Border Wars and Climate Change: The Impact on the Evolution of the External Defense System of the Hexi Corridor in the Past 2000 Years
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Research Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Method
3. Spatiotemporal Evolution of the Military Defense System Scale in the Hexi Corridor
3.1. Time-Varying Characteristics of the Scale of the Military Defense System in the Hexi Corridor
3.2. Spatial Variation Characteristics of the Military Defense System Scale in the Hexi Corridor
3.3. Division of Military Defense Levels in the Hexi Corridor
3.4. Environmental Landscape Characteristics of Military Defense Sites in Different Periods
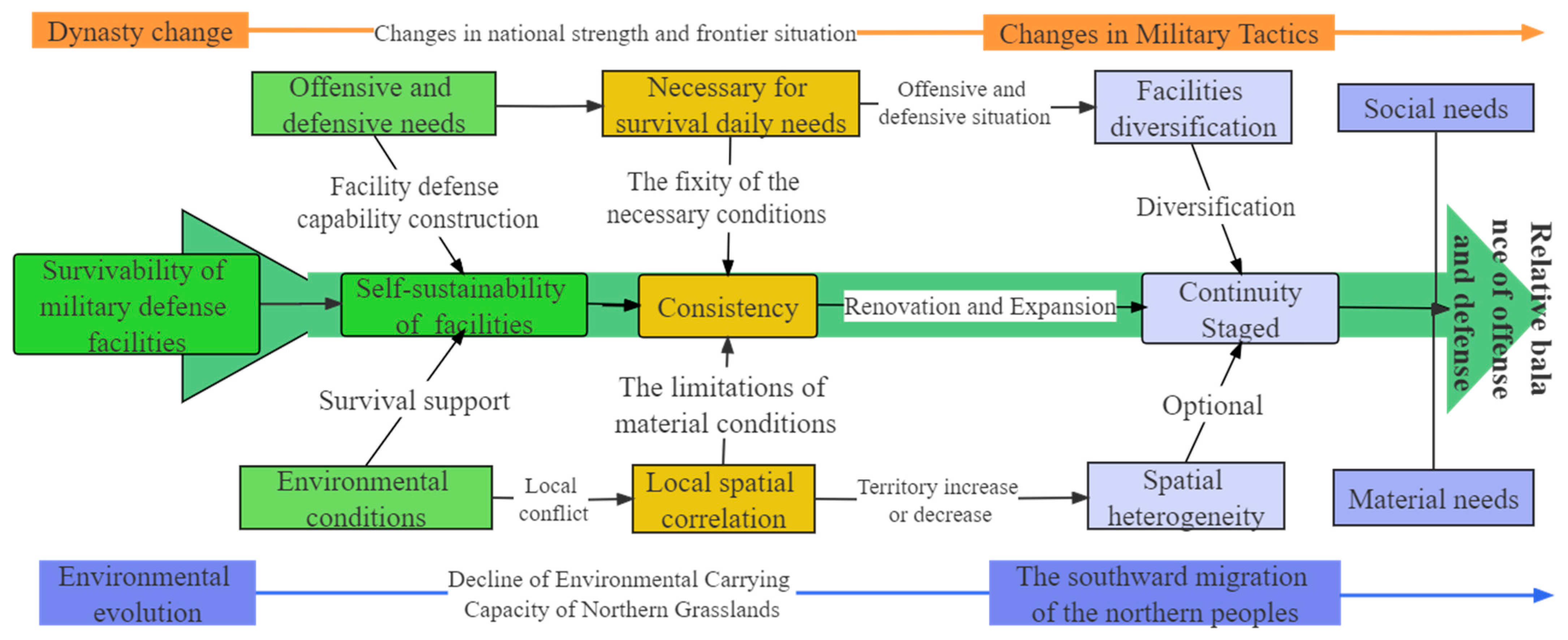
4. Discussion
4.1. The Possible Relationship Between the Temporal and Spatial Changes of the Military Defense System in the Hexi Corridor and Climate Change
4.2. The Impact of Frontier Wars on the Rise and Fall of the Hexi Corridor Military System
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Z. A Study on the Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Beijing Ming Great Wall Heritage. Arid Area Resour. Environ. 2022, 36, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Spatial distribution of military defense settlements on the Great Wall of the Ming Dynasty based on Voronoi diagram. J. Hebei Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2014, 34, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Research on the Spatial Layout of the Beacon Transmission System in Datong Town, the Military Defense Settlement System of the Ming Great Wall. New Archit. 2017, 2, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X. Research on the Planning and Layout Mechanism of the Ming Great Wall Military Defense System. Doctoral Dissertation, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X. Military Defense Features and Image Protection of Pianguan Great Wall. Shanxi Arch. 2016, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y. The wisdom contained in the construction of ancient military defense spaces: Taking the military defense fortress settlements of the Great Wall as an example. Archit. Eng. Technol. Des. 2019, 4, 3394. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Spatial analysis of the great wall ji town military settlements in the ming dynasty: Research and conservation. Ann. GIS 2018, 24, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Research on the human settlement environment of military defensive castles along the Ming Great Wall in Yulin area. Doctoral Dissertation, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. A Textual Research on the Date of Construction of the Zhaonan Great Wall in the Warring States Period. Chin. Hist. Geogr. Theory Ser. 2022, 4, 148–153+147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Qs, A.; Tja, B.; Xz, C. Characteristics of the site selection and the layout of the great wall of the ming dynasty from a military perspective: Xiaohekou section as an example. Front. Archit. Res. Engl. Ed. 2020, 9, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y. The fractal structure of the Ming Great Wall Military Defense System: A revised horizon over the relationship between the Great Wall and the military defense settlements. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 33, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, W.; Cui, K.; Guo, Z.; Wu, G.; Ren, X. An exploration of the military defense system of the Ming Great Wall in Qinghai Province from the perspective of castle-based military settlements. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2021, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Bachagha, N.; Yao, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, P.; Zhu, L.; Shao, J.; Wang, X. Identifying Linear Traces of the Han Dynasty Great Wall in Dunhuang Using Gaofen-1 Satellite Remote Sensing Imagery and the Hough Transform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Pang, Y. Illustration on the defense system of the Great Wall in Jin dynasty. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical and Control Engineering, Yichang, China, 16–18 September 2011; pp. 5966–5968. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Resarch of Hebei Military Defense Region Before the Chuanyuanzhimeng in the Northern Song Dynasty. J. Hebei Univ. 2012, 31, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J. The Historical Evolution of the Defense System of the Great Wall in Ancient China. Mil. Hist. 2019, 5, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W. On the Mongolian Issue in the Early Hongwu Period and the Construction of the Military Defense System in the Ming Dynasty. Orient. Collect. 2018, 1, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H. The relevant background and evolution track of the administrative system in the Ordos Plateau in the Sui Dynasty. J. Ningxia Norm. Univ. 2017, 1, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X. Looking at the Great Wall from a foreign land—The concept of the Great Wall exercised by the Korean Yan during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. Hist. Mon. 2017, 6, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C. From the construction of the Great Wall in the Warring States Period and the formation of the common region of the Huaxia people. J. Hebei Norm. Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 5, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Jin, S.; Liao, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Rong, D.; Yang, Z. National Geomatics Center of China, et al Stereo mapping of ming great wall with remote sensing. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 2290–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L. Research on the Nine Frontier Military System in the Middle and Late Ming Dynasty; Jilin People’s Publishing House: Jilin, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, N. On the distribution of the Great Walls in Northwest China and their historical military geography (Part 2). Chin. Hist. Geogr. Theory Collect. 1994, 25, 311–312. [Google Scholar]
- Mischke, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Lai, Z.; Long, H. Landscape Response to Climate and Human Impact in Western China During the Han Dynasty. In Socio-Environmental Dynamics along the Historical Silk Road; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Su, Y.; Fang, X. To what extent did changes in temperature affect China’s socioeconomic development from the Western Han Dynasty to the Five Dynasties period? J. Quat. Sci. 2020, 35, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Liu, L.; Fang, X.; Ma, Y.N. The relationship between climate change and wars waged between nomadic and farming groups from the Western Han Dynasty to the Tang Dynasty period. Clim. Past 2015, 12, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, Q.; Jia, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Wan, Z.; Wang, Y. The temporal and spatial evolution and mechanism of early social history in northern China driven by climate and environment. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 9, 1580–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Fang, X.; Su, Y. Climate change, fiscal cycle and dynasty change in China in the past 2000 years. Quat. Stud. 2020, 40, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Archaeological Society. Yearbook of Chinese Archeology (2008–2020); Cultural Relics Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X. Investigation and Research on Hexi Hansai; Cultural Relics Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gansu Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology. Gansu Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archeology Important Archaeological Discoveries in Gansu 2000–2019; Cultural Relics Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Masana, M. Research on the Historical Geography of the Hexi Corridor; China Tibetology Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.; Xiao, F.; Fu, X.; Li, L. Witness of Grassland Civilization Ejina Banner; Sunshine Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J. Historical and Geographical Research on Silk Road Traffic Lines (Chinese Section); Jiangsu People’s Publishing House: Nanjing, China, 2012.
- Zu, R.Z. NOAA/WDS Paleoclimatology—Zu—Qilan Mountains—JUSP—ITRDB CHIN003; NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information: Asheville, NC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Qin, C.; Wang, J.L.; He, M.H.; Melvin, T.M.; Osborn, T.J.; Briffa, K.R. (2014a-02-10): NOAA/WDS Paleoclimatology—Yang—Haiyagou—JUPR—ITRDB CHIN070; NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information: Asheville, NC, USA, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Qin, C.; Wang, J.L.; He, M.H.; Melvin, T.M.; Osborn, T.J.; Briffa, K.R. (2014b-02-10): NOAA/WDS Paleoclimatology—Yang—Zhamashi—JUPR—ITRDB CHIN071]; NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information: Asheville, NC, USA, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Quantitative Temperature and Monsoon Precipitation Data Sets for the Past 5000 Years in Northern China; National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, J. (2020-05-12): NOAA/WDS Paleoclimatology—Hexi Corridor, Northwestern China 1556 Year scPDSI Reconstruction; NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information: Asheville, NC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Kong, D.; Wang, S. The vegetation map at the 1:4,000,000 of China (1979). National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis. China soil Map Based Harmo-Nized World Soil Database (HWSD) (v1.1). National Tibetan Plateau Data Center. Available online: https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en/data/611f7d50-b419-4d14-b4dd-4a944b141175 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Zhou, C.; Cheng, W. National Tibetan Plateau Data Center. 1: 1,000,000 Geomorphological Map of Western China. Available online: https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en/data/bb79d39c-6da0-4c0f-b089-61eb671803c9/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Elith, J.; Phillips, S.J.; Hastie, T.; Dudík, M.; Chee, Y.E.; Yates, C.J. A statistical explanation of MaxEnt for ecologists. Divers. Distrib. 2015, 17, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Xiao, T.; Bi, F.; Shi, Y. Analysis of Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Cultivated Land Quantity in Metropolises Based on Kernel Density Estimation—Taking Tianjin as an Example. Chin. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2019, 40, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Hu, Y. Environmental health risk detection with GeogDetector. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 33, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B. Book of Han; Shanghai Ancient Books Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T. Ming History: Military Chronicles; Zhonghua Book Company: Beijing, China, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, Z. Analysis of the Military River Defense Spatial Pattern of the Ming Great Wall: Taking the Shanxi Section of the Yellow River as an Example. Landsc. Archit. 2024, 32, 124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y. A Preliminary Study on the Military Defense System of Luoyang in the Eastern Han Dynasty. Res. Qin Han Dynast. 2020, 1, 7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Academy of Military. Sciences General Military History of China; Military Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.; Wu, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Pigment content and environmental significance of lake sediments in Juyanhai, Inner Mongolia in the past 2600 years. Acta Sedimentum Sin. 2000, 18, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. A 1556 year-long early summer moisture reconstruction for the Hexi corridor, northwestern China. Chin. Sci. 2019, 62, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Kang, X.; Shi, Y. The 10-year-scale climate change of Dulan tree rings in the last 2000 years and its comparison with temperature proxy data in other regions of China. Geogr. Sci. 2000, 20, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Qin, D.; Shao, X.; Chen, T.; Ren, J. Tree ring records of temperature changes in the central Qilian Mountains in the past millennium. Chin. Sci. Ser. D 2004, 34, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.E. The spatio-temporal evolution of the Chongzhen drought (1627–1644) in China and its impact on famine. Clim. Past 2024, 20, 2287–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.W.; Brook, G.A.; Railsback, L.B.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Alexander, C.; Reeder, P. Stalagmite evidence from belize indicating significant droughts at the time of preclassic abandonment, the maya hiatus, and the classic maya collapse. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2007, 250, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsonis, A.A.; Swanson, K.L.; Sugihara, G.; Tsonis, P.A. Climate change and the demise of Minoan civilization. Clim. Past 2010, 6, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, G.H.; Gnther, D.; Peterson, L.C.; Sigman, D.M.; Hughen, K.A.; Aeschlimann, B. Climate and the Collapse of Maya Civilization. Science 2003, 299, 1731–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Fang, X.; Zheng, J. Learning from the historical impacts of climatic change in China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2014, 29, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, W. A Computer Movie Simulating Urban Growth in the Detroit Region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhai, X. The Relationship between Climate Change and the Interaction between Sedentary and Nomadic Groups in Northern China over the Past 2000 Years. In The Social Impacts of Climate Change in China over the Past 2000 Years; Springer: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S. History of Transportation in China; Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 1993. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, R. Huarong Intersection: Dunhuang Ethnicity and Transportation Between China and the West; Gansu Education Publishing House: Gansu, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. What is special about spatial data? Alternative perspectives on spatial data analysis. Technical Report of National Center for Geographic Infor mation and Analysis No. 89–4. 1989. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3ph5k0d4 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Turchin, P. Historical Dynamics: Why States Rise and Fall: Why States Rise and Fall; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhan, Z.; Lin, C.; He, Y.; Li, F. Climate change and China’s war, social unrest and dynastic change. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 2468–2474. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Dodson, J.; Yan, H.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Lee, H.F.; Pei, Q.; Cheng, B.; Li, C.; et al. Quantifying climatic variability in monsoonal northern china over the last 2200 years and its role in driving chinese dynastic changes. Quat. Sci. Rev. Int. Multidiscip. Rev. J. 2017, 159, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Southward Migration of Nomadic People in Northern China and Climate Change in the Past 2000 Years; Geographical Science: Changchun, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Population transfer in the ethnic structure of the ancient Hexi Corridor. Guizhou Ethn. Stud. 2018, 39, 4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, S.; Tu, L.; Liu, X. Monsoon Precipitation, Economy and Wars in Ancient China. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiang, S.M.; Burke, M.; Miguel, E. Quantifying the Influence of Climate on Human Conflict. Science 2013, 341, 1235367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Su, Y.; Fang, X. Wars among the northern farmers and herdsmen from the Western Han Dynasty to the Qing Dynasty in China and their relationship with temperature changes. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2016, 52, 8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
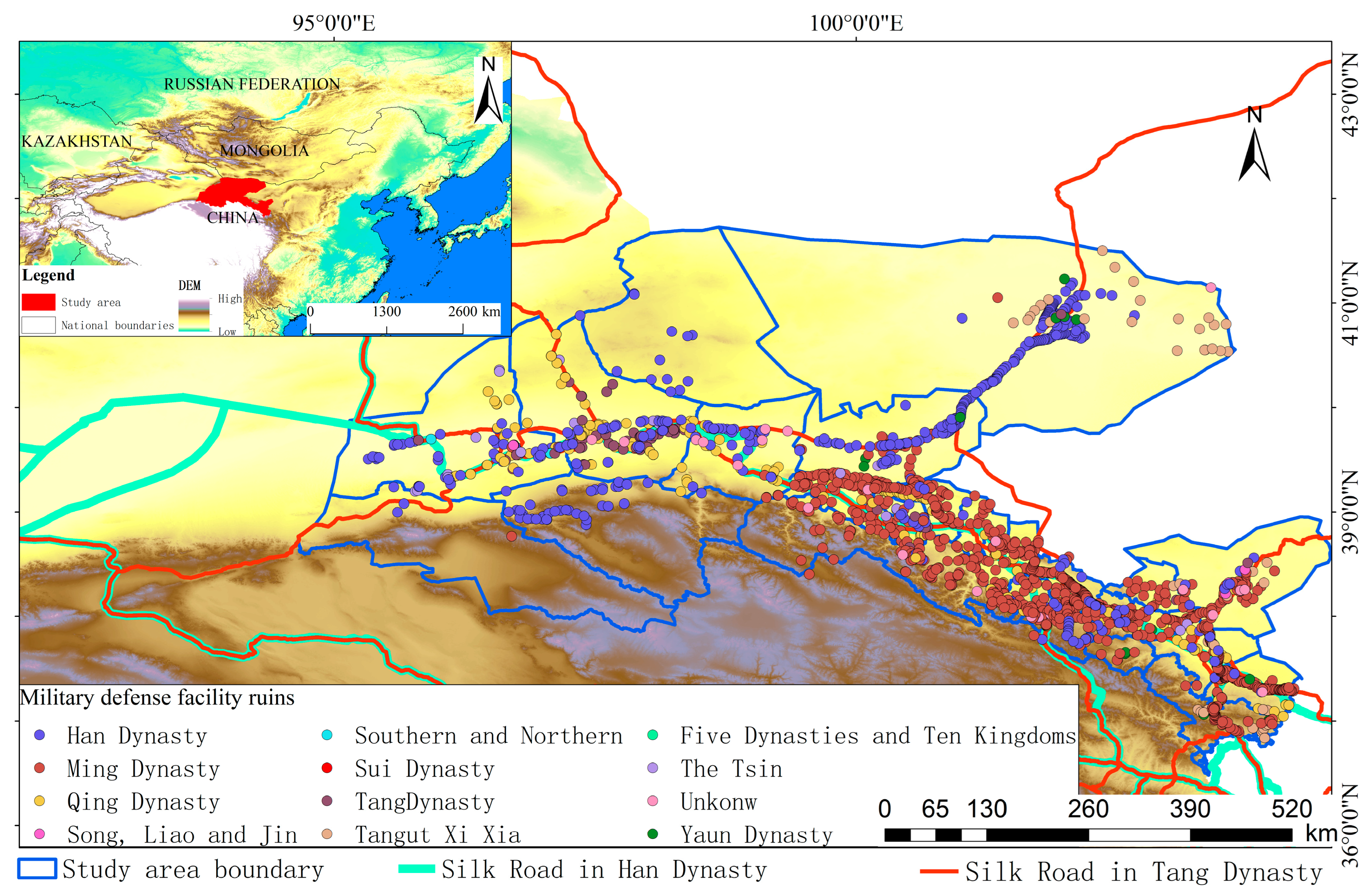
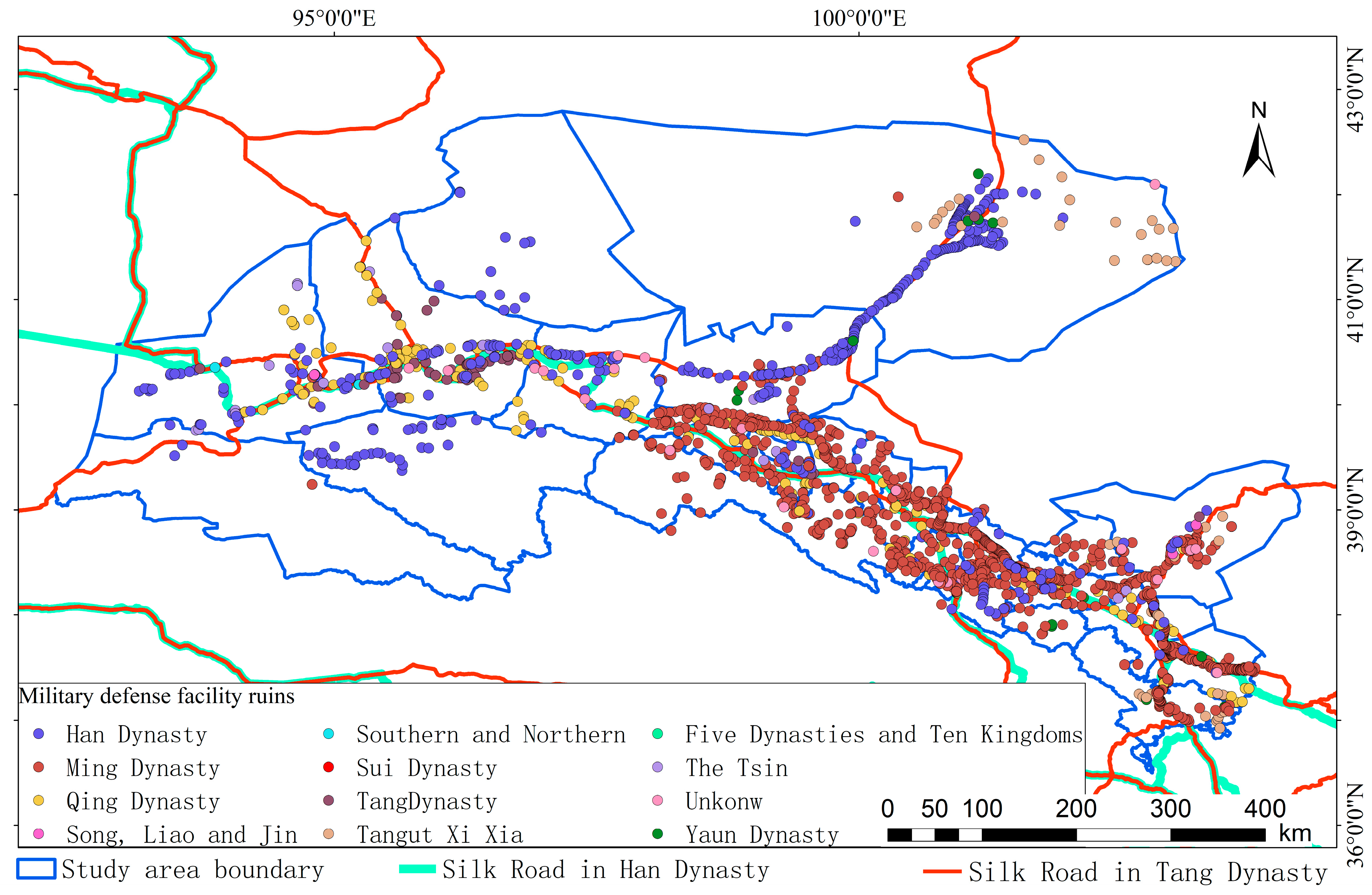
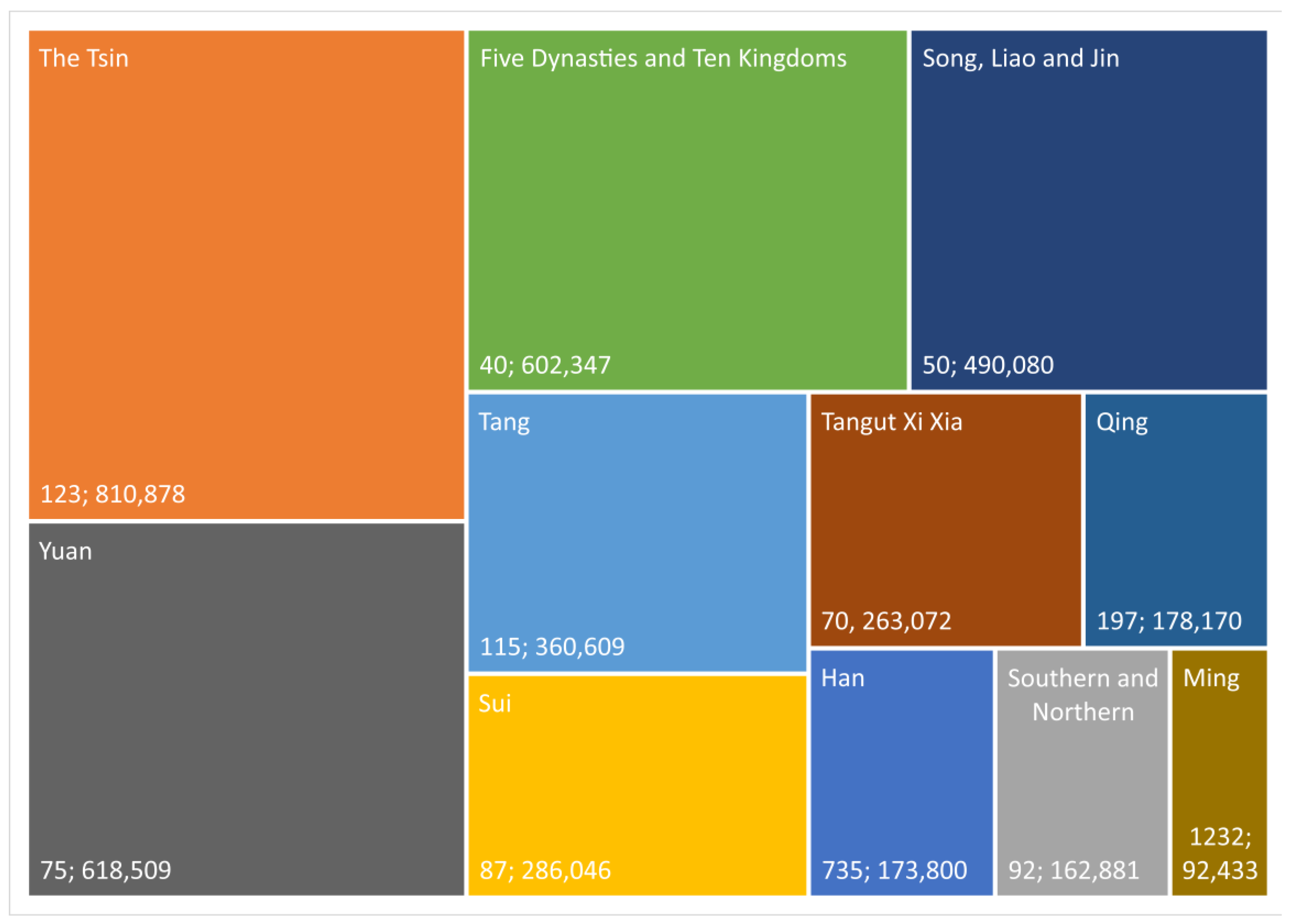



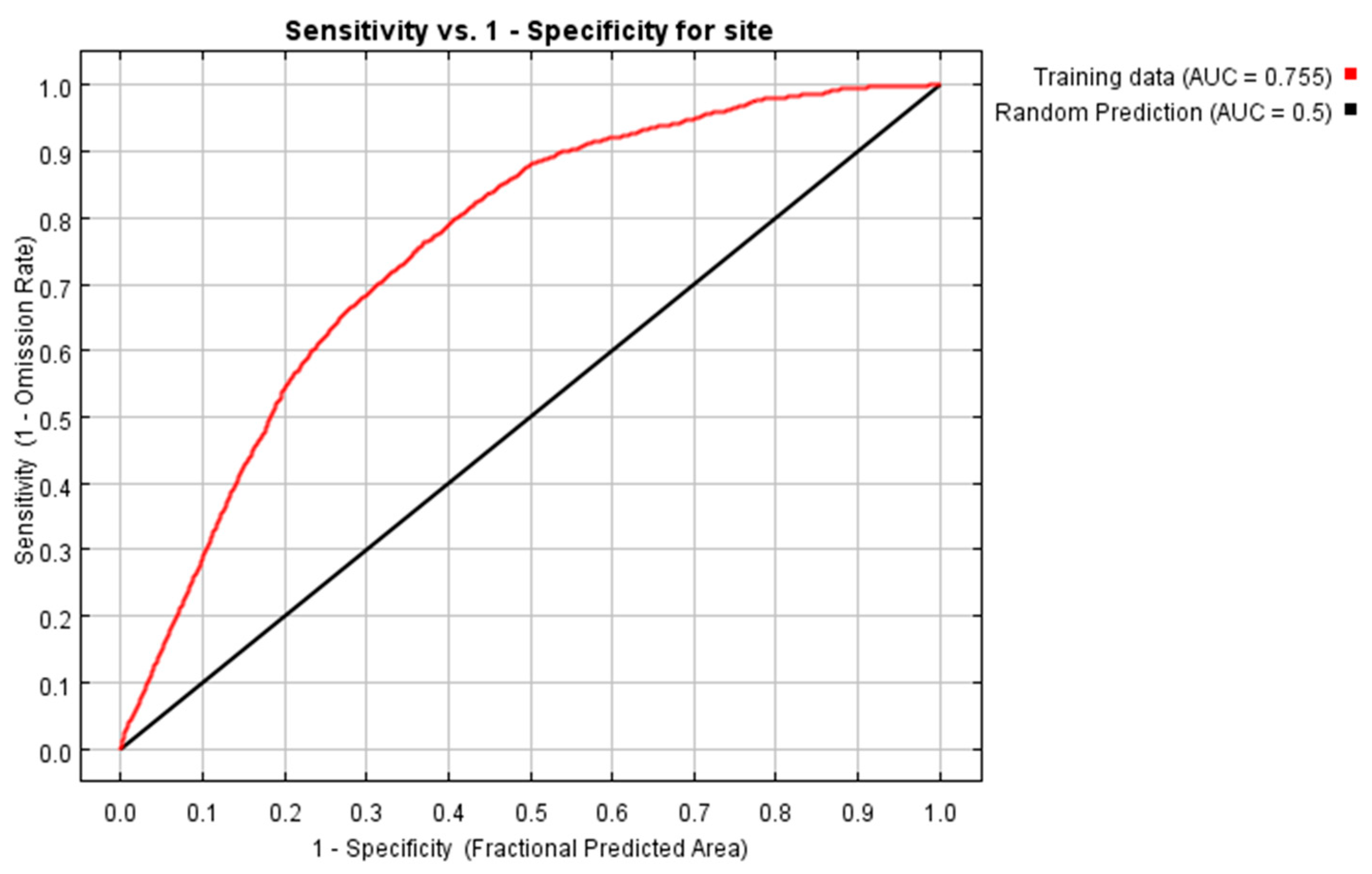

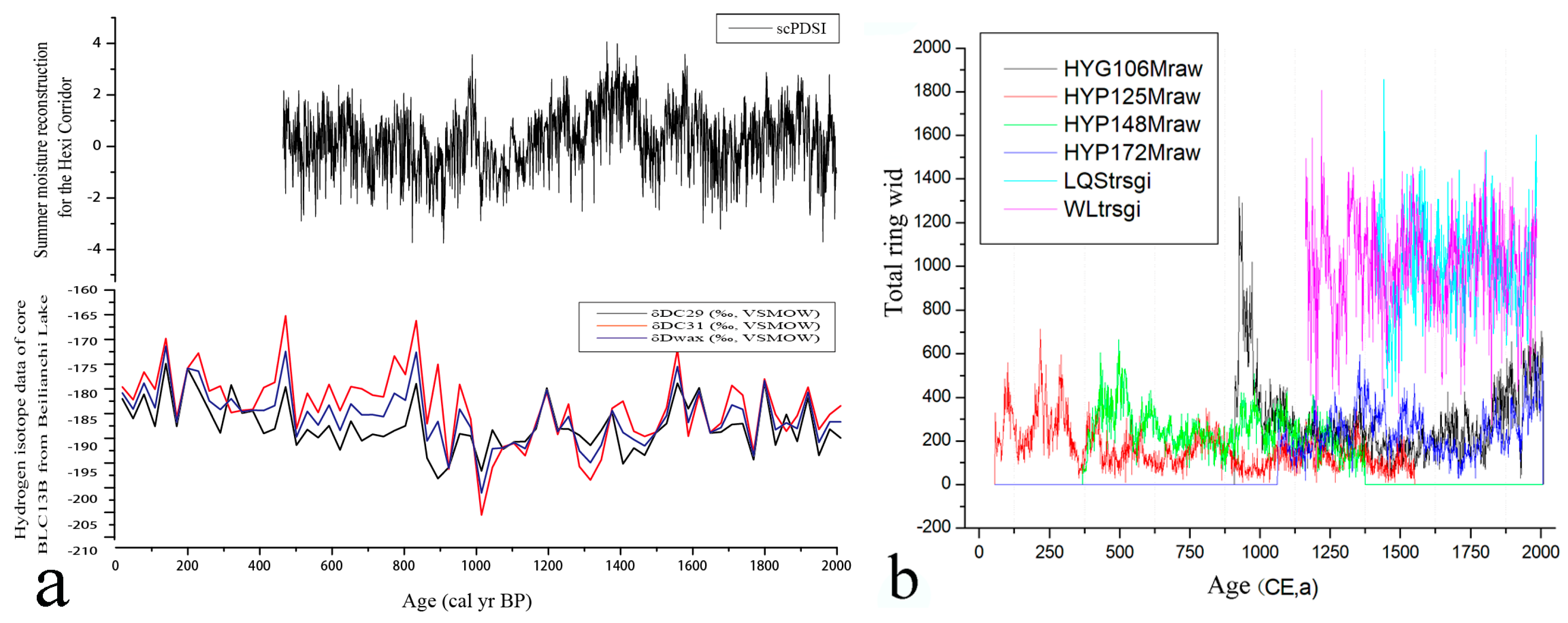
| Item | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Han Dynasty | 3.40 | 30 | 0.12 | 2.5 |
| The Tsin Dynasty | 4.46 | 20 | 0.01 | 5 |
| Southern and Northern Dynasties | 4.49 | 20 | 1.00 | 2.5 |
| Sui Dynasty | 4.64 | 20 | 1.00 | 5 |
| Tang Dynasty | 4.19 | 20 | 0.01 | 2.5 |
| Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms | 4.20 | 20 | 1.00 | 2.5 |
| Song, Liao, and Jin Dynasties | 4.48 | 20 | 0.01 | 2.5 |
| Tangut Xixia | 7.19 | 20 | 0.18 | 5 |
| Yuan Dynasty | 4.50 | 20 | 0.01 | 2.5 |
| Ming Dynasty | 5.14 | 30 | 0.15 | 2.5 |
| Qing Dynasty | 4.13 | 20 | 0.01 | 2.5 |
| Item | Slope (°) | Aspect (°) | Altitude (m) | Distance from River (km) | Geomorphological | Soil | Vegetation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q statistic | 0.0362 | 0.0191 | 0.3883 * | 0.1560 * | 0.1761 * | 0.1286 * | 0.0000 |
| p-value | 1.0000 | 0.1295 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0022 | 1.0000 |
| Dynasty | Han | Wei Tsin | North and South | Sui | Tang | Five and Ten Kingdoms | Song, Liao, and Jin (Western Xia) | Yuan | Ming | Qing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total times | 148 | 89 | 41 | 9 | 80 | 9 | 200 | 30 | 203 | 23 |
| Frequency/(10a)−1 | 7.23 | 12.51 | 2.43 | 2.5 | 2.78 | 1.7 | 6.43 | 3.09 | 7.36 | 0.86 |
| High incidence period | 110s–120s BC; 170S BC | 270s CE; 310s CE | 620s CE | 980s–990s CE; 1080s CE | 1120s–1130s CE; 1230s–1260s CE | 1270s CE | 1370s CE; 1540s–1560s CE; 1580s CE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Tan, B. Border Wars and Climate Change: The Impact on the Evolution of the External Defense System of the Hexi Corridor in the Past 2000 Years. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030335
Wang X, Tan B. Border Wars and Climate Change: The Impact on the Evolution of the External Defense System of the Hexi Corridor in the Past 2000 Years. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(3):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030335
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinmin, and Bo Tan. 2025. "Border Wars and Climate Change: The Impact on the Evolution of the External Defense System of the Hexi Corridor in the Past 2000 Years" Atmosphere 16, no. 3: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030335
APA StyleWang, X., & Tan, B. (2025). Border Wars and Climate Change: The Impact on the Evolution of the External Defense System of the Hexi Corridor in the Past 2000 Years. Atmosphere, 16(3), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030335






