Estimation of High Spatial Resolution CO2 Concentration in China from 2010 to 2022 Based on Multi-Source Carbon Satellite Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. XCO2 Data
2.1.1. GOSAT Satellite Data
2.1.2. OCO-2 Satellite Data
2.1.3. CarbonTracker Model Simulation Data
2.2. TCCON Site Observation Data
2.3. Auxiliary Data
2.4. Methodology
2.4.1. Prior CO2 Profile Adjustment
2.4.2. Grid Integration
2.4.3. Machine Learning-Based Ensemble Model for XCO2 Estimation (MLE)
3. Results and Discussion
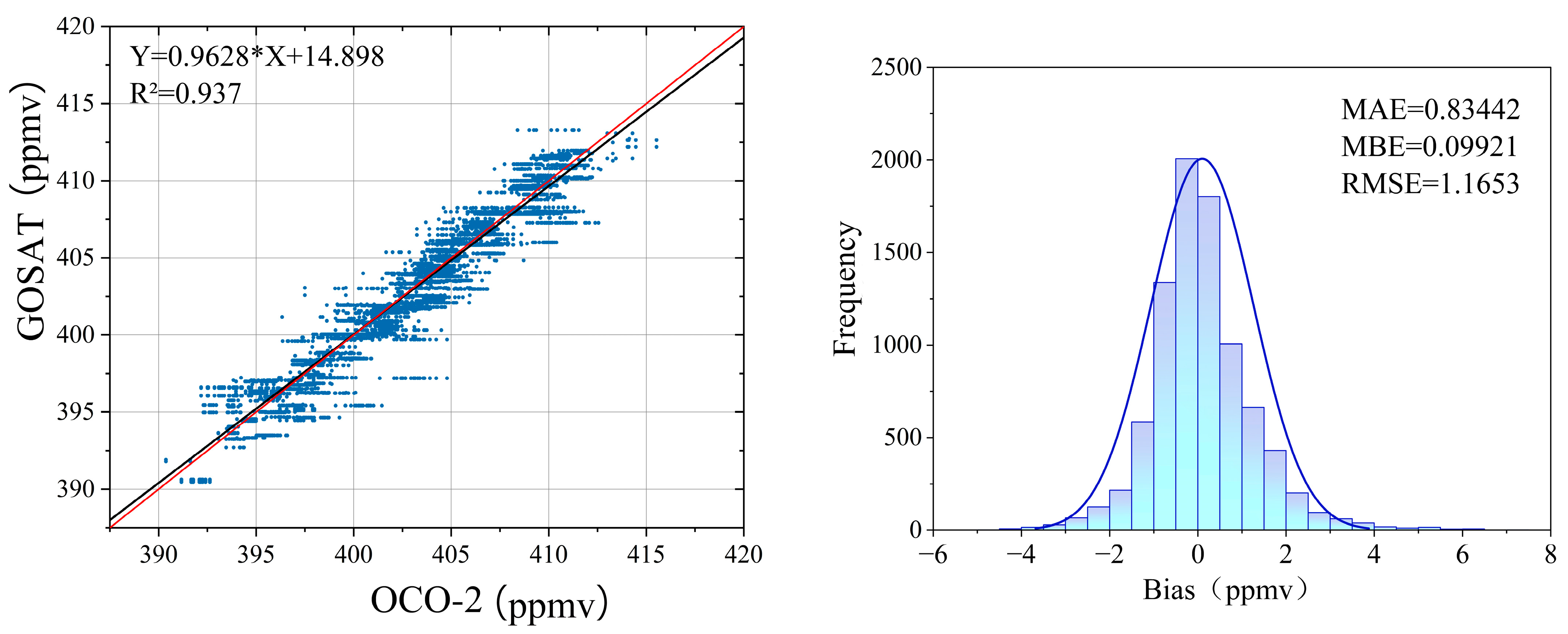
3.1. Prior CO2 Profile Adjustment
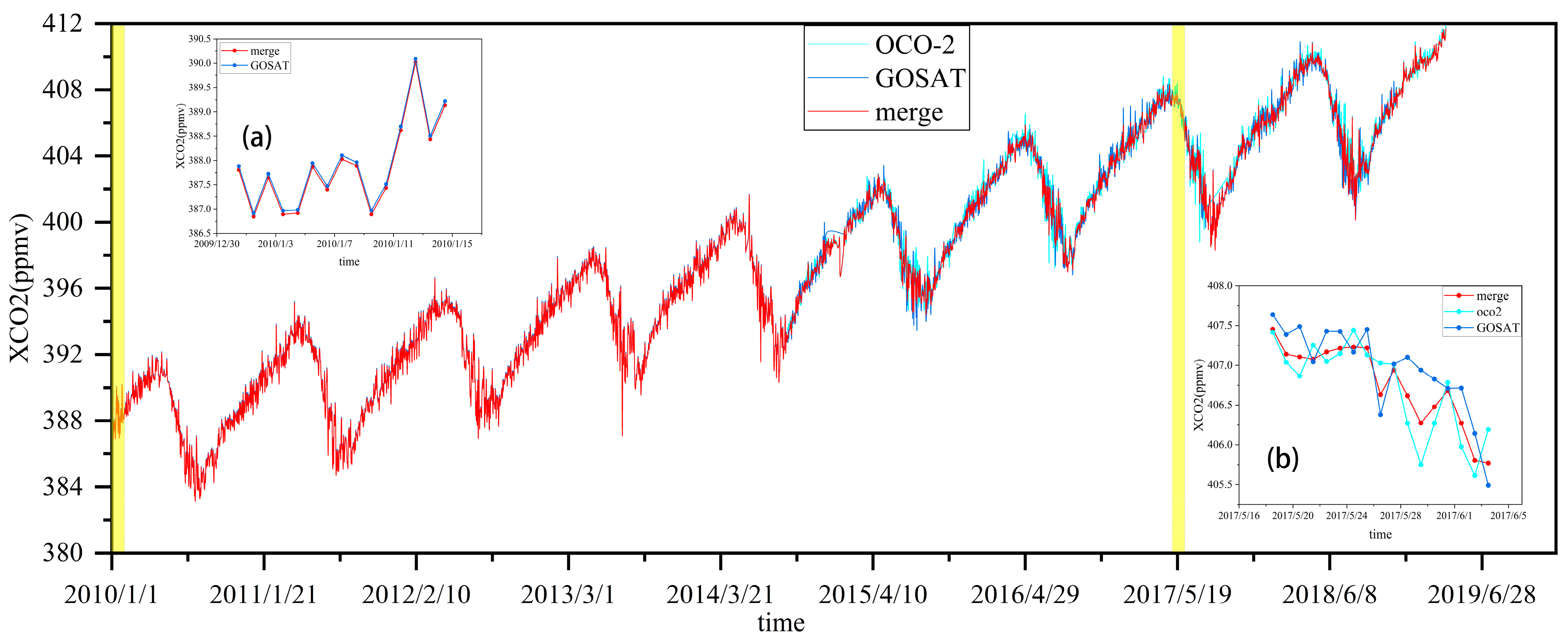
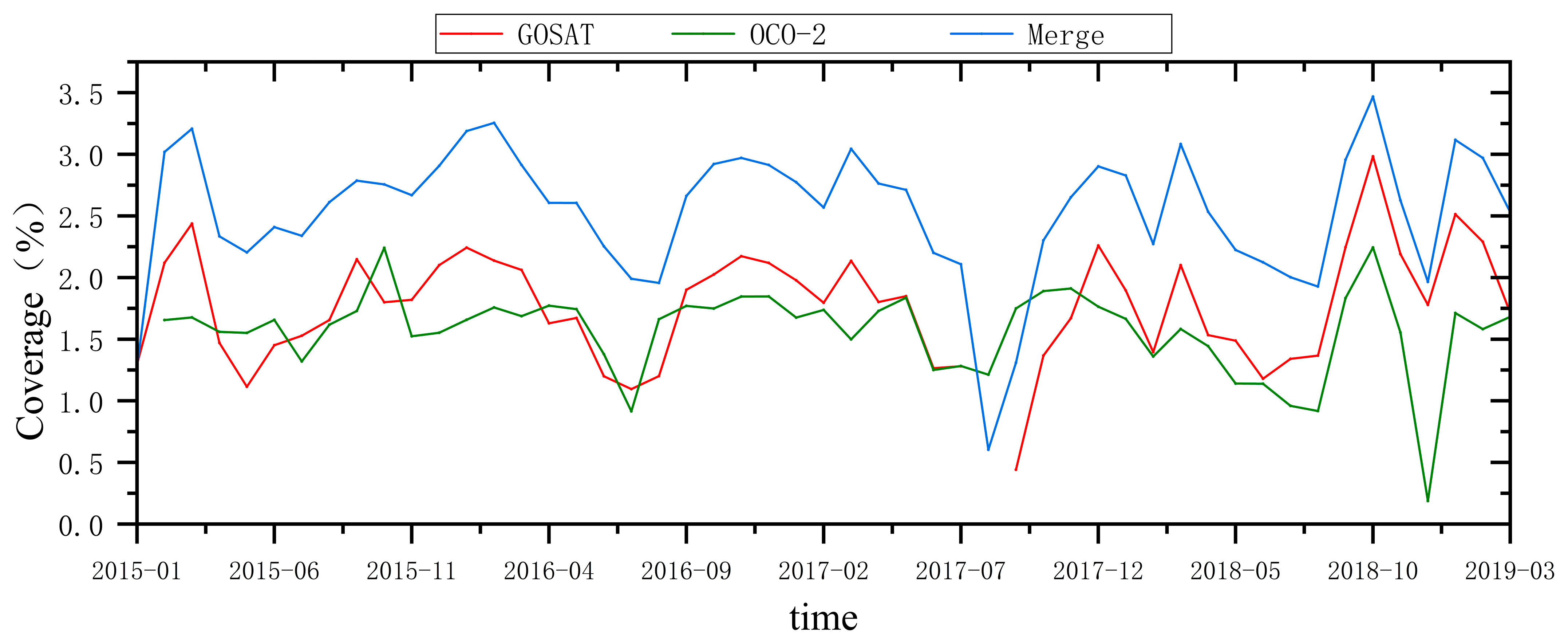
3.2. Grid Integration
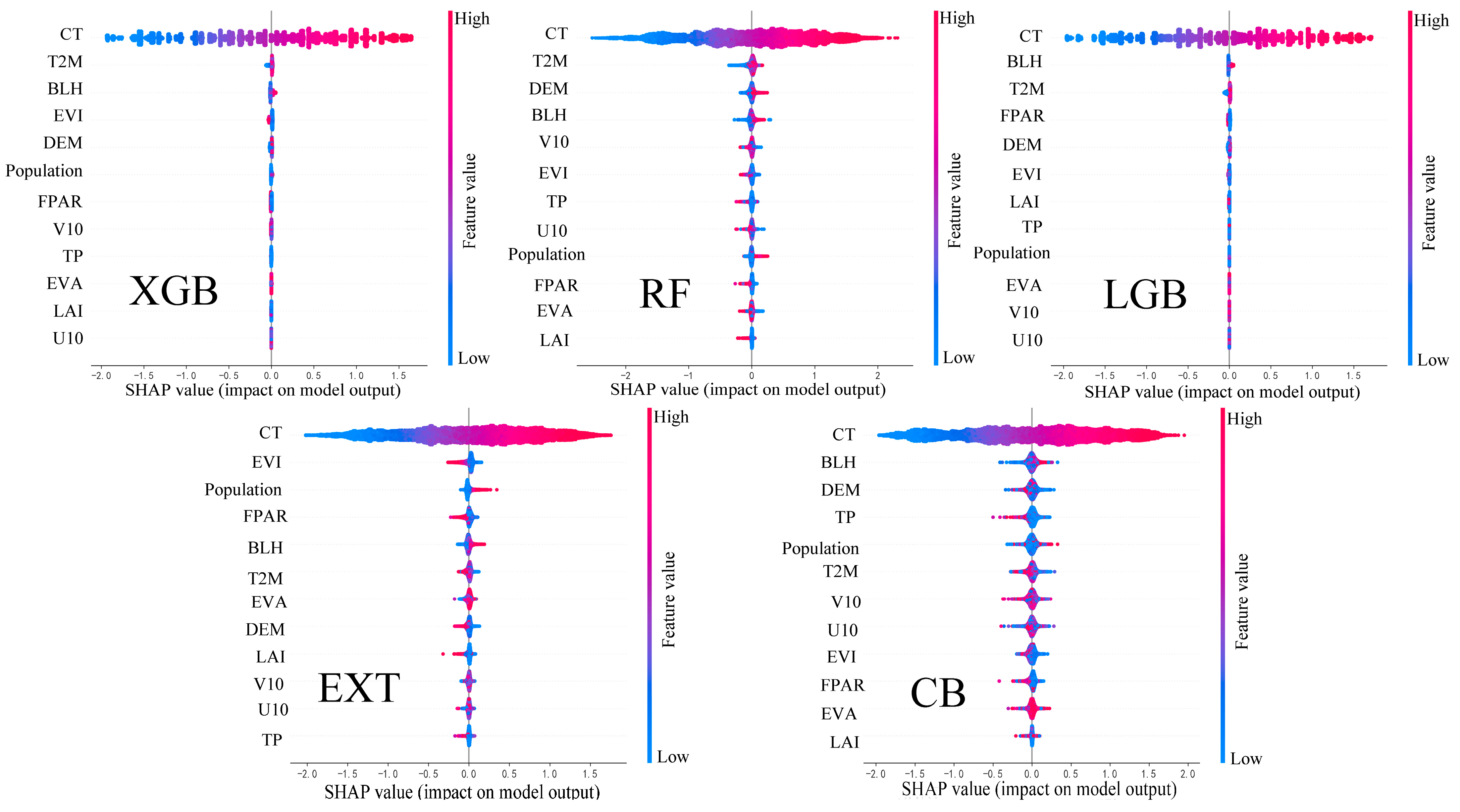
3.3. Variable Importance Estimation
3.4. Validation of the Reconstructed XCO2
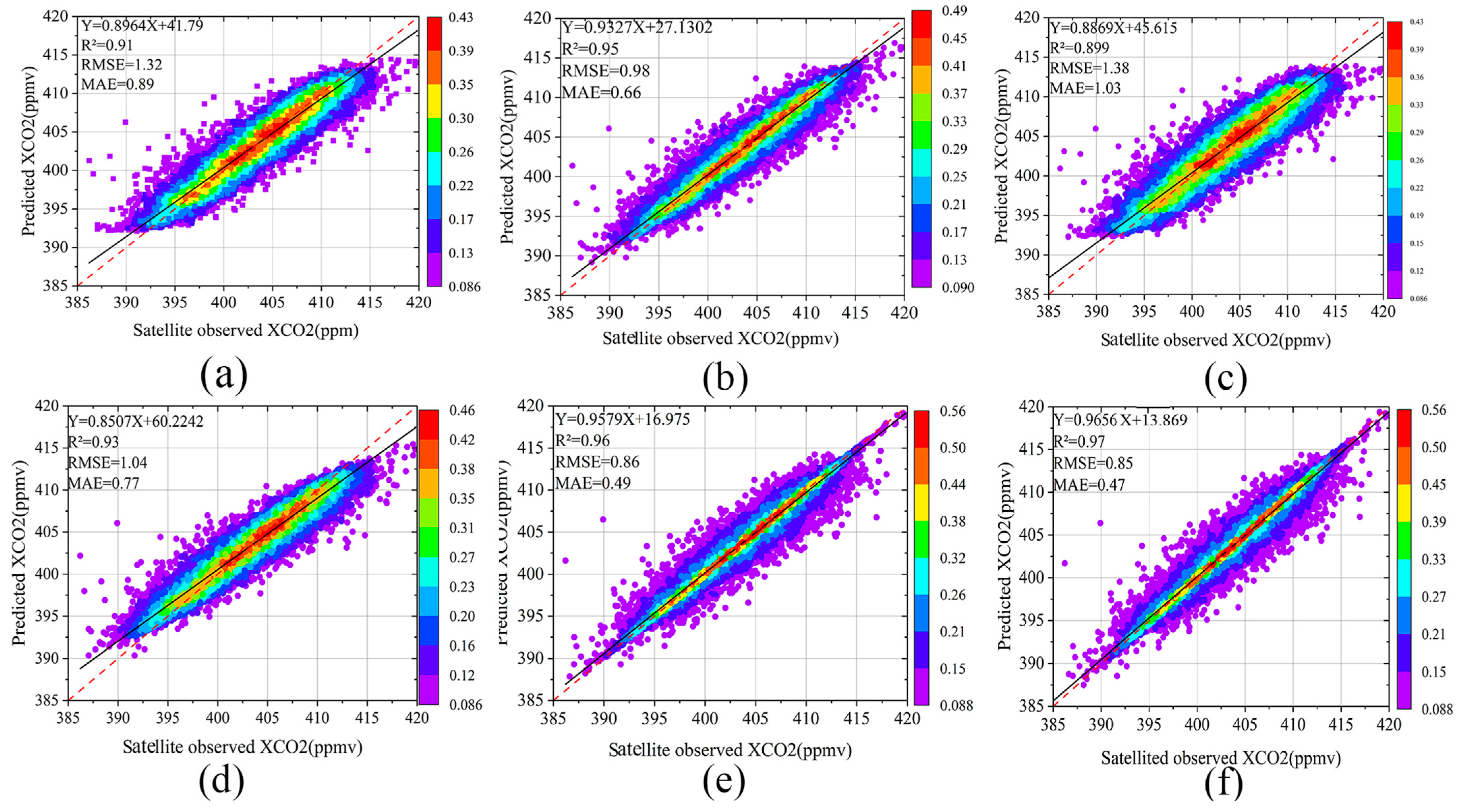
3.4.1. Performance Validation of the MLSM-XE Model
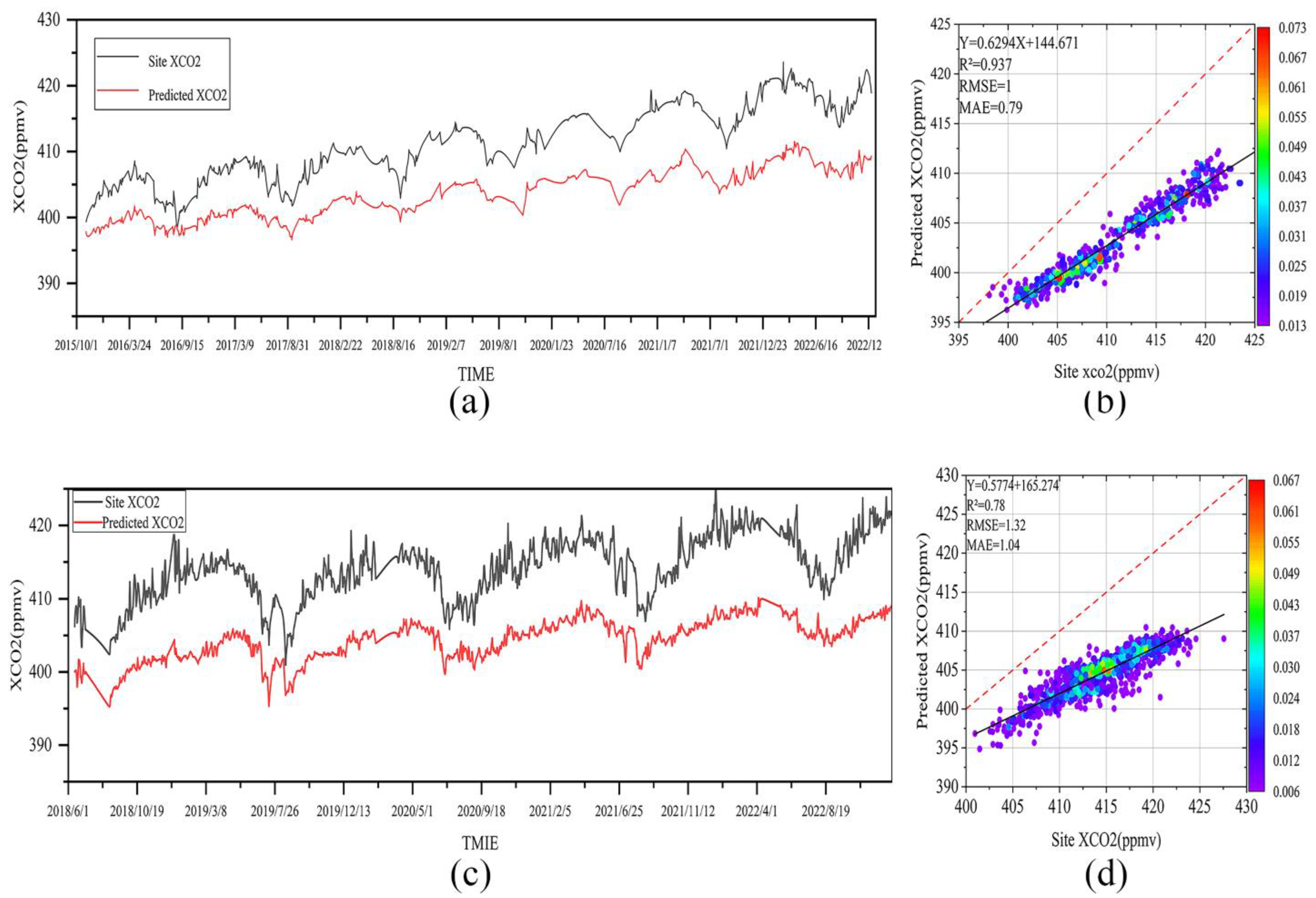
3.4.2. Validation with Ground-Based Monitoring Stations
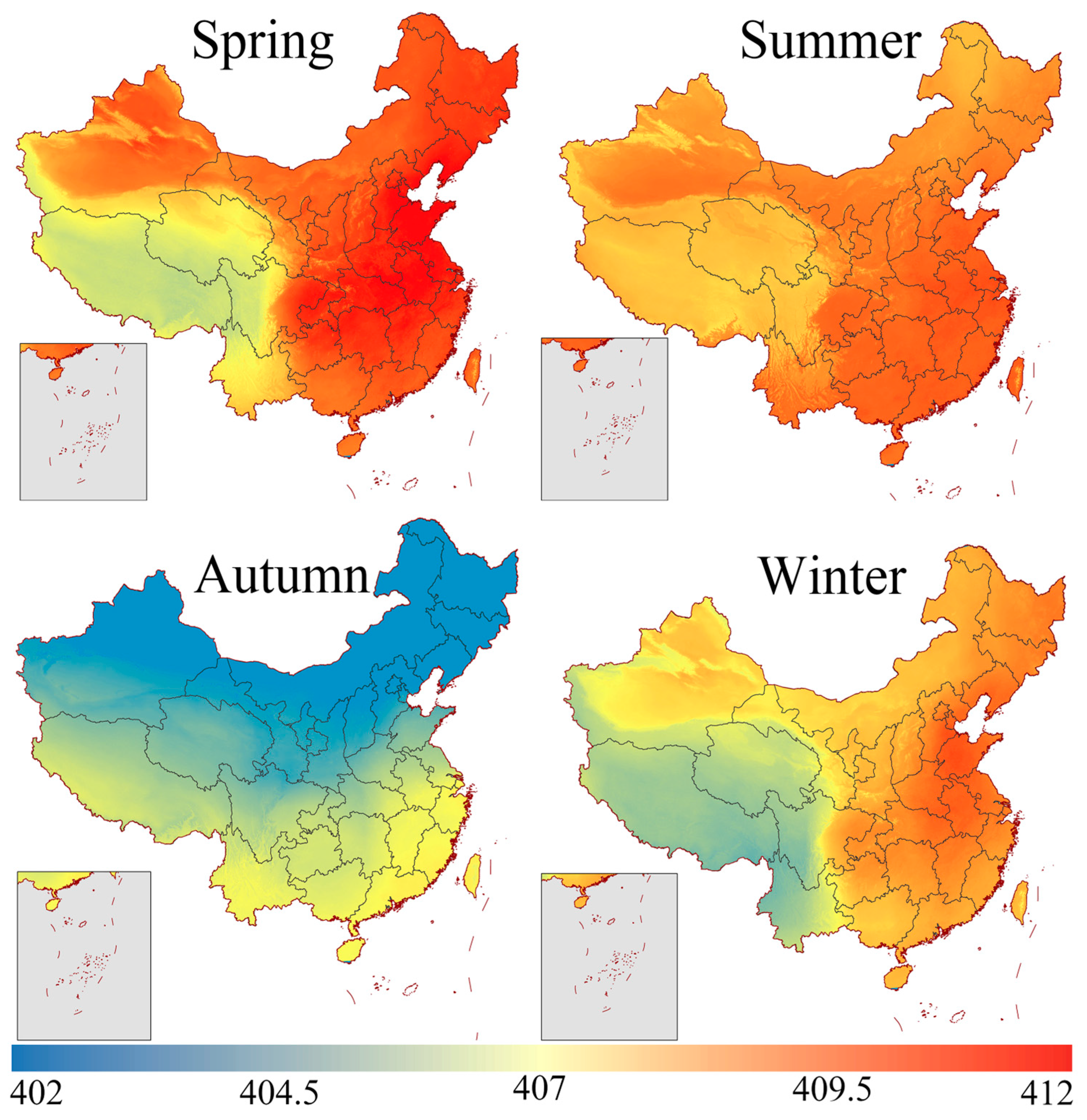
3.5. Spatial Distribution of CO2 in China
3.6. Long-Term Variation Characteristics of CO2 Concentrations in China
3.7. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The XCO2 product data from the GOSAT and OCO-2 satellites were successfully integrated, resulting in a more complete overall time series. This effectively reduced the spatiotemporal data gaps caused by the limited observations from a single satellite, enhancing the data coverage.
- (2)
- A machine learning ensemble model for estimating regional XCO2 in China was successfully developed, achieving strong performance in sample-based cross-validation (R2 = 0.97, RMSE = 0.85 ppmv) and ground validation (R2 values of 0.93 and 0.78, with corresponding RMSEs of 1.00 ppmv and 1.32 ppmv).
- (3)
- The seasonal characteristics of XCO2 concentrations in China were revealed: the highest concentrations typically occurred in the spring, followed by a decrease in summer to the lowest values, gradually rising with seasonal changes and reaching a peak again in the following spring. As for annual variation, the XCO2 concentrations in China have been rising year by year, but air pollution control and energy-saving policies have slowed the upward trend of XCO2. The fluctuations in XCO2 concentrations from 2010 to 2022 reveal that China faces dual challenges of economic development and environmental protection in addressing climate change and carbon emission pressures. While rapid economic growth and urbanization have driven increasing energy demand, thereby exacerbating CO2 emissions, environmental protection policies and sustainable development initiatives have effectively slowed the rate of XCO2 concentration growth. Consequently, the annual variations in CO2 concentrations are influenced not only by natural factors but also profoundly shaped by socioeconomic factors, such as policy adjustments and industrial transformation. With the maturation of clean energy technologies and strengthened policy guidance, China’s CO2 concentrations are expected to trend toward a more stable and low-carbon trajectory.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AR5 Synthesis Report: Climate Change 2014—IPCC[EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/syr/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Wunch, D.W.P.O. A method for evaluating bias in global measurements of CO2 total columns from space. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 20899–20946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Gong, J.; Chen, J. Recent Progress in Numerical Atmospheric Modeling in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 938–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Shivadekar, S.; Chukkapalli, S.S.L.; Halem, M. Satellite data fusion of multiple observed XCO2 using compressive sensing. In Proceedings of the Signal Processing, Sensor/Information Fusion, and Target Recognition XXIX, Online, 27 April–8 May 2020; Volume 11423, pp. 219–231. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Liu, Z.; Shao, P.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Weng, L.; Wang, Y.; Di, L.; Xia, M. Study on high temporal and spatial resolution XCO2 concentration estimation based on carbon satellite data. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 47, 976–992. [Google Scholar]
- Siabi, Z.; Falahatkar, S.; Alavi, S.J. Spatial distribution of XCO2 using OCO-2 data in growing seasons. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jia, K.; Wei, X.; Xia, M.; Chen, Z.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Yuan, B.; Tao, G.; et al. High-spatiotemporal resolution mapping of spatiotemporally continuous atmospheric CO2 concentrations over the global continent. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girach, I.A.; Ponmalar, M.; Murugan, S.; Rahman, P.A.; Babu, S.S.; Ramachandran, R. Applicability of Machine Learning Model to Simulate Atmospheric CO2 Variability. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4107306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seamless Mapping of Long-Term (2010–2020) Daily Global XCO2 and XCH4 from the Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite (GOSAT), Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2 (OCO-2), and CAMS Global Greenhouse Gas Reanalysis (CAMS-EGG4) with a Spatiotemporally Self-Supervised Fusion Method[EB/OL]. Available online: https://essd.copernicus.org/articles/15/3597/2023/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- He, Q.; Ye, T.; Chen, X.; Dong, H.; Wang, W.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y. Full-coverage mapping high-resolution atmospheric CO2 concentrations in China from 2015 to 2020: Spatiotemporal variations and coupled trends with particulate pollution. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, G. Mapping contiguous XCO2 by machine learning and analyzing the spatio-temporal variation in China from 2003 to 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Study on Spatialization and Spatiotemporal Variation of Atmospheric XCO2 in China Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yokota, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Eguchi, N.; Ota, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Watanabe, H.; Maksyutov, S. Global Concentrations of CO2 and CH4 Retrieved from GOSAT: First Preliminary Results. SOLA 2009, 5, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldering, A.; O’Dell, C.W.; Wennberg, P.O.; Crisp, D.; Gunson, M.R.; Viatte, C.; Avis, C.; Braverman, A.; Castano, R.; Chang, A.; et al. The Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2: First 18 months of science data products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Gong, W.; Han, G.; Xiang, C. Comparison of Satellite-Observed XCO2 from GOSAT, OCO-2, and Ground-Based TCCON. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, N. Quality controls, bias, and seasonality of CO2 columns in the boreal forest with Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, Total Carbon Column Observing Network, and EM27/SUN measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 5033–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W.; Jacobson, A.R.; Sweeney, C.; Andrews, A.E.; Conway, T.J.; Masarie, K.; Miller, J.B.; Bruhwiler, L.M.P.; Pétron, G.; Hirsch, A.I.; et al. An atmospheric perspective on North American carbon dioxide exchange: CarbonTracker. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18925–18930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunch, D.; Toon, G.C.; Wennberg, P.O.; Wofsy, S.C.; Stephens, B.B.; Fischer, M.L.; Uchino, O.; Abshire, J.B.; Bernath, P.; Biraud, S.C.; et al. Calibration of the total carbon column observing network using aircraft profile data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyükçakir, B.; Mutlu, A.Y. Comparison of Hilbert Vibration Decomposition with Empirical Mode Decomposition for Classifying Epileptic Seizures. In Proceedings of the 2018 52nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 28–31 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, H.; Hayashi, K.; Saeki, T.; Maksyutov, S.; Nasuno, I.; Shimono, Y.; Hirose, Y.; Takaichi, K.; Kanekon, S.; Ajiro, M.; et al. Global mapping of greenhouse gases retrieved from GOSAT Level 2 products by using a kriging method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 1509–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Zhao, C.; Andrews, A.E.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Sweeney, C.; Bianco, L.; Wilczak, J.M.; Fischer, M.L. Seasonal variations in N2O emissions from central California. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L16801–L16805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M. Study on the Response of Atmospheric CO2 Concentration Changes Monitored by Multi-Source Carbon Satellite Remote Sensing to Anthropogenic Emissions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, C.D.; Connor, B.J. Intercomparison of remote sounding instruments. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree|Semantic Scholar[EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/LightGBM%3A-A-Highly-Efficient-Gradient-Boosting-Tree-Ke-Meng/497e4b08279d69513e4d2313a7fd9a55dfb73273 (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System|Semantic Scholar[EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/XGBoost%3A-A-Scalable-Tree-Boosting-System-Chen-Guestrin/26bc9195c6343e4d7f434dd65b4ad67efe2be27a (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Dorogush, A.V.; Ershov, V.; Gulin, A. CatBoost: Gradient boosting with categorical features support. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.11363. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A. Balancing the Global Carbon Budget. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2007, 35, 313–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Xia, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Shao, P. Biochar and effective microorganisms promote Sesbania cannabina growth and soil quality in the coastal saline-alkali soil of the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Meteorological News Press. China Greenhouse Gas Bulletin 2013. Chin. Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 355. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, A.; Liu, Q.; Lian, X.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Wu, X. Impact of extreme climate events on carbon cycle of terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 49, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Xi, C.; Ping, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Luo, Q.; Cui, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wan, L.; Hou, X.; et al. Bioinformatics Analysis and Experimental Identification of Immune-Related Genes and Immune Cells in the Progression of Retinoblastoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; He, H.; Li, J.; Wu, L. Estimating CO2 concentration during the growing season from MODIS and GOSAT in East Asia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 4363–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Y. An Ensemble Model-Based Estimation of Nitrogen Dioxide in a Southeastern Coastal Region of China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Lei, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, M.; Wu, C.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Welp, L.R. Spatio-Temporal Mapping of Multi-Satellite Observed Column Atmospheric CO2 Using Precision-Weighted Kriging Method. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gai, R. Estimation of CO2 column concentration in spaceborne shortwave infrared based on machine learning. Chin. Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, X.; Lu, N.; Ju, W.; Jiang, F.; Yin, Z.; Liu, G.; et al. Global Carbon Inventory Satellite Remote Sensing Monitoring Methods, Progress and Challenges. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 26, 243–267. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Sheng, M.; Xiao, W.; Yang, F.; Lin, B.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y. Spatial and temporal changes of XCO2 and anthropogenic CO2 emissions in China based on multi-source carbon satellite fusion products. Chin. Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar]






| Data Type | Data Source | Data Name | Spatial Resolution | Time Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite Data | GOSAT | XCO2 | 10.5 km | 3 days |
| OCO-2 | XCO2 | 2.25 × 1.29 km | 16 days | |
| Model Simulation Data | CarbonTracker | XCO2 | 2° × 3° | 1 day |
| Site Observation Data | TCCON | CO2 | ~2 m | |
| Vegetation Index Data | MODIS | EVI | 500 m | 16 days |
| FPAR | 500 m | 4 days | ||
| LAI | 500 m | 8 days | ||
| Meteorological Reanalysis Data | ERA5 | T2M | 0.25° | 3 h |
| TP | 0.25° | 3 h | ||
| EVA | 0.25° | 3 h | ||
| BLH | 0.25° | 3 h | ||
| U10 | 0.25° | 3 h | ||
| V10 | 0.25° | 3 h | ||
| Elevation Data | ASTER | DEM | 30 m | |
| Population Density Data | LandScan | Population | 1 km | 1 year |
| Parameter Category | Parameter Name | EXT | RF | CB | XGB | LGB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Config | n_estimators | 150 | 245 | 496 | 450 | 480 |
| random_state | 50 | 50 | 50 | 42 | 50 | |
| Tree Structure | max_depth | 25 | 25 | 16 | 23 | 10 |
| max_features | “sqrt” | 0.99 | - | - | - | |
| num_leaves | - | - | - | - | 390 | |
| Split Control | min_samples_split | 2 | 3 | - | - | - |
| min_samples_leaf | 2 | 2 | - | min_child_weight = 9 | min_data_in_leaf = 27 | |
| Regularization | bootstrap | - | TRUE | Bayesian | subsample = 0.89 | bagging_fraction = 0.9 |
| l2_leaf_reg | - | - | 4.55 | reg_lambda = 0.2 | reg_lambda = 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, S.; Dong, H.; Zhang, B.; Huang, H. Estimation of High Spatial Resolution CO2 Concentration in China from 2010 to 2022 Based on Multi-Source Carbon Satellite Data. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050621
Cai S, Dong H, Zhang B, Huang H. Estimation of High Spatial Resolution CO2 Concentration in China from 2010 to 2022 Based on Multi-Source Carbon Satellite Data. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(5):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050621
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Shanzhao, Heng Dong, Bo Zhang, and Huan Huang. 2025. "Estimation of High Spatial Resolution CO2 Concentration in China from 2010 to 2022 Based on Multi-Source Carbon Satellite Data" Atmosphere 16, no. 5: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050621
APA StyleCai, S., Dong, H., Zhang, B., & Huang, H. (2025). Estimation of High Spatial Resolution CO2 Concentration in China from 2010 to 2022 Based on Multi-Source Carbon Satellite Data. Atmosphere, 16(5), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050621





