Causes and Transmission Characteristics of the Regional PM2.5 Heavy Pollution Process in the Urban Agglomerations of the Central Taihang Mountains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Summary of Datasets and Research Methods
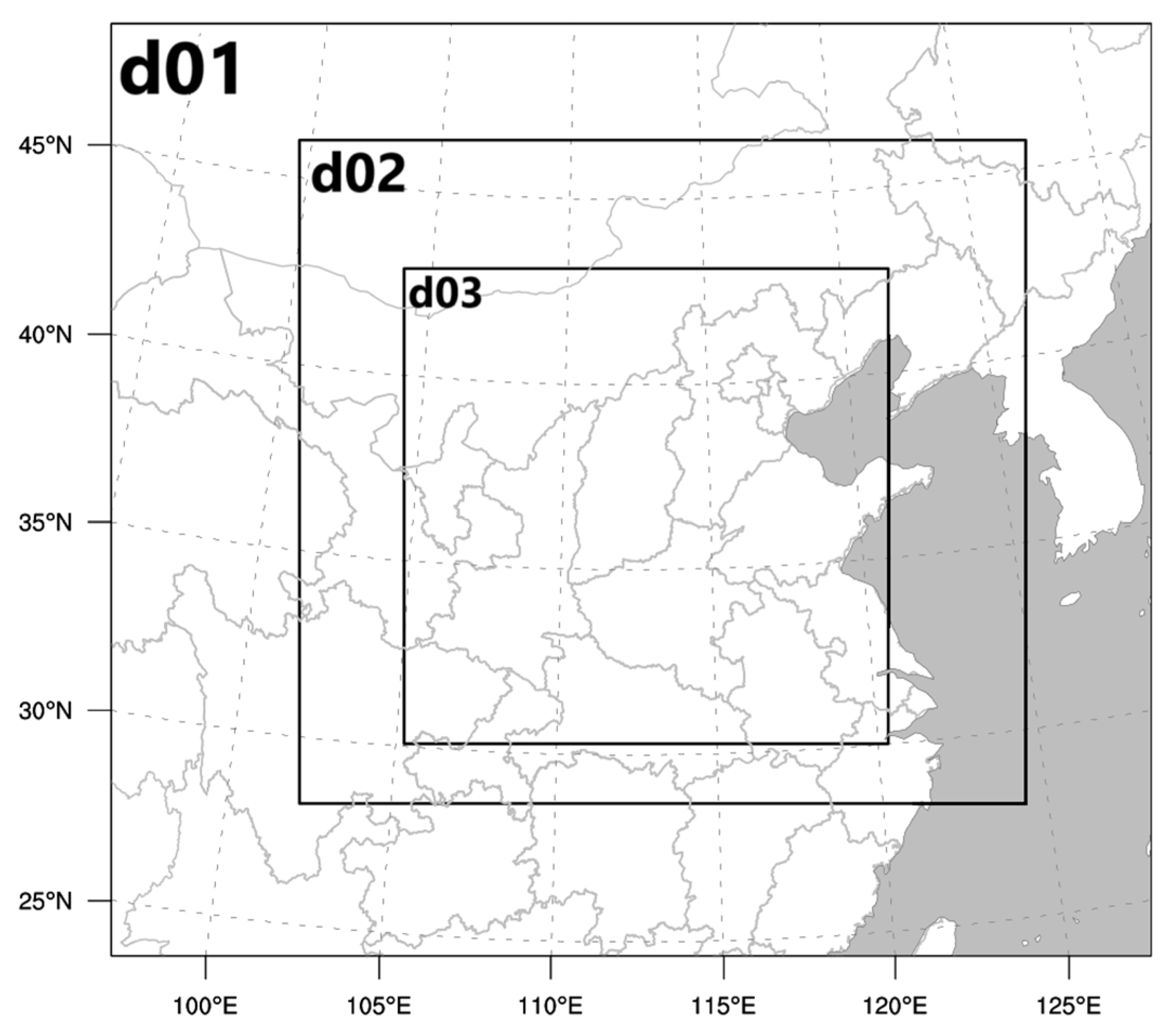
2.1. Overview of the Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. WRF/WRF-HYSPLIT Parameter Settings
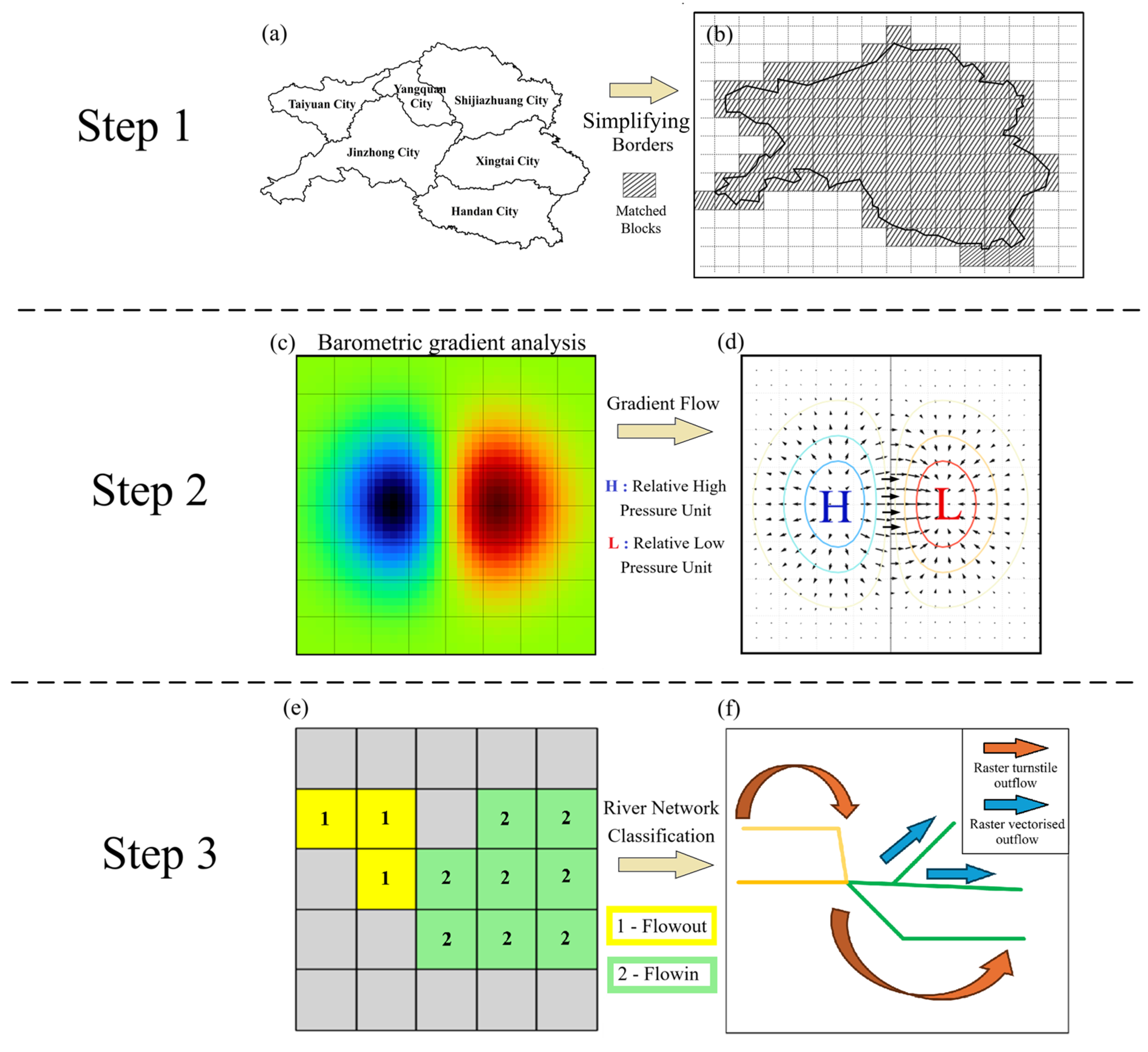
2.3. APTQM-PM2.5
- (1)
- Geographic framework construction and initial flow assignment
- (2)
- Gradient analysis and airflow direction division
- (3)
- River network classification and flow intensity analysis
3. Analysis of Results
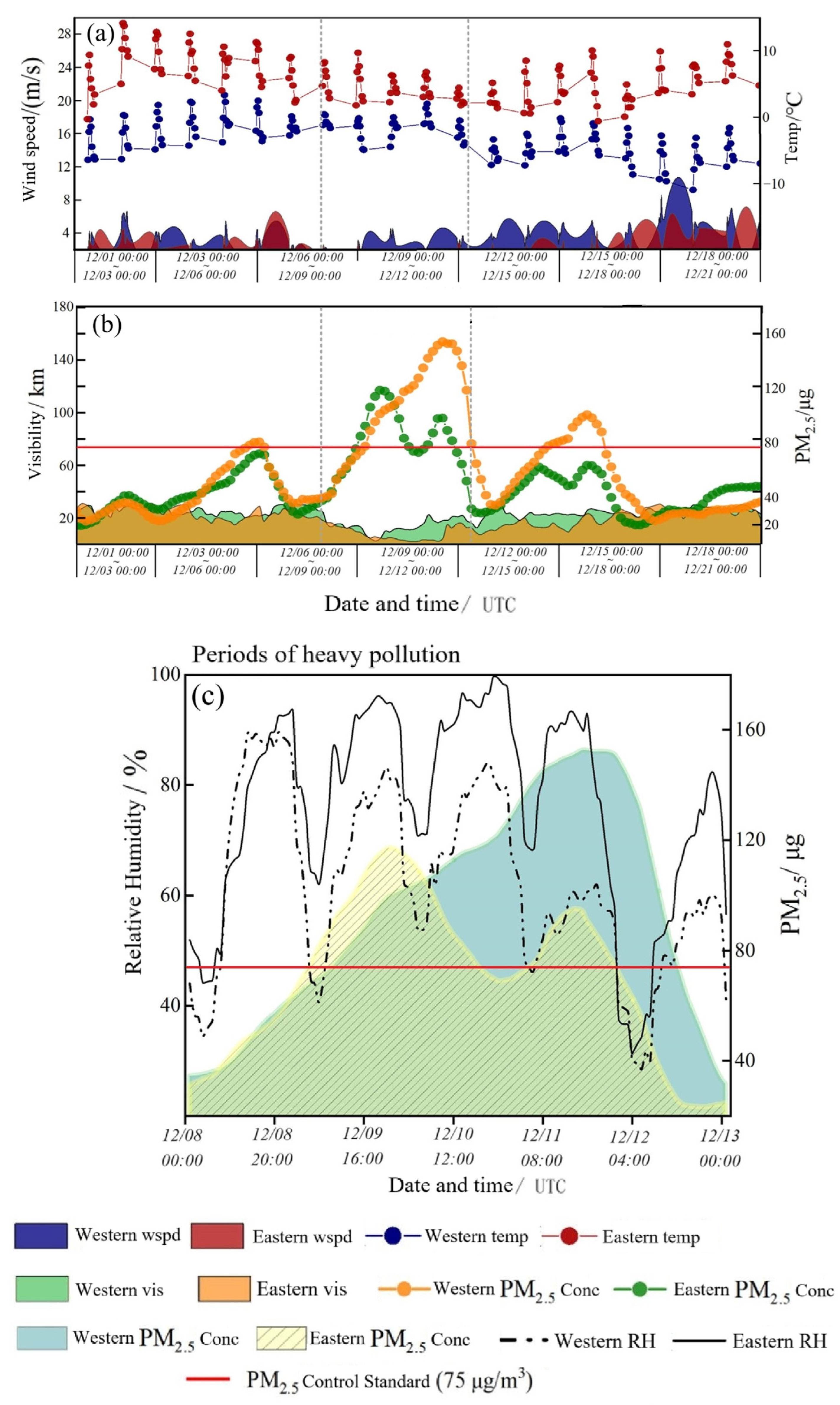
3.1. Heavy Pollution Processes Analysis
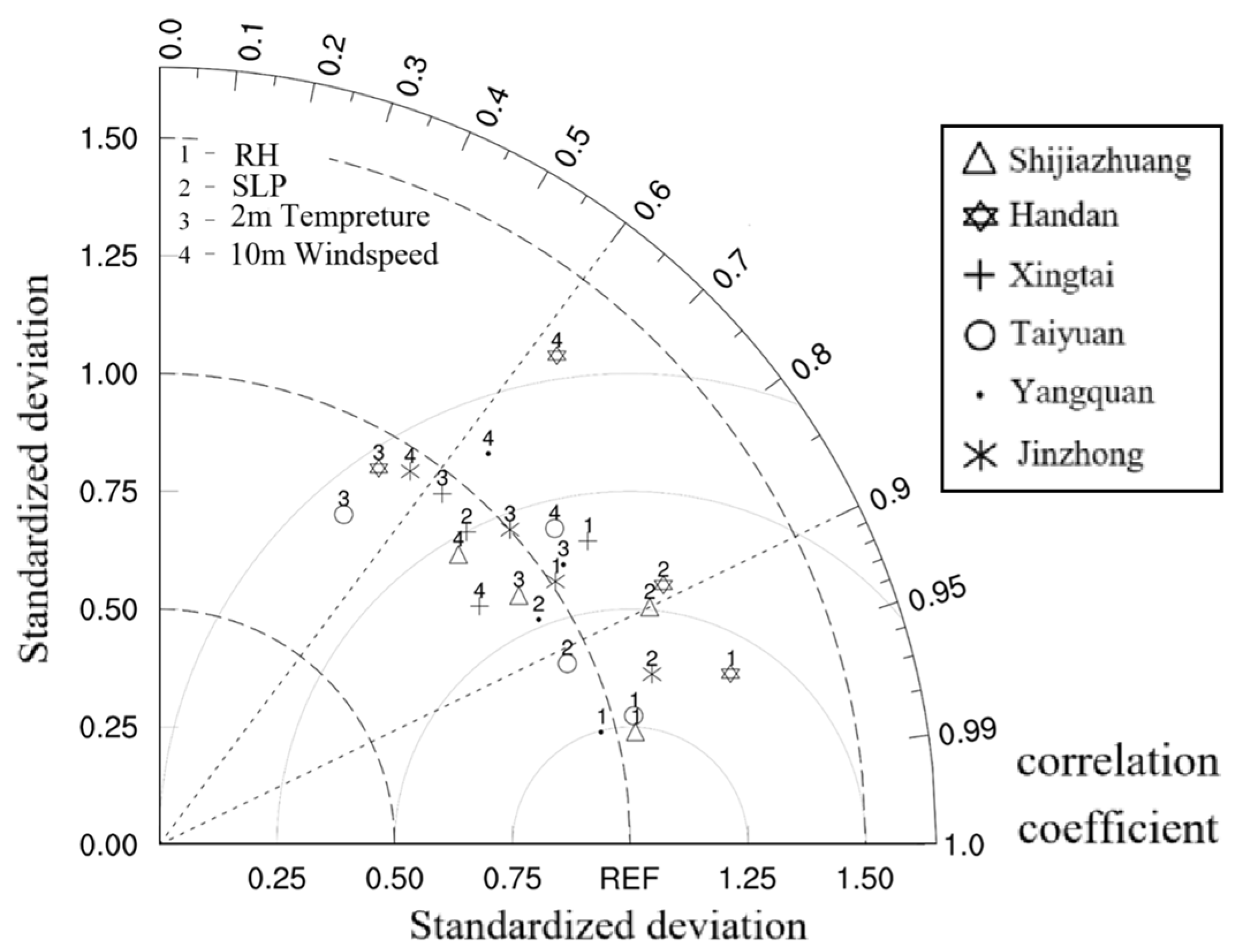
3.2. Numerical Simulation Results Analysis
- (1)
- Evaluation of WRF model simulation results
- (2)
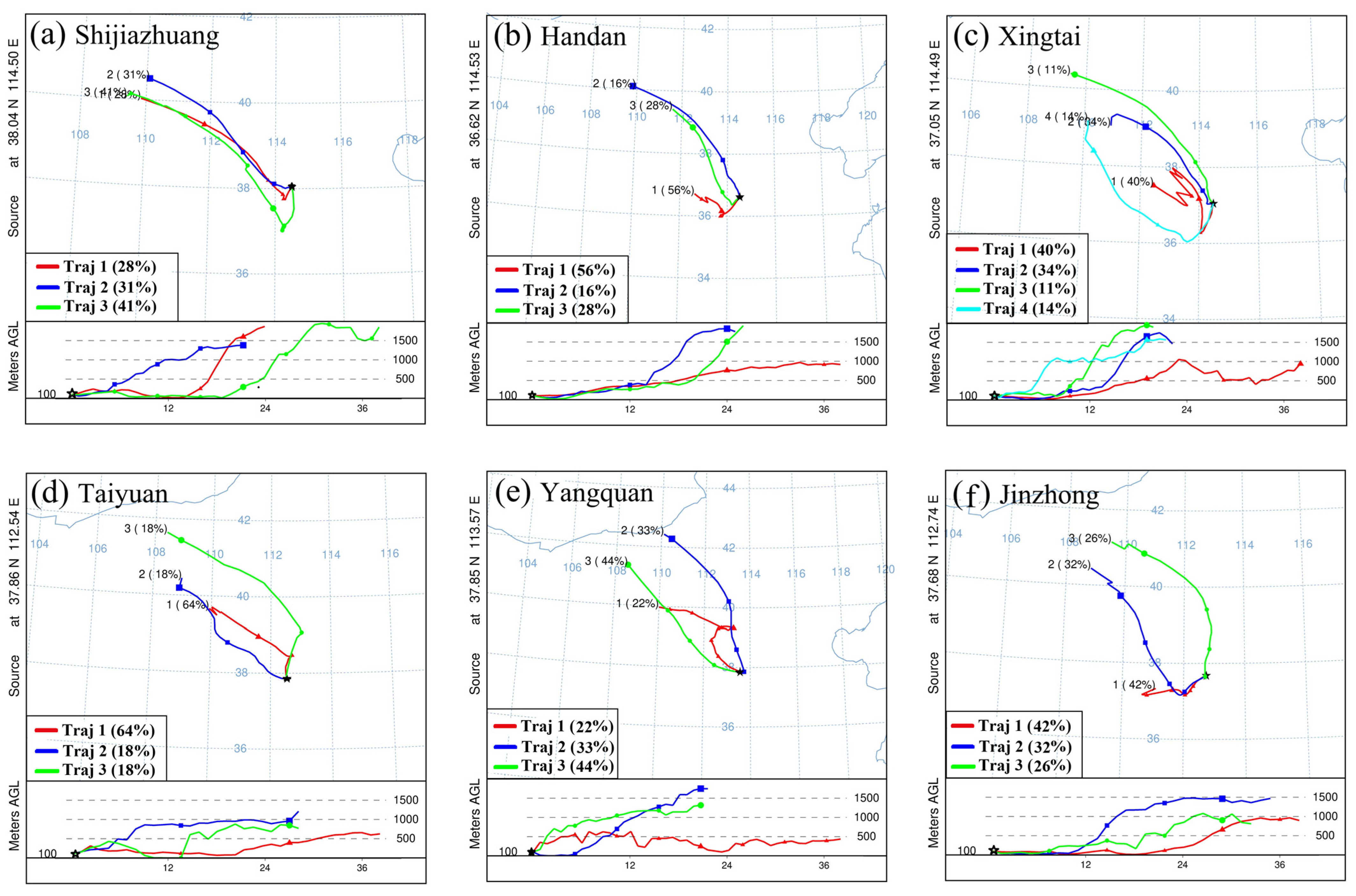
- Analysis of HYSPLIT simulation results
3.3. Analysis of the Circulation Situation During Heavy Pollution
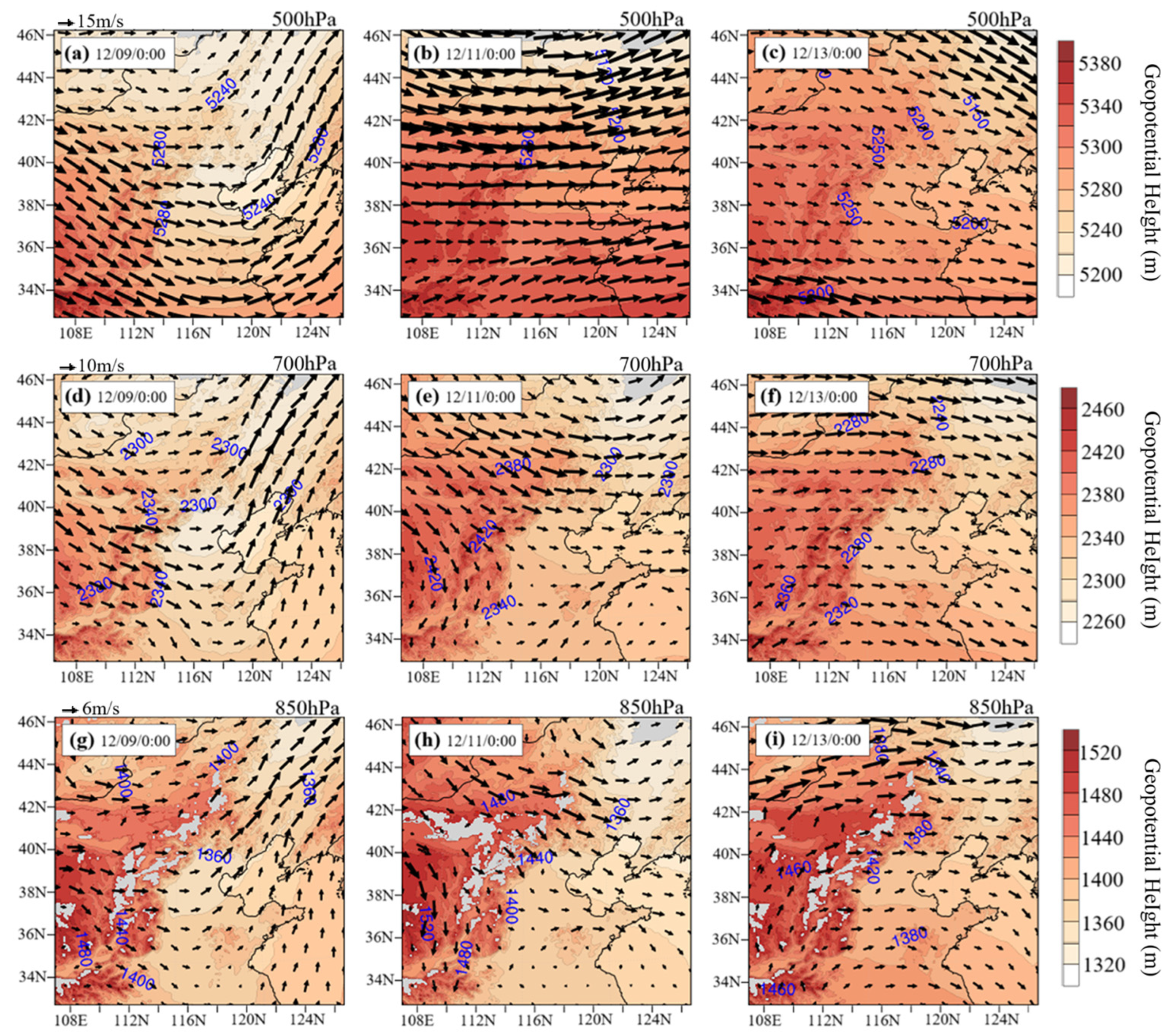
- (1)
- High-altitude horizontal circulation
- (2)
- Vertical circulation changes
3.4. Analysis of APTQM-PM2.5 Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CTHM | Central of Taihang Mountains |
| APTQM | Atmospheric Pollutant Transport Quantification Model |
| WRF | Weather research and forecasting (WRF Model) |
| HYSPLIT | Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory Model |
| NECP | National Centers for Environmental Prediction |
| FNL | Final Operational Global Analysis data |
| CMA | The China Meteorological Administration |
| NUAQRPP | The National Urban Air Quality Real-Time Publishing Platform |
| NGSEM | The National General Station of Environmental Monitoring |
References
- Huang, H.; Jiang, P.; Chen, Y.X. Analysis of the Social and Economic Factors Influencing PM2.5 Emissions at the City Level in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClellan, R.O. Providing Context for Ambient Particulate Matter and Estimates of Attributable Mortality. Risk Anal. 2016, 36, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J. Change of Composition, Source Contribution, and Oxidative Effects of Environmental PM2.5 in the Respiratory Tract. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 11605–11611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lall, R.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Distributed Lag Analyses of Daily Hospital Admissions and Source-Apportioned Fine Particle Air Pollution. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermayurisca, F.; Taneepanichskul, N. Estimation of premature death attributed to short- and long-term PM2.5 exposure in Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.R.; Lee, H.J. Ambient PM2.5 exposure and rapid population aging: A double threat to public health in the Republic of Korea. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 119032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Circular of the State Council on the Issuance of the Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Air Pollution. 2025. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2013-09/12/content_2486773.htm (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Yao, L.; Chu, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Editorial: Atmospheric chemistry in the urban air. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1166400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, J.; Sun, D.; Xu, W.; Han, Y.; Zheng, J.; Peng, J.; Yang, S. Urban air pollution monitoring using scanning Lidar. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Assessing urban atmospheric environmental efficiency and factors influencing it in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Kulesza, R.J.; Doty, R.L.; D’Angiulli, A.; Torres-Jardón, R. Megacities air pollution problems: Mexico City Metropolitan Area critical issues on the central nervous system pediatric impact. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, A.O.; Senff, C.J.; Alvarez, R.J., II; Banta, R.M.; Hardesty, R.M. Long-range transport of ozone from the Los Angeles Basin: A case study. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L06807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakidou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kindap, T.; Im, U.; Vrekoussis, M.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Dermitzaki, E.; Unal, A.; Koçak, M.; Markakis, K.; et al. Megacities as hot spots of air pollution in the East Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koracin, D.; Vellore, R.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Watson, J.G.; Koracin, J.; McCord, T.; DuBois, D.W.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Kumar, N.; Knipping, E.M.; et al. Regional Source Identification Using Lagrangian Stochastic Particle Dispersion and HYSPLIT Backward-Trajectory Models. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Sun, M.; Yan, M.; Lu, M.; Liu, W. Comparative study of migration trajectories of the brown planthopper, nilaparvata lugens, in China based on two trajectory models. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 6122–6138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. GIS-Based Study on the Historical Evolution and Spatial Characteristics of Traditional Settlements in the Northern Three Defiles of the Taihang Mountains. Master’s Thesis, Norinco University, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, H.; Lu, W.; You, H. Analysis of water vapor characteristics of four winter heavy precipitation in Yunnan based on HYSPLIT model. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2024, 44, 833–846. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X. A Rapid Computational Method for Quantifying Inter-Regional Air Pollutant Transport Dynamics. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. Evaluation of Environmental Protection Policies and Mechanisms in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Air Pollution Transmission Corridor Cities. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai University of Finance and Economics (SUFE), Shanghai, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Pattern of PM2.5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Air Pollution Transmission Corridor Area from 2000 to 2015. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C. Analysis of PM2.5 and O3 pollution characteristics and influencing factors in Shanxi Province. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2024, 44, 299–309. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Xu, Z.; Ma, T.; Liu, S.; Yan, L.; Liu, J. Characterization of PM2.5 pollution in cities along the Taihang Mountains during the heating season from 2016 to 2018. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 4521–4529. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Zhe, D.; Jia, Q.; He, L. Spatial Differentiation of Habitat Quality on Different Topographic Gradients in Taihang Mountains and Its Influencing Factors—A Case Study of Fuping County, Hebei Province, China. For. Ecol. Sci. 2022, 37, 426–436. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, H.; Xing, Y. Analysis of spatial heterogeneity and driving factors of haze in Shanxi Province. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B. Why eight defile—“Taihang eight defile” concept of formation and reflection. J. Chin. Hist. Geogr. 2023, 38, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Namdev, P.; Sharan, M.; Srivastava, P.; Mishra, S.K. An updated parameterization of the unstable atmospheric surface layer in the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) modeling system. Geosci. Model Dev. 2024, 17, 8093–8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Dudhia, J.; Chen, S. A Revised Approach to Ice Microphysical Processes for the Bulk Parameterization of Clouds and Precipitation. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2004, 132, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y. The effect of MYJ and YSU schemes on the simulation of boundary layer meteorological factors of WRF. Chin. J. Geophys. 2012, 55, 2239–2248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Stein, A.F.; Isakov, V.; Godowitch, J.; Draxler, R.R. A hybrid modeling approach to resolve pollutant concentrations in an urban area. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 9410–9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, H.P.; Desamsetti, S.; Langodan, S.; Karumuri, R.K.; Singh, S.; Hoteit, I. Atmospheric conditions and air quality assessment over NEOM, kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 230, 117489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Stein, A.F.; Maldonado, P.G.; de la Campa, A.M.S.; Gonzalez-Castanedo, Y.; Castell, N.; de la Rosa, J.D. Size distribution and concentrations of heavy metals in atmospheric aerosols originating from industrial emissions as predicted by the HYSPLIT model. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 71, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Zhou, C.; Lu, S.; Wu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yu, L.; Yin, C. Analyses of winter circulation types and their impacts on haze pollution in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 192, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.Y. Characteristics of Winter Haze Pollution in the Fenwei Plain and the Possible Influence of EU During 1984-2017. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.T.; Suneel, V.; Gulakaram, V.S.; Sravani, C.L. Extraction of persistent lagrangian coherent structures for the pollutant transport prediction in the Bay of Bengal. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8761. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shao, J.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.; He, C. Investigation of the impact mechanisms and patterns of meteorological factors on air quality and atmospheric pollutant concentrations during extreme weather events in Zhengzhou city, Henan Province. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csavina, J.; Field, J.; Félix, O.; Corral-Avitia, A.Y.; Sáez, A.E.; Betterton, E.A. Effect of wind speed and relative humidity on atmospheric dust concentrations in semi-arid climates. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M. Study on Air Pollution Characteristics and Pollutant Transmission in Typical Cities in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and Surrounding Areas. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University (ECNU), Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J. Study on the Relationship Between Urbanization and Spatial and Temporal Evolution of PM2.5 Concentration in Shanxi Province Based on Remote Sensing Data. Master’s Thesis, Tung Wah University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.; Wu, S.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Tian, B.; Yu, Y.; Ma, N.; Ji, P.; Zhang, B. Synoptic Weather Patterns and Atmospheric Circulation Types of PM2.5 Pollution Periods in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, B.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, J. Numerical study of the effects of local atmospheric circulations on a pollution event over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evan, A.T.; Kossin, J.P.; Chung, C.; Ramanathan, V. Arabian Sea tropical cyclones intensified by emissions of black carbon and other aerosols. Nature 2011, 479, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charabi, Y.; Al-Bulooshi, A.; Al-Yahyai, S. Assessment of the impact of the meteorological meso-scale circulation on air quality in arid subtropical region. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2329–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Correlation Coefficient (r) | Eastern | Western |
|---|---|---|
| Mean temperature | −0.2573 * | 0.30 ** |
| Mean wind speed | −0.22 * | −0.47 ** |
| Mean relative humidity | 0.52 ** | 0.36 ** |
| Types | Main Pathway Regions | Percentage% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern | 1 | Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Hebei Provinces | 32.7 |
| 2 | Shanxi, Hebei Provinces | 32 | |
| 3 | Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Henan and Hebei Provinces | 35.3 | |
| Western | 1 | Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Shanxi Province | 11 |
| 2 | Inner Mongolia, Shanxi Province | 14.7 | |
| 3 | Inner Mongolia, North Shaanxi Province and Shanxi Province | 31.3 | |
| 4 | Shaanxi Province, Shanxi (South Shaanxi, Henan and Shanxi Province) | 43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X. Causes and Transmission Characteristics of the Regional PM2.5 Heavy Pollution Process in the Urban Agglomerations of the Central Taihang Mountains. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020205
Yang L, Wang G, Wang Y, Ma Y, Zhang X. Causes and Transmission Characteristics of the Regional PM2.5 Heavy Pollution Process in the Urban Agglomerations of the Central Taihang Mountains. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(2):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020205
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Luoqi, Guangjie Wang, Yegui Wang, Yongjing Ma, and Xi Zhang. 2025. "Causes and Transmission Characteristics of the Regional PM2.5 Heavy Pollution Process in the Urban Agglomerations of the Central Taihang Mountains" Atmosphere 16, no. 2: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020205
APA StyleYang, L., Wang, G., Wang, Y., Ma, Y., & Zhang, X. (2025). Causes and Transmission Characteristics of the Regional PM2.5 Heavy Pollution Process in the Urban Agglomerations of the Central Taihang Mountains. Atmosphere, 16(2), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020205









