Physicochemical Characteristics of Individual Indoor Airborne Particles in the High Lung Cancer Rate Area in Xuanwei, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sampling and Experiments
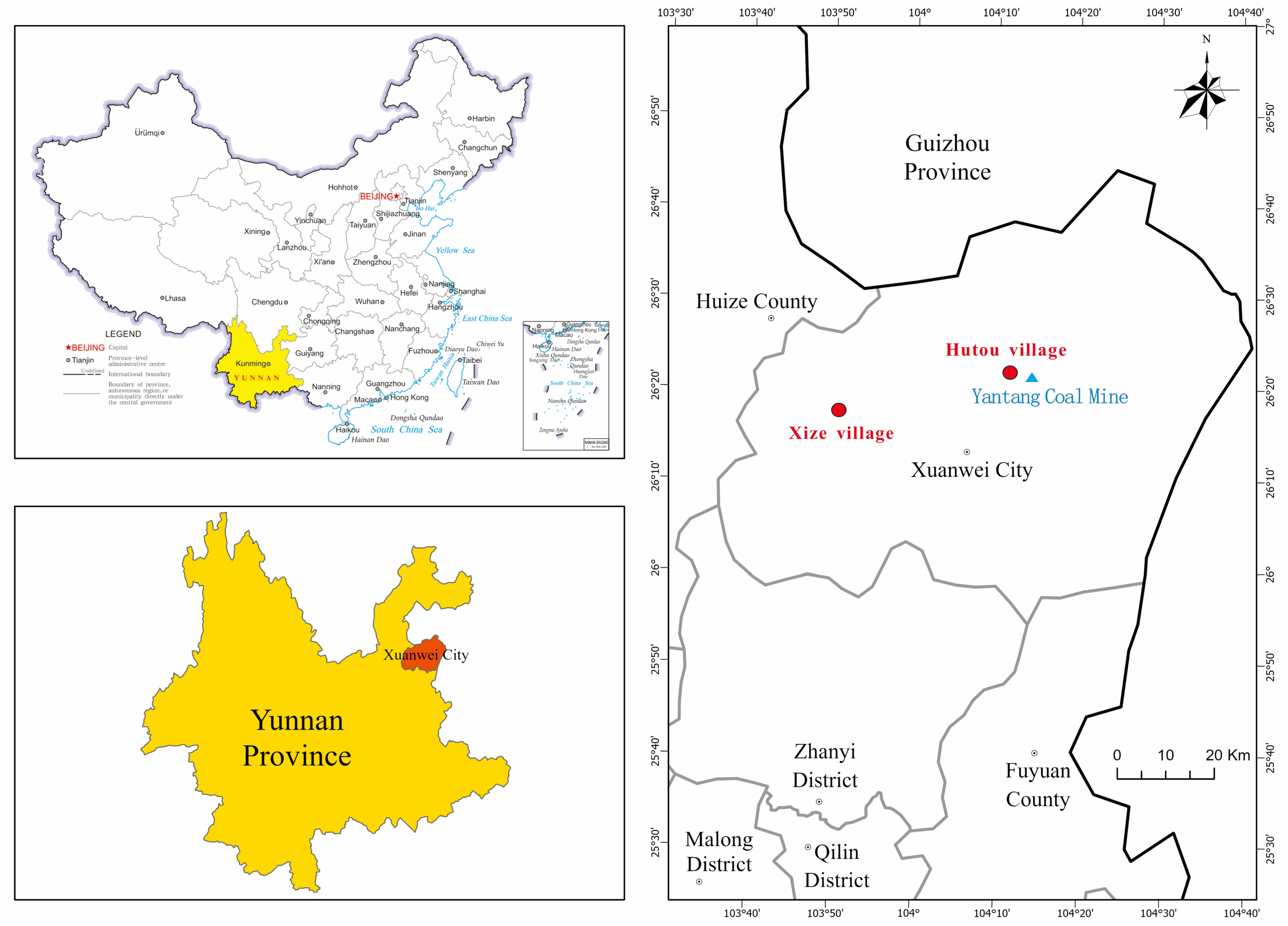
2.1. Sampling
2.2. TEM-EDX
3. Results
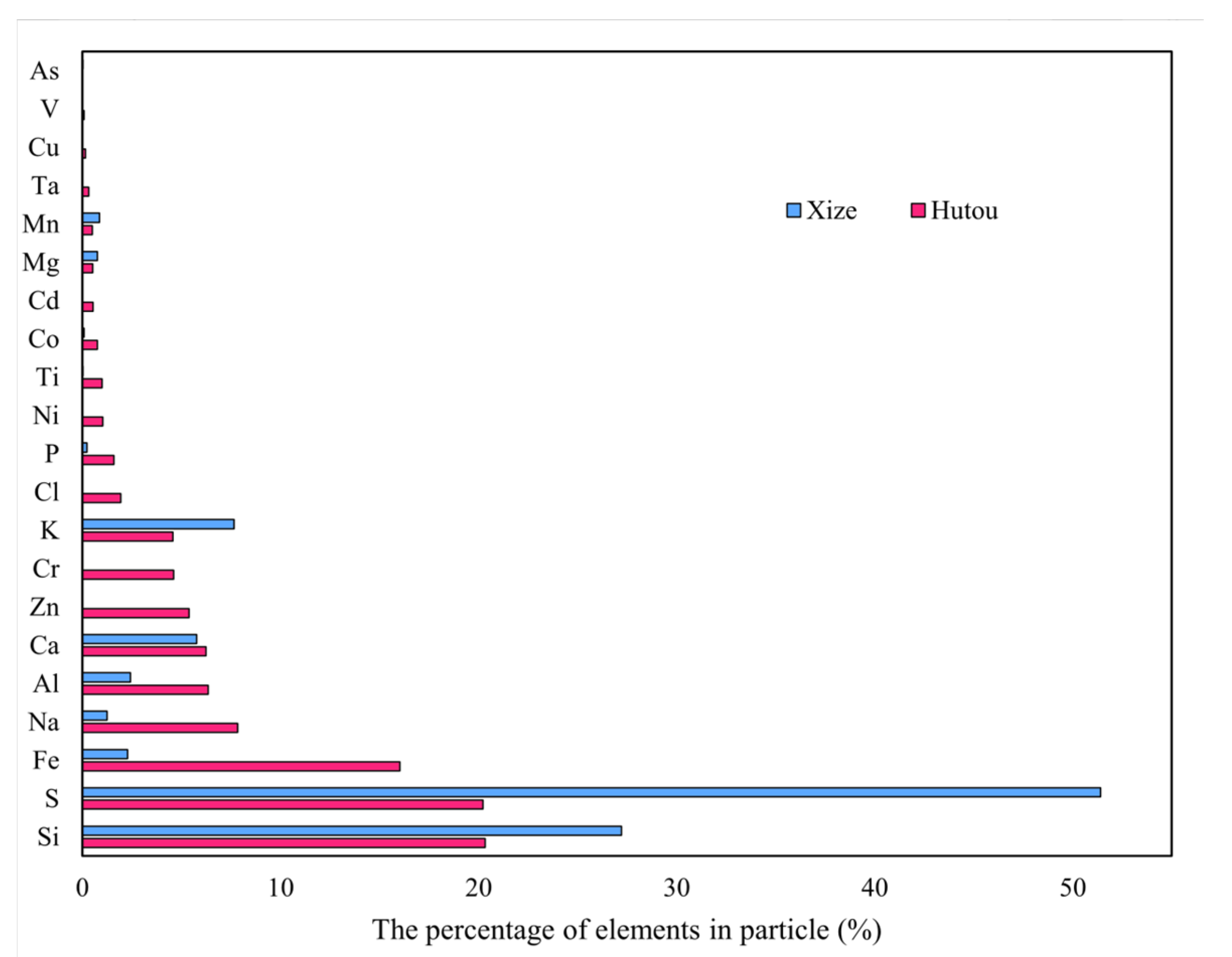
3.1. Element Frequency in Individual Particles of Different Sizes
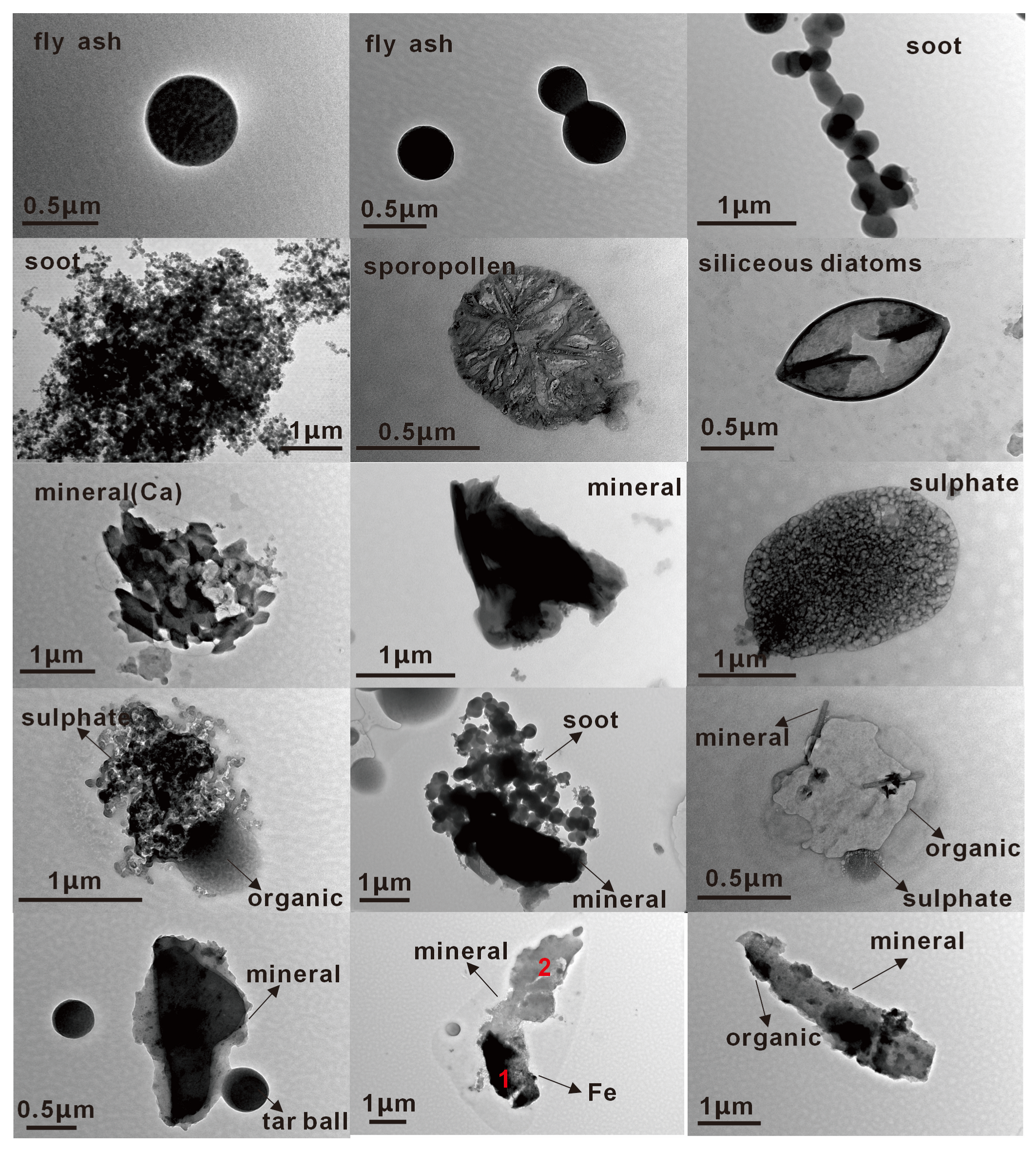
3.2. Individual Particle Types
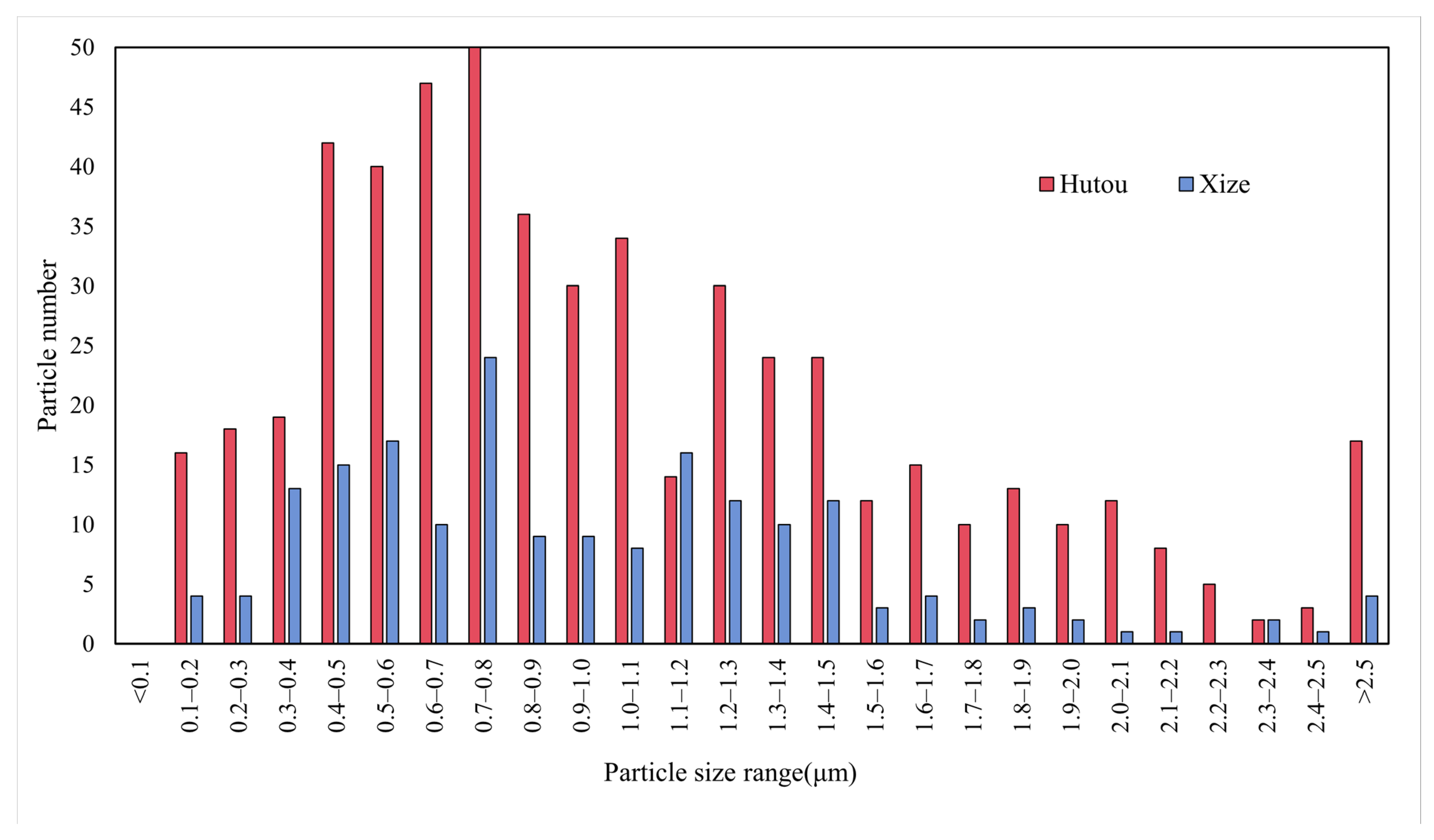
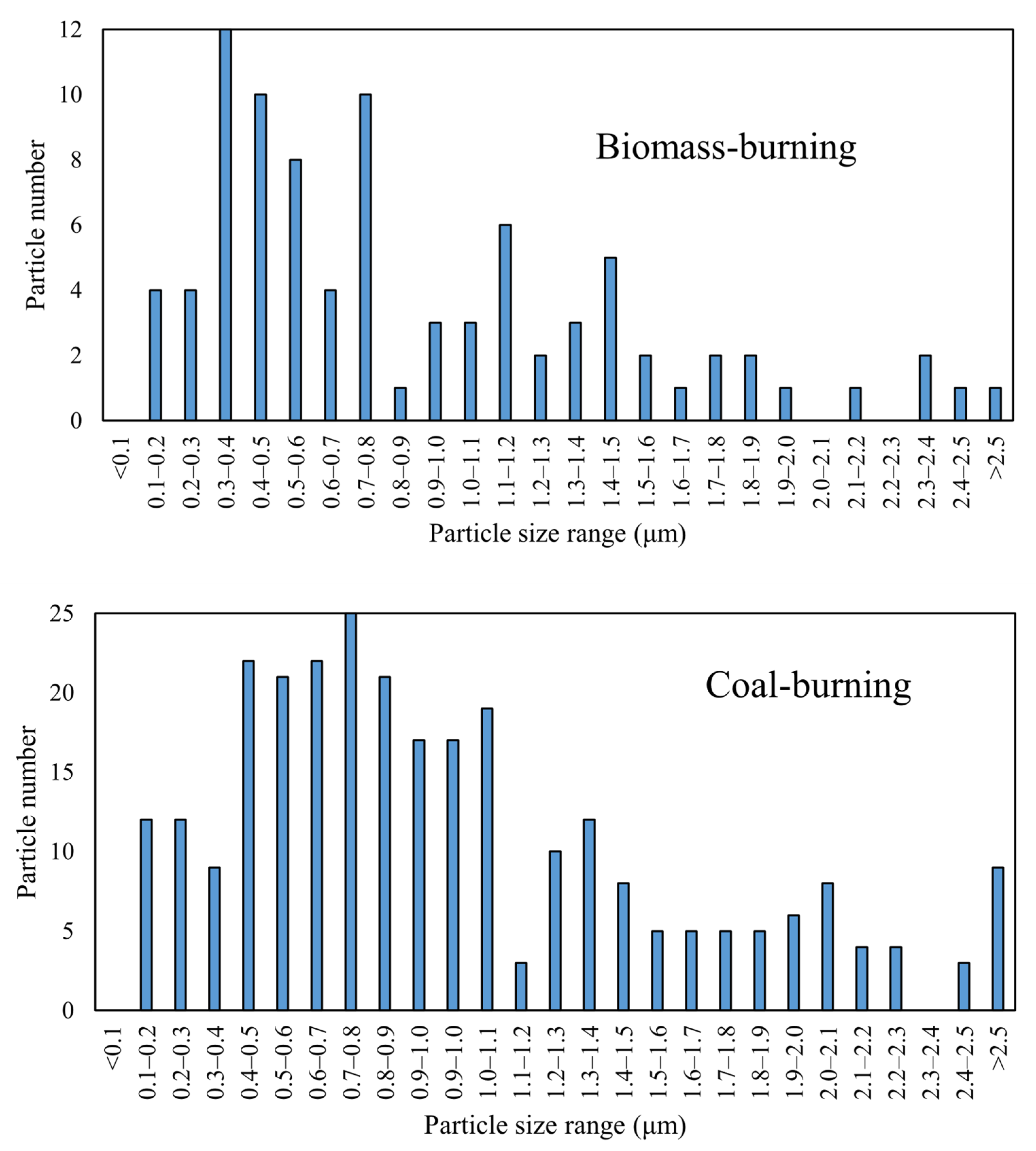
3.3. Size Distribution of Individual Particles in Xuanwei
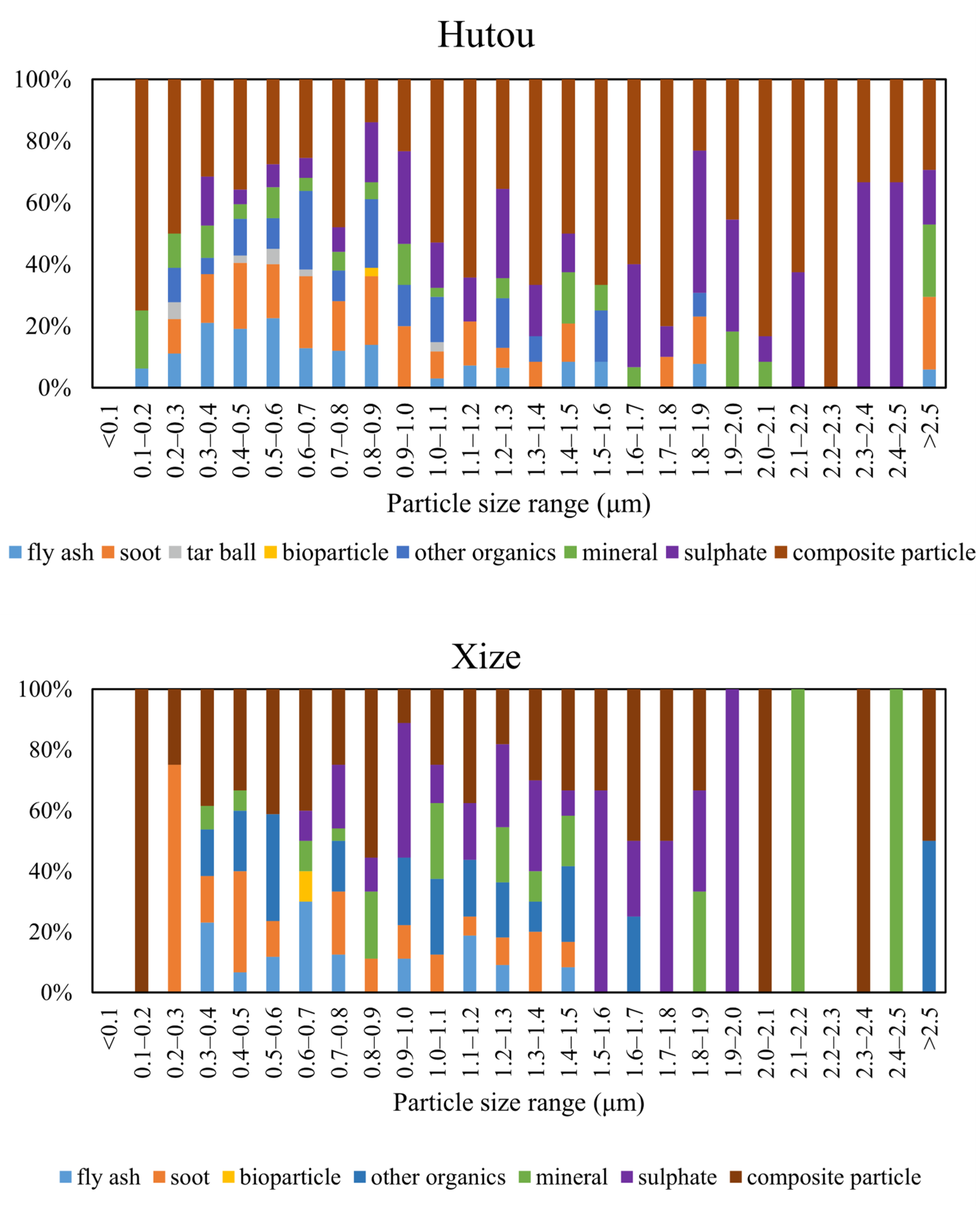
3.4. Size Distribution of Different Individual Particle Types
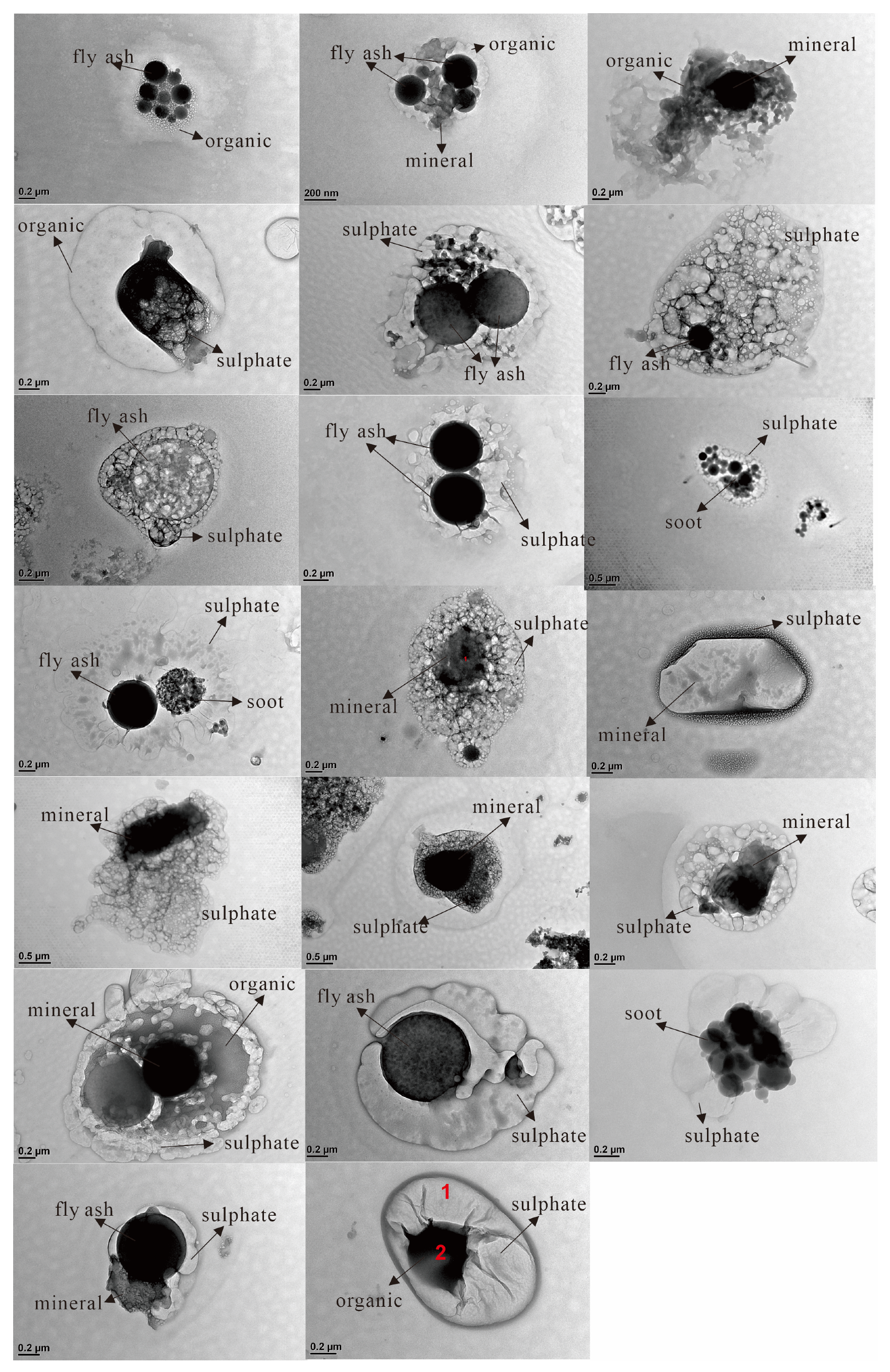
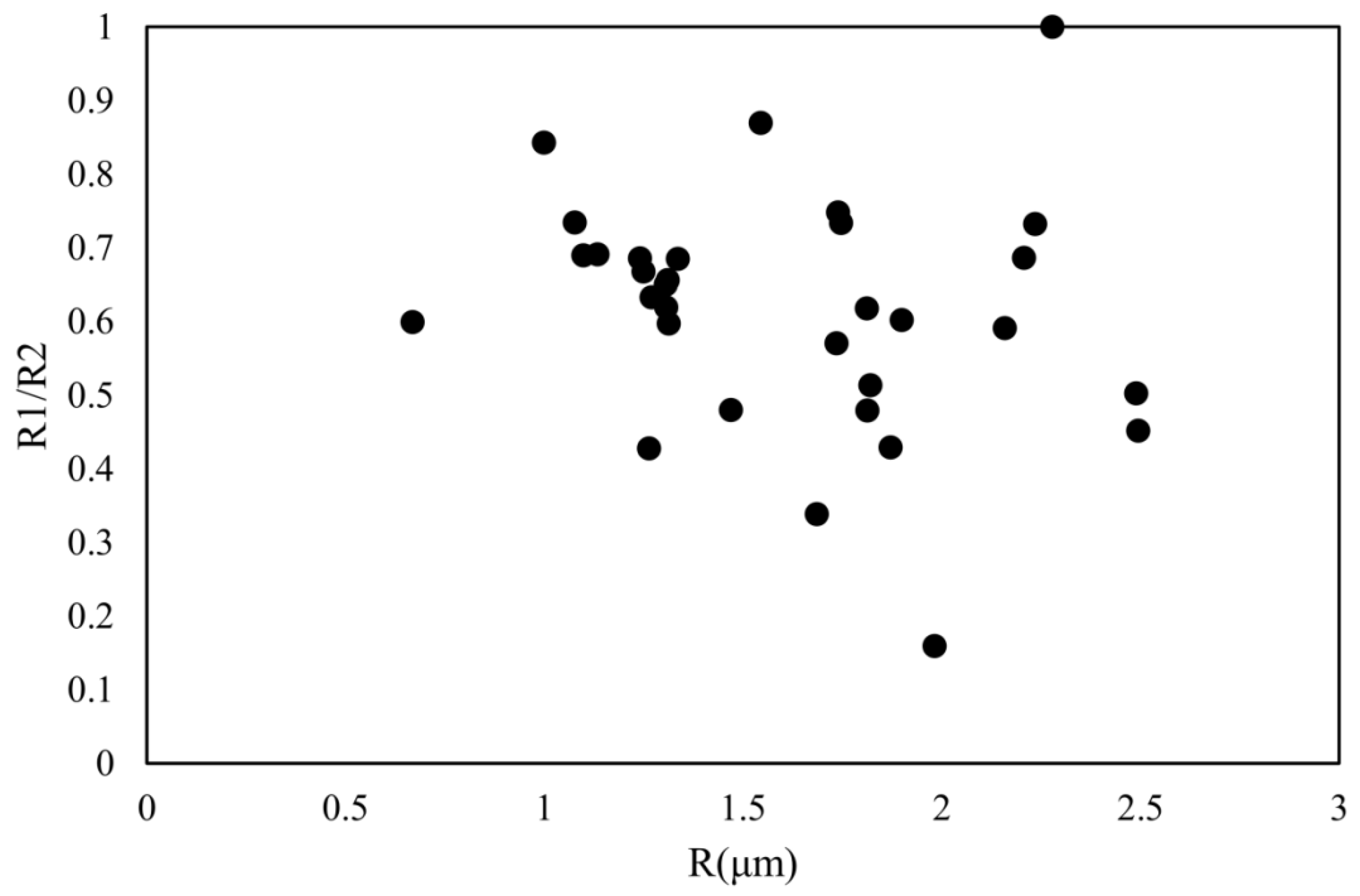
3.5. The Core-Shell Structure of Airborne Particles in Xuanwei
4. Discussion
4.1. The Features of Coal-Burning Particles in Xuanwei
4.2. The Aging State of Core-Shell Particles in Xuanwei
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, L.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Feng, X.L.; Jiao, J.W.; Wang, W.H.; Zhou, Y.P. The toxicology of particulate matter emitted from coal combustion and the geological origin of lung cancer epidemic in Xuanwei City, Yunan Province, China. Coal Geol. Explor. 2023, 51, 45–58, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumford, J.L.; He, X.Z.; Chapman, R.S.; Cao, S.R.; Harius, D.B.; Li, X.M.; Xia, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.L.; Xu, C.W.; Chuang, J.C.; et al. Lung cancer and indoor air pollution in Xuanwei, China. Science 1987, 235, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Zhao, G.Q.; Xiao, Y.Z.; Chen, X.B.; Ma, Q.L.; Lei, Y.J.; Yang, K.Y. Trend analysis of lung cancer mortality from high incidence areas in Yunnan Province. Cancer Res. Prev. Treat. 2011, 38, 98–100, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Ren, H.X.; Chen, Y.; Hao, X.; Shi, Q.P.; Xiao, Y.Z. Trend analysis of lung cancer mortality in area with high incidence from 1973 to 2005. Chin. Gen. Pract. 2009, 12, 2279–2282, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y.; Liu, L.Q.; Zou, X.N.; Ma, X.Y.; Ning, B.F.; Ning, Y.F.; Wan, X. Epidemiological features of lung cancer mortality between 1990 and 2016 in Xuanwei City, Yunnan Province. Acta Acad. Med. Sin. 2019, 41, 338–343, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Q.; Chapman, R.S.; Schreinemachers, D.M.; Tian, L.; He, X. Household stove improvement and risk of lung cancer in Xuanwei, China. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumford, J.L.; Helmes, C.T.; Lee, X.; Seidenberg, J.; Nesnow, S. Mouse skin tumorigenicity studies of indoor coal and wood combustion emissions from homes of residents in Xuan Wei, China with high lung cancer mortality. Carcinogenesis 1990, 11, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Chapmant, R.S. An epidemiological study of lung cancer in Xuan wei county, China: Current progress. Case-control study on lung cancer and cooking fuel. Environ. Health Persp. 1991, 94, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Doenward, G.S.; Hu, W.; Large, D.; Veld, H.; Xu, J.; Reiss, B.; Wu, G.P.; Wei, F.S.; Chapman, R.S.; Rothman, N.; et al. Heterogeneity in coal composition and implications for lung cancer risk in Xuanwei and Fuyuan counties, China. Environ. Int. 2014, 68, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BeruBe, K.A.; Sexton, K.J.; Jones, T.P.; Moreno, T.; Anderson, S.; Richards, R.J. The spatial and temporal variations in PM10 mass from six UK homes. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 324, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, D.J.; Kelly, S.; Spiro, B.; Tian, L.; Shao, L.; Finkelman, R.; Zhang, M.; Somerfield, C.; Plint, S.; Ali, Y.; et al. Silica-volatile interaction and the geological cause of the Xuan Wei lung cancer epidemic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9016–9021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Downward, G.S.; Reiss, B.; Xu, J.; Bassig, B.A.; Hosgood, H.D.; Zhang, L.L.; Seow, W.J.; Wu, G.P.; Chapman, R.S.; et al. Personal and Indoor PM2.5 Exposure from Burning Solid Fuels in Vented and Unvented Stoves in a Rural Region of China with a High Incidence of Lung Cancer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8456–8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L. Coal Combustion Emissions and Lung Cancer in Xuan Wei, China. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.W.; Lucas, D.; Fischer, S.L.; Lee, S.C.; Hammond, S.K.; Koshland, C.P. Particle and gas emissions from a simulated coal-burning household fire pit. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2503–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.T.; Liu, X.; Wu, G.H.; Chen, L.F. Association between tumor necrosis factor-α -308 Gauss/A polymorphism and risk of silicosis and coal workers pneumoconiosis in Chinese population. Inhal. Toxicol. 2018, 30, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Yi, F.; Hao, X.; Yu, S.; Ren, J.; Wu, M.; Feng, J.; Yonemochi, S.; Wang, Q. Physicochemical properties and ability to generate free radicals of ambient coarse, fine, and ultrafine particles in the atmosphere of Xuanwei, China, an area of high lung cancer incidence. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shao, L.; Zhang, D.; Ro, C.-U.; Hu, M.; Bi, X.; Geng, H.; Matsuki, A.; Niu, H.; Chen, J. A review of single aerosol particle studies in the atmosphere of East Asia: Morphology, mixing state, source, and heterogeneous reactions. J. Clean Prod. 2015, 112, 1330–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pósfai, M.; Buseck, P.R. Nature and climate effects of individual tropospheric aerosol particles. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 2010, 38, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Zaizen, Y.; Kajino, M.; Igarashi, Y. Mixing state of regionally transported soot particles and the coating effect on their size and shape at a mountain site in Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5386–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Quan, X.; Wang, W. Morphology, composition and mixing state of individual carbonaceous aerosol in urban Shanghai. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Kang, S.; Jung, H.J.; Choël, M.; Kim, H.; Ro, C.U. Characterization of individual submicrometer aerosol particles collected in Incheon, Korea, by quantitative transmission electron microscopy energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 2156–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Shao, L.Y. observation of nitrate coatings on atmospheric mineral dust particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Collett, J.L., Jr.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Wang, W.X. Microscopic evaluation of trace metals in cloud droplets in an acid precipitation region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4172–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Shao, L.; Zhang, D. Aged status of soot particles during the passage of a weak cyclone in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2699–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.B.; Zhang, D.Z.; Hayashi, M.; Ogata, H.; Ji, H.Z.; Fujiie, W. Influences of sulfate and nitrate on the hygroscopic behaviour of coarse dust particles. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chen, H.; Du, J.; Yang, X.; Gao, S.; Chen, J.; Geng, F. Evolution of the mixing state of fine aerosols during haze events in Shanghai. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bi, X.; Li, L.; Chan, L.Y.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Z. Mixing state of individual submicron carbon-containing particles during spring and fall seasons in urban Guangzhou, China: A case study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4723–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shao, L.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; et al. Mixing state and hygroscopicity of dust and haze particles before leaving Asian continent. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.Y.; Liu, P.J.; Jones, T.; Yang, S.S.; Wang, W.H.; Zhang, D.Z.; Li, Y.W.; Yang, C.X.; Xing, J.P.; Hou, C.; et al. A review of atmospheric individual particle analyses: Methodologies and applications in environmental research. Gondwana Res. 2022, 110, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Shao, L.Y.; Jones, T.; Hu, Y.; Adams, R.; BéruBé, K. Hemolysis of PM10 on RBCs in vitro: An indoor air study in a coal-burning lung cancer epidemic area. Geosci. Front. 2021, 13, 101176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.L.; Shao, L.Y.; Xi, C.X.; Jones, T.P.; Zhang, D.Z.; BéruBé, K.A. Particle-induced oxidative damage by indoor size-segregated particulate matter from coal-burning homes in the Xuanwei lung cancer epidemic area, Yunnan Province, China. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesterberg, T.; Anderson, R.; Bernstein, D.M.; Bunn, W.B.; Chase, G.A.; Jankousky, A.L.; Marsh, G.M.; McClellan, R.O. Product stewardship and science: Safe manufacture and use of fiber glass. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 62, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toner, S.M.; Shields, L.G.; Sodeman, D.A.; Prather, K.A. Using mass spectral source signatures to apportion exhaust particles from gasoline and diesel powered vehicles in a freeway study using UF-ATOFMS. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.W.; Shao, L.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, W.H.; Yang, C.X.; Li, W.J.; Fang, Z. Fresh organic and soot particles from crop straw burning: Morphology, composition and size distribution. Geol. J. 2023, 58, 12–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Shao, L.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, N.; Zhou, H.; Li, W.J. Morphology and elemental composition of individual solid dust particles: From different sources to the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 338, 120842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Ding, X.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ma, W.; et al. Morphological and elemental classification of freshly-emitted individual particles from field and laboratory residential biomass burning. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2023JD040379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Wu, C.; Schindler, M.; Silva, L.F.O.; Ma, B.; Ma, X.; Ji, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, H.; Bao, X.; et al. Characterization of PM2.5 carbonaceous components in a typical industrial city in China under continuous mitigation measures. Toxics 2024, 12, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Riemer, N.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Adachi, K.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Z.; Laskin, A. Microphysical properties of atmospheric soot and organic particles: Measurements, modeling, and impacts. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Iwasaka, Y.; Shi, G.Y.; Zang, J.Y.; Hu, M.; Li, C.Y. Separated status of the natural dust plume and polluted air masses in an Asian dust storm event at coastal areas of China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D06302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, cloud microphysics, and fractional cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reus, M.; Fischer, H.; Sander, R.; Gros, V.; Kormann, R.; Salisbury, G.; Van Dingenen, R.; Williams, J.; Ollner, M.Z.; Lelieveld, J. Observations and model calculations of trace gas scavenging in a dense Saharan dust plume during MINATROC. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1787–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, K.A.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; DeMott, P.J.; Petters, M.D.; Prenni, A.J.; Carrico, C.M. Hygroscopicity and cloud droplet activation of mineral dust aerosol. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L08805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Stordal, F. Global sensitivity experiments of the radiative forcing due to mineral aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 18193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.C.; Guazzotti, S.A.; Sodeman, D.A.; Prather, K.A. Direct observations of the atmospheric processing of Asian mineral dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 1213–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. The influence of pollution on the shortwave Albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.B. Biomass Burning Impacts on the Haze Weather and Its Emission Factorsand PM Chemical Composition. Ph.D. Thesis, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, China, 2014. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Shi, G.Y.; Iwasaka, Y.; Hu, M. Mixture of sulfate and nitrate in coastal atmospheric aerosols: Individual particle studies in Qingdao (36°04′N,120°21′E), China. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2669–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Suh, I.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.; Fortner, E.C.; Tie, X.X.; Molina, L.T.; Molina, M.J. Atmospheric new particle formation enhanced by organic acids. Science 2004, 304, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.B.; Zhang, D.Z.; Ji, H.Z.; Hasegawa, S.; Hayashi, M. Modification of soot by volatile species in an urban atmosphere. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 389, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarathasan, P.; Blais, E.; Saravanamuthu, A.; Bielecki, A.; Mukherjee, B.; Bjarnason, S.; Guénette, J.; Goegan, P.; Vincent, R. Nitrative stress, oxidative stress and plasma endothelin levels after inhalation of particulate matter and ozone. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Buseck, P.R. Internally mixed soot, sulfates, and organic matter in aerosol particles from Mexico City. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 6469–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, R.M.; Sciare, J.; Poulain, L.; Crippa, M.; Wiedensohler, A.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Baltensperger, U.; Sarda-Estève, R.; McGuire, M.L.; Jeong, C.H.; et al. Quantitative determination of carbonaceous particle mixing state in Paris using single-particle mass spectrometer and aerosol mass spectrometer measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 9479–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shao, L. Mixing and water-soluble characteristics of particulate organic compounds in individual urban aerosol particles. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D02301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, S.; Osada, K.; Takami, A. Morphological features of soot-containing particles internally mixed with water-soluble materials in continental outflow observed at Cape Hedo, Okinawa, Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D17207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteaker, J.R.; Suess, D.T.; Prather, K.A. Effects of meteorological conditions on aerosol composition and mixing state in Bakersfield, CA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2345–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.P.; Shao, L.Y.; Chen, F.F.; Wang, W.H.; Zhang, D.Z. Characteristics and aging of traffic-emitted particles with sulfate and organic compound formation in Urban Air. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Ro, C.-U. Direct observation of nitrate and sulfate formations from mineral dust and sea-salts using low-Z particle electron probe X-ray microanalysis. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3869–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Gao, Y.T.; Shao, L.Y.; Fan, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.W.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhou, X.Y. Chemical compositions and possible transportation of PM2.5 during two haze periods in a coastal city of the North China Plain. Geol. J. 2023, 58, 4417–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, F.; Ding, X.; Shi, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Li, W. Quantifying evolution of soot mixing state from transboundary transport of biomass burning emissions. iScience 2023, 26, 108125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, A.; BeruB, K.; Jones, T.; Maynardc, R.; Richardsa, R. Killer smog of London, 50 years on:particle properties and oxidative capacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 334–335, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.D.; Ghio, A.J.; Samet, J.M.; Devlin, R.B. Cytokine production by human airway epithelial cells after exposure to an air pollution particle is metal-dependent. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1997, 146, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Reed, W.; Wu, W.; Bromberg, P.A.; Graves Lee, M.; Samet, J.M. Zn2+induced IL-8 expression involves AP-1, JNK, and ERK activities in human airway epithelial cells. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 290, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Shao, L.Y.; Li, J.; Chang, L.L.; Zhang, D.Z.; Zhang, C.C.; Jiang, J.K. Characteristics of individual particles emitted from an experimental burning chamber with coal from the lung cancer area of Xuanwei, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.J.; Shao, L.Y.; Li, Y.W.; Wang, W.H.; Zhang, M.Y.; Yang, C.X.; Niu, H.Y.; Feng, X.L.; Zhang, D.Z. Compositions, sources, and aging processes of aerosol particles during winter hazes in an inland megacity of NW China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
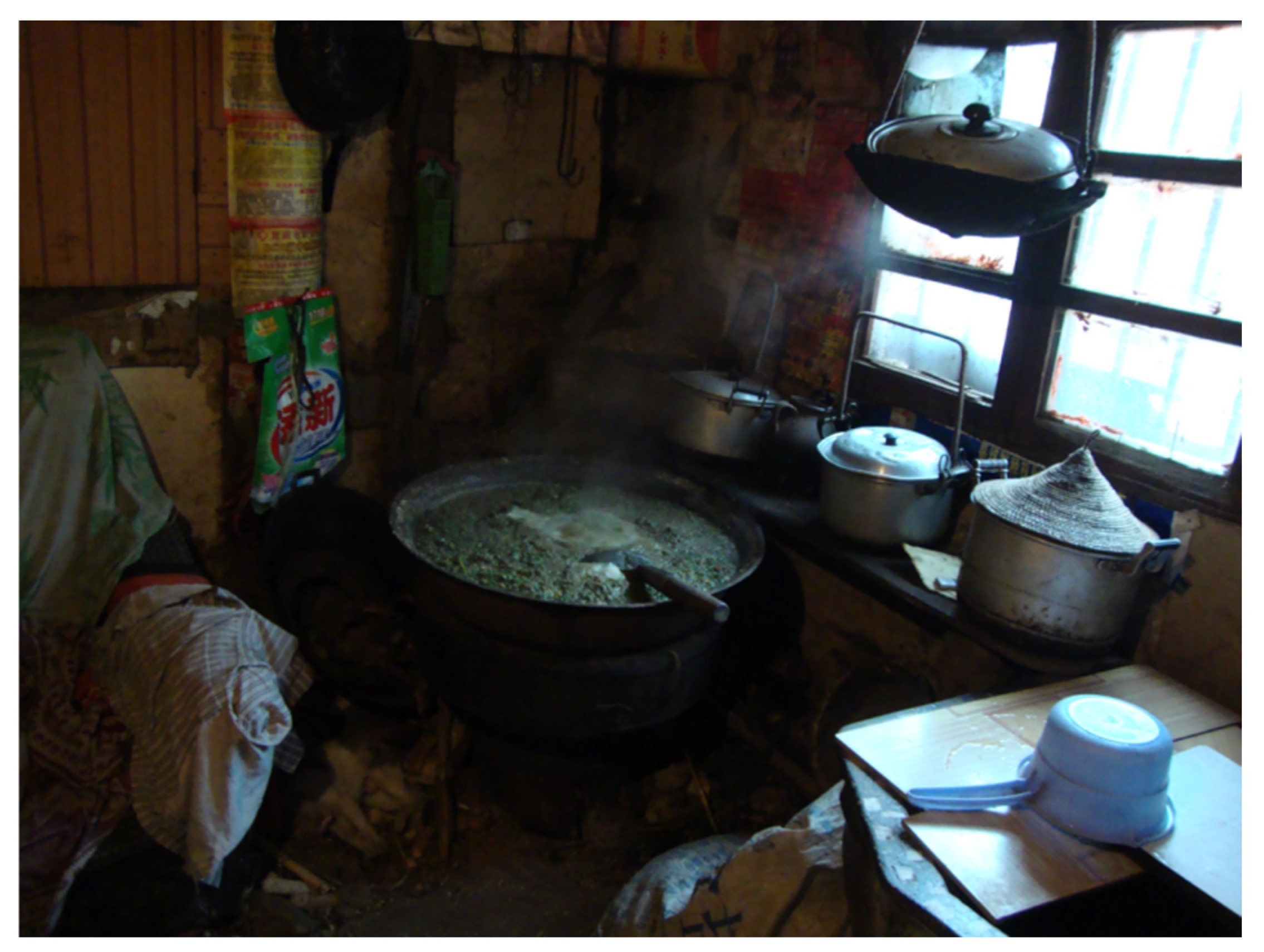

| Sample No. | TEM No. | T/°C | RH /% | P/hPa | Duration/s | Date and Start Time | Sampling Site | Fuel | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A1 | 12 | 75.4 | 810.1 | 60 | 2013.11.16 8:50 | HT | coal | |
| 2 | A3 | 12.2 | 70.7 | 810.5 | 60 | 2013.11.16 9:49 | HT | electricity | |
| 3 | B5 | 15.4 | 83.1 | 808.8 | 60 | 2013.11.17 9:04 | HT | coal | cooking |
| 4 | D5 | 15.9 | 76.7 | 809.3 | 40 | 2013.11.18 9:36 | HT | coal | cooking |
| 5 | F3 | 13.7 | 80.1 | 807.7 | 40 | 2013.11.19 9:30 | HT | electricity | cooking |
| 6 | K5 | 9.3 | 85.6 | 804.4 | 90 | 2013.11.22 10:00 | HT outdoor | Sunny | |
| 7 | P5 | 18.8 | 45.6 | 817.3 | 60 | 2013.11.24 16:00 | XZ | biomass | cooking |
| 8 | T1 | 11.1 | 72.8 | 815.1 | 60 | 2013.11.26 9:45 | XZ outdoor | Sunny |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Shao, L.; BéruBé, K.; Wang, N.; Hou, C.; Fan, J.; Jones, T. Physicochemical Characteristics of Individual Indoor Airborne Particles in the High Lung Cancer Rate Area in Xuanwei, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020187
Hu Y, Shao L, BéruBé K, Wang N, Hou C, Fan J, Jones T. Physicochemical Characteristics of Individual Indoor Airborne Particles in the High Lung Cancer Rate Area in Xuanwei, China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(2):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020187
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Ying, Longyi Shao, Kelly BéruBé, Ningping Wang, Cong Hou, Jingsen Fan, and Tim Jones. 2025. "Physicochemical Characteristics of Individual Indoor Airborne Particles in the High Lung Cancer Rate Area in Xuanwei, China" Atmosphere 16, no. 2: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020187
APA StyleHu, Y., Shao, L., BéruBé, K., Wang, N., Hou, C., Fan, J., & Jones, T. (2025). Physicochemical Characteristics of Individual Indoor Airborne Particles in the High Lung Cancer Rate Area in Xuanwei, China. Atmosphere, 16(2), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020187









