Abstract
The assessment of air pollution is an important and relevant issue that requires continuous monitoring and control, especially in urban spaces. However, using instrumental air quality measurement techniques and deploying meters throughout the city is extremely expensive, so a biological alternative can be used—a bioindicator, i.e., a species whose vital functions or morphological structure can reveal the qualitative state of the environment. In this work, the lichen Hypogymnia physodes L. was used to analyze air pollution in areas of the provincial city of Opole, southern Poland. Microscope and chemotaxonomy methods were used in the laboratory to confirm field identification of lichens (atlases and keys). The selected elements, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb, were determined using atomic absorption spectrometry, and direct mercury analyzer was used to analyzed Hg concentration. Factor analysis (FA) was performed to associate elements with possible sources of air pollution. The highest concentrations of analytes were found at measurement points close to railway roads (Fe = 5131 mg/kg) and streets with heavy traffic (Pb = 101 mg/kg). Statistically significant differences (p < 0.001) were found between the concentrations of individual elements, which have positive correlation coefficients higher than 0.65. Based on the research carried out, different anthropogenic and traffic-related activities can be considered as one of the main sources of air pollution in Opole City based on the results of FA. Using an additional lichen scale, it can be concluded that the areas surveyed in the town of Opole can be classified as zone IV—characterized by an increase in the number of leaf lichens (additionally co-occurring lichens of the Polycauliona candelaria species), i.e., an area with an average level of air pollution (based also on contamination factor [CF] and pollution load index [PLI]). Accumulation concentrations of heavy metals in lichen were metal-specific and varied spatially, thus reflecting local differences in heavy metal deposition. The research presented here proves that low-cost passive biomonitoring can effectively support classical methods of assessing air pollution in urban spaces.
1. Introduction
Lichens, which are symbiotic organisms composed of fungi and algae, are particularly sensitive to atmospheric pollutants due to their widespread occurrence and unique physiological characteristics. They have the ability to absorb and accumulate air pollutants, particularly heavy metals. Accumulation of these metals is a critical problem, especially in urban environments. Emissions from human activities, such as traffic and industrial processes, can lead to elevated concentrations of heavy metals in the atmosphere, which lichens can absorb from wet and dry deposition [1]. Studies have shown that lichens can accumulate heavy metals in much higher quantities than plants, highlighting their suitability for biological monitoring [2]. Some lichen species (such as Hypogymnia physodes) have been shown to absorb heavy metals such as lead and cadmium, directly reflecting the concentration of these pollutants in the atmosphere [3,4]. Lichens are highly sensitive to air pollutants, especially sulfur dioxide and nitrogen compounds, making them reliable indicators of atmospheric contamination [5].
The selection of lichen species is fundamental, as this directly influences their sensitivity and response detection toward atmospheric contaminants. In general, lichen can be grouped into fruticose, foliose, and crustose (functional groups) based on their morphology [6]. They exhibit varying levels of sensitivity, with fruticose lichens recognized for their heightened sensitivity to air pollution compared to their foliose and crustose counterparts, which makes them more suitable for biomonitoring purposes [7]. Species such as Evernia prunastri and Xanthoria parietina have been widely studied for their capabilities to accumulate heavy metals and other contaminants, making them excellent candidates for monitoring air quality [8,9]. Furthermore, sampling strategies must utilize species that thrive in impacted areas, allowing for effective comparisons across different environmental gradients [10]. The spatial distribution of sampling sites should reflect environmental gradients impacted by known pollution sources. This design principle is further emphasized by studies conducted in urban environments, where lichen diversity often corresponds to pollution gradients, demonstrating that areas with better air quality can support a wider range of lichen species [11].
For lichen samples, cleaning them must be the first step in sample preparation as removing any particulate matter or external contaminants and debris is vital; this is often done through rinsing with deionized water [12,13]. Once cleaned, samples need to be dried adequately to prevent decomposition. This is usually completed at controlled temperatures to prevent degradation, thereby preserving the lichen’s structural integrity for subsequent analysis [14,15]. Following drying, homogenization is necessary for a uniform particulate size that enhances digestion efficiency and analytical accuracy [16]. This process is typically achieved through mechanical grinding [17]. Subsequently, the samples are subjected to digestion, which is a vital step wherein organic matter is broken down, often through methods involving strong acids like nitric acid, allowing for the release of trace elements for subsequent analysis [18,19].
Analytical techniques for detecting heavy metals in lichen samples have advanced significantly. Methods such as Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS), Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-AES), and Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) are predominantly utilized due to their sensitivity and ability to analyze multiple elements simultaneously [20,21]. The latter techniques, specifically ICP-MS, are recognized for their detection limits, which can reach parts per trillion, proving particularly advantageous in biomonitoring studies where pollutant concentrations are typically low [11]. Quality control is paramount throughout the analytical process, often using certified reference materials and conducting duplicate analyses to validate findings and assess the precision of the results [22,23].
Data analysis techniques in lichen biomonitoring frequently employ various statistical methods to interpret the results effectively. One robust approach includes multivariate analyses that can elucidate relationships between pollutant levels and biological responses in lichens [24]. Factor Analysis (FA) is commonly used to determine underlying data structures and assess the contributions of different pollutants to the variance observed in lichen health and accumulation patterns [25]. It can also effectively reduce data complexity, highlighting key relationships between multiple variables [26]. Moreover, contamination indices, such as the Enrichment Factor (EF), are used to assess the extent to which certain metals are present in lichens relative to background levels [27,28]. The Pollution Load Index (PLI) assists researchers in evaluating the overall quality of the environment based on lichen metal accumulation, facilitating easier comparisons across different regions [29]. These indices facilitate comparisons across different geographical areas and temporal studies, thereby enhancing the comprehensive assessment of air pollution impacts through lichen biomonitoring [30].
Lichen biomonitoring has become a key methodology for assessing air pollution in urban areas. Air quality has a direct impact on the diversity, composition, and viability of lichens, making them excellent bioindicators for environmental monitoring [31,32,33]. Changes in species diversity may indicate different levels of pollution stress, as epiphytic lichens tend to decrease in biodiversity as pollution levels increase [31,34]. In contrast, other lichen species can thrive, thus serving as resistant indicators of certain types of pollution [35]. In addition, the physiological characteristics of lichens increase their usefulness in biomonitoring. Their ability to directly absorb airborne substances, combined with the absence of an epidermal layer, allows lichens to integrate pollutants into their biological systems, enabling the quantification of chemical constituents indicative of air quality. This bioaccumulation of pollutants can provide insights into long-term pollution trends as lichens typically reflect chronic exposures rather than transient pollution spikes [33,36].
In addition to their role in assessing air pollution, lichens show considerable potential in inferring trends related to atmospheric deposition over time. Monitoring initiatives using lichen transplants or sampling of lichen thalli from different locations have been used to develop air pollution maps, identifying areas of major concern in urban environments [37,38]. Spatial patterns of lichen diversity can serve as indicators to simultaneously assess air quality and human health risks [11]. Lichen thalli exposed to higher levels of industrial emissions can reveal higher concentrations of heavy metals compared to those in less polluted areas, thus providing a tangible measure of changes in urban air quality [1,39]. Unlike technical equipment, lichen biomonitoring provides long-term and integrative data on pollution levels. This method is non-invasive and can be applied over large areas without disturbing the environment. Urban planning and public health strategies benefit from lichen monitoring by identifying pollution hotspots and tracking the effectiveness of emission reduction efforts [40,41,42]. Such studies are particularly important in dense urban conglomerates, where changes in air quality can significantly affect public health outcomes.
The aim of the study was to analyze air pollution using lichens of the species H. physodes on the example of the city of Opole, Poland. The study covered city parks, heavily populated housing estates, and traffic routes with different traffic volumes. Passive biomonitoring was carried out in places where classical monitoring was not carried out, and the level of exposure of inhabitants to heavy metals present in atmospheric aerosol is unknown. At the same time, hypotheses were raised: (1) biomonitoring using lichens provides an answer to the question of what urban residents breathe, (2) lichens can be used as a source of information on air quality in areas where classical monitoring is not carried out.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
To conduct the research part of this study, measurement points were selected, located in the central part of the city of Opole [50°39′53″ N, 17°55′37″ E] (Opolskie Province, PL) in Figure 1. The character of the location and GPS information regarding the area consisting of a pattern of different land use patterns in the city center were determined (see Table S1). This region, consisting of the built environment, includes different land uses, such as parks, university campus, the city’s central business district, and residential areas. It offers diversity in terms of pollutant sources.
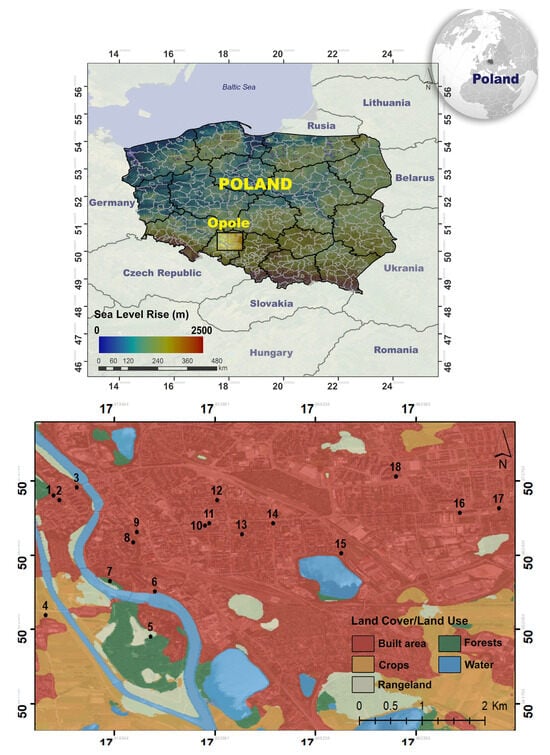
Figure 1.
Measurement points in the center of Opole. Black dots represent the sampling sites.
Opole is the capital of the Opole Province. Opole is a 128,000-strong provincial city located in southern Poland near the Czech Republic (54 km to the border) and Germany (240 km to the border). Opole has convenient and fast rail connections, the density of which is twice the national average. There are two river ports within the administrative boundaries of the municipality, on the Oder River. The city itself has an efficient public transport system. The public bicycle system is also becoming more important, and 35% of the road network in Opole is made up of traffic calmed zones and cycle paths (124 km) [43]. Most anthropogenic areas are located in the city center. The percentage of built-up area in relation to the total area of the city was 21.3% in 2020. Built-up areas increase their area in the city’s spatial structure, mainly at the expense of agricultural areas [44].
2.2. Lichen Identyfication and Analytical Measurements
The lichen H. physodes was used for the analysis. This species was chosen because of its fairly common occurrence in Opole and the Opole Silesia area in general [45]. Its ability to bioaccumulate heavy metals has already been demonstrated in the introduction, as well as indicated by other national and international studies [46,47]. Lichen atlases and keys were used in the field to identify the species. After collection, samples were confirmed to ensure species homogeneity using an IPOS-810 microscope (Delta Optical, Poland) in the laboratory of the MCBR UO (International Research and Development Centre of the University of Opole). Chemotaxonomy methods were additionally used in the laboratory to confirm field identification. Chemotaxonomy is a field of research that uses the chemical composition of plants to classify them. Secondary metabolites, such as flavonoids, alkaloids and terpenoids, are used to establish relationships between plants and their evolutionary history. Chemotaxonomy is also used in the study of lichen species (see Figure 2), where secondary metabolites play a key role in their systematics [48].

Figure 2.
(a) Lichen thalli before reagent addition, (b) Yellow/orange discoloration of the thalli by the alcoholic solution of para-phenylene diamine (Pd+) indicates the presence of physodalic acid (red circle). This acid belongs to the depsidones, a specific group of polyphenols found in lichens. It is a secondary metabolite found mainly in some species of lichens, especially from the genera Hypogymnia and Physcia [49].
Lichens were collected in September 2024 (autumn/fall). At each measurement point, 10 trees were selected (18 measurement points with 10 trees each), from which the material for testing was manually collected (3 thalli from each tree; 30 thalli from each measuring point), into paper bags. The uptake of lichens from trees of similar age and bark structure was also taken into account [50]. In this study, adult thalli (laciniae > 5 cm) growing on bark more than 1.5 m above the ground were collected [15]. After homogenization of the collected samples from each location, 3 samples were selected to represent a given measurement point: 18 measurement locations × 3 subsamples = 54 samples (in total).
After initial cleaning in the field, H. physodes lichens were then transported to the laboratory and dried at 60 °C for 12 h to obtain dry mass (d.m.). Samples were homogenized in a mortar and stored in tight polyethylene containers. The material prepared in this way was subjected to a mineralization process. Lichen samples weighing 0.500 ± 0.001 g d.m. were digested in a Speedwave 4 microwave mineralizer from Berghoff (DE). The samples were flooded with a mixture of 65% nitric acid (V) and 30% hydrogen peroxide in a ratio of 3:1 and left for 15–20 min for preliminary digestion. The entire mineralization process was carried out at 180 °C for 45–50 min. After the mineralization process was completed, the solutions were filtered into 20 cm3 measuring flasks and topped up with demineralized water with a conductivity of κ = 0.5 μS/cm. Reagents supplied by MERCK were employed for solution preparation. Quantitative determination of heavy metals (Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb) in the mineralized samples was carried out using a flame atomic absorption spectrometer (F-AAS), model iCE 3500 (3000 series), manufactured by Thermo Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). Table S2 shows the detection and quantification limits of heavy metals, which characterize the iCE 3500 spectrometer [51]. The instrument was calibrated using single-element standard solutions from ANALYTIKA Ltd. (Khodlova, Czech Republic). The highest concentrations of the calibration standards—2.0 mg/dm3 for Cd; 5.0 mg/dm3 for Ni, Cu, Zn, and Pb; 7.5 mg/dm3 for Mn; and 10.0 mg/dm3 for Fe—were defined as the upper limits of the linear calibration range. Concentrations of heavy metals determined in the certified reference materials BCR-482 (lichen) and BCR-414 (plankton), provided by the Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements (IRMM, Geel, Belgium), are presented in Table S3 [52]. Table S3 presents the average values of the relative standard deviation (RSD) [%] for the three analytical replicates of lichen samples. A low percentage of the average RSD values (<2.50%) means that the scatter of the results is small. This indicates the high accuracy of the applied research equipment (see Table S4).
Averaged lichen samples weighing 0.0400 ± 0.001 g d.m. were also analyzed in the AMA 254 mercury analyzer from Altec Ltd., CZ. For mercury, the detection limits (IDL) and quantification limits (IQL) of the instrument are 0.003 ng (0.03 µg Hg/dm3) and 0.01 ng (0.1 µg Hg/dm3), respectively, in the tested sample. Standards from ANALYTIKA Ltd. (CZ) were used to calibrate the instrument. In total, eight analyses were performed in each of the 54 samples (number of analyzed heavy metals), which were performed in three analytical replicates, which gives a total of: 54 samples × 8 elements × 3 replicates = 1296 analyses.
2.3. Data Processing
The measurement values in the samples collected from 18 different points in the city center of Opole were processed in their locations. Spatial distribution maps were generated using the spatial analysis tool for data management available in ArcGIS software version 10.7.1, to spatially understand the accumulation of elements in lichen to relate them to land use [53,54].
For descriptive analysis, the minimal and maximal values, mean with standard deviation (SD), were calculated for each analyzed element. Shapiro–Wilk’s test was used to check data normality due to sample sizes. Descriptive statistics, including minimum, maximum, mean, and standard deviation (SD), were calculated for each analyzed element. The Shapiro–Wilk test was employed to assess the normality of data distribution, given the sample sizes [55]. Therefore, differences between the concentrations of the elements in the lichen were evaluated by the Student t-test. Sometimes, non-parametric tests were used for these analyses. A difference was considered to be statistically significant when p < 0.05. The relationships between elements were verified using Pearson’s and Spearman’s rank correlation, respectively. Based on the distribution characteristics, differences in elemental concentrations in lichen samples were evaluated using the Student’s t-test; where assumptions of normality were not met, appropriate non-parametric tests were applied. Statistical significance was accepted at p < 0.05. Correlations between elements were assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient for parametric data and Spearman’s rank correlation for non-parametric data, respectively [56,57]. Statistica (ver. 13.3) and Microsoft Excel 2021 software were used to process and present the data. Data analysis and charts visualization were performed using Statistica software (version 13.3) and Microsoft Excel 2021.
Factor analysis with eigenvalue-based principal component factorization was used to clarify associations between elements that had similar origins at the sampling sites and infer possible sources of heavy metals [58]. The contamination factor (CF) is defined as the ratio between the mass fraction of an element in the lichen samples and its background level in the lichen:
where Cs is the concentration of a specific element at any sampling site, and Cb is the background level for the same metal. CF < 1 indicates no contamination; 1–2—suspected; 2–3.5—slight; 3.5–8—moderate; 8–27—severe; and >27—extreme [59]. In our study, due to the lack of background values, we used ‘reference plant’ data [60]. The Pollutant Load Index (PLI) represents the nth-order geometric mean of the entire set of CF values:
where n is the total number of polluting elements. According to the degree of pollution, PLI data were classified as unpolluted (PLI < 1), unpolluted to moderately polluted (1 < PLI < 2), moderately polluted (2 < PLI < 3), moderately to heavily polluted (3 < PLI < 4), heavily polluted (4 < PLI < 5), or very heavily polluted (5 < PLI) [61].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Heavy Metal Accumulation and Correlation
Figure 3 shows the distribution of element concentrations in lichen samples collected in the center of Opole in the Opolskie Province. The metal concentrations in lichen samples differed significantly (p < 0.001) and varied at different sampling sites because the minimum, maximum, and SD values varied considerably, e.g., Mn (range: 1417–5131 mg/kg d.m., SD: 948 mg/kg d.m.). The values we obtained are quite typical and similar for urban areas with this level of air pollution [62]. The concentrations obtained depend, of course, on the sampling location [63]. High concentrations of zinc, mean 470.8 mg/kg, were determined in lichen samples collected in the vicinity of the Bukowno smelter near Olkusz in southern Poland [4], and this concentration was 4 times higher than the one we determined. For comparison, lichens collected from Base Stations of Integrated Monitoring of the Environment were characterized by low concentrations: Cd = 0.36, and Pb = 8.51 ug/g [64], which significantly differs and is many times lower than the concentrations we determined in the urban area of Opole, which proves the significance of the influence of the sampling location on the final result. Analysis of the above results (see Figure 3 below) indicates that the average values of element concentrations in lichens can be arranged in the following descending series: Fe > Zn > Mn > Pb > Cu > Ni > Cd > Hg.
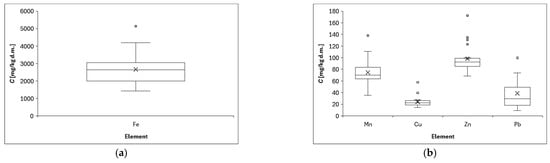
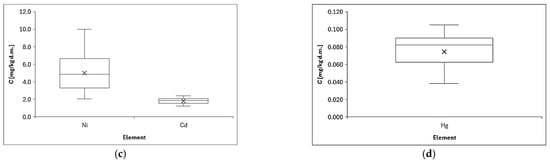
Figure 3.
Distribution of element concentrations: (a) Fe, (b) Mn, Cu, Zn, Pb, (c) Ni, Cd, and (d) Hg determined in lichens collected from all measurement points; (X) indicates the mean value, and the horizontal dash (−) is the median value. Chart whiskers from bottom to top indicate min and max data, respectively.
Some of the analyzed metals in the lichen samples were associated with one another; for example, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Pb had correlation coefficients higher than 0.65. These were mainly positive correlations of the following nature: moderate, strong, and very strong (see Figure 4 and description below). Significantly positive correlations have been found in other research into lichen that was conducted in other countries, including between the concentrations of Cu and Pb or Cu and Zn [65] and between Mn and Ni (0.67), and Fe and Mn (0.65) [66]. These results indicated that these heavy metals often appear simultaneously and might come from the same pollution sources [67].
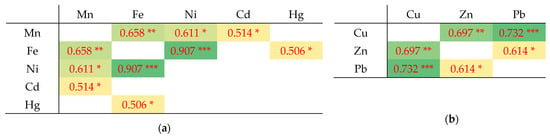
Figure 4.
Coefficients of (a) Pearson’s, (b) Spearman rank correlation between elements in lichen samples. The color intensity corresponds to a strong correlation: yellow and light green indicates a moderate and strong positive correlation, and dark green indicates a very strong positive correlation [68]. Values are statistically significant at the level * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. For clarity, nonsignificant correlations are left blank without numerical value.
3.2. Lichen Pollution Indicators
Factor analysis was performed to analyze the correlation results of metals further. Two main factors were extracted and accounted for 78.3% of the total variance of data from the sampling sites (Table 1). Factor 1 mainly comprised the metals of Fe, Cu, Zn, Pb, and Hg and represented 64.2% of the total variance. The association of these metals with the first factor was likely to be the result of anthropogenic activities, including automobile transportation (traffic) and industrial emissions [69]. Moreover, studies have utilized methods such as principal component analysis (PCA) to assess the correlation between heavy metal accumulation in lichens and atmospheric quality indices, revealing that increased vehicle traffic and industrial activities correlate strongly with higher metal concentrations in lichens [70]. Factor 2 explained 14.1% of the total variance and was mainly influenced by loadings of Mn and Cd. This association was likely to be related to manufacturing processes and heat production, such as coal-fired boiler works or oil burning [69,71]. In various geographic contexts, lichens have demonstrated their utility in assessing heavy metal contamination resulting from localized industrial activities. In urban settings, the correlation of heavy metal levels in lichen specimens with traffic density has been quantified, reliably reflecting urban pollution metrics [14]. Furthermore, the sensitivity of different lichen species to heavy metals highlights the importance of selecting appropriate species for specific monitoring objectives, taking into account their unique physiological responses and levels of metal tolerance [26,72].

Table 1.
Factor analysis of metals in lichen samples.
The CF and PLI values are shown in the table below (Table 2). Based on the values obtained, there is a diversity of contamination depending on the ring-element. The calculated mean CF indicates the occurrence of almost all categories: no contamination (Mn, Hg), suspected (Zn, Pb), slight (Ni, Cu), severe (Fe), and extreme (Cd) contamination. The variability of the PLI, on the other hand, is no longer so divergent, and the mean value, 1.90 [-], indicates an ‘unpolluted to moderately polluted’ level. It is also important to analyze the values for individual points (see Figure 5 below). The most frequent maximum CF values for individual elements indicate point no. 15 (Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn) as well as the PLI value at this point being the highest at 2.42 [-]. Based on the CF values of several heavy metals, the PLI offers a single value reflecting the cumulative pollution load. Studies indicate that when PLI values exceed 1, this indicates a level of contamination that may pose an ecological risk requiring remedial action [73]. The sampling location is crucial for the values obtained. When lichens were collected in Morocco in rural sites, the four lichens species recorded very low PLI values, close to 0.5, which expresses a very low pollution load and good air quality. At the urban sites, the PLI value exceeds the tolerance threshold of Ramalina pollinaria (PLI ≤ 1.5) which explains their disappearance from the urban industrial sites. Xanthoria calcicola and Xanthoria parietina record very high PLI, reflecting maximum polymetallic contamination and poor air quality [74]. The PLI values obtained at Roma ranged from 1.29 to 5.57. The highest value was obtained near Roma Camp at point S1; it was characterized by the highest concentrations of elements (e.g., Ni, Pb or Fe), but no specific sources or activities influencing these concentrations and values of these indices were indicated beyond a general formulation of ‘anthropic emissions’ and pollution load due to airborne particulate matter [75]. The interaction of different indicators, such as CF and PLI, together with direct biological monitoring through lichens, provides a holistic approach to environmental assessment. In various studies, the combination of numerical indicators of pollution and biological indicators has allowed for a nuanced interpretation of pollution dynamics. For example, a sediment analysis in Bangladesh used both CF and PLI along with lichen monitoring to assess pollution, elucidating the multifactorial nature of pollution and its impact on local ecosystems and human health [76,77].

Table 2.
Contamination factor (CF) and pollution load index (PLI) values for elements determined in lichen samples collected in Opole city.
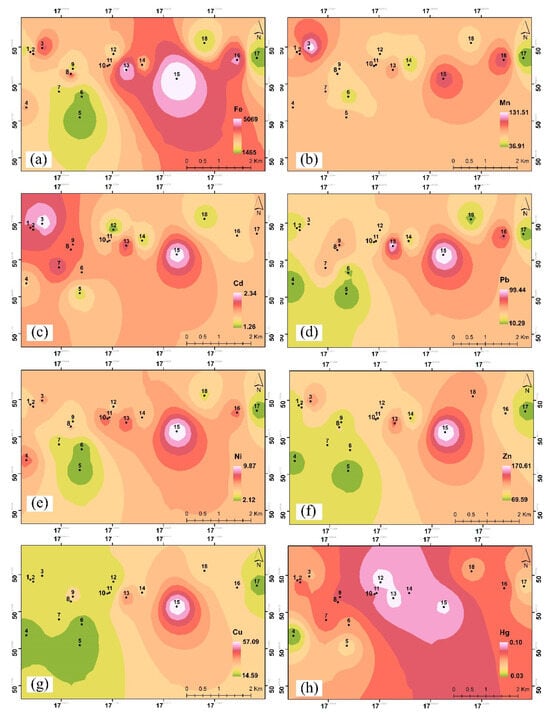
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of metals: (a) Fe, (b) Mn, (c) Cd, (d) Pb, (e) Ni, (f) Zn, (g) Cu, and (h) Hg in the lichen samples. Black dots represent the sampling sites. From green to red-white color represent the lowest to the highest concentration of each element.
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Pollution in the City
The variability of concentrations in the study area can be presented spatially to better illustrate the distribution of metals in the study area; therefore, such a map was prepared (Figure 5). The areas including the University of Opole Campus, Church on Karol Miarka Street and First Tax Office are considered focal points for heavy metal pollution. The location around the bridge is close to a road with high car traffic in Nysa Łużycka Bridge to the Zaodrze Small Park area, with a high spatial pattern of Fe, Mn, Cd, and Zn. Bolko Island, well away from roads on which cars travel, and the Cycle bridge at the Młynówka Canal, a considerable distance from the roads, have the lowest distribution of heavy metal pollution.
Figure 5 shows the spatial variations of the accumulation of elements in lichen samples from the research study site. The highest Fe concentration was recorded at point no. 15, C = 5131 mg/kg d.m. Samples were taken from trees located near a railway line. The friction of train wheels on the rails could have caused abrasion of the metal, releasing iron oxides into the air due to the release of rust particles [78]. The lowest Fe concentration level was recorded at point no. 5, C = 1417 mg/kg d.m. This is a recreational park. This location is densely planted with trees, which acts as a barrier to the penetration of pollutants inside the park [79,80]. Based on the Ni results, we see an identical situation as with the Fe concentration levels, where the highest concentration is 10.0 mg/kg d.m. at point no. 15 and the lowest is 2.03 mg/kg d.m. at point no. 5. The high concentration at point no. 15 is also related to the railways located nearby. The highest Mn level was at point no. 3 (C = 138 mg/kg d.m.), located at a bridge and a road with high traffic intensity. Abrasion of tires and brake pads generates dust that may contain Mn [81]. The lowest concentration of Mn (C = 35.0 mg/kg d.m.) was recorded at point no. 17, and the samples were taken from a place with relatively low traffic intensity and a large distance from industrial plants. Liu et al. showed that lichens near roads accumulate high concentrations of traffic-related metals, particularly Cd, Pb, and Zn, and that their metal profiles evolved in response to decreasing Pb emissions from vehicles over time [82]. The concentrations indicated in this study, however, are half or less than half than those we recorded, which indicates how much the choice of the appropriate species and study site (in this case the influence of anthropopression and pollution) influences the result. The mercury concentrations we observed can practically be considered insignificant/not influential on the level of pollution in the city, referring and comparing to literature studies. An exemplary study was conducted in southern Tuscany, where mercury concentrations were monitored in species such as Flavoparmelia caperata, Parmelia saxatilis, and Xanthoria parietina. The study showed that Hg accumulation in these lichens is mainly from atmospheric sources, and that these organisms can effectively integrate local emission patterns over time. Concentrations of 180–3600 ng/g were recorded in lichens collected in the area surrounding the dismissed Abbadia San Salvatore Hg mine (Monte Amiata district, Italy [83]. Vannini et al. highlighted [84] that E. prunastri rapidly reflects changes in environmental mercury concentrations, making it particularly suitable for monitoring short-term pollution in urban environments. However, species differences in mercury accumulation further complicate the use of lichens as biomonitors. This is supported by the work of Kováčik et al., who found that epiphytic lichens exhibit species-dependent Hg accumulation (~80 ng/g Hg content in H. physodes) [85]. It should be remembered that the occurrence of individual lichen species that accumulate specific elements is strongly dependent on the level of air pollution in a given area [86]. The frequent co-occurrence of the Polycauliona candelaria species (see Figure S1) confirmed the degree of pollution in the city—an area characterized by an increase in the number of foliaceous lichens [87] with an average level of air pollution. Lichens of this species were not collected by us because they are protected.
4. Limitations
Given the local nature of the research, we are aware of the limitations that are associated with case study type research. We have tried to address the limitations as well as the external variables that affect the quality of the research obtained. For example, Stojanowska et al. showed that different lichen species, such as Pseudevernia furfuracea, exhibited varying degrees of bioaccumulation after exposure to heavy metals, which may be influenced by climatic conditions such as drought, potentially leading to inconsistent monitoring results. This study indicates that lichen species may not be equally effective under all conditions, highlighting the importance of environmental influences [6]. In this case, the conditions under which the lichens were sampled were maintained (the same for all measurement sites), but we did not analyze the meteorological data and their potential impact on metal deposition in the lichens.
Furthermore, the spatial distribution of lichens also affects their usefulness in biomonitoring. Will-Wolf et al. emphasize that, although lichens can successfully indicate air pollution over large geographical areas, their effectiveness may be compromised if they are not sampled in a stratified manner that takes into account local environmental heterogeneities [88]. Particularly in regions affected by point sources of pollution, Heiner et al. emphasize the importance of site selection and distance from pollution sources to accurately assess lichen health and metal accumulation patterns [89]. In this case, we only showed sampling at a dozen sites in the city center. This certainly had an impact on the overall picture of pollution in the area. In the future, it would be advisable to adopt a methodology that takes into account monitoring primarily, for example, the area of the entire city within the administrative boundaries, a regular sampling plot, as well as taking into account the seasonality or periodicity of existing air quality monitoring using lichens as biomonitors of heavy metals. Monitoring of other pollutants, such as PAH and microplastics, should also be undertaken in the future [22,90].
Lichens also show varying degrees of bioindication capacity depending on the specific pollutants being monitored. Research indicates that, while epiphytic lichens are excellent indicators of atmospheric heavy metals, they may not be as effective for other pollutants, such as sulphur compounds or agrochemicals [91]. This illustrates the complexity involved in selecting suitable lichen species for biomonitoring specific pollutants. In the case of our study, the species used, H. physodes, is a suitable biomonitor for assessing air pollution in terms of heavy metal concentrations [92].
Finally, practical challenges, such as the need for expertise in lichen taxonomy and the inconspicuous nature of some species, can hinder effective monitoring. Attanayaka and Wijeyaratne highlighted that a lack of comprehensive taxonomic knowledge can hinder the use of lichens in air quality monitoring, particularly in regions where understanding of local species is limited [93]. In this case, the identification atlases and keys we used, together with the use of chemotaxonomy, ruled out the possibility of confusion or mismatched species. As previously shown, an additional taxon was identified and confirmed according to the lichen scale and the extent/level of contamination using specific lichen species.
5. Conclusions
In the era of climate warming, changes in the environment and the impact of these changes on human health, as well as cheap and effective methods of assessing pollution, including atmospheric aerosol, are sought. The passive biomonitoring method using lichens responds to this need. Lichens, as has been shown, can be a source of information on the level of air pollution in urban agglomerations and green enclaves, where the air should potentially be clean. Using the lichen scale and photos of each sample taken, we can state that the studied areas of the city of Opole can be classified as zone IV—the study area is an area with an average level of air pollution.
Accumulation concentrations of heavy metals in lichen were metal-specific and varied spatially, thus reflecting local differences in heavy metal deposition. High metal concentrations near major roads and industrial plants indicated that anthropogenic factors were mainly responsible for changes in atmospheric metal pollution. The FA has identified several sources, such as emissions from motorized transport and manufacturing industries, that contribute to the presence of trace elements in the atmospheric particulate.
These results are supported by data on the CF and PLI indicators, and Opole can generally be characterized as ‘moderately polluted’. The sensitivity of the relevant biomonitor (characterized, for example, by chemotaxonomy), together with the pollution indicators, made it possible to assess the degree of pollution in the city center.
The conducted studies positively verified the hypotheses and confirmed that passive biomonitoring using lichens could effectively assess air pollution, including heavy metals, and identify potential pollution sources.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos16050576/s1, Figure S1: The centrally located thallus of Polycauliona candelaria against the background of Hypogymnia physodes on the bark of the tree located at point no. 15; Table S1: Characteristics of the area of study, Opole city; Table S2: Limits of detection (IDL) and quantification (IQL) for the iCE 3500 atomic absorption spectrometer from Thermo Electron Corporation (USA) [mg/dm3]; Table S3: Comparison of measured and certified concentrations in BCR-482 lichen and BCR-414 plankton; Table S4: Mean values of relative standard deviation (RSD) [%] for the performed analytical replicates of lichen samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.B., P.Ś. and M.R.; methodology, L.B., P.Ś. and M.R.; validation, O.I., K.I. and M.R.; formal analysis, L.B., P.Ś. and M.R.; investigation, L.B. and P.Ś.; resources, L.B.; data curation, P.Ś.; writing—original draft preparation, L.B. and P.Ś.; writing—review and editing, O.I., K.I. and M.R.; visualization, L.B., P.Ś., O.I. and K.I.; supervision, O.I., K.I. and M.R.; project administration, P.Ś. and M.R.; funding acquisition, M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out at MCBR UO (International Research and Development Center of the University of Opole), which was established as part of a project co-financed by the European Union under the European Regional Development Fund, RPO WO 2014-2020, Action 1.2 Infrastructure for R&D. Agreement No. RPOP.01.02.00-16-0001/17-00 dated 31 January 2018.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ristic, S.; Kosanic, M.; Rankovic, B.; Stamenkovic, S. Lichens as Biological Indicators of Air Quality in the Urban Area of Kursumlija (Southern Serbia). Kragujev. J. Sci. 2017, 39, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostryukova, A.M.; Krupnova, T.G.; Mashkova, I.V.; Schelkanova, E.E. Monitoring Air Quality Using Lichens in Chelyabinsk, Russian Federation. Int. J. GEOMATE 2017, 12, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, B.; Tarasek, A.; Hajduk, J. Trace Element Concentrations in Lichens Collected in the Beskidy Mountains, the Outer Western Carpathians. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska, M.; Klimek, B. Trace Element Concentrations in Tree Leaves and Lichen Collected Along a Metal Pollution Gradient Near Olkusz (Southern Poland). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 100, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, M.; Bhardwaj, S.; Kumar, V.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Lichens as Effective Bioindicators for Monitoring Environmental Changes: A Comprehensive Review. Total Environ. Adv. 2024, 9, 200085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanowska, A.; Rybak, J.; Bożym, M.; Olszowski, T.; Bihałowicz, J.S. Spider Webs and Lichens as Bioindicators of Heavy Metals: A Comparison Study in the Vicinity of a Copper Smelter (Poland). Sustainability 2020, 12, 8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niepsch, D.; Clarke, L.J.; Newton, J.; Tzoulas, K.; Cavan, G. High Spatial Resolution Assessment of Air Quality in Urban Centres Using Lichen Carbon, Nitrogen and Sulfur Contents and Stable-Isotope-Ratio Signatures. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 58731–58754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslać Mikulec, M.; Likić, S.; Antonić, O.; Tkalec, M. Any Way the Wind Blows Does Really Matter in Lichen Response to Air Pollution from an Oil Refinery. Toxics 2025, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Wang, J.G.; Xia, Y.; Yang, M.J.; Liu, S.W.; Zhao, L.C.; Guo, X.P.; Jiang, Y.J.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.F.; et al. Elemental Compositions of Lichens from Duolun County, Inner Mongolia, China: Origin, Road Effect and Species Difference. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukabayeva, Z.; Abiyev, S.; Silybayeva, B.; Assanova, U.; Sharipkhanova, A.; Sagdatkyzy, B. Epiphytic and Epigeal Lichens as Bioindicators of Air Pollution in the Burabay National Park, Kazakhstan. Biodiversitas 2023, 24, 2701–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Ochoa, M.A.; Vélez-Monsalve, L.C.; Saldarriaga-Molina, J.C. Spatial Distribution of Lichen Communities and Air Pollution Mapping in a Tropical City: Medellín, Colombia. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2021, 69, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, L.; Bandoni, E.; Sanità di Toppi, L. Lichens and Mosses as Biomonitors of Indoor Pollution. Biology 2023, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhardi, J.A.; García-Tenorio, R.; Díaz Francés, I.; Bonotto, D.M.; Marcelli, M.P. Natural Radionuclides in Lichens, Mosses and Ferns in a Thermal Power Plant and in an Adjacent Coal Mine Area in Southern Brazil. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 167, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriyyah, P.N. Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Parmeliaceae Lichens and Mahogany Bark in Multiple Locations within Bandung City, Indonesia. Acta Biochim. Indones. 2023, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Vannini, A.; Pagano, L.; Bartoli, M.; Fedeli, R.; Malcevschi, A.; Sidoli, M.; Magnani, G.; Pontiroli, D.; Riccò, M.; Marmiroli, M.; et al. Accumulation and Release of Cadmium Ions in the Lichen Evernia prunastri (L.) Ach. and Wood-Derived Biochar: Implication for the Use of Biochar for Environmental Biomonitoring. Toxics 2024, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciani, F.; Fornasaro, S.; Benesperi, R.; Bianchi, E.; Cabassi, J.; Di Nuzzo, L.; Grifoni, L.; Venturi, S.; Costagliola, P.; Rimondi, V. Mercury Accumulation Efficiency of Different Biomonitors in Indoor Environments: The Case Study of the Central Italian Herbarium (Florence, Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 124232–124244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, T.; Degrave, W.M.S.; Duarte, G.F. Lichens and Health—Trends and Perspectives for the Study of Biodiversity in the Antarctic Ecosystem. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coufalík, P.; Zvěřina, O. Accurate Determination of Trace Gallium in Antarctic Terrestrial Flora Using Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. At. Spectrosc. 2024, 45, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarova, M.; Grifoni, L.; Aherne, J.; Loppi, S. Comparison of Lichens and Mosses as Biomonitors of Airborne Microplastics. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osyczka, P.; Boroń, P.; Lenart-Boroń, A.; Rola, K. Modifications in the Structure of the Lichen Cladonia Thallus in the Aftermath of Habitat Contamination and Implications for Its Heavy-Metal Accumulation Capacity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1950–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protano, C.; Owczarek, M.; Fantozzi, L.; Guidotti, M.; Vitali, M. Transplanted Lichen Pseudovernia Furfuracea as a Multi-Tracer Monitoring Tool Near a Solid Waste Incinerator in Italy: Assessment of Airborne Incinerator-Related Pollutants. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niepsch, D.; Clarke, L.J.; Jones, R.G.; Tzoulas, K.; Cavan, G. Lichen Biomonitoring to Assess Spatial Variability, Potential Sources and Human Health Risks of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Airborne Metal Concentrations in Manchester (UK). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viso, S.; Rivera, S.; Martinez-Coronado, A.; Esbrí, J.M.; Moreno, M.M.; Higueras, P. Biomonitoring of Hg0, Hg2+ and Particulate Hg in a Mining Context Using Tree Barks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagic-Serdar, R.; Markovic, M.; Rakonjac, L. Lichens As the Biological Indicators of Air Pollution in the Bio-Monitoring System Used on Icp Sample Plots Level II in Serbia. Agric. For. 2023, 69, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernat Popa, M.M.; Rusănescu, C.O. The Efficiency of Lichens in Air Biomonitoring in Teleorman County. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, A.; Işık, V.; Aydın, S.S. Heavy Metal Biomonitoring Study Using Transplanted Lichen, Pseudevernia furfuracea (L.) Zopf, in Kirikkale, Turkey. MOJ Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2023, 8, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, P.; Chiva, S.; Catalá, M.; Garmendia, A.; Casale, M.; Gomez, J.; Pazos, T.; Giordani, P.; Calatayud, V.; Barreno, E. Lichen Biodiversity and Near-Infrared Metabolomic Fingerprint as Diagnostic and Prognostic Complementary Tools for Biomonitoring: A Case Study in the Eastern Iberian Peninsula. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.S.; Perez Catan, S.; Di Fonzo, C.; Dopchiz, L.; Arribere, M.A.; Ansaldo, M.; Messuti, M.I.; Bubach, D.F. Lichen as Biomonitor of Atmospheric Elemental Composition from Potter Peninsula, 25 de Mayo (King George) Island, Antarctica. Ann. Mar. Sci. 2018, 2, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuzaan, P.; Batsuren, Z.; Enkhtuya, O.; Sosorburam, E.; Damdinsuren, B. Analysis of Lichen and Moss Samples by the EDXRF Method. X-Ray Spectrom. 2025, 54, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardiani, T.; Khoiron, N.; Meilinda, M. The Utilization of Lichen As Biomonitoring NO2 Gas Emission in The City of Palembang. Al-Kauniyah J. Biol. 2024, 17, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belguidoum, A.; Haichour, R.; Lograda, T.; Ramdani, M. Biomonitoring of Air Pollution by Lichen Diversity in the Urban Area of Setif, Algeria. Biodiversitas 2022, 23, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biase, L.; Di Lisio, P.; Pace, L.; Arrizza, L.; Fattorini, S. Use of Lichens to Evaluate the Impact of Post-Earthquake Reconstruction Activities on Air Quality: A Case Study from the City of L’Aquila. Biology 2022, 11, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, A.; Rasli, F.N.; Juhari, M.L. Lichen as the Biological Indicator for Detection of Environmental Tobacco Smoke (ETS) at the Public Office Building in Selangor, Malaysia. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, H.T.; Geiser, L.H.; Jovan, S.; Neitlich, P. Epiphytic Macrolichen Indication of Air Quality and Climate in Interior Forested Mountains of the Pacific Northwest, USA. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 53, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnan, Y.; Probst, A.; Séjalon-Delmas, N. Evaluation of Lichen Species Resistance to Atmospheric Metal Pollution by Coupling Diversity and Bioaccumulation Approaches: A New Bioindication Scale for French Forested Areas. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamo, D.A.; Chaubey, A.K.; Hailu, A.T.; Hibstie, A.Y. Analysis of Atmospheric Air Pollutants Using Lichens as a Bio-Monitor by Calibration Free-Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Technique. Eur. J. Appl. Phys. 2023, 5, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, A.; Vardar, Ç.; Aksoy, A.; Ünal, E. Biomonitoring of Heavy Metals Deposition with Pseudevernia furfuracea (L.) Zopf in Çorum City, Turkey. Health Sci. Q. 2018, 2, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, S.P.; Yurukova, L.D.; Velcheva, I.G. Lichen-Bags as a Biomonitoring Technique in an Urban Area. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2015, 13, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullin, R.T.; Bennett, L.L.; Bjorgan, O.J.; Bourque, D.A.; Burke, C.J.; Clarke, M.A.; Gutgesell, M.K.; Krawiec, P.L.; Malyon, R.; Mantione, A.; et al. Relationships between Air Pollution, Population Density, and Lichen Biodiversity in the Niagara Escarpment World Biosphere Reserve. Lichenologist 2016, 48, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frati, L.; Brunialti, G. Recent Trends and Future Challenges for Lichen Biomonitoring in Forests. Forests 2023, 14, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekuria, G. Air Pollution: A Review of Its Impacts on Health and Ecosystems, and Analytical Techniques for Their Measurement and Modeling. J. Environ. Inform. Lett. 2023, 10, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Gordillo, A.; Ruiz-Correa, S.; Robledo-Valero, V.; Hernández-Rosales, C.; Arriaga, S. Recent Advancements in Low-Cost Portable Sensors for Urban and Indoor Air Quality Monitoring. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 1931–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opole City Hall About the City. Available online: https://www.opole.pl/dla-inwestora/o-miescie (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Wiatkowska, B.; Słodczyk, J.; Stokowska, A. Spatial-Temporal Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Urban Areas Using Remote Sensing Images and GIS Analysis: The Case Study of Opole, Poland. Geosciences 2021, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniański, G.Z. The Lichen Biota of Opole Silesia (South Poland) Part 1. The List of Lichen Species; University of Opole Publishing House: Opole, Poland, 2010; ISBN 978-83-7395-383-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kozłowski, R.; Ludew, M. Possibilities of Using Lichen Hypogymnia physodes (L.) Nyl. to Assess the Impact of the Cement Industry on the Natural Environment of Białe Zagłębie. Przegląd Geogr. 2025, 97, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adžemović, S.; Aliefendić, S.; Mehić, E.; Ranica, A.; Vehab, I.; Alagić, N.; Delibašić, Š.; Herceg, K.; Karić, M.; Hadžić, B.; et al. Estimation of Atmospheric Deposition Utilizing Lichen Hypogymnia Physodes, Moss Hypnum Cupressiforme and Soil in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Heidmarsson, S.; Olafsdottir, E.S.; Buonfiglio, R.; Kogej, T.; Omarsdottir, S. Secondary Metabolites from Cetrarioid Lichens: Chemotaxonomy, Biological Activities and Pharmaceutical Potential. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fałtynowicz, W. Porosty w Lasach. Przewodnik Terenowy Dla Leśników i Taksatorów; Dominiewska, A., Ed.; Centrum Informacyjne Lasów Państwowych: Warszawa, Poland, 2012; ISBN 9788361633822. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, B. How to Collect and Study Lichens. Bryologist 1905, 8, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. ICE 3000 Series AA Spectrometers Operator’s Manual; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 44, pp. 1–1, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Świsłowski, P.; Nowak, A.; Rajfur, M. Is Your Moss Alive during Active Biomonitoring Study? Plants 2021, 10, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinkaralar, O.; Isinkaralar, K.; Bayraktar, E.P. Monitoring the Spatial Distribution Pattern According to Urban Land Use and Health Risk Assessment on Potential Toxic Metal Contamination via Street Dust in Ankara, Türkiye. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinkaralar, O.; Isinkaralar, K.; Sevik, H. Health for the Future: Spatiotemporal CA-MC Modeling and Spatial Pattern Prediction via Dendrochronological Approach for Nickel and Lead Deposition. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Pandey, C.M.; Singh, U.; Gupta, A.; Sahu, C.; Keshri, A. Descriptive Statistics and Normality Tests for Statistical Data. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2019, 22, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocianowski, J.; Wrońska-Pilarek, D.; Krysztofiak-Kaniewska, A.; Matusiak, K.; Wiatrowska, B. Comparison of Pearson’s and Spearman’s Correlation Coefficients Values for Selected Traits of Pinus sylvestris L. Biom. Lett. 2024, 61, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauke, J.; Kossowski, T. Comparison of Values of Pearson’s and Spearman’s Correlation Coefficients on the Same Sets of Data. Quaest. Geogr. 2011, 30, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Fan, M.; Hu, R.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y. Mosses Are Better than Leaves of Vascular Plants in Monitoring Atmospheric Heavy Metal Pollution in Urban Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.A.; Carballeira, A. Evaluation of Contamination, by Different Elements, in Terrestrial Mosses. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 40, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markert, B. Establishing of “Reference Plant” for Inorganic Characterization of Different Plant Species by Chemical Fingerprinting. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1992, 64, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wu, P.; Yang, F.; Sun, D.L.; Zhang, D.X.; Zhou, Y.K. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution and Human Health Risks in Urban Soils around an Electronics Manufacturing Facility. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzych, A.; Zduńczyk, A.; Astel, A. Epiphytic Lichens as Bioindicators of Air Pollution by Heavy Metals in an Urban Area (Northern Poland). J. Elem. 2016, 21, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanty, A.; Węgrzyn, M.; Wietrzyk-Pełka, P.; Fołta, M.; Krośniak, M.; Podolak, I.; Zagrodzki, P. Quantitative Variations of Usnic Acid and Selected Elements in Terricolous Lichen Cladonia Mitis Sandst., with Respect to Different Environmental Factors—A Chemometric Approach. Phytochemistry 2021, 192, 112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicka-Kapusta, K.; Zakrzewska, M.; Gdula-Argasińska, J.; Bydłoń, G. Air Pollution in the Base Stations of the Environmental Integrated Monitoring System in Poland. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 82, 465–475. [Google Scholar]
- Ramić, E.; Huremović, J.; Muhić-Šarac, T.; Đug, S.; Žero, S.; Olovčić, A. Biomonitoring of Air Pollution in Bosnia and Herzegovina Using Epiphytic Lichen Hypogymnia Physodes. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koroleva, Y.; Revunkov, V. Air Pollution Monitoring in the South-East Baltic Using the Epiphytic Lichen Hypogymnia Physodes. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Isley, C.F.; Handley, H.K.; Taylor, M.P. Atmospheric Sources of Anthropogenic and Geogenic Trace Metals in Australian Lichen and Fungi. Anthropocene 2021, 33, 100279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghanathan, N. Assortativity Analysis of Real-World Network Graphs Based on Centrality Metrics. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2016, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörter, M.; Karadeniz, H.; Saklangıç, U.; Yenisoy-Karakaş, S. The Use of Passive Lichen Biomonitoring in Combination with Positive Matrix Factor Analysis and Stable Isotopic Ratios to Assess the Metal Pollution Sources in Throughfall Deposition of Bolu Plain, Turkey. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rhzaoui, G.; Divakar, P.K.; Crespo, A.; Tahiri, H. Biomonitoring of Air Pollutants by Using Lichens (Evernia prunastri) in Areas between Kenitra and Mohammedia Cities in Morocco. Lazaroa 2015, 36, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrica, D.; Lo Medico, F.; Alaimo, M.G. Air Quality Assessment by the Determination of Trace Elements in Lichens (Xanthoria calcicola) in an Industrial Area (Sicily, Italy). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rola, K.; Latkowska, E.; Ogar, W.; Osyczka, P. Towards Understanding the Effect of Heavy Metals on Mycobiont Physiological Condition in a Widespread Metal-Tolerant Lichen Cladonia Rei. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiku, M.; Kelmendi, M.; Kadriu, S. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution of Sedimentation in the Sitnica River Based on Pollution Indicators. Nauk. Visnyk Natsionalnoho Hirnychoho Universytetu 2021, 6, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Mohammed, L.; Abdelhay, E.G. Use of New Indices for the Assessment of Air Quality in the Safi Region (Morocco) Using Lichen Biomonitoring of Air Contamination by Trace Elements. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 111, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.; Caricchi, C.; Guidotti, M.; Owczarek, M.; Macrì, P.; Nazzari, M.; Amoroso, A.; Di Giosa, A.; Listrani, S. Combined Magnetic, Chemical and Morphoscopic Analyses on Lichens from a Complex Anthropic Context in Rome, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, Z.; Chowdhury, M.S.A.; Hossain, M.D.; Nakagami, K. Contamination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in the Sediment of Turag River, Bangladesh: An Index Analysis Approach. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, M.R.J.; Hossain, M.B.; Kumar, R.; Ullah, M.A.; Al Nahian, S.; Rima, N.N.; Choudhury, T.R.; Liba, S.I.; Yu, J.; Khandaker, M.U.; et al. Spatial Distribution and Risk Assessments Due to the Microplastics Pollution in Sediments of Karnaphuli River Estuary, Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. The Influence of Iron Oxides on Wheel–Rail Contact: A Literature Review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2018, 232, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.H.; Lin, C.S.; Lu, S.Y.; Lin, J.C.; Wang, H.H.; Liu, C.P. Effect of Air Quality Improvement by Urban Parks on Mitigating PM2.5 and Its Associated Heavy Metals: A Mobile-Monitoring Field Study. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.N.; Kwak, M.J.; Je, S.M.; Lee, J.K.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Jeong, S.G.; Choi, Y.S.; Woo, S.Y. Morpho-Physio-Biochemical Attributes of Roadside Trees as Potential Tools for Biomonitoring of Air Quality and Environmental Health in Urban Areas. Land 2021, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Ma, T.; Mendez-Jimenez, D.; Cobb, L.C.; Frederickson, C.; Fang, T.; Hwang, B.; Shiraiwa, M.; et al. Metal Contents and Size Distributions of Brake and Tire Wear Particles Dispersed in the Near-Road Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.J.; Fang, S.B.; Liu, S.W.; Zhao, L.C.; Guo, X.P.; Jiang, Y.J.; Hu, J.S.; Liu, X.D.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.D.; et al. Lichen Elemental Composition Distinguishes Anthropogenic Emissions from Dust Storm Inputs and Differs among Species: Evidence from Xilinhot, Inner Mongolia, China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimondi, V.; Benesperi, R.; Beutel, M.W.; Chiarantini, L.; Costagliola, P.; Lattanzi, P.; Medas, D.; Morelli, G. Monitoring of Airborne Mercury: Comparison of Different Techniques in the Monte Amiata District, Southern Tuscany, Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, A.; Jamal, M.B.; Gramigni, M.; Fedeli, R.; Ancora, S.; Monaci, F.; Loppi, S. Accumulation and Release of Mercury in the Lichen Evernia prunastri (L.) Ach. Biology 2021, 10, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováčik, J.; Husáková, L.; Piroutková, M.; Babula, P. Mercury Content and Amelioration of Its Toxicity by Nitric Oxide in Lichens. Plants 2023, 12, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słaby, A.; Lisowska, M. Epiphytic Lichen Recolonization in the Centre of Cracow (Southern Poland) as a Result of Air Quality Improvement. Pol. J. Ecol. 2012, 60, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Matwiejuk, A.; Kałuska, A. Lichens of Sokółka (Podlasie, NE Poland) as Indicators of the State of Air Pollution. Ochr. Sr. Zasobów Nat. 2014, 25, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Will-Wolf, S.; Jovan, S.; Amacher, M.C. Lichen Elemental Content Bioindicators for Air Quality in Upper Midwest, USA: A Model for Large-Scale Monitoring. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 78, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiner, M.; Grimm, T.; Smith, H.; Leavitt, S.D.; Christensen, W.F.; Carling, G.T.; St. Clair, L.L. Multivariate Receptor Modeling with Widely Dispersed Lichens as Bioindicators of Air Quality. Environmetrics 2023, 34, e2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurozzi, D.; Gallitelli, L.; Cesarini, G.; Romano, S.; Orsini, M.; Scalici, M. Passive Biomonitoring of Airborne Microplastics Using Lichens: A Comparison between Urban, Natural and Protected Environments. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, S.; Vergara, M.; Rivadeneira, B.; Rodríguez, J.; Carpio, A. Use of Lichens as Bioindicators of Contamination by Agrochemicals and Metals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 49214–49226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meysurova, A.F.; Notov, A.A.; Pungin, A.V.; Skrypnik, L.N. Application of Optical Spectroscopy for the Analysis of Physiological Characteristics and Elemental Composition of Lichens of the Genus Hypogymnia with Different Degrees of Anthropotolerance. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2024, 91, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attanayaka, A.N.P.M.; Wijeyaratne, S.C. Corticolous Lichen Diversity, a Potential Indicator for Monitoring Air Pollution in Tropics. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2013, 41, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).