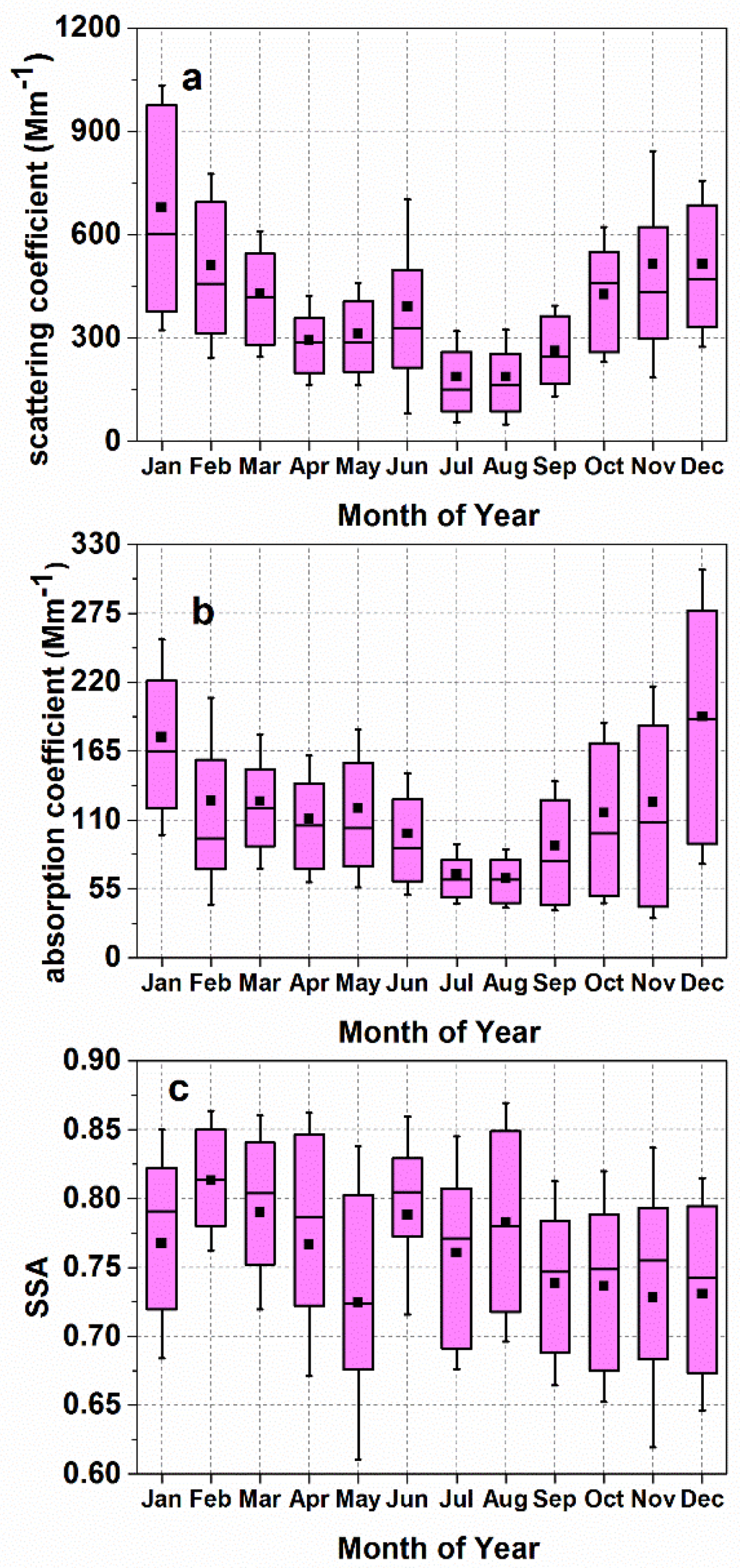
Figure 4.
Box plots of annual variation of aerosol optical parameters including mean value (solid black square), median (horizontal line within the box), 25th and 75th percentiles (upper and lower edges of box), and standard deviation (shorter horizontal lines) for different months: (a) aerosol scattering coefficients (); (b) aerosol absorption coefficients (); (c) single scattering albedo (SSA).
Wind speed was also an important factor affecting the aerosol optical properties in different seasons. As shown in Figure 6a, the mean monthly wind speed in Wuhan was large in summer and low in winter. The largest mean value occurred in August, and the lowest was in January. Wuhan has plain terrain with no strong pollution sources nearby. Thus, winds accompanied by cleaner air masses could transport pollutants out of Wuhan to purify the atmosphere. Therefore, the summer with high wind speed had lower and than that in winter with low wind speed. Precipitation scavenging was also an important mechanism for cleaning aerosol particles from the atmosphere [8]. As shown in Figure 6b, the precipitation measured in Wuhan showed that the average monthly precipitation in summer was approximately five times that in winter. The stronger and more abundant precipitation may be an important reason for the low level of and in summer. At the Baolian site, the abundant rainfall and frequent northern wind in September and October was also related to the dispersion of aerosols, which primarily resulted in a decrease in [22].
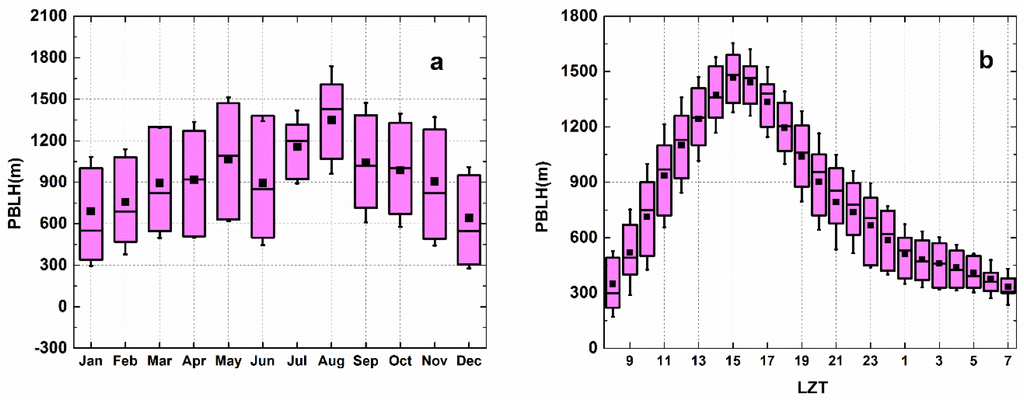
Figure 5.
Box-and-whisker plots of seasonal and diurnal variation of planetary boundary layer height (PBLH). The plots illustrate the mean value (solid black square), median (horizontal bar in box), 25th and 75th percentiles (lower and upper ends of box), standard deviation (horizontal upper and lower lines): (a) seasonal variation of PBLH; (b) diurnal variation of PBLH.
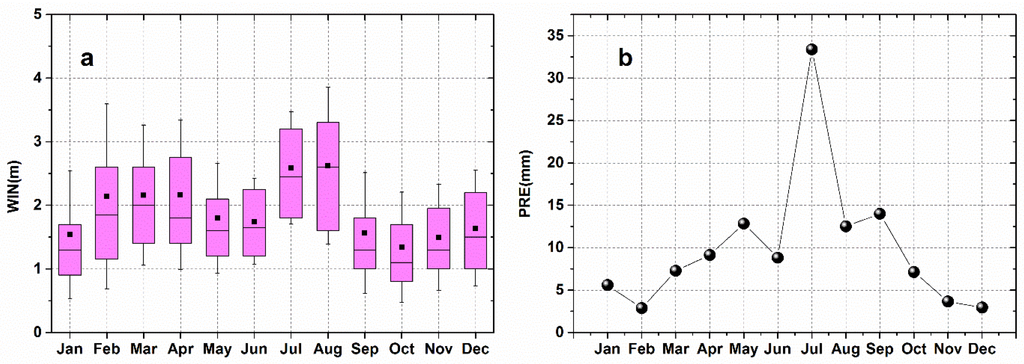
Figure 6.
Meteorological condition in Wuhan during the experiment period. (a) Box plots of seasonal variation of wind speed means (solid black square), median (horizontal line within the box), 25th and 75th percentiles (upper and lower edges of the box, respectively), and standard deviation (shorter horizontal lines) for different months; (b) average monthly precipitation.
In Figure 4c, the SSA showed only slight annual variations. The mean monthly SSA was highest in February (0.82) and June (0.79) and lowest in May (0.72). The mean values of SSA were 0.76, 0.78, 0.73 and 0.77 for spring, summer, autumn and winter, respectively. Ma et al. reported that the values of SSA may be the result of local emission and the formation of secondary aerosols [8]. As shown in Figure 7a–c, SO2, CO and NOx all showed significant seasonal variations with large values in winter and small values in summer. In winter, air pollution events such as haze occur frequently in Wuhan. During these events, secondary aerosol production by photochemical processes of gaseous precursors results in abundant non-light-absorbing elements such as organic matter and sulfates in particulates [8], therefore yielding a relatively high level of SSA. In Figure 7d, the scattering Ångström exponent revealed a relatively high value during the whole year. The mean scattering Ångström exponent was 1.59 in Wuhan, indicating that aerosols were mainly fine particulate. In summer, due to increased rainfall, coarse particles were eliminated and aerosol hygroscopic growth due to relatively high atmospheric humidity can lead to higher SSA [44]. At the same time, summer is the crop-harvesting season in China, large amounts of biomass (such as straw) were combusted and a great deal of aerosol pollutant can be emitted into the atmosphere in Hubei and surrounding provinces. Large amounts of pollutant from biomass combustion can be brought into Wuhan through air mass transport and solidification, condensation, and secondary particles can increase light scattering to result in increases in SSA in May and June [40].
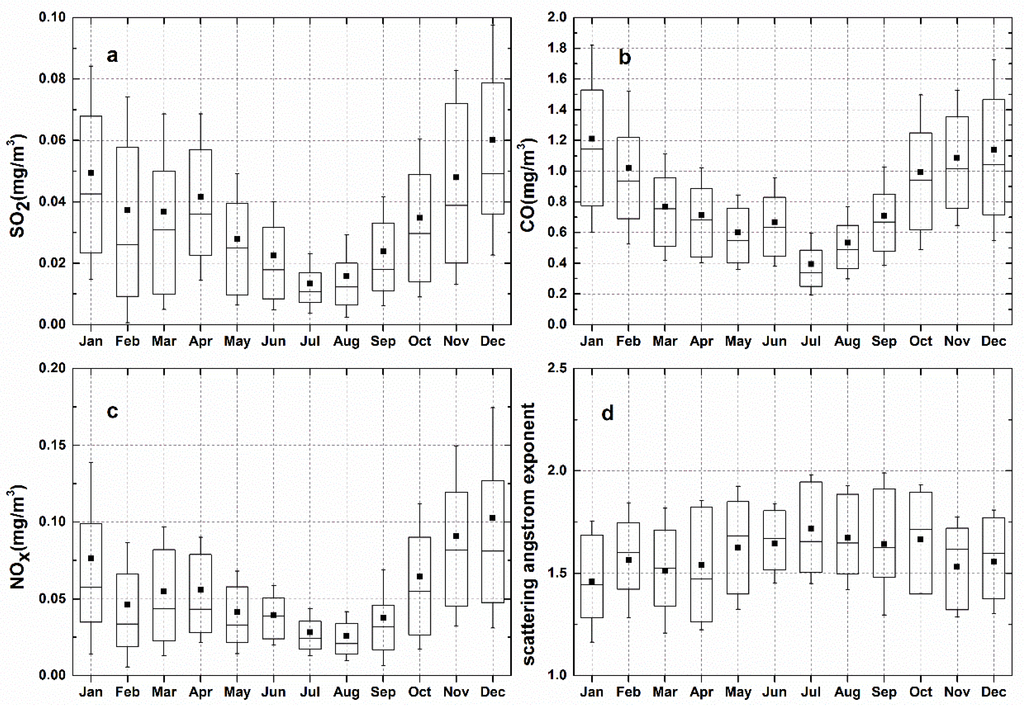
Figure 7.
Box-and-whisker plots of seasonal variation of gases mass concentrations and scattering Ångström exponent. The plots illustrate the mean value (solid black square), median (horizontal bar in box), 25th and 75th percentiles (lower and upper ends of box), standard deviation (horizontal upper and lower lines): (a) SO2; (b) CO; (c) NOx; (d) scattering Ångström exponent.
3.3. Diurnal Variation of Aerosol Scattering and Absorption Properties
Figure 8 exhibited diurnal curves of , , and SSA based on hourly means. The values of had two peaks at 7:00 LZT and 1:00 LZT; those of were 421 Mm−1 and 401 Mm−1, respectively, and those of were at 7:00 LZT (140 Mm−1) and 21:00 LZT (151 Mm−1), respectively. In Shanghai city, also an urban site, the diurnal variations in and were similar to those in Wuhan city, where and also had peaks at 8:00 LZT and 20:00 LZT, respectively [26]. It can be seen form Figure 5b that Wuhan displayed significant diurnal variation in PBLHs. The PBLHs rise gradually from 08:00 LZT and reached its peak at 15:00 LZT under the effects of increasing solar radiation and the intensification of atmosphere convection and turbulence. Subsequently, with the arrival of dusk, the atmospheric thermodynamic effect weakened and the PBLHs gradually reduced until the following sunrise when the cycle repeated. The and values then decreased and achieved the minimum in the midafternoon (15:00 LZT). This may explain why the developed PBL thermal turbulences favored the dilution of particle pollutants during strong atmospheric mixing in the well-mixed PBL at noon, resulting in a low concentration of aerosols at the Earth’s surface. The and increased until reaching the night peak and maintained high between 1:00 LZT and 7:00 LZT. This situation can be attributed to that stable nocturnal PBL formation leading to low atmospheric aerosol diffusion after sunset (18:00 LZT), and pollutants were bounded in the shallow PBLH to result in higher aerosol concentrations at the surface [21,22,26]. At the same time, the phenomenon of aerosol dry deposition can also enhance the concentration of aerosols at night.
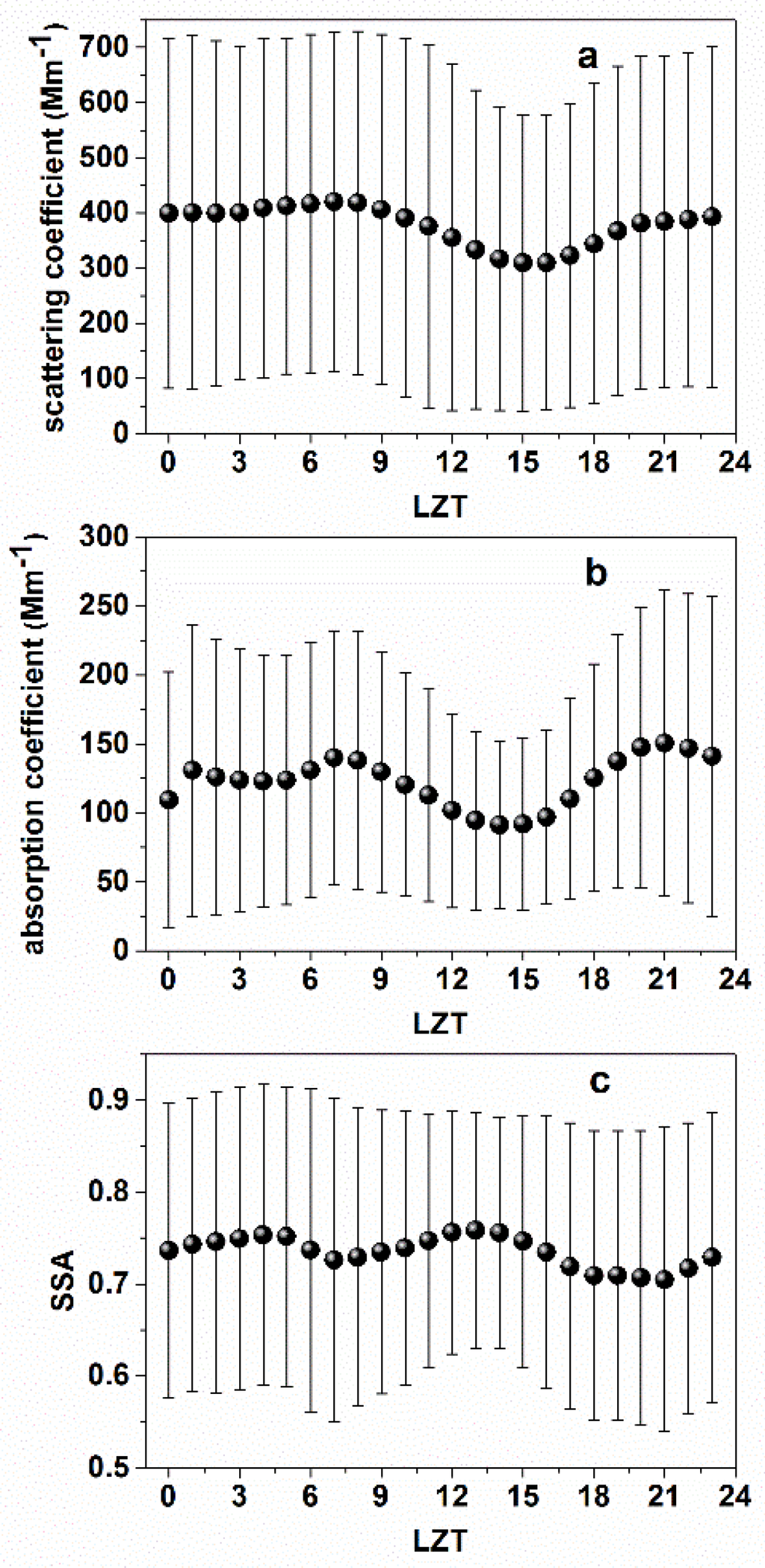
Figure 8.
Diurnal changes in aerosol optical properties at the Laboratory for Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing (LIESMARS) site. The short horizontal lines represent the standard deviation: (a) aerosol scattering coefficients (); (b) aerosol absorption coefficients (); (c) single scattering albedo (SSA).
As shown in Figure 8c, SSA also exhibited a bimodal distribution at 4:00 LZT in the morning (0.75), and at 13:00 LZT at noon (0.76). In Shanghai city, the morning peak occurred at 4:00 LZT, and the noon peak (daily maximum) occurred at 13:00 LZT, which is the same as Wuhan’s [26]. SSA was relatively low during traffic rush hours (around 7:00 LZT), which indicates that increased faster than . The values of SSA increased from 7:00 LZT to 13:00 LZT, indicating that light absorption aerosols such as BC dissipated faster than light scattering particulates. Some studies reported that the noon peak could have resulted from the breakout of a large number of secondary aerosols due to the photochemical reactions of gaseous precursors and the increased loading of light-scattering aerosols at noon [8,18,21,26].
4. Conclusions
To explore the aerosol scattering and absorption properties in Central China, we conducted a five-year experiment to uninterruptedly investigate aerosol scattering coefficients, absorption coefficients, and SSA at the LIESMARS site, an urban station in Wuhan City, between 1 December 2009 and 31 March 2014. For the entire period, the overall averages of , , and SSA were 377.54 Mm−1, 119.06 Mm−1, and 0.73, respectively. Moreover, , , and SSA were primarily at the ranges of 0–600 Mm−1, 0–200 Mm−1, and 0.55–0.95, respectively.
and exhibited significant annual changes. Both values were large in winter and low in summer, which was essentially due to the meteorological conditions (PBLH, wind seed and rainfall) and annual changes in local emissions. The values of SSA showed weak annual variation. High values occurred in summer and winter. This is related to the generation of secondary aerosols in winter hazes and aerosols hygroscopic growth in summer. The large SSA in June can be attributed to the biomass combustion in Hubei and surrounding provinces. In diurnal variation, and both showed bimodal distributions, which could be the result of dense traffic emissions during morning rush hours and shallow stable PBLHs at night. SSA also exhibited a bimodal distribution with low values during traffic rush hours (around 7:00 LZT), which indicates that increased faster than . The values of SSA increased from 7:00 LZT to 13:00 LZT, indicating that light absorption aerosols such as BC dissipated faster than light scattering particulates.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported financially by the Major Project of Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for High-efficiency Utilization of Solar Energy (HBSZD2014002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No.41127901), Chen Guang Project of Wuhan (Program No.2014070404010198), the program of Key Laboratory for National Geographic Census and Monitoring, National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation (No.2014NGCM) and the Scientific and Technological Project of Wuhan City (The Research of the Cause and Source of Haze in Wuhan City). We offer heartfelt thanks to the editor for the help and refining of the manuscript. We also thank every member of the team at the LISMARS site.
Author Contributions
The study was completed with cooperation of all authors. Miao Zhang and Wei Gong designed the research topic. Miao Zhang conducted the experiment and wrote the paper. Ge Han, Xin Ma and Zhongmin Zhu checked the experimental results. All authors agreed to submission of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Twomey, S. The influence of pollution on the shortwave albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D. TRMM observed first direct evidence of smoke from forest fires inhibiting rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 3105–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D. Suppression of rain and snow by urban and industrial air pollution. Science 2000, 287, 1793–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Kahn, R.; Levy, R.; Verduzco, C.; Villeneuve, P.J. Global estimates of ambient fine particulate matter concentrations from satellite-based aerosol optical depth: Development and application. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Z.; Huang, M.; Ma, X.; Tie, X. Aircraft study of aerosol vertical distributions over Beijing and their optical properties. Tellus B 2009, 61, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. In Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, Final Draft Underlying Scientific-Technical Assessment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- Anderson, T.L.; Masonis, S.J.; Covert, D.S.; Ahlquist, N.C.; Howell, S.G.; Clarke, A.D.; McNaughton, C.S. Variability of aerosol optical properties derived from in situ aircraft measurements during ACE-Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Birmili, W.; Müller, T.; Tuch, T.; Cheng, Y.F.; Xu, W.Y.; Wiedensohler, A. Tropospheric aerosol scattering and absorption over central Europe: A closure study for the dry particle state. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6241–6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delene, D.J.; Ogren, J.A. Variability of aerosol optical properties at four North American surface monitoring sites. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfi, M.; Ripoll, A.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Climatology of aerosol optical properties and black carbon mass absorption cross section at a remote high altitude site in the Western Mediterranean Basin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 3777–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Dubovik, O.; O’Neill, N.T.; Remer, L.A.; Eck, T.F.; Savoie, D. Measurement of atmospheric optical parameters on US Atlantic coast sites, ships, and Bermuda during TARFOX. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 9887–9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, P.; Coffman, D.; Bates, T.; Miller, T.; Johnson, J.; Welton, E.; Sheridan, P.J. Aerosol optical properties during INDOEX 1999: Means, variability, and controlling factors. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, INX2–INX19. [Google Scholar]
- Magi, B.I.; Hobbs, P.V.; Schmid, B.; Redemann, J. Vertical profiles of light scattering, light absorption, and single scattering albedo during the dry, biomass burning season in southern Africa and comparisons of in situ and remote sensing measurements of aerosol optical depths. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Schmid, O.; Yang, H.; Chand, D.; Zhen Yu, J.; Zeng, L.M.; Zhang, Y.H. Optical properties and chemical composition of the atmospheric aerosol in urban Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6335–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Sugimoto, N. Optical properties of atmospheric aerosols obtained by in situ and remote measurements during 2006 Campaign of Air Quality Research in Beijing (CAREBeijing-2006). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D00G02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyamani, H.; Olmo, F.J.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Light scattering and absorption properties of aerosol particles in the urban environment of Granada, Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2630–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Wiedensohler, A.; Eichler, H.; Su, H.; Gnauk, T.; Brüggemann, E.; Zhang, Y.H. Aerosol optical properties and related chemical apportionment at Xinken in Pearl River Delta of China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6351–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Tang, J.; Huang, J.; Mao, J.T.; Zhou, X.J.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, H.G. The measurement of aerosol optical properties at a rural site in Northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Damiri, B.; Goloub, P.; Li, Z.; Zhou, T. Instrument calibration and aerosol optical depth validation of the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D03206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, H.; Wang, P. Study on the aerosol optical properties and their relationship with aerosol chemical compositions over three regional background stations in China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhao, C.S.; Nowak, A.; Müller, T.; Pfeifer, S.; Cheng, Y.F.; Wiedensohler, A. Aerosol optical properties in the North China Plain during HaChi campaign: An in-situ optical closure study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5959–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Pu, W.; Meng, W.; Xu, X. Scattering properties of the atmospheric aerosol in Beijing, China. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Ma, J.; Yan, P.; Pan, X. Impacts of pollution and dust aerosols on the atmospheric optical properties over a polluted rural area near Beijing city. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, O.; Chand, D.; Andreae, M.O. Aerosol optical properties in urban Guangzhou. In Proceedings of the PRD Workshop, Beijing, China, 13–14 January 2005.
- Ansmann, A.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D.; Wandinger, U.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q. High aerosol load over the Pearl River Delta, China, observed with Raman lidar and Sun photometer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L13815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tao, J.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, T.; Leng, C.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Z. Measurements of surface aerosol optical properties in winter of Shanghai. Atmos. Res. 2012, 109, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zuo, J.; Bi, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Chang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, B.; et al. An overview of the semi-arid climate and environment research observatory over the Loess Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 25, 906–921. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, B.; Bi, J. Surface measurements of aerosol properties over northwest China during ARM China 2008 deployment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D00K27. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, B. Toward characterization of the aerosol optical properties over Loess Plateau of Northwestern China. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2011, 112, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.L.; Covert, D.S.; Marshall, S.F.; Laucks, M.L.; Charlson, R.J.; Waggoner, A.P.; Bates, T.S. Performance characteristics of a high-sensitivity, three-wavelength, total scatter/backscatter nephelometer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1996, 13, 967–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintzenberg, J.; Charlson, R.J. Design and applications of the integrating nephelometer: A review. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1996, 13, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Laborde, M.; Kassell, G.; Wiedensohler, A. Design and performance of a three-wavelength LED-based total scatter and backscatter integrating nephelometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.D.A.; Rosen, H.; Novakov, T. The aethalometer—An instrument for the real-time measurement of optical absorption by aerosol particles. Sci. Total Environ. 1984, 36, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingartner, E.; Saathoff, H.; Schnaiter, M.; Streit, N.; Bitnar, B.; Baltensperger, U. Absorption of light by soot particles: Determination of the absorption coefficient by means of aethalometers. J. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhnert, U.; Turner, D.D.; Crewell, S. Ground-based temperature and humidity profiling using spectral infrared and microwave observations. Part I: Simulated retrieval performance in clear-sky conditions. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Cimini, D.; de Angelis, F.; Dupont, J.C.; Pal, L.; Haeffelin, M. Mixing layer height retrievals by multichannel microwave radiometer observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, T.; Nakajima, T.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N.; Kinne, S. Single-scattering albedo and radiative forcing of various aerosol species with a global three-dimensional model. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, V.; Li, Z. Detection, variations and intercomparison of the planetary boundary layer depth from radiosonde, lidar and infrared spectrometer. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhu, Z. Aerosol optical properties of a haze episode in Wuhan based on ground-based and satellite observations. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 699–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, M.H.; Cass, G.R.; Xu, J.; Fang, C.; Zeng, L.M.; Yu, T.; Chameides, W.L. Aerosol radiative, physical, and chemical properties in Beijing during June 1999. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 17969–17980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bergin, M.H.; Yu, X.; Liu, G.; Zhao, J.; Carrico, C.M.; Baumann, K. Measurement of aerosol chemical, physical and radiative properties in the Yangtze delta region of China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Müller, D.; Gross, S.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Freudenthaler, V.; Weinzierl, B.; Veira, A.; Petzold, A. Optical and microphysical properties of smoke over Cape Verde inferred from multiwavelength lidar measurements. Tellus B 2011, 63, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z. Long-term observations of aerosol optical properties at Wuhan, an urban site in Central China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).