A Rapid Computational Method for Quantifying Inter-Regional Air Pollutant Transport Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
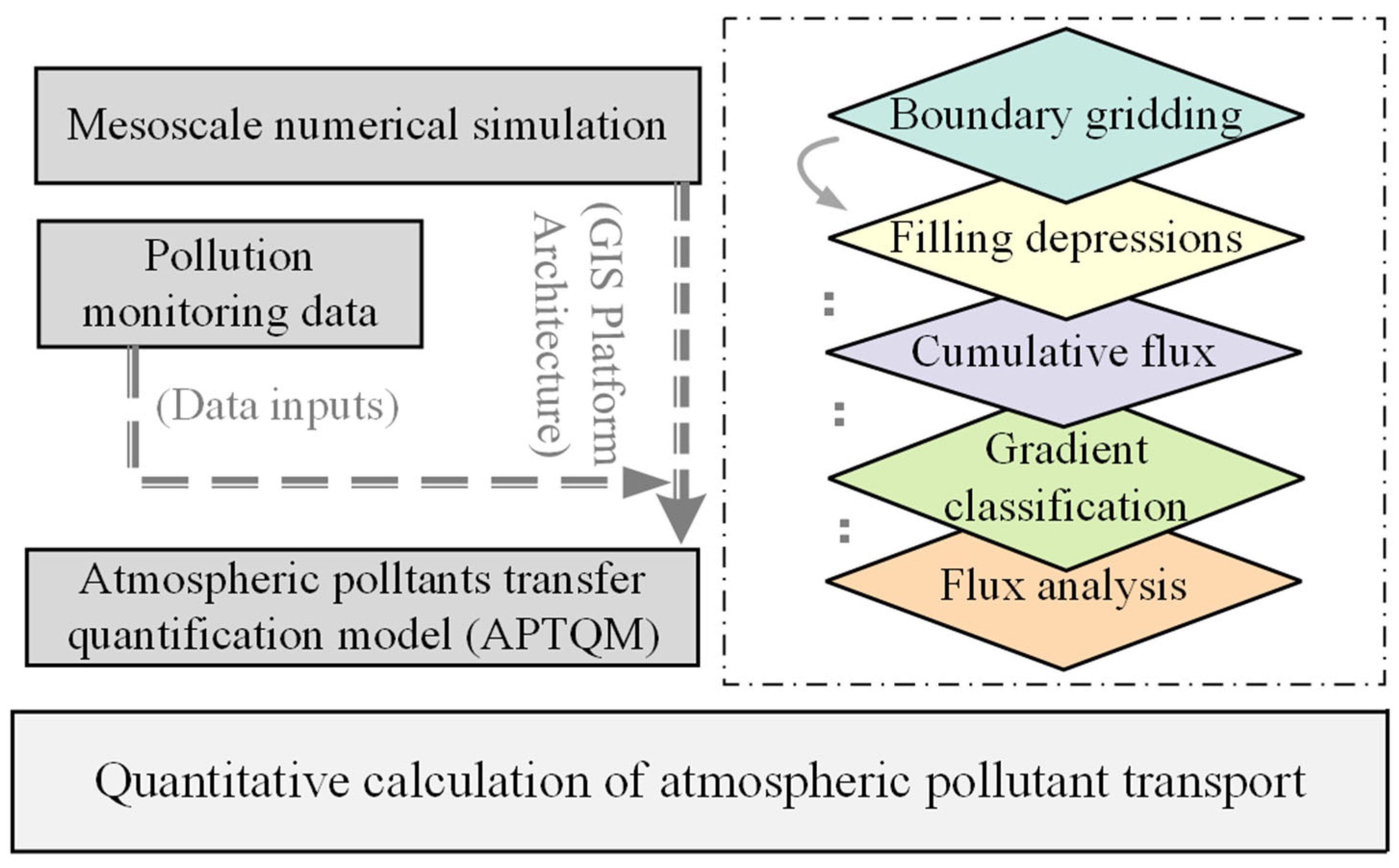
2.1. Establishment of Method
- (1)
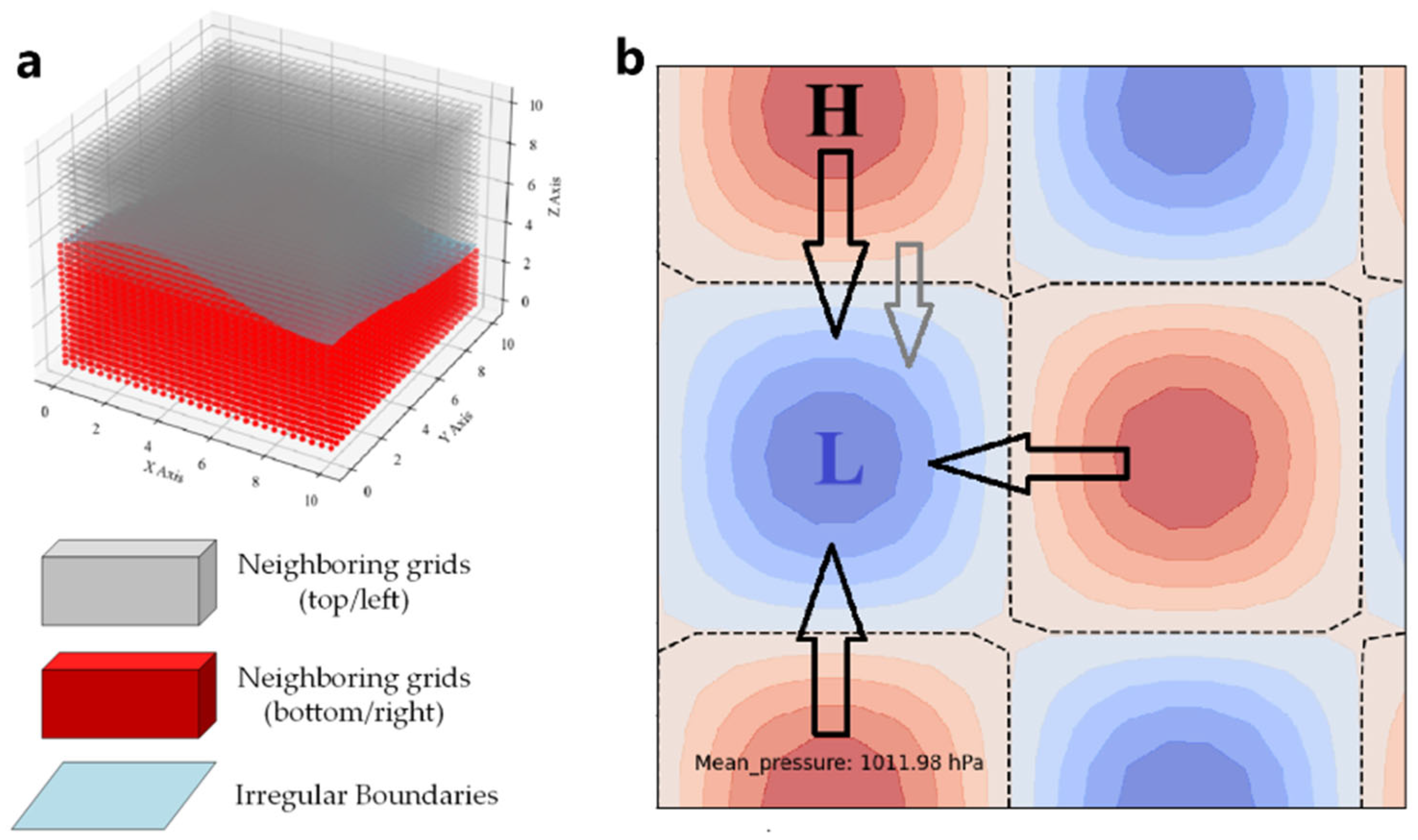
- Area gridding and boundary processing
- (2)
- Depression filling and pressure gradient analysis
- (3)
- Atmospheric flow analysis and quantification methods
2.2. Validation of Method
3. Application, Validation and Discussion
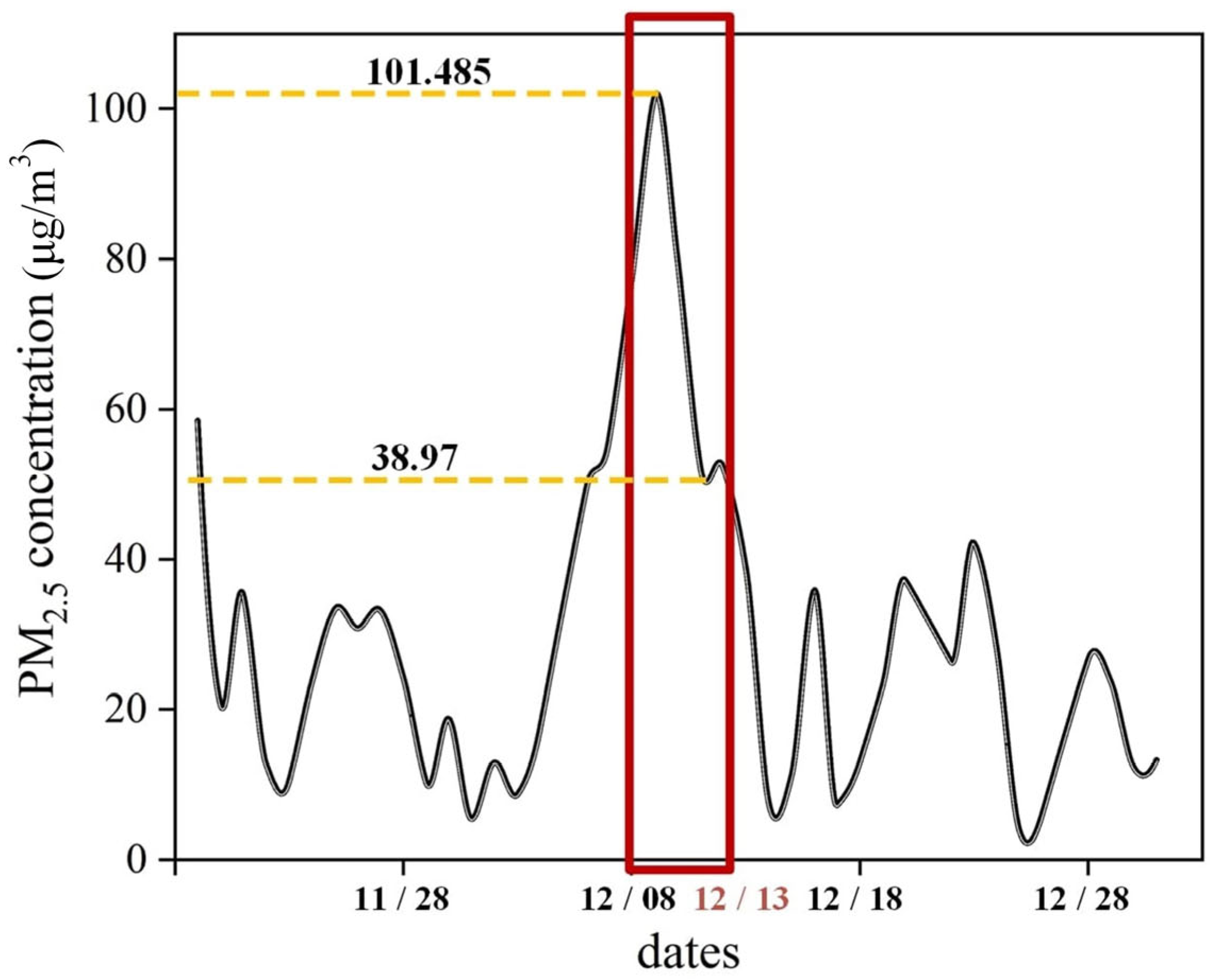
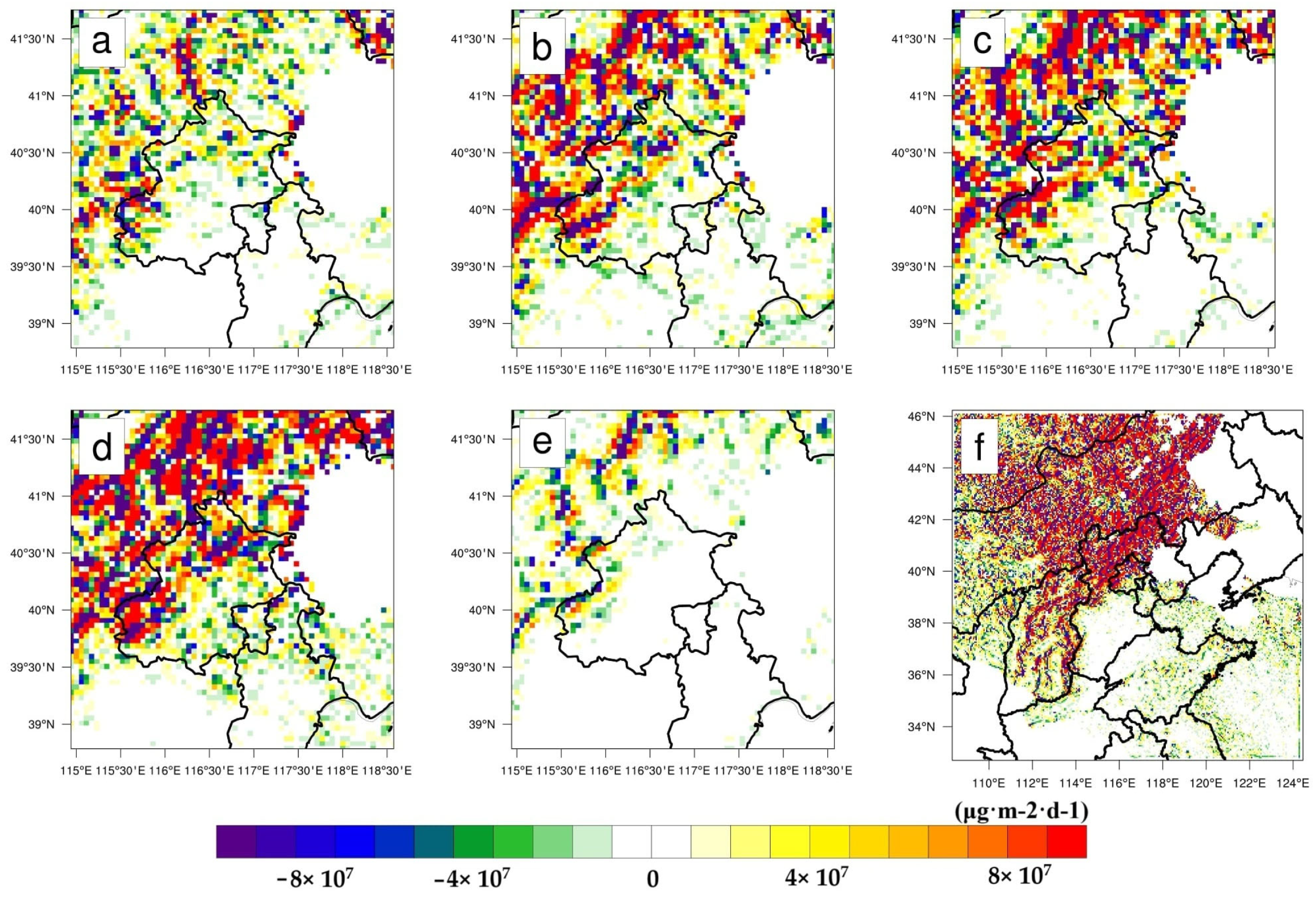
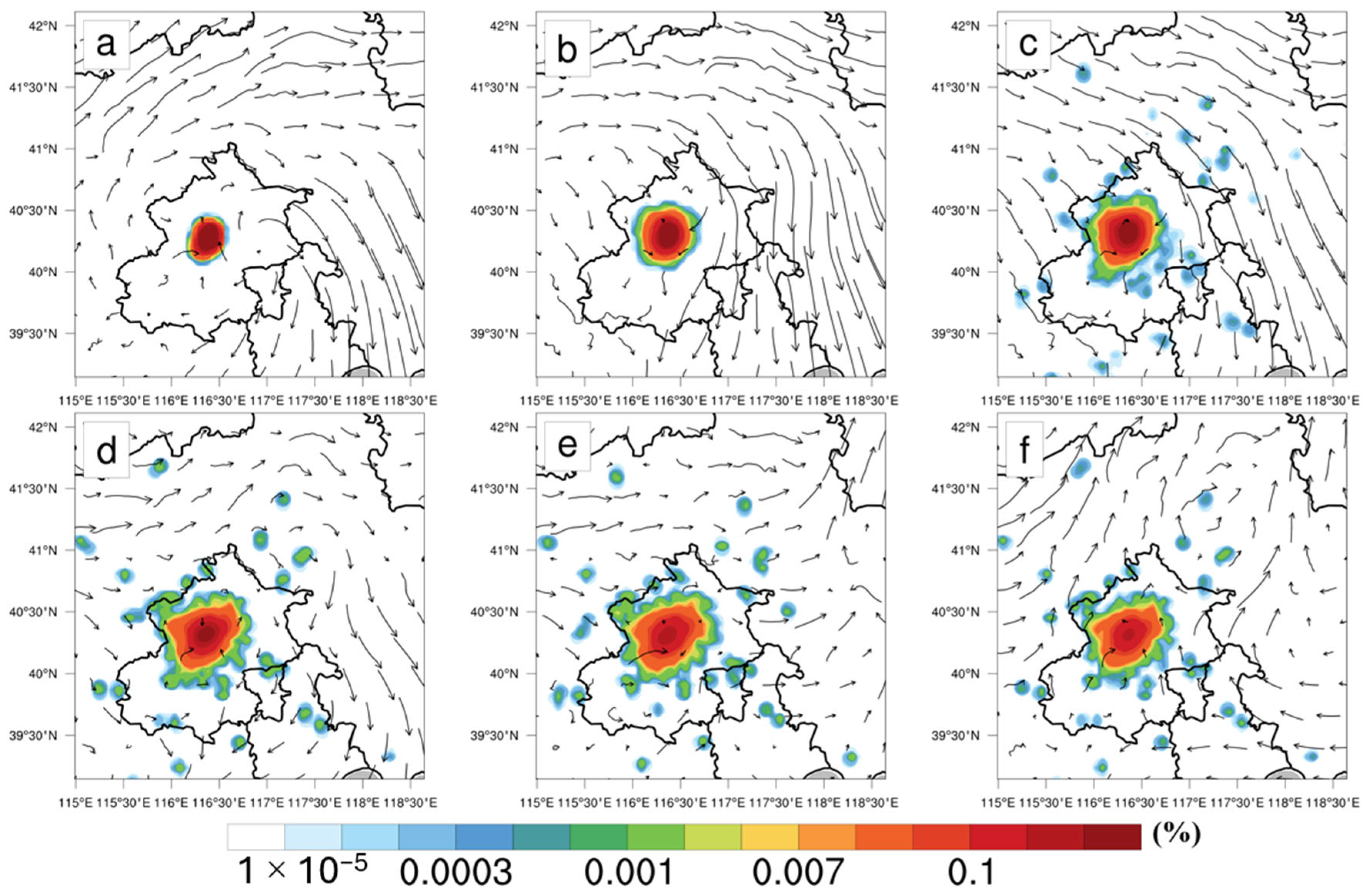
3.1. Case Selection and Numerical Simulation
- (a)
- A pronounced northwest–southeast transport corridor, evidenced by concentrated high-value regions.
- (b)
- Substantial negative flux at the southern boundary (mean: −4.1 × 108 μg·m−2·d−1).
- (c)
- Persistent positive flux at the eastern boundary (mean: 1.67 × 108 μg·m−2·d−1).
3.2. Validation Analysis
- (1)
- Quantitative comparison
- (2)
- Analysis of Source Areas
3.3. Effects of Buoyancy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APTQM | Atmospheric pollutant transport quantification model |
| 4D flux methods | Four-dimensional flux method |
| WRF | Weather research and forecasting (WRF Model) |
| FLEXPART | Flexible particle dispersion model (FLEXPART Model) |
| NECP | National Centers for Environmental Prediction |
| FNL | Final Operational Global Analysis data |
| MEIC | Multi-resolution Emission Inventory model for Climate and air pollution research |
References
- Yan, F.; Chen, W.; Jia, S.; Zhong, B.; Yang, L.; Mao, J.; Chang, M.; Shao, M.; Yuan, B.; Situ, S.; et al. Stabilization for the secondary species contribution to PM2.5 in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) over the past decade, China: A meta-analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 242, 117817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jing, S.; Peng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yan, R.; Wang, Q.; Lou, S.; Cheng, T.; Huang, C. Strong regional transport of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during wintertime in Shanghai megacity of China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Hama, S.; Omidvarborna, H.; Sharma, A.; Sahani, J.; Abhijith, K.; Debele, S.E.; Zavala-Reyes, J.C.; Barwise, Y.; Tiwari, A. Temporary reduction in fine particulate matter due to ‘anthropogenic emissions switch-off’ during COVID-19 lockdown in Indian cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; He, S.; Zhou, H. Spatio-temporal characteristics and convergence trends of PM2.5 pollution: A case study of cities of air pollution transmission channel in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.-C.; Yeh, S.-W.; Jeong, J.I.; Park, R.J.; Yoo, C.; Yoon, J.-H. Intrinsic atmospheric circulation patterns associated with high PM2.5 concentration days in South Korea during the cold season. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Wu, S.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Tian, B.; Yu, Y.; Ma, N.; Ji, P.; Zhang, B. Synoptic Weather Patterns and Atmospheric Circulation Types of PM2.5 Pollution Periods in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Mao, W.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, L. Non-Linear Response of PM2.5 Pollution to Land Use Change in China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J.; Cong, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C. Comparison of dry and wet deposition of particulate matter in near-surface waters during summer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-D.; Cheng, X.-F.; He, Y.-T.; Kong, L.-S.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Li, B. Environmental pollution, trade openness and the health of middle-aged and elderly people: An analysis of threshold effect based on data from 111 prefecture-level cities in China. Arch. Public Health 2024, 82, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, J. Impact of Environmental Pollution on Health-Evidence from Cities in China. Soc. Work Public Health 2020, 35, 413–430. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xie, Y. Health and economic benefits of clean air policies in China: A case study for Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Liao, Z.; Bian, J.; Bai, Z.; Shi, H.; Xuan, Y.; Yao, Z.; Chen, H. Vertical distribution of tropospheric ozone and its sources of precursors over Beijing: Results from ~20 years of ozonesonde measurements based on clustering analysis. Atmos. Res. 2023, 284, 106610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, M.; Ma, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Größ, J.; Fan, Z.; Wang, M.; Wiedensohler, A. Hygroscopicity of aerosol particles composed of surfactant SDS and its internal mixture with ammonium sulfate at relative humidities up to 99.9%. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 298, 119625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Shi, Y.; Su, C.; Yuan, J.; Johnson, A.C.; Jenkins, A.; Ferrier, R.C.; Chen, D.; Tian, H.; et al. Interaction between pollution and climate change augments ecological risk to a coastal ecosystem. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2018, 4, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Actions on Air Quality: A Global Summary of Policies and Programmes to Reduce Air Pollution. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/actions-air-quality-global-summary-policies-and-programmes-reduce-air-pollution (accessed on 9 January 2025).
- Ambient (outdoor) air pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed on 9 January 2025).
- Streets, D.G.; Fu, J.S.; Jang, C.J.; Hao, J.; He, K.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Air quality during the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, N.; Gokhale, S. Transported aerosols regulate the pre-monsoon rainfall over north-east India: A WRF-Chem modelling study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 6197–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulan, W.; Yuanhang, Z.; Liuju, Z.; Jinlong, L.; Qun, Y. Interaction of Air Pollution among Cities in the Pearl River Delta Region. China Environ. Sci. 2005, 25, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Meiyuan, H.; Zifa, W.; Dongyang, H.; Huaying, X.; Ling, Z. Modeling studies on sulfur deposition and transport in East Asia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 85, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, M.Y.; Obolkin, V.A.; Khodzher, T.V.; Molozhnikova, Y.V. Variability of the Ground Concentration of Particulate Matter PM1–PM10 in the Air Basin of the Southern Baikal Region. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2024, 36, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, B.; Kremser, S.; Mikaloff-Fletcher, S.; Bodeker, G.; Bird, L.; Dale, E.; Lin, D.; Olivares, G.; Somervell, E. The MAPM (Mapping Air Pollution eMissions) method for inferring particulate matter emissions maps at city scale from in situ concentration measurements: Description and demonstration of capability. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 14089–14108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldellis, J.; Chalvatzis, K.; Spyropoulos, G. Chalvatzis and G.C. Spyropoulos, Transboundary air pollution balance in the new integrated European environment. Environ. Sci. Policy 2007, 10, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W. Analysis on the Characteristics of Horizontal Transport of the Atmospheric Pollutant over the Yangtze Delta. Res. Environ. Sci. 2008, 21, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zifa, W. Simulation of the Impacts of Regional Transport on Summer Ozone Levels Over Beijing. Chin. J. Nat. 2008, 30, 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, E.; Chung, J.; Sandberg, M.; Ito, K. Influence of chemical reactions and turbulent diffusion on the formation of local pollutant concentration distributions. Build. Environ. 2020, 168, 106487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Song, Y.H.; Uhm, K.-B.; Turner, R.W.; Lee, J.-H.; Roderick, G.K. Simulation of the Long Range Migration of Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stal), by Using Boundary Layer Atmospheric Model and the Geographic Information System. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2000, 3, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanghe, K.; Guo, X.; Ahmad, S.; Tian, F.; Nabi, G.; Strelnikov, I.I.; Li, K.; Zhao, K. FRESF model: An ArcGIS toolbox for rapid assessment of the supply, demand, and flow of flood regulation ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, M.; Dandpat, A.K.; Naik, B. Hydrological modeling with respect to impact of land-use and land-cover change on the runoff dynamics in Budhabalanga river basing using ArcGIS and SWAT model. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Zong, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, H. Study on the influence of meteorological conditions and the street side buildings on the pollutant dispersion in the street canyon. Build. Simul. 2016, 9, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Hu, W.; Yin, M.-Q. An Investigation of the Correlation between Pollutant Dispersion and Wind Environment: Evaluation of Static Wind Speed. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4311–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.L. Incorporating the Work Done by Vertical Density Fluxes in Both Kinetic and Thermal Energy Conservation Equations to Satisfy Total Energy Conservation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, K.G. The Flow of Mechanical Energy in Convective Boundary Layers. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2012, 145, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Q. New method for investigating regional interactions of air pollutants. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2012, 32, 528–536. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Wu, L.; Wang, X. Application of four-dimensional flux method in PM2.5 regional transport in the Pearl River Delta during the autumn season. China Sci. 2019, 14, 85–91+97. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.P.; Mo, H.H.; Yang, L.T.; Cai, Z.J.; Wu, G.T.; Bai, Y.J.; Deng, S.X.; Situ, S.P.; Chang, M.; Wang, X.M. Quantification of Ozone Pollution Transport Based on Four-dimensional Flux Method in Foshan, China. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 4262–4270. [Google Scholar]
- Gang, T.; Yuhu, H.; Gang, L. Establishment and Application of Four-dimensional Fluxes Emission Factor Model for Construction Fugitive Dust. Environ. Sci. 2009, 30, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, F.; Cheng, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Qu, Y.; An, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Divergent summertime surface O3 pollution formation mechanisms in two typical Chinese cities in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and Fenwei Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Yan, X.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. Temperature and phase evolution and density distribution in cross section and sound evolution during the release of dense CO2 from a large-scale pipeline. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2020, 96, 103011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Yoshie, R. Effect of atmospheric stability on air pollutant concentration and its generalization for real and idealized urban block models based on field observation data and wind tunnel experiments. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2020, 207, 104380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhao, C.; Kwan, M.-P.; Cai, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; et al. Influence of meteorological conditions on PM2.5 concentrations across China: A review of methodology and mechanism. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhu, S.; Yu, H. Dynamical downscaling of temperature extremes over China using the WRF model driven by different lateral boundary conditions. Atmos. Res. 2022, 278, 106348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.; Rocha, A.; Gómez-Gesteira, M.; Santos, C. A sensitivity study of the WRF model in wind simulation for an area of high wind energy. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 33, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuy, S.; Lee, H.S.; Chreng, K. Offshore wind resource mapping in Cambodia: Sensitivity assessment of the weather research and forecasting model. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; Wotawa, G.; Seibert, P.; Kromp-Kolb, H. Interpolation Errors in Wind Fields as a Function of Spatial and Temporal Resolution and Their Impact on Different Types of Kinematic Trajectories. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1995, 34, 2149–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; Seibert, P. Accuracy of trajectories as determined from the conservation of meteorological tracers. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 124, 1465–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, S. Downward trend of NO2 in the urban areas of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 2014 to 2020: Comparison of satellite retrievals, ground observations, and emission inventories. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 295, 119531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Times(mm/d) | Transport Strength (μg·m−2·d−1) | Net Flux (μg·d−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern | Southern | Western | Northern | ||
| 12/8 | 1.366 × 108 | −1.447 × 108 | −3.192 × 107 | −3.23 × 107 | −3.227 × 107 |
| 12/9 | −3.496 × 107 | −2.563 × 108 | 1.515 × 108 | 7.625 × 107 | −6.346 × 107 |
| 12/10 | 3.433 × 108 | −1.05 × 109 | 6.735 × 106 | 2.492 × 107 | −6.749 × 108 |
| 12/11 | 3.281 × 108 | −4.653 × 108 | 6.337 × 106 | 1.857 × 108 | 5.475 × 107 |
| 12/12 | 2.007 × 107 | −1.323 × 108 | 1.597 × 106 | −2.207 × 107 | −1.327 × 108 |
| Sum | 8.29 × 108 | −2.05 × 109 | 1.34 × 108 | 2.33 × 108 | −8.49 × 108 |
| Average | 1.67 × 108 | −4.10 × 108 | 2.68 × 107 | 4.65 × 107 | −1.70 × 108 |
| Times (mm/d) | Transport Strength (μg·m−2·d−1) | Net Flux (μg·d−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern | Southern | Western | Northern | ||
| 12/8 | 1.286 × 108 | 3.616 × 108 | −3.959 × 107 | −2.484 × 107 | −1.112 × 107 |
| 12/9 | −2.871 × 107 | 3.361 × 108 | 9.611 × 108 | 6.283 × 107 | −6.922 × 107 |
| 12/10 | 2.898 × 108 | −1.96 × 109 | 5.354 × 106 | 2.462 × 107 | −5.847 × 108 |
| 12/11 | 3.4 × 108 | −5.388 × 108 | 5.246 × 106 | 1.042 × 108 | 4.022 × 107 |
| 12/12 | 2.91 × 107 | −1.021 × 108 | 1.675 × 106 | −2.835 × 107 | −1.963 × 108 |
| Sum | 7.95 × 108 | −9.0 × 109 | 9.34 × 108 | 1.38 × 108 | −8.21 × 108 |
| Average | 1.52 × 109 | −3.81 × 108 | 1.87 × 108 | 2.77 × 107 | −1.64 × 108 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X. A Rapid Computational Method for Quantifying Inter-Regional Air Pollutant Transport Dynamics. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020163
Yang L, Wang G, Wang Y, Wang Y, Ma Y, Zhang X. A Rapid Computational Method for Quantifying Inter-Regional Air Pollutant Transport Dynamics. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(2):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020163
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Luoqi, Guangjie Wang, YeGui Wang, Yibai Wang, Yongjing Ma, and Xi Zhang. 2025. "A Rapid Computational Method for Quantifying Inter-Regional Air Pollutant Transport Dynamics" Atmosphere 16, no. 2: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020163
APA StyleYang, L., Wang, G., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Ma, Y., & Zhang, X. (2025). A Rapid Computational Method for Quantifying Inter-Regional Air Pollutant Transport Dynamics. Atmosphere, 16(2), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020163









