Tracking Long-Term Ozone Pollution Dynamics in Chinese Cities with Meteorological and Emission Attribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
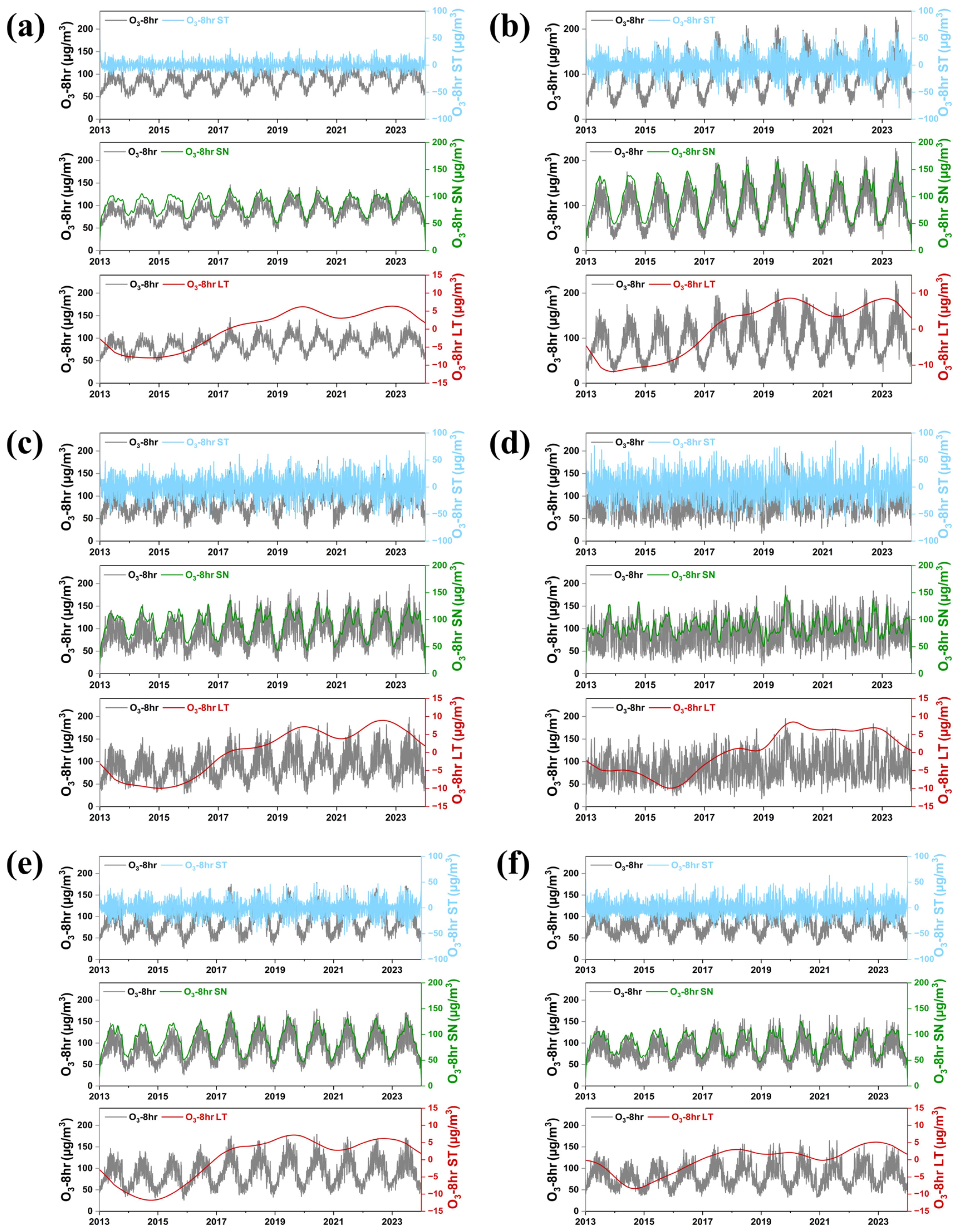
2.2. Separation of Temporal Scales Using the KZ Filter
2.3. Meteorological Adjustment Utilizing Time Series Decomposition
2.4. Long-Term Trends of Local and Non-Local Emissions
3. Results
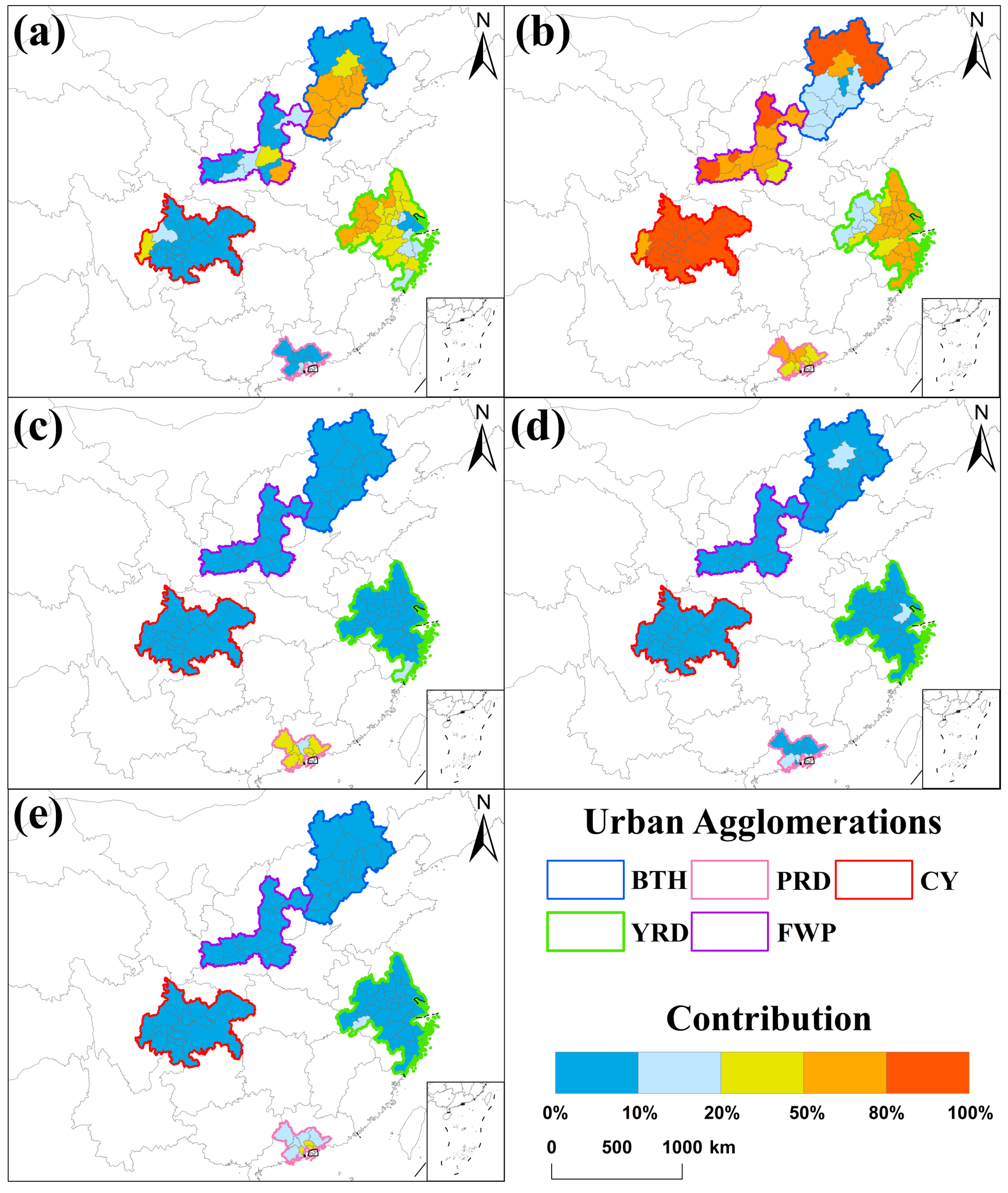
3.1. Spatial and Seasonal Variability of O3-8h Concentrations in China
3.2. Temporal Decomposition of O3-8h Concentrations
3.3. Contribution of Meteorological Factors to O₃-8h
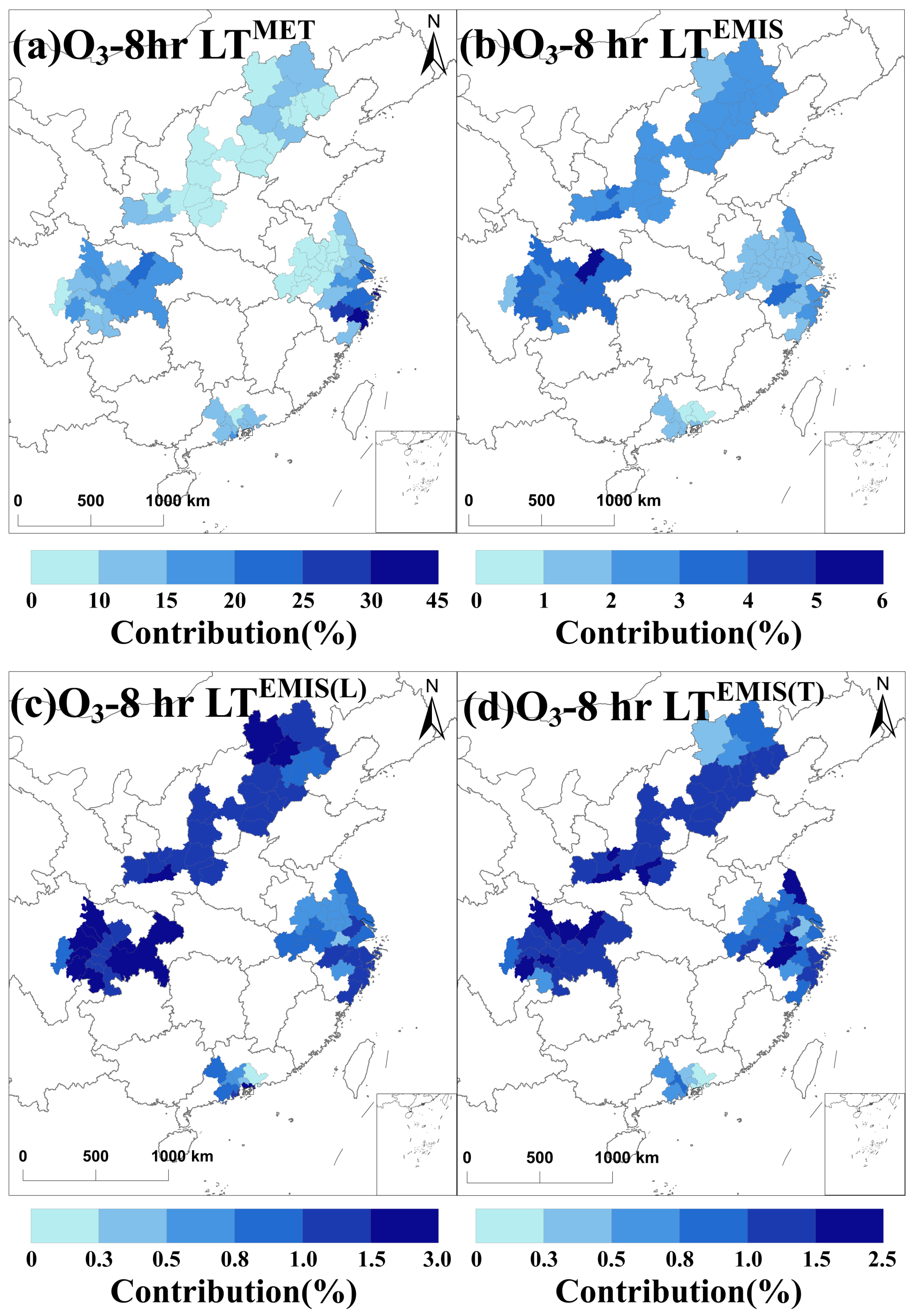
3.4. Quantitative Analysis of Meteorological and Emission Contributions to Long-Term O3-8h Trends
4. Discussion
4.1. Regional Variations in the Spatiotemporal Distribution of O3-8h in China
4.2. Interaction Between Meteorological and Emission Factors
4.3. Emission Source Apportionment and Control Strategy Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zong, L.; Wang, M.; Xie, Z.; Ho, H.C.; Gao, M.; et al. Substantially Underestimated Global Health Risks of Current Ozone Pollution. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, H. Global Air Quality and Pollution. Science 2003, 302, 1716–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Zhu, J.; Shah, V.; Shen, L.; Bates, K.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, S. A Two-Pollutant Strategy for Improving Ozone and Particulate Air Quality in China. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Council. Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan. 2013. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2013-09/12/content_2486773.htm (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Wang, Y.; Wild, O.; Chen, H.; Gao, M.; Wu, Q.; Qi, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. Acute and Chronic Health Impacts of PM2.5 in China and the Influence of Interannual Meteorological Variability. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 229, 117397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Council. Three-Year Action Plan for Winning the Blue Sky Defense Battle. 2018. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2018-07/03/content_5303158.htm (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Li, G.; Bei, N.; Cao, J.; Wu, J.; Long, X.; Feng, T.; Dai, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Tie, X. Widespread and Persistent Ozone Pollution in Eastern China during the Non-Winter Season of 2015: Observations and Source Attributions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2759–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T. Worsening Urban Ozone Pollution in China from 2013 to 2017–Part 2: The Effects of Emission Changes and Implications for Multi-Pollutant Control. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6323–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavinezhad, S.; Choi, Y.; Pouyaei, A.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Nelson, D.L. A Comprehensive Investigation of Surface Ozone Pollution in China, 2015–2019: Separating the Contributions from Meteorology and Precursor Emissions. Atmos. Res. 2021, 257, 105599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Wang, T.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, P.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Yuan, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, S. Influence of Atmospheric Particulate Matter on Ozone in Nanjing, China: Observational Study and Mechanistic Analysis. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.; Song, T.; Gong, Z.; Ji, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Tang, G.; Huo, Y.; et al. Contrasting Trends of PM2.5 and Surface-Ozone Concentrations in China from 2013 to 2017. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Zhang, T.; Kinney, P.L.; Henneman, L.R.F. Fine Particulate Matter and Ozone Variability with Regional and Local Meteorology in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 338, 120793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R. A Review of Current Knowledge Concerning PM2. 5 Chemical Composition, Aerosol Optical Properties and Their Relationships across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9485–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Bates, K.H. Anthropogenic drivers of 2013–2017 trends in summer surface ozone in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Hong, J.; Zhang, L.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Severe Surface Ozone Pollution in China: A Global Perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N.; Noone, K. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change. Phys. Today 1998, 51, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Guo, M.; Cheng, M.; Gu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, X.; Chai, F. Prospect of China’s Ambient Air Quality Standards. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Shen, L.; Lu, X.; De Smedt, I.; Liao, H. Increases in Surface Ozone Pollution in China from 2013 to 2019: Anthropogenic and Meteorological Influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11423–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Crutzen, P.J. Influences of Cloud Photochemical Processes on Tropospheric Ozone. Nature 1990, 343, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Liao, H.; Fu, Y. Quantifying the Anthropogenic and Meteorological Influences on Summertime Surface Ozone in China over 2012–2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, K.; Zhu, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H. Severe Air Pollution Events Not Avoided by Reduced Anthropogenic Activities during COVID-19 Outbreak. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 158, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Wang, Z.; Lin, W.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Ji, D.; Ma, Z. Air Pollution over the North China Plain and Its Implication of Regional Transport: A New Sight from the Observed Evidences. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Geng, C.; Li, L.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, B.; Yang, W.; Wang, X. Meteorological Impacts on Surface Ozone: A Case Study Based on Kolmogorov–Zurbenko Filtering and Multiple Linear Regression. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1081453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.L.; Beringer, J.; Nicholls, N.; Hyndman, R.J.; Tapper, N.J. Quantifying the Influence of Local Meteorology on Air Quality Using Generalized Additive Models. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Liu, S.C. Contributions of Meteorology and Anthropogenic Emissions to the Trends in Winter PM2.5 in Eastern China 2013–2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 11945–11955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, G.; Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; He, K.; Zhang, Q. Separating emission and meteorological contributions to long-term PM₂.₅ trends over eastern China during 2000–2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9475–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Niu, J.; Wang, Z.; Pan, X.; Su, F.; Yao, D.; Zhu, M.; Yan, J.; Yan, J.; Yao, G. A Comprehensive Investigation of PM2.5 in the Huaihe River Basin, China: Separating the Contributions from Meteorology and Emission Reductions. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Lin, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, X. Driving Force of Meteorology and Emissions on PM2.5 Concentration in Major Urban Agglomerations in China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; An, J. Quantitative Impacts of Meteorology and Emissions on the Long-Term Trend of O3 in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), China from 2015 to 2022. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 149, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Dai, Q.; Fan, W.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; Feng, Y. Impacts of Meteorology and Precursor Emission Change on O3 Variation in Tianjin, China from 2015 to 2021. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 126, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Geng, G.; Xue, T.; Liu, S.; Cai, C.; He, K.; Zhang, Q. Tracking PM2.5 and O3 Pollution and the Related Health Burden in China 2013–2020. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6922–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, G.; Xiao, Q.; Meng, X.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, T. Estimating Spatiotemporal Variation in Ambient Ozone Exposure during 2013–2017 Using a Data-Fusion Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14877–14888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskridge, R.E.; Ku, J.Y.; Rao, S.T.; Porter, P.S.; Zurbenko, I.G. Separating Different Scales of Motion in Time Series of Meteorological Variables. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1997, 78, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.T.; Zurbenko, I.G. Detecting and Tracking Changes in Ozone Air Quality. Air Waste 1994, 44, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Park, D.-S.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Youn, D.; Lim, Y.B.; Kim, Y. Effects of Meteorology and Emissions on Urban Air Quality: A Quantitative Statistical Approach to Long-Term Records (1999–2016) in Seoul, South Korea. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16121–16137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo–Castaneda, D.M.; Calesso Teixeira, E.; Norte Pereira, F. Time–Series Analysis of Surface Ozone and Nitrogen Oxides Concentrations in an Urban Area at Brazil. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Cheng, X.; Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Bai, Z.; Xu, H.; Azzi, M.; Zhao, H. Meteorological Influences on PM2.5 Variation in China Using a Hybrid Model of Machine Learning and the Kolmogorov-Zurbenko Filter. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, B.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Mousavinezhad, S.; Lops, Y.; Pouyaei, A.; Choi, Y. Contributions of Meteorology to Ozone Variations: Application of Deep Learning and the Kolmogorov-Zurbenko Filter. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, T.; Bai, Y.; Kong, S.; Zheng, H.; Hu, W.; Ma, X.; Xiong, J. Meteorology Impact on PM2.5 Change over a Receptor Region in the Regional Transport of Air Pollutants: Observational Study of Recent Emission Reductions in Central China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 3579–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Kong, S.; Seo, J.; Yan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Harrison, R.M. Achievements and Challenges in Improving Air Quality in China: Analysis of the Long-Term Trends from 2014 to 2022. Environ. Int. 2024, 183, 108361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Luo, H.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, C.; Lin, X.; Louie, P.K.K.; Chen, D.; Bian, Y. Quantitative Impacts of Meteorology and Precursor Emission Changes on the Long-Term Trend of Ambient Ozone over the Pearl River Delta, China, and Implications for Ozone Control Strategy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 12901–12916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Lu, T.; Bao, M.; Deng, X.; Hu, X. Pollution Patterns and Their Meteorological Analysis All over China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Xie, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Xu, M.; Chen, B.; Li, S.; Zhuang, B.; Li, M. Surface Ozone in the Yangtze River Delta, China: A Synthesis of Basic Features, Meteorological Driving Factors, and Health Impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J. Synthetically Impacts of the Topography and Typhoon Periphery on the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Structure and Special Regional Pollution Pattern of O3 in North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 330, 120566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Qu, Y.; Wu, H.; Fan, J.; Shao, M.; Xie, M. Deciphering the Seasonal Dynamics of Multifaceted Aerosol-Ozone Interplay: Implications for Air Quality Management in Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduwais, A.K.; Dasari, H.P.; Karumuri, R.K.; Gandham, H.; Koteswararao, V.; Saharwardi, M.S.; Ashok, K.; Hoteit, I. Spatiotemporal Variability of Surface Ozone and Associated Meteorological Conditions over the Arabian Peninsula. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 102210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, B.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Fu, T.-M.; Zhang, Q. Interannual and decadal changes in tropospheric ozone in China and the associated chemistry-climate interactions: A review. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences 2019, 36, 1087–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabunshchik, V.; Nikiforova, A.; Lineva, N.; Drygval, P.; Gorbunov, R.; Gorbunova, T.; Kerimov, I.; Pham, C.N.; Bratanov, N.; Kiseleva, M. The Dynamics of Air Pollution in the Southwestern Part of the Caspian Sea Basin (Based on the Analysis of Sentinel-5 Satellite Data Utilizing the Google Earth Engine Cloud-Computing Platform). Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, B.; Liang, Y.; Hu, T.; Liu, R. Impacts of Meteorological Conditions on Autumn Surface Ozone During 2014–2020 in the Pearl River Delta, China. Earth Space Sci. 2023, 10, e2022EA002742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Su, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Liao, H. Ozone Pollution in China Affected by Climate Change in a Carbon Neutral Future as Predicted by a Process-Based Interpretable Machine Learning Method. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL109520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Ding, A. Understanding Ozone Pollution in the Yangtze River Delta of Eastern China from the Perspective of Diurnal Cycles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Lin, W.; Zhao, H.; Ren, S.; Zhou, G.; Chen, J.; Xu, X. First Long-Term Surface Ozone Variations at an Agricultural Site in the North China Plain: Evolution under Changing Meteorology and Emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y. Influence of the West Pacific Subtropical High on Surface Ozone Daily Variability in Summertime over Eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Wang, P.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H. Drivers of Alleviated PM2.5 and O3 Concentrations in China from 2013 to 2020. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 197, 107110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ma, M.; Liu, M.; Meng, F.; Fu, P.; Xing, H.; Bi, J.; Zheng, Z.; Lv, Y. Quantitative Estimation of the Impacts of Precursor Emissions on Surface O3 and PM2.5 Collaborative Pollution in Three Typical Regions of China via Multi-Task Learning. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
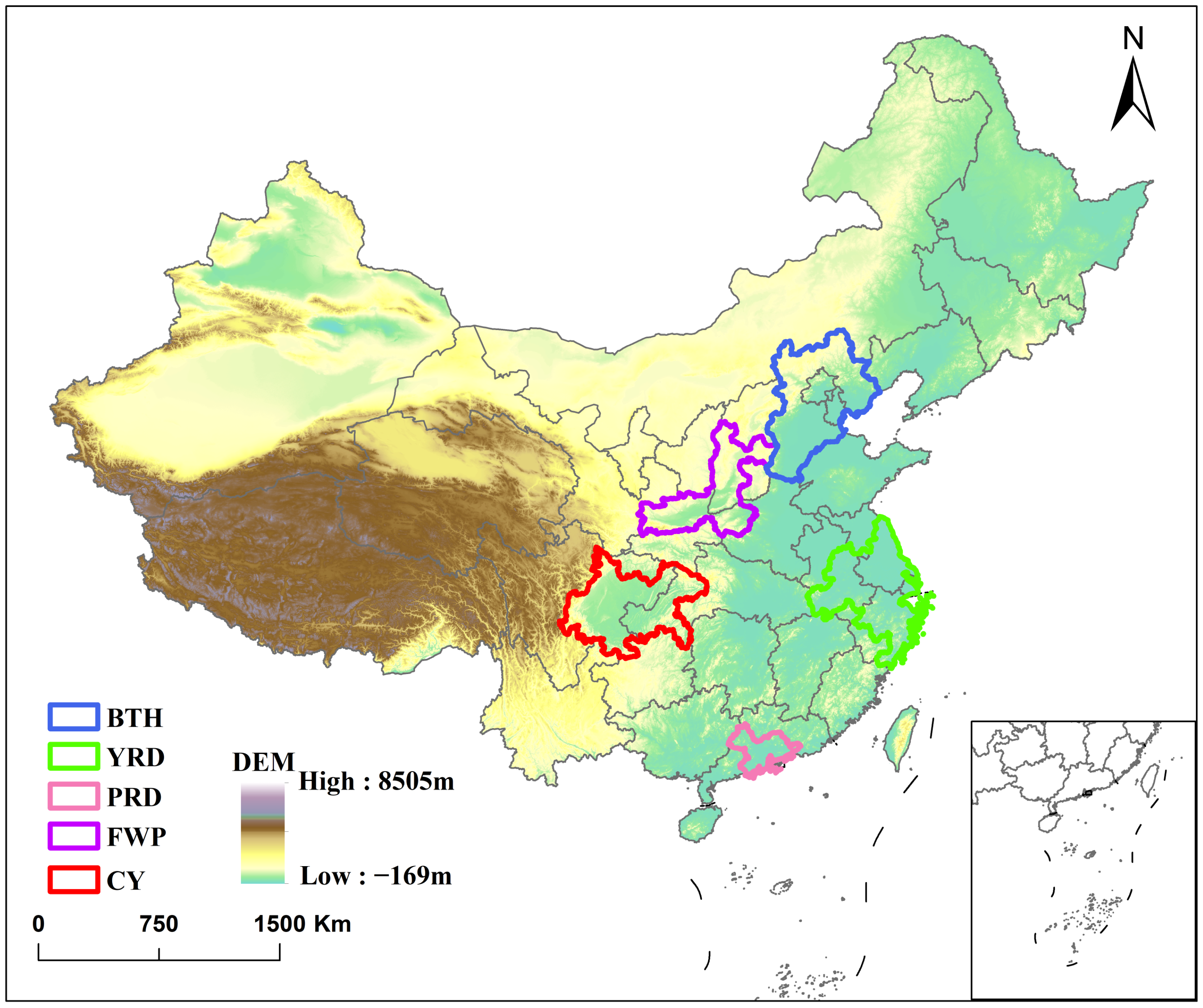
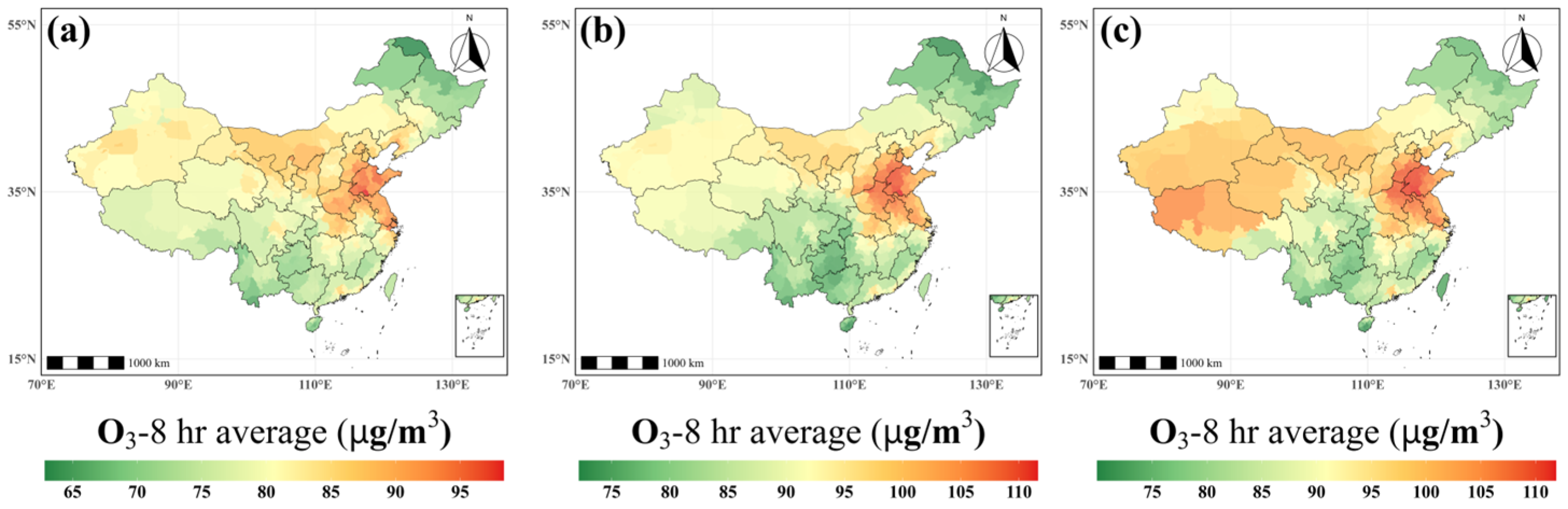
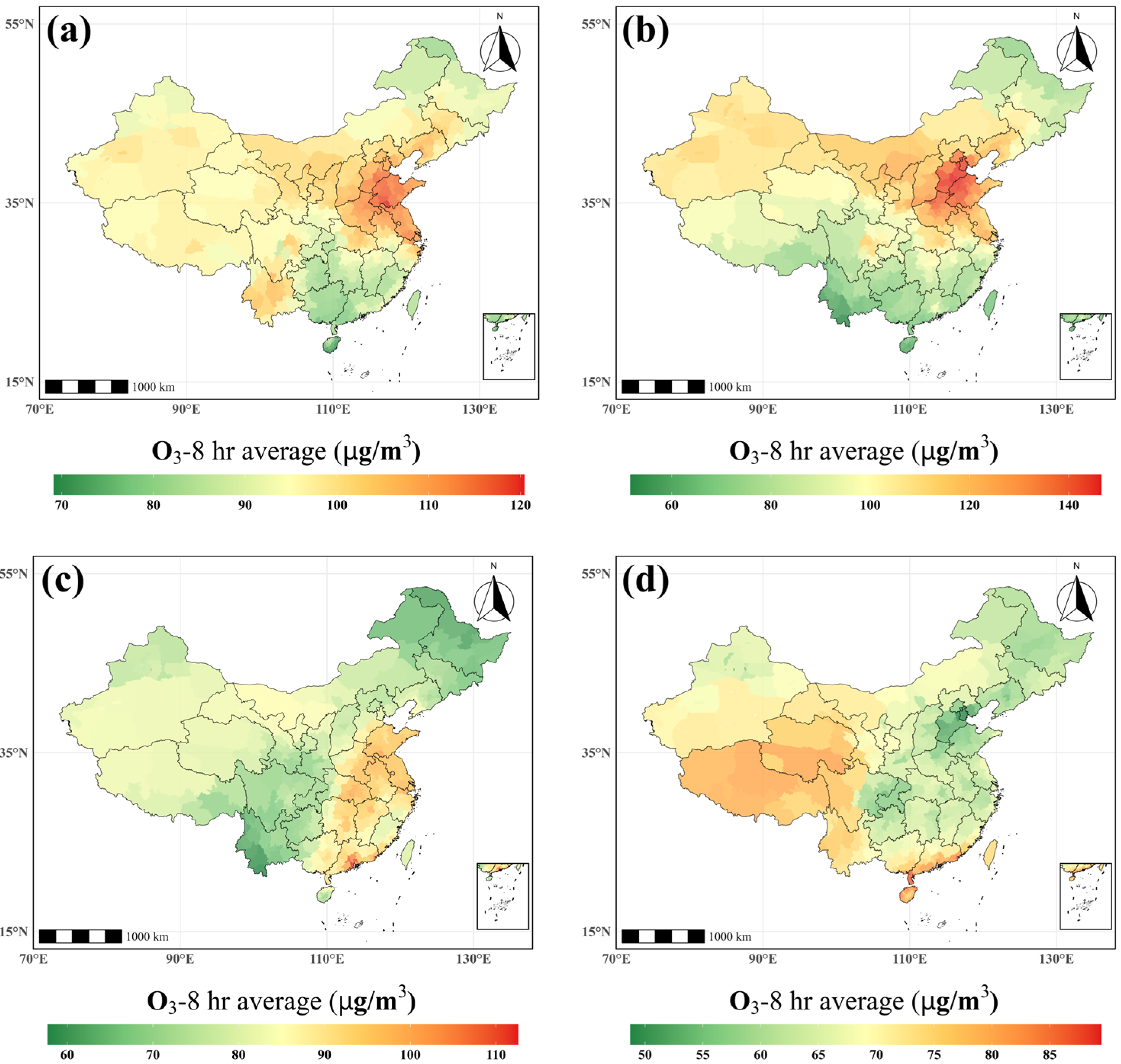
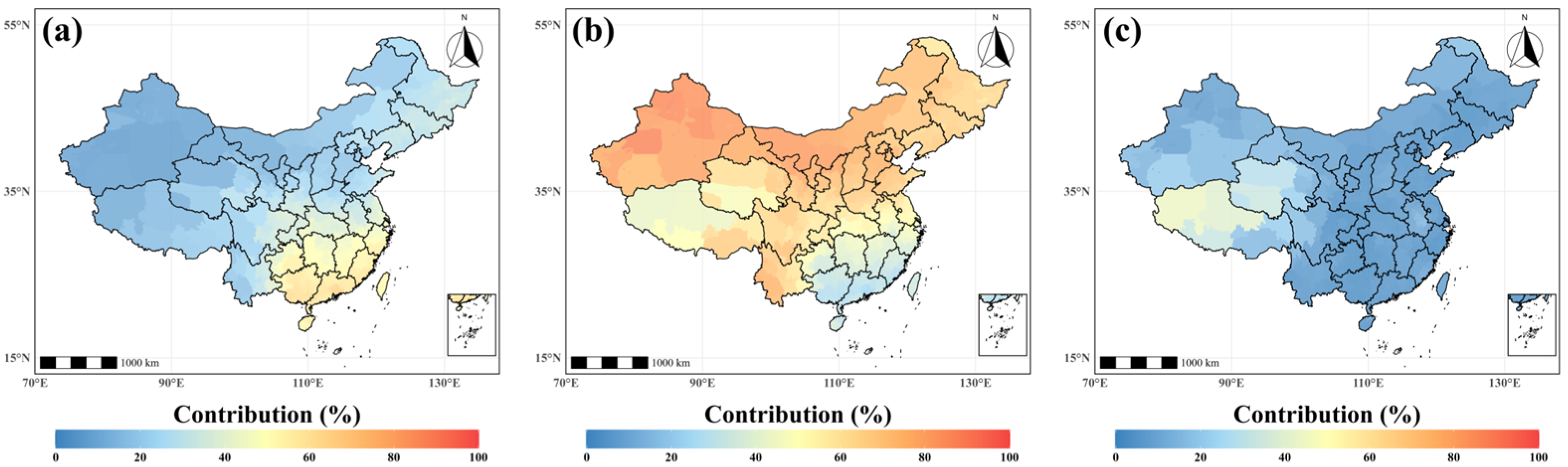


| Variable | Source | Spatial Res. | Temporal Res. | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3-8h | TAP (1) | 0.1° × 0.1° | Daily | |
| T | ERA5 (2) | 0.25° × 0.25° | Hourly | |
| d2m | ERA5 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Hourly | For RH calc. |
| PS | ERA5 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Hourly | |
| UVB | ERA5 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Hourly | |
| u10, v10 | ERA5 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Hourly | For WS/WD calc. |
| WS | Calculated (3) | N/A | Daily | Deriv. from u10 and v10 |
| WD | Calculated | N/A | Daily | |
| RH | Calculated | N/A | Daily | Deriv. from T and d2m |
| Region | Validation R2 | Validation MSE | Test R2 | Test MSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTH | 0.987 | 16.2 | 0.987 | 17.6 |
| YRD | 0.976 | 14.7 | 0.974 | 15.2 |
| PRD | 0.962 | 13.5 | 0.964 | 12.0 |
| FWP | 0.981 | 13.0 | 0.982 | 12.5 |
| CY | 0.984 | 7.1 | 0.984 | 6.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Wu, T.; Li, P.; Zhou, P. Tracking Long-Term Ozone Pollution Dynamics in Chinese Cities with Meteorological and Emission Attribution. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070768
Li H, Liu X, Liu Z, Li M, Wu T, Li P, Zhou P. Tracking Long-Term Ozone Pollution Dynamics in Chinese Cities with Meteorological and Emission Attribution. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):768. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070768
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongrui, Xiaoyong Liu, Zijian Liu, Mengyang Li, Tong Wu, Peicheng Li, and Peng Zhou. 2025. "Tracking Long-Term Ozone Pollution Dynamics in Chinese Cities with Meteorological and Emission Attribution" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070768
APA StyleLi, H., Liu, X., Liu, Z., Li, M., Wu, T., Li, P., & Zhou, P. (2025). Tracking Long-Term Ozone Pollution Dynamics in Chinese Cities with Meteorological and Emission Attribution. Atmosphere, 16(7), 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070768






