Applicability Assessment of ERA5 Surface Wind Speed Data Across Different Landforms in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.1.1. CN05.1 Gridded Observational Dataset
2.1.2. Global Landform Data
2.1.3. ERA5 Reanalysis Dataset
2.2. Methods
3. Results
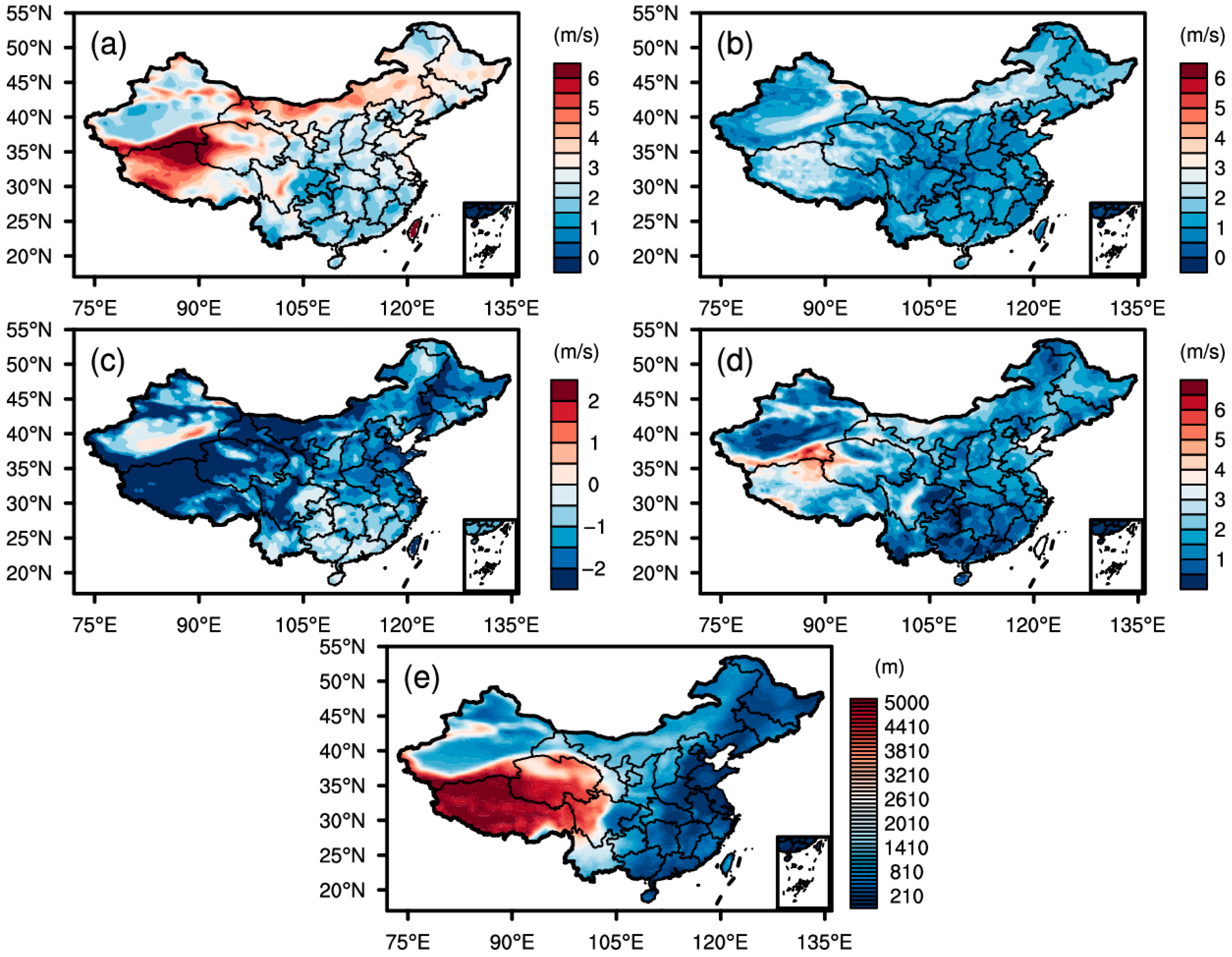
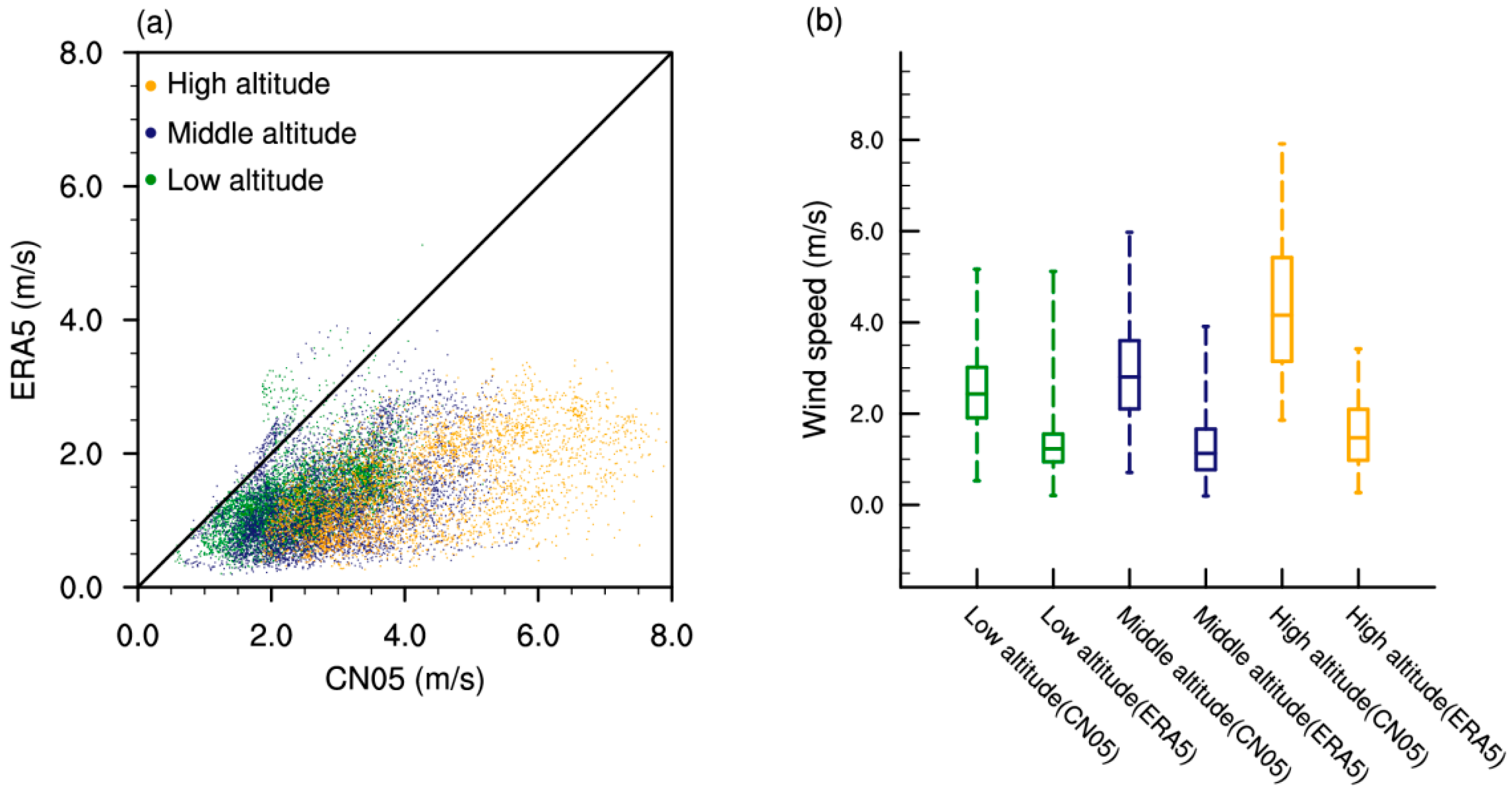
3.1. Spatial Heterogeneity of Wind Speed Biases
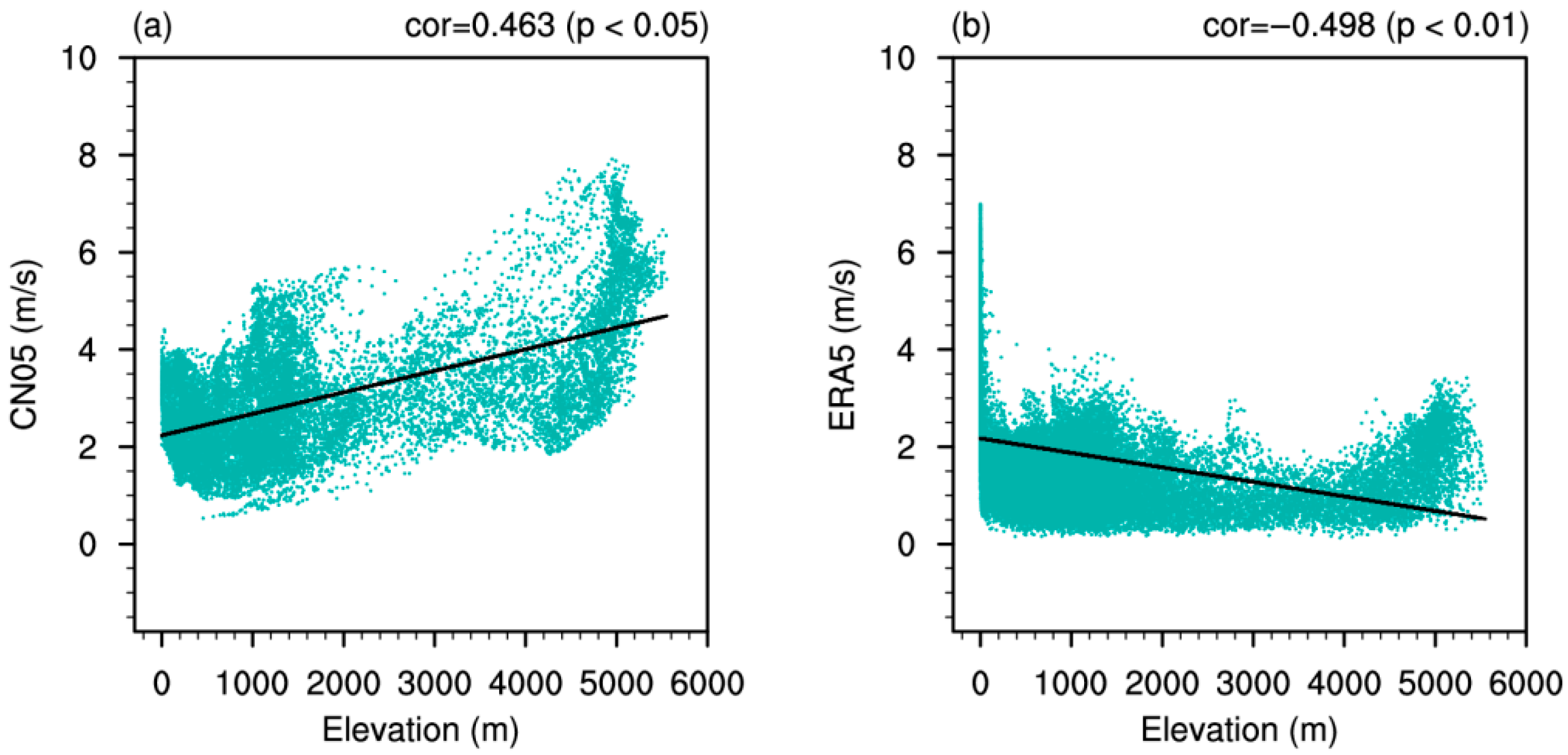
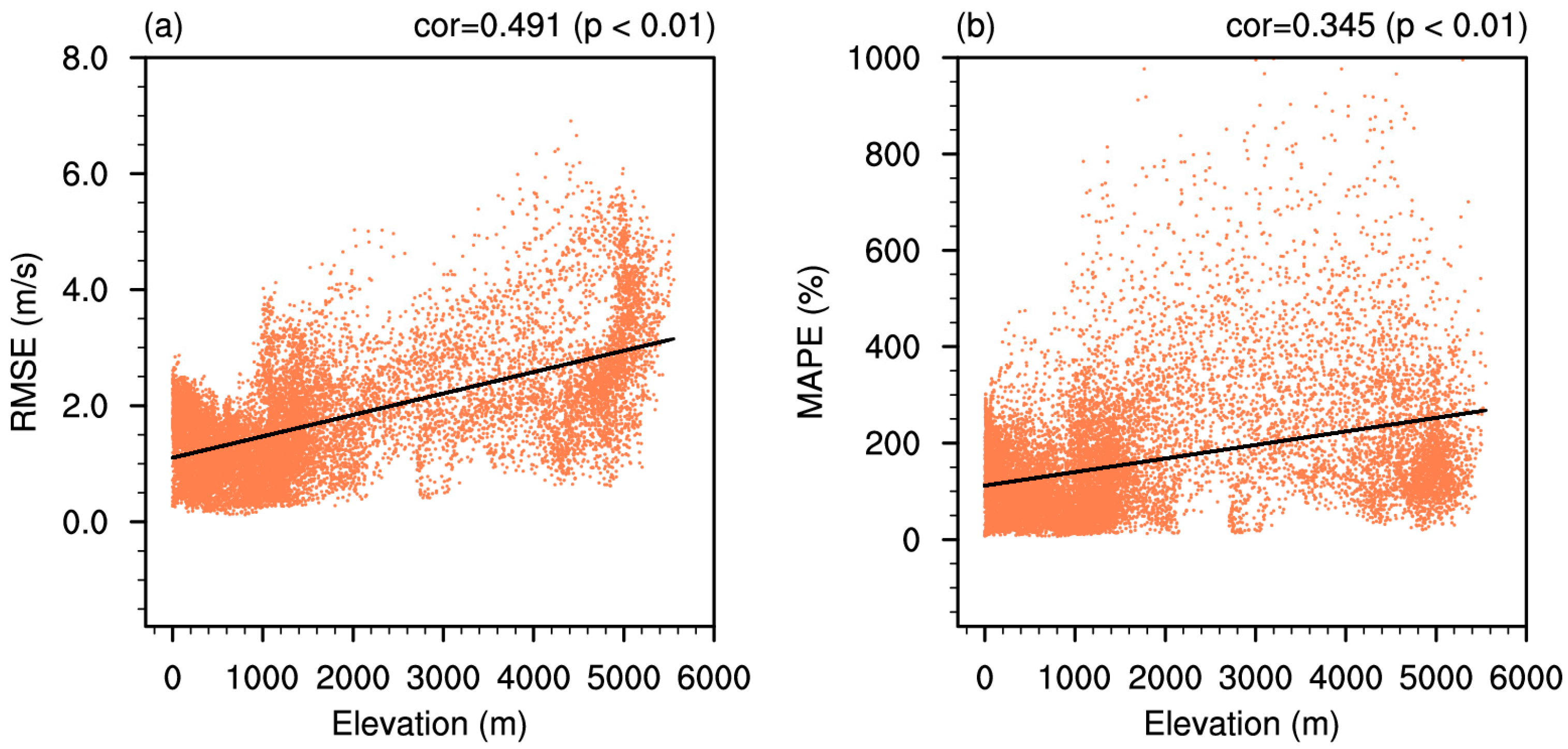
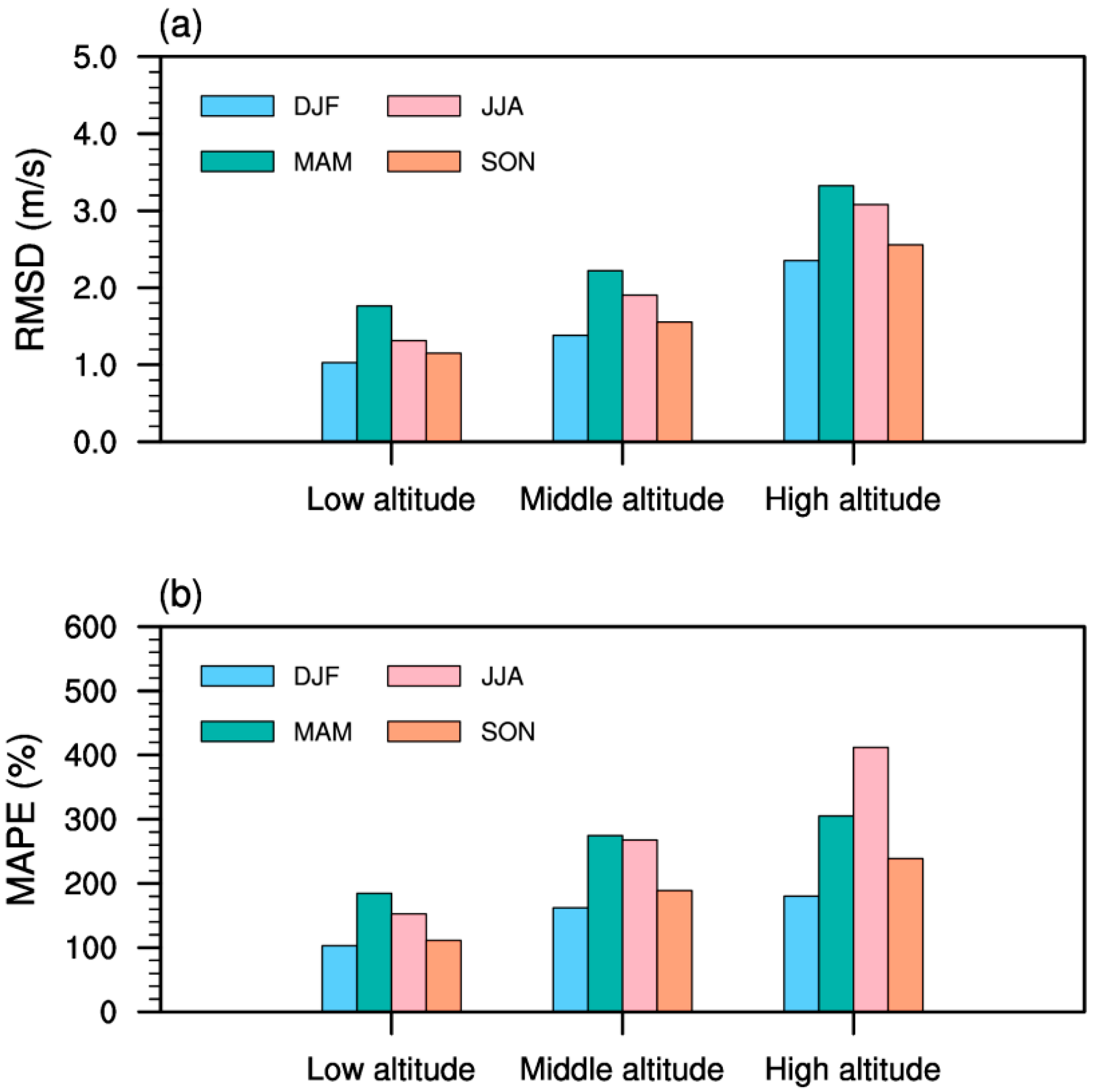
3.2. Elevation-Dependent Error Patterns
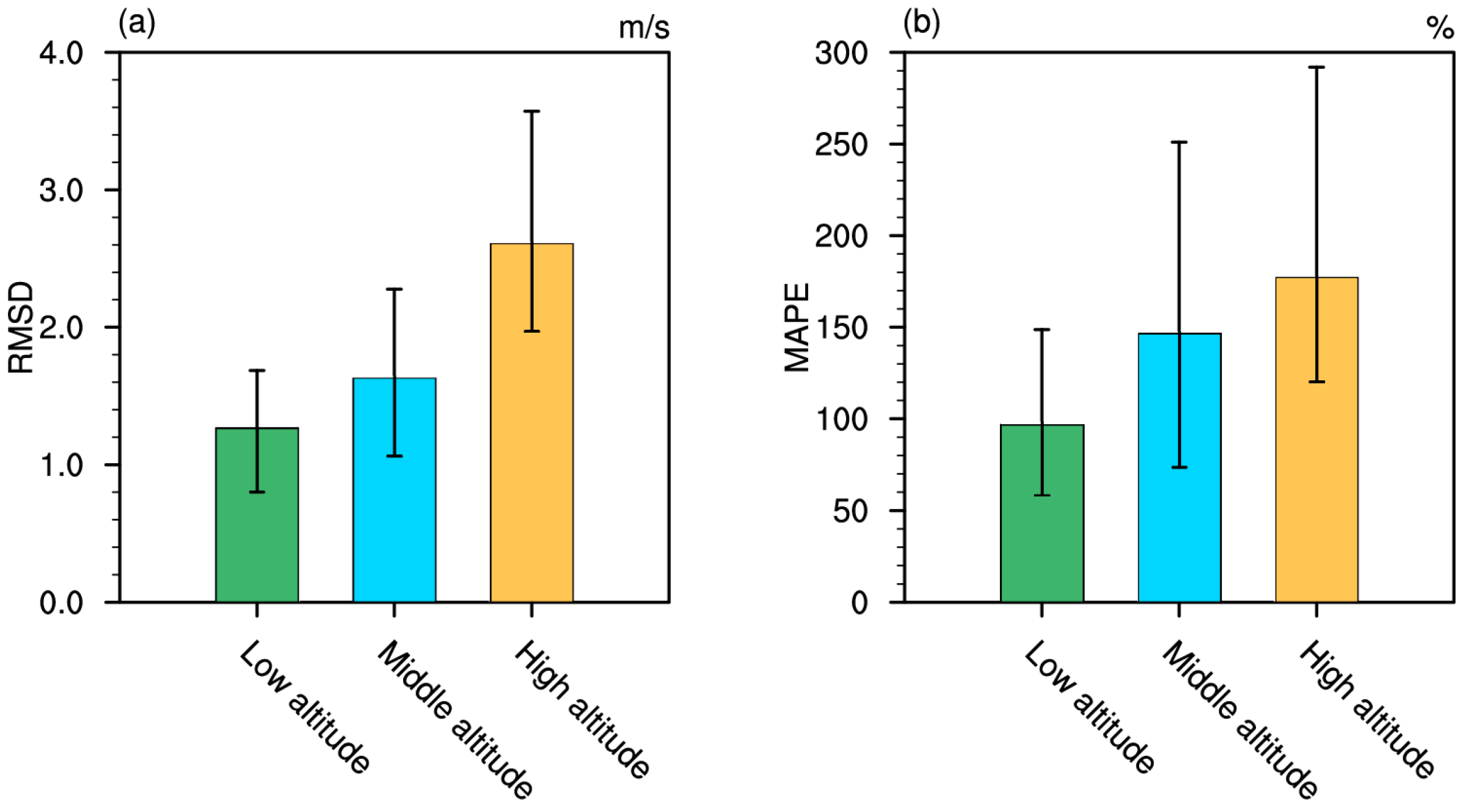
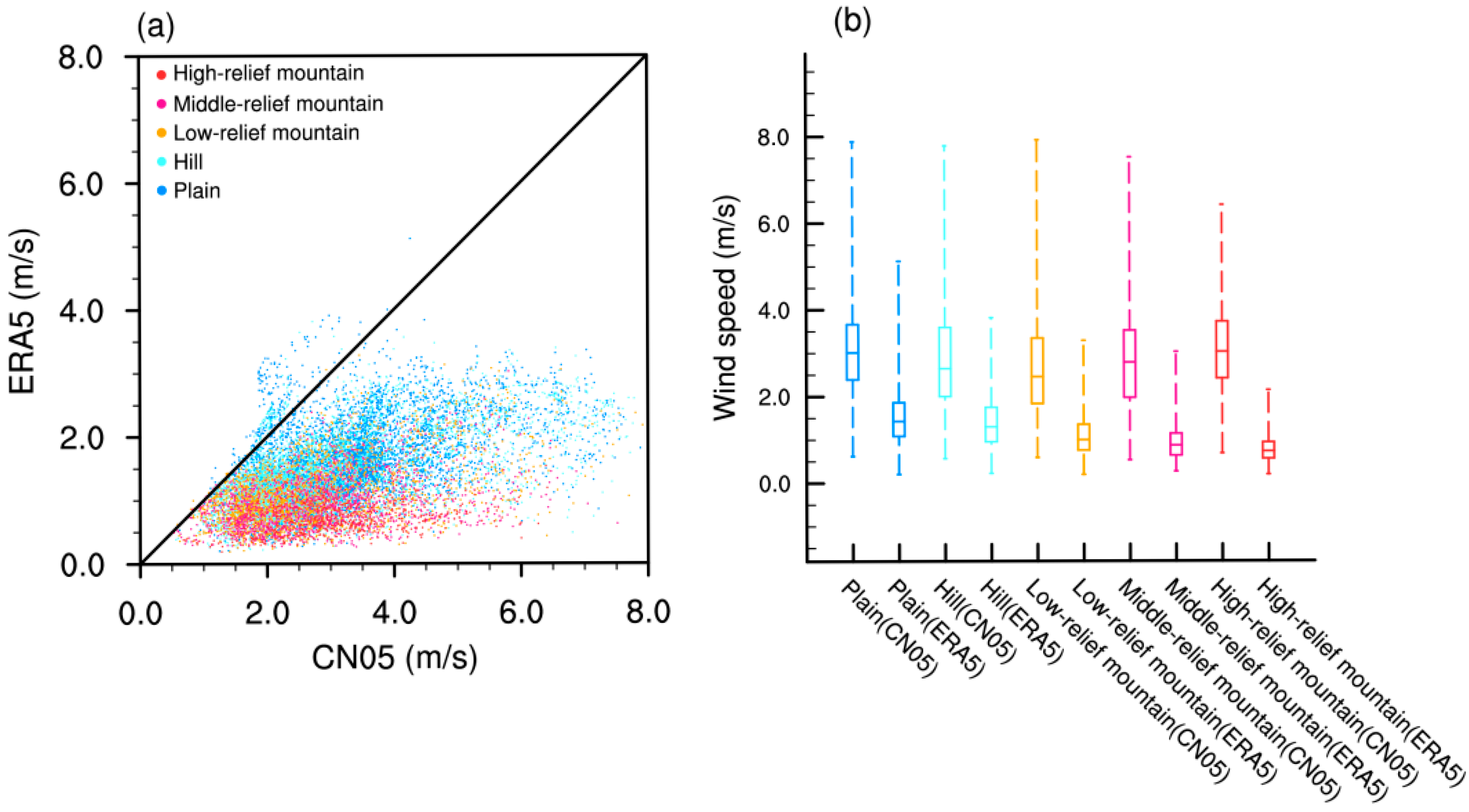
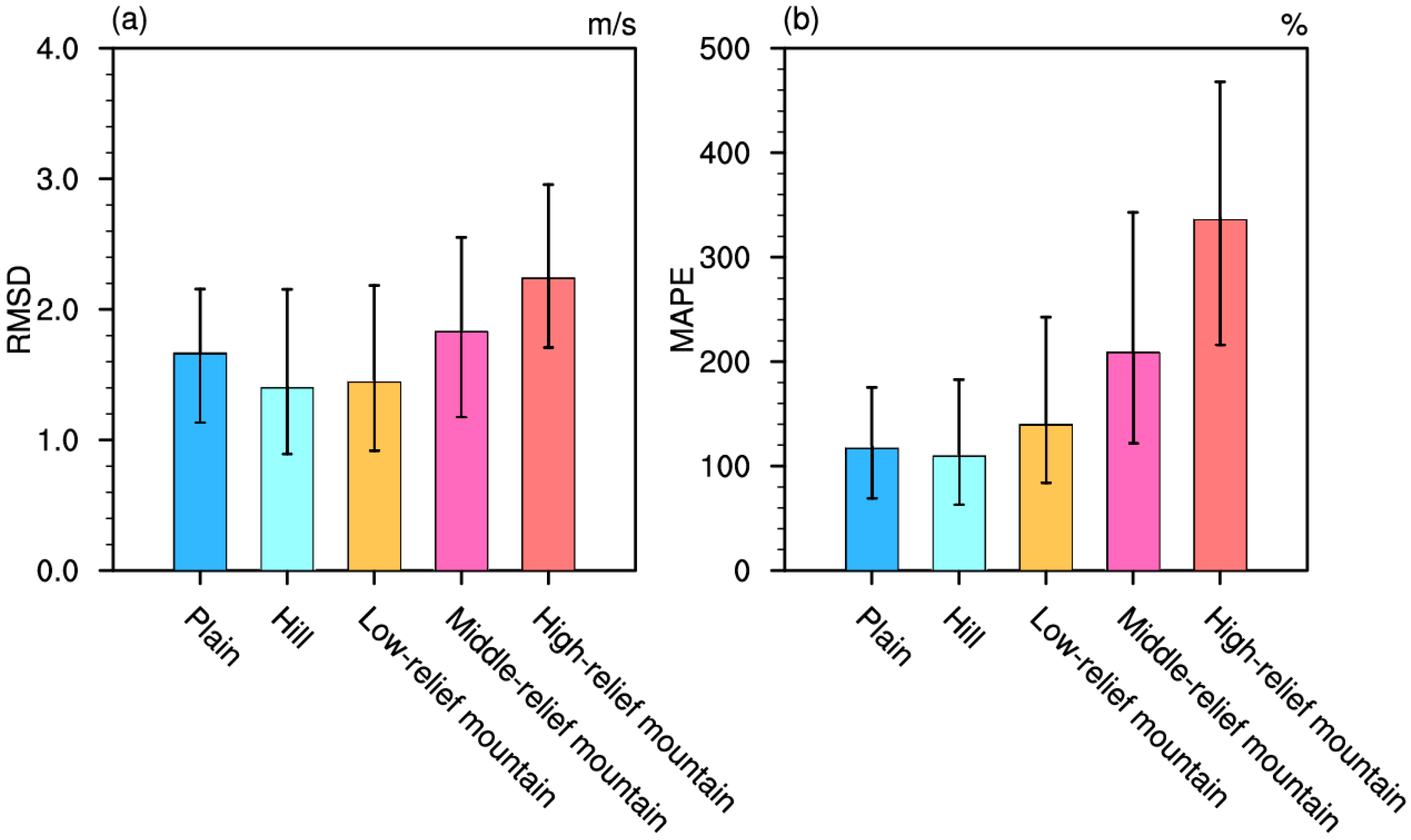
3.3. Terrain-Induced Variability Analysis
4. Conclusions
5. Discussion
5.1. Reasons for ERA5’s Failure to Capture Orographic Effects
5.2. Limitations and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McVicar, T.R.; Roderick, M.L.; Donohue, R.J.; Li, L.T.; Van Niel, T.G.; Thomas, A.; Grieser, J.; Jhajharia, D.; Himri, Y.; Mahowald, N.M.; et al. Global review and synthesis of trends in observed terrestrial near-surface wind speeds: Implications for evaporation. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416–417, 182–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhou, B.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Shi, Y. Projected changes in haze pollution potential in China: An ensemble of regional climate model simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10109–10123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Ziegler, A.D.; Searchinger, T.; Yang, L.; Chen, A.; Ju, K.; Piao, S.; Li, L.Z.X.; Ciais, P.; Chen, D.; et al. A reversal in global terrestrial stilling and its implications for wind energy production. Nat. Clim. Change 2019, 9, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, R.A.; Peel, A.M.; Lowe, L.; Srikanthan, R.; McVicar, T.R. Estimating actual, potential, reference crop and pan evaporation using standard meteorological data: A pragmatic synthesis. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1331–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.J.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, X.Z. Effects of surface wind speed decline on modeled hydrological conditions in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2803–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, L.N.; Cao, L.J.; Yan, Z.; Wu, Y. Decreasing atmospheric visibility associated with weakening winds from 1980 to 2017 over China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Li, K.; Liao, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, L. Weather conditions conducive to Beijing severe haze more frequent under climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valjarević, A. Long-term remote sensing-based methods for monitoring air pollution and cloud cover in the Balkan countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 27155–27171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Zou, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Cheng, H.; Kang, L.; Zhang, C. Variation of strong dust storm events in northern China during 1978−2007. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, S.C.; Barthelmie, R.J. A global assessment of extreme wind speeds for wind energy applications. Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Q. Advances of surface wind speed changes over China under global warming. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2020, 31, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Huang, G.; Hu, K.; Niyogi, D. Observed and global climate model based changes in wind power potential over the Northern Hemisphere during 1979–2016. Energy 2019, 167, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zha, J.; Zhao, D.; Yang, Q. Changes in terrestrial near-surface wind speed and their possible causes: An overview. Clim. Dynam. 2018, 51, 2039–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Cuo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C. Varied spatiotemporal changes in wind speed over the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings in the past decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 5956–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.L.; Shen, C.; Wu, J.; Zhao, D.M.; Fan, W.X.; Jiang, H.P.; Azorin-molina, C.; Chen, D. Effects of Northern Hemisphere annular mode on terrestrial near-surface wind speed over eastern China from 1979 to 2017. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2022, 13, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Li, Z.; Xie, S.; Huang, L.; Meng, L.; Li, X.; Zhong, K. Dynamic Variations in Wind Speed Intensity Across China and Their Association with Atmospheric Circulation Patterns. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 60, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azorin-Molina, C.; Menendez, M.; McVicar, T.R.; Acevedo, A.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Cuevas, E.; Minola, L.; Chen, D. Wind speed variability over the Canary Islands, 1948–2014: Focusing on trend differences at the land–ocean interface and below–above the trade-wind inversion layer. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 4061–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Chen, D.; McVicar, T.R.; Guijarro, J.A.; Deng, K.Q.; Minola, L.; Lee, J.; Son, S.W.; Ma, H.; et al. Variability and trends of near-surface wind speed over the Tibetan Plateau: The role played by the westerly and Asian monsoon. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2024, 15, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, D.; McVicar, T.R.; Guijarro, J.A.; Chappell, A.; Deng, K.; Minola, L.; Kong, F.; et al. Rapid urbanization induced daily maximum wind speed decline in metropolitan areas: A case study in the Yangtze River Delta (China). Urban Clim. 2022, 43, 101147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. Effects of land use and cover change on surface wind speed in China. J. Arid Land 2019, 11, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zha, J.; Zhao, D. Evaluating the effects of land use and cover change on the decrease of surface wind speed over China in recent 30 years using a statistical downscaling method. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Wu, J.; Zhao, D. Changes of probabilities in different wind grades induced by land use and cover change in Eastern China Plain during 1980–2011. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2016, 17, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Xu, H.; Yang, K.; Tang, H.; Deng, J.; Xu, M.; Ning, G.; Huang, G. The reversal of surface wind speed trend in Northeast China: Impact from aerosol emissions. Clim. Dyn. 2025, 63, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Yue, X.; Liao, H. Co-Benefits of Mitigating Aerosol Pollution to Future Solar and Wind Energy in China Toward Carbon Neutrality. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL109296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z.; Kaufman, Y.J. Wind reduction by aerosol particles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L24814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azorin-Molina, C.; Pirooz, A.A.S.; Bedoya-Valestt, S.; Utrabo-Carazo, E.; Andres-Martin, M.; Shen, C.; Minola, L.; Guijarro, J.A.; Aguilar, E.; Brunet, M.; et al. Biases in wind speed measurements due to anemometer changes. Atmos. Res. 2023, 289, 106771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azorin-Molina, C.; Asin, J.; McVicar, T.R.; Minola, L.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Chen, D. Evaluating anemometer drift: A statistical approach to correct biases in wind speed measurement. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, K. Stilling and recovery of the surface wind speed based on observation, reanalysis, and geostrophic wind theory over China from 1960 to 2017. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 3989–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; Su, J.; Gou, J. Surface wind speed changes and their potential impact on wind energy resources across China during 1961-2021. GeoHealth 2023, 7, e2023GH000861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Xue, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, F.; Thompson, L.; Cui, P.; Koike, T.; Lau, W.K.M.; Lettenmaier, D.; Mosbrugger, V.; et al. Recent Third Pole’s Rapid Warming Accompanies Cryospheric Melt and Water Cycle Intensification and Interactions between Monsoon and Environment: Multidisciplinary Approach with Observations, Modeling, and Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Skerlak, B.; Rotach, M.W.; Añel, J.A.; Su, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, M. Reasons for the extremely high-ranging planetary boundary layer over the western Tibetan Plateau in winter. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 2021–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Q. Land–Climate Interaction Over the Tibetan Plateau. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Climate Science; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Qian, Y.; Berg, L.K.; Ma, P.-L.; Wharton, S.; Bulaevskaya, V.; Yan, H.; Hou, Z.; Shaw, W.J. Sensitivity of Turbine-Height Wind Speeds to Parameters in Planetary Boundary-Layer and Surface-Layer Schemes in the Weather Research and Forecasting Model. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2017, 162, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Lou, W.; Gu, Y.; Liao, S.; Lu, Z.; Cai, W. Judgment criteria for significant wind speed-up regions in natural complex terrain. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2024, 249, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbig, N.; Mott, R.; van Herwijnen, A.; Winstral, A.; Jonas, T. Parameterizing surface wind speed over complex topography. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafin, S.; Adler, B.; Cuxart, J.; De Wekker, S.F.J.; Gohm, A.; Grisogono, B.; Kalthoff, N.; Kirshbaum, D.J.; Rotach, M.W.; Schmidli, J.; et al. Exchange Processes in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Over Mountainous Terrain. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Conklin, D.R.; Unsworth, M.H. Local atmospheric decoupling in complex topography alters climate change impacts. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 30, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Scheperset, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennermann, K.; Berrisford, P. What Are the Changes from ERA-Interim to ERA5? 2023. Available online: https://confluence.ecmwf.int/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=74764925 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Hoffmann, L.; Günther, G.; Li, D.; Stein, O.; Wu, X.; Griessbach, S.; Heng, Y.; Konopka, P.; Müller, R.; Vogel, B.; et al. From ERA-Interim to ERA5: The considerable impact of ECMWF’s next-generation reanalysis on Lagrangian transport simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3097–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Spang, R. An assessment of tropopause characteristics of the ERA5 and ERA-Interim meteorological reanalyses. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 4019–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, Q.; Ming, B.; Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Feng, G.; Shang, J. Assessment of Wind and Solar Power Potential and Their Temporal Complementarity in China’s Northwestern Provinces: Insights from ERA5 Reanalysis. Energies 2023, 16, 7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, G.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.; Ren, J. Ensemble Bayesian modelaveraging projections of wind-speed extremes for wind energy applications over China under climate change. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2023JD038806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.M.; Lima, D.C.; Nogueira, M. Global offshore wind energy resources using the new ERA-5 reanalysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1040a2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulazia, A.; Nafarrate, A.; Ibarra-Berastegi, G.; Sáenz, J.; Carreno-Madinabeitia, S. The Consequences of Air Density Variations over Northeastern Scotland for Offshore Wind Energy Potential. Energies 2019, 12, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, L.F.D.; Shadman, M.; Assad, L.P.D.; Silva, C.; Landau, L.; Estefen, S.F. Assessment of the offshore wind technical potential for the Brazilian Southeast and South regions. Energy 2020, 196, 117097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.H.; Karathanasi, F.E.; Zaragkas, D.K. Exploiting offshore wind and solar resources in the Mediterranean using ERA5 reanalysis data. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 237, 114092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefabas, K.L.; Söder, L.; Mamo, M.; Olauson, J. Modeling of Ethiopian Wind Power Production Using ERA5 Reanalysis Data. Energies 2021, 14, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.A.G.; Barriga, J.E.C.; Martínez, J.A. Wind power assessment in the Caribbean region of Colombia, using ten-minute wind observations and ERA5 data. Renew. Energy 2021, 172, 158–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Liu, Y.; Chappell, A.; Dong, L.; Xu, R.; Ekström, M.; Fu, T.; Zeng, Z. Evaluation of Global Reanalysis Land Surface Wind Speed Trends to Support Wind Energy Development Using In Situ Observations. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2021, 60, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, Z.; Zou, L. Evaluation of Near-Surface Wind Speed Changes during 1979 to 2011 over China Based on Five Reanalysis Datasets. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, G. Analysing the uncertainties of reanalysis data used for wind resource assessment: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minola, L.; Zhang, G.; Ou, T.; Kukulies, J.; Curio, J.; Guijarro, J.A.; Deng, K.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Shen, C.; Pezzoli, A.; et al. Climatology of near-surface wind speed from observational, reanalysis and high-resolution regional climate model data over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2024, 62, 933–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Su, H.; Zeng, X.; Posselt, D.J.; Wong, S.; Chen, S.; Stoffelen, A. Uncertainty of Atmospheric Winds in Three Widely Used Global Reanalysis Datasets. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2024, 63, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Y. Changes in surface wind speed and its different grades over China during 1961–2020 based on a high-resolution dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 42, 3954–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, L.; Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Guo, C.; Liang, S.; Tu, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, X. Evaluation of near-surface wind speed climatology and long-term trend over China’s mainland region based on ERA5 reanalysis. Clim. Environ. Res. 2021, 26, 299–311. Available online: http://www.iapjournals.ac.cn/qhhj/articl (accessed on 2 May 2025). (In Chinese).
- Molina, M.O.; Gutiérrez, C.; Sánchez, E. Comparison of ERA5 surface wind speed climatologies over Europe with observations from the HadISD dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 4864–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, G. Reliability of ERA5 Reanalysis Data for Wind Resource Assessment: A Comparison against Tall Towers. Energies 2021, 14, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, S.; Keller, J.D.; Wahl, S. Evaluation of wind speed estimates in reanalyses for wind energy applications. Adv. Sci. Res. 2021, 18, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.J. A gridded daily observation dataset over China region and comparison with the other datasets. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 1102–1111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.; Giorgi, F.; Chen, D. Changes of effective temperature and cold/hot days in late decades over China based on a high resolution gridded observation dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37 (Suppl. 1), 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.; Lister, D.; Hulme, M.; Makin, I. A highresolution data set of surface climate over global land areas. Clim. Res. 2002, 21, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, M.; Erfanian, A.; Wang, G. Modeling the dynamic vegetation–climate system over China using a coupled regional model. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 6027–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Gao, S.; Cui, Y. The optimal wind speed product selection for wind energy assessment under multi-factor constraints. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2025, 24, 100883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Guo, J.; Bao, Z.; Pan, Z.; Hou, B. Projection of wind energy potential over Northern China using a regional climate model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Y.; Xu, Y. Evaluation and projection of surface wind speed over China based on CMIP6 GCMs. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, W.; Ye, T. Dataset of trend-preserving bias-corrected daily temperature, precipitation and wind from NEX-GDDP and CMIP5 over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Data Brief 2020, 31, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, S.; Deng, H.; Tao, J.; Hua, W. Influence of Model Resolution on Wind Energy Simulations over Tibetan Plateau Using CMIP6 HighResMIP. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, F.; Xiong, L. Nanjing Normal University. 2023. Global Basic Landform Units Datasets (2023), Version 1. Yangtze River Delta Science Data Center, National Earth System Science Data Sharing Infrastructure, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. Available online: https://www.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=28050973505297 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Xiong, L.; Li, S.; Tang, G.; Strobl, J. Geomorphometry and terrain analysis: Data, methods, platforms and applications. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 233, 104191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Tang, G.; Yang, X.; Li, F. Geomorphology-oriented digital terrain analysis: Progress and perspectives. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 456–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiong, L.; Tang, G.; Strobl, J. Deep learning-based approach for landform classification from integrated data sources of digital elevation model and imagery. Geomorphology 2020, 354, 107045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, X.; Na, J.; Liu, K.; Jia, Y.; Xiong, L. Regional topographic classification in the North Shaanxi Loess Plateau based on catchment boundary profiles. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2017, 41, 302–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Rozum, I.; et al. ERA5 Hourly Data on Single Levels from 1979 to Present. In Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). Available online: https://oneclimate.acdguide.cloud.edu.au/records/4nkjk-0r931 (accessed on 14 June 2018).
- Uppala, S.M.; Kållberg, P.; Simmons, A.; Andrae, U.; Bechtold, V.D.C.; Fiorino, M.; Gibson, J.; Haseler, J.; Hernandez, A.; Kelly, G.; et al. The ERA-40 re-analysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 2961–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, P.; Rutyna, I.; Baczyński, D.; Kopyt, M. Evaluation Metrics for Wind Power Forecasts: A Comprehensive Review and Statistical Analysis of Errors. Energies 2022, 15, 9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Lv, S.X. Forecasting energy consumption and wind power generation using deep echo state network. Renew. Energy 2020, 154, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, G.A.; Gandhi, P.R. Statistical and ANN based prediction of wind power with uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 23–25 April 2019; pp. 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Zhao, X.; Tseng, M.L.; Tan, R.R. Short-term wind power forecasting based on support vector machine with improved dragonfly algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei Pirooz, A.A.; Flay, R.G.J. Comparison of Speed-Up Over Hills Derived from Wind-Tunnel Experiments, Wind-Loading Standards, and Numerical Modelling. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2018, 168, 213–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.L.; Li, J.W.; Flay, R.G.J. Field measurements and wind tunnel investigation of wind characteristics at a bridge site in a Y-shaped valley. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2020, 202, 104199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lystad, T.M.; Fenerci, A.; Øiseth, O. Evaluation of mast measurements and wind tunnel terrain models to describe spatially variable wind field characteristics for long-span bridge design. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 179, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdier, B. Evaluation of ERA5, MERRA-2, COSMO-REA6, NEWA and AROME to simulate wind power production over France. Adv. Sci. Res. 2020, 17, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, I.; Zadra, A.; Wedi, N. Impact of Orographic Drag on Forecast Skill. n.d. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/en/newsletter/150/meteorology/impact-orographic-drag-forecast-skill (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Jiménez, P.A.; Dudhia, J. Improving the representation of resolved and unresolved topographic effects on surface wind in the WRF model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-G.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kang, Y.-H. Comparative Evaluation of the Third-Generation Reanalysis Data for Wind Resource Assessment of the Southwestern Offshore in South Korea. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waewsak, J.; Chancham, C.; Chiwamongkhonkarn, S.; Gagnon, Y. Wind Resource Assessment of the Southernmost Region of Thailand Using Atmospheric and Computational Fluid Dynamics Wind Flow Modeling. Energies 2019, 12, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minola, L.; Zhang, F.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Safaei Pirooz, A.A.; Flay, R.G.J.; Hersbach, H.; Chen, D. Near-surface mean and gust wind speeds in ERA5 across Sweden: Towards an improved gust parametrization. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 887–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, X.J.; Shen, Y.; Xu, C.H.; Shi, Y.; Giorgi, F. A daily temperature dataset over China and its application in validating a RCM simulation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, P.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L. Applicability Assessment of ERA5 Surface Wind Speed Data Across Different Landforms in China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080956
Zuo P, Chen X, Zhu L. Applicability Assessment of ERA5 Surface Wind Speed Data Across Different Landforms in China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(8):956. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080956
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Peng, Xiangdong Chen, and Lihua Zhu. 2025. "Applicability Assessment of ERA5 Surface Wind Speed Data Across Different Landforms in China" Atmosphere 16, no. 8: 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080956
APA StyleZuo, P., Chen, X., & Zhu, L. (2025). Applicability Assessment of ERA5 Surface Wind Speed Data Across Different Landforms in China. Atmosphere, 16(8), 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080956





