Abstract
The iron and steel industry is one of the main industrial contributors to air pollution. The aim of our study is to analyze modern studies on air pollution by the iron and steel industry, as a result of which the geography and research directions and the degree of development of current issues will be assessed, and the most cited articles and journals will be identified. A review of contemporary research (2018–2024) was conducted on the basis of articles with a digital object identifier (DOI) using machine learning methodologies (VOSviewer software version 1.6.20). The number of articles selected was 80. The heat map of study density clearly showed that the geographic distribution of studies was extremely uneven. A total of 65% of the studies were conducted in China, 9% in Nigeria, 6% in Russia, 3% in Poland, and 3% in Turkey. The remaining 14% of articles represent a series of single studies conducted in 11 countries. The revealed geographical imbalance between countries with developed production and the number of studies conducted in them shows a significant shortcoming in monitoring research. Most of the studies (20%) were devoted to the assessment of multicomponent emissions. A special place among them was occupied by the inventory of emissions using various methods. The next main directions in terms of the number of articles were aimed at studying the toxic metal emissions (19%), at the analysis of organic emissions (19%), at the modeling and forecasting of emissions (18%), and at particulate matter studies (15%). The main features of the articles for each direction are briefly noted. Citation analysis made it possible to compile a rating of articles of greatest scientific interest and the most authoritative journals. Citation network analysis revealed important insights into the structure of scientific communication in the monitoring of atmospheric pollution from the iron and steel industry. The results of our review will contribute to the consolidation of scientists, the identification of gaps in scientific knowledge, and the improvement of environmental policy and technological solutions.
1. Introduction
Atmospheric pollution by industrial emissions is an important environmental problem [1]. Deteriorating air quality not only significantly impacts the environment but is also recognized as one of the leading risk factors for human health, contributing to the development of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, stroke, cancer, and premature mortality worldwide [2,3]. Air pollution also has a major impact on the world economy [4]. Therefore, continuous integrated pollution monitoring is urgently needed to understand the spatiotemporal dynamics of air pollution, identify vulnerable populations and ecosystems, and develop integrated approaches to pollution control and mitigation. In this context, one of the important problems is the correct organization of monitoring and obtaining accurate and reliable information over large areas [5,6].
Iron and steel enterprises are one of the main industries in terms of pollutant emissions [7,8]. The main sources of pollution are considered to be sintering plants—enterprises engaged in the production of cast iron and steel. Their activities emit significant amounts of particulate matter, carbon dioxide, sulfur, and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere [9]. Chlorine, fluorine, arsenic, phenols, and other carcinogenic substances are released in smaller quantities. Their concentrations exceed the maximum permissible values; generally, exceedances occur only on industrial sites. It is generally accepted that the impacts of harmful substance emissions at distances of several hundred kilometers from the source do not pose a particular danger. However, monitoring data show that this is not always true; for example, sulfur compounds can sometimes spread more than a thousand kilometers from the source of emissions [10,11]. It is very important to assess the multiple emissions of pollutants, as well as to analyze their distribution depending on meteorological conditions and distance from the emission source [9,12,13].
Many studies are aimed at assessing CO2 emissions from the iron and steel industry and developing technologies to minimize them [14,15,16]. Much less research is directed at assessing emissions of other gases (SO2, NOx, H2S), although their impact on the environment and human health is very significant. The main production process of SO2 and NOx emissions is sintering, so it is usually the subject of more research.
Particulate matter (dust) from metallurgical enterprises poses a significant risk of contamination of soil and plant systems, as well as a threat to human health, as they contain heavy metals [17,18]. The most powerful sources of dust are considered to be open-hearth and converter steelmaking plants. Currently, open-hearth furnaces are considered an outdated technology and are used less and less. The appearance of dust during their use is caused by the oxidation of the metal charge. Dust and heavy metals enter the air during the oxidation of charge impurities (slag, ore, limestone, scale, dolomite), which are filled with furnace fuel. Boiling steel also releases metal and slag vapors of oxides and gases. The most dangerous dust for humans is considered to be dust with a dispersion of up to 7 microns since its particles penetrate the lung tissue, accumulate there, and can provoke disease.
Significant quantities of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are emitted into the atmosphere during the operation of the iron and steel enterprises. The main source of volatile organic compounds is the iron ore sintering process. VOCs consist of hundreds of compounds and considerably contribute to the creation of ozone in the troposphere [19,20]. Currently, the amount of VOC emissions is not sufficiently regulated [21], and monitoring studies are of great scientific interest.
Facilities producing iron and steel represent an important source of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), posing a substantial threat to environmental safety within the area [22]. PAHs are persistent organic pollutants with strong carcinogenic, mutagenic, or teratogenic effects. Therefore, their monitoring in environmental objects is an extremely important and urgent task [23].
Dioxins and furans are of particular interest to scientists among the organic air pollutants [24,25]. They are characterized by resistance to decomposition, the ability to concentrate (bioaccumulation), and high toxicity. The term “dioxins” is often used for a family of structurally and chemically related polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs), as well as for some dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Thermal metallurgical processes produce off-gases that typically contain dioxins in the range of 0.3–30 ng I-TEQ/Nm3 [26]. Research into the mechanisms of dioxin formation and destruction in various technological processes in iron and steel smelter remains relevant. The efficiency of capturing these hazardous substances depends on the gas cleaning systems used. For example, the use of an electrostatic precipitator has reduced PCDD/F emissions by 75% [27].
Monitoring studies of all emitted pollutants are extremely important. Emission inventories are compiled to quantify the impact of emissions on the environment. Of particular interest are comprehensive studies that consider the combined impact of emissions on air quality. However, questions remain about the adequacy of the existing methodology for multicomponent emissions.
From all of the above, it is clear that the ferrous metallurgy industry has a strong impact on air quality and human health, so it is important to improve pollutant monitoring systems, environmental policies, production technologies, and emission capture [13,28]. However, it is impossible to propose new solutions to existing issues without a comprehensive analysis of ongoing research, implemented environmental initiatives, and current technological processes.
The increasing volume of scientific results, ideas, and applied developments increases the risk that researchers will not keep up with the evolution of their discipline and the introduction of innovations. As a result, the likelihood of losing relevance and reducing the scientific and practical value of research increases [29]. To solve these problems, systematic reviews and meta-analyses are widely used—methods of qualitative information synthesis that allow you to select the most significant theoretical and applied achievements from a variety of publications on a given topic and thereby facilitate orientation in the current state of science [30,31]. Generalizing studies is important not only for researchers but also for those who shape scientific policy or make practical decisions.
The aim of our research is to analyze modern studies on air pollution by iron and steel enterprises. As a result, we will evaluate the geography of research, analyze the directions of research and the degree of development of topical issues, and identify the most cited articles and journals.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was conducted using the PRISMA guidelines [32] and guidelines for environmental science studies [33]. Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, Mendeley, and SciProfiles were selected to search for information. “Air pollution from iron and steel smelter”, “Iron and steel industry emissions”, and “Ferrous metallurgy emissions” were the search terms. Articles were analyzed over the last 7 years (2018–2024). The total number of verified records was 17,800 for the first request, 18,900 for the second request, and 17,200 for the third request. The following criteria were used to select the relevant data: publication in a journal, the presence of an English abstract, air pollution research, and the digital object identifier (DOI). Carbon dioxide emissions were not taken into account separately. Studies on CO2 emissions were included in the analysis only if they also studied other pollutants, such as SO2, NO, particulate matter (dust), and organic substances. Issues of emission reduction analysis were also not considered unless specific monitoring studies were presented.
The abstracts were subjected to analysis in order to determine the necessity of exclusion or inclusion of the record information. The data were meticulously documented in an Excel spreadsheet (Microsoft Excel 2019 MSO, version 2211, Yekaterinburg, Russia). At the culminating stage of the process, duplicate records were excluded. This research stage was conducted between April and June 2025. The number of records selected for further analysis was 80. Figure 1 shows the distribution of studies by year.
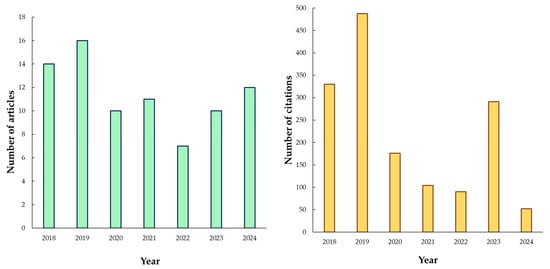
Figure 1.
Trends in number of selected publications and number of citations over the past 7 years.
The VOSviewer program (version 1.6.20) was selected for the analysis of citations of publications and journals. VOSviewer is a software program that is currently being utilized extensively in contemporary research to analyze bibliographic data and visualize findings across a broad spectrum of scientific disciplines [34,35]. VOSviewer uses machine learning to cluster and build visual maps of relationships. The machine learning method used is based on the latest developments in the fields of network science and bibliometry and is an alternative to multidimensional scaling [36,37]. A text file containing a set of DOIs of articles was loaded into VOSviewer. VOSviewer identifies all DOIs, then downloads bibliographic data for all available articles from databases. Citation data were retrieved on 28 June 2025.
The GeoCharts library (Google, package react-google-charts) [38] was used to visualize the distribution of studies by country. A JavaScript application with the ReactJS framework [39] was also used.
3. Results
The assessment of iron and steel industry emissions is of constant interest to scientists. Over the past seven years (2018–2024), 80 articles have been devoted to monitoring atmospheric pollution. There have been no comprehensive reviews of the impact of the iron and steel smelters on air quality. Only two review studies were identified that met the analysis criteria. They aimed to summarize the emission reduction experience of the Chinese iron and steel industry [40] and develop a technology system for reducing pollution and carbon emissions [28].
3.1. Geographical Distribution of Studies
Geography of studies on monitoring air pollution from iron and steel industry over the past seven years has been visualized as a map (Figure 2).
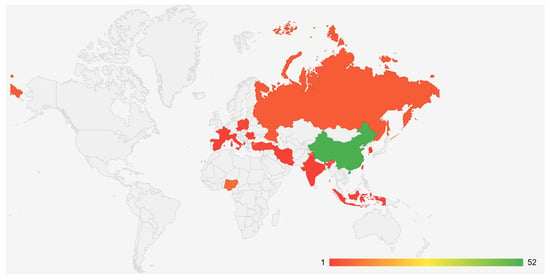
Figure 2.
Geography of studies on monitoring air pollution from iron and steel industry over the past seven years. 1–52: the number of studies.
The analysis of articles showed a quite wide geography of research, but more than half of the research is concentrated in China (65%). A total of 9% and 6% of the studies were conducted in Nigeria and Russia, respectively. Over the past seven years, only two studies on monitoring atmospheric pollution from iron and steel enterprises have been conducted in Poland [41,42] and Turkey [43,44]. Single studies were conducted in 11 countries: Spain [45], Indonesia [46], Italy [47], Republic of Korea [48], Czech Republic [49], Taiwan [50], France [51], Iran [52], India [53], Albania [54], and Romania [13]. Also, a study was conducted to analyze emissions over a large area covering Australia, Canada, and 28 European countries [55].
3.2. Research Topics Analysis
The directions of research on the impact of ferrous metallurgy on air quality were diverse (Figure 3). It was sometimes quite difficult to differentiate between the directions since they were interconnected.
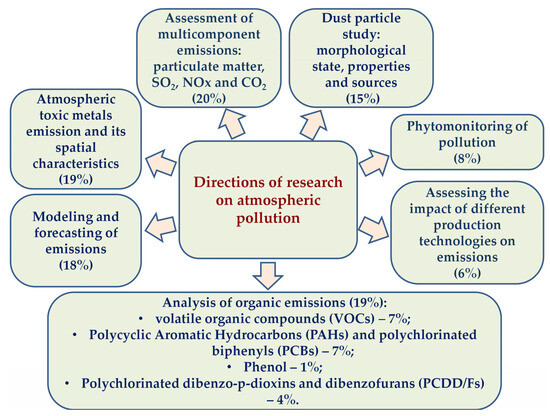
Figure 3.
Research directions of articles (2018–2024) on atmospheric pollution.
A large group of studies was devoted to the assessment of multicomponent emissions: SO2, NOx, CO2, and particulate matter (20% of articles) (Table 1). In this research area, we have combined articles on both the analysis of emissions from specific enterprises and on the problems of atmospheric pollution by iron and steel enterprises on a national scale. Several articles have been published on the subject in Russia. The aim of these articles was to identify the impact of ferrous metallurgy on air quality as part of the environmental aspect of sustainable territorial development [7,56]. In India, researchers identified the potential for environmental pollution and assessed ways to reduce emissions in 17 major polluting industries, including the iron and steel sector [53]. In China, scientists analyzed the drivers of air pollutant emissions in the iron and steel industry. Factors such as environmental regulations, pollutant generation intensity, energy structure, technological advances, and scale effects were studied using the logarithmic mean Divisia index method [17]. Additionally, researchers showed that China’s Continuous Emission Monitoring System can be effectively used for emission tracking [57,58]. Data from this system have enabled detailed estimation of multi-component air emissions from sintering operations in the industry [58] and have also supported the development of hourly, plant-level emission inventories [57]. To evaluate the environmental impacts of core production processes in integrated iron and steel plants, the Total Environmental Impact Score approach was introduced, which incorporates both pollutant concentrations and exhaust gas flow rates, as well as the number of emission sources [59]. In Iran, researchers investigated air pollutants—including PM2.5, PM10, CO, CO2, NOx, and SOx—in the ferroalloy sector by using air quality monitoring instruments [52]. It should also be noted that studies have been conducted on air pollution monitoring based on the chemical analysis of precipitation, including snow [60]. The authors demonstrated the effectiveness of this approach, which is an important finding.

Table 1.
Studies of multi-component emissions from iron and steel enterprises for 2018–2024.
Studies on the inventory of pollutant emissions should be noted separately. Six studies focused on emissions inventories in China for both individual regions: Baoshan District, Shanghai [61], the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region [62], and the entire country [63,64,65,66] (Table 1). In 2019, the unit-based and source-specific pollutant emission inventory (2010–2015) for the Chinese iron and steel industry was published [64]. An emission inventory (2015) based on the bottom-up approach was also presented [63]. A comprehensive inventory of air pollutants and CO2 emissions from 2005 to 2021 was compiled based on a unified emission source structure, taking into account the influence of activity level, technology development, and emission control policy [65]. Another study presented an integrated emission inventory in 2020 from 811 iron and steel enterprises and five key production processes [66]. The results show that sintering is the main source of air pollution, contributing 71% of SO2 emissions, 73% of NOx, and 54% of PM2.5 emissions [66]. In 2023, a review was published summarizing the experience of reducing emissions in China’s iron and steel industry [40].
A large group of studies was devoted to assessing atmospheric toxic metal emissions and their spatial characteristics (19% of articles) (Table 2). A multi-method and multi-matrix approach was applied to separate emissions from a smelter in Noumea (New Caledonia) from geogenic sources and model the subsequent health risk [51]. Enrichment factors identified elevated levels of smelter-related trace elements: S = 7, Ni = 6, and Cr = 4, and Zn = 4 [51]. Fang and colleagues studied the sources, chemical behavior transformations, and whole process distribution of Hg, As, and Pb during the whole process of iron and steel production [67]. The results showed that the main source of emissions for Hg was sintering (36.8% of the total process emissions), for As and Pb, it was the blast furnace process (75.2% and 59.1%) [67]. Scientists developed an emission inventory of five heavy metals (Hg, As, Pb, Cd, Cr) using environmental statistics data in Guangdong Province [68] and also conducted an inventory of emissions of twelve hazardous trace elements in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region using interannual dynamic emission factors determined using S-shaped curves [69]. It was found that the iron and steel industry was the source of As (24%), Pb (21%), Cd, and Cr emissions (82%) [68], and monthly variations of trace elements emissions exhibit seasonal peak-to-valley characteristics [69]. Monthly total atmospheric deposition rates around the Ile-Ife smelter (Nigeria) were determined (from 0.69 to 4.62 gm−3), and their chemical analysis was performed using the proton-induced X-ray emission method. Total concentrations of twenty-three elements ranged from 1.23 to 13.63 mg/m3 [70]. Analysis of road dust in a steel industry town in China showed average concentrations of Cd (2.26 mg/kg), Ni (83.5 mg/kg), Cu (164 mg/kg), Pb (272 mg/kg), and Cr (700 mg/kg) [71]. A study on trace element pollution in different particulate matter fractions (2.1–9.0 μm, 1.1–2.1 μm, and 1.1 μm) was conducted in the areas surrounding iron and steel plants in Kunming, Wuhan, Nanjing, and Ningbo (China) [72]. The emission factor, the weight of potentially toxic elements (Pb, Cd, Hg, As, and Cr (VI)) per unit of energy, and the weight of sinter produced were estimated for coal-fired boilers and sinter furnaces integrated into a steel plant in Taiwan [50]. Positive Matrix Factorization model and various contamination indices (enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, contamination factor, potential ecological risks index, Nemerov integrated pollution index, and Nemerov integrated risk index) were used to assess the contamination level and identify sources and health risks of ten potentially toxic elements in indoor and outdoor areas surrounding a major scrap-iron recycling plant in north-central Nigeria [73]. It was found that Cd had the highest pollution level and showed high potential to cause cancer in children during the two seasons studied [73].

Table 2.
Studies of atmospheric toxic metal emissions and their spatial characteristics from iron and steel enterprises for 2018–2024.
Two studies focused on estimating emissions of a neurotoxic pollutant such as mercury [75,76]. Hourly gaseous elemental mercury was determined inside (0.97–503 ng/m3) and at the boundary (0.05–113 ng/m3) of a typical iron and steel plant in the Yangtze River Delta (China). Particle-bound mercury concentrations were one to four orders of magnitude higher than urban and suburban ambient levels [75]. It has been established that particle-bound mercury mainly originated from sintering and coke-making processes in iron–steel enterprises [75]. Chinese researchers conducted a modeling of mercury concentration and deposition in the central Pearl River Delta region at a resolution of 1 km × 1 km using the Hg version of the California Puff Dispersion Modeling system with added mercury environmental processes [76]. It was found that the contribution of iron and steel production to Hg deposition was 3.5%.
The study on thallium emissions is worth mentioning separately. The authors focused on the mechanisms of the physical phase evolution, migration pathways, and emission characteristics of Tl in steelworks in China [77]. It was shown that iron concentrate is the primary source of thallium; the quantities of Tl input, output, and circulation were found to be 425, 365, and 49.7 mg/t-CS, respectively [77].
The focus of scientific research on radionuclides has also been revealed. Normalized stack emissions factors of radionuclides from crude steel production were first reported for China [74]. It was concluded that sintering was the main process that emitted natural radionuclides, the main ones being 222Rn (86.4 GBq/Mt), 210Pb (13.4 GBq/Mt), and 210Po (1.71 GBq/Mt) [74].
The next two studies [20,48] analyze the content of both organic matter and heavy metals and are a transition to the next direction (analysis of organic emissions—19% of articles, Table 3). Comprehensive monitoring of 130 hazardous air pollutants (volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbonyls, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, phthalates, and heavy metals) was conducted in Pohang, home to Korea’s largest steel plant [48]. Benzo[a]pyrene was shown to have the highest cancer risk, followed by As, formaldehyde, benzene, and dibenz[a,h]pyrene [48]. The second paper was devoted to the assessment of ten trace elements and sixty-four volatile organic compounds in the Yangtze River Delta region of China [20]. The average concentration of trace metals was 227 ng m−3. Zn, Pb, and Mn were the top trace metals. The average mixing concentration of volatile organic compounds was 58.2 ppbv, where alkanes, alkenes, and aromatics were the major components. Benzene and ethylene were the most abundant volatile organic compounds [20]. The following study in this region found that VOCs were more sensitive to O3 pollution in areas with high pollution levels, while in areas with low pollution levels, VOCs were more sensitive to PM2.5 pollution [78]. In two other articles, the researchers considered the emission characteristics and reactivity of volatile organic compounds were considered for typical high-energy-consuming industries in North China [79] and for an integrated iron and steel plant in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei [19]. It was established that the VOC emissions from iron and steel industries were 290 Gg in 2018 [79]. The concentration of total VOCs emitted by different processes in the steel plant ranged from 141 to 364 μg/m3 and varied in the order: sinter tail > coking ≈ sinter-head > converter > air heater [19]. The contribution of volatile organic compounds to ozone formation in various industrial processes was also assessed [19]. It is worth mentioning a theoretical paper that summarized the VOC emission status and standards of the steel industry in China and abroad and analyzed the formation of VOCs in the sintering process of iron ore [21].
Monitoring studies were conducted on the content of such hazardous substances with highly carcinogenic, mutagenic, or teratogenic effects as dioxins: polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) [55,80,81], polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) [43,82], polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) [22,23,43,83], and phenol [84].
The iron ore sintering process is the main source of PCDD/Fs emissions in ferrous metallurgy. The researchers discussed the formation mechanism and emission characteristics of dioxin in iron ore sintering and summarized new technologies for reducing PCDD/Fs emissions [80]. Australian scientists examined the trend in dioxin emissions from 1990–2017 from various industrial sources, including the iron and steel industry, using emission data from national inventory databases in Australia, Canada, and 28 European countries. They found that the blast furnace process was the main source of dioxin emissions compared to the electric arc furnace process [55]. Chinese researchers studied emissions of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans for eight iron and steel smelting enterprises [81]. Their results showed that the concentrations of PCDD/Fs ranged from 0.05 to 2.93 ng I-TEQ Nm−3 in flue gas and 0.05 to 0.35 pg I-TEQ m−3 in ambient air [81].

Table 3.
Studies of analyses of organic emissions from iron and steel enterprises for 2018–2024.
Table 3.
Studies of analyses of organic emissions from iron and steel enterprises for 2018–2024.
| Country | Year | Region; Enterprise | Analyzed Substances | Features of the Study | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 2018 | Entire country | VOCs | Analysis of emissions and standards of steel industry. | [21] |
| Typical iron ore sintering plant | PCDD/Fs | Generation mechanism of PCDD/Fs and the new developments and technologies of PCDD/Fs emission reduction. | [80] | ||
| 2019 | Laiwu city | PAHs | Distribution pattern, emission characteristics of 16 PAHs in download ash and dust. | [22] | |
| 2020 | Yangtze River Delta | VOCs | Assessment of emissions (2018–2019), the ozone formation potential, and secondary organic aerosol formation of VOCs. Analysis of the influence of VOCs emissions on regional ozone and particulate pollution using the sensitivity analysis approach. | [78] | |
| Anshan city | PAHs | Evaluation of the occurrence and variation in concentrations, sources and cancer risk of PM2.5-bound PAHs using source-oriented positive matrix factorization model and PAH diagnostic ratios. | [83] | ||
| 2021 | Laiwu city | PAHs | Assessment of 16 PAHs content in dust and human health risks using the toxic equivalency value (TEQBaP) and incremental lifetime cancer risk (ILCR) estimation. | [23] | |
| 8 iron and steel smelters | PCDD/Fs | PCDD/Fs concentrations and distributions, emission factors and amounts. | [81] | ||
| 2022 | North China | VOCs | Emission characteristics of 102 VOC species from various sources (sintering, pelletizing, steel smelting, a coke oven, and others) in 2018. | [79] | |
| 2023 | Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei | VOCs | Analysis of VOCs sources and VOCs contribution to ozone formation in combination with ozone formation potential. | [19] | |
| Turkey | 2018 | Dilovasi region | PAHs, PCBs | Study of possible sources and carcinogenic health risks using the positive matrix factorization and USEPA approach. | [43] |
| Australia, Canada, European Union | 2019 | 30 countries | dioxins | The trend in dioxin emissions during 1990–2017 from various industrial sources using the national inventory databases. | [55] |
| Russia | 2022 | Perm | Phenol | Specific hapten sensitization in children living under excessive aerogenic exposure to phenol. | [84] |
| Nigeria | 2024 | Scrap iron recycling plant | PCBs | The concentration, indoor-outdoor and seasonal change, sources, and health effects of PCBs in particulate-bound dust. | [82] |
Note: Two articles [20,48] in this direction are already given in Table 2.
The contents of sixteen kinds of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the download ash and dust emissions from iron and steel enterprises in Laiwu city of North China were studied using gas chromatography-mass spectrometer [22]. It was found that the total mass concentration of PAHs ranged from 2.82 ± 0.25 to 19.43 ± 2.55 μg m−3 in the dust emissions samples, with the highest values in the coking process. The dominant compounds were high-molecular-weight (four-to-six-ring) PAHs [22]. Studies of the environmental impacts and potential health risks of 16 PAHs from dust were also conducted for this region [23]. Air pollution by PM2.5-related PAHs was estimated in Anshan city with a developed iron and steel industry using the positive matrix factorization model and source-specific PAH diagnostic coefficients, and the lifetime cancer risk of the population was estimated using the PMF-ILCR model [83]. In addition, the possible sources and carcinogenic health risks of PAHs and PCBs were investigated in the Dilovasi region, Turkey, using the positive matrix factorization and USEPA approach [43]. Nigerian scientists studied the concentration, indoor-outdoor and seasonal variations, sources, and health impacts of PCBs in dust near a scrap iron recycling plant. They concluded that 5 Cl atoms PCB accounted for the majority of PCBs (41% overall). Estimation of the incremental lifetime risk of cancer showed that ingestion of dust posed the greatest risk, followed by dermal exposure, and inhalation posed the least risk [82].
Phenol pollution of atmospheric air is a health hazard to the population, especially children living in the area affected by emissions from the iron and steel industry. Russian scientists have established that the hapten-associated increase in the level of IgG specific to phenol in preschool children is associated with excessive phenol pollution [84].
Quite a large number of studies are devoted to modeling and forecasting of iron and steel industry emissions (Figure 3). An analysis of global iron and steel industry emissions over the past 60 years and forecasting up to 2050 was conducted [14]. The researchers assessed emissions of carbon dioxide and air pollutants, including heavy metals and polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and dibenzofurans. Also, the inherent potential of measures to adjust the composition of raw materials and technological structure, as well as to control the size of the iron and steel industry to achieve carbon emission reduction and pollution emission reduction, was studied for the period of 2022 to 2035 [12]. It was found that a reduction of pollutant emissions by 20–31% (excluding dust emissions) could be achieved by 2025 under a high steel scrap ratio scenario.
Several studies have investigated the potential effects of prevailing local atmospheric conditions on the dispersion pattern of emissions from a scrap-iron and steel smelter in Ile-Ife, Nigeria [85,86]. The American Meteorological Society/EPA Regulatory Model (AERMOD) was adopted to predict the atmospheric dispersion of particulate matter emissions around the source [85]. The model of the conditional probability function was used to determine the directional dependence of the local source of the gaseous pollutant. Weak relationships were found between the meteorological factors and other gaseous pollutants (NO, NO2, CO, O3) other than CO2 for both day and nighttime periods [86].
The Long Short Term Memory approach has demonstrated a link between reducing pollutant emissions and the principle of sustainable development [87].
Chinese scientists have carried out a lot of research on modeling emissions from iron and steel enterprises, assessing the effectiveness of pollution control and the impact of political decisions on air quality. The data envelopment analysis model with undesirable output and the Malmquist–Luenberger index model were used to calculate the pollution control effectiveness and its variation trend for 42 Chinese iron and steel enterprises from 2005 to 2014 [88]. A comprehensive approach was developed to estimate the co-benefits of energy efficiency improvement, resource saving, and air pollution reduction from 2015 to 2050 [89]. The air quality impacts of the steel industry in China were modeled using the Comprehensive Air Quality Model with Extensions to estimate the change in emission contribution after the implementation of current standards in 2012 [90]. A bottom-up simulation model was developed to consider combinations of policy targets, crude steel demand, and technology development options. The model combines air pollutant emission reduction with carbon neutrality pathways to assess the synergistic effects of different emission reduction strategies in China’s iron and steel industry [91].
Quite a lot of research has been carried out for the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region [11,62,92,93]. The impact of the iron and steel industry on the regional PM2.5 concentration was simulated by a two-layer nested meteorology-air quality coupling model system with Particulate Source Apportionment Technology [62]. Also, a multidisciplinary approach was used to assess the impact of ferrous metallurgy enterprises on air pollution in January 2012, using the Weather Research and Forecasting with Chemistry (WRF/Chem) model, the multi-regional input-output (MRIO) model, and a health assessment model [92]. For Tangshan, the researchers developed an Air Pollutant and Carbon Emissions and Air Quality model to identify enterprises with significant air pollution and carbon emissions and substantial contributions to air pollutant concentrations [11]. The emission models of air pollutants and CO2 in the steel industry of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region were evaluated using the coordinate system of joint control effects, marginal abatement cost curve, and numerical simulation. The synergistic advantages of typical technologies were also considered [93].
The local database of particulate matter chemical source profiles in the metallurgical industry in China was created and applied to the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) modeling for SO42− and NO3− concentrations [94]. This model is a comprehensive multipollutant air quality modeling system developed and maintained by the US Environmental Protection Agency’s Office of Research and Development. Chinese scientists showed that the model simulation accuracy was improved with the local chemical source profiles compared with the SPECIATE database [94]. Spanish scientists predicted the average monthly concentration of PM10 using four different mathematical models: vector autoregressive moving-average, autoregressive integrated moving-average (ARIMA), multilayer perceptron neural networks, and support vector machines with regression. They found that the ARIMA model works better than other models when forecasting for one month in advance, while support vector regression gives the best results when forecasting for a period of one to nine months [45]. These articles are transitional to the next direction of research (dust particle study).
Studies on the morphological state, properties, and sources of dust are highlighted as a separate group and make up 15% of the number of articles on air pollution from the iron and steel industry. The airborne content of different particle size ranges of dust was investigated from Cilegon, Indonesia [46], and six sites in China: Shanghai [95], Kunming, Wuhan, Nanjing, and Ningbo [96]; Panzhihua [97,98]. Particulate matter of different sizes was identified and analyzed: PM10 [41,46], PM2.5 [46,95,99], PM2.1 [97], and PM1 [96,98]. Chinese scientists found that the average mass concentration of dust particles was highest in the sintering process, followed by puddling, steelmaking, and rolling processes [94]. Emission studies have typically focused on stack sources, but the physical and chemical characteristics of fugitive emission sources throughout the iron and steel production process have also been studied [18,100]. The emission factor, particle size distribution, and morphological and chemical profiles of fugitive particulate matter were analyzed [18]. The magnetic properties and chemical composition of dust emitted by various anthropogenic sources, including ferrous metallurgy (more than 80% of the total magnetic particle emission), were studied [101]. It was found that magnetite is the dominant magnetic contributor. Their morphological studies also showed that nanoscale magnetite contained in particles obtained from steel mills corresponds to magnetite found in human tissue [101]. Particulate matter in the workplace air in a metallurgical plant was studied by synergistically using two different approaches: analysis of respirable fraction concentrations using conventional sampling and concentration equipment and ultrafine particle size distribution using an Electric Low-Pressure Impactor (ELPI+™) [47]. Chinese scientists found that policies aimed at mitigating PM2.5 pollution had significant co-benefits for reducing CO2 [99].
Jabłońska M. and Janeczek J. [41] showed that the combination of meteorological data and mineralogical studies of airborne individual particles allows distinguishing between sources of similar mineral tracers located in different sectors of the wind rose and provides evidence for speciation of elements, for example, such as Zn and Cl.
A total of 8% of articles on the analysis of the impact of iron and steel industry on air quality are devoted to phytomonitoring of atmospheric pollution (Figure 2). Analysis of the concentration of potentially toxic metals in mosses was often carried out as a passive monitoring to assess atmospheric deposition [44,49,54,102,103]. Scientists used the following terrestrial mosses: Hypnum cupressiforme (Hedw.) [44,54] and Brachythecium rutabulum (Hedw.) [49]. It was found that the content of elements in mosses significantly depends not only on the distance from the industrial source, but also on the sampling season and PM10 concentration [49]. Other researchers have shown that Sc, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, and Cu accumulated and were preferentially absorbed by lichens and mosses from airborne particles [103]. Very strong and significant inter-elemental correlations were found between Cr, Ni, Co, and Fe [54]. A single study of air pollution biomonitoring using herbaceous plants (Taraxacum officinale Wigg.) was conducted in Poland [42].
We decided to highlight five articles in the direction devoted to assessing the impact of different production technologies on pollutant emissions. The researchers assessed the industrial flow of materials for the basic oxygen furnace and electric arc furnace steelmaking processes and found that the emission intensity for the basic oxygen furnace process is significantly higher: 7.7 times for dust, 2.6 times for CO2, 92.6 times for SO2, 33.5 times for NO2, and 12 times for CO [104]. Russian scientists systematized the characteristics of emissions and analyzed different methods of capturing metallurgical dust, organic, and inorganic gas substances [105]. Chinese scientists have developed a liquid phase proportion control technology for magnesia flux pellets and established a blast furnace smelting demonstration project to utilize a high proportion of flux pellets (80%) to realize the reduction of SO2 and NOx emissions [106]. A collaborative technology system to reduce pollution and carbon emissions in China’s steel industry was demonstrated [28]. A method for pollutant management in steel production used in Romania was presented; it employs the Best Available Techniques reference document for iron and steel production to directly collect pollutants from the adopted electric arc furnace technology [13].
3.3. Citation Analysis
The top seven most cited papers on air pollution in the iron and steel industry are listed in Table 4. Over the past seven years, the most frequently cited publication on the research topic was an article by Chinese researchers on the analysis of emission sources and trace element contents of dust particles (PM2.5) in the atmosphere of Shanghai city [95]. The second most frequently cited study was also conducted by Chinese researchers and focused on the assessment of multicomponent emissions [22]. The third most frequently cited article addressed emission standards in iron and steel production in China and also belongs to the research direction on multicomponent emissions [57]. A review on reduction technology of air pollutant in current China’s iron and steel industry [40] ranked seventh in terms of citation, and the second review [106] was not included in this top at all. As a result of the analysis, we found that the articles on the assessment of multicomponent emissions had the highest citation rate. The top seven also included research directions on the study of dust particles [95] and the modeling and forecasting of emissions [90].

Table 4.
The top seven most cited articles for 2018–2024 on monitoring of air pollution from iron and steel industry.
Figure 4 shows the network of interrelations of articles based on citations. The analysis was conducted on articles that had been cited at least once. Of the 80 articles analyzed, only 41 were grouped into clusters. The lines indicate citations between articles. A total of 11 clusters were identified. Most of these were very small, comprising only two to four papers. The largest cluster, which is highlighted in red in Figure 4, included six articles. The present cluster encompassed publications that have been cited to a moderate or low extent. The most frequently cited articles in this cluster were two in number [40,68]. The citation metrics of these articles were recorded at 72 and 53, respectively. This cluster was located separately from all other clusters and had no relationships with any others, except with those articles that are related to cluster 8 and highlighted in brown. The red and brown clusters were thus consolidated into a single, larger group of articles that were distinctly isolated from all other articles. The two clusters, delineated in turquoise and purple, also formed a somewhat isolated group of articles. Each of these clusters comprises four articles. It has been determined that the turquoise cluster includes the most cited article [94]. Following a thorough analysis of the purple cluster, it was determined that a single article has received more than 50 citations [94]. The frequency of citations of other articles from these clusters is much lower.
The remaining articles, with the exception of those that constituted cluster 10 [18,97], were connected into a single, extensive cluster group. Nevertheless, it is our opinion that inter-cluster relationships were inadequately expressed. Only one paper lay at the center of these relationships [14]. This paper linked the individual clusters within this group. The largest cluster in this group was highlighted in green. This cluster included six papers. The most cited papers from this group of clusters [57,64,65] were included in this cluster.
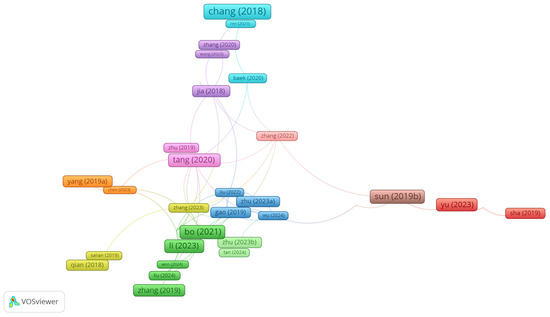
Figure 4.
Citation-based analysis of the article interconnection network. chang (2018)—[95]; ren (2023)—[20]; zhang (2020)—[78]; wang (2023)—[19]; baek (2020)—[48]; jia (2018)—[94]; zhang (2022)—[18]; zhu (2019)—[88]; tang (2020)—[90]; yang (2019a)—[92]; chen (2023) -[11]; liu (2022)—[58]; zhu (2023a)—[28]; sun (2019b)—[59]; yu (2023)—[40]; sha (2019)—[68]; gao (2019)—[63]; wu (2024)—[66]; bo (2021)—[57]; zhu (2023b)—[106]; li (2023)—[65]; tan (2024)—[12]; salian (2019)—[55]; qian (2018)—[80]; wen (2024)—[93]; liu (2024)—[91]; zhang (2019)—[89]; zhang (2023)—[14].
3.4. Analysis of Source Contribution to Research
The findings of research conducted on the subject of monitoring air pollution from the iron and steel industry over the past seven years have been published in 45 scientific journals. The six journals with the highest number of articles and citations were identified and listed in Table 5. The “Science of the Total Environment” and “Journal of Cleaner Production” have been identified as the leading publications in terms of the number of articles and citations. The “Journal of Cleaner Production” is widely regarded as the preeminent publication in this field, as evidenced by its consistently high citation rates. It is evident from the analysis of Table 5 that the six scientific journals under consideration are, in general, actively cited. This finding serves to substantiate the hypothesis that the articles contained within are of a high scientific standard and that they are of interest to readers.

Table 5.
Top six journals by number of citations and articles over the past 7 years.
4. Discussion
The growing global concern over industrial air pollution is clearly reflected in the steady academic interest in emissions from the iron and steel industry. Between 2018 and 2024, 80 scientific articles were identified that addressed the monitoring of atmospheric pollutants associated with iron and steel production. However, only two review articles met the selection criteria, indicating a significant gap in a comprehensive, integrative analysis of existing studies. The reviews by Yu et al. [40] and Zhu, Liu et al. [28] focused specifically on China and highlighted emission reduction strategies and the development of technological systems to mitigate both pollution and carbon emissions. Our bibliometric review makes up for the lack of comprehensive research conducted at the global level. The global focus and completeness of the analyzed articles distinguish the review from other, more specific studies and make it interesting and important for both researchers and monitoring practitioners in many countries. The review’s significance also lies in its clear demonstration that air pollution from ferrous metallurgy emissions remains an acute global problem that cannot be solved by one country alone. Combined efforts from researchers and policymakers around the world are required.
Our analysis revealed that the geographical distribution of research was extremely uneven, with significant variations in the representation of different countries. Although studies were conducted in more than 15 countries, the majority (65%) originated in China. This dominance reflects China’s dual status as both the world’s leading steel producer and one of the nations most affected by industrial emissions. China’s central role in this field is further underscored by the high citation rates and international visibility of its publications. In contrast, contributions from other countries remain relatively limited: Nigeria (9%) and Russia (6%) were the only countries with more than two publications meeting the inclusion criteria. Countries such as Turkey (a top 10 steel producer) and Poland (a top 20 steel producer) have published only two air pollution monitoring studies over the past 7 years. In addition, the leading iron- and steel-producing countries, such as India and the Republic of Korea, were represented by single studies, while other countries in the top 10, such as the United States, Japan, and Germany, had no publications. However, Indonesia, Romania, and Albania, which have less developed ferrous metallurgy, were also represented by single studies. Of particular note is one transnational study by Salian et al. [55], which assessed emissions across Australia, Canada, and the European Union. However, such large-scale comparative studies remain rare.
The revealed geographical imbalance between countries with developed production and the number of environmental air quality studies conducted in them shows a significant shortcoming in monitoring studies. We hope that our results will serve as an incentive for conducting studies in other countries with a high level of steel production. However, it should be noted that only articles with DOI were selected for the analysis. Thus, the total number of publications may be higher, but they do not meet the selected quality criteria. Also, the geographical imbalance highlights the need for more international studies to comprehensively understand global emission patterns.
The limited number of review articles, combined with the concentration of research within a few countries, points to a fragmentation of knowledge that may impede the development of universally applicable mitigation strategies for metallurgical impacts. The absence of a strong global synthesis leaves room for uncertainty in environmental policy development and hampers the dissemination of advanced technological expertise. Bridging this gap is essential for developing effective international standards and coordinated responses to air pollution from the iron and steel industry.
The impact of the iron and steel industry on air quality was assessed across a fairly wide range of directions (Figure 2). Most of the research has focused on the assessment of multicomponent emissions, reflecting the understanding of the importance of an integrated approach to pollutant emissions from industrial enterprises. Articles in this direction have a high citation rate, for example, studies by Sun et al. [22], Wang et al. [64], Bo et al. [57] (Table 4). Their high citation counts indicate that interdisciplinary approaches—incorporating atmospheric science, engineering, and policy—are particularly valued. These works provide essential data and frameworks for quantifying and mitigating the diverse pollutants emitted by steelmaking activities.
Quite a lot of attention from researchers was paid to the following three directions: toxic metal emissions and their spatial characteristics, analysis of organic emissions, and modeling and forecasting of emissions. Recently, research into the assessment of organic pollutants has become extremely relevant due to their high carcinogenicity [107,108]. Monitoring studies were conducted on the content of volatile organic compounds, carbonyls, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls, phenol, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, and dibenzofurans. The researchers studied the characteristics of organic emissions from the iron and steel industry, the reactivity and contribution of volatile organic compounds to ozone formation, the mechanisms of formation of various organic pollutants, assessed the risk of cancer, and summarized new technologies for reducing their emissions. Over the past seven years, no emphasis has been placed on methodological research to improve methods for determining organic pollutants in the air near ferrous metallurgy.
Modeling and forecasting of emissions from industrial enterprises are the most important directions necessary for improving the policies and technologies of production processes in order to minimize environmental risks and ensure sustainable development of regions. Researchers have conducted various studies on modeling and forecasting emissions from the iron and steel industry. The following models were used: the American Meteorological Society/EPA Regulatory Model (AERMOD) [85], the Long Short Term Memory approach [87], the conditional probability function (CPF) model [86], the model with undesirable output and the Malmquist–Luenberger index model [88], the Weather Research and Forecasting with Chemistry (WRF/Chem) model [92], the Comprehensive Air Quality Model with Extensions (CAMx) [90], and others. The Tang et al. article [90] on modeling was ranked in the top seven by citations (Table 1). The high citation rate of this article demonstrates that air quality impact models are becoming critical areas of research, supporting both regulatory compliance and the pursuit of sustainable industrial development. Currently, research on monitoring air pollution from different sources using the Internet of Things and AI techniques is gaining popularity [109,110].
A total of 15% of all articles published over the past seven years on the topic studied were devoted to dust particle study (morphological state, properties, and sources). The most cited article, by Chang et al. [95], demonstrates the high relevance of studies focusing on particulate matter (PM2.5) and its trace element composition in urban industrial environments. This study, centered in Shanghai, reflects growing concerns about the health impacts of fine particles, particularly in densely populated metropolitan areas. The prominence of this article suggests that research that links emission sources to environmental and health outcomes is of critical importance to the scientific community. Research into the disposal of difficult-to-treat dust and sludge produced from the steel industry is in high demand [111].
Relatively little research (six articles) has been devoted to such a promising direction as phytomonitoring of air quality. Although phytomonitoring is of increasing interest as a cheap method of analysis in which a representative number of samples is taken, it is possible to determine the territorial distribution of polluted air masses, and at the same time to assess the negative impact on biota [112,113,114]. However, the choice of a bioindicator is an important and complex task. The main criterion for selection is the high sensitivity of the organism to the effects of pollutants. Plants are most often used for biomonitoring, as they have a highly sensitive photosynthetic apparatus [115,116]. Mosses and lichens have proven themselves to be good for assessing air quality [44,117]. Fungi are used less often but are promising bioindicators of atmospheric pollution [118,119]. According to our review, over the past seven years, terrestrial mosses have been most frequently used for phytoindication of pollution from iron and steel enterprises. Lichens and one herbaceous species (Taraxacum officinale Wigg.) have also been used. Fungi and woody species were not represented.
Research aimed at assessing the impact of different production technologies on pollutant emissions has high practical potential. However, over the past seven years, only five articles have been published in this direction.
It is worth noting separately the studies on the impact of air quality inside and outside iron and steel enterprises on human health. Some of the studies we reviewed assessed not only the pollutants themselves but also their possible impact on population morbidity, including oncology [20,43,48,82,92]. This review does not include medical studies. However, we believe that some of them are worth mentioning. Heavy metals that control risk factors for cardiovascular diseases in patients with myocardial infarction in the steel industrial city were considered [120]. The content of heavy metals in the hair [121] and urine [122] of workers at a steel plant was studied.
Continuous emission monitoring and development of pollutant emission inventories are important and pressing environmental issues. Integrating information on sources and spatial–temporal patterns of emission, pollutant types, and emission inventories provides a comprehensive and standardized basis for evaluating the state of the atmosphere. The utility of emission inventories extends well beyond environmental diagnostics. For policymakers, they provide the empirical foundation for setting emission limits, developing air quality management plans, prioritizing regulatory interventions, and evaluating the effectiveness of implemented measures. For researchers, emission inventories serve as primary datasets for atmospheric modeling, allowing for the simulation of pollutant dispersion, deposition, and chemical transformation. They help identify long-term trends, detect deviations indicative of environmental crises, and develop adaptive strategies to protect public health and ecosystem stability. Also, the inventories facilitate international cooperation in addressing transboundary pollution and climate change. The development and refinement of integrated emission inventories will remain critical to ensuring sustainable environmental management and maintaining air quality in the context of industrial intensification and climate change.
The analysis of the most cited articles on air pollution near iron and steel industry reveals significant insights into the dominant research directions and key contributors within this field over the past seven years. The results underscore China’s central role as both a major producer of steel and a focal point of environmental research. However, despite the growing need for synthesizing knowledge, only one review article [40] was included in the top seven, while another [28] failed to reach similar citation impact. This finding implies that original research articles—especially those offering novel data and methodologies—currently exert greater influence in this research landscape than reviews. Nonetheless, reviews may play an increasingly important role as the field matures and requires synthesizing research to enhance collaboration and develop new policy solutions and technology pathways.
Overall, citation analysis reveals a clear thematic prioritization in the global scientific discourse: the assessment of multicomponent emissions and the detailed characterization of particulate pollutants are seen as highly impactful areas of inquiry. These findings highlight the scientific significance and global relevance of environmental studies focused on the iron and steel industry, particularly in rapidly industrializing nations. Moreover, they point to an urgent and ongoing demand for research that not only elucidates pollution mechanisms but also advances practical solutions for emission reduction, thereby contributing to global environmental and public health objectives.
The citation network analysis presented in Figure 3 provides important insights into the structure of scholarly communication within the field of air pollution associated with the iron and steel industry. The network, which includes only articles cited at least once, revealed a fragmented citation landscape, with only 41 out of 80 articles forming identifiable clusters. This finding reflects the relatively nascent and still-developing nature of the research field, where interconnections between studies remain limited and specialized subfields are only beginning to emerge. The lack of strong inter-cluster connections suggests that the field is still in the process of consolidating a coherent research framework. This fragmentation, however, also points to an opportunity for future synthesis and interdisciplinary collaboration. Bridging the gaps between isolated clusters could enhance the cumulative knowledge base and promote more integrated approaches to addressing the environmental challenges posed by the iron and steel industry. From a broader perspective, this analysis contributes novel insights to the global scientific community by illustrating the current citation architecture of a critical environmental research domain. It underscores the need for more cross-referencing, collaborative studies, and theoretical integration across geographical and thematic boundaries. Such developments would not only strengthen the field’s intellectual cohesion but also facilitate more effective policy guidance and technological innovation aimed at reducing industrial air pollution. As such, the results of this study provide a valuable foundation for future meta-research and strategic planning in environmental science and industrial sustainability.
The analysis of publication sources related to air pollution from the iron and steel industry over the past seven years reveals the prominent role played by a select group of scientific journals in shaping and disseminating knowledge in this field. A total of 45 journals have contributed to the scholarly discourse, yet the six most cited and productive journals—listed in Table 5—stand out as central platforms for high-impact research. Among them, Science of the Total Environment and the Journal of Cleaner Production emerge as particularly influential, both in terms of publication volume and citation performance. The Journal of Cleaner Production, in particular, holds a leading position, with its five articles garnering the highest cumulative citation count (419). This suggests that it serves not only as a prolific publication outlet but also as a preferred source for foundational and frequently referenced research. Similarly, Science of the Total Environment also plays a significant role, with seven articles cited a total of 381 times. Its strong performance reinforces the observation that high-impact research in this area is often published in journals that cater to a broad environmental science readership and emphasize integrated assessments of anthropogenic pollution. Other journals such as Atmospheric Environment and Environmental Pollution also show noteworthy citation metrics, indicating that atmospheric modeling, pollutant dispersion, and related environmental health impacts are critical components of the current research agenda.
The consistent citation activity across these six journals supports the conclusion that research in this domain is not only methodologically rigorous but also of substantial relevance to the global scientific community. These journals serve as hubs for the exchange of knowledge and ideas related to monitoring, modeling, and mitigating air pollution from heavy industry. In summary, this journal-based analysis contributes novel insights by highlighting the key publication venues that are driving forward research on industrial air pollution. It underscores the scientific significance and growing maturity of the field, while also offering guidance for future researchers on where to target their contributions for maximum visibility and impact. These findings are valuable not only for bibliometric mapping but also for advancing international collaboration, promoting dissemination of best practices, and supporting evidence-based environmental policymaking at the global level.
From a global scientific perspective, our findings highlight the importance and novelty of the more integrative review studies. Our research analysis would improve scientific understanding of emission dynamics in different economic, regulatory, and technological contexts. Our results clearly demonstrate that advancing this field requires sustained research output and greater collaboration between countries, disciplines, and institutions. The results presented here serve as a call to action for the global scientific community to address these disparities and contribute to a more cohesive and comprehensive environmental research agenda.
5. Conclusions
A review of contemporary research (2018–2024) on the monitoring of air pollution from the iron and steel industry was conducted on the basis of articles with DOI using machine learning methodologies (VOSviewer software version 1.6.20).
The results indicated that the geographic distribution of studies was extremely uneven. A total of 65% of the studies were conducted in China, with 9% in Nigeria, 6% in Russia, 3% in Poland, and 3% in Turkey. The remaining 14% of articles represent a series of single studies conducted in 11 countries. The revealed geographical imbalance between countries with developed production and the number of studies conducted in them shows a significant shortcoming in monitoring research.
The range of research directions for assessing the impact of the iron and steel industry on air quality was quite broad. Seven research directions were identified for categorizing the studies. The largest number of studies (20%) was devoted to the assessment of multicomponent emissions. A special place among them was occupied by the inventory of emissions using various methods. The next directions in terms of the number of articles were aimed at studying the atmospheric toxic metal emissions and their spatial characteristics (19%), at the analysis of organic emissions (19%), and at modeling and forecasting of emissions (18%). Slightly fewer studies (15%) have been directed at studying the sources of emissions of particulate matter (dust) of different sizes (PM10, PM2.5, PM2.1, PM1), their morphological state, and properties. Six articles focused on the phytomonitoring of air pollution. It has been established that terrestrial mosses have been used most frequently. The researchers also studied the impact of different production technologies on emissions.
Citation analysis allowed us to identify articles of greatest scientific interest. A rating of articles and journals was compiled. The most cited publications over the past 7 years are articles by Chinese researchers devoted to the analysis of emission sources and trace element contents of dust particles (PM2.5) in the atmosphere of Shanghai city and to the assessment of multicomponent emissions using the Total Environmental Impact Score. The “Science of the Total Environment” and “Journal of Cleaner Production” have been identified as the leaders in terms of the number of articles and citations.
Citation network analysis revealed important insights into the structure of scientific communication in the monitoring of air pollution from the iron and steel industry. A lack of strong inter-cluster links was found, which indicates insufficient consolidation of researchers.
Our systematic review allowed us to summarize and analyze a large number of studies on air pollution monitoring from the iron and steel industry and identified the most significant theoretical and applied articles. The results obtained will contribute to the consolidation of scientists, identifying gaps in scientific knowledge, improving environmental policies, and technological solutions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.Z.; methodology, E.Z. and N.I.; formal analysis, E.Z. and N.I.; investigation, E.Z. and N.I.; writing—original draft preparation, E.Z., N.I. and S.A.; writing—review and editing, E.Z., N.I. and S.A.; visualization, E.Z. and N.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The studies were carried out as a part of the state assignment of the Zavaritsky Institute of Geology and Geochemistry of Ural Branch of Russian Academy (state registration no. 123011800011-2) and as a part of the state assignment of the Institute Botanic Garden, the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (state registration no. 123112700125-1).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Arshad, K.; Hussain, N.; Ashraf, M.H.; Saleem, M.Z. Air pollution and climate change as grand challenges to sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriyari, H.A.; Nikmanesh, Y.; Jalali, S.; Tahery, N.; Zhiani Fard, A.; Hatamzadeh, N.; Zarea, K.; Cheraghi, M.; Mohammadi, M.J. Air pollution and human health risks: Mechanisms and clinical manifestations of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. Toxin Rev. 2022, 41, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofremu, G.O.; Raimi, B.Y.; Yusuf, S.O.; Dziwornu, B.A.; Nnabuife, S.G.; Eze, A.M.; Nnajiofor, C.A. Exploring the relationship between climate change, air pollutants and human health: Impacts, adaptation, and mitigation strategies. Green Energy Resour. 2025, 3, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivarethinamohan, R.; Sujatha, S.; Priya, S.; Gafoor, A.; Rahman, Z. Impact of air pollution in health and socio-economic aspects: Review on future approach. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.E.; Badamasi, H.; Unimke, A.A.; Durumin Iya, N.I.; Olubunmi, A.D.; Okoro, C.; Okezie, O.; Olaleye, A.A. An Overview of Recent Analytical Techniques for Air Quality Monitoring and Assessment. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2025, 21, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Brown, D.J.; Wright, P.; Khasawneh, A.M.; Taylor, B.; Kaiwartya, O. Innovations in Air Quality Monitoring: Sensors, IoT and Future Research. Sensors 2025, 25, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glushakova, O.V.; Chernikova, O.P. Influence of ferrous metallurgy enterprises on atmospheric air quality as an environmental component of sustainable development of territories. Report 1. Steel Transl. 2021, 51, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tian, H.; Fu, Z.; Bai, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, H.; Cui, J.; et al. Historical inventories and future scenarios of multiple hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) emissions from the iron and steel production industry in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.M.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Bui, H.M. Modelling Air Pollution from Steel Plants and Determining the Safety Distance for the Surrounding Area in Phu My Town, Ba Ria-Vung Tau Province, Vietnam. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2025, 34, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orelkina, D.I.; Petelin, A.L.; Polulyakh, L.A. Analysis of the spatial distribution of secondary gas emissions in the outer influence zone of steel industry. Izv. Ferr. Metall. 2015, 58, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Li, J.; You, Q.; Wang, Z.; Shan, W.; Bo, X.; Zhu, R. Improving the Air Quality Management: The Air Pollutant and Carbon Emission and Air Quality Model for Air Pollutant and Carbon Emission Reduction in the Iron and Steel Industries of Tangshan, Hebei Province, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Liu, F.; Li, J. An Integrated Analysis on the Synergistic Reduction of Carbon and Pollution Emissions from China’s Iron and Steel Industry. Engineering 2024, 40, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, D.O.; Trifu, A.; Darabont, D.C. A comparative study on the effectiveness of pollutants control measures adopted in the steel industry to reduce workplace and environmental exposure: A case study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y.; Meng, J.; Li, J.; He, J.; Guo, P.; Dai, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, R.; et al. Iron and steel industry emissions: A global analysis of trends and drivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 16477–16488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Cheng, S.; Tong, Y.; Li, G.; Yue, T. An Approach to CO2 Emission Reduction in the Iron and Steel Industry: Research Status and Development Trends of Integrated Absorption-Mineralization Technologies. Sustainability 2025, 17, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Wang, D.; Yu, X.; Ma, S.; Zhao, W.; Cui, C.; Meng, J.; Tao, S.; Guan, D. Global iron and steel plant CO2 emissions and carbon-neutrality pathways. Nature 2023, 622, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Shao, Q.; Wei, Y. Factor decomposition and decoupling analysis of air pollutant emissions in China’s iron and steel industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15267–15277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Physical and chemical characterization of fugitive particulate matter emissions of the iron and steel industry. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Bo, X.; Dan, M.; Shu, M. Volatile organic compounds constituents of a typical integrated iron and steel plant and influence on O3 pollution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 3323–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Dong, W.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, J. Identification of priority pollutants at an integrated iron and steel facility based on environmental and health impacts in the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Qin, S.; Jiang, X. Research development of VOCs emission reduction during iron ore sintering in steel industry. Iron Steel 2018, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, C.; Ding, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, G. Distribution Pattern, Emission Characteristics and Environmental Impact of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Download Ash and Dust from Iron and Steel Enterprise. Molecules 2019, 24, 3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Ding, C.; Chen, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y. Environment impact and probabilistic health risks of PAHs in dusts surrounding an iron and steel enterprise. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkok, S.K.; Kibet, J.K.; Kinyanjui, T.K.; Okanga, F.I. A review of persistent organic pollutants: Dioxins, furans, and their associated nitrogenated analogues. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, N.; Somanathan, A.; Tirpude, A.; Pillai, A.M.; Mondal, P.; Arfin, T. Dioxins and their impact: A review of toxicity, persistence, and novel remediation strategies. Anal. Methods 2025, 17, 1698–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buekens, A.; Stieglitz, L.; Hell, K.; Huang, H.; Segers, P. Dioxins from thermal and metallurgical processes: Recent studies for the iron and steel industry. Chemosphere 2001, 42, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łechtańska, P.; Wielgosiński, G.; Grochowalski, A.; Holtzer, M.; Ćwiąkalski, W. Dioxin emission from some metallurgical processes. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 61, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; He, H. Technical development and prospect for collaborative reduction of pollution and carbon emissions from iron and steel industry in China. Engineering 2023, 31, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusenbauer, M.; Haddaway, N.R. Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta-analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 11, 181–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, K.; Pullin, A.S. Assessing the risk of bias in choice of search sources for environmental meta-analyses. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 11, 698–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusenbauer, M. The age of abundant scholarly information and its synthesis–A time when ‘just google it’ is no longer enough. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengist, W.; Soromessa, T.; Legese, G. Method for conducting systematic literature review and meta-analysis for environmental science research. Methodsx 2020, 7, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okolie, C.C.; Danso-Abbeam, G.; Groupson-Paul, O.; Ogundeji, A.A. Climate-Smart Agriculture Amidst Climate Change to Enhance Agricultural Production: A Bibliometric Analysis. Land 2023, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.; Zolotova, E. Vegetation Dynamics Studies Based on Ellenberg and Landolt Indicator Values: A Review. Land 2024, 13, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltman, L.; Van Eck, N.J. A new methodology for constructing a publication-level classification system of science. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 2378–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltman, L.; Van Eck, N.J. A smart local moving algorithm for large-scale modularity-based community detection. Eur. Phys. J. B 2013, 86, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeoCharts Quick Start. Available online: https://developers.google.com/chart/interactive/docs/gallery/geochart (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Stefanov, S. React: Up & Running: Building Web Applications, 1st ed.; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2016; 222p. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Xu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, A. A review on reduction technology of air pollutant in current China’s iron and steel industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M.; Janeczek, J. Identification of industrial point sources of airborne dust particles in an urban environment by a combined mineralogical and meteorological analyses: A case study from the Upper Silesian conurbation, Poland. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Respondek, Z.; Isinkaralar, O.; Świsłowski, P.; Isinkaralar, K.; Rajfur, M. Biomonitoring with the Use of the Herbal Plant Taraxacum officinale as a Source of Information on Environmental Contamination. Plants 2024, 13, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, B.; Yurdakul, S.; Gungormus, E.; Ozturk, F.; Sofuoglu, S.C. Source apportionment and carcinogenic risk assessment of passive air sampler-derived PAHs and PCBs in a heavily industrialized region. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinkaralar, O.; Świsłowski, P.; Isinkaralar, K.; Rajfur, M. Moss as a passive biomonitoring tool for the atmospheric deposition and spatial distribution pattern of toxic metals in an industrial city. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, P.J.G.; Lasheras, F.S.; García-Gonzalo, E.; Juez, F.J.d.C. Estimation of PM 10 concentration from air quality data in the vicinity of a major steelworks site in the metropolitan area of Avilés (Northern Spain) using machine learning techniques. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 3287–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawati, I.; Ermawati, R.; Kang, K.; Chang, I.; Hong, K.; Ervina, E.; Ariani, A.; Fauzi, I.; Syah, I.L.; Sefriana, F.; et al. preliminary result of air quality identification and analysis of PM10 and PM2.5 in steel industrial area, Cilegon, Banten. J. Ris. Teknol. Pencegah. Pencemaran Ind. 2019, 10, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcias, G.; Fostinelli, J.; Catalani, S.; Uras, M.; Sanna, A.M.; Avataneo, G.; De Palma, G.; Fabbri, D.; Paganelli, M.; Lecca, L.I.; et al. Composition of Metallic Elements and Size Distribution of Fine and Ultrafine Particles in a Steelmaking Factory. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, K.M.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Seo, Y.K.; Baek, S.O. Characterization and health impact assessment of hazardous air pollutants in residential areas near a large iron-steel industrial complex in Korea. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1754–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlíková, I.; Motyka, O.; Plášek, V.; Bitta, J. Monitoring of Heavy Metals and Nitrogen Concentrations in Mosses in the Vicinity of an Integrated Iron and Steel Plant: Case Study in Czechia. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutuku, J.K.; Lee, Y.Y.; Huang, B.W.; Chen, W.H.; Hou, W.C. Assessment of the emission factors for potentially toxic elements from coal-fired boilers and sintering furnaces in a steel production plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, K.L.; Gillings, M.M.; Isley, C.F.; Gunkel-Grillon, P.; Taylor, M.P. Trace element contamination of soil and dust by a New Caledonian ferronickel smelter: Dispersal, enrichment, and human health risk. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrjo, F.; Baghkhanipour, M.; Alam, A. Investigating the environmental status of air pollution in Iran’s ferroalloy industries (IFI). Sustain. Earth Trends 2022, 2, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, P.; Agrawal, S. A pollution assessment of grossly polluting industries in India. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2022, 30, 30–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, S.S.; Bekteshi, L.; Allajbeu, S.; Lazo, P. Moss biomonitoring of air quality linked with trace metals pollution around a metallurgical complex in Elbasan, Albania. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2024, 17, 2045–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salian, K.; Strezov, V.; Evans, T.J.; Taylor, M.; Nelson, P.F. Application of national pollutant inventories for monitoring trends on dioxin emissions from stationary industrial sources in Australia, Canada and European Union. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glushakova, O.V.; Chernikova, O.P. Influence of ferrous metallurgy enterprises on atmospheric air quality as an ecological component of territories sustainable development. Report 2. Izv. Ferr. Metall. 2021, 64, 561–571. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, X.; Jia, M.; Xue, X.; Tang, L.; Mi, Z.; Wang, S.; Cui, W.; Chang, X.; Ruan, J.; Dong, G.; et al. Effect of strengthened standards on Chinese ironmaking and steelmaking emissions. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Yi, H.; Tang, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Gao, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y. Air pollutant emission and reduction potentials from the sintering process of the iron and steel industry in China in 2017. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, J.; Wu, J. Assessment of multi-air emissions: Case of particulate matter (dust), SO2, NOx and CO2 from iron and steel industry of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, M.A.; Vodoleev, A.S.; Andreeva, O.S.; Domnin, K.I. Ecomonitoring of sanitary protection zone of metallurgical enterprise: Snow and soil cover. Izv. Ferr. Metall. 2023, 66, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Yao, L.; Liu, L.; Xian, A.; Chen, H.; Dong, W.; Chen, J. Baosteel emission control significantly benefited air quality in Shanghai. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.J.; Lang, J.L.; Cheng, S.Y.; Jia, J.; Wang, X.Q. Air pollutant emission inventory from iron and steel industry in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and its impact on PM2.5. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2018, 39, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Gao, W.; Song, K.; Na, H.; Tian, F.; Zhang, S. Spatial and temporal dynamics of air-pollutant emission inventory of steel industry in China: A bottom-up approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 143, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lei, Y.; Yan, L.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Q.; He, K. A unit-based emission inventory of SO2, NOx and PM for the Chinese iron and steel industry from 2010 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Zheng, H.; Han, L.; Qiu, X.; Wen, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Emission trends of air pollutants and CO2 in China from 2005 to 2021. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 2279–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Tang, Q.; Xue, W.; Shi, X.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Jiang, C.; Yan, G.; Wang, J. Quantifying China’s iron and steel industry’s CO2 emissions and environmental health burdens: A pathway to sustainable transformation. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnology 2024, 20, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Gao, J.; Tong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, S.; Li, G.; Yue, T. Advances in the sources, chemical behaviour, and whole process distribution of Hg, As, and Pb in the iron and steel smelting industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Q.; Lu, M.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Jia, G.; Xiao, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Anthropogenic atmospheric toxic metals emission inventory and its spatial characteristics in Guangdong province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Tian, H.; Hao, Y.; Gao, J.; Hao, J.; Wang, Y.; Hua, S.; Wang, K.; Liu, H. A high-resolution emission inventory of anthropogenic trace elements in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region of China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeh, G.C.; Ugwo, J.P.; Adebiyi, F.M.; Abiye, O.E.; Onwudiegwu, C.A.; Obiajunwa, E.I. Proton-induced X-ray emission (PIXE) analysis of trace elements of total atmospheric deposit (TAD) around a smelting industry: Aerial pollution monitor. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, X. Status, spatial distribution, and health risk assessment of potentially harmful element from road dust in steel industry city, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Strezov, V.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, X.; Kan, T.; Evans, T. Contamination identification, source apportionment and health risk assessment of trace elements at different fractions of atmospheric particles at iron and steelmaking areas in China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlade, B.T.; Adeniran, J.A.; Abdulraheem, K.A.; Odediran, E.T.; Atanda, A.S.; Oyeneye, A.K.; Akapo, R.A.; Yusuf, R.O. Heavy Metals Analysis in the Vicinity of a Northcentral Nigeria Major Scrap-Iron Smelting Plant. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2024, 18, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pan, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, Z.; Pan, J.; et al. Stack releases of radionuclides from an integrated steel plant in China. J. Environ. Radioact. 2018, 195, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Fu, Q.; Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, X.; Liao, H.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W. Investigate the impact of local iron–steel industrial emission on atmospheric mercury concentration in Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5862–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Lin, C.J.; Jang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Xing, J.; Yu, L. Source contribution analysis of mercury deposition using an enhanced CALPUFF-Hg in the central Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, H.; She, X.; Ren, K.; You, X.; Wang, J.; Zuo, H.; Wang, G.; Xue, Q. Substance-flow analysis and emission-reduction strategies for thallium in the steel industry process. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 185, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, S.; Fu, Q.; Han, D.; Chen, X.; Fu, S.; Huang, X.; Cheng, J. Impact of VOCs emission from iron and steel industry on regional O3 and PM2.5 pollutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28853–28866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Cheng, S.; Wang, K.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, H.; Duan, W. Emission characteristics and reactivity of volatile organic compounds from typical high-energy-consuming industries in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Chun, T.; Long, H.; Li, J.; Di, Z.; Meng, Q.; Wang, P. Emission reduction research and development of PCDD/Fs in the iron ore sintering. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.; Ma, Y.; Chen, T.; Lin, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, S.; Li, X.; Yan, J. PCDD/Fs characteristics in flue gas and surrounding environment of iron and steel smelting industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14092–14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeniran, J.A.; Ogunlade, B.T.; Abdulraheem, K.A.; Odediran, E.T.; Atanda, A.S.; Oyeneye, A.K.; Yusuf, R.O. Concentration and sources of persistent organic pollutants within the vicinity of a scrap-iron smelting plant: Seasonal pattern and health risk assessment. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2024, 42, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Z. Source apportionment and toxicity assessment of PM2. 5-bound PAHs in a typical iron-steel industry city in northeast China by PMF-ILCR. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgikh, O.V.; Dianova, D.G. Peculiarities detected in formation of specific hapten sensitization to phenol in children. Health Risk Anal. 2022, 1, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, O.J.; Igbayo, A.N.; Olise, F.S.; Owoade, K.O.; Abiye, O.E.; Ayoola, M.A.; Hopke, P.K. Simulation of Point Source Pollutant Dispersion Pattern: An Investigation of Effects of Prevailing Local Weather Conditions. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 3, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omokungbe, O.R.; Olufemi, A.P.; Toyeje, A.B.; Abiodun, P.O. Investigating the evolution of gaseous air pollutants with prevailing meteorology across selected sites within a pollution hotspot in Ile-Ife, Southwestern Nigeria. Discov. Environ. 2023, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, M.; Magazzino, C. A machine learning analysis of the relationship among iron and steel industries, air pollution, and economic growth in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Jiang, F. Pollution control efficiency of China’s iron and steel industry: Evidence from different manufacturing processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J. Energy and resource conservation and air pollution abatement in China’s iron and steel industry. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 147, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xue, X.; Jia, M.; Jing, H.; Wang, T.; Zhen, R.; Huang, M.; Tian, J.; Guo, J.; Li, L.; et al. Iron and steel industry emissions and contribution to the air quality in China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 237, 117668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, P.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, S. Co-abatement of carbon and air pollutants emissions in China’s iron and steel industry under carbon neutrality scenarios. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 191, 114140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tao, W.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, K.; Yi, K.; Xiao, Y.; Tao, S. The contribution of the Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei region’s iron and steel industry to local air pollution in winter. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Deng, Z.; Ma, X.; Xing, Y.; Pan, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tharaka, W.A.N.D.; Hua, T.; Shen, L. Analysis of the synergistic benefits of typical technologies for pollution reduction and carbon reduction in the iron and steel industry in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Cheng, S.; Yao, S.; Xu, T.; Zhang, T.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Duan, W. Emission characteristics and chemical components of size-segregated particulate matter in iron and steel industry. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 182, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Huang, K.; Xie, M.; Deng, C.; Zou, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. First long-term and near real-time measurement of trace elements in China’s urban atmosphere: Temporal variability, source apportionment and precipitation effect. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11793–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, X.; Kan, T.; Strezov, V.; Nelson, P.; Evans, T.; Jiang, Y. Characterization of size resolved atmospheric particles in the vicinity of iron and steelmaking industries in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; He, M.; Cheng, X.; Su, T.; Ni, S.; Zhang, C. Contamination, morphological status and sources of atmospheric dust in different land-using areas of a steel-industry city, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y. Characteristics and Source Analysis of PM1 in a Typical Steel-Industry City, Southwest China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Jiang, K.; Meng, J.; Guan, D.; Xu, Y.; Tao, S. Multi-objective analysis of the co-mitigation of CO2 and PM2.5 pollution by China’s iron and steel industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Luo, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, T.; Ye, M. Influence of pollutants’ control facilities on PM2.5 profiles emitted from an iron and steel plant. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Wu, D.; Li, Z.; Chu, S.Q.; Ding, X.; Tang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Q. Magnetic particles unintentionally emitted from anthropogenic sources: Iron and steel plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olise, F.S.; Ogundele, L.T.; Olajire, M.A.; Oloyede, F.A.; Fawole, O.G.; Ezeh, G.C. Biomonitoring of environmental pollution in the vicinity of iron and steel smelters in southwestern Nigeria using transplanted lichens and mosses. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olise, F.S.; Ogundele, L.T.; Olajire, M.A.; Owoade, O.K. Seasonal Variation, Pollution Indices and Trajectory Modeling of Bio-monitored Airborne Particulate Around Two Smelting Factories in Osun State, Nigeria. Aerosol Sci. Eng. 2020, 4, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, W.; Zhao, L.; Cai, J. Material metabolism and environmental emissions of BF-BOF and EAF steel production routes. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2018, 39, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butorina, I.V.; Butorina, M.V. Modern methods for purification of emissions from ferrous metallurgy enterprises. Chernye Met. 2021, 2021, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Yao, Q.; Li, Y. Multi-process and multi-pollutant control technology for ultra-low emissions in the iron and steel industry. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Kumari, M.; Kumar, R.; Iqbal, K.; Thakur, I.S. Persistent organic pollutants in the environment: Risk assessment, hazards, and mitigation strategies. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 19, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, T.; Li, P.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Jiang, G. Identification and prioritization of environmental organic pollutants: From an analytical and toxicological perspective. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 10584–10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, J.; Dutta, M.; Marques, G. Sensors for indoor air quality monitoring and assessment through Internet of Things: A systematic review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, P.; Natrayan, L.B.T.J.R.R.G.S.; Geetha, B.T.; Beulah, J.R.; Sumathy, R.; Varalakshmi, G.; Neelakandan, S. IoT enabled environmental toxicology for air pollution monitoring using AI techniques. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, H.; Wang, J.; She, X.; Wang, G.; Zuo, H.; Xue, Q. Current status of the technology for utilizing difficult-to-treat dust and sludge produced from the steel industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 132909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, D.; Deb, K.; Padhy, P.K. Ecophysiological responses of tree species due to air pollution for biomonitoring of environmental health in urban area. Urban Clim. 2021, 35, 100741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Dutta, R.; Das, P. Greenery planning for urban air pollution control based on biomonitoring potential: Explicit emphasis on foliar accumulation of particulate matter (PM) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 355, 120524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, K.; Kumari, A. Assessing phytomonitoring potential employing air pollution tolerance index and oxidative stress markers for selective flora in metrocity-Lucknow, India. J. Atmos. Chem. 2025, 82, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Khan, I.; Kundu, D.; Das, K.; Datta, J.K. Ecophysiological evaluation of tree species for biomonitoring of air quality and identification of air pollution-tolerant species. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, F.; Improta, G.; Triassi, M.; Castiglione, S.; Cicatelli, A. Air quality biomonitoring through Olea europaea L.: The study case of “Land of pyres”. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, M.E.; Cecchetti, G. Biological monitoring: Lichens as bioindicators of air pollution assessment—A review. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 114, 471–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, D.M.; Procópio, D.P.; Zamuner, C.K.; Nóbrega, B.B.; Bettim, M.R.; de Rezende, G.; Lopes, P.M.; Pereira, A.B.D.; Bechara, E.J.H.; Oliveira, A.G.; et al. Fungal bioassays for environmental monitoring. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 954579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnasuriya, S.D.; Udayanga, D.; Manamgoda, D.S.; Biles, C. Fungi as environmental bioindicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Kaur, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Joshi, A. Heavy metals controlling cardiovascular diseases risk factors in myocardial infarction patients in critically environmentally heavy metal-polluted steel industrial town Mandi-Gobindgarh (India). Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 3215–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, Z.; Aziz, F. Heavy metal accumulation in dust and workers’ scalp hair as a bioindicator for air pollution from a steel factory. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, P.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Xi, S. Metal Biomonitoring and Comparative Assessment in Urine of Workers in Lead-Zinc and Steel-Iron Mining and Smelting. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 189, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).