Climatology of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Using ERA5: Spatio-Temporal Variations and Controlling Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Boundary Layer Height Retrieved from ERA5
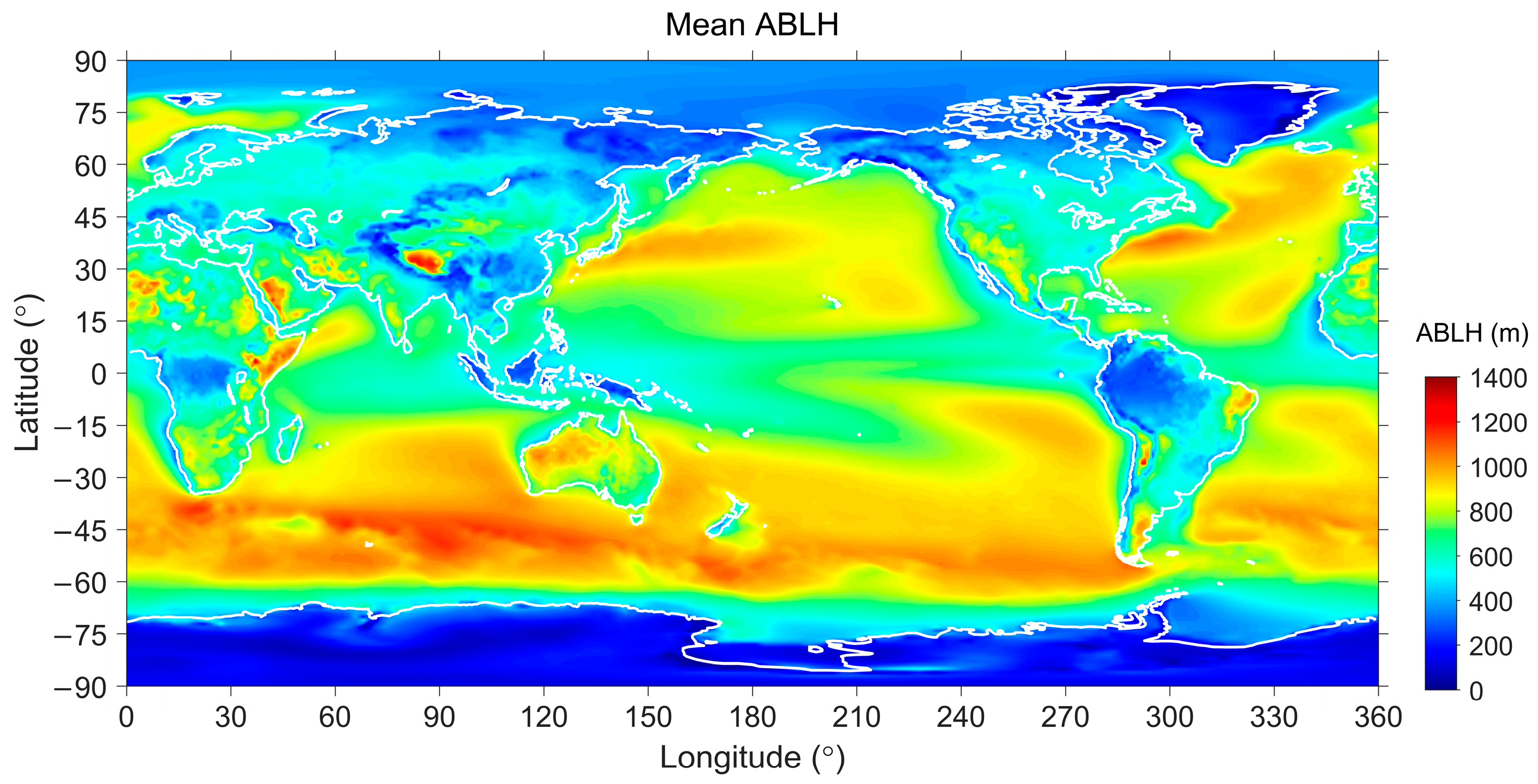
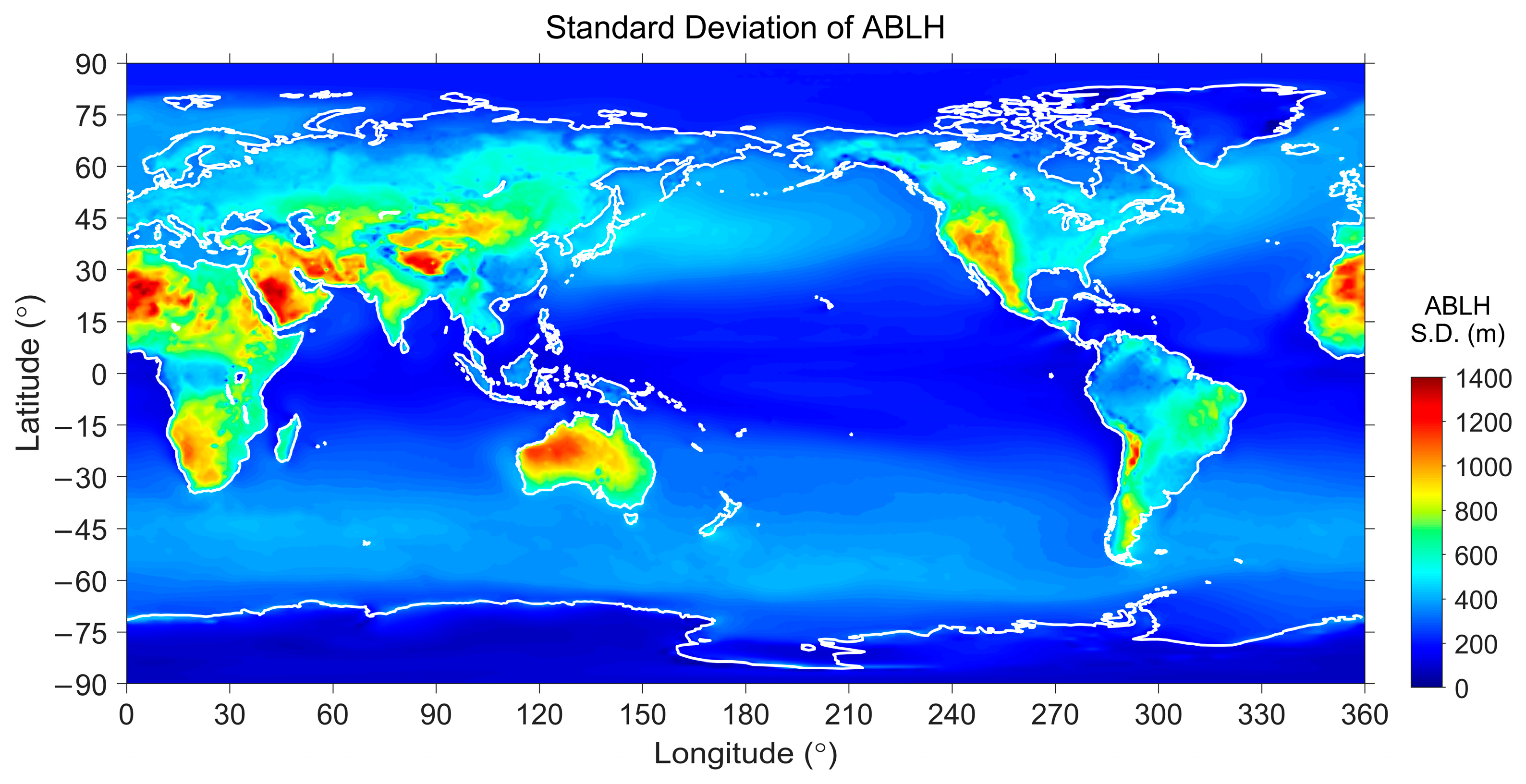
3. General Climatology of the ABLH
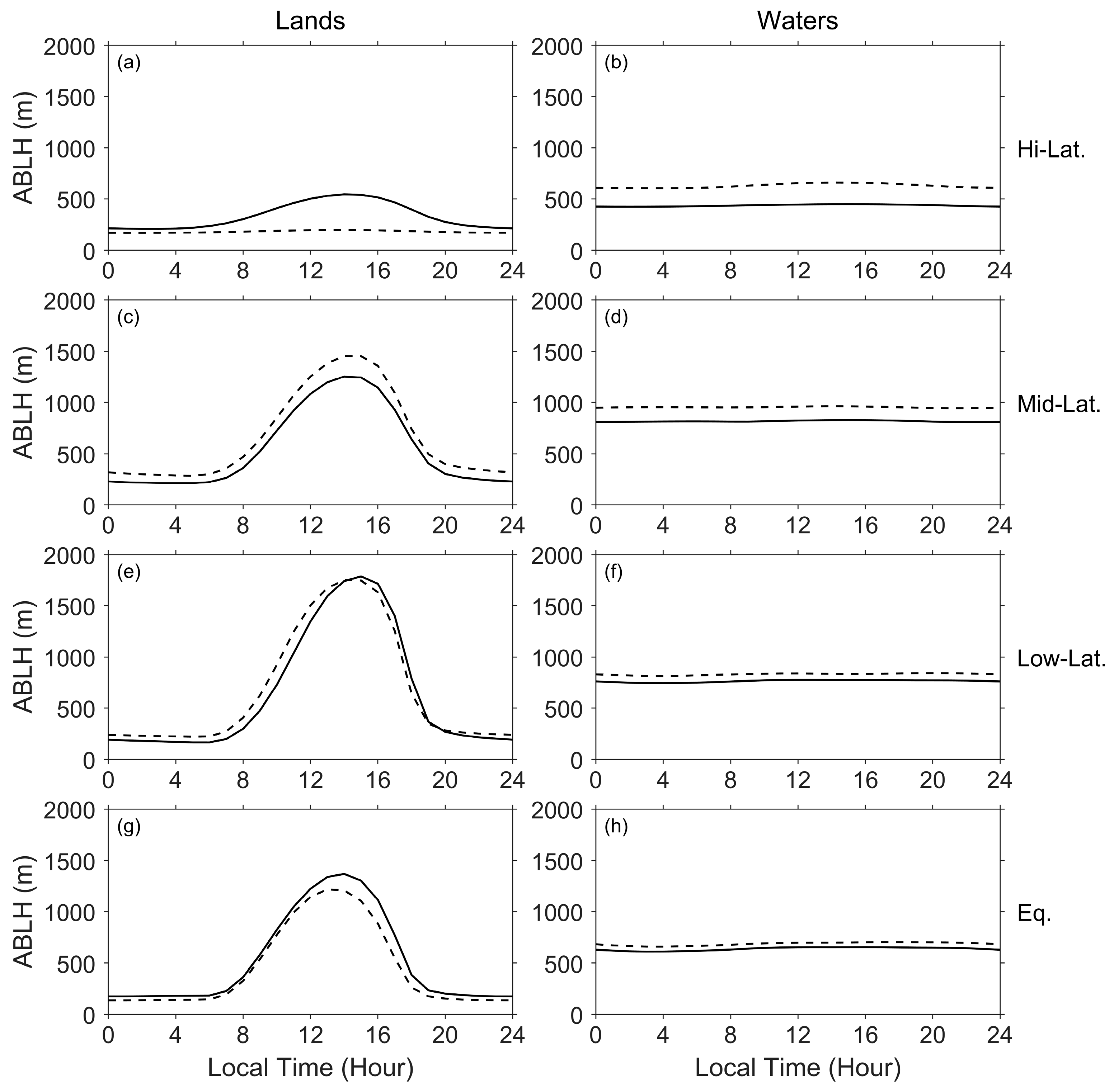
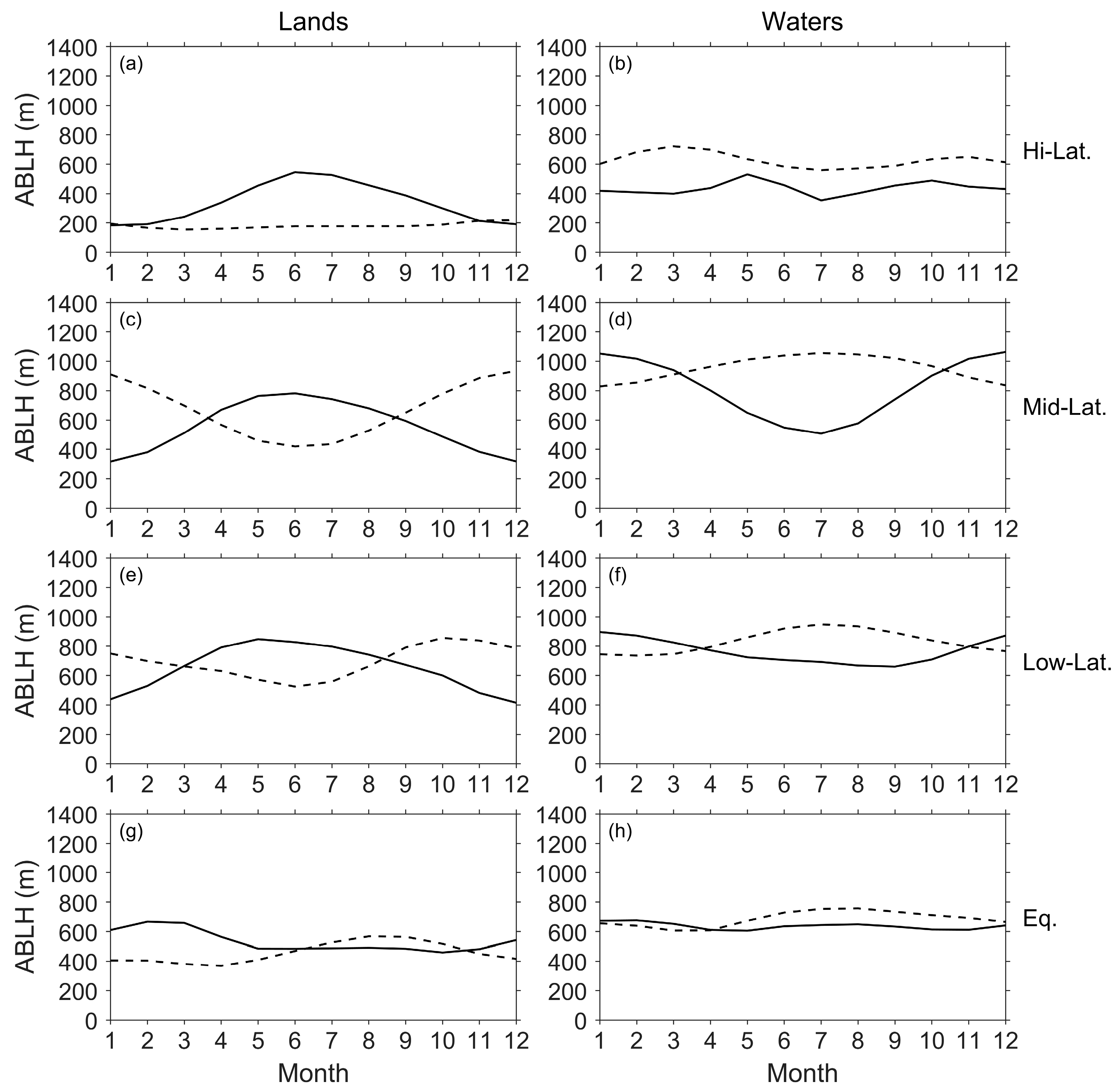
- Equatorial region/latitude(s): the area at latitudes less than or equal to 10°.
- Low latitude(s): the areas at latitudes between 11° and 30°.
- Mid-latitude(s): the areas at latitudes between 31° and 60°.
- High latitude(s): the areas at latitudes equal to or greater than 61°.
3.1. Long-Term Mean ABLH
3.2. Diurnal Variation in the ABLH
3.3. Seasonal Variation in the ABLH
3.4. Monthly and Hourly ABLH Maps
4. Weather Conditions and Correlation Analyses
4.1. Meteorological Parameters as Proxies of Weather Conditions
4.2. Correlation Analyses: A Short Preface
4.3. Spatial Correlation Analyses
4.3.1. Spatial Analysis Results over Lands
4.3.2. Spatial Analysis Results over Waters
4.3.3. Short Summary of the Spatial Analyses
4.4. Temporal Correlation Analyses
5. Controlling Factors of the ABLH
5.1. Synoptic-Scale Weather Systems
5.1.1. Convergence Zones
5.1.2. Extratropical Cyclones and Frontal Systems
5.2. Ocean–Atmosphere Interactions
5.2.1. Ocean Currents
5.2.2. ABLH Response to El Niño/La Niña Events
5.3. Topographic Effects
5.4. Desert and Hot Semi-Arid Climates
5.5. Monsoon and Seasonal Precipitation
6. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABL | Atmospheric boundary layer |
| ABLH | Atmospheric boundary layer height |
| PBL | Planetary boundary layer |
| EZ | Entrainment zone |
| CI | Capping inversion |
| ML | Mixed layer |
| SST | Sea surface temperature |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| AGL | Above ground level |
| LT | Local time |
| UT | Universal time |
| T2M | 2 m temperature |
| TP | Total precipitation |
| TCWV | Total column water vapor |
| ITCZ | Intertropical convergence zone |
| SPCZ | South Pacific convergence zone |
| SACZ | South Atlantic convergence zone |
| SIOCZ | South Indian Ocean convergence zone |
| NWP | Northwest Pacific Ocean off Japan |
| NA | North Atlantic Ocean off North America |
| ONI | Oceanic Niño Index |
| ABLH_Diff | ABLH difference between El Niño and La Niña conditions |
| T2M_Diff | T2M difference between El Niño and La Niña conditions |
| TP_Diff | TP difference between El Niño and La Niña conditions |
| TCWV_Diff | TCWV difference between El Niño and La Niña conditions |
References
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R. Practical Meteorology: An Algebra-Based Survey of Atmospheric Science; Version 1.02b ed.; University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Garratt, J.R. The Atmospheric Boundary Layer; Cambridge University Press: Melbourne, Australia, 1994; p. 336. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Wang, B. The role of longwave radiation and boundary layer thermodynamics in forcing tropical surface winds. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 1049–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtslag, A.A.M.; Svensson, G.; Baas, P.; Basu, S.; Beare, B.; Beljaars, A.C.M.; Bosveld, F.C.; Cuxart, J.; Lindvall, J.; Steeneveld, G.J.; et al. Stable atmospheric boundary layers and diurnal cycles: Challenges for weather and climate models. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1691–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.; Hartmann, D.L.; Klein, S.A. The role of clouds, water vapor, circulation, and boundary layer structure in the sensitivity of the tropical climate. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2359–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerlinger, P.; Moore, F.R. Atmospheric Structure and Avian Migration. In Current Ornithology; Power, D.M., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; pp. 109–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, H.D.; Young, G.S.; Yates, M.A.; Fuller, M.R.; Seegar, W.S. Measurements of thermal updraft intensity over complex terrain using American white pelicans and a simple boundary-layer forecast model. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2002, 104, 167–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, J.T.; Bildstein, K.L.; Bohrer, G.; Winkler, D.W. Movement ecology of migration in turkey vultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19102–19107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bott, A. A numerical model of the cloud-topped planetary boundary-layer: Impact of aerosol particles on the radiative forcing of stratiform clouds. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 123, 631–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.M.; Anderson, J.R.; Quinn, P.K.; McInnes, L.M.; Brechtel, F.J.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Pósfai, M.; Thomson, D.S.; Buseck, P.R. Influence of sea-salt on aerosol radiative properties in the Southern Ocean marine boundary layer. Nature 1998, 392, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, S.C.; Dickinson, R.E. Radiative effects of aerosols on the evolution of the atmospheric boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, AAC 3-1–AAC 3-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Xia, X.; Tao, M.; Zhu, L. Modeling the feedback between aerosol and meteorological variables in the atmospheric boundary layer during a severe fog–haze event over the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petäjä, T.; Järvi, L.; Kerminen, V.M.; Ding, A.J.; Sun, J.N.; Nie, W.; Kujansuu, J.; Virkkula, A.; Yang, X.; Fu, C.B.; et al. Enhanced air pollution via aerosol-boundary layer feedback in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.; Bretherton, C.S. Boundary layer depth, entrainment, and decoupling in the cloud-capped subtropical and tropical marine boundary layer. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3576–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, B.; Hall, A.; Stevens, B. What controls the mean depth of the PBL? J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3157–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, G.; Ratnam, M.V. Identification of atmospheric boundary layer height over a tropical station using high-resolution radiosonde refractivity profiles: Comparison with GPS radio occultation measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D16101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Sokolovskiy, S.V.; Lenschow, D.H. Estimating atmospheric boundary layer depth using COSMIC radio occultation data. J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 68, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, C.O.; Waliser, D.E.; Chan, S.K.; Li, J.-L.; Tian, B.; Xie, F.; Mannucci, A.J. Planetary boundary layer heights from GPS radio occultation refractivity and humidity profiles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D16117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Beljaars, A.; Golaz, J.-C.; Jacobson, A.R.; Medeiros, B. Climatology of the planetary boundary layer over the continental United States and Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D17106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Engeln, A.; Teixeira, J. A planetary boundary layer height climatology derived from ECMWF reanalysis data. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 6575–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, G.; Kishore, P.; Ratnam, M.V.; Ravindra Babu, S.; Velicogna, I.; Jiang, J.H.; Ao, C.O. Global climatology of planetary boundary layer top obtained from multi-satellite GPS RO observations. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 52, 2385–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, W.P.; Eloranta, E.W. Lidar measurements of wind in the planetary boundary layer: The method, accuracy and results from joint measurements with radiosonde and kytoon. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1986, 25, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempreviva, A.M.; Gryning, S.-E. Mixing height over water and its role on the correlation between temperature and humidity fluctuations in the unstable surface layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2000, 97, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Bergström, H. An auxiliary tool to determine the height of the boundary layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2005, 115, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.J.; Ao, C.O.; Li, K. Estimating climatological planetary boundary layer heights from radiosonde observations: Comparison of methods and uncertainty analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D16113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.J.; Derbyshire, S.H.; Belcher, S.E. Tethered balloon observations of the nocturnal stable boundary layer in a valley. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2000, 97, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. A review of techniques for diagnosing the atmospheric boundary layer height (ABLH) using aerosol lidar data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecklund, W.L.; Carter, D.A.; Balsley, B.B. A UHF wind profiler for the boundary layer: Brief description and initial results. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1988, 5, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.R.; Ecklund, W.L.; Carter, D.A.; Gage, K.S.; Ethier, S.A. Research applications of a boundary-layer wind profiler. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 74, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, L.; Wilczak, J.M. Convective boundary layer depth: Improved measurement by doppler radar wind profiler using fuzzy logic methods. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmis, C.G.; Sgouros, G.; Tombrou, M.; Schäfer, K.; Münkel, C.; Bossioli, E.; Dandou, A. A comparative study and evaluation of mixing-height estimation based on sodar-RASS, ceilometer data and numerical model simulations. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2012, 145, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, D.; De Angelis, F.; Dupont, J.C.; Pal, S.; Haeffelin, M. Mixing layer height retrievals by multichannel microwave radiometer observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, U.; Rocadenbosch, F.; Crewell, S. Synergetic use of LiDAR and microwave radiometer observations for boundary-layer height detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 3945–3948. [Google Scholar]
- Smedman, A.-S.; Tjernström, M.; Högström, U. The near-neutral marine atmospheric boundary layer with no surface shearing stress: A case study. J. Atmos. Sci. 1994, 51, 3399–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedman, A.; Högström, U.; Bergström, H.; Rutgersson, A.; Kahma, K.K.; Pettersson, H. A case study of air-sea interaction during swell conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 25833–25851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryning, S.-E.; Batchvarova, E. Marine boundary layer and turbulent fluxes over the Baltic Sea: Measurements and modelling. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2002, 103, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath-Spangler, E.L.; Denning, A.S. Global seasonal variations of midday planetary boundary layer depth from CALIPSO space-borne LIDAR. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetzer, E.J.; Teixeira, J.; Olsen, E.T.; Fishbein, E.F. Satellite remote sounding of atmospheric boundary layer temperature inversions over the subtropical eastern Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L17102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.P.A.; Teixeira, J.; Soares, P.M.M.; Miranda, P.M.A.; Kahn, B.H.; Dang, V.T.; Irion, F.W.; Fetzer, E.J.; Fishbein, E. Infrared sounding of the trade-wind boundary layer: AIRS and the RICO experiment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L24806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Engeln, A.; Teixeira, J.; Wickert, J.; Buehler, S.A. Using CHAMP radio occultation data to determine the top altitude of the Planetary Boundary Layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L06815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolovskiy, S.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Rocken, C.; Schreiner, W.S.; Hunt, D.; Anthes, R.A. Monitoring the atmospheric boundary layer by GPS radio occultation signals recorded in the open-loop mode. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L12813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Bian, L.; et al. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13309–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrisford, P.; Dee, D.; Poli, P.; Brugge, R.v.d.; Fielding, K.; Fuentes, M.; Kållberg, P.W.; Kobayashi, S.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.H. The ERA-Interim Archive, Version 2.0; European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Complete ERA5 from 1979: Fifth Generation of ECMWF Atmospheric Reanalyses of the Global Climate. Available online: https://doi.org/10.24381/cds.adbb2d47 (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, K.; Liao, H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, K.; Lv, Y.; Shao, J.; Yu, T.; Tong, B.; et al. Investigation of near-global daytime boundary layer height using high-resolution radiosondes: First results and comparison with ERA5, MERRA-2, JRA-55, and NCEP-2 reanalyses. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 17079–17097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias-Júnior, C.Q.; Carneiro, R.G.; Fisch, G.; D’Oliveira, F.A.F.; Sörgel, M.; Botía, S.; Machado, L.A.T.; Wolff, S.; Santos, R.M.N.d.; Pöhlker, C. Intercomparison of planetary boundary layer heights using remote sensing retrievals and ERA5 reanalysis over central Amazonia. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, K.N.; Kumar, P.; Lal, S.; Kamat, D. Investigation of atmospheric boundary layer characteristics using ceilometer lidar, COSMIC GPS RO satellite, radiosonde and ERA-5 reanalysis dataset over western Indian region. Atmos. Res. 2022, 268, 105999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, V.A.; Ritvanen, J.; Urbancic, G.; Statnaia, I.; Batrak, Y.; Moisseev, D.; Kurppa, M. Boundary-layer height and surface stability at Hyytiälä, Finland, in ERA5 and observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2022, 15, 3075–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slättberg, N.; Lai, H.-W.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, D. Spatial and temporal patterns of planetary boundary layer height during 1979–2018 over the Tibetan Plateau using ERA5. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 3360–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECMWF. IFS Documentation CY41R2—Part IV: Physical Processes. In IFS Documentation CY41R2; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECMWF. ERA5: Data Documentation. Available online: https://confluence.ecmwf.int/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=76414402 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Schneider, T.; Bischoff, T.; Haug, G.H. Migrations and dynamics of the intertropical convergence zone. Nature 2014, 513, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, D.G. The South Pacific convergence zone (SPCZ): A review. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1994, 122, 1949–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Lengaigne, M.; Lintner, B.R.; Widlansky, M.J.; van der Wiel, K.; Dutheil, C.; Linsley, B.K.; Matthews, A.J.; Renwick, J. South Pacific Convergence Zone dynamics, variability and impacts in a changing climate. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.M.V.; Jones, C.; Liebmann, B. Extreme precipitation events in southeastern south America and large-scale convective patterns in the South Atlantic convergence zone. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 2377–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.M.V.; Jones, C.; Liebmann, B. The South Atlantic convergence zone: Intensity, form, persistence, and relationships with intraseasonal to interannual activity and extreme rainfall. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 88–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.H. The South Indian convergence zone and interannual rainfall variability over Southern Africa. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 3789–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barimalala, R.; Desbiolles, F.; Blamey, R.C.; Reason, C. Madagascar influence on the South Indian Ocean Convergence Zone, the Mozambique Channel Trough and southern African rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 11380–11389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, C.D.; Henson, R. Meteorology Today: An Introduction to Weather, Climate, and the Environment, 13th ed.; Cengage Learning: Belmont, TN, USA, 2021; p. 736. [Google Scholar]
- Oceanic Niño Index. Available online: https://origin.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/ensostuff/ONI_v5.php (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Folland, C.K.; Renwick, J.A.; Salinger, M.J.; Mullan, A.B. Relative influences of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation and ENSO on the South Pacific Convergence Zone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 21-21–21-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Wigley, T.M.L. Global patterns of ENSO-induced precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, V.R.; Doyle, M.E.; Camilloni, I.A. Precipitation trends in southeastern South America: Relationship with ENSO phases and with low-level circulation. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2008, 93, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotsos, C.A. The global signature of the ENSO and SST-like fields. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 113, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEBCO_2022 Grid. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5285/e0f0bb80-ab44-2739-e053-6c86abc0289c (accessed on 28 June 2022).
- Gadgil, S. The Indian monsoon and its variability. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2003, 31, 429–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, J.A.; Liebmann, B.; Grimm, A.M.; Misra, V.; Silva Dias, P.L.; Cavalcanti, I.F.A.; Carvalho, L.M.V.; Berbery, E.H.; Ambrizzi, T.; Vera, C.S.; et al. Recent developments on the South American monsoon system. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 32, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Hoell, A.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Michaelsen, J. The East African Monsoon System: Seasonal Climatologies and Recent Variations. In The Monsoons and Climate Change: Observations and Modeling; de Carvalho, L.M.V., Jones, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
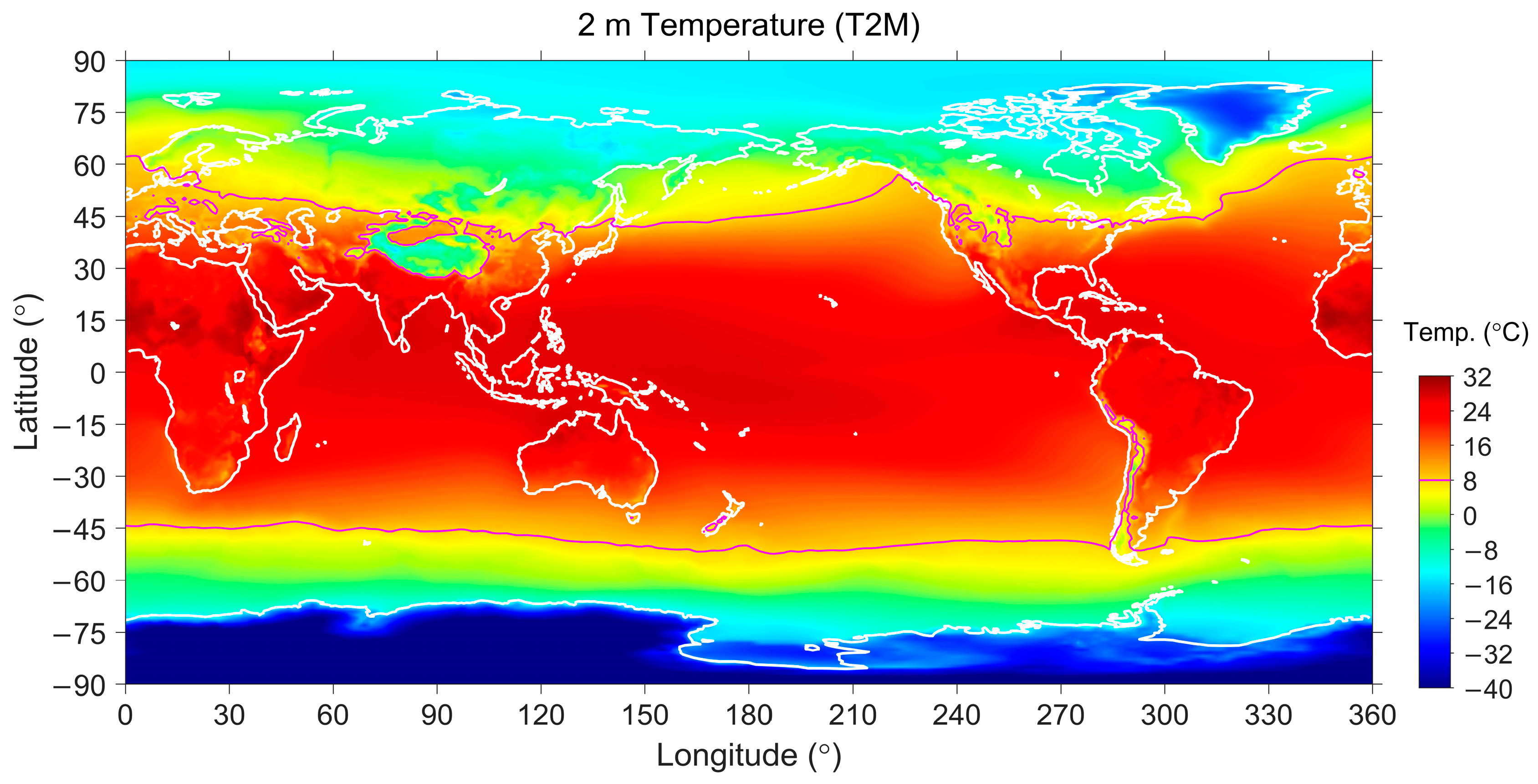
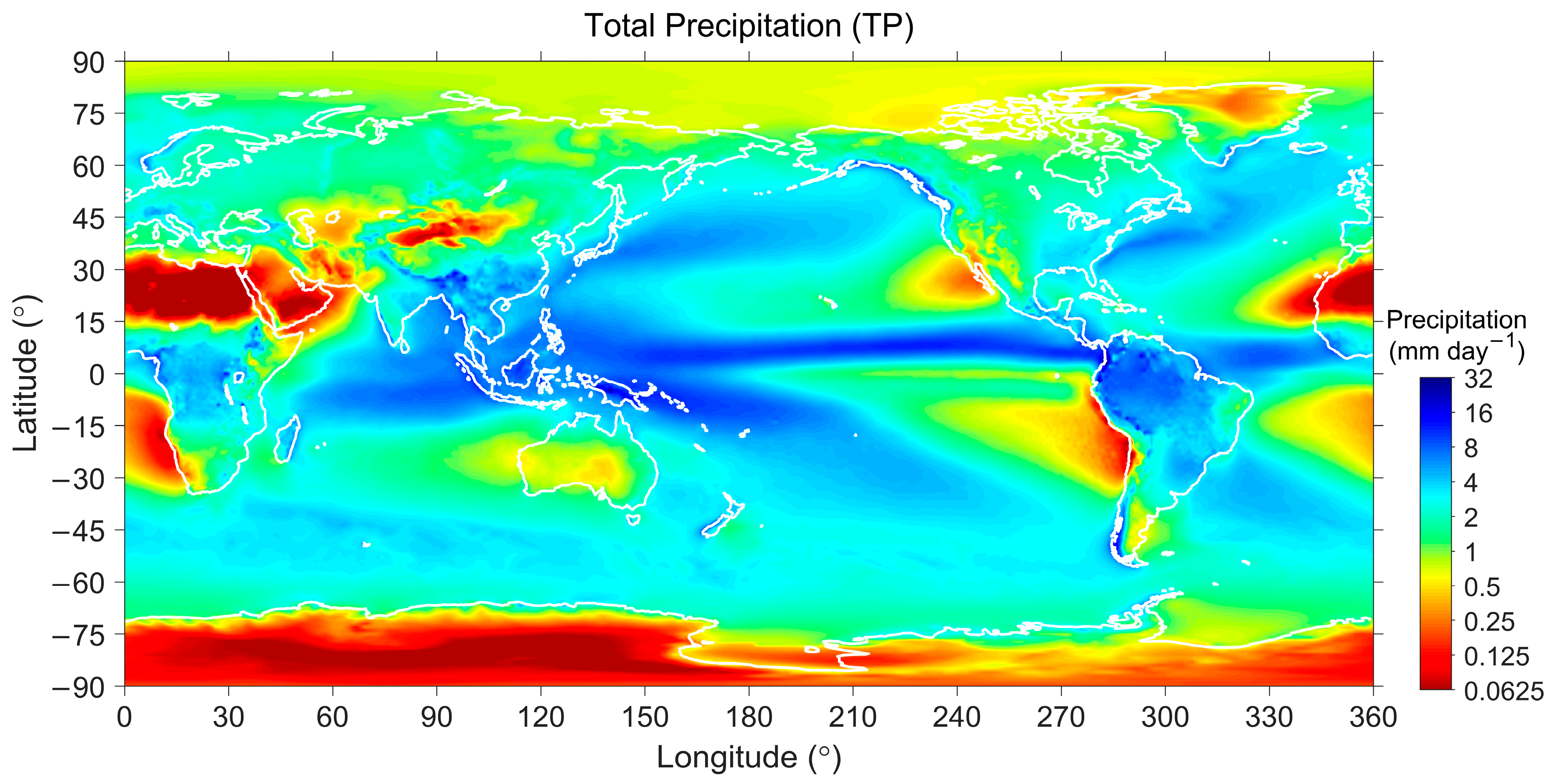
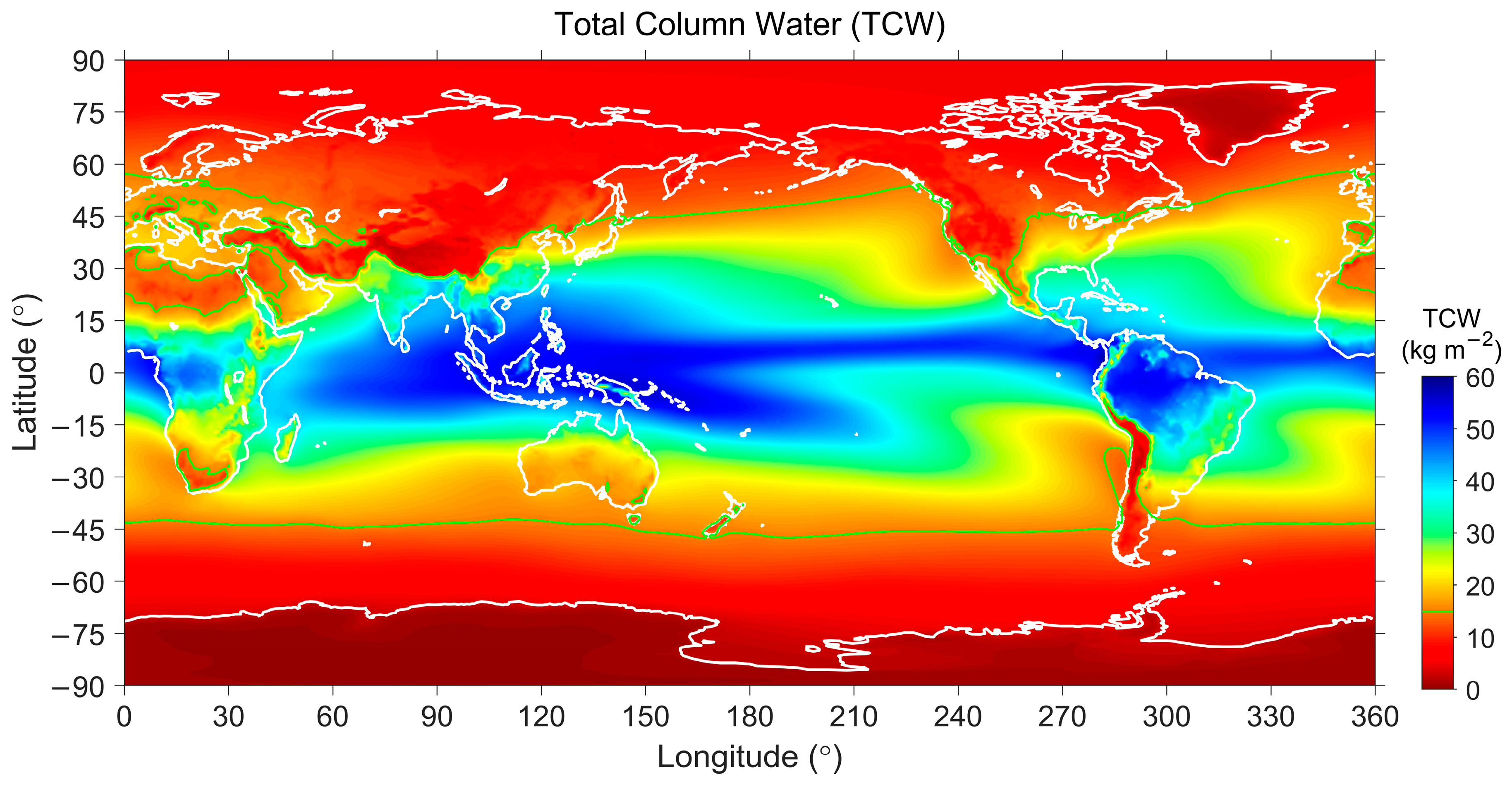

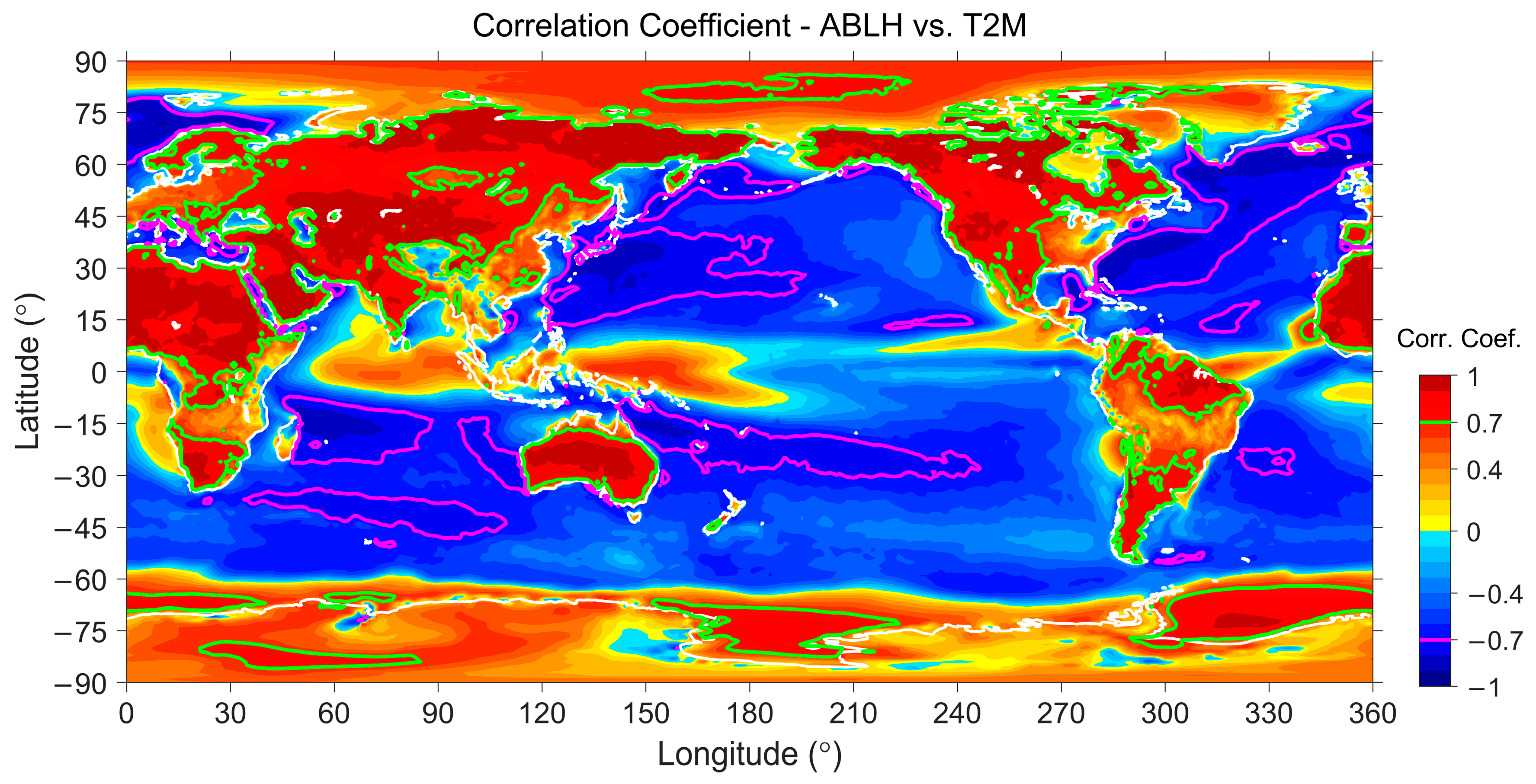
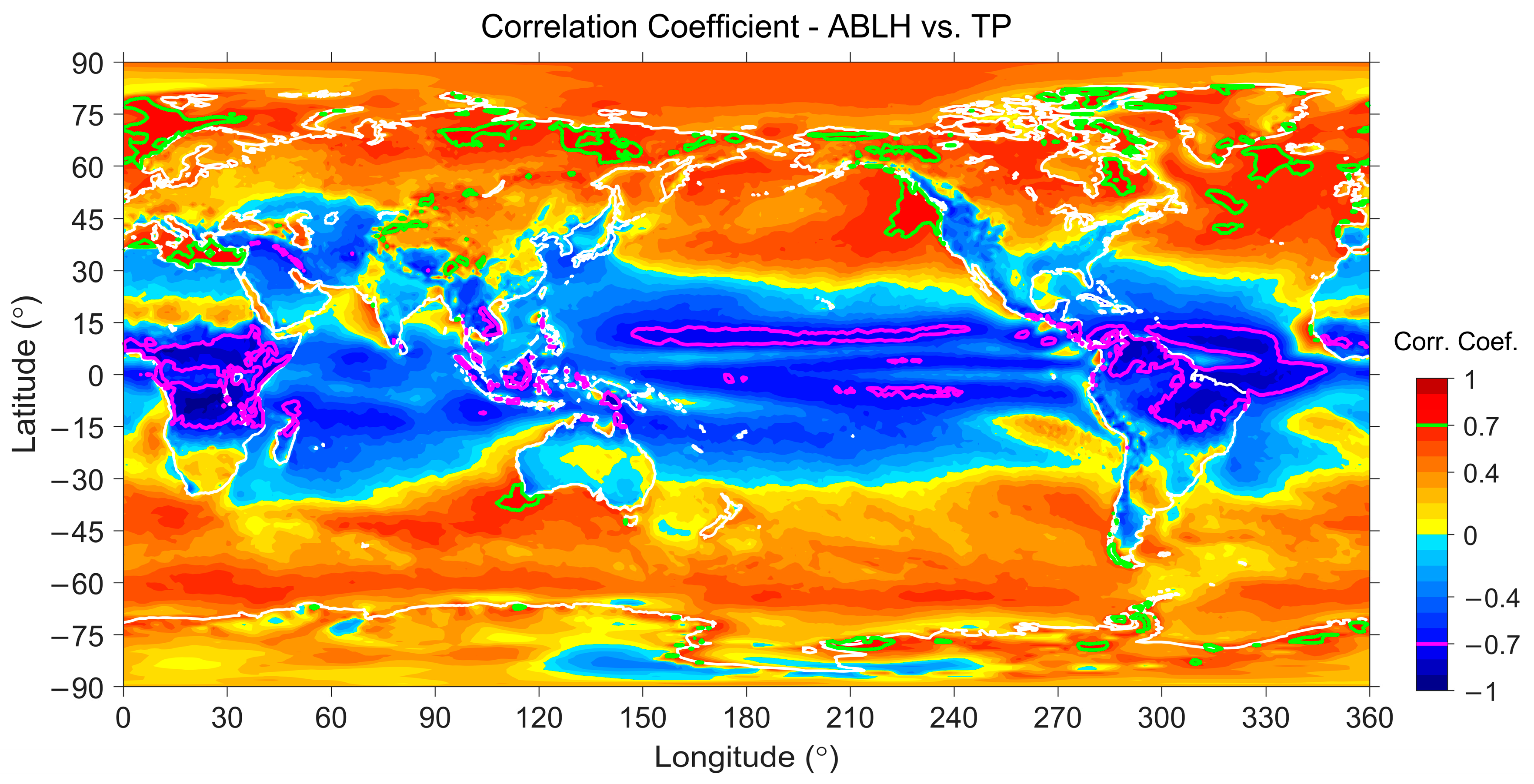
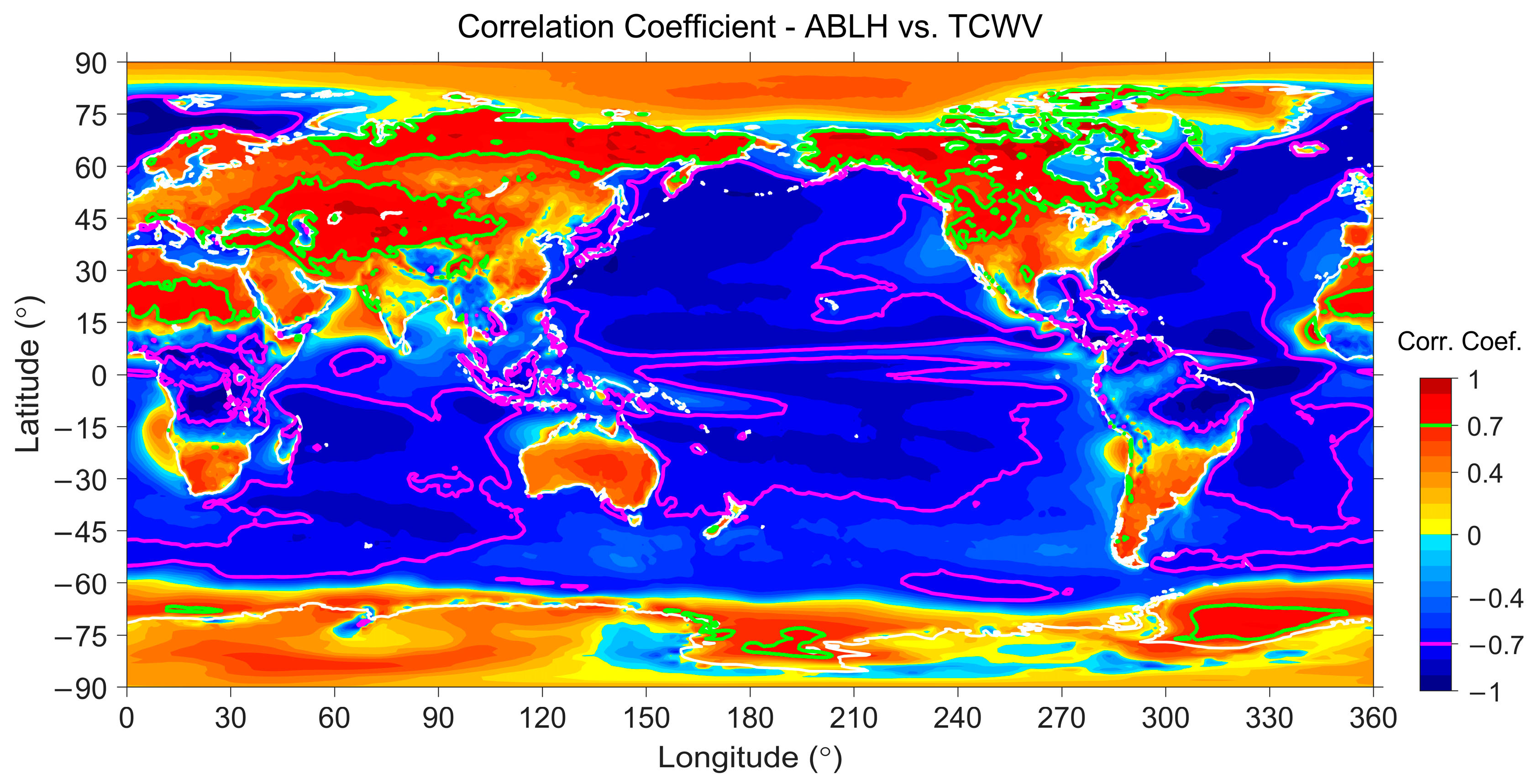
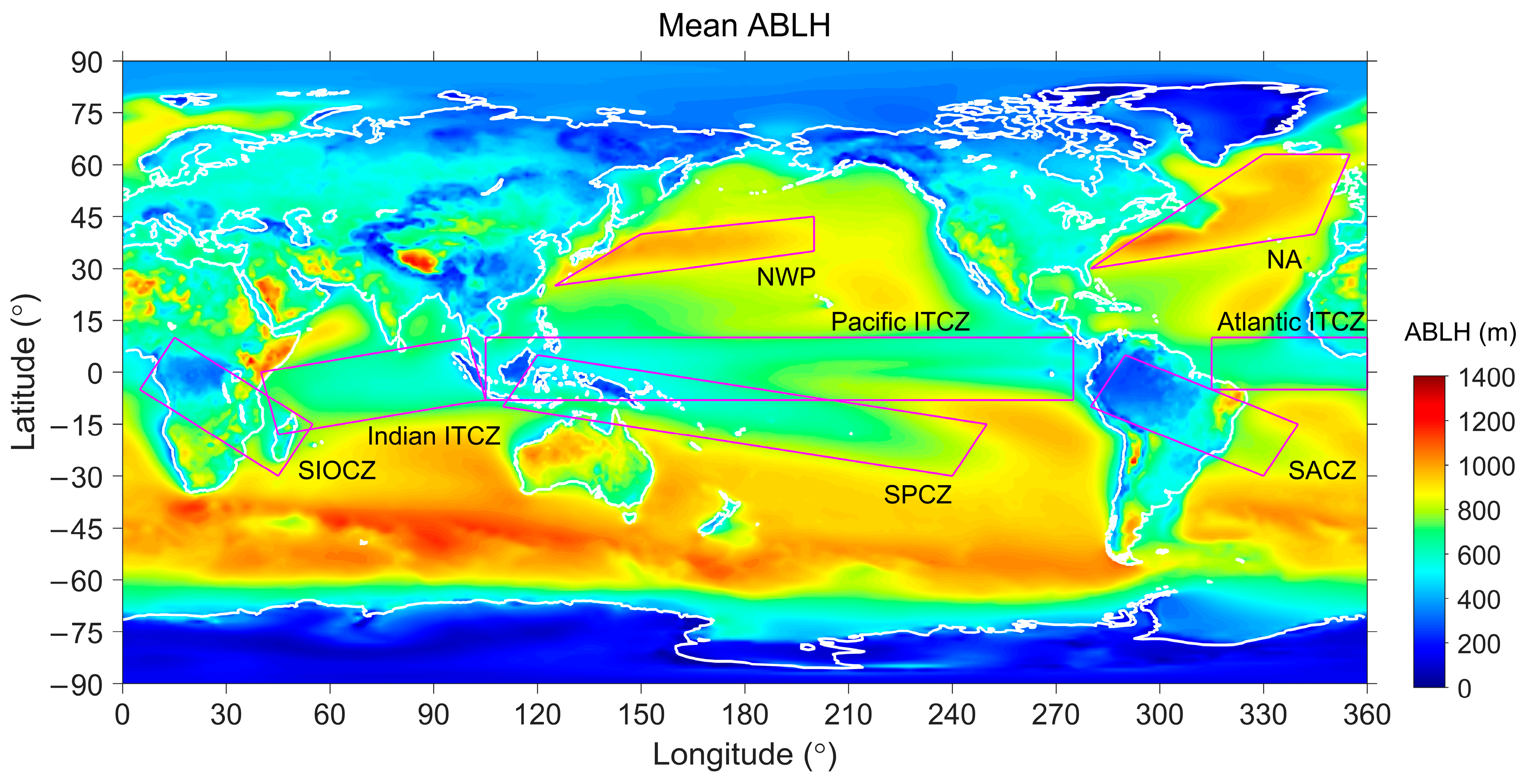

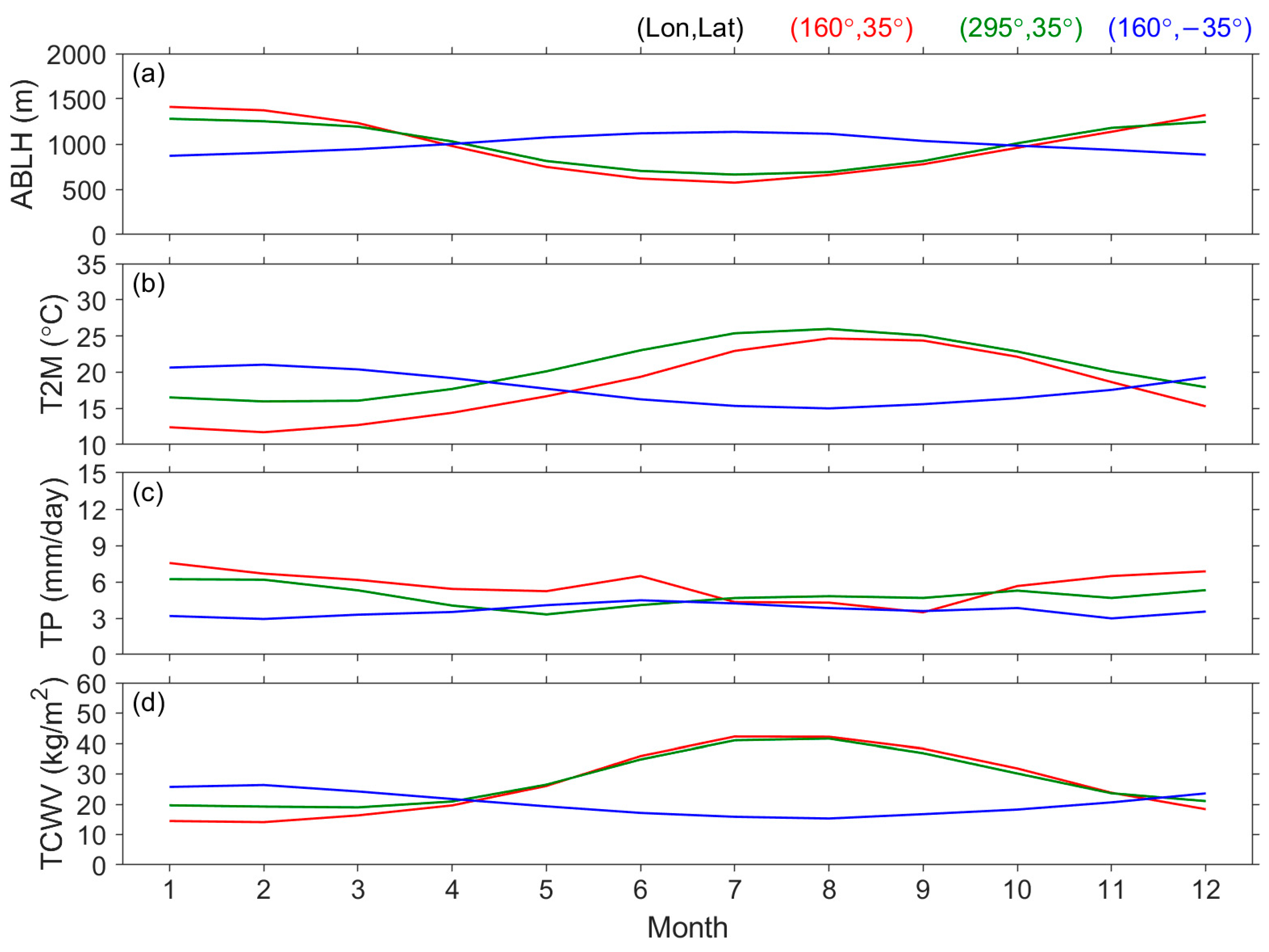

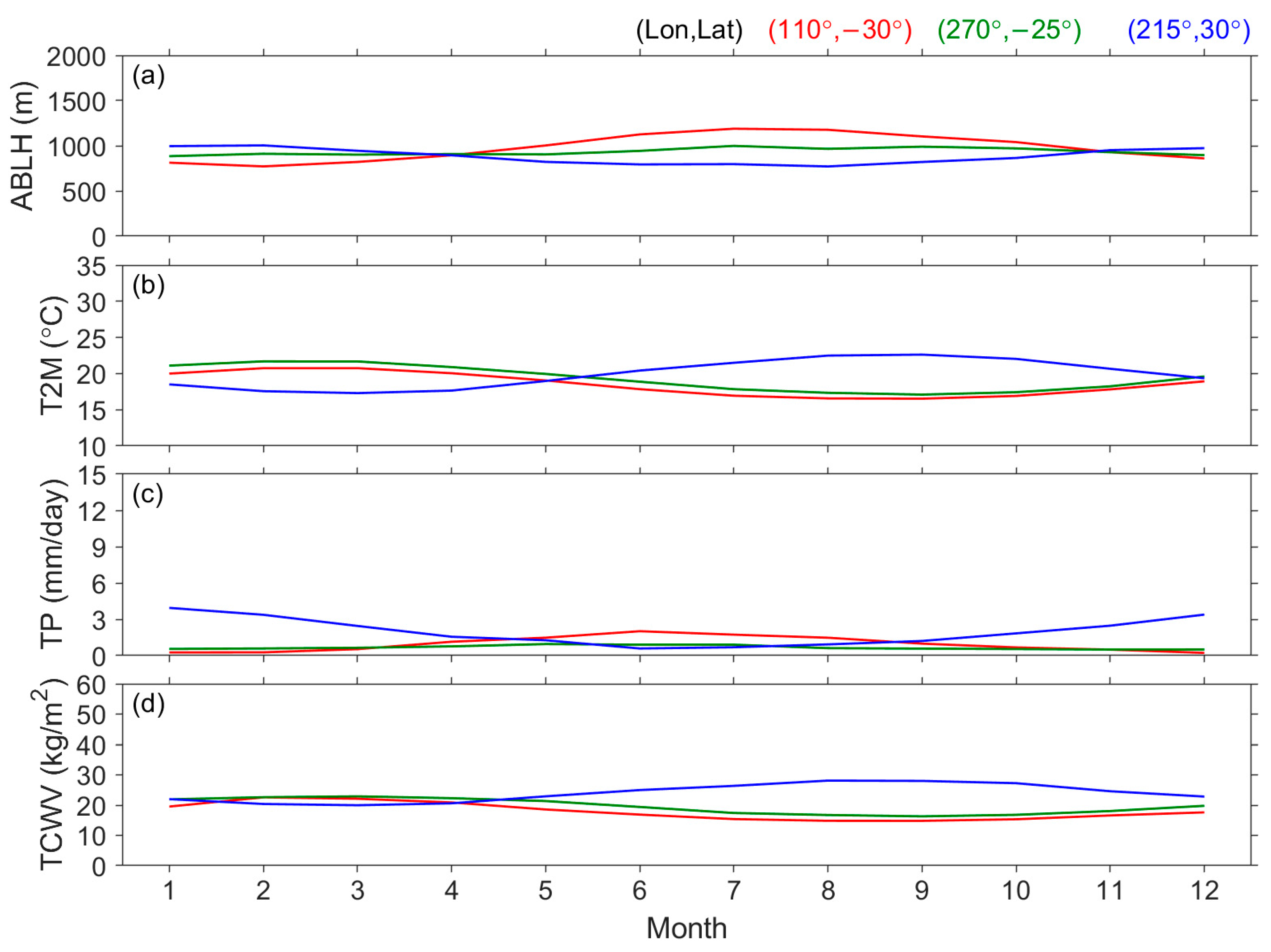
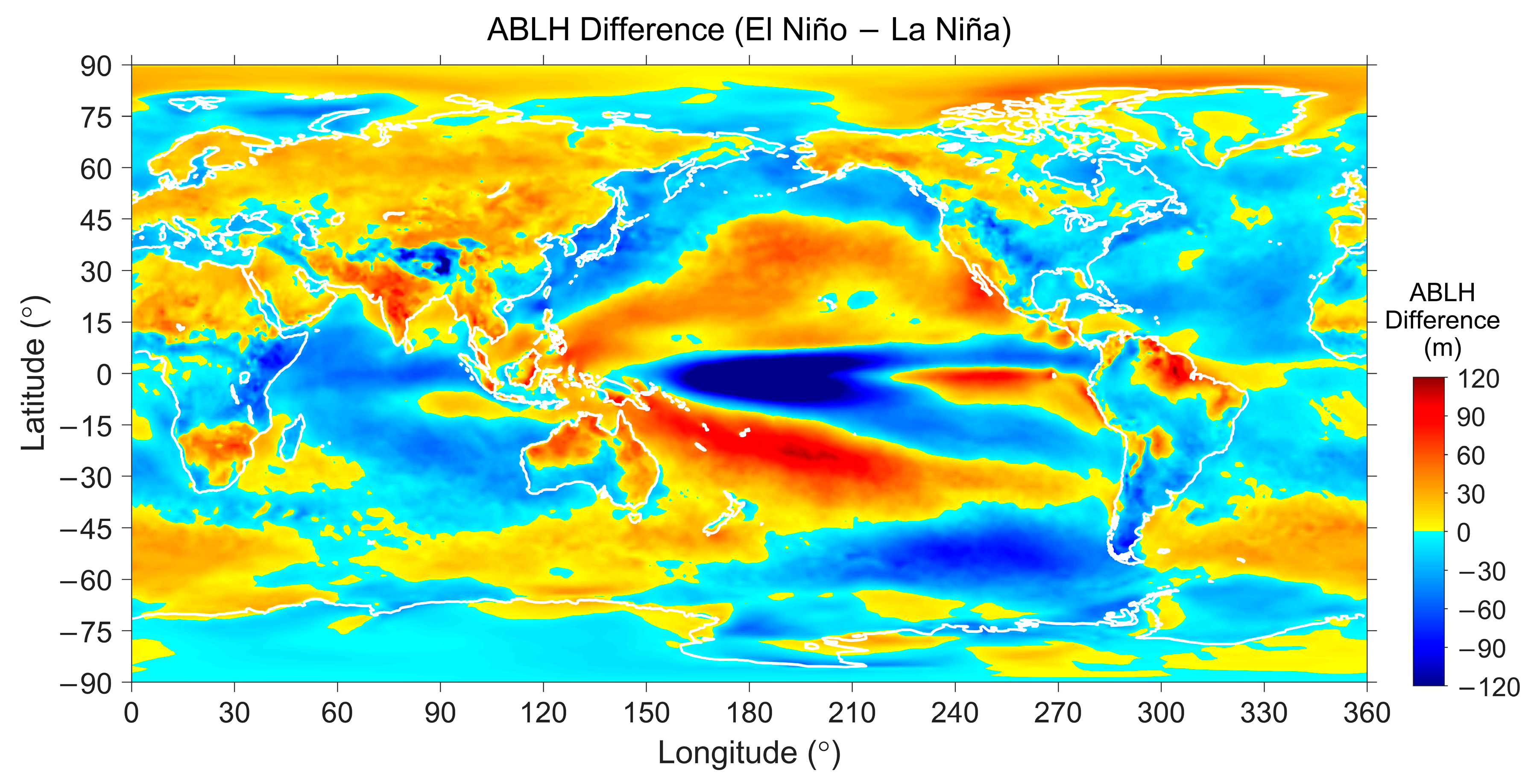
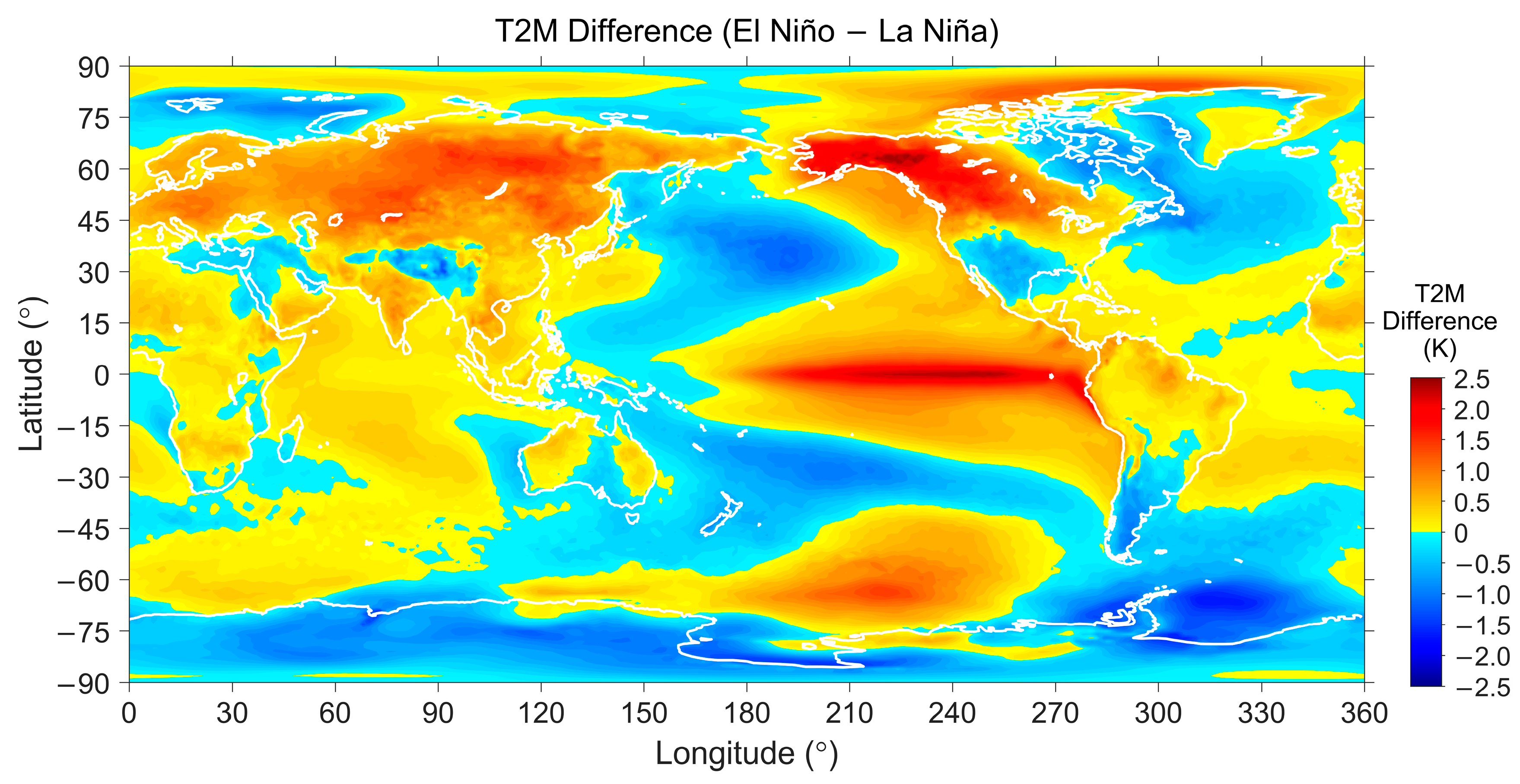

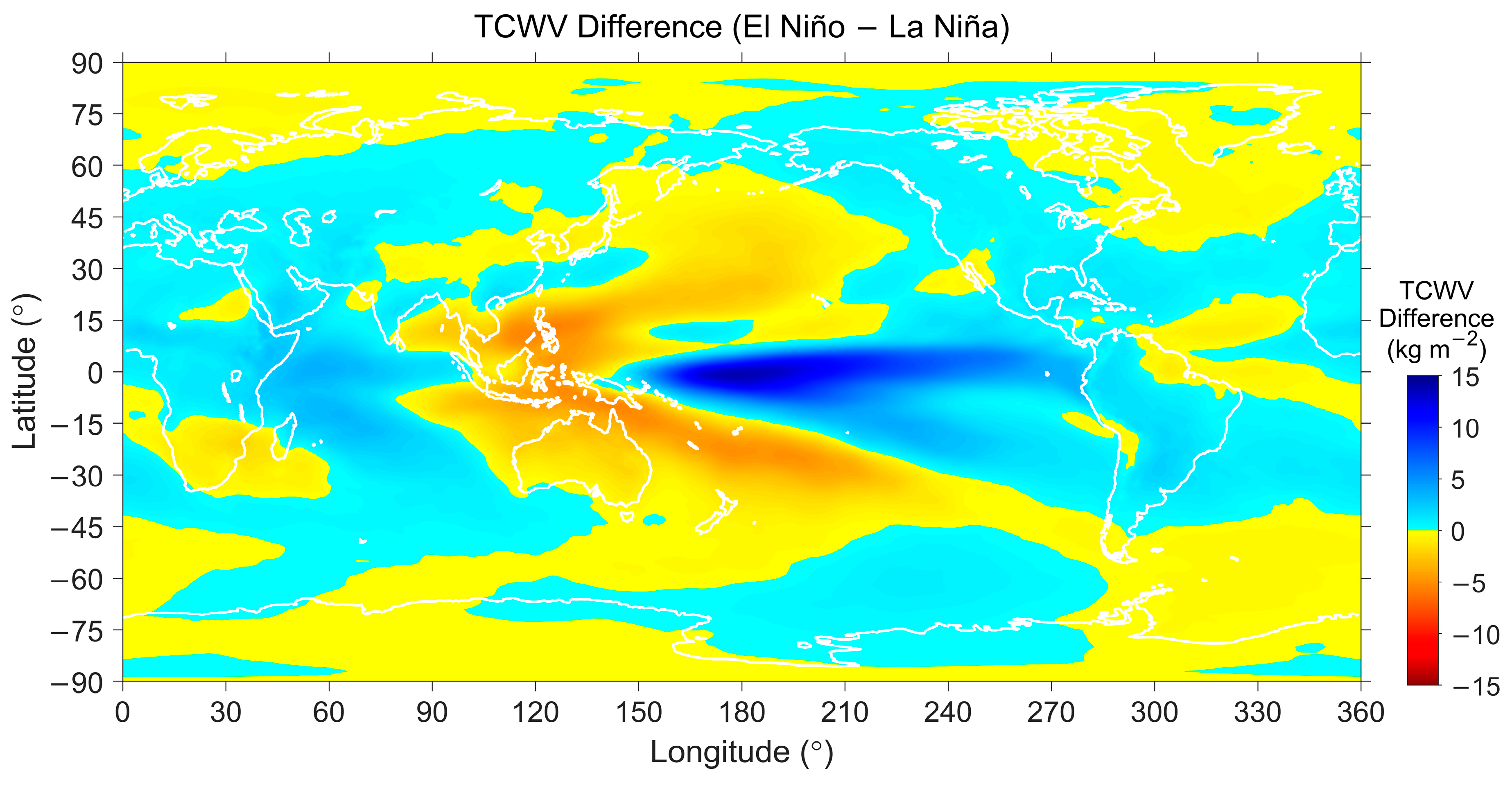

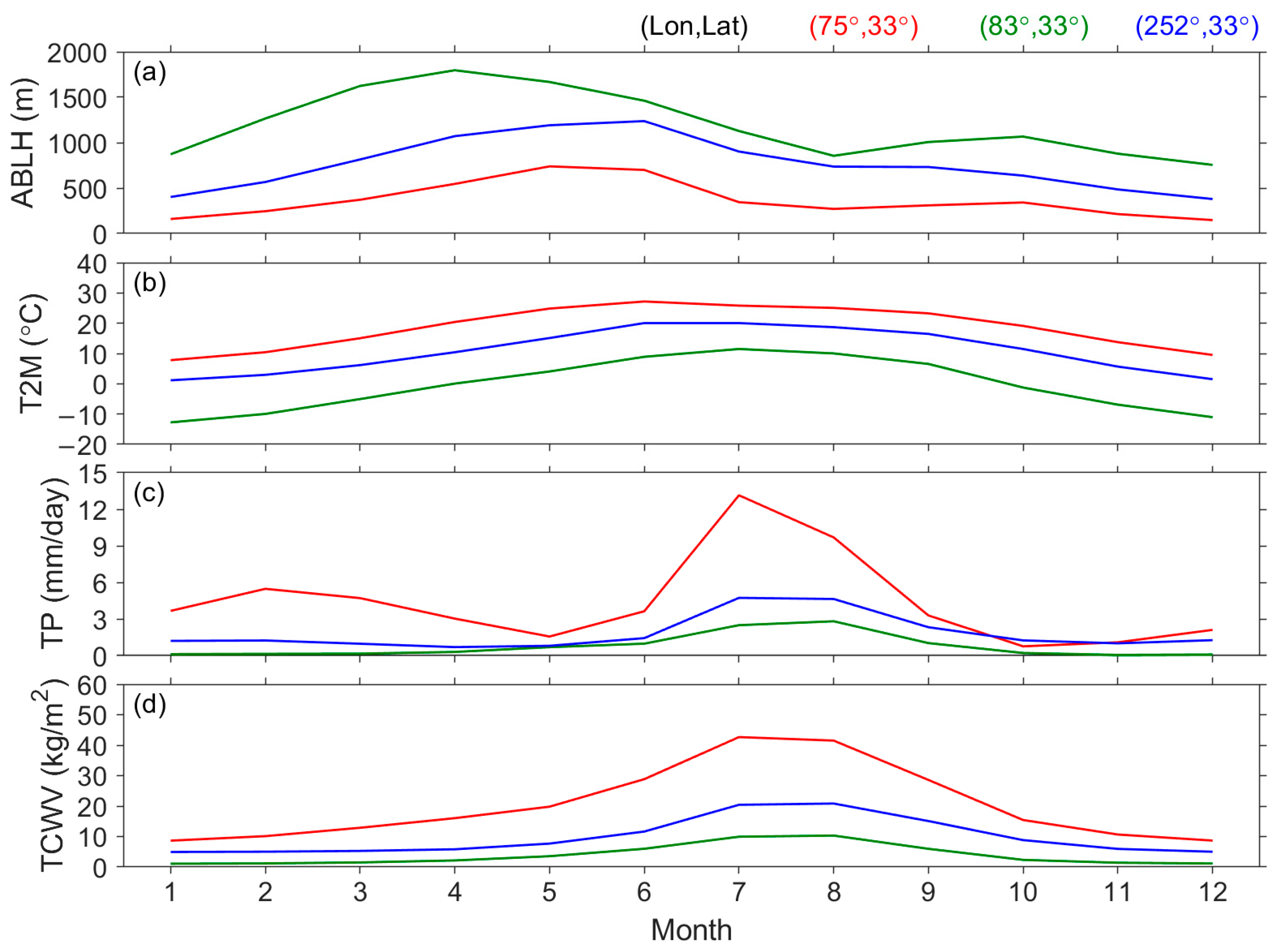
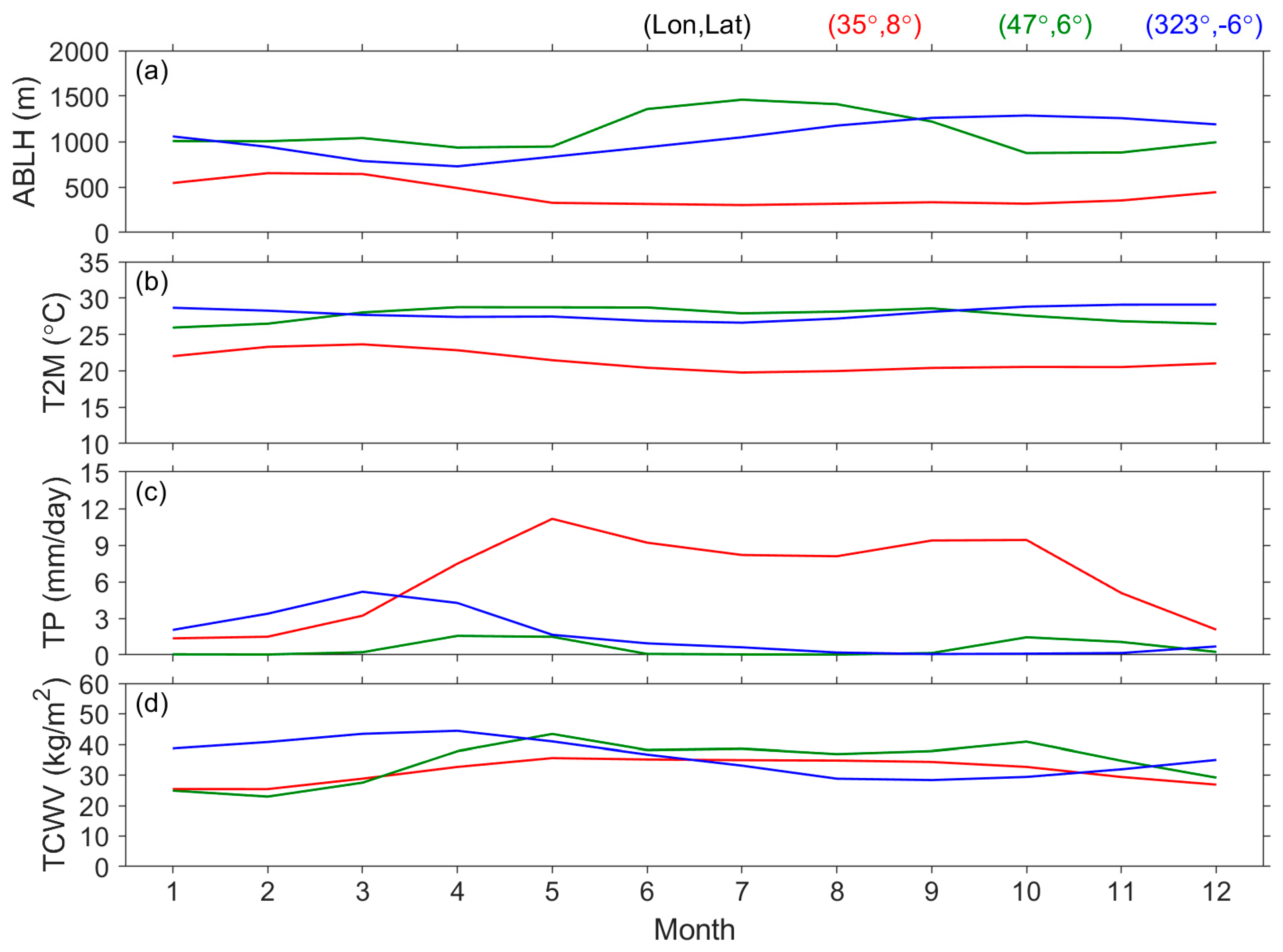
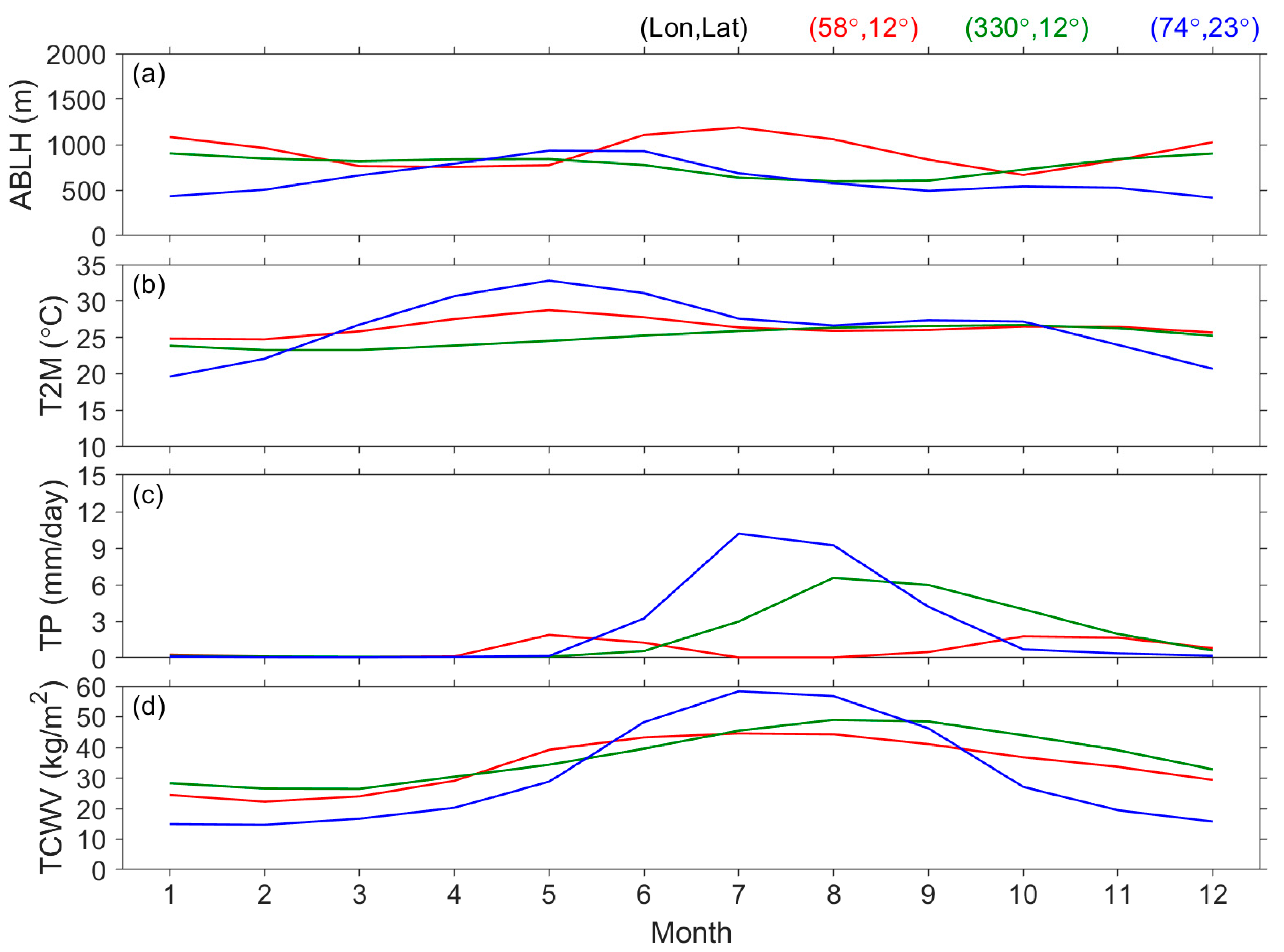
| Surface | Lands | Waters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | T2M | TP | TCWV | T2M | TP | TCWV |
| Global | 0.844 | 0.157 | 0.558 | 0.455 | 0.195 | 0.099 |
| Northern High | 0.786 | 0.411 | 0.825 | 0.931 | 0.877 | 0.854 |
| Northern Mid | 0.463 | −0.562 | 0.074 | 0.428 | 0.629 | 0.479 |
| Northern Low | 0.382 | −0.680 | −0.411 | −0.347 | −0.224 | −0.287 |
| Northern Equatorial | 0.409 | −0.725 | −0.473 | −0.024 | −0.347 | −0.656 |
| Southern Equatorial | 0.097 | −0.677 | −0.552 | −0.281 | −0.619 | −0.849 |
| Southern Low | 0.191 | −0.763 | −0.417 | −0.481 | −0.431 | −0.599 |
| Southern Mid | 0.049 | −0.700 | −0.304 | 0.013 | 0.415 | −0.021 |
| Southern High | 0.546 | 0.517 | 0.346 | 0.906 | 0.744 | 0.847 |
| Surface | Lands | Waters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | T2M_Diff | TP_Diff | TCWV_Diff | T2M_Diff | TP_Diff | TCWV_Diff |
| Global | 0.532 | −0.363 | −0.303 | −0.223 | −0.553 | −0.668 |
| Northern High | 0.788 | 0.343 | 0.404 | 0.813 | 0.447 | 0.130 |
| Northern Mid | 0.566 | −0.329 | −0.138 | −0.495 | −0.008 | −0.598 |
| Northern Low | 0.606 | −0.394 | −0.053 | −0.205 | −0.211 | −0.423 |
| Northern Equatorial | 0.712 | −0.703 | −0.805 | −0.248 | −0.814 | −0.807 |
| Southern Equatorial | 0.653 | −0.545 | −0.749 | 0.060 | −0.775 | −0.748 |
| Southern Low | 0.636 | −0.623 | −0.663 | −0.798 | −0.648 | −0.804 |
| Southern Mid | 0.765 | −0.464 | −0.584 | −0.630 | 0.298 | −0.525 |
| Southern High | 0.527 | 0.156 | 0.130 | 0.409 | 0.420 | 0.018 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.-S.; Pan, C.-J. Climatology of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Using ERA5: Spatio-Temporal Variations and Controlling Factors. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050573
Yang S-S, Pan C-J. Climatology of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Using ERA5: Spatio-Temporal Variations and Controlling Factors. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(5):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050573
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shih-Sian, and Chen-Jeih Pan. 2025. "Climatology of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Using ERA5: Spatio-Temporal Variations and Controlling Factors" Atmosphere 16, no. 5: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050573
APA StyleYang, S.-S., & Pan, C.-J. (2025). Climatology of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Using ERA5: Spatio-Temporal Variations and Controlling Factors. Atmosphere, 16(5), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050573






