Abstract
This study provides a comprehensive evaluation of dust events over Iran, using synoptic data from 286 meteorological stations. The dust events are classified according to synoptic dust codes as suspended dust and others (i.e., blowing dust, dust storms) and based on their intensity with horizontal visibility ≤1, 3, 5, and 10 km. Severe events (visibility ≤ 1 km) of suspended dust (code 06) occurred primarily in the western parts of Iran, while blowing dust events of moderate or severe intensity dominated over the south and eastern Iran, thus revealing a contrasting spatial distribution regarding the type and frequency of dust events. Furthermore, a distinct seasonality is revealed in the number of dust events, since suspended dust maximized in SW Iran from March to July, highly associated with Shamal winds, while blowing dust storms over south and east Iran maximized from April to August. Zabol city, east Iran, and some stations along the coast of the Arabian Sea are highly impacted by this type of dust storm throughout the year. Trend analysis revealed a notable increase in frequency of dust events during the period 1994–2023, particularly in the western part of Iran, mostly attributed to transboundary dust from the Mesopotamian plains. The large increase in dust activity during 1994–2009 was followed by a decrease during the 2010s at many stations, while notable differences were observed in the spatial distribution of the trends in suspended and blowing dust. An inverse correlation between dust events and precipitation anomalies was observed, since years with abnormal precipitation (e.g., 2019; 138% increase) were related to a substantial decrease in dust occurrence. Over an 11-year period, surface dust concentrations exceeded the annual PM10 threshold of 50 µg/m3 on more than 800 days, with maximum concentrations reaching up to 1411 µg/m3. This highlights the urgent need for effective management strategies to mitigate the impacts of dust storms on air quality and public health in Iran.
1. Introduction
Air pollution is a major global environmental hazard, linked to approximately 7 million deaths globally, with recent estimates reporting annual fatalities ranging from 4 to 9 million, particularly in low- and middle-income countries [1,2,3,4]. Mineral dust is recognized as the most abundant natural aerosol along the global dust belt [5,6,7]. Dust storms play a significant role in environmental processes, including impacts on solar and terrestrial radiation [8,9,10], cloud condensation nuclei, the hydrological cycle [11], marine life [12], vegetation, and ecosystems [13,14,15]. The frequency and intensity of these phenomena exhibit an increasing tendency in some arid and semi-arid regions due to climate change and global warming, which may lead to reduced vegetation cover and increased wind speeds, affecting public health (e.g., cardiovascular and respiratory diseases), agriculture, electricity power lines and transportation, marine ecosystems, and atmospheric chemical composition [16,17,18,19,20].
The relationship between large-scale atmospheric circulation and dust activity in the Middle East is complex, with changes in sea surface temperature, synoptic meteorology, and the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) influencing dust variations and intensity [21,22,23,24]. During summer, the ITCZ shifts to higher latitudes, affecting some regions of the Middle East. This convergence zone can create favorable conditions for enhancing convection, leading to increased convective storms. If these convective storms lack sufficient moisture supply, the associated downdrafts or gust fronts can trigger and intensify dust storms in dust source areas [22]. Recent trends on Aerosol optical depth (AOD) from 1980 to 2018/20 showed a decrease in southeastern Europe and eastern Mediterranean and an increase in the desert regions of the Middle East [25,26,27,28,29], which were associated with changes in soil moisture, precipitation, and surface winds [30]. The increase in AOD is linked with decreased precipitation, soil moisture, and increased temperature over the past decades, linking the sensitivity of dust emissions to climate change. A correlation study between AOD, NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), precipitation, and wind speed showed that the AOD posed a negative correlation with NDVI and precipitation in 51% of the Iranian territory, while it showed a positive correlation with temperature and wind speed in 68% and 50% of the country’s area, respectively [31]. On the other hand, AOD indicated an increasing trend in 71% of the Iranian territory, which depends on changes in vegetation cover and climatic factors such as precipitation, temperature, and wind speed [32]. A significant upward trend in dust emissions was also observed over Iran, accompanied by a notable increase in winter AOD from 2000 to 2010 [33] and a downward trend from 2010 to 2018 [29].
Recent studies highlighted the meteorological dynamics driving dust emissions, including the influence of low-level jet (LLJ) on dust propagation and transport [34,35,36,37,38]. Yu et al. [39] examined the summer northern winds in the Middle East capable of transporting dust from the Tigris and Euphrates basin to the Persian Gulf and Arabia, while the LLJ and orographic effects on dust propagation along the Mesopotamian plains and SW Iran were documented in several studies [38,40,41,42,43,44,45,46]. The transition from a normal dust period to an active dust period in the Middle East between 2006 and 2007 has been attributed to the coordinated relationship between the Southern Oscillation of El Niño and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation [47]. The combined effect of these two large-scale teleconnection patterns has contributed to prolonged dryness over the region and increased dust activity. Stronger northern winds during the mid-2000s favored the escalation in dust activity in central Iraq and the eastern and southern Arabian Peninsula [39], also affecting SW Iran [48,49].
Recent assessments showed increasing dust levels in the Middle East, especially in spring and summer [50], influenced by various atmospheric dynamics [51,52,53,54]. Mobarak Hassan [55] analyzed the synoptic effects of wind direction on dust transport over the Persian Gulf in 2017. Those results indicated that the establishment of a high-pressure center over Syria caused pressure gradients in Iraq, leading to northwesterly winds at 20 knots at 925 hPa, which facilitated dust transport from Iraq to southwestern Iran. Hashemi Deyin et al. [37] investigated the effect of the low-level jet (LLJ) on dust propagation in western and southwestern Iran from 2007 to 2017 using reanalysis ERA5 and observational data, revealing that the highest frequency of dust in Ahvaz city occurred in July 2009, with 30 dusty days. Additionally, the steep north-to-south pressure gradient, due to the high-pressure system over northern Iraq and the Zagros Mountains, combined with the low-pressure center over southwestern Iran, is the most significant forcing leading to strong north/northwest winds and LLJ in this area [42].
Several previous studies have analyzed the spatio-temporal distribution of the frequency of dust events in the Middle East [56] and Iran, but most of them covered a limited area (regional scale) and few meteorological stations [48,57,58,59,60,61,62]. Rashki et al. [58] analyzed the dust days (frequency, seasonality) at stations across the eastern part of Iran, while recent studies [61,62,63] examined the dust days (spatio-temporal distribution) according to their type and intensity at stations around dried lakes and in three highly polluted Iranian provinces. More recently, Mahmoudi and Ikegaya [64] examined the spatio-temporal distribution of frequency in dust days per year over Iran, classifying them into three groups of suspended dust, rising dust, and dust storms. They used about 400 stations during the period 2010–2021, examining the seasonality, variation, and spatial distribution of each group of dust days. However, a comprehensive analysis of the seasonality and trends of different types of dust events over all of Iran, based on station data and their relationship with meteorological dynamics, is still missing.
This gap of knowledge is attempted to be closed in this study, which investigates various aspects related to dust phenomena over Iran, including the different types of dust events, their frequency and intensity, their temporal distribution, and their relationship with precipitation anomalies and atmospheric circulation. For this purpose, dust-related codes and visibility data are investigated in 286 weather stations all over Iran covering the period 2009–2022. According to the type and intensity of the dust events, contrasting spatial distributions were obtained over the country, which are related to wind regimes and dust plumes originated from local, regional, or distant sources. The current approach differs from that of Mahmoudi and Ikegaya [64], since we considered and analyzed the dust events (as per their code) without averaging them as daily averaged (dust days) on a monthly and annual basis, since the information may be lost in case of different weather phenomena (suspended dust, blowing dust, dust storm) occurring during the same day. Furthermore, we also examined the dust types according to their intensity, considering the visibility reduction as a criterion. Therefore, according to its intensity, the spatial distribution and seasonality of a specific dust type may be changed across the Iranian territory. Furthermore, model outputs for surface dust concentrations, obtained from the Sand and Dust Storm Warning and Assessment System (SDS-WAS), are utilized to determine percentages and dust levels at stations all over Iran. NCEP/NCAR and ERA5 reanalysis data were used to examine the large-scale pressure patterns and atmospheric circulation for periods characterized by abnormal rainfall and drought conditions that are related to gaps and peaks in dust occurrence. This study tries to enhance current understanding of dust dynamics, seasonality, and intensity of dust events and their implications on environmental and public health through comprehensive data analysis across Iran.
2. Study Area
In this study, a comprehensive investigation of the sand and dust storms (SDS) phenomena is performed in the arid and semi-arid regions of Iran, with a particular focus on their type, intensity, frequency, and persistence. Iran is a country lying in the dust belt between 25° to 40° N and 44° to 63° E, and its area is 164 million , with a population of more than 90 million people [62]. Figure 1 shows the spatial distribution of the 286 synoptic stations that provided concurrent reports of dust codes and visibility from 2009 to 2022. Although the synoptic weather stations are distributed all over Iran, their density is higher in the north and western parts of the country, while in the arid and desert areas in the east, the station’s coverage is scarce.
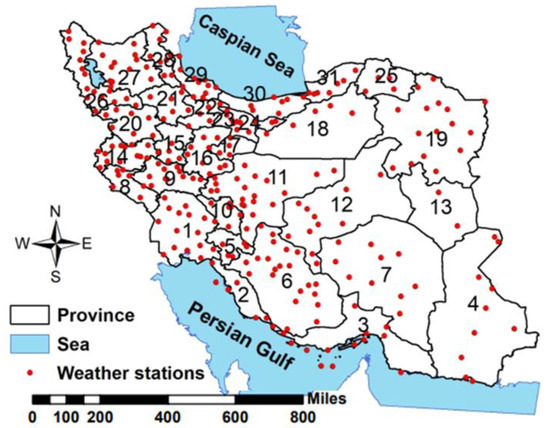
Figure 1.
Spatial distribution of the synoptic stations across Iran used in this study. The numbers refer to Iranian provinces: 1-Khuzestan, 2-Bushehr, 3-Hormozgan, 4-Sistan and Baluchestan, 5-Khohgiluyeh Va Boyerahmad, 6-Fars, 7-Kerman, 8-Ilam, 9-Lorestan, 10-Chaharmahal Va Bakhtiari, 11-Esfahan, 12-Yazd, 13-South Khorasan, 14-Kermanshah, 15-Hamedan, 16-Markazi, 17-Qom, 18-Semnan, 19-Razavi Khorasan, 20-Kordestan, 21-Zanjan, 22-Qazvin, 23-Alborz, 24-Tehran, 25-North Khorasan, 26-West Azerbaijan, 27-East Azerbaijan, 28-Ardebil, 29-Gilan, 30-Mazandaran, and 31-Golestan.
3. Data Set and Methodology
This study utilized synoptic meteorological data that provide significant temporal and spatial coverage of dust events across Iran. The data used in this research consisted of surface weather observations collected every three hours (00, 03, 06, 09, 12, 15, 18, and 21 UTC) during the period 2009 to 2022. The records from the weather stations usually classify four main types of SDS episodes: (i) Code 06 (WW06): Widespread suspended dust that has not been raised by wind at the station or nearby (characterized by very low wind speed and horizontal visibility of less than 10 km), (ii) Blowing Dust: dust raised by wind near the station with visibility between 1000 and 10,000 m, (iii) Sand and Dust Storm: Visibility less than 1000 m, and (iv) Severe Sand and Dust Storm: Visibility less than 200 m. The dust-related codes are summarized in Table 1, which provides a comprehensive overview of the various present weather (WW) codes assigned to SDS events reflecting their severity and characteristics, in accordance with the guidelines established by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) [60,65,66].

Table 1.
Present weather (WW) codes related to SDS events.
Since the last three types of dust storms are associated with intense wind conditions, they are henceforth referred to as “blowing dust”. Therefore, the dust events were divided and analyzed as two main types: Suspended Dust (code WW06) and Blowing Dust (other codes listed in Table 1, excluding WW06). Considering that the meteorological stations under review may, for various reasons such as equipment malfunctions and a lack of weather reports at scheduled times during the study period, the number of reports submitted by each station was initially counted. Stations with significant gaps in their submitted reports were excluded from the analysis. Additionally, it is important to note that reports on horizontal visibility and present weather phenomena were recorded visually by observers, and therefore, an examination of the type of equipment or calibration processes was not conducted in this study.
Moreover, it should be noted that most dust events were reported as WW06 and WW07, while other dust-related codes were rare across all the stations [59,64,67]. After evaluating the data quality from approximately 330 synoptic stations, 286 stations with continuous data on wind speed and direction, horizontal visibility, and phenomenon type during the period 2009–2022 were selected for analysis. To assess the intensity of dust events, four classifications based on horizontal visibility range (HVR) were considered: (i) 0 (km) ≤ HVR < 1 (km) for characterizing strong dust events, (ii) 1 (km) ≤ HVR < 3 (km) for moderate dust events, (iii) 3 (km) ≤ HVR < 5 (km) for weak dust events, and (iv) 5 (km) ≤ HVR < 10 (km) for very weak dust events. In this study, more emphasis is given on the first two categories: strong and moderate dust events. The frequency of dust events refers to the number of reported dust cases in the three-hour synoptic reports. The frequency and intensity of suspended dust and blowing dust were examined at each station based on the various classes of horizontal visibility reduction. Furthermore, the spatial distribution and trends of dust events were analyzed, along with precipitation anomalies in Iran, over a 30-year period (1994–2023) without HVR data. Focus was also given on anomalies of dust events and precipitation in 2009 and 2019, when abnormal and weak dust activities were strongly related to negative (positive) precipitation anomalies.
Furthermore, for specific seasons of these years, an analysis of the large-scale atmospheric circulation patterns was conducted using NCEP/NCAR (National Center for Environmental Prediction/National Center for Atmospheric Research) and ERA5 reanalysis data [68,69]. This investigation focused on the fields of sea level pressure, geopotential height, and lower tropospheric wind, along with their anomalies, compared to the climatic baseline of 1991–2020. More specifically, the analysis targeted the spring seasons of 2009 and 2019, as well as July 2009, to identify significant atmospheric effects and their implications in the modulation of dust activity.
In addition, the models’ outputs of the Sand and Dust Storm Warning and Assessment System (SDS-WAS) in Barcelona, Spain, were utilized to determine percentages and standard levels from the predicted surface dust concentrations all over Iran, covering the period from 2012 to 2022. All dust concentration data were collected and analyzed by using the numerical prediction models of the SDS-WAS processing center (including data from 10 modeling systems), which have been available since 2012 at three-hour intervals, 8 times per day [67]. In this study, two central descriptors (mean and median of the multi-model) were computed on a daily basis, exhibiting adequate temporal coverage. To produce these data, model outputs were interpolated nonlinearly onto a grid with dimensions of 0.5 × 0.5 degrees over Iran, and the values were used as daily dust concentrations at the 286 sites. Therefore, time series of daily predicted median concentrations from 21 January 2012 to 1 May 2022 were created for each station, considering the geographical coordinates. The concentration at the 80th percentile was defined as a high threshold, the 90th percentile was considered as the very high threshold, and the 95th percentile as the severe dust threshold. In this classification, the 100th percentile includes the maximum values during the study period. The percentile values of dust concentrations were displayed at each station based on the established classes of PM10 in the Air Quality Index (AQI) [67], in a way to provide an approximate representation of the potential dust pollution across Iran.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Frequency Distribution of Suspended and Blowing Dust Events
This section examines the frequency (total number of occurrences) distribution of dust events over the Iranian territory, according to their types and intensity, providing insights about the spatial distribution and the dust hotspot regions. To analyze the intensity of suspended dust events (code WW06) and blowing dust (other related codes), these dust types were categorized into two groups: (i) events with horizontal visibility less than or equal to 5 km (strong and moderate) and (ii) events with visibility between 5 and 10 km (weak dust events). During the study period, the suspended dust events at the examined stations that resulted in visibility <5 km ranged from 0 to 2774, while events leading to visibility between 5 and 10 km varied from 0 to 4147 (Figure 2a,b). Such types of dust events predominantly affected the western half of Iran, while the events with lower intensity are also frequent in the central Iranian Plateau, possibly favored by soil emissions from desiccated lakes [70,71,72]. The overall pattern of these occurrences aligned with the Zagros Mountain range, with the highest frequencies observed in the southwestern and western regions, as well as along the Persian Gulf coast. These areas are mostly impacted by dust storms originating from outside Iran, primarily from the Mesopotamian plains and eastern part of the Arabian Peninsula [73,74,75,76,77].
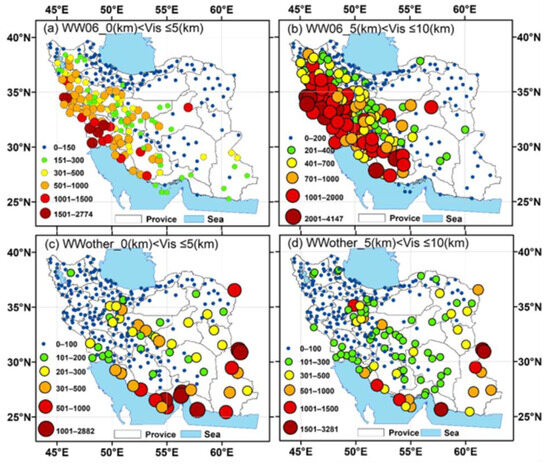
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of dust events categorized by weather code (WW06 and WW other) and horizontal visibility (reduced to 0–5 km and 5–10 km) in Iran. The size and color of the stations represent the frequency of dust events, specifically indicating the total number of occurrences detected over the 10-year study period.
In contrast, the spatial distribution patterns of blowing dust, which is often caused by local dust storms under intense winds, also include haboobs and dust-devil phenomena [78], exhibiting notable differences in the western half of Iran compared to suspended dust patterns, although some similarities were observed in the central regions of Iran and the northern Persian Gulf coast. More specifically, during the study period, the blowing dust events with visibility reduction of 5 km varied from 0 to 2882, while those associated with visibility between 5 and 10 km ranged from 0 to 3281 (Figure 2c,d). The majority of events with visibility between 0 and 5 km were recorded in the eastern arid/desert regions of Iran and also along the coastal waters of the Strait of Hormuz and the Arabian Sea [79,80]. Furthermore, significant frequency of intense, moderate, and weak blowing dust phenomena was also noted in the central Iranian Plateau, associated with dried lakes and emissions from Kavir and Lut Deserts [64,72,81]. The southeastern part of Iran (Sistan and Baluchestan Province) is primarily affected by blowing dust events, with very low occurrence of suspended dust. Frequent dust events in this region are driven by the intense Levar wind [82,83] that facilitates dust emissions from the desiccated Hamoun (Sistan) and Jaz Mourian lakes [77,83,84,85,86,87,88]. It should be noted that the highest number of blowing dust events for both visibility groups was detected in Zabol, Sistan Basin [89], thus rendering it the most dust-impacted city in Iran from blowing dust and dust storm phenomena.
Current spatial distributions of the frequency of suspended dust and other types (blowing dust, dust storms) were similar to those analyzed previously at regional scales in Iran or using fewer meteorological stations. In this respect, Modarres and Sadeghi [57] reported the highest frequency of dust days in southeastern Iran during spring and summer, while Mesbahzadeh et al. [81] highlighted Zabol and Zahedan as the most dust-impacted stations in east Iran. Baghbanan et al. [79] reported that the highest frequency of dust storm events was in May–July at 44 weather stations across Iran. Furthermore, Beyranvand et al. [90], also highlighted SW Iran as the region with the highest frequency of suspended dust events, while Zabol was the station with the highest frequency of rising dust, by examining 44 stations across Iran from 1987 to 2016. These results were in agreement with more recent ones by Mahmoudi and Ikegaya [64] and Alizadeh-Choobari et al. [89], who analyzed several meteorological stations across the country.
4.2. Intensity of Dust Storms
This section analyzes the spatial distribution of suspended dust (code WW06) and other dust types (blowing dust, dust storms, etc. listed in Table 1), according to their intensity. In this respect, events with visibility less than or equal to 1 km were classified as severe, while those with visibility between 1 and 3 km were assumed as moderate. During the study period, the statistical analysis showed that the severe suspended dust events varied from 0 to 1134 and mostly occurred in the western and southwestern parts of Iran (Khuzestan and Ilam Provinces) (Figure 3a). Therefore, it can be concluded that this type of dust event occurs mostly in areas influenced by the western dust corridors, and the sources of these storms are primarily located outside Iran, particularly in the Mesopotamian Plain and the Syrian-Iraqi Desert [91,92,93]. However, intense local dust phenomena may also arise from erodible soils in Ilam and Khuzestan Provinces due to environmental degradation and increased land susceptibility to wind erosion [94,95,96]. The suspended dust storms affect nearly all regions west of the Zagros mountains, as well as the southern Urmia Lake Basin in NW Iran [60], and some parts in central and southeastern Iran, but with lower intensity (Figure 3b). On the contrary, this type of dust event is rare in central-east Iran, with few stations presenting increased frequencies.
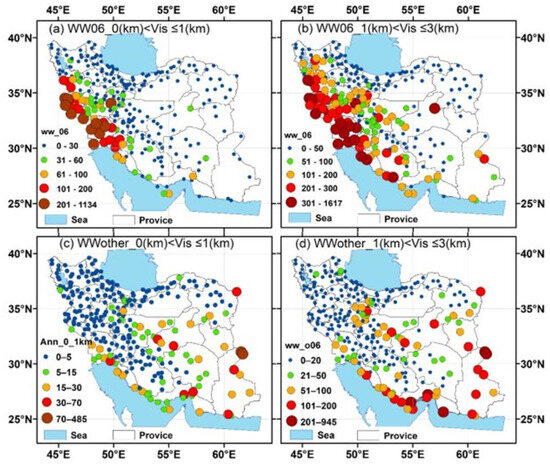
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of dust events categorized by weather code (WW06 and WW other) and horizontal visibility (reduced to 0–1 km and 1–3 km) in Iran. The size and color of the stations represent the frequency of dust events, highlighting the total number of occurrences within each horizontal visibility class over the 10-year period.
Regarding the blowing dust events, the spatial distribution patterns remarkably changed (Figure 3c,d). The range of occurrences of severe blowing dust varied from 0 to 485 events, with the highest frequencies in the eastern (Zabol, Zahak stations in Sistan) and central arid regions, as well as along the Persian Gulf coast (Figure 3c). The blowing dust events of moderate intensity present a very similar spatial distribution pattern, but with nearly doubled frequency in comparison with severe events (Figure 3d). It is important to notice that the intensity of dust storms decreases with increasing distance from the dust sources, so the severe dust spatial patterns may indicate that the sources of these dust storms are located near the meteorological stations, thus considering them as dust hotspot regions.
4.3. Seasonality of Suspended Dust
The monthly distribution of the dust events is examined in the weather stations all over Iran to analyze the seasonality of dust storms, although it is well known that dust activity over the Middle East maximizes in spring and summer [28,46,71]. For this purpose, the monthly spatial distribution of the suspended dust events is shown in Figure 4. In January, these events that exceeded 100 were primarily concentrated in Khuzestan Plain (SW Iran). Gradually, the number of dust events expanded to encompass larger regions in the western half of Iran, peaking in intensity, frequency, and affected areas during June and July (Figure 4a–g). From April to July, stations in the arid central Iranian Plateau also exhibited high frequencies of suspended dust occurrence, while stations in northern Iran (Caspian Sea region) and in the eastern part display a marginal seasonality in this type of dust event, with frequencies ranging from 0 to 30 events throughout the year, except for a few stations influenced by the Lut Desert and Sistan Basin.
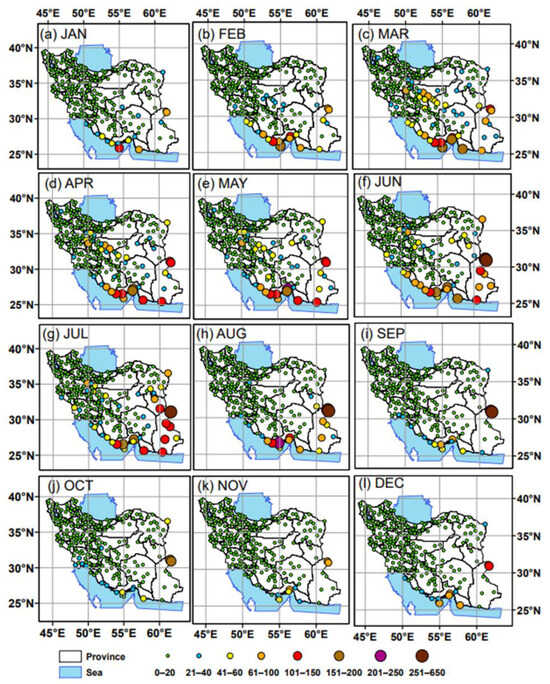
Figure 4.
Monthly distribution of suspended dust event frequency (WW06) across Iran from 2009 to 2022. The size and color of the stations represent the total number of occurrences detected over a 10-month period within each horizontal visibility class.
A significant decreasing trend in dust frequency is observed from August to October (Figure 4h,i), and the number of dust events decreased tremendously in November and December across all stations in Iran, ranging from 0 to 60 episodes (Figure 4k,l). The temporal distribution of suspended dust events indicated that blowing and dust-storm activity from the western corridor was at its lowest from September to January, while it increased sharply from March to July [28]. Due to arid and hot conditions during summer, re-suspension of settled dust particles due to human activities and traffic in urban environments may potentially cause numerous air pollution problems, with direct and indirect consequences for human health in the affected areas, especially in the Khuzestan Province [97,98].
4.4. Seasonality of Blowing Dust
Figure 5 shows the monthly frequency distribution of blowing dust that includes all dust-related codes except WW06. In January (Figure 5a), all weather stations reported fewer than 50 dust events, except for some stations in the coastal Persian Gulf and in the Sistan Basin, where dust episodes exceeded 100. As expected from previous analysis, the dust events of this type happened more frequently along the northern coast of the Persian Gulf and in the Sistan Basin, since these areas include main dust sources, i.e., Jazmurian, Hamouns, and Makran desert valleys [85]. The dust frequency distribution in February (Figure 5b) was similar to that in January, with the main differences being the increased number of dust events and the expansion of the affected areas. The increasing trend in blowing dust episodes in the northern Persian Gulf and eastern regions continued from April to July (Figure 5d–g), with dust occurrence exceeding 400 events. The highest number of dust episodes occurred in Zabol station, Sistan Basin, with blowing dust events exceeding 400 from June to September. From August onward, the blowing dust events decreased drastically in all stations across Iran, except for the Sistan Basin (Zabol station) and a few stations in Hormuz Strait, which remained dust active even during winter (Figure 5g–l). The city of Zabol is one of the dustiest cities in the Middle East, and the Zabol station reported dust events at least during one third of the year [61]. Overall, blowing dust and dust storm episodes are very few during the cold months, while they exhibited the highest frequency in spring and summer, as was observed in previous studies at local/regional scales [60,61]. Mahmoudi and Ikegaya [55] also reported the highest frequency of all types of dust days during the late spring and early summer, but without noting the time shift in the maximum frequency of blowing dust later in summer with respect to suspended dust. These results suggest that early-spring precipitation may play a significant role in controlling the annual and seasonal variability of the dust storms [27], which will be analyzed in the following.
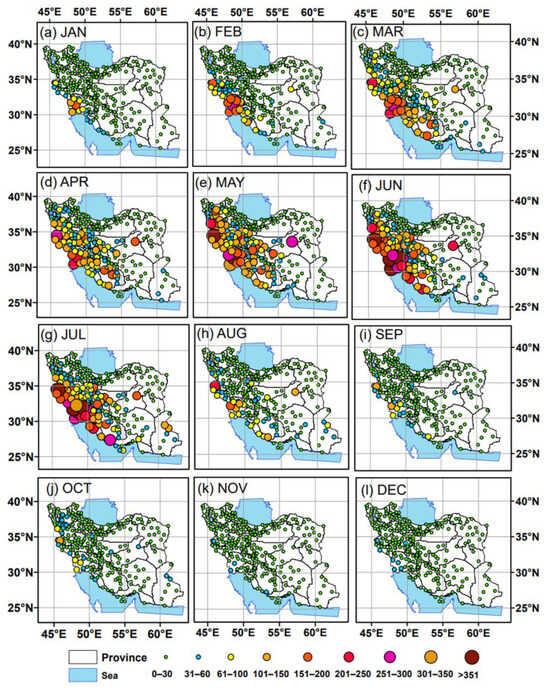
Figure 5.
Monthly distribution of the frequency of blowing dust and dust-storm events across Iran from 2009 to 2022. The size and color of the stations denote the monthly total number of occurrences detected over a 10-month period within each horizontal visibility class.
4.5. Percentage of Daily Surface Particle Concentrations
This section analyzes the spatial distribution of the daily surface dust concentrations, as simulated by SDS-WAS models. The 80th, 90th, 95th, and 100th (maximum values) percentiles of the simulated surface dust concentrations are shown in Figure 6. The suspended particle concentrations at the 80th percentile varied between the stations from 27 µg/m3 to 276 µg/m3. Notably, the northwest region, the southern shores of the Caspian Sea, and some elevated stations in the Zagros Mountains (green in Figure 6a) exhibit the lowest dust concentrations between 0–54 µg/m3. In contrast, the most stations recorded concentrations ranging from 55 µg/m3 to 155 µg/m3 and only Khuzestan plain exhibited concentrations exceeding 155 µg/m3. During the 11-year period from 2012 to 2022, surface dust concentrations above 54 µg/m3 were recorded for more than 800 days in most cities across Iran, significantly exceeding the annual PM10 concentration level of 50 µg/m3 set by WHO [99]. At the 90th percentile, the range of suspended particle concentrations varied from 39 µg/m3 to 391 µg/m3, while concentrations below 54 µg/m3 observed only in a small region in northwest Iran (Figure 6b). High dust concentrations above 155 µg/m3 were detected in western and southwestern Iran, where some stations recorded values exceeding 355 µg/m3, along the Persian Gulf coast, and in the arid southeastern areas (Figure 6b).
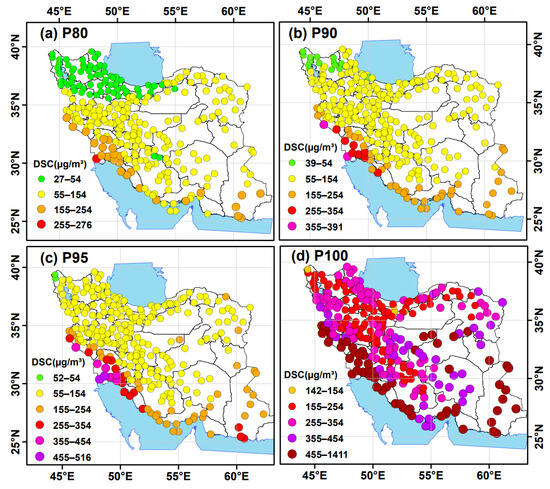
Figure 6.
The 80th (a), 90th (b), and 95th (c) percentiles and the maximum values 100th (d) of the simulated dust surface concentration (DSC) of suspended particles in the Iranian stations. The data were derived from the median of multi-model outputs (SDS-WAS) covering the period from 2012 to 2022. The size and color of the stations denote the frequency of dust events.
At the 95th percentile, the range of surface dust concentrations varied from 52 µg/m3 to 591 µg/m3. Apart from the high concentrations (above 155 µg/m3) along the western and eastern dust corridors, stations with high dust concentrations were also sporadically found in the northeastern and central parts of Iran (Figure 6c). The maximum (100th percentile) of daily surface concentrations recorded in Iranian cities varied from 142 µg/m3 to 1411 µg/m3, with the highest values found in stations located in the western and eastern dust corridors, as well as along the coastal Persian Gulf, the Arabian Sea, and in cities adjacent to the central deserts of Iran (Figure 6d). These very high dust levels may be responsible for hazardous health conditions in several Iranian cities with serious respiratory and cardiovascular diseases [10,97,100,101,102].
4.6. Spatio-Temporal Trends of Dust Events
Figure 7 shows the evolution of dust frequency at nine important stations in Iran, (i) Tehran (the capital and most populated city with more than 10 million), (ii) Tabriz in NW Iran and close to Urmia Lake, which suffers from saline dust storms raised from the dried lake beds [99,100,101,102], (iii, iv) Ilam and Kermanshah in west of Iran that mostly affected by dust storms originated from the Iraqi deserts [43,48], (v) Ahvaz in SW Iran, which is known as one of the most dusty and polluted cities in the world [103,104,105,106,107], (vi) Bushehr in northern shore of the Persian Gulf [108,109,110,111], (vii) Zabol in east Iran that is the one of the dustiest cities in the world [24,112,113,114], (viii) Mashhad in northeast Iran, which is the 2nd most populated city and, (ix) Isfahan in the central Iranian Plateau, which is affected by Kavir Desert. It should be noted that the trend analysis covered the 30-year period (1994–2023), with available dust codes but not horizontal visibility data. Most of the stations, especially those with a dominance of suspended dust (in blue), located in western and central Iran, exhibit a higher frequency of dust events during the mid-end of the 2000s, related to prolonged drought in the Middle East region [21,47,48,115], while another long-term drought during 1999–2003 affected mostly the stations in east Iran (Figure 7). Droughts in the Middle East region have negative consequences in a series of environmental and socio-economic issues, while they control the dust activity and long-term trends [116,117,118,119,120,121]. The stations in the west and south of Iran present a remarkable increase in dust frequency during 2008–2013, while the stations in the eastern and central Iran display different long-term dust patterns, which maximize during the beginning of the 2000s. Furthermore, another common characteristic between the stations is the high dust frequency in 2022, which is related to a sharp decrease in precipitation over Iran. Zabol station exhibits high dust frequency (blowing dust and dust storms) throughout the examined period, highly affected by local dust storms from the Hamoun dried lake beds under intense Levar winds [82,121,122,123]. In Mashhad, the blowing dust frequency was high from 1994 to 2004 and sharply decreased afterwards, while the frequency of suspended dust increased after the mid-2000s. Dust sources in Afghanistan and Turkmenistan and the Aral Sea-dried area mostly affected the air quality in the city [124]. In the majority of the stations, the highest dust frequency occurred in 2009, which was considered the dustiest year in Iran [59], while the highest annual number of dust events was 1023 in Zabol city during 2001.
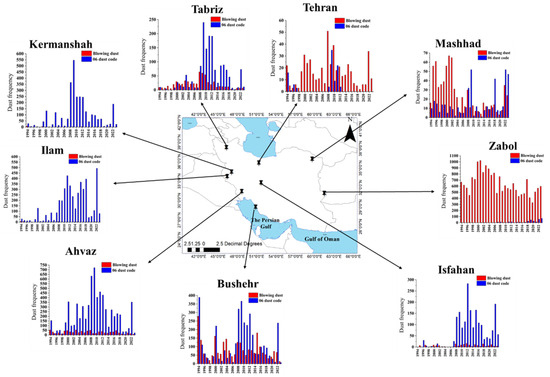
Figure 7.
Annual variation of dust frequency at nine important stations in Iran from 1994 to 2023.
The analysis showed that suspended dust events (code WW06) exhibited distinct characteristics compared to blowing dust/dust storms, in view of frequency, intensity, affected areas, and duration. Seasonal and annual averages of suspended dust frequency in all stations indicated that most dust events occurred in summer 2009 (Figure 8a), and especially in July 2009, in accordance with a similar study in SW Iran [48]. Dust events presented a remarkable increase from 2008 to 2012 during spring and summer. However, in most years after 2011, summer dust events have been substantially decreased, while the spring dust events surpassed those of other seasons, thus indicating an early shift in suspended dust activity over several Iranian stations. Notably, spring 2022 marked the second peak of the maximum dust events over the past 30 years, following the summer peak in 2009 (Figure 8a). This shift in the peak of the suspended dust events from mid-summer to spring needs further investigation in future studies, particularly concerning the impacts of global warming and climate change (deficit of winter-spring precipitation) on dust events.
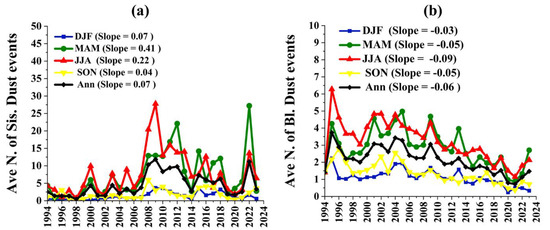
Figure 8.
Seasonal and annual averages of Suspended Dust Events (a) and Blowing Dust Events (b) over the Iranian stations during the period 1994–2023.
On the other hand, blowing dust events averaged over all stations displayed different seasonal and annual patterns during 1994–2023 (Figure 8b). Blowing dust events exhibit less seasonality, although summer is the most favorable season for their occurrence. Summertime blowing dust was higher in 1994–2009 and progressively decreased afterwards. In general, this decrease in blowing dust events during the last decade is shown in all seasons and was consistent with the decrease in summer and winter AODs over Iran [25,29]. Further analysis revealed a higher decreasing trend in summer with –0.096 events per year, on average, while the declining trends in other seasons were −0.05 in spring and autumn and −0.03 in winter.
The average annual number of dust events over a 30-year period (1994–2023) in all meteorological stations in Iran provides useful insights regarding the dust climatology and the areas susceptible to dust storms. At stations in northern Iran, the annual mean dust occurrence is typically below 30 events (Figure 9a). In contrast, western, southern, and southeastern regions, along with some central areas, report over 100 dust events annually, and some weather stations reported even more than 150 dust events. Dust occurrence is high along a corridor extending from the Mesopotamian plains towards west/southwest Iran, the northern coasts of the Persian Gulf, and southeast Iran. The annual distribution and seasonality of dust events are influenced by the proximity to the dust sources, atmospheric conditions (notably precipitation and wind speed), droughts, and human activities at city scales [49,68].
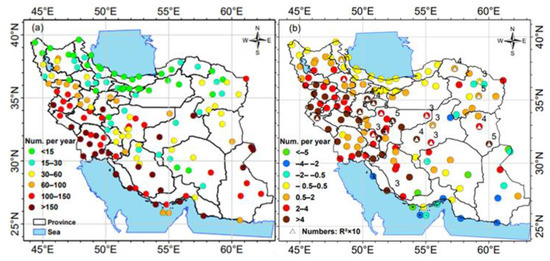
Figure 9.
Panel (a) illustrates the average annual number of dust events recorded at meteorological stations across Iran from 1994 to 2023. Panel (b) presents the trend of dust events (number per year), highlighting 21 stations with significant positive trends (R2 > 0.3). The white triangles within the colored circles indicate these stations, while the black numbers above the circles represent the R2 values multiplied by 10.
Trend analysis of total dust events from 1994 to 2023 (Figure 9b) revealed weak and non-significant changes at the most stations in the northern regions, with slope values between −0.5 and 0.5 dust events per annum. Although some eastern stations exhibit negative trends (from −2 to −6 dust events per year), positive trends are observed at stations in western, central, and northeastern Iran, indicating an increase in dust activity during the last 3 decades. Among the 21 stations with significant positive trends (R2 > 0.3), most of them are located in the central Iranian Plateau and a few in northeastern Iran.
The eastern dust corridor is characterized by dust storms moving from the north to south, where topography plays a crucial role in channeling winds and increasing dust production. The decreasing tendency in dust activity during the last three decades at several stations in east Iran, including the Sistan Basin (i.e., Zabol station; Figure 7), is mainly driven by the abnormally high dust activity during the beginning of the 2000s due to extensive drought [24], as verified by negative trends in AOD over east Iran during the last decades [59,93].
On the other hand, the western dust corridor spans from northwest Iraq and northeastern Syria to the northern Persian Gulf, featuring low-lying lands with alluvial silt soils conducive to dust generation [125]. Progressive increase in dryness over this area, escalated during the intense drought at the mid-end of the 2000s, has resulted in an increase of dust activity over southwest Iran [126,127]. Note also the increasing trend in dust events at stations around the Urmia Lake (NW Iran), attributed to the lake’s desiccation and increased saline SDS emissions from the dried playas during the last decades [61,128,129,130]. On the other hand, multi-decadal changes in atmospheric circulation patterns, low- and high-pressure systems, precipitation redistribution, soil moisture, and wind speed may significantly modulate the annual variability and trends in dust activity over the Middle East and Iran, which generally revealed a large increasing trend till about 2010 and a decrease during the 2010s [23,29]. Comprehensive assessment of the dust regionalization and associated linkage with synoptic weather conditions over Iran are documented in previous studies [59,61].
The trend analysis (slope values) of the average annual dust events (suspended and blowing dust) was divided into the two contrasting periods 1994–2009 and 2010–2023 (Figure 10). The spatial distribution of the two dust types across Iran during the examined periods (1st and 3rd rows in Figure 10) displays similar patterns to those discussed in previous sections, while the differences between the two periods are mostly detected in the number (frequency) and not in the spatial distribution of the dust types. During the period 1994–2009, the annual mean dust events present a large increasing trend in the western part of Iran (Figure 10d), and the same pattern is shown for the suspended dust events (Figure 10e) that prevailed in this region. Many stations in SW, south, and east Iran exhibited statistically significant positive trends in suspended dust events during 1994–2009, with an increase of more than three events per year. Blowing dust also exhibits an increasing tendency over Iran during the same period but with lower trends, whereas some stations along the southern coast presented a slight decrease in blowing dust phenomena (Figure 10e).
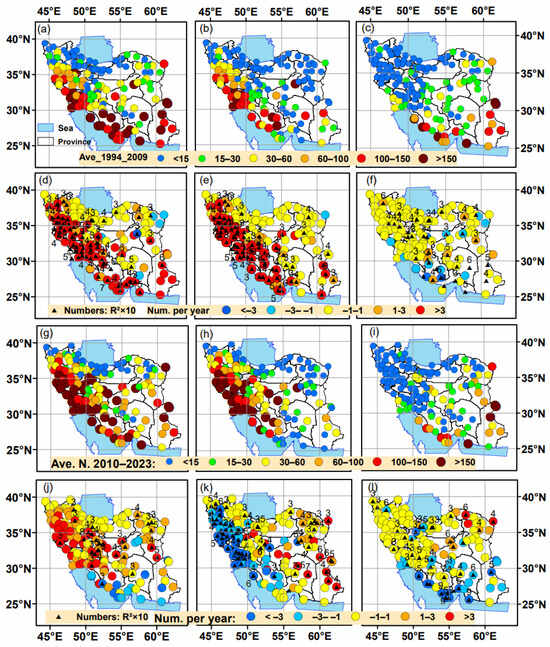
Figure 10.
Average annual number of total dust events (a), suspended dust (b), and blowing dust (c) from 1994 to 2009 across Iran and from 2010 to 2023 (g–i). Trend analysis (slope values) of total dust events (d), suspended dust (e), and blowing dust (f) at each station from 1994 to 2009 and respective trends from 2010 to 2023 (j–l). The black triangles inside the colored circles indicate stations with statistically significant trends (R2 greater than 0.3). The numbers next to these stations represent the R2 values multiplied by 10.
From 2010 to 2023, western and central parts of Iran exhibited an increasing trend in total dust events (Figure 10j), which is mainly driven by a statistically increasing trend in blowing dust phenomena (Figure 10l). On the contrary, southern stations revealed a decrease in total dust events during 2010–2023 (Figure 10j). The suspended dust exhibited a highly decreasing trend in the western part of Iran (Figure 10k), which is related to the decrease in dust activity at normal levels over the Mesopotamian plains and Iraqi deserts after the abnormal high during 2008–2012. Thus, the general decrease in dust activity over the Middle East during the last decade [27,29] is responsible for this declining trend in west Iran. On the contrary, some stations in southeast Iran exhibited an increase in suspended dust phenomena during 2010–2023 (Figure 10k), and they seem to be affected by different sources (dried lakes) and meteorological phenomena. Blowing dust presents a declining trend during 2010–2023 over south and east Iran, while the most stations in the western part exhibit positive (and statistically significant) trends (Figure 10l). Overall, the trends in dust activity over Iran present notable spatio-temporal changes related to the period and the type of dust event. Current results showed that for the better examination of the spatio-temporal evolution of dust activity and the distribution of dust events over Iran, several weather stations with multiple data (phenomenon codes and visibility recordings) should be analyzed.
Nasabpour et al. [50] assessed the spatio-temporal changes in dust over Iran using AOD470 data from the MODIS (MCD19A2) sensor, showing that the highest dust levels occurred from April to July. Additionally, trend analysis indicated that in April, there was an increase in dust intensity with a probability of over 70% in the most studied areas. The trends for May, June, and July showed significant increases in various regions of the western, northern, and eastern parts of the country, with probabilities exceeding 70%. Dadashi Roudbari et al. [66] investigated the trend in the number of dusty hours at 81 stations in Iran during the period 1980–2015, using observation and reanalysis (MACC) data. Overall, the dust maximum frequency was observed at 12:00 GMT, while the minimum was at 00:00 GMT, with the stations in south, SW Iran [45] and the Sistan Basin [83] exhibiting the largest number of dusty hours and days and similar trends to our findings for the total dust events.
4.7. Influence of Precipitation Anomalies on Dust Events
Dust events were influenced by various factors, including land surface characteristics, weather conditions, climate change, and human interventions. In arid and semi-arid regions like Iran, where soil moisture and vegetation cover are low, drought (characterized by reduced precipitation) and surface wind speed may significantly control the variability and trends in dust activity [29,61,121]. To investigate the relationship between dust storm occurrence and drought, it is essential to analyze the anomalies in precipitation affecting the dust source areas. The atmospheric dynamics over the eastern Mediterranean are known as a primary forcing mechanism for influencing precipitation anomalies and controlling dust production over the Middle East—particularly in the western corridor—especially during severe and widespread drought events [39,40,47,131,132,133].
In this study, an assessment of the relationship between precipitation and frequency of dust events in Iran is attempted. The precipitation data at each station (depending on availability) were obtained from 1994 to 2023, and the average annual precipitation over Iran was estimated at 220.1 mm, with the highest seasonal average (93.8 mm) in winter and lowest (12.2 mm) in summer (Table 2). The correlations between monthly, seasonal, and annual precipitation and the average number of dust events are very weak during summer due to negligible rainfall, but a significant negative trend is shown in spring (slope: −0.3) and on an annual basis (slope: −0.37) (Table 2). The monthly results show that the precipitation in January-April is a regulatory factor for dust activity and frequency of dust events over Iran, as justified by previous studies [27,29].

Table 2.
Precipitation average (PA) and linear correlation between precipitation and the frequency of dust events in all weather stations in Iran from 1994 to 2023.
Figure 11 shows the evolution of the annual and spring (MAM) precipitation anomalies, along with the anomalies on the average number of dust events, averaged over all stations from 1994 to 2023. In general, the positive precipitation anomalies are mostly associated with negative ones in dust events, revealing a correlation coefficient of r = −0.4 between the annual precipitation and dust-event anomalies (Figure 11a). Positive precipitation anomalies ranged from 23.6 mm to 63.4 mm in 1994–1998, resulting in a decrease in the average number of dust events by 16.5 to 57.3. A similar feature is shown from 2003 to 2008. However, from 2008 to 2013, positive anomalies in dust occurrence were observed over Iran and reached a peak in 2008 and 2009. This five-year period marked the longest duration of abnormal dust activity over Iran, especially in the western part, attributed to a drought shift in the Fertile Crescent in Iraq [47]. 2009 has been recognized as the dustiest year at many stations across Iran (see Figure 7 and Figure 8), and July 2009 was the dustiest month in most stations [59]. This period was characterized by a deficit of precipitation over most of the stations, with the largest declines in 2008 and 2010. On the contrary, the substantial increase in precipitation in 2019 and 2020 was associated with a significant decrease in dust occurrences. Conversely, a secondary dust peak was recorded in 2022, coinciding with large negative precipitation anomalies in 2021–2022 (Figure 11a).
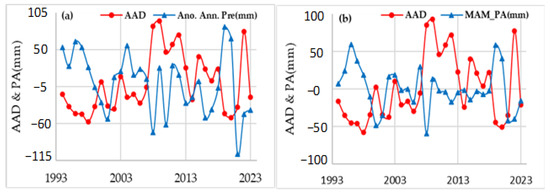
Figure 11.
Temporal evolution of the annual anomalies in dust event frequency (AAD) and in annual precipitation (mm) averaged over all stations in Iran (a). Same as in (a), but for the anomaly in spring precipitation (March-April-May, MAM) compared to the climatic average of the period 1994–2023 (b).
Years 2008 and 2019 exhibited pronounced spikes in precipitation anomalies and dust events. In 2008, the precipitation deficit compared with the period average was 67%, with specific seasonal changes of −22% in spring, −67% in summer, −111% in autumn, and −85% in winter. In 2019, the annual precipitation change was 138%, with spring, summer, autumn, and winter anomalies at 177%, 64%, 104%, and 130% of the annual average, respectively. This finding indicates that fluctuations in spring precipitation may play a crucial role in controlling the dust occurrence in Iran. In this respect, further analysis between spring precipitation anomalies and the average number of dust events from 1994 to 2023 (Figure 11b) revealed similar results with a correlation of r = −0.46. Spring rainfall anomalies exhibited similarities with the annual ones, with some years characterized by significant changes in rainfall amount and notable inverse relationships with dust-event anomalies, indicating that the spring precipitation is a major regulatory factor for the summer dust activity [27].
4.8. Atmospheric Circulations Affecting Dust Events
This section examines the pressure patterns and large-scale atmospheric circulations that serve as primary forcing mechanisms behind substantial changes in dust event frequency over Iran. The analysis focuses on the spring season (March, April, May) of 2009, which is characterized by the least precipitation and the highest occurrences of dust storms, as well as on spring 2019, which experienced the highest rainfall and the fewest dust events during the examined period. Additionally, July 2009 was also analyzed as the month with the highest dust activity in 30 years [56].
In spring 2009, a high-pressure system was established over the Atlantic Ocean (Azores anticyclone), extending across western Europe. Simultaneously, another high-pressure system was positioned over southeastern Kazakhstan, extending toward the Aral Sea [134,135,136,137,138,139]. This configuration created a belt of high pressure at latitudes approximately between 30° N and 45° N (Figure 12a), which may significantly affect precipitation over central Asia [140,141]. In addition, a strong low-pressure area (the Icelandic Low) was present in the North Atlantic, while the sea-level pressure anomalies compared to the 1991–2020 climate period indicated a significant strengthening of the Icelandic Low and Azores High, resulting in a positive NAO (North Atlantic Oscillation) phase. Additionally, negative pressure anomalies of about 2 mb were observed over the northern Caspian Sea and parts of Russia. At the 500 hPa level in spring 2009, a high-altitude ridge over Europe was accompanied by positive height anomalies of approximately 40 gpm (colored orange and red in Figure 12b). On the contrary, a trough extended from Russia through the Middle East to the eastern Mediterranean with negative height anomalies of up to 50 gpm (colored green and blue in Figure 12b).
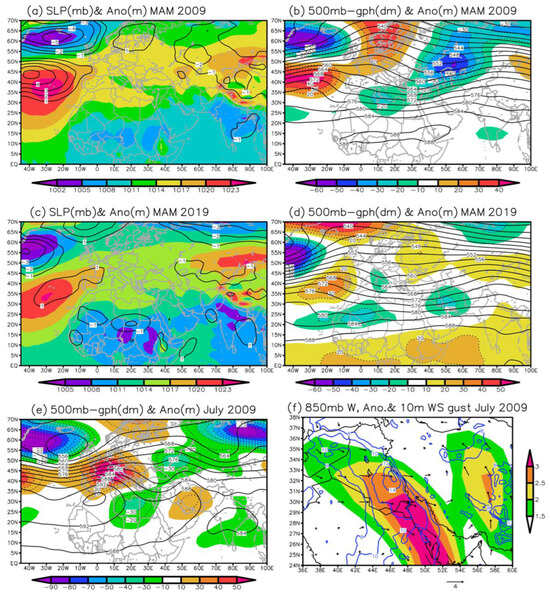
Figure 12.
(a) Sea level pressure (SLP) in spring (MAM) 2009 in a color-shaded representation, alongside its anomaly relative to the climate period 1991–2020, depicted by black contours. (b) Geopotential height at the 500 hPa level in spring 2009 (black contours), and its corresponding anomaly shown with color shading and dotted contours, compared to the 1991–2020 climate baseline. (c) Sea Level Pressure in spring (MAM) 2019 (color-shaded), with its anomaly indicated by black contours, relative to the 1991–2020 climate period. (d) Same as in (b), but for spring 2019. (e) Same as in (b,d), but for July 2009. (f) Anomaly of wind vectors at the 850 hPa level in July 2009 relative to the 1991–2020 climate period, depicted with black vectors and color shading representing wind speed, along with the average wind gusts at 10 m (blue contours). The abbreviations W and WS denote wind vector and wind speed, respectively.
In contrast, spring 2019 displayed a rather normal pressure belt at latitudes around 30° N to 45° N (Figure 12c), with the Azores High becoming narrower and showing a positive anomaly of about 1 mb. However, at the south of this high-pressure belt, low-pressure areas were intensified, suggesting the formation of two storm pathways—one to the north and another to the south of the high-pressure zone. The 500-hPa trough and its negative anomalies over Iran (colored green and blue in Figure 12d) facilitate the movement of humid air masses from the eastern Mediterranean and increased precipitation in the Middle East, including vast areas of Iran. A comparison of Figure 12b,d, particularly in the areas with pronounced height anomalies over the Middle East, highlights the remarkable differences between atmospheric circulation patterns associated with low precipitation patterns and high dust occurrence and those characterized by heavy rainfall and fewer dust events.
Figure 12e illustrates the geopotential height at the 500 hPa level for July 2009, along with its anomalies relative to the 1991–2020 period. The synoptic map illustrates the expansion of a pressure ridge from the Persian Gulf to Iran, while positive anomalies (10–30 gpm) prevailed over Iran, indicating subsidence that facilitated dry conditions. This system coincides with a 500 hPa height trough extending from the Black Sea to the eastern Mediterranean and North Africa. The intensified pressure gradient over the Middle East played a crucial role in amplifying the northwesterly Shamal winds [52] across the Mesopotamian Plain (positive anomalies of above 2.5 m/s). As a result, a low-level jet developed in these regions (Figure 12f), leading to the generation of strong gusty winds at 10 m. The monthly mean wind speed reached high values of up to 16 m/s, which is capable of triggering severe dust storms that affected west Iran through the western dust corridor [83]. A significant portion of the dust plumes was transported by prevailing northwesterly winds towards the Persian Gulf and southern Iran. Another fraction of these dust plumes, having ascended to higher altitudes, was carried westward over the Zagros Mountains, also affecting parts of central and northwestern Iran.
5. Conclusions
This study analyzed the spatio-temporal evolution, distribution, and trends of dust events of different types (suspended dust vs. blowing dust) and intensities over Iran, aiming to assess the seasonality, surface dust concentrations, trends, and meteorological influence. The spatial distribution analysis revealed that severe suspended dust events (WW06 dust code) and blowing dust events were concentrated in specific areas, particularly in western/southwestern Iran and in southern coast and eastern arid regions, respectively. Both dust types exhibited a distinct seasonality across the country, with maxima in April-July for the suspended dust in the western part and in May-August for blowing dust in east Iran. This regional susceptibility highlights the need for localized strategies that consider both natural and anthropogenic factors contributing to dust rising and propagation. Furthermore, most stations, especially in the western and central parts of Iran, exhibited an increasing tendency of dust events from 1994 to 2023, with the period 2008–2012 being the most dust-laden. Conversely, stations in the east presented a decreasing trend in dust events after the peak in dust activity during the beginning of the 2000s.
The analysis of sand and dust storms in Iran revealed a complex interplay between meteorological conditions, geographical regions, and factors, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to address this growing environmental challenge. The significant increase in dust storm occurrences—particularly in the western part of Iran, where more than 150 dust events were reported annually—underscores the critical need for enhanced monitoring and warning systems. The health implications of dust storms are significant too, as daily particle concentrations frequently exceeded the WHO’s annual PM10 guideline of 50 µg/m3 throughout the country, reaching up to 1411 µg/m3 in certain areas. This poses serious risks to public health, particularly for vulnerable populations, including children and the elderly.
Current findings showed that years with enhanced spring precipitation were correlated with a sharp decrease in dust events. For instance, in 2019, when precipitation increased by 138%, dust occurrence dropped dramatically to as low as 30 events annually. Conversely, negative precipitation anomaly was associated with peaks in dust activity, reaching up to 2774 events. This inverse relationship suggests that fluctuations in spring (and annual) precipitation could serve as valuable predictive indicators for dust storm occurrence, allowing for proactive measures to be implemented. Future research should focus on integrating advanced climatic models and technologies to improve forecasting capabilities and develop targeted interventions. This includes exploring the relationships among land use changes, drought conditions, and dust generation, as well as assessing the effectiveness of potential mitigation strategies. In addition, collaboration with local communities and stakeholders is essential when developing adaptive management practices that enhance resilience to dust storms. In conclusion, addressing the challenges posed by sand and dust storms in Iran requires a multifaceted approach that combines scientific research, policymaking, and community engagement. By understanding the dynamic factors influencing dust events and their impacts, we can develop more effective strategies to protect air quality and public health in affected areas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.H.H., A.R.S.A. and D.G.K.; methodology, N.H.H. and A.R.S.A.; software, N.H.H., C.O., A.F.K. and D.G.K.; validation, N.H.H., A.F.K. and A.R.S.A.; formal analysis, A.R.S.A., N.H.H., D.G.K. and C.O.; resources, N.H.H.; data curation, A.R.S.A. and A.F.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.R.S.A. and D.G.K.; writing—review and editing, A.R.S.A., D.G.K., N.H.H. and C.O.; visualization, N.H.H., A.R.S.A. and D.G.K.; supervision, A.R.S.A. and D.G.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sets supporting reported results are PM10 via SDS-WAS (https://sds-was.aemet.es/products/dust-products-catalogue, accessed on 12 March 2025).
Acknowledgments
We are thankful for data derived from the Barcelona supercomputer center in this study via (https://sds-was.aemet.es/products/dust-products-catalogue, accessed on 12 March 2025). The authors are greatly thankful to the Iranian meteorological organization (IRIMO) for dust-related codes.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Nasim Hossein Hamzeh was employed by the company Air and Climate Technology Company (ACTC). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Report on Surveillance of Antibiotic Consumption: 2016–2018 Early Implementation. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241514880 (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Antoniadis, V.; Shaheen, S.M.; Levizou, E.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Vithanage, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J. A critical prospective analysis of the potential toxicity of trace element regulation limits in soils worldwide: Are they protective concerning health risk assessment?—A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 819–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohra, K.; Vodonos, A.; Schwartz, J.; Marais, E.A.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Mickley, L.J. Global mortality from outdoor fine particle pollution generated by fossil fuel combustion: Results from GEOS-Chem. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110754–110780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Interim Case Reporting form for 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) of Confirmed and Probable Cases: WHO Minimum Data Set Report form, 21 January 2020 (No. WHO/2019-nCoV/Surveillance_CRF/2020.1); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schepanski, K. Transport of Mineral Dust and Its Impact on Climate. Geosciences 2018, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, S.-A.; Salamalikis, V.; Kazantzidis, A. Aerosol classification in Europe, Middle East, north Africa and arabian peninsula based on AERONET version 3. Atmos. Res. 2020, 239, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Kazadzis, S.; Taylor, M.; Athanasopoulou, E.; Speyer, O.; Raptis, P.I.; Marinou, E.; Proestakis, E.; Solomos, S.; Gerasopoulos, E. Dust impact on surface solar irradiance assessed with model simulations, satellite observations and ground-based measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2435–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostamandi, S.; Ukhov, A.; Engelbrecht, J.; Shevchenko, I.; Osipov, S.; Stenchikov, G. Fine and Coarse Dust Effects on Radiative Forcing, Mass Deposition, and Solar Devices Over the Middle East. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, J.M.; Boucher, O. Estimates of the direct and indirect radiative forcing due to tropospheric aerosols: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2000, 38, 513–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Pal, I. Dust storm and its environmental implications. J. Eng. Comput. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Abuduwaili, J.; Liu, D.; Wu, G. Saline dust storms and their ecological impacts in arid regions. J. Arid Land 2010, 2, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, G.; Babu, K.N.; Solanki, H.A. Monitoring bio-optical response of coastal waters surrounding the Indian subcontinent to atmospheric dust deposition using satellite data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 5523–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Muraleedharan, P.M.; Prakash Babu, C. Mid-troposphere transport of Middle-East dust over the Arabian Sea and its effect on rainwater composition and sensitive ecosystems over India. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmard, Z.; Kouchaksaraei, M.T.; Bahrami, H.A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Modarres Sanavi, S.A.M.; Struve, D.; Ammere, C. Soil dust effects on morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of four tree species of semiarid regions. Eur. J. For. Res. 2019, 139, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelstaedter, S.; Kohfeld, K.E.; Tegen, I.; Harrison, S.P. Controls of dust emissions by vegetation and topographic depressions: An evaluation using dust storm frequency data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, M.; Ueda, K.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Michikawa, T.; Onozuka, D. Health effects of Asian dust events: A review of the literature. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi 2010, 65, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, S.A.; Hussain, H.H.; Leh, N.S.H.N.; Razali, M.S. Effects of dust on the performance of PV panels. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 58, 588–593. [Google Scholar]
- Choobari, O.A.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. The global distribution of mineral dust and its impacts on the climate system: A review. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Climate effects of dust aerosols over East Asian arid and semiarid regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Adebiyi, A.A.; Albani, S.; Balkanski, Y.; Checa-Garcia, R.; Chin, M.; Colarco, P.R.; Hamilton, D.S.; Huang, Y.; Ito, A.; et al. Contribution of the world’s main dust source regions to the global cycle of desert dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 8169–8193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Notaro, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Alkolibi, F.; Fadda, E.; Bakhrjy, F. Climatic Controls on the Interannual to Decadal Variability in Saudi Arabian Dust Activity: Toward the Development of a Seasonal Dust Prediction Model: Saudi Arabian Dust Prediction. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 1739–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Mofidi, A.; Minvielle, F.; Chiapello, I.; Legrand, M.; Dumka, U.C.; Francois, P. Effects of Monsoon, Shamal and Levar winds on dust accumulation over the Arabian Sea during summer—The July 2016 case. Aeolian Res. 2019, 36, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labban, A.H.; Mashat, A.S.; Awad, A.M. The Variability of the Siberian High Ridge over the Middle East. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 41, 104–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Maleki, S.; Middleton, N. An investigation into climatic and terrestrial drivers of dust storms in the Sistan region of Iran in the early twenty-first century. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.; Wu, R.; Aldabash, M. Long-term AOD trend assessment over the Eastern Mediterranean region: A comparative study including a new merged aerosol product. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 238, 117736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.; Wu, R.; Lelieveld, J.; Yousefi, R.; Aldabash, M. Winter AOD trend changes over the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East region. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 5516–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.; Wu, R.; Yousefi, R.; Wang, F.; Ge, Q.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Wang, J.; Alpert, P.; Munawar, I. Spatio-temporal changes of spring-summer dust AOD over the Eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East: Reversal of dust trends and associated meteorological effects. Atmos. Res. 2023, 281, 106509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, R.; Wang, F.; Ge, Q.; Shaheen, A. Long-term aerosol optical depth trend over Iran and identification of dominant aerosol types. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, R.; Wang, F.; Ge, Q.; Shaheen, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Analysis of the winter AOD trends over Iran from 2000 to 2020 and associated meteorological effects. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingmüller, K.; Pozzer, A.; Metzger, S.; Stenchikov, G.L.; Lelieveld, J. Aerosol optical depth trend over the Middle East. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5063–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari Damaneh, H.; Sayadi, Z.; Khoorani, A. Evaluation of spatiotemporal changes and correlations of aerosol optical depth, NDVI and climatic data over Iran. Iran. J. Range Desert Res. 2021, 28, 772–786. (In Persian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubin, B.; Sajedi Hosseini, F.; Rahmati, O.; Mehdizadeh Youshanloei, M.; Jalali, M. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Dust Days in Western Azarbaijan Province, Determination of The Influencing Factors and Source of Events. Desert Manag. 2022, 10, 71–86. (In Persian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, R.; Wang, F.; Ge, Q.; Lelieveld, J.; Shaheen, A. Aerosol trends during the dusty season over Iran. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Westphal, D.L.; Holt, T.R.; Xu, Q. Numerical simulation of a low-level jet over complex terrain in southern Iran. Mon. Weather Rev. 2000, 128, 1309–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, S.; Schepanski, K.; Heinold, B.; Knippertz, P. Climatology of Nocturnal Low-Level Jets over North Africa and Implications for Modeling Mineral Dust Emission. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6100–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, D.; Sun, S. On the Orographically Generated Low-Level Easterly Jet and Severe Downslope Storms of March 2006 over the Tacheng Basin of Northwest China. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 1667–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi Devin, M.; Ranjbar SaadatAbadi, A.; Fattahi, E.; Karami, S.; Sehat Kashani, S. Study of the effect of low-level jets on genesis and transport of dust in the west and southwest of Iran. Iran. J. Geophys. 2022, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parno, R.; Meshkatee, A.H.; Mobarak Hassan, E.; Hamzeh, N.H.; Chel Gee Ooi, M.; Habibi, M. Investigating the Role of the Low-Level Jet in Two Winters Severe Dust Rising in Southwest Iran. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Notaro, M.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Garay, M.J. Climatology of summer Shamal wind in the Middle East. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidi, A.; Zarrin, A. On the Existence of Summer Shamal Wind Induced by the Zagros Mountains in the Middle East. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubhi, Y.; Awad, A.M.; Mashat, A.S.; Labban, A.H. Climatology of the spring subtropical jet stream over the Middle East and its effect on the synoptic characteristics of dust systems over the northern Arabian Peninsula. Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidi, A.; Zarrin, A.; Hassani, S.; Soltani, M. Dynamics of a severe summer Shamal wind and its induced dust storm in the Middle East: A diagnostic study based on numerical simulation. Atmos. Res. 2024, 314, 107800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroushani, M.A.; Opp, C.; Groll, M.; Nikfal, A. Evaluation of WRF-Chem Prediction for Dust Deposition in Southwestern Iran. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, S.; Hamzeh, N.H.; Noori, F.; Ranjbar, A. Investigation of dust storms in Ilam and the performance analysis of simulation of 6 numerical prediction models at a severe dust storm in west of Iran. J. Air Pollut. Health 2019, 2, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroushani, M.A.; Opp, C.; Groll, M. Investigation of aeolian dust deposition rates in different climate zones of southwestern Iran. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroushani, M.A.; Opp, C.; Groll, M. Spatial and temporal gradients in the rate of dust deposition and aerosol optical thickness in southwestern Iran. J. Arid Land 2021, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaro, M.; Yu, Y.; Kalashnikova, O.V. Regime shift in Arabian dust activity, triggered by persistent Fertile Crescent drought. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 10–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, N.H.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Rashki, A.; Mohammadpour, K. Long-Term Variability of Dust Events in Southwestern Iran and Its Relationship with the Drought. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1350–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, A.R.S.; Hamzeh, N.H.; Chel Gee Ooi, M.; Kong, S.S.K.; Opp, C. Investigation of two severe shamal dust storms and the highest dust frequencies in the south and southwest of Iran. Atmosphere 2022, 12, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasabpour, M.S.; Salajegheh, A.; Khosravi, H.; Nasiri, A.; Ranjbar Saadat Abadi, A. Investigating the Trend of Dust Changes in The Eastern Half of Iran. Desert Manag. 2023, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y. Impacts of aerosol direct radiative effect on global and regional climate changes from 2001 to 2010. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 9932–9948. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, B.D.; Flamant, C.; Chaboureau, J.P.; Banks, J.; Cuesta, J.; Brindley, H.; Oolman, L. Dust emission and transport over Iraq associated with the summer Shamal winds. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.; Chaboureau, J.-P.; Nelli, N.; Cuesta, J.; Alshamsi, N.; Temimi, M.; Pauluis, O.; Xue, L. Summertime dust storms over the Arabian Peninsula and impacts on radiation, circulation, cloud development and rain. Atmos. Res. 2021, 250, 105364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, Z.; Teymouri, P.; Darvishi Boloorani, A.; Mesdaghini, A.; Middleton, N.; Griffin, D.W. An overview of bioaerosol load and health impacts associated with dust storms: A focus on the Middle East. Atmos. Environ. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Mobarak Hassan, E. Effective Synoptic Structures in the Supporting Dust Storms over the Persian Gulf. J. Oceanogr. 2019, 10, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Irannejad, P.; Shao, Y. Climatology of the Middle East Dust Events. Aeolian Res. 2013, 10, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarres, R.; Sadeghi, S. Spatial and Temporal Trends of Dust Storms across Desert Regions of Iran. Nat. Hazards 2018, 90, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Sepehr, A. Statistical evaluation of the dust events at selected stations in southwest Asia: From the Caspian Sea to the Arabian Sea. Catena 2018, 165, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, N.H.; Karami, S.; Opp, C.; Fattahi, E.; Jean-François, V. Spatial and temporal variability in dust storms in the Middle East, 2002–2018: Three case studies in July 2009. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, A.R.S.; Shukurov, K.A.; Hamzeh, N.H.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Opp, C.; Shukurova, L.M.; Ghasabi, Z. Dust events over the Urmia Lake Basin, NW Iran, in 2009–2022 and their potential sources. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, N.H.; Abadi, A.R.S.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Mirzaei, E.; Shukurov, K.A.; Sotiropoulou, R.-E.P.; Tagaris, E. The Importance of Wind Simulations over Dried Lake Beds for Dust Emissions in the Middle East. Atmosphere 2023, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatabadi, A.R.; Hamzeh, N.H.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Ghasabi, Z.; Penchah, M.M.; Sotiropoulou, R.-E.P.; Habibi, M. Optimization and evaluation of the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model for wind energy resource assessment and mapping in Iran. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, N.H.; Abadi, A.R.S.; Alam, K.; Shukurov, K.A.; Opp, C. Long-Term Wind and Air Temperature Patterns in the Southeastern Region of Iran through Model Simulation and Ground Observations. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, L.; Ikegaya, N. Identifying the Distribution and Frequency of Dust Storms in Iran Based on Long-Term Observations from over 400 Weather Stations. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzadfar, F.; Yousefi, M.; Jafari-Khounigh, A.; Khorrami, Z.; Haghdoost, A.; Shadmani, F.K. Trend and projection of non-communicable diseases risk factors in Iran from 2001 to 2030. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadashi Roudbari, A.A.; Ahmadi, M. An assessment of change point and trend of diurnal variation of dust storms in Iran: A multi-instrumental approach from in situ, multi-satellite, and reanalysis dust product. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Abadi, A.R.S.; Hamzeh, N.H.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Vuillaume, J.F.; Shukurov, K.A.; Gharibzadeh, M. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of PM2.5 and PM10 Concentrations and Assessment of Public Health Risk in the Three Most Polluted Provinces of Iran. Sustainability 2024, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woolen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelona Dust Regional Center. Available online: https://dust.aemet.es (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Mesbahzadeh, T.; Salajeghe, A.; Sardoo, F.S.; Zehtabian, G.; Ranjbar, A.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Miglietta, M.M.; Mirakbari, M. Climatology of dust days in the Central Plateau of Iran. Nat. Hazards 2020, 104, 1801–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrari, A.; Panchanathan, A.; Haghighi, A.T. Dust over water: Analyzing the impact of lake desiccation on dust storms on the Iranian Plateau. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, K.; Sciortino, M.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Classification of weather clusters over the Middle East associated with high atmospheric dust-AODs in West Iran. Atmos. Res. 2021, 259, 105682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarak Hassan, E.; Alizadeh, O. Dust events in southwestern Iran: Estimation of pm10 concentration based on horizontal visibility during dust events. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 5159–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafarian, P.; Kabiri, K.; Delju, A.H.; Fallahi, M. Spatio-temporal variability of dust events in the northern Persian Gulf from 1991 to 2020. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafarian, P.; Mohammadpour Penchah, M. Wind resource assessment over the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea using a numerical model simulation and satellite data. J. Ocean Eng. Mar. Energy 2023, 9, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmabadi, H.; Saeedi, M.; Roy, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Quantifying the contribution of Middle Eastern dust sources to PM10 levels in Ahvaz, Southwest Iran. Atmos. Res. 2023, 295, 106993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, S.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Ghassabi, Z.; Khansalari, S. Investigation and model simulation of dry and moist (haboob) convective dust storms in Yazd Province, central Iranian plateau. Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 16, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghbanan, P.; Ghavidel, Y.; Farajzadeh, M. Spatial analysis of spring dust storms hazard in Iran. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 139, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, F.; Khalesifard, H.R. Characterization of released dust over open waters in the south of the Iran Plateau based on satellite and ground-based measurements. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbahzadeh, T.; Miglietta, M.M.; Sardoo, F.S.; Krakauer, N.; Hasheminejad, M. Regional Analysis of Dust Day Duration in Central Iran. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawar-Reza, P. Numerical Analysis of the’120 Day Wind’over the Sistan Region, South-West Asia with TAPM. Clean Air Environ. Qual. 2008, 42, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, H.; Opp, C.; Groll, M.; Gohardoust, A. Wind regime and sand transport in the Sistan and Registan regions (Iran/Afghanistan). Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie 2019, 62 (Suppl. S1), 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Mohamadifar, A.; Sorooshian, A.; Jansen, J. Machine-learning algorithms for predicting land susceptibility to dust emissions: The case of the Jazmurian Basin, Iran. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, M.; Afzali, K.N.; Jahan, S.; Strezov, V.; Soleimani-Sardo, M. Pollution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Jazmurian playa in southeast Iran. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvishi Boloorani, A.; Najafi, M.S.; Soleimani, M.; Papi, R.; Torabi, O. Influence of Hamoun Lakes’ dry conditions on dust emission and radiative forcing over Sistan plain, Iran. Atmos. Res. 2022, 272, 106152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rami, A.; Hamidi, M.; Neya, B.N. Atmospheric analysis of dust storms in Sistan region. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2022, 227, 105800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Khusfi, Z.; Zandifar, S.; Ebrahimi-Khusfi, M.; Tavakoli, V. Heavy metal mapping, source identification, and ecological risk assessment in the International Hamoun wetland, Sistan region, Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 29321–29335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Choobari, O.; Ghafarian, P.; Owlad, E. Temporal Variations in the Frequency and Concentration of Dust Events over Iran Based on Surface Observations. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyranvand, A.; Azizi, G.; Alizadeh-Choobari, O.; Darvishi Boloorani, A. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Incidence of Dust Events over Iran. Nat. Hazards 2019, 97, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.S.; Moradi, H.; Shrifikia, M. Evaluation of dust storm temporal distribution and the relation of the effective factors with the frequency of occurrence in Khuzestan Province from 2000 to 2015. Geogr. Data 2019, 28, 191–203. [Google Scholar]
- Salmabadi, H.; Khalidy, R.; Saeedi, M. Transport routes and potential source regions of the Middle Eastern dust over Ahvaz during 2005–2017. Atmos. Res. 2020, 241, 104947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Mielonen, T.; Farajzadeh, M. Climatology of atmospheric dust corridors in the Middle East based on satellite data. Atmos. Res. 2022, 280, 106454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Molaverdi, M.; Jabbari, I.; Fathnia, A. Geomorphological and Spatial Analysis of Dust sources in Ilam Province, Iran. Sediment. Geol. 2022, 436, 106168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Rahimi, D.; Najafi, M.R.; Zakerinejad, R. The Effect of Environmental Degradation and Climate on Dust in Khuzestan Province, Iran. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhashemi, S. Preparing a map of the sensitivity of the lands of Ilam province to dust production using data mining models. Environ. Eros. Res. 2024, 14, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Daryanoosh, S.M.; Amrane, A.; Polosa, R.; Hopke, P.K.; Goudarzi, G.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Sicard, P.; Armin, H. Impact of Middle Eastern Dust storms on human health. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsani, M.H.; Shirmardi, M.; Alavi, N.; Maleki, H.; Sorooshian, A.; Babaei, A.; Asgharnia, H.; Marzouni, M.B.; Goudarzi, G. Evaluation of the relationship between PM10 concentrations and heavy metals during normal and dusty days in Ahvaz, Iran. Aeolian Res. 2018, 33, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H. WHO air quality guidelines need to be adopted. Int. J. Public Health 2021, 66, 1604483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.J.A.; Ebrahimzadeh, L.; Eslami, A.; Bidarpoor, F. Effects of dust storm events on emergency admissions for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in Sanandaj, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouri, N.; Karimi, B.; Kolivand, A.; Mirhoseini, S.H. Ambient dust pollution with all-cause, cardiovascular and respiratory mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, G.; Daryanoosh, S.M.; Godini, H.; Hopke, P.K.; Sicard, P.; De Marco, A.; Rad, H.D.; Harbizadeh, A.; Jahedi, F.; Mohammadi, M.J.; et al. Health risk assessment of exposure to the Middle-Eastern Dust storms in the Iranian megacity of Kermanshah. Public Health 2017, 148, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Yunesian, M.; Naseri, S.; Taghipour, H.; Rastkari, N.; Nazmara, S.; Mahvi, A.H. Physico-chemical characterization of ambient air particulate matter in Tabriz, Iran. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 92, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroughani, M.; Hashemi, H.; Hosseini, S.H.; Pourhashemi, S.; Berndtsson, R. Desiccating Lake Urmia: A New Dust Source of Regional Importance. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, C.; Middleton, N.; Kang, U.; Liniger, H. Shrinking Water Bodies as Hotspots of Sand and Dust Storms: The Role of Land Degradation and Sustainable Soil and Water Management. Catena 2021, 207, 105669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazzadeh, M.; Yadeghari, A.; Gholampour, A. Temporal and spatial variations of deposition and elemental composition of dust fall and its source identification around Tabriz, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmeddin, A.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Lahijanzadeh, A. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in road dust from urban industrial areas of Ahvaz megacity, Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 1187–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Sorooshian, A.; Goudarzi, G.; Nikfal, A.; Baneshi, M.M. Temporal profile of PM10 and associated health effects in one of the most polluted cities of the world (Ahvaz, Iran) between 2009 and 2014. Aeolian Res. 2016, 22, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, G.; Sorooshian, A.; Maleki, H. Local and Long-range transport dust storms over the city of Ahvaz: A survey based on spatiotemporal and geometrical properties. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2020, 177, 3979–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broomandi, P.; Dabir, B.; Bonakdarpour, B.; Rashidi, Y. Identification of the sources of dust storms in the City of Ahvaz by HYSPLIT. Pollution 2017, 3, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Goudarzi, G.; Shirmardi, M.; Khodarahmi, F.; Hashemi-Shahraki, A.; Alavi, N.; Ankali, K.A.; Babaei, A.A.; Soleimani, Z.; Marzouni, M.B. Particulate matter and bacteria characteristics of the Middle East Dust (MED) storms over Ahvaz, Iran. Aerobiologia 2014, 30, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Choobari, O.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. The wind of 120 days and dust storm activity over the Sistan Basin. Atmos. Res. 2014, 143, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Ezeliora, C.D.; Sharki, S.H.; Osagie, C.; Ghosh, S.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Khan, N.A. Assessment of health impacts attributed to PM10 exposure during 2015–2017 in Zabol City, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 4123–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberifar, R.; Moosa Kazemi, S.M.; Karimian Pour, F. Investigating the Viability of Cities Located in Environmentally Sensitive Areas, Case Study: Zabol City. J. Urban Ecol. Res. 2024, 15, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Javadian, M.; Behrangi, A.; Sorooshian, A. Impact of Drought on Dust Storms: Case Study over Southwest Iran. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniewski, D.; Van Campo, E.; Weiss, H. Drought is a recurring challenge in the Middle East. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3862–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zittis, G.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Lelieveld, J. Dust storms in the Eastern Mediterranean: Natural or anthropogenic? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1811–1830. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, M.; Ahmadalipour, A.; Moradkhani, H. Drought and food security in the middle east: An analytical framework. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 281, 107816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafadi, K.; Al-Ansari, N.; Mokhtar, A.; Mohammed, S.; Elbeltagi, A.; Sh-Sammen, S.; Bi, S. An evapotranspiration deficit-based drought index to detect variability of terrestrial carbon productivity in the Middle East. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 014051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pary, A.T.; Rastgoo, P.; Opp, C.; Zeuss, D.; Abera, T.A. Impacts of drought severity and frequency on natural vegetation across Iran. Water 2024, 16, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyranvand, A.; Azizi, G.; Alizadeh, O.; Darvishi Boloorani, A. Dust in Western Iran: The emergence of new sources in response to shrinking water bodies. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavieh, A.; Sedaghat, A.; Ayodele, R.; Mostafaeipour, A. Worldwide wind energy status and the characteristics of wind energy in Iran, case study: The province of Sistan and Baluchestan. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2017, 36, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, O.; Abniki, M.; Babaei, M.; Irannejad, P. Climatology and the dynamic mechanism of the Levar wind and dust events in eastern Iran. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 9288–9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, A.; Shahbazi, R.; Sheikh, M.; Lak, R.; Ahmadi, N.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Behrooz, R.D.; Sotiropoulou, R.E.P.; Tagaris, E. Environmental pollution and human health risks associated with atmospheric dust in Zabol City, Iran. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2024, 17, 2491–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi Moradian, J.; Hosseinzadeh, S.R. The study of desert dust in Mashhad Metropolis using satellite images and synoptic datasets (2009–2013). J. Geogr. Environ. Hazards 2015, 4, 35–57. [Google Scholar]
- Darvishi Boloorani, A.; Papi, R.; Soleimani, M.; Karami, L.; Amiri, F.; Samany, N.N. Water bodies changes in Tigris and Euphrates basin has impacted dust storms phenomena. Aeolian Res. 2021, 50, 100698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, A.; Hashemi, H.; Zhao, P.; Brogaard, S.; Eklund, L.; Hassan, H.H.; Mansourian, A. Spatiotemporal variability of dust storm source susceptibility during wet and dry periods: The Tigris-Euphrates River Basin. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 15, 101953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmady-Birgani, H.; Ravan, P.; Schlosser, J.S.; Cuevas-Robles, A.; Azadi Aghdam, M.; Sorooshian, A. On the chemical nature of wet deposition over a major desiccated lake: Case study for Lake Urmia basin. Atmos. Res. 2020, 234, 104762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzehpour, N.; Mahdavinia, G.R.; Rahmati, M. Sand sheets—The major dust source in the western Lake Urmia playa—A comprehensive study of the soil-dust properties and stabilization. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2024, 39, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, A.; Shahbazi, F.; Oustan, S.; Jafarzadeh, A.A.; Minasny, B. Spatial distribution of iron forms and features in the dried lake bed of Urmia Lake of Iran. Geoderma Reg. 2020, 21, e00275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basart, S.; Pérez, C.; Nickovic, S.; Cuevas, E.; Baldasano, J. Development and evaluation of the BSC-DREAM8b dust regional model over Northern Africa, the Mediterranean and the Middle East. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2012, 64, 18539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolari, A.J.; Li, D.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Katul, G.G.; Assouline, S. Climate, not conflict, explains extreme Middle East dust storm. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 114013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomos, S.; Ansmann, A.; Mamouri, R.E.; Binietoglou, I.; Patlakas, P.; Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V. Remote sensing and modelling analysis of the extreme dust storm hitting the Middle East and eastern Mediterranean in September 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4063–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issanova, G.; Abuduwaili, J. Aeolian Processes as Dust Storms in the Deserts of Central Asia and Kazakhstan; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; He, M.; Bai, M.; Ge, Q. Meteorological drought and its large-scale climate patterns in each season in Central Asia from 1901 to 2015. Clim. Change 2021, 166, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamadjanova, G. Variability of the Steering Factors for Extreme Hydrometeorological Events in Central Asia and Its Relation to the Formation of Mudflows in the Piedmont Areas of Uzbekistan. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nobakht, M. Characterisation of Dust Sources in Central Asia Using Remote Sensing. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Reading, Reading, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.X.; Claiborn, C.; Lei, J.Q.; Vaughan, J.; Wu, S.X.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Wang, Y.D.; Huang, S.Y.; et al. Aeolian dust in Central Asia: Spatial distribution and temporal variability. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 238, 117734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Samat, A.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ge, Y.; De Maeyer, P.; Van de Voorde, T. Temporal characterization of sand and dust storm activity and its climatic and terrestrial drivers in the Aral Sea region. Atmos. Res. 2022, 275, 106242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Q.Q.; Ye, L.; Lin, X.; Lu, S.; Jiao, Y.; Li, R.; Meng, G.; Wang, Y.; et al. Influence of mountain orientation on precipitation isotopes in the westerly belt of Eurasia. Glob. Planet. Change 2024, 240, 104543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Lu, S.; Chen, L.; Jiao, Y.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Regional differences in the effects of atmospheric moisture residence time on precipitation isotopes over Eurasia. Atmos. Res. 2025, 314, 107813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).