Characteristics of Black Carbon Aerosol during the Chinese Lunar Year and Weekdays in Xi’an, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Research Site
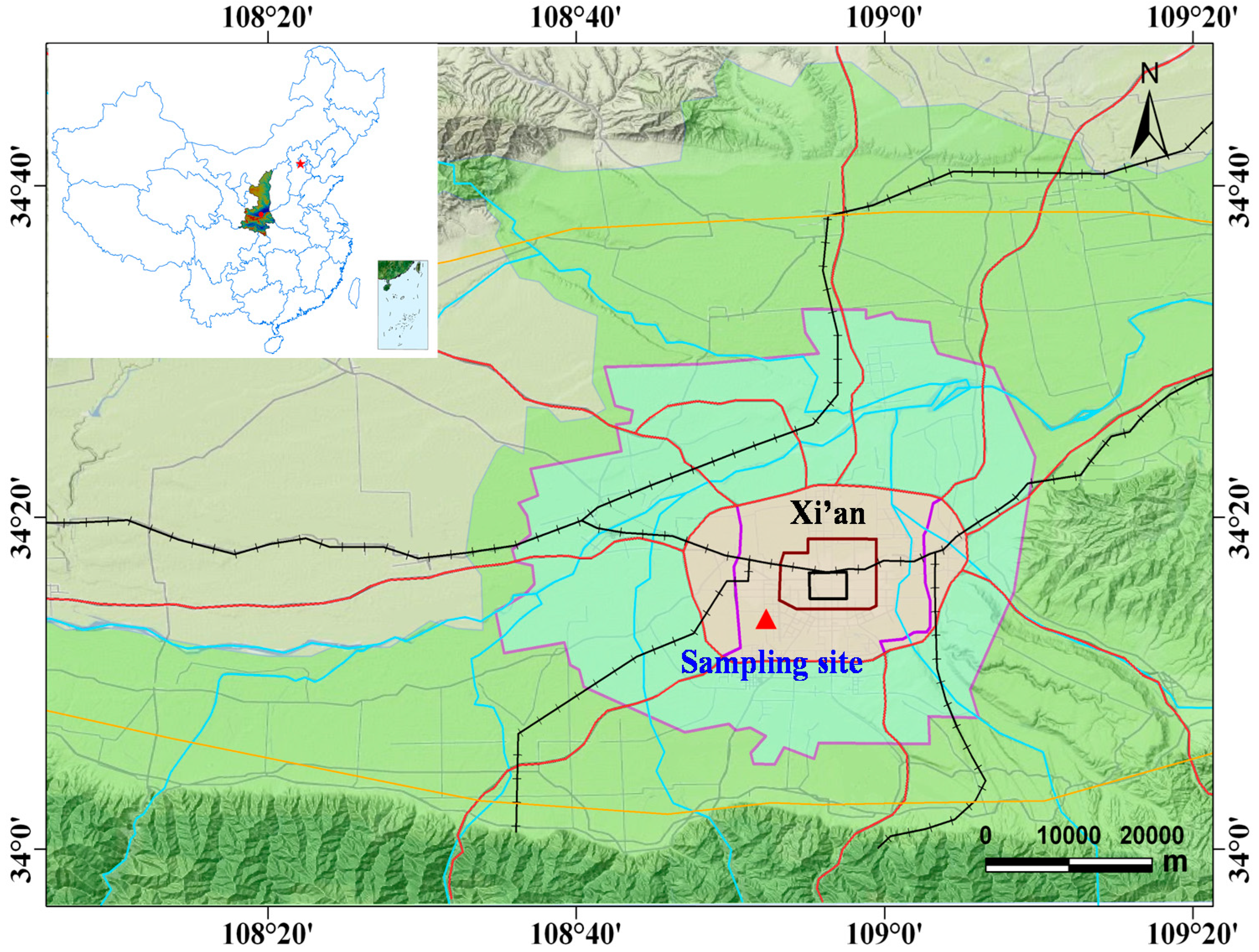
2.2. rBC and CO Measurements
2.3. Local Meteorological Conditions

3. Results and Discussion
3.1. rBC Loadings
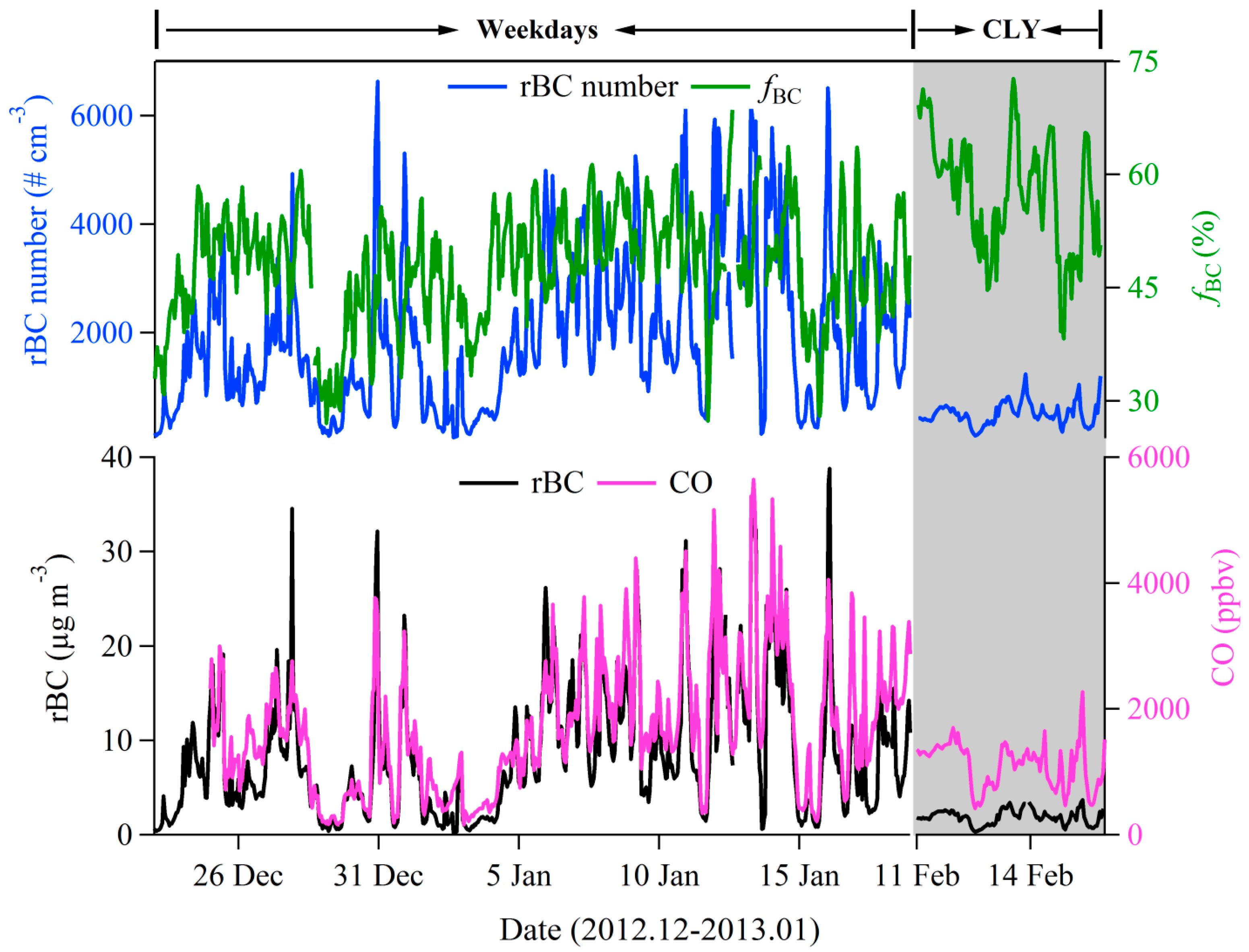
| Chinese Lunar Year | Weekdays | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rBC (cm−3) | rBC (μg·m−3) | fBC (%) | rBC (cm−3) | rBC (μg·m−3) | fBC (%) | |
| Average | 503 | 1.9 | 57.5 | 1850 | 8.4 | 48.3 |
| SD | 212 | 0.8 | 8.2 | 1242 | 6.5 | 6.9 |
| Maximum | 1231 | 3.9 | 76.1 | 6505 | 38.8 | 63.6 |
| Minimum | 99 | 0.2 | 26.7 | 65 | 0.2 | 27.3 |

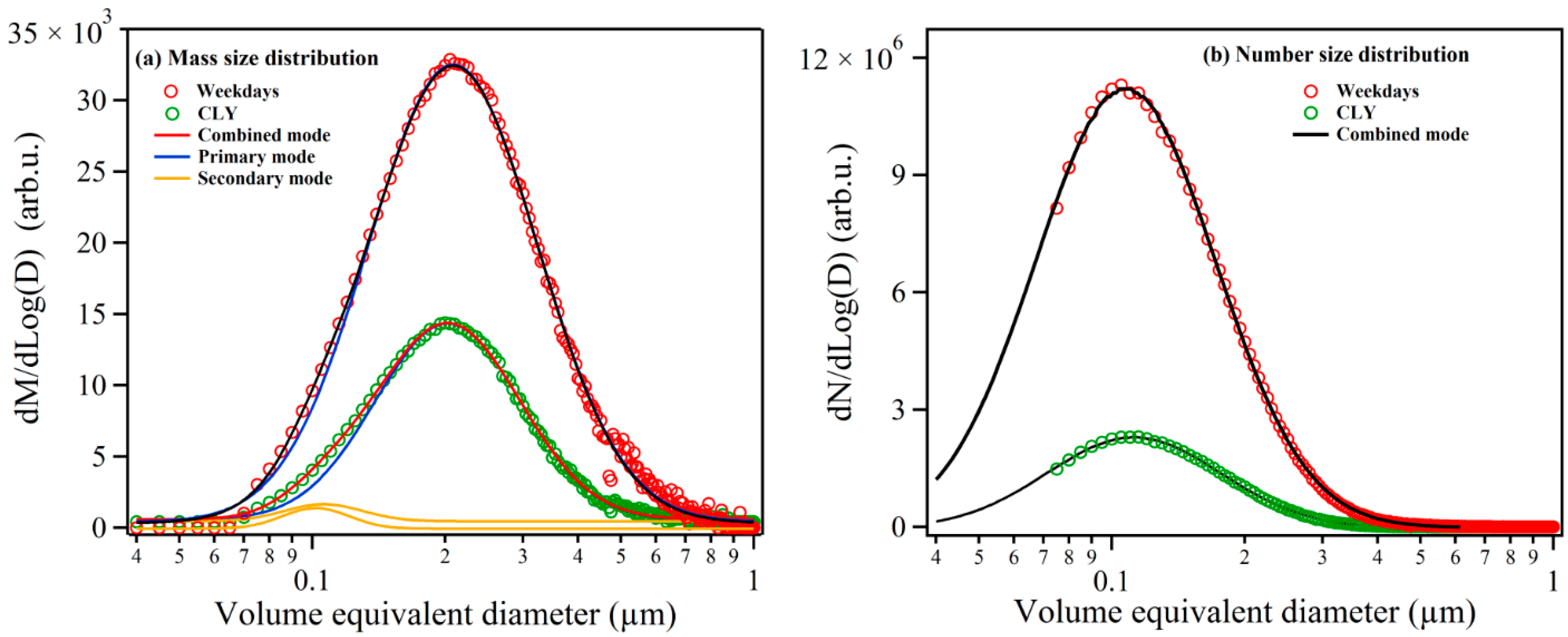
3.2. rBC Mass Size and Mixing State
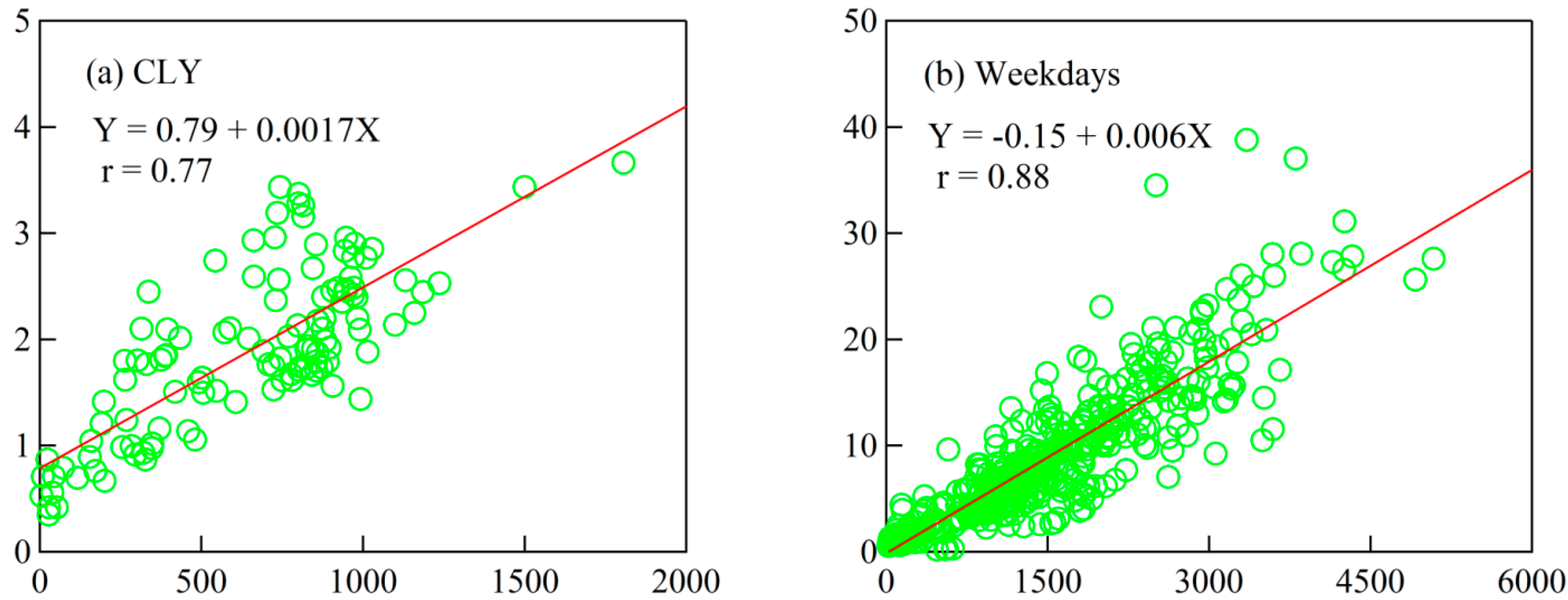
2.3. Relationship between rBC and CO
| Location | Sampling Period | rBC/ΔCO | Method a | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xi’an, China | December 2012/January 2013 February 2013 | 0.0060 0.0017 | SP2 | This study |
| Beijing, China | November 2005–October 2006 | 0.0035–0.0058 | TOT | [12] |
| Guangzhou, China | July 2006 | 0.0045 | EC-OC aerosol analyser | [45] |
| Multiple sites in Europe | April/May/September 2008 | 0.0008–0.0062 | SP2 | [44] |
| Tokyo, Japan | May 2003–February 2005 | 0.0057 | TOT | [40] |
| Nagoya, Japan | March 2003 | 0.0063 | Light absorption | [40] |
| Mexico | April 2003/2005 | 0.001 | SP2 | [45] |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.E.; Lee, K.; Mueller, D. Effect of internal mixture on black carbon radiative forcing. Tellus 2012, 64, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; de Angelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar]
- Twohy, C.H.; Poellot, M.R. Chemical characteristics of ice residual nuclei in anvil cirrus clouds: Evidence for homogeneous and heterogeneous ice formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordukhovich, I.; Wilker, E.; Suh, H.; Wright, R.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Schwartz, J. Black carbon exposure, oxidative stress genes, and blood pressure in a repeated-measures study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.J.; Xu, H.M.; Xu, Q.; Chen, B.H.; Kan, H.D. Fine particulate matter constituents and cardiopulmonary mortality in a heavily polluted Chinese city. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindell, D.; Kuylenstierna, J.C.I.; Vignati, E.; van Dingenen, R.; Amann, M.; Klimont, Z.; Anenberg, S.C.; Muller, N.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Raes, F.; et al. Simultaneously mitigating near-term climate change and improving human health and food security. Science 2012, 335, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Wang, Q.Y.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Tie, X.X.; Shen, Z.X.; Wang, P.; An, Z.S. Impacts of aerosol compositions on visibility impairment in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Cao, J.J.; Tao, J.; Li, N.; Su, X.L.; Chen, L.A.; Wang, P.; Shen, Z.X.; Liu, S.X.; Dai, W.T. Long-term trends in visibility and at Chengdu, China. PLoS One 2013, 8, e68894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Streets, D. Primary anthropogenic aerosol emission trends for China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 931–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Kondo, Y.; Oshima, N.; Takegawa, N.; Miyazaki, Y.; Hu, M.; Lin, P.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sugimoto, N.; et al. Temporal variations of elemental carbon in Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D23202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Tie, X.X.; Xu, B.Q.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Zhu, C.S.; Li, G.H.; Liu, S.X. Measuring and modeling black carbon (BC) contamination in the SE Tibetan Plateau. J. Atmos. Chem. 2010, 67, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Spackman, J.R.; Fahey, D.W.; Gao, R.S.; Lohmann, U.; Stier, P.; Watts, L.A.; Thomson, D.S.; Lack, D.A.; Pfister, L.; et al. Coatings and their enhancement of black carbon light absorption in the tropical atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D03203. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Kondo, Y.; Moteki, N.; Takegawa, N.; Sahu, L.; Takami, A.; Hatakeyama, S.; Yonemura, S.; Blake, D. Radiative impact of mixing state of black carbon aerosol in Asian outflow. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D24210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysel, M.; Laborde, M.; Olfert, J.S.; Subramanian, R.; Gröhn, A.J. Effective density of aquadag and fullerene soot black carbon reference materials used for SP2 calibration. Atmos. Measur. Tech. 2011, 4, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Sahu, L.; Moteki, N.; Khan, F.; Takegawa, N.; Liu, X.; Koike, M.; Miyakawa, T. Consistency and traceability of black carbon measurements made by laser-induced incandescence, thermal-optical transmittance, and filter-based photo-absorption techniques. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Wu, F.; Chow, J.C.; Lee, S.C.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.W.; An, Z.S.; Fung, K.K.; Watson, J.G.; Zhu, C.S.; et al. Characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon during fall and winter of 2003 in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Zhu, C.S.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Han, Y.M.; Wang, G.; Shen, Z.; An, Z.S. Black carbon relationships with emissions and meteorology in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.S.; Schwarz, J.P.; Kelly, K.K.; Fahey, D.W.; Watts, L.A.; Thompson, T.L.; Spackman, J.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Cross, E.S.; Han, J.H.; et al. A novel method for estimating light-scattering properties of soot aerosols using a modified single-particle soot photometer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moteki, N.; Kondo, Y. Effects of mixing state on black carbon measurements by laser-induced incandescence. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 398–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Huang, R.-J.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.M.; Wang, G.H.; Li, G.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Dai, W.T.; Zhang, R.J.; Zhou, Y.Q. Mixing state of black carbon aerosol in a heavily polluted urban area of China: Implications for light absorption enhancement. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Gao, R.S.; Fahey, D.W.; Thomson, D.S.; Watts, L.A.; Wilson, J.C.; Reeves, J.M.; Darbeheshti, M.; Baumgardner, D.G.; Kok, G.L.; et al. Single-particle measurements of midlatitude black carbon and light-scattering aerosols from the boundary layer to the lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.; Turner, N.; Sandberg, J. Particle identification by laser-induced incandescence in a solid-state laser cavity. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 3726–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slowik, J.G.; Cross, E.S.; Han, J.H.; Davidovits, P.; Onasch, T.B.; Jayne, J.T.; Williams, L.R.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Worsnop, D.R.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; et al. An inter-comparison of instruments measuring black carbon content of soot particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moteki, N.; Kondo, Y. Dependence of laser-induced incandescence on physical properties of black carbon aerosols: Measurements and theoretical interpretation. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, M.; Mertes, P.; Zieger, P.; Dommen, J.; Baltensperger, U.; Gysel, M. Sensitivity of the single particle soot photometer to different black carbon types. Atmos. Measur. Tech. 2012, 5, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Sun, T.L.; Zeng, L.W.; Yu, G.H.; Luan, S.J. Black carbon aerosol characterization in a coastal city in South China using a single particle soot photometer. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 51, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moteki, N.; Kondo, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Takegawa, N.; Komazaki, Y.; Kurata, G.; Shirai, T.; Blake, D.; Miyakawa, T.; Koike, M. Evolution of mixing state of black carbon particles: Aircraft measurements over the western Pacific in March 2004. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; He, L.Y.; Xue, L.; Sun, T.L.; Zeng, L.W.; Gong, Z.H.; Hu, M.; Zhu, T. Highly time-resolved chemical characterization of atmospheric fine particles during 2010 Shanghai World Expo. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 4897–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Matsuura, S.; Yamaguchi, D.; Umemura, T.; Hanada, E.; Orihara, H.; Tanaka, S.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, Y.; et al. The impact of the pollution control measures for the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games on the chemical composition of aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2789–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Stark, H.; Spackman, J.R.; Ryerson, T.B.; Peischl, J.; Swartz, W.H.; Gao, R.S.; Watts, L.A.; Fahey, D.W. Heating rates and surface dimming due to black carbon aerosol absorption associated with a major U.S. city. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L15807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Schwarz, J.P.; Cao, J.J.; Gao, R.S.; Fahey, D.W.; Hu, T.F.; Huang, R.-J.; Han, Y.M.; Shen, Z.X. Black carbon aerosol characterization in a remote area of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, western China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.F.; Gao, R.S.; Schwarz, J.P.; He, L.Y.; Fahey, D.W.; Watts, L.A.; McComiskey, A.; Cooper, O.R.; Sun, T.L.; Zeng, L.W.; et al. Black carbon measurements in the Pearl River Delta region of China. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D12208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Gao, R.S.; Spackman, J.R.; Watts, L.A.; Thomson, D.S.; Fahey, D.W.; Ryerson, T.B.; Peischl, J.; Holloway, J.S.; Trainer, M.; et al. Measurement of the mixing state, mass, and optical size of individual black carbon particles in urban and biomass burning emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffet, R.C.; Prather, K.A. In-situ measurements of the mixing state and optical properties of soot with implications for radiative forcing estimates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11872–11877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liggio, J.; Gordon, M.; Smallwood, G.; Li, S.M.; Stroud, C.; Staebler, R.; Lu, G.; Lee, P.; Taylor, B.; Brook, J.R. Are emissions of black carbon from gasoline vehicles underestimated? Insights from near and on-road measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4819–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Komazaki, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Moteki, N.; Takegawa, N.; Kodama, D.; Deguchi, S.; Nogami, M.; Fukuda, M.; Miyakawa, T.; et al. Temporal variations of elemental carbon in Tokyo. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D12205. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgardner, D.; Raga, G.; Peralta, O.; Rosas, I.; Castro, T.; Kuhlbusch, T.; John, A.; Petzold, A. Diagnosing black carbon trends in large urban areas using carbon monoxide measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, R.R.; Andreae, M.O.; Campos, T.; Mayol-Bracero, O.L.; Neusuess, C.; Streets, D.G. Analysis of black carbon and carbon monoxide observed over the Indian Ocean: Implications for emissions and photochemistry. J. Geophys. Res. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, J.R.; Schwarz, J.P.; Gao, R.S.; Watts, L.A.; Thomson, D.S.; Fahey, D.W.; Holloway, J.S.; de Gouw, J.A.; Trainer, M.; Ryerson, T.B. Empirical correlations between black carbon aerosol and carbon monoxide in the lower and middle troposphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L19816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pna, X.L.; Kanaya, Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Liu, Y.; Pochanart, P.; Akimoto, H.; Sun, Y.L.; Dong, H.B.; Li, J.; Irie, H.; et al. Correlation of black carbon aerosol and carbon monoxide in the high-altitude environment of Mt. Huang in Eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9735–9747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMeeking, G.; Hamburger, T.; Liu, D.; Flynn, M.; Morgan, W.; Northway, M.; Highwood, E.; Krejci, R.; Allan, J.; Minikin, A.; et al. Black carbon measurements in the boundary layer over western and northern Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 9393–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, D.; Kok, G.; Raga, G. On the diurnal variability of particle properties related to light absorbing carbon in Mexico City. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.L.; Sahu, L.K.; Kondo, Y.; Takegawa, N.; Han, S.; Jung, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Fan, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Shammaa, M.H.; et al. Temporal variations of black carbon in Guangzhou, China, in summer 2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6471–6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, J.; Han, Y.; Ni, H.; Zhang, N.; Huang, R. Characteristics of Black Carbon Aerosol during the Chinese Lunar Year and Weekdays in Xi’an, China. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 195-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6020195
Wang Q, Liu S, Zhou Y, Cao J, Han Y, Ni H, Zhang N, Huang R. Characteristics of Black Carbon Aerosol during the Chinese Lunar Year and Weekdays in Xi’an, China. Atmosphere. 2015; 6(2):195-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6020195
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiyuan, Suixin Liu, Yaqing Zhou, Junji Cao, Yongming Han, Haiyan Ni, Ningning Zhang, and Rujin Huang. 2015. "Characteristics of Black Carbon Aerosol during the Chinese Lunar Year and Weekdays in Xi’an, China" Atmosphere 6, no. 2: 195-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6020195
APA StyleWang, Q., Liu, S., Zhou, Y., Cao, J., Han, Y., Ni, H., Zhang, N., & Huang, R. (2015). Characteristics of Black Carbon Aerosol during the Chinese Lunar Year and Weekdays in Xi’an, China. Atmosphere, 6(2), 195-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6020195








