A Monitoring and Sampling Platform for Air Pollutants on a Rotary-Wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle: Development and Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Flight Platform
2.1.1. UAV Configuration
2.1.2. Ambient Air Quartz Sampling Canister
2.1.3. Sensor Selection
2.1.4. Integration of the Sampling Equipment
2.2. Offline Analysis of VOC Samples
2.3. Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance Test of the Quartz Sampling Canister
3.1.1. Adsorption Loss Test
3.1.2. Canister Stability
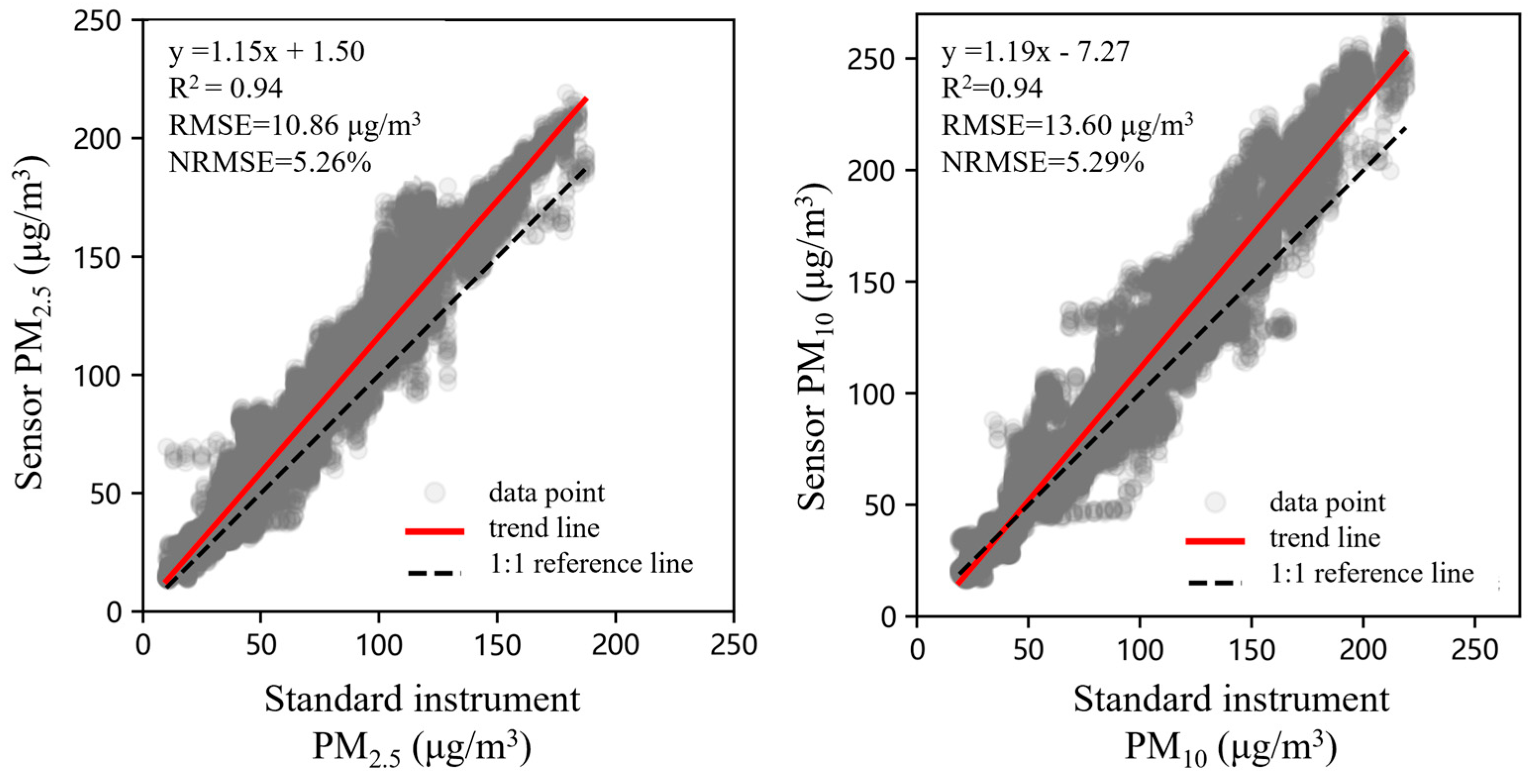
3.2. Sensor Performance Test and Results
3.3. Simulation of Sampling Flow Field of Four-Rotor UAV
3.4. Field Experiments
3.4.1. Sampling Site
3.4.2. Vertical Profile of Meteorological Parameters
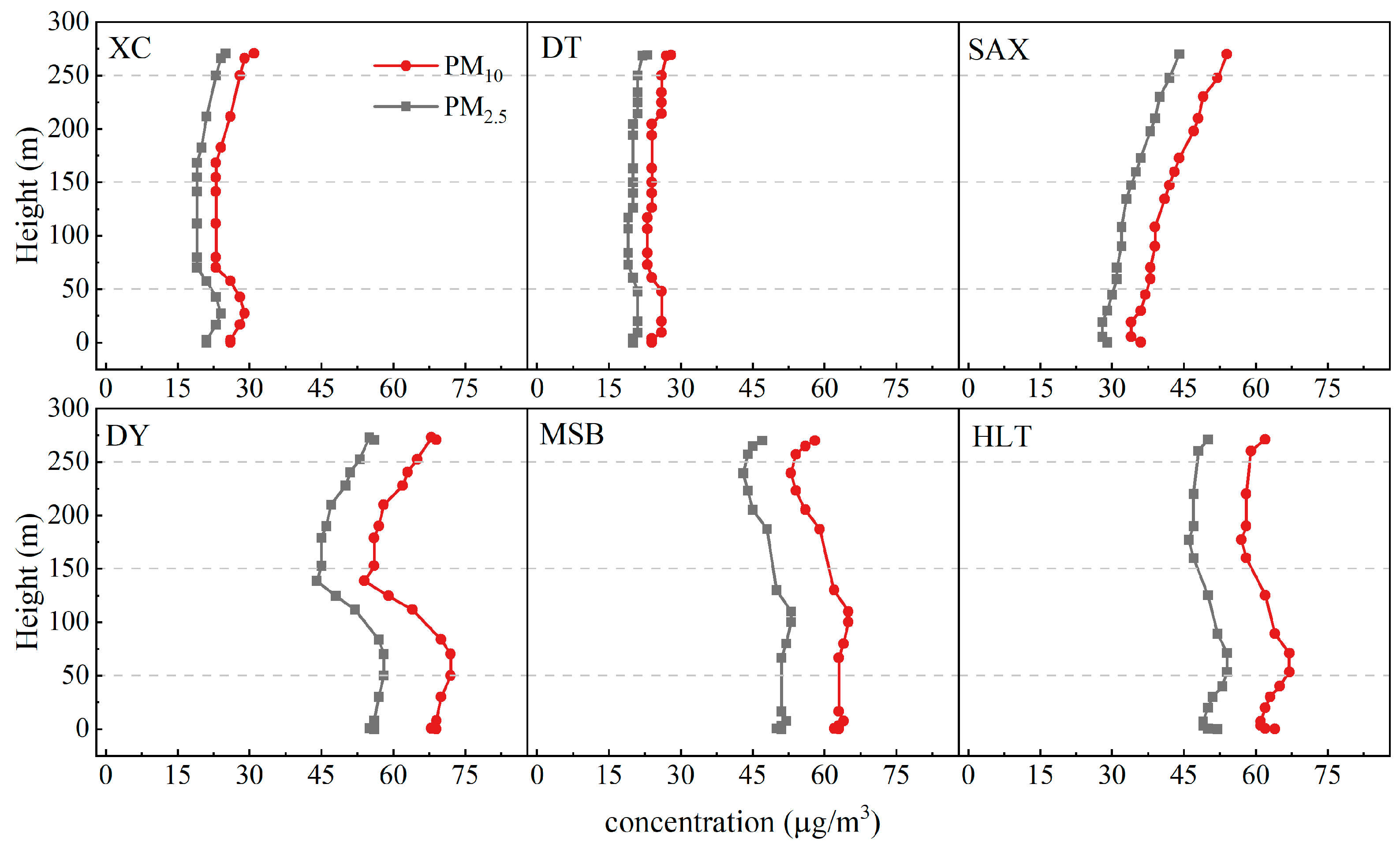
3.4.3. Vertical Profile of Particulate Matter
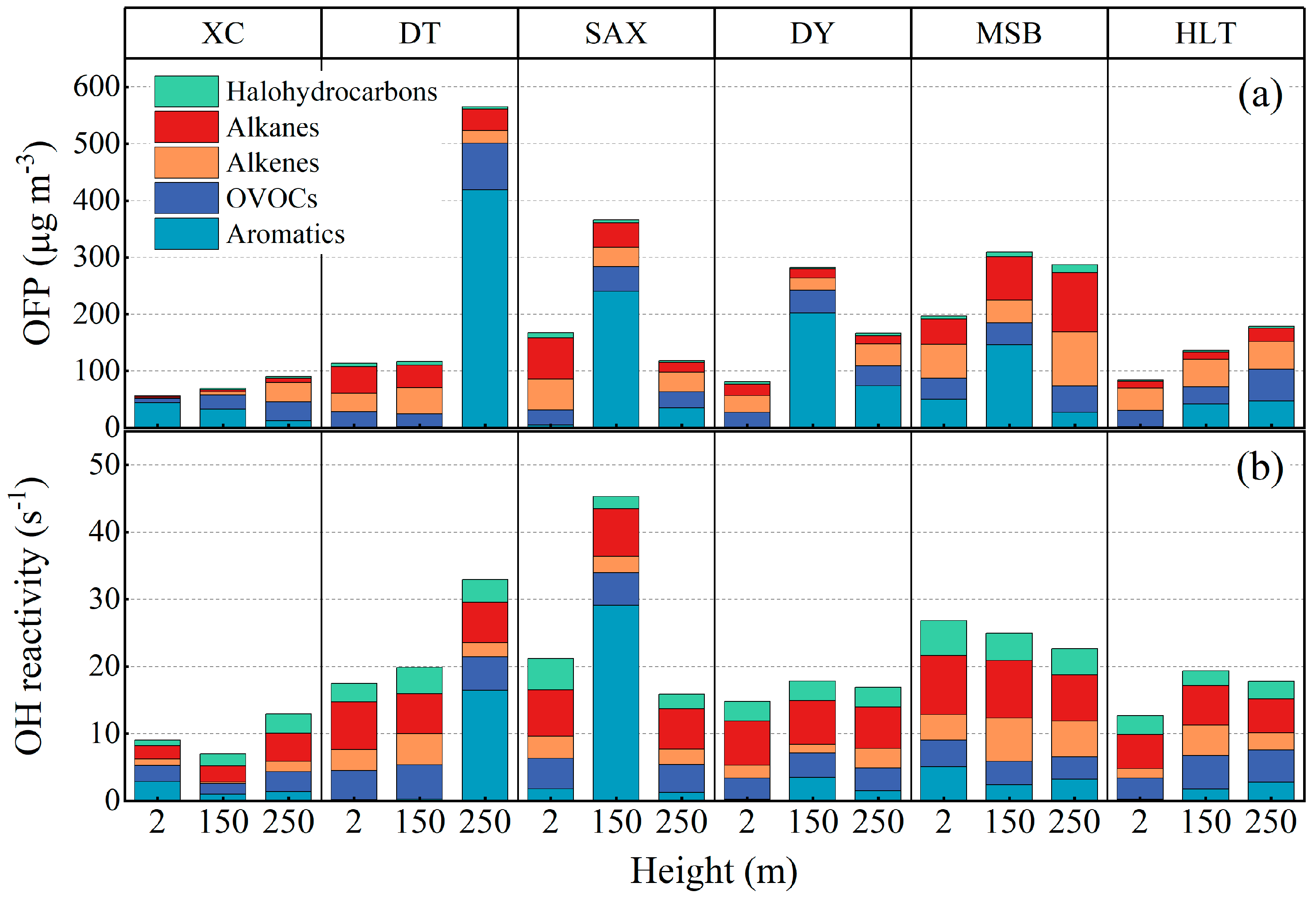
3.4.4. Vertical Profile of VOCs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PM2.5 | fine particulate matter |
| O3 | ozone |
| VOCs | volatile organic compounds |
| OVOCs | oxygenated VOCs |
| NOx | nitric oxide |
| CO | carbonic oxide |
| UAV | unmanned aerial vehicle |
| CFD | computational fluid dynamics |
| ppbv | parts per billion by volume |
| P | atmospheric pressure |
| T | temperature |
| RH | relative humidity |
| SiO2 | silicon dioxide |
| RD | relative deviation |
| RMSE | the root means square error |
| NRMSE | the normalized root mean square error |
| TVOC | total volatile organic compounds |
| BLH | boundary layer heights |
| OFP | ozone formation potential |
References
- Nault, B.A.; Jo, D.S.; McDonald, B.C.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Day, D.A.; Hu, W.; Schroder, J.C.; Allan, J.; Blake, D.R.; Canagaratna, M.R.; et al. Secondary organic aerosols from anthropogenic volatile organic compounds contribute substantially to air pollution mortality. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 11201–11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Zhu, J.; Shah, V.; Shen, L.; Bates, K.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, S. A two-pollutant strategy for improving ozone and particulate air quality in China. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Sera, F.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Tong, S.; Lavigne, E.; Correa, P.M.; Ortega, N.V.; Achilleos, S.; et al. Interactive effects of ambient fine particulate matter and ozone on daily mortality in 372 cities: Two stage time series analysis. Br. Med. J. 2023, 383, e075203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hien, V.T.D.; Lin, C.; Thanh, V.C.; Oanh, N.T.K.; Thanh, B.X.; Weng, C.E.; Yuan, C.S.; Rene, E.R. An overview of the development of vertical sampling technologies for ambient volatile organic compounds (VOCs). J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Yuan, B.; Mo, Z.; Tan, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; He, X.; Shao, M. Progress on the vertical observation methods of volatile organic compounds and their applications within the atmospheric boundary layer. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 4098–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, T.; Tang, G.; Bai, Y.; Kong, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, J.; Tan, C.; Shu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Vertical changes of PM(2.5) driven by meteorology in the atmospheric boundary layer during a heavy air pollution event in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, C.; Liu, C.; Hong, Q.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Lin, J.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Hu, Q.; et al. Vertical distributions and potential sources of wintertime atmospheric pollutants and the corresponding ozone production on the coast of Bohai Sea. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 319, 115721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, T.; Fu, W.; Wang, Z.; Shi, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Shu, Z. Vertical distribution of aerosols and association with atmospheric boundary layer structures during regional aerosol transport over central China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 124967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xu, Y.H.; Xu, J.C.; Lian, M.L.; Zhang, W.; Wu, W.H.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhao, J.B. The Vertical Distribution of VOCs and Their Impact on the Environment: A Review. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Huang, S.; Yuan, B.; Pei, C.; Song, Q.; Qi, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; et al. Deriving emission fluxes of volatile organic compounds from tower observation in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 139763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zha, F.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, B.; Liu, B.; Tang, G. Vertical evolution of the concentrations and sources of volatile organic compounds in the lower boundary layer in urban Beijing in summer. Chemosphere 2023, 332, 138767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Ling, Z.H.; Cheng, H.R.; Simpson, I.J.; Lyu, X.P.; Wang, X.M.; Shao, M.; Lu, H.X.; Ayoko, G.; Zhang, Y.L.; et al. Tropospheric volatile organic compounds in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1021–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Huang, S.; Yuan, B.; Pei, C.; Song, Q.; Qi, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Shao, M. Tower-based measurements of NMHCs and OVOCs in the Pearl River Delta: Vertical distribution, source analysis and chemical reactivity. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.H.; Wang, H.L.; Jing, S.A.; Zhou, M.; Lou, S.R.; Qu, K.; Qiu, W.Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.L.; Gao, Y.Q.; et al. Vertical Profiles of Volatile Organic Compounds in Suburban Shanghai. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, K.R.; Heald, C.L.; Allen, H.M.; Apel, E.C.; Arnold, S.R.; Blake, D.R.; Brune, W.H.; Chen, X.; Commane, R.; Crounse, J.D.; et al. Constraining remote oxidation capacity with ATom observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7753–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yu, G.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zeng, L.; Huang, X. Vertical distribution monitoring of near-surface atmospheric VOCs in Shenzhen based on UAV-borne. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 44, 3021–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.G.; Oram, D.E.; Reeves, C.E. Measurements of volatile organic compounds over West Africa. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5281–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.; Zhang, Q.; Tie, X.; Huang, M.; Ma, X.; Deng, Z.; Yu, Q.; Quan, J.; Zhao, C. Aircraft measurements of O3, NOx, CO, VOCs, and SO2 in the Yangtze River Delta region. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koßmann, M.; Vogel, H.; Vogel, B.; Vögtlin, R.; Corsmeier, U.; Fiedler, F.; Klemm, O.; Schlager, H. The composition and vertical distribution of volatile organic compounds in southwestern Germany, eastern France and northern Switzerland during the TRACT campaign in September 1992. Phys. Chem. Earth 1996, 21, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, Z.C.J.; Robinson, M.A.; Barsanti, K.C.; Bourgeois, I.; Coggon, M.M.; Di Gangi, J.P.; Diskin, G.S.; Flocke, F.M.; Franchin, A.; Fredrickson, C.D.; et al. Nighttime and daytime dark oxidation chemistry in wildfire plumes: An observation and model analysis of FIREX-AQ aircraft data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 16293–16317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Zhu, L.; Xing, C.; Hu, Q.; Lin, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.; Liu, T.; Su, W.; Liu, C. Inferring vertical variability and diurnal evolution of O3 formation sensitivity based on the vertical distribution of summertime HCHO and NO2 in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Bao, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Moshary, F.; Arend, M.; Wang, Y.; Lee, X. A high-resolution modeling study of a heat wave-driven ozone exceedance event in New York City and surrounding regions. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xiu, G.; Zhou, L.; Bian, Q.; Duan, Y.; Fei, D.; Wang, D.; Fu, Q. Vertical distribution of volatile organic compounds within the lower troposphere in late spring of Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 186, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Wang, J.; Yin, B.; Zhao, R.; Li, P.; Yang, W.; Xiao, Z.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Bai, Z. Vertical distribution of volatile organic compounds conducted by tethered balloon in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 95, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, D.S.; Tiwari, S.; Dumka, U.C.; Srivastava, A.K.; Safai, P.D.; Ghude, S.D.; Chate, D.M.; Rao, P.S.P.; Ali, K.; Prabhakaran, T.; et al. Tethered balloon-born and ground-based measurements of black carbon and particulate profiles within the lower troposphere during the foggy period in Delhi, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Huo, J.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ding, A.; Fu, Q.; Luo, J.; Fei, D.; Xiu, G.; Huang, K. Vertical distribution and transport of air pollutants during a regional haze event in eastern China: A tethered mega-balloon observation study. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tang, G.; Wang, Y.; Mai, R.; Yao, D.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y. Vertical Evolution of Boundary Layer Volatile Organic Compounds in Summer over the North China Plain and the Differences with Winter. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Tang, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Vertical characteristics of VOCs in the lower troposphere over the North China Plain during pollution periods. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscano, P.; Gioli, B.; Dugheri, S.; Salvini, A.; Matese, A.; Bonacchi, A.; Zaldei, A.; Cupelli, V.; Miglietta, F. Locating industrial VOC sources with aircraft observations. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.K.; Wang, T.; Simpson, I.J.; Ding, A.J.; Gao, J.; Blake, D.R.; Wang, X.Z.; Wang, W.X.; Lei, H.C.; Jing, D.Z. Vertical distributions of non-methane hydrocarbons and halocarbons in the lower troposphere over northeast China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6501–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Ding, A.; Gao, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Lei, H.; Jin, D.; Qi, Y. Aircraft measurements of the vertical distribution of sulfur dioxide and aerosol scattering coefficient in China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Stehr, J.W.; Marufu, L.T.; Li, Z.; Dickerson, R.R. Aircraft measurements of SO2 and aerosols over northeastern China: Vertical profiles and the influence of weather on air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-km-resolution high-quality PM2.5 data records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal variations and policy implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xue, R.; Gu, C.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, B. Constructing the 3D Spatial Distribution of the HCHO/NO2 Ratio via Satellite Observation and Machine Learning Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 4047–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Q.Q.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xing, C.Z.; Ou, J.P.; Tan, W.; Liu, H.R.; Huang, X.Q.; Wu, Z.F. Vertical distribution and temporal evolution of formaldehyde and glyoxal derived from MAX-DOAS observations: The indicative role of VOC sources. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 122, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavent, N.; Garcia-Nieto, D.; Wang, S.; Saiz-Lopez, A. MAX-DOAS measurements and vertical profiles of glyoxal and formaldehyde in Madrid, Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, K.A.; Wang, D.; Ye, J.H.; de Fouchier, J.B.; Guimaraes, P.C.; Batista, C.E.; Souza, R.A.F.; Alves, E.G.; Gu, D.; Guenther, A.B.; et al. A sampler for atmospheric volatile organic compounds by copter unmanned aerial vehicles. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 3123–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R. Understanding the drone epidemic. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2014, 30, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.D.; Li, X.; Zeng, L.M.; Yu, X.A.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.H.; Huang, X.F.; Zhang, D.M.; Xu, H.B.; Lin, S.C.; et al. Development of multi-channel whole-air sampling equipment onboard an unmanned aerial vehicle for investigating volatile organic compounds’ vertical distribution in the planetary boundary layer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, E.S.F.; Fladeland, M.; Liem, J.; Kolyer, R.; Gupta, M. Greenhouse gas analyzer for measurements of carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor aboard an unmanned aerial vehicle. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 169, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, E.; Hills, A.J.; Hornbrook, R.S.; Shertz, S.; Gabbard, S.; Stephens, B.B.; Helmig, D.; Apel, E.C. Unpiloted Aircraft System Instrument for the Rapid Collection of Whole Air Samples and Measurements for Environmental Monitoring and Air Quality Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5657–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Z.R.; Wang, D. Using unmanned aerial vehicle to investigate the vertical distribution of fine particulate matter. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.D.H.; Lin, C.T.; Weng, C.E.; Yuan, C.S.; Lee, C.W.; Hung, C.H.; Bui, X.T.; Lo, K.C.; Lin, J.X. Vertical stratification of volatile organic compounds and their photochemical product formation potential in an industrial urban area. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.W.; Liu, B.; Ye, J.H.; Jia, T.J.; Khuzestani, R.B.; Jia, Y.S.; Cheng, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, C.; et al. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Measurements of Volatile Organic Compounds over a Subtropical Forest in China and Implications for Emission Heterogeneity. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2021, 5, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Yuan, C.-S. VOC Sampler on a Drone Assisting in Tracing the Potential Sources by a Dispersion Model—Case Study of Industrial Emissions. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2023, 23, 230169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.M.; Stokes, M.D.; Bonnardel, J.; Bertram, T.H. Characterization of a Quadrotor Unmanned Aircraft System for Aerosol-Particle-Concentration Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijling, B.; Jiang, Q.; de Jonge, D.; Bocconi, S. Field calibration of electrochemical NO2 sensors in a citizen science context. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1297–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Villani, M.G.; Aleixandre, M.; Bonavitacola, F. Field calibration of a cluster of low-cost available sensors for air quality monitoring. Part A: Ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 215, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Shaw, M.D.; Gillot, S.; Lewis, A.C. The impacts of water vapour and co-pollutants on the performance of electrochemical gas sensors used for air quality monitoring. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 266, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.H.; Liu, Y.F.; Yuan, C.S.; Chen, W.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Hung, C.H.; Lin, C.; Jen, Y.H.; Ie, I.R.; Yang, H.Y. Vertical Profile and Spatial Distribution of Ozone and Its Precursors at the Inland and Offshore of an Industrial City. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Liu, C.C.; Chen, W.H.; Yuan, C.S.; Lin, C. Assessing the altitude effect on distributions of volatile organic compounds from different sources by principal component analysis. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 972–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, T.F.; Salimi, F.; Morton, K.; Morawska, L.; Gonzalez, F. Development and Validation of a UAV Based System for Air Pollution Measurements. Sensors 2016, 16, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L.; Deng, W.; Xu, M.; Xu, G.; Li, L.; Hewitt, A. Numerical simulation of the downwash flow field and droplet movement from an unmanned helicopter for crop spraying. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2020, 174, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajcin, M.; Simonovic, A.; Ivanov, T.; Komarov, D.; Stupar, S. Numerical analysis of a hypersonic turbulent and laminar flow using a commercial CFD solver. J. Therm. Sci. 2016, 20, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.; Zhao, H. Analysis of internal flow field performance of hydrocyclone based on CFD. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2383, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urech, P.R.W.; Mughal, M.O.; Bartesaghi-Koc, C. A simulation-based design framework to iteratively analyze and shape urban landscapes using point cloud modeling. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2022, 91, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Yang, S.H.; Liu, X.X.; Wang, J.; Norton, T.; Chen, J.; Tan, Y. The computational fluid dynamic modeling of downwash flow field for a six-rotor UAV. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2018, 5, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Qin, D.; Zhang, J.Y. Effect of RANS Turbulence Model on Aerodynamic Behavior of Trains in Crosswind. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 32, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-C.; Horng, S.-H.; Liao, P.-N. Stability of Trace-Level Volatile Organic Compounds Stored in Canisters and Tedlar bags. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2003, 3, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, N.; Tsuji, A.; Nakamura, N.; Daishima, S.; Cardin, D.B. Stabilities of 58 volatile organic compounds in fused-silica-lined and SUMMA polished canisters under various humidified conditions. J. Environ. Monit. 2002, 4, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

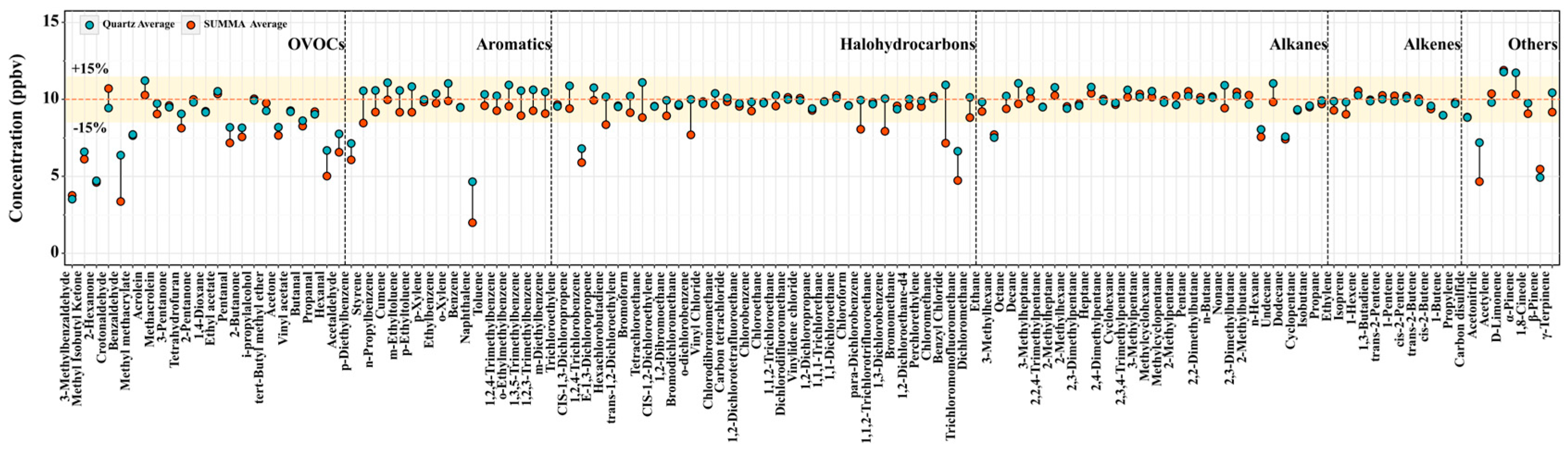


| Species | Quartz (ppbv) | SUMMA (ppbv) | RD-Quartz | RD-SUMMA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkanes | 9.9 ± 0.90 | 9.7 ± 0.82 | −1.29% | −3.32% |
| Alkenes | 9.8 ± 0.33 | 9.8 ± 0.54 | −1.87% | −2.00% |
| Halohydrocarbons | 9.8 ± 0.88 | 9.1 ± 1.20 | −1.82% | −8.92% |
| Aromatics | 10.0 ± 1.64 | 8.8 ± 1.95 | −0.30% | −12.53% |
| OVOCs | 8.4 ± 1.81 | 8.0 ± 2.18 | −16.35% | −20.26% |
| Terpenes | 9.7 ± 2.82 | 9.2 ± 2.37 | −2.74% | −8.10% |
| Organosulfur | 8.8 ± 0.35 | 10.0 ± 1.11 | −11.76% | −0.33% |
| Nitrile | 7.2 ± 0.40 | 4.9 ± 0.31 | −28.05% | −51.19% |
| Alkynes | 9.8 ± 0.70 | 10.3 ± 0.05 | −1.98% | 3.27% |
| VOC Groups | 2 m | 150 m | 250 m | 2 m | 150 m | 250 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XC | DT | |||||
| Alkanes | 1.4 | 2.7 | 5.4 | 18.1 | 19 | 10.8 |
| Alkenes | 0.01 | 0.3 | 2 | 1.6 | 3 | 1.1 |
| Aromatics | 1.9 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 63.4 |
| OVOCs | 0.5 | 1.3 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 2 | 5.6 |
| Halohydrocarbons | 1.8 | 2 | 2.7 | 19.3 | 18.9 | 12.1 |
| TVOCs | 5.6 | 7.9 | 13.3 | 42.1 | 43.3 | 92.9 |
| SAX | DY | |||||
| Alkanes | 16 | 13.3 | 9.5 | 11.2 | 8.9 | 11.4 |
| Alkenes | 3.5 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2 | 2.6 |
| Aromatics | 0.7 | 97.1 | 1.9 | 12.3 | 9.2 | 3.5 |
| OVOCs | 2.4 | 3.2 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 2.6 |
| Halohydrocarbons | 13.6 | 12.3 | 3.5 | 4.9 | 4.8 | 5.5 |
| TVOCs | 36.2 | 128 | 19.1 | 33.6 | 27.6 | 25.7 |
| MSB | HLT | |||||
| Alkanes | 18.6 | 25.5 | 36.3 | 10.1 | 9.8 | 13.1 |
| Alkenes | 3.7 | 5.4 | 6.2 | 2.6 | 3.7 | 3.6 |
| Aromatics | 3.3 | 9 | 4.5 | 0.7 | 2.3 | 8.4 |
| OVOCs | 2.5 | 3.6 | 3.3 | 2 | 2.6 | 3.9 |
| Halohydrocarbons | 11.5 | 21.4 | 43.1 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 5.2 |
| TVOCs | 39.6 | 64.8 | 93.4 | 19.9 | 22.8 | 34.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, X.; Dou, X.; Liu, H.; Shi, G.; Xiang, X.; Tan, Q.; Song, D.; Huang, F.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, H.; et al. A Monitoring and Sampling Platform for Air Pollutants on a Rotary-Wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle: Development and Application. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050613
Kong X, Dou X, Liu H, Shi G, Xiang X, Tan Q, Song D, Huang F, Zhou X, Jiang H, et al. A Monitoring and Sampling Platform for Air Pollutants on a Rotary-Wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle: Development and Application. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(5):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050613
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Xiaodie, Xiaoya Dou, Hefan Liu, Guangming Shi, Xingyu Xiang, Qinwen Tan, Danlin Song, Fengxia Huang, Xiaoling Zhou, Hongbin Jiang, and et al. 2025. "A Monitoring and Sampling Platform for Air Pollutants on a Rotary-Wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle: Development and Application" Atmosphere 16, no. 5: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050613
APA StyleKong, X., Dou, X., Liu, H., Shi, G., Xiang, X., Tan, Q., Song, D., Huang, F., Zhou, X., Jiang, H., Wang, P., Zhou, L., & Yang, F. (2025). A Monitoring and Sampling Platform for Air Pollutants on a Rotary-Wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle: Development and Application. Atmosphere, 16(5), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050613








