Abstract
Airborne particulate matter (PM) is one of the most urgent urban environment problems in the world today. The urban ecosystem has been identified as a potentially promising solution to reduce the airborne PM based on the ability of plants to retain PM. Numerous studies have been conducted to explore the process and mechanism of atmospheric PM retention by plant leaves in the past. In this study, in order to better summarize previous research, particularly the impact of leaf traits on PM retention, and to provide guidance for the selection of tree species for nature-based urban PM solutions, a systematic review was carried out using the method recommended in the PRISMA, and a total of 49 articles were selected. It was found that: 1. Asian countries contribute the majority of the proportion (32, 65%). Following behind are European countries (13, 26.5%). The American countries contribute two cases. 2. Among all the tree species, Ginkgo biloba (16), Euonymus japonicus (11), Magnolia denudate (9), Styphnolobium japonicum (9), Magnolia grandiflora (8), and Prunus cerasifera (8) emerged as hot species in research. 3. Leaf area and shape emerged as the two most frequently discussed macro-indicators, while roughness, hairiness, and stomatal characteristics were the top three micro-indicators explored. 4. Roughness and stomata, respectively, play crucial roles in capturing larger PM particles and retaining fine and ultrafine PM through their recessed structures. Trichomes decrease the likelihood of particle resuspension and boosts the efficiency of PM retention. 5. Leaves with high rigidity and complex multi-faceted leaf shapes are typically presumed to exhibit higher PM retention efficiency for higher edge effects and increased interleaf turbulence. Furthermore, with rigidity and edge effects ensured, a larger leaf area is beneficial for retaining PM.
1. Introduction
With the current rapid urbanization, traffic and industrial activities have become more intense and frequent, while transport and industrial activities are considered to be the most important source of PM [1]. Thus, airborne particulate matter (PM, i.e., particles 0.001–100 μm in size) [2] is one of the most urgent urban environmental problems in the world today [3]. Meanwhile, the United Nations (UN) has forecasted that the urban population will break through more than 2.5 billion by 2050 [4]. This projection implies that a greater number of individuals will be at risk of developing cardiovascular and respiratory diseases due to exposure to PM10 [5,6,7]. PM10, defined as particulate matter where 50% of all particles are less than 10 μm in aerodynamic diameter, can penetrate airways and reach the upper lung regions [8].
The urban ecosystem has been identified as a potentially promising solution to reduce the airborne PM based on the ability of plants to retain PM [1,9]. It is a kind of implementation of nature-based solutions (NBS) in urban environments for their sustainability and harmlessness [10]. Modeling studies indicate that trees could potentially serve as a solution to clean the air of PM in urban environments. For instance, trees planted in the Greater London area are estimated to annually remove between 800 and 2000 tons of PM10 [11]. Similarly, public trees in Strasbourg, France, are projected to remove 11.77 tons of PM10 and 4.51 tons of PM2.5 each year [12]. In addition, a study conducted in Beijing, China, revealed that the number of PM particles on plant leaves reached up to 50,961.50 mm−2 [13]. With the huge potential benefits of urban plants in purifying airborne PM, numerous studies have been conducted to explore the process and mechanism of atmospheric particulate matter retention by plants, and leaves, as the most important organ of airborne PM retention [6,14,15].
However, despite numerous studies exploring the relationship between leaf traits and PM retention, little research has clearly summarized the connection between individual leaf traits and PM retention capacity. Moreover, systematic reviews that identify the most efficient leaf trait for capturing deposited particulate matter are notably scarce [1].
This paper provides a systematic review of the literature on the relationship between leaf trait indicators and PM retention over the past 15 years, detailing and summarizing the impact of various macroscopic and microscopic leaf traits on leaf PM retention, providing guidance for the selection of tree species for nature-based urban PM solutions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Screening
The systematic reviews were carried out using the method recommended in the PRISMA statement [16]. Literature searching was performed by using the database of Web of Science. The literature was screened using the following phrases: “PM retention” or “PM deposition” or “PM accumulation” or “PM detention” or “PM capture” or “PM retain” and “leaf” or “leaves”. Papers meeting the following criteria were chosen: (1) were published in a peer-reviewed journal between 2010 and 2025; (2) concentration of background particulate matter concentration was clearly quantified; (3) PM deposited on leaves was quantified and presented in concentration or number; (4) sampling location was clear; and (5) leaf traits or species were defined.
2.2. Data Analysis
Firstly, the selected literature was reviewed thoroughly to extract valuable data and information. For cases where data were not reported in the article but presented in charts, we used the WebPlotDigitizer tool (https://apps.automeris.io/wpd4/, accessed on 10 November 2024) to extract data from the charts representing the exact concentrations. Secondly, hot indicators were extracted from the selected literature and divided into two principal groups: macro-morphology and micro-morphology, according to the characteristics of the hot indicators. Thirdly, a statistical analysis was performed on these indicators by year.
Geographical scope was obtained from the selected literature, including cities and the longitude and latitude of the test sites (if the latitude and longitude of the city where the experiment was located were not specified, the geographical coordinates of its center of mass were obtained from (http://www.maps4gis.com/jsonwd/chaxun.html, accessed on 27 September 2024) as a substitute for the latitude and longitude of the city).
3. Results
After strictly following the methods recommended in the PRISMA statement, a total of 49 articles were selected that met the requirements (Figure 1, Table 1).
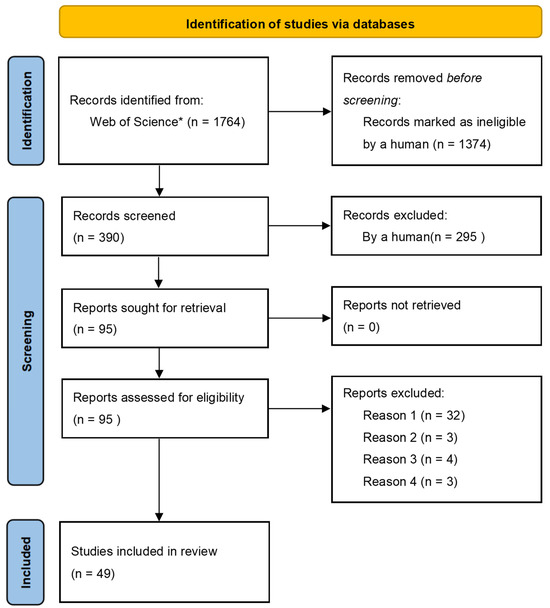
Figure 1.
Systematic filtration and selection process of literature. * The search formula used in the WOS database is TS = (“particulate matter” or “PM”) AND TS = (“retention” or “deposition” or “accumulation” or “detention” or “capture” or “retain”) AND TS = (“leaf” or “leaves”). Reason 1: Studies were published in a peer-reviewed journal between 2010 and 2025. Reason 2: Concentration of background particulate matter concentration was clearly quantified. Reason 3: PM deposited on leaves was quantified and presented in concentration or number. Reason 4: Sampling location was clear. Reason 5: Leaf traits or species were defined.

Table 1.
Classification results and experimental location of the 49 selected papers.
3.1. Geographical Scope
The 49 selected papers that met the requirements came from 16 countries, including China (25), South Korea (4), United Kingdom (4), Iran (1), Italy (2), India (1), Poland (2), Norway (1), Belgium (2), Germany (1), Brazil (1), Australia (1), Singapore (1), Colombia (1), South Africa (1), and Russia (1). Among them, Asian countries (China, South Korea, Iran, India, and Singapore) contributed the majority of the proportion (32, 65%). Following behind were European countries (United Kingdom, Italy, Poland, Norway, Belgium, Germany, and Russia) with (13, 26.5%). The American countries (Brazil and Colombia) contributed two cases. An African country (South Africa) and an Oceanian country (Australia) contributed one case each (Figure 2).
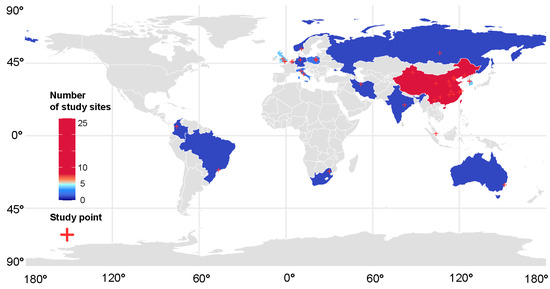
Figure 2.
Global sites of study on leaf PM retention.
3.2. Interannual Trends in the Number of Publications and Hot Indicators
By reviewing the selected literature thoroughly, a total of 10 hot indicators of leaf traits were found, including 5 macro-indicators and 5 micro-indicators. Among them, the 5 macro-indicators are only species (OS); leaf shape (LS); leaf area (LA); one-sided leaf area per unit of dry mass (special leaf area, SLA); and length of leaf, width of leaf, and length–width ratio (L, W, L–W R). The 5 micro-indicators are stomatal conductance (SC); stoma (S, including stoma density and stoma size); hairs/trichomes (H, including length and density of leaf hairs); wax layer (WL); and roughness (R, including wrinkles, ridge, furrows, and grooves of leaf).
Over the past decade, starting from 2011, the number of publications on the relationship between leaf traits and PM retention has generally shown an upward trend, peaking in 2020 (8 papers) (Figure 3). It shows that this field has gradually attracted the attention of researchers. From the perspective of the degree of involvement of the two principal groups, scholars pay more attention to micro traits than macro traits. Meanwhile, according to the percentage accumulation chart of hot indicators over the years, except for the year 2024 when the macroindicators had one more data point than the micro-indicators and the year 2022 when they were equal, micro-indicators received more attention in other years (Figure 3). Among all the macro-indicators, LA and LS are the two most frequently discussed indicators, with a total of 14 and 21 mentions, respectively, in all the selected literature. While, among all the micro-indicators, R, H, and S are the three most frequently discussed indicators in all the selected literature, with a total of 35, 30, and 27 mentions each (Table 2).
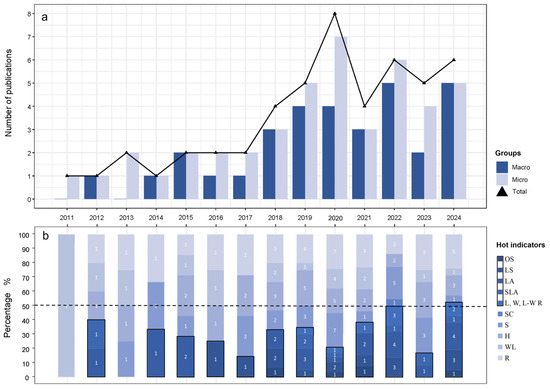
Figure 3.
Interannual trends in hot indicators and the number of publications. (a) Interannual trends in the number of publications on PM retention. (b) Interannual trends in hot indicators of leaf traits. Note: OS (only species); LS (leaf shape); LA (leaf area); SLA (special leaf area); L, W, L–W R (length of leaf, width of leaf, and length–width ratio); SC (stomatal conductance); S (stoma, including stoma density and stoma size); H (hairs/trichomes, including length and density of leaf hairs); WL (wax layer); R (roughness, including wrinkles, ridge, furrows, and grooves of leaf).

Table 2.
Annual number of literature reporting hot indicators. Note: OS (only species); LS (leaf shape); LA (leaf area); SLA (special leaf area); L, W, L–W R (length of leaf, width of leaf, and length–width ratio); SC (stomatal conductance); S (stoma, including stoma density and stoma size); H (hairs/trichomes, including length and density of leaf hairs); WL (wax layer); R (roughness, including wrinkles, ridge, furrows, and grooves of leaf).
3.3. Main Species Involved in the Study of Selected Publications
In the selected literature, a total of 268 plant species were involved, among them, broadleaf trees were the main research subjects, accounting for 93.66% (251/268) of all studied tree species, while only 17 coniferous species were reported. Through the statistical analysis of the number of reports for each tree species, it was found that: Ginkgo biloba (16 studies), Euonymus japonicus (11 studies), Magnolia denudate (9 studies), Styphnolobium japonicum (9 studies), Magnolia grandiflora (8 studies), and Prunus cerasifera (8 studies) are research hotspots (Figure 4).
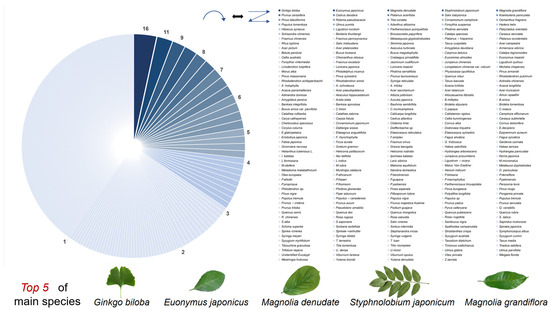
Figure 4.
Reported tree species and their frequencies from selected publications. Note: 1. each sector of the pie chart on the left, clockwise from dark to shallow, corresponds to a tree species arranged in a zigzag pattern on the right (as indicated by the symbol above the center of the two images). 2. The numbers above the sectors in the pie chart represent the statistical number of that tree species.
4. Discussion
4.1. Macro-Morphology
Numerous studies have indicated that leaf shape and size influence the ability of plants to capture PM [36].
4.1.1. Leaf Area
The size of leaves significantly influences the density of PM retained on leaf surfaces (p < 0.05, r = −0.415, n = 36) [20]. In terms of PM capture efficiency, smaller leaves exhibit a higher density of PM retention, and needle leaves are generally believed to have a higher PM retention capacity than broad leaves [30,41,57,60]. This phenomenon is believed to be attributed to the reduced tendency of smaller leaves to move with the wind, coupled with larger edge effects (higher perimeter-to-surface area ratio) in smaller leaves, resulting in a higher rate of PM impaction [18,26]. The leaf edge is a further macromorphological characteristic together with the leaf shape, identified as driving parameters for PM capture [10]. However, some researchers have observed that the smallest leaves exhibit the least effective PM accumulation. They attribute this result to the lower rigidity of the selected leaves and their consequent reduced ability to withstand polluted airflow, which diminishes turbulence around the leaf boundary and reduces the amount of PM retained on the leaf surface [61]. That is to say, it is higher rigidity, rather than a smaller area, that makes PM retention more efficient. Therefore, species with higher rigidity and complex morphology are the most effective in retaining PM [62].
4.1.2. Leaf Shape
The influence of different leaf shapes on the PM retention capacity were studied by cutting the same plant leaf material into different shapes of the same size (28.9 cm2), and the results showed that palmate shapes seem significantly more efficient in trapping PM (including PM1, PM2.5 and PM10) compared to elliptical or linear leaves (p < 0.001), as they may create more turbulence in the boundary air layer with their complex shape and “tip-like” areas [26]. This conclusion was further confirmed by subsequent studies [10,36,63]. Xu et al. discovered that the aspect ratio exhibited a negative and significant correlation with PM retention capacity at the 0.05 significance level (r = −0.402, n = 36), suggesting that narrow leaves retain less PM compared to wider leaves [20]. This finding aligns with Weerakkody et al.’s observations that narrow leaves can bend more easily with wind flow without swaying, potentially leading to lower turbulence levels, which is disadvantageous for PM impaction onto leaves [26]. Additionally, Leonard et al. suggested that leaves with narrow bases have higher surface-specific drag and flutter more erratically than leaves with broader bases, which may cause the resuspension of PM [14]. To conclude, palmate leaves with a lower aspect ratio and broader bases are more likely to retain more PM.
4.1.3. SLA
Muhammad et al. suggested that SLA (together with the leaf dissection index, LDI) is a good predictor of PM accumulation and immobilization by vegetation, as a proxy for the complex interactions of various leaf morphological characteristics [56]. Vásquez-Bedoya et al. found that [57] leaf SLA showed a positive significant correlation with PM retention (PM10: p < 0.05; PM2.5: p < 0.001). However, Koch et al. hold the opposite conclusion that leaves with larger SLA accumulate less PM for the reason that leaves with a smaller area tend to be rigid at the same dry mass [9], which is consistent with the conclusion made by Park et al. [21]. Generally, the smaller the SLA within the same leaf area, the greater the rigidity of the leaf. However, once rigidity reaches a certain threshold, further decreases in SLA have little effect on retaining PM. Therefore, under the condition that SLA can ensure a certain level of rigidity, the larger the SLA of leaves with the same mass, the larger the area that can be formed to retain PM.
4.2. Micro-Morphology
The micro-morphology of leaves, such as stomatal density, waxy layer thickness, trichomes and roughness, is closely related to its PM retention capacity [18,30,36].
4.2.1. Stomata
The number and density of stomata were significantly positively correlated with PM retention. Li et al. found that species with better PM retention capacity have a large stomatal density, and this characteristic makes it easier for particles to gather around the stomatal aperture (PM2.5: R = 0.96, p < 0.01) [30]. In addition, larger stomatal density can make the transpiration of the leaves stronger, which makes it easier for particles to be distributed, resulting in an increased deposition rate of particles [41,64,65]. It is worth mentioning that compared with short diameter and small area of the stomata, a longer stomatal diameter has more negative effect on PM retention (PM10: R = −0.43; PM2.5: R = −0.44) [30]. However, disagreement on the impact of the presence and density of stomata on PM retention still exists. Mo et al. reported results indicating that plant leaves with low stomatal density facilitate PM retention, as minimal PM retention occurs near the stomata [66]. Shao et al. reported that a significant relationship between the size and open status of the stomata and PM retention was not found [33], while Redondo-Bermudez et al. found that stomatal density was positively correlated with PM retention only when the grooves around the stomata are deep and wide enough to retain PM [67]. To sum up, the retention of PM by stomata in leaves primarily depends on their recessed structures. Stomata that are excessively smooth cannot effectively retain PM, while, when the stomatal depression structure is effective, a higher density of stomata correlates with greater efficiency in dust retention. Additionally, a longer stomatal diameter can decrease the PM retention effect.
4.2.2. Trichomes/Hairs
Trichomes are an important trait that play a role in the deposition of PM [57]. Compared with trichomes-removed or smooth leaves, leaves with the trichomes present showed better PM retention capacity [28,33,68]. Trichomes increase the leaf area by several folds and provide an additional surface for particulate retention [69]. Moreover, leaf trichomes can reduce resuspension by wind or rain and increase the surface roughness [27,70]. By observing SEM images, leaves with larger trichomes and hairs were found responsible for capturing larger PM with size ranges higher than the respirable range, while smooth leaves with smaller leaf hairs retained smaller particles, which comes under the respirable range [39]. However, some research still exists that did not find the interaction between amount and length of trichomes and PM accumulation [9,61,71].
4.2.3. Wax Layer
The amount of wax differed significantly among species [51]. Compared with broad-leaved tree species, leaves of coniferous plants are wavy with deep regular textures, and more oil is secreted between the texture, resulting in thick wax layers, which are conducive to the trapping of more particles on the leaf surface [30]. The wax PM showed significant positive correlations with epicuticular wax loads (Kruskal–Wallis test, p < 0.001) [21,51].
4.2.4. Roughness
Roughness is a comprehensive index used to describe the protrusions and depressions on leaf surfaces caused by micro-characteristics such as wrinkles, ridges, and grooves. A rough leaf surface has a stronger PM retention capacity than a smooth surface [18,61], and high leaf roughness can enhance the PM retention capacity when other leaf traits are similar [20]. Among the features that affect the surface roughness, grooves are the focus. Dense and deep grooves can increase the roughness of the leaf surface, which is beneficial for adsorbing PM and preventing PM resuspension [72,73]. In contrast, leaves with shallower grooves are less able to absorb dust [26]. In addition, the width of grooves is also positively correlated with the retention of PM [74], for the narrower the width of grooves, the smaller the contact area between PM and the grooves, and the lower the PM retention. It is found that the particles are concentrated precisely into grooves [36].
5. Conclusions
Numerous studies have shown that the dust retention capacity of leaves is determined by both macroscopic and microscopic leaf traits (Figure 5). The real-world effectiveness of these traits in capturing and retaining PM can be enhanced or limited by other influential variables [1,19,20]. No single leaf trait can dominate all other traits to determine the retention capacity of PM [17].
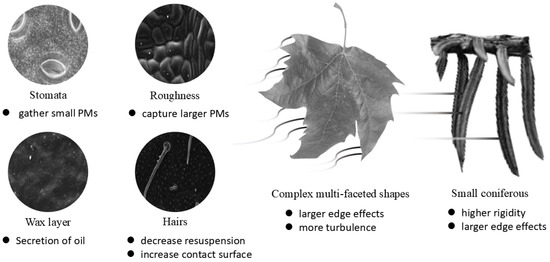
Figure 5.
A brief summary of the impact of leaf macro and micro traits on PM retention. The electron microscope images of the microscopic traits are from the following sources: Stomata [30], Roughness [20], Wax layer [38], Hairs [38].
Generally speaking, the PM retention per unit area of leaves is primarily related to their microscopic traits. Roughness affects the retention of larger PM, and the wider and denser the grooves, the greater the space available for retaining particles. Additionally, some tree species can secrete oils, which increases the PM retention efficiency of the wax layer. Stomata are more effective in retaining fine and ultrafine PM [21,39]. Trichomes, to some extent, increase the contact area between the leaf surface and airborne PM, thereby reducing the possibility of particle resuspension and enhancing the PM retention efficiency of the leaves.
The overall PM retention of leaves is linked to their macroscopic traits based on the unit PM retention. Large leaf areas are often considered to have lower unit PM retention efficiency, because under the same SLA conditions, large leaves tend to be softer and have lower rigidity, reducing their ability to withstand polluted airflow and increasing their tendency to move with the wind, which leads to a reduction in the amount of PM retained on the leaf surface. However, when considering overall dust retention, a larger leaf area is not necessarily disadvantageous for leaf PM retention. Regarding the leaf shape, existing research generally supports that palmate shapes seem more efficient in PM trapping compared to elliptical or linear leaves, as they may create more turbulence in the boundary air layer with their complex shape and have higher edge effects.
Different leaf traits have varying effects on the retention of particles of different sizes. Therefore, in the construction of urban forest communities, we can maximize the capture of airborne PM by combining different tree species. However, in past studies, the recommendations provided by researchers were often based on the idealized assumption that leaf traits are only related to species and overlooked the fact that leaf traits can also change with variations in pollutant concentrations. It is important to note that the concentration level of pollutants not only determines the background value of PM but also affects the development and expression of plant leaf traits. The same batch of plants will exhibit different PM retention capabilities in different PM pollution environments, showing different rankings [32]. For instance, it is found that the stomatal widths and lengths in the leaves of the 10 plant species differed considerably in different urban areas [31]. Thus, in the process of urban forest construction, the selection of dust-retention tree species not only needs to consider the combination of leaf traits but also the pollution resistance of the tree species themselves.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.X., D.C. and S.Y.; methodology, W.X. and D.C.; software, W.X.; formal analysis, W.X. and Y.L. (Yongjun Lin); investigation, W.X. and Z.S.; data curation, W.X. and Y.L. (Yuchong Long); writing—original draft, W.X.; writing—review and editing, W.X. and S.Y.; visualization, W.X.; supervision, S.Y.; project administration, S.Y.; funding acquisition, S.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32171865).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PM | Particulate matter |
| OS | Only species, papers solely focus on tree species without detailing specific leaf traits |
| LS | Leaf shape |
| LA | Leaf area |
| SLA | Special leaf area, one-sided leaf area per unit of dry mass |
| L, W, L–W R | Length of leaf, width of leaf, and length–width ratio |
| SC | Stomatal conductance |
| S | Stomata |
| H | Hairs/trichomes |
| WL | Wax layer of leaf surface |
| R | Roughness of leaf surface |
References
- Corada, K.; Woodward, H.; Alaraj, H.; Collins, C.M.; de Nazelle, A. A systematic review of the leaf traits considered to contribute to removal of airborne particulate matter pollution in urban areas. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.D.; Xia, J.J.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, W. Additional focus on particulate matter wash-off events from leaves is required: A review of studies of urban plants used to reduce airborne particulate matter pollution. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 48, 126559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects 2018 Revison: Key Facts 2018. Available online: https://medbox.org/document/world-urbanization-prospects-the-2018-revision-key-facts (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Maher, B.A.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Davison, B.; Karloukovski, V.; Clarke, R. Impact of Roadside Tree Lines on Indoor Concentrations of Traffic-Derived Particulate Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13737–13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Yin, S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, Y.R.; Zhu, Y.H.; Yan, J.L. A high-resolution study of PM2.5 accumulation inside leaves in leaf stomata compared with non-stomatal areas using three-dimensional X-ray microscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Gong, J.R.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, B.; Zhu, C.C.; Shi, J.Y.; Yue, K.X. Comparison of the suitability of plant species for greenbelt construction based on particulate matter capture capacity, air pollution tolerance index, and antioxidant system. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, P.E.; Ovrevik, J.; Låg, M.; Refsnes, M.; Nafstad, P.; Hetland, R.B.; Dybing, E. Particulate matter properties and health effects:: Consistency of epidemiological and toxicological studies. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 559–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Wuyts, K.; Denys, S.; Samson, R. The influence of plant species, leaf morphology, height and season on PM capture efficiency in living wall systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgrigna, G.; Baldacchini, C.; Dreveck, S.; Cheng, Z.; Calfapietra, C. Relationships between air particulate matter capture efficiency and leaf traits in twelve tree species from an Italian urban-industrial environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallis, M.; Taylor, G.; Sinnett, D.; Freer-Smith, P. Estimating the removal of atmospheric particulate pollution by the urban tree canopy of London, under current and future environments. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 103, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmi, W.; Weber, C.; Rivière, E.; Blond, N.; Mehdi, L.; Nowak, D. Air pollution removal by trees in public green spaces in Strasbourg city, France. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 17, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.N.; Zhang, G.; An, H.L.; Yin, W.L.; Xia, X.L. Quantifying the particulate matter accumulation on leaf surfaces of urban plants in Beijing, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, R.J.; McArthur, C.; Hochuli, D.F. Particulate matter deposition on roadside plants and the importance of leaf trait combinations. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 20, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, Z.Y.; Song, X.P.; Lai, H.R.; Tan, H.T.W. Particulate matter mitigation via plants: Understanding complex relationships with leaf traits. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Grp, P. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement (Reprinted from Annals of Internal Medicine). Phys. Ther. 2009, 89, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.S.; Yan, Q.; He, P.; Zhen, Z.L.; Jing, Y.D.; Duan, Y.H.; Chen, X.X. Combined effects of different leaf traits on foliage dust-retention capacity and stability. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Xu, L.S.; Duan, Y.H.; Pan, L.C.; Wu, Z.W.; Chen, X.L. Influence of leaf morphological characteristics on the dynamic changes of particulate matter retention and grain size distributions. Environ. Technol. 2024, 45, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.S.; Yan, Q.; Lin, Y.C.; Zhen, Z.L.; Liu, L.W.; Duan, Y.H. Selective retention of particulate matter by nine plant species in central Shanxi Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 35902–35910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.S.; He, P.; Duan, Y.H.; Yu, Z.T.; Yang, F. Synergy of different leaf traits determines the particulate matter retention capacity and its susceptibility to rain wash-off. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.K.; Kwak, M.J.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Jeong, S.G.; Son, J.A.; Oh, C.Y.; Je, S.M.; Chang, H.N.; et al. Relationship between Leaf Traits and PM-Capturing Capacity of Major Urban-Greening Species. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Kim, D.; Park, S.H.; Woo, S.Y.; Nie, H.; Kim, S.H. Particulate Matter (PM) Adsorption and Leaf Characteristics of Ornamental Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) Cultivars and Two Common Indoor Plants (Hedera helix L. and Epipremnum aureum Lindl. & Andre). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Wang, S.J.; Chen, Q.B. Potential of Thirteen Urban Greening Plants to Capture Particulate Matter on Leaf Surfaces across Three Levels of Ambient Atmospheric Pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.S.; Xu, W.; Mo, L.; Heal, M.R.; Xu, X.W.; Yu, X.X. Quantifying particulate matter accumulated on leaves by 17 species of urban trees in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12545–12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, C.; Cui, K.D.; Duan, J.; Wu, X.Y.; Yan, P.B.; Rodriguez, C.; Fu, H.M.; Deng, T.; Zhang, S.W.; Liu, J.Q.; et al. The retention characteristics for water-soluble and water-insoluble particulate matter of five tree species along an air pollution gradient in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 145497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerakkody, U.; Dover, J.W.; Mitchell, P.; Reiling, K. Evaluating the impact of individual leaf traits on atmospheric particulate matter accumulation using natural and synthetic leaves. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 30, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerakkody, U.; Dover, J.W.; Mitchell, P.; Reiling, K. Quantification of the traffic-generated particulate matter capture by plant species in a living wall and evaluation of the important leaf characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Lim, Y.; Kim, J.E.; Baek, S.G.; Seo, S.M.; Kim, K.N.; Woo, S.Y. The Removal Efficiencies of Several Temperate Tree Species at Adsorbing Airborne Particulate Matter in Urban Forests and Roadsides. Forests 2019, 10, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.J.; Lee, J.K.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Lim, Y.J.; Lee, K.A.; Son, J.A.; Oh, C.Y.; Kim, I.; Woo, S.Y. Surface-Based Analysis of Leaf Microstructures for Adsorbing and Retaining Capability of Airborne Particulate Matter in Ten Woody Species. Forests 2020, 11, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Liao, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.F.; Ye, Z.Q.; Chen, C.; Huang, Y.Q.; Liu, Y. A Study on the Leaf Retention Capacity and Mechanism of Nine Greening Tree Species in Central Tropical Asia Regarding Various Atmospheric Particulate Matter Values. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.N.; Wu, Y.H.; Li, Z.Z.; Wen, Z.B. Differences in particulate matter retention and leaf microstructures of 10 plants in different urban environments in Lanzhou City. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 103652–103673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkaee, S.; Shirvany, A.; Moeinaddini, M.; Sabbagh, F. Assessment of Particulate Matter, Heavy Metals, and Carbon Deposition Capacities of Urban Tree Species in Tehran, Iran. Forests 2024, 15, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Wang, L.H.; Sun, F.B.; Li, G.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Zeng, X.R.; Yan, H.; Dong, L.; Bao, Z.Y. Study on different particulate matter retention capacities of the leaf surfaces of eight common garden plants in Hangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.K.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, H.; Zhang, T. How Does Leaf Surface Micromorphology of Different Trees Impact Their Ability to Capture Particulate Matter? Forests 2018, 9, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhu, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z. Leaf Surface Micro-morphological Features and Its Retention Ability of Particulate Matters for 9 Plant Species at the Roadside of Beijing. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 26, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar]
- Santunione, G.; Barbieri, A.; Sgarbi, E. Analysis of particulate matter (PM) trapped by four different plant species in an urban forest: Quantification and characterization. Trees For. People 2024, 16, 100585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.K.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.C.; Zhang, T.; Meng, H.; Gong, J.L.; Zhang, Z. Particulate Matter and Trace Metal Retention Capacities of Six Tree Species: Implications for Improving Urban Air Quality. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Shu, D.; Yang, B.; Cui, Y.; Ding, F. Properties and Spatio-Temporal Variation of Leaf Retained Particulate Matters of the Main Tree Species Planted in Guiyang City. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2020, 56, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, A.; Gajbhiye, T.; Pandey, M.; Tirkey, A.; Kim, K.H.; Pandey, S.K. A practical option for the selection of suitable plants for the management of airborne particulate matter (PM). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 11537–11548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Xie, B.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y. Accumulation of Particulate Matter on Leaves of Nine Urban Greening Plant Species with Different Micromorphological Structures in Beijing. Res. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 384–392. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.X.; Liu, C.M.; Zhang, L.; Zou, R.; Zhang, Z.Q. Variation in Tree Species Ability to Capture and Retain Airborne Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, H. Retention Capability of PM2.5 and It’s Explanation by Leaf Surface Micro-structure of Common Broad-leaved Plant Species in Beijing. Xibei Zhiwu Xuebao 2014, 34, 2432–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæbo, A.; Popek, R.; Nawrot, B.; Hanslin, H.M.; Gawronska, H.; Gawronski, S.W. Plant species differences in particulate matter accumulation on leaf surfaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Lei, Y.; He, D. Dust-retention Capability and Leaf Traits of Common Park Greening Plant Species in Zhengzhou City. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2021, 36, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, P.; Xie, M.; Wan, H.; Su, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Yu, L. Dust-retention capability and leaf surface micromorphology of 15 broad-leaved tree species in Wuhan. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Zhang, T.R.; Sun, F.B.; Song, X.M.; Zhang, Y.K.; Huang, F.; Yuan, C.Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, G.H.; Qi, F.; et al. The relationship between particulate matter retention capacity and leaf surface micromorphology of ten tree species in Hangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, S.; Jiang, C.; Xiong, F.; Zhu, P.; Zhou, P. PM2.5 deposition velocity and impact factors on leaves of typical tree species in Shanghai. J. East China Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2016, 6, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Qiu, K.Y.; Pott, R. Reduction of urban traffic-related particulate matter-leaf trait matters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5825–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Liu, Y.; Lai, S.; Gu, X.; Liu, Q.; Gong, P. Effects of Particulate Matter Retained by Eight Urban Tree Leaves and Their Relationships between Leaf Trait in Nanchang. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2020, 35, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zampieri, M.C.T.; Sarkis, J.E.S.; Pestana, R.C.B.; Tavares, A.R.; Melo-de-Pinna, G.F.A. Characterization of Tibouchina granulosa (Desr.) Cong. (Melastomataceae) as a biomonitor of air pollution and quantification of particulate matter adsorbed by leaves. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popek, R.; Gawronska, H.; Wrochna, M.; Gawronski, S.W.; Sæbo, A. Particulate Matter on Foliage of 13 Woody Species: Deposition on Surfaces and Phytostabilisation in Waxes—A 3-Year Study. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2013, 15, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhijith, K.V.; Kumar, P. Quantifying particulate matter reduction and their deposition on the leaves of green infrastructure. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Umut, H.; Munila, A.; Chen, H.; Aliya, B. Effects of leaf microstructure characteristics of urban trees on atmospheric particulates retention capacity. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 2228–2236. [Google Scholar]
- Blanusa, T.; Fantozzi, F.; Monaci, F.; Bargagli, R. Leaf trapping and retention of particles by holm oak and other common tree species in Mediterranean urban environments. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierzanowski, K.; Popek, R.; Gawronska, H.; Sæbo, A.; Gawronski, S.W. Deposition of Particulate Matter of Different Size Fractions on Leaf Surfaces and in Waxes of Urban Forest Species. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2011, 13, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Wuyts, K.; Samson, R. Atmospheric net particle accumulation on 96 plant species with contrasting morphological and anatomical leaf characteristics in a common garden experiment. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 202, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-Bedoya, M.; Arboleda-Restrepo, L.; Posada-Bermúdez, A.; Giraldo, L.; Mejía-Calderón, V.; Ramírez-Villa, A.; Jiménez-Londoño, D.; Quintero-Vallejo, E. Atmospheric particulate matter deposition in herbaceous species on a university campus in colombia. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2024, 40, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Struwig, M.; Siebert, S.J. Identifying Common Trees and Herbaceous Plants to Mitigate Particulate Matter Pollution in a Semi-Arid Mining Region of South Africa. Climate 2023, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, T.A.; Shergina, O.V. Diversity and negative effect of PM0.3–10.0 adsorbed by needles of urban trees in Irkutsk, Russia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 119243–119259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.K.; Wang, B.; Niu, X. Relationship between Leaf Surface Characteristics and Particle Capturing Capacities of Different Tree Species in Beijing. Forests 2017, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, N.J.; Krix, D.; Irga, P.J.; Torpy, F.R. Airborne particulate matter accumulation on common green wall plants. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2020, 22, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerakkody, U.; Dover, J.W.; Mitchell, P.; Reiling, K. Particulate matter pollution capture by leaves of seventeen living wall species with special reference to rail-traffic at a metropolitan station. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 27, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelli, S.; Marignani, M.; Barni, E.; Petraglia, A.; Puglielli, G.; Wellstein, C.; Acosta, A.T.R.; Bolpagni, R.; Bragazza, L.; Campetella, G.; et al. Plant-environment interactions through a functional traits perspective: A review of Italian studies. Plant Biosyst. 2019, 153, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, J.; Koch, K.; Kaiser, H. Deliquescence of Deposited Atmospheric Particles on Leaf Surfaces. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2001, 1, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Wang, Y.H.; Yang, J.; Xie, B.Z.; Shi, H. Morphological Structure of Leaves and Particulate Matter Capturing Capability of Common Broad-leaved Plant Species in Beijing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Technology and Management Science (ITMS), Tianjin, China, 27–28 March 2015; pp. 581–584. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, L.; Ma, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.S.; Sun, F.B.; Lun, X.X.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, J.G.; Yu, X.X. Assessing the Capacity of Plant Species to Accumulate Particulate Matter in Beijing, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Bermudez, M.D.; Gulenc, I.T.; Cameron, R.W.; Inkson, B.J. ‘Green barriers’ for air pollutant capture: Leaf micromorphology as a mechanism to explain plants capacity to capture particulate matter. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Park, J.; Jung, S.Y.; Lee, S.J. Effect of trichome structure of Tillandsia usneoides on deposition of particulate matter under flow conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigioniero, A.; Postiglione, A.; Zuzolo, D.; Niinemets, Ü.; Tartaglia, M.; Scarano, P.; Mercurio, M.; Germinario, C.; Izzo, F.; Trifuoggi, M.; et al. Leaf surface functional traits influence particulate matter and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons air pollution mitigation: Insights from Mediterranean urban forests. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Guan, D.S.; Song, W.W.; Huang, K.Y. Capture of heavy metals and sulfur by foliar dust in urban Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, K.; Ottelé, M.; Giulini, S.; Magliocco, A.; Roccotiello, E. Quantification of fine dust deposition on different plant species in a vertical greening system. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 100, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speak, A.F.; Rothwell, J.J.; Lindley, S.J.; Smith, C.L. Urban particulate pollution reduction by four species of green roof vegetation in a UK city. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Wang, B.; Wei, W.J. Response of the particulate matter capture ability to leaf age and pollution intensity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 34258–34269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, C.X. Quantifying PM2.5 capture capability of greening trees based on leaf factors analyzing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21176–21186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).