Seasonal Characteristics and Source Analysis of Water-Soluble Ions in PM2.5 in Urban and Suburban Areas of Chongqing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
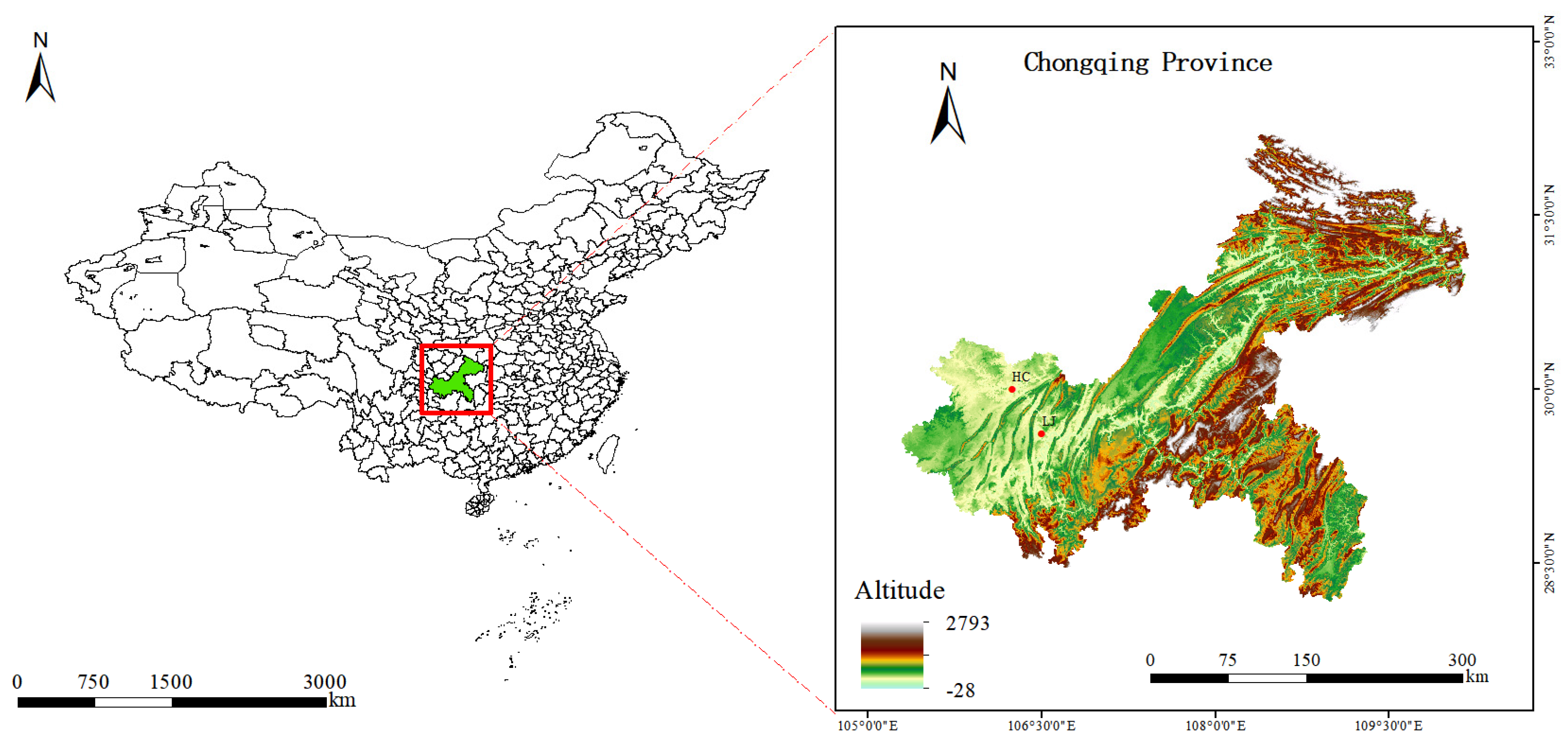
2.1. Point and Sample Collection
2.2. Component Analysis Method
2.3. PMF Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PM2.5 Mass Concentration and Seasonal Characteristics
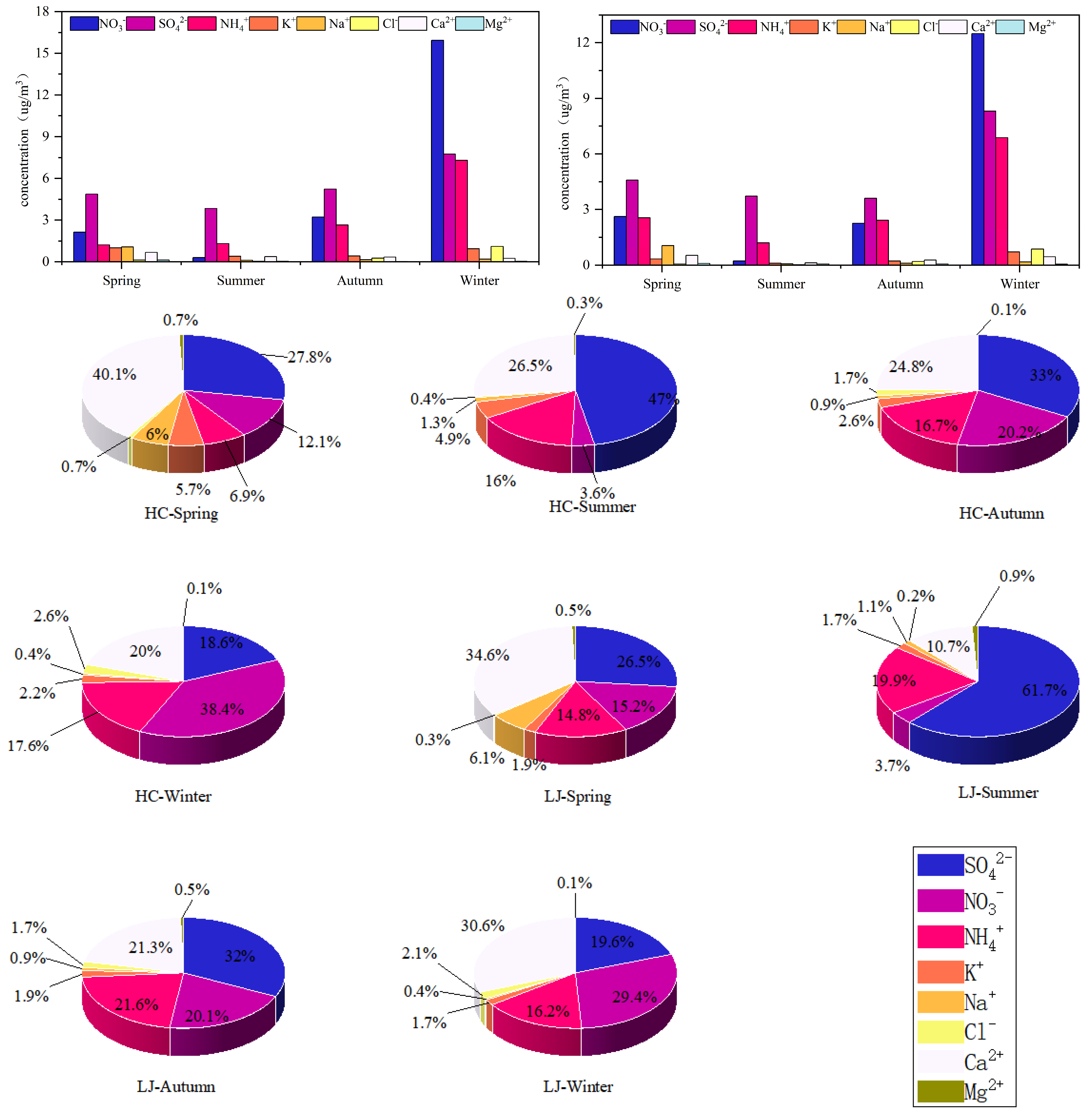
3.2. Water-Soluble Inorganic Ionic Components and Seasonal Characteristics
3.2.1. Characterization of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ion Concentrations
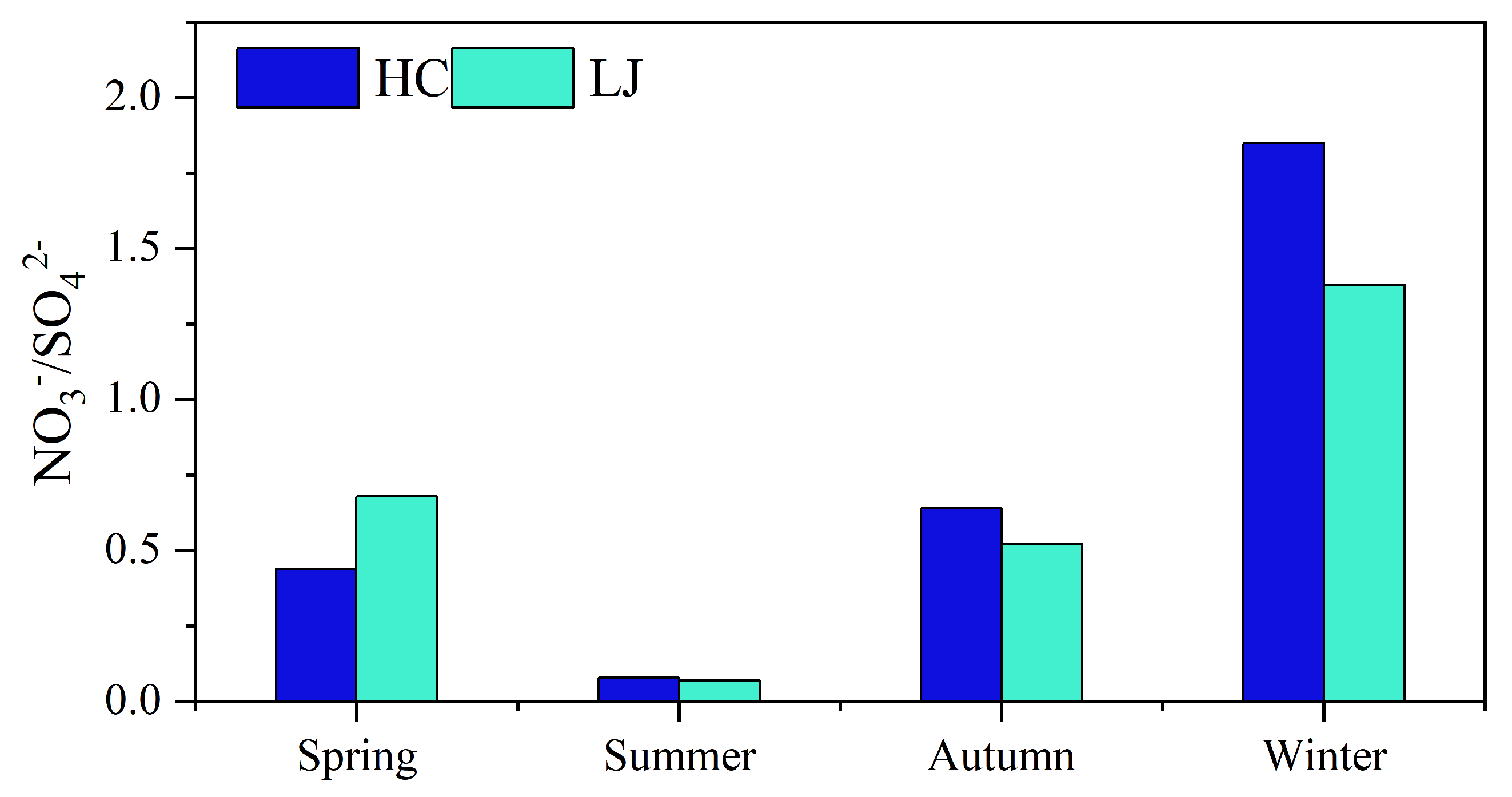
3.2.2. Characterization of SOR and NOR Changes
3.2.3. Cation–Anion Balance Analysis
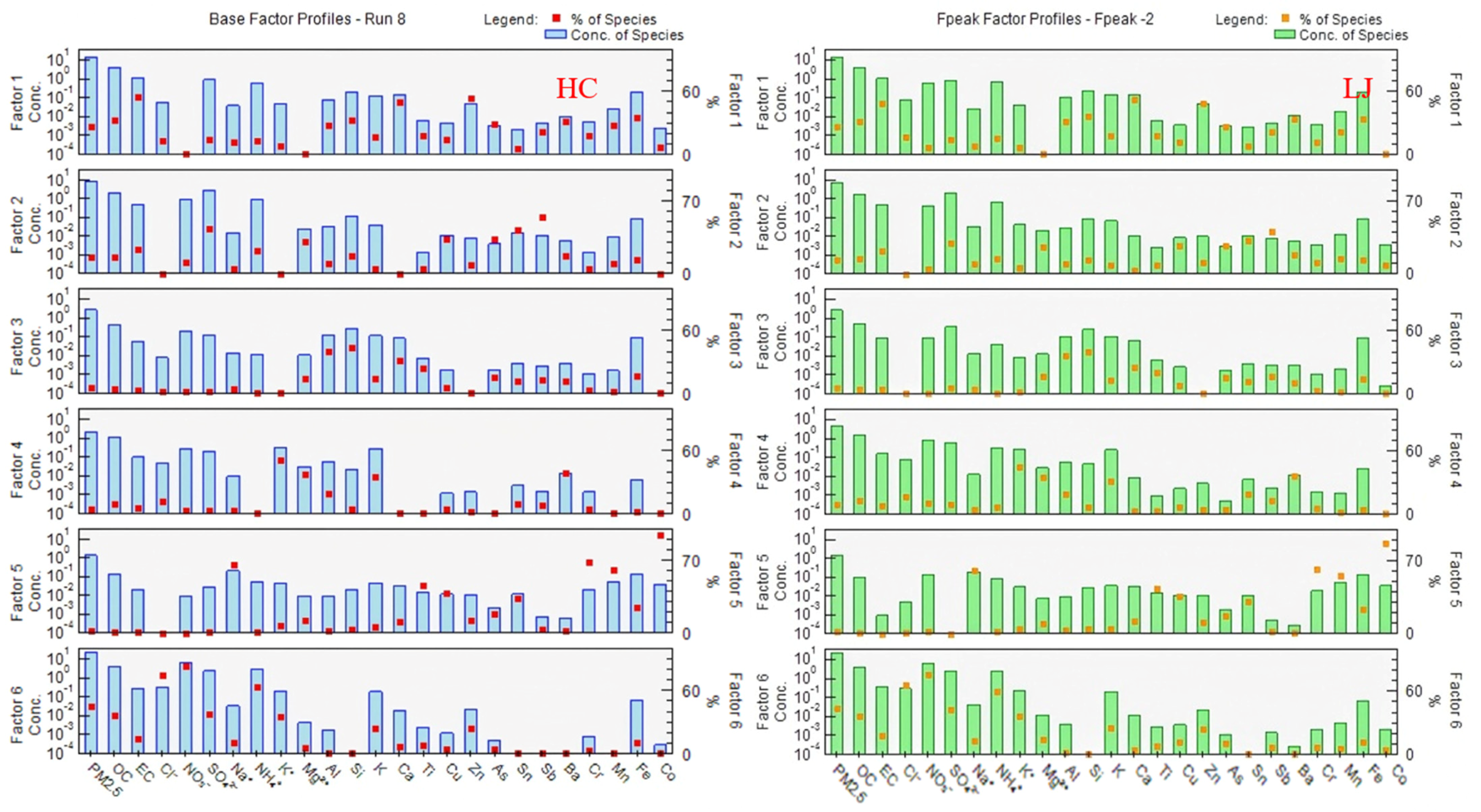
3.3. Analysis of PM2.5 Sources
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ni, Y.; Shi, G.; Qu, J. Indoor PM2.5, Tobacco Smoking and Chronic Lung Diseases: A Narrative Review. Environ. Res. 2020, 181, 108910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, M.A.; Kindzierski, W.B. Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) in Edmonton, Canada: Source Apportionment and Potential Risk for Human Health. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, S.-T.; Wu, Q.-J.; Li, X.-Y.; Gao, C.; Liu, Y.-S.; Jiang, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Sun, H.; Chang, Q.; Zhao, Y.-H. Long-Term PM2.5 Exposure and Various Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, R.; Pearson, D.; Ebisu, K.; Malig, B. Association Between PM2.5 and PM2.5 Constituents and Preterm Delivery in California, 2000–2006. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2017, 31, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reff, A.; Bhave, P.V.; Simon, H.; Pace, T.G.; Pouliot, G.A.; Mobley, J.D.; Houyoux, M. Emissions Inventory of PM2.5 Trace Elements across the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5790–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallraff, J.P.; Ungeheuer, F.; Dombrowski, A.; Oehlmann, J.; Vogel, A.L. Occurrence and In Vitro Toxicity of Organic Compounds in Urban Background PM2.5. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arhami, M.; Shahne, M.Z.; Hosseini, V.; Haghighat, N.R.; Lai, A.M.; Schauer, J.J. Seasonal Trends in the Composition and Sources of PM2.5 and Carbonaceous Aerosol in Tehran, Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, C.; Hao, J.; Liu, H.; Hua, S.; Tian, H. Temporal-Spatial Characteristics and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 as Well as Its Associated Chemical Species in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region of China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-P.; Cai, M.-J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, J.-B.; Yan, J.-P.; Schwab, J.J.; Yuan, C.-S. Chemical Nature of PM2.5 and PM10 in the Coastal Urban Xiamen, China: Insights into the Impacts of Shipping Emissions and Health Risk. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 227, 117383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, R.; Xin, J.; Zhang, W.; Tian, Y.; Xu, X.; Wen, T.; Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Z. The Environmental Benefit of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Coal Banning Area for North China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Z. Demarcation of Coordinated Prevention and Control Regions in the Yangtze River Delta Based on Spatio-Temporal Variations in PM2.5 and O3 Concentrations. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zeng, W.; Chang, S.; Wang, L.; Liao, C.; Zhang, Y. CO2 Synergistic Emission Reduction and Health Benefits of PM2.5 Reaching WHO-III Level in Pearl River Delta. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 326, 120441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C. Cascading Failure Mechanism of Major Drainage System in Mountainous City: Taking the Basin of the Main Urban Area of Chongqing as an Example, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Yang, A.; Wang, Y. Characteristics, Drivers, and Development Modes of Rural Space Commercialization under Different Altitude Gradients: The Case of the Mountain City of Chongqing. Land 2023, 12, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y. Spatial Correlation Effect of Haze Pollution in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0311574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhong, M.; Zuong, B.; Luo, K. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of PM2.5 in Chongqing Urban Areas. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2016, 37, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Yan, S. Zoning and Optimization Strategies of Land Spatial Ecological Restoration in Liangjiang New Area of Chongqing Based on the Supply–Demand Relationship of Ecosystem Services. Land 2023, 12, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Min, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, S. Analysis on Seasonal Variation and Influencing Mechanism of Land Surface Thermal Environment: A Case Study of Chongqing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, J. Multi-Objective Land Use Optimization Based on Integrated NSGA–II–PLUS Model: Comprehensive Consideration of Economic Development and Ecosystem Services Value Enhancement. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.-L.; Li, J.-W.; Gong, C.-M.; Zhong, S.-Q.; Wei, C.-F. Driving Forces and Their Interactions of Soil Erosion in Soil and Water Conservation Regionalization at the County Scale with a High Cultivation Rate. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 2502–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Research on Rural Industry Revitalization in Chongqing. 2022. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27163/d.cnki.gjlnu.2022.000184 (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Tian, X. Research on the Spatial Response of Industrial Development in the Core Area of Chengdu and Chongqing. 2021. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27670/d.cnki.gcqdu.2021.004598 (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Karakas, F.; Imamoglu, I.; Gedik, K. Positive Matrix Factorization Dynamics in Fingerprinting: A Comparative Study of PMF2 and EPA-PMF3 for Source Apportionment of Sediment Polychlorinated Biphenyls. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reff, A.; Eberly, S.I.; Bhave, P.V. Receptor Modeling of Ambient Particulate Matter Data Using Positive Matrix Factorization: Review of Existing Methods. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cheng, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y. Climatic Characterisation of Strong Convective Weather in the Longdong Region, 1970–2019. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2023, 17, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Research on the Origin and Distribution of Offshore Wind and Wave Energy Resources Influencing Adverse Weather Constraints. 2022. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27314/d.cnki.gsscu.2022.000134 (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, K.; Peng, K.; Yang, J. Analysis of Air Quality Characteristics and Pollution Source Areas in Guiyang City, 2023. Green Technol. 2024, 26, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, K.; Jiang, Y.; Rao, Z.; Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Luo, X.; Feng, Q. Variation Trend and Pollution Characteristics of Ambient Air Quality in Sichuan Province from 2015 to 2022. Environ. Monit. China 2024, 40, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.N.; Zhang, J.; Hu, H.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H. Seasonal Variation Characteristics of Carbonaceous Fraction in PM2.5 of Urban Expressways Area in Wuhan City. Environ. Monit. China 2025, 41, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, J.; Jiang, M.; Cai, Z.; Yao, Q.; Han, S. Aerosol Optical Properties and Direct Radiative Forcing in Tianjin. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 44, 6590–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Cao, F.; Lin, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y. Size Distribution and Source Apportionment of Chemical Compositions in Nanjing Atmospheric Particulate Matter. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 33, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelson, A.; Seinfeld, J. Thermodynamic Prediction of the Water Activity, NH4NO3 Dissociation Constant, Density and Refractive Index for the NH4NO3-(NH4) 2SO4-H2O System at 25 °C. Atmos. Environ. 1982, 16, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoto, R.; Duce, R.; Savoie, D.; Prospero, J.; Talbot, R.; Cullen, J.; Tomza, U.; Lewis, N.; Ray, B. Relationships among Aerosol Constituents from Asia and the North Pacific during PEM-West A. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Tang, A.; Yuan, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Zheng, A. The Ion Chemistry and the Source of PM2.5 Aerosol in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3771–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lin, S.; Yang, H.; Du, R.; Xia, J.; Qi, B.; Liu, G.; Li, F.; Yang, M.; Gai, X. Pollution Characteristics and Light Extinction Contribution of Water-soluble Ions of PM2.5 in Hangzhou. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 2656–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W. Research on Catalytic Oxidation of NO and Mechanism of Sulfur Resistance over Supported-Perovskites. 2015. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=aR5N6Ks7Vo1A0MmP9oDQnZQbZTU6zBVC4vOx9ZMw0zUKFWrXaNxHmVrq6Um9wHtj1nz5Bi8_RObJJ9T55iKnv29aCb-DBHNG_Strv885NVe1ghXFJwuXcQA-hG4ftglZXvoXoxpRVQvozTkarZs-lFppIfwbr1wB26m2ph1Z56bFMKvW6aXLhgCj3Zcw09dvFtiWgfopqUo=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Stelson, A.; Seinfeld, J.H. Relative Humidity and Temperature Dependence of the Ammonium Nitrate Dissociation Constant. Atmos. Environ. 1982, 16, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.S.; Stutz, J. Nighttime Radical Observations and Chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6405–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaijie, H.; Youjiang, H.; Xin, Y.; Cheng, M.; Fuqiang, L.; Yujie, P.; Bin, L. Research on the Characteristics of Atmospheric NH3 Pollution and Influencing Factors in Shihezi City. Environ. Eng. 2024, 42, 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, K.; Gong, Y.; Dong, H.; Song, M.; Lu, K. Characteristics of Water-Soluble Inorganic in PM2.5 in Kunming, Based on Line Monitoring. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2025, 61, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, G.; Sheng, H.; Yue, L.; Sun, P.; Luo, Y.; Cao, J.; Cao, X.; Chen, Y. PM2.5 Pollution Characteristics and Source Apportionment in A Typical Industrial City of Henan Province During Autumn and Winter. Environ. Eng. 2024, 42, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Lei, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Yin, L.-H.; Wang, C. Analysis of PM2.5 Components During Continuous Spring Pollution in Sichuan Basin Based on WRF-CMAQ Model. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 33, 1214–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sha, J.; Gui, J.; Gao, W.; Fei, X.; Xu, P.; Hu, B.; Yang, A. Research on the Characteristics, Sources, and Formation Influence of Water-Soluble Inorganic Components in PM2.5 in Huaxi District, Guiyang. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 45, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Characteristics and Sources of Pm,S Components in the eastern Part of North China Plain. 2020. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.26939/d.cnki.gbhgu.2020.000634 (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Peng, Y. Pollution Characteristics, Influencing Factors and Sources of Secondary Inorganic Components in PM10 in Jinhua Urban Area. 2021. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27464/d.cnki.gzsfu.2021.000518 (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Shen, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Diao, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhao, T. Changes of Wet Precipitation Flux and Pollutants Associated with at Chongqing Urban Station from 2008 to 2020 and Influencing Factors. Earth Environ. 2024, 52, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J. The Holiday Effect of Environmental Air Quality in Urumgi City. Arid Environ. Monit. 2025, 39, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Li, Y.; You, Z.; Ni, Y.; Luo, L. Analysis of the Causes of Synergistic O3 and PM2.5 Pollution in Winter in Haikou, a Clean Air Region. Environ. Chem. 2025, 44, 890–902. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Wang, C.; Cheng, S. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Double-High PM2.5-O3 Composite Pollution in Baoding City. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 1285–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xie, Y.; Yang, X.; Wei, J.; Yong, J.; Guo, H. Characteristics of Changes and Traceability Analysis of Atmospheric Pollutants in Shaanxi Province, 2017–2022—Taking PM2.5 and O3 as an Example. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 45, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Guan, C.; Shi, J. Characterization and Prediction of near-Surface PM2.5 and O3 Pollution in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2025, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wu, G. Advances in Affecting Factors of Ammonia Emission in Farmland. J. China Agric. Univ. 2019, 24, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, F. Pollution Characteristics of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 from a Mountainous City in Southwest China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; USEPA Office of Research and Development: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Taghvaee, S.; Sowlat, M.H.; Mousavi, A.; Hassanvand, M.S.; Yunesian, M.; Naddafi, K.; Sioutas, C. Source Apportionment of Ambient PM2.5 in Two Locations in Central Tehran Using the Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopke, P.K.; Dai, Q.; Li, L.; Feng, Y. Global Review of Recent Source Apportionments for Airborne Particulate Matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cai, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, J. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 During Haze Episodes in Shanghai by the PMF Model with PAHs. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, K.; Han, J.; Ying, Q.; Hopke, P.K. Sources of Humic-like Substances (HULIS) in PM2.5 in Beijing: Receptor Modeling Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Yu, M.; Cai, X.; Du, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.; Yan, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, Z. High-Time-Resolution Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing with Multiple Models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6595–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, W. A Graph-Based LSTM Model for PM2.5 Forecasting. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrobek, D.; Krzywanski, J.; Sosnowski, M.; Kulakowska, A.; Zylka, A.; Grabowska, K.; Ciesielska, K.; Nowak, W. Implementation of Deep Learning Methods in Prediction of Adsorption Processes. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2022, 173, 103190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Analysis Project | Instrumentation | Reference Method | Component |
|---|---|---|---|
| carbon component | DRI model 2015, United States | QX/T 70-2007 | OC, EC |
| water-soluble ions | Dionex Integrion HPIC, United States | HJ 799-2016 | F−, Cl−, SO42−, NO3− |
| HJ 800-2016 | Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, NH4+ | ||
| elemental composition | BRUKER S8 Tiger, Germany | HJ 830-2017 | Al, Ca, Fe, K, Mg, Na, P, Si, Li, Be, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Mo, Cd, Sb, Ba, Pb, Sc, Sn |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, S.; Wang, J.; Fu, M.; Yu, J.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Y. Seasonal Characteristics and Source Analysis of Water-Soluble Ions in PM2.5 in Urban and Suburban Areas of Chongqing. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091047
Tang S, Wang J, Fu M, Yu J, Huang W, Zhou Y. Seasonal Characteristics and Source Analysis of Water-Soluble Ions in PM2.5 in Urban and Suburban Areas of Chongqing. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(9):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091047
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Simei, Jun Wang, Min Fu, Jiayan Yu, Wei Huang, and Yu Zhou. 2025. "Seasonal Characteristics and Source Analysis of Water-Soluble Ions in PM2.5 in Urban and Suburban Areas of Chongqing" Atmosphere 16, no. 9: 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091047
APA StyleTang, S., Wang, J., Fu, M., Yu, J., Huang, W., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Seasonal Characteristics and Source Analysis of Water-Soluble Ions in PM2.5 in Urban and Suburban Areas of Chongqing. Atmosphere, 16(9), 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091047







