Methodological Development for Studying the Chemical Composition of Exhaust Particle Emissions: Application to a Passenger Vessel Operating on Marine Gas Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vessel and Engine Description
2.2. Measurement Campaigns
2.3. Sampling and Exhaust Emission Measurements
- a
- At berth: engine idling;
- b
- Maneuvering in port: engine providing slight thrust to keep the ship pressed against the dock. Maneuvering while arriving or departing a port were generally very brief;
- c
- Cruising at different engine loads: the crew regulates the engine load so the ship can accelerate or decelerate depending on external conditions.
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Analytical Method
2.6. Extraction Method Optimization
2.7. Calculation of Emission Factors
- is the emission factor of species i;
- Peng is the engine power evaluated from the exhaust flow rat (Qm);
- Qv is the exhaust gas flow, in m3·h−1, calculated from Qm data obtained through post-processing of Pitot measurements (kg·h−1) and the corresponding densities (ρ, in kg·m−3), using Equation (2):
- is the sum of the emission factors of the identified species i. can be calculated from the measured pollutant emission factors () using Equation (5):
2.8. Materials
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overview of the Main Results of the Three Measurement Campaigns
3.2. Particle Emissions
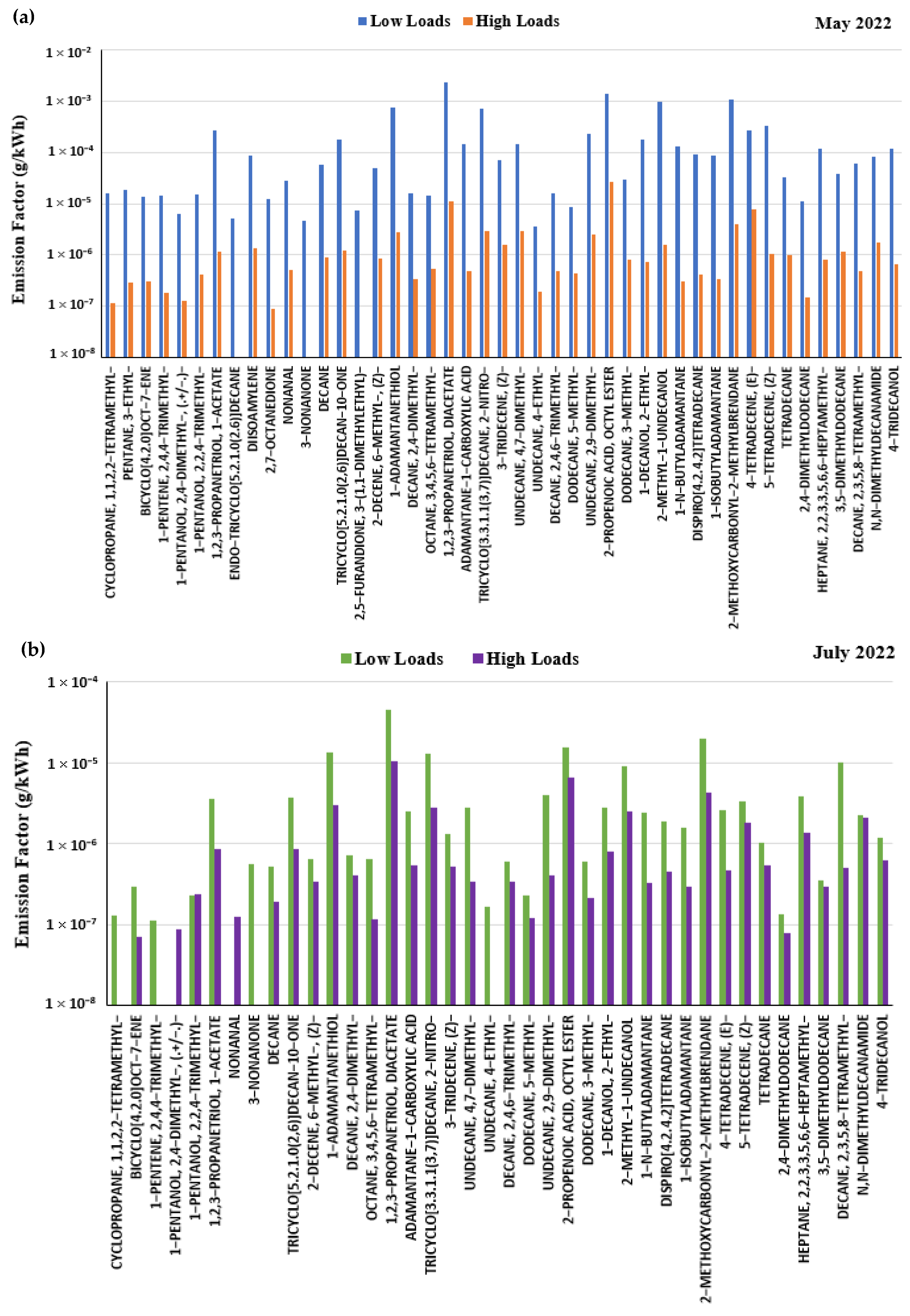
3.3. Organic Compound Emissions and Their Composition
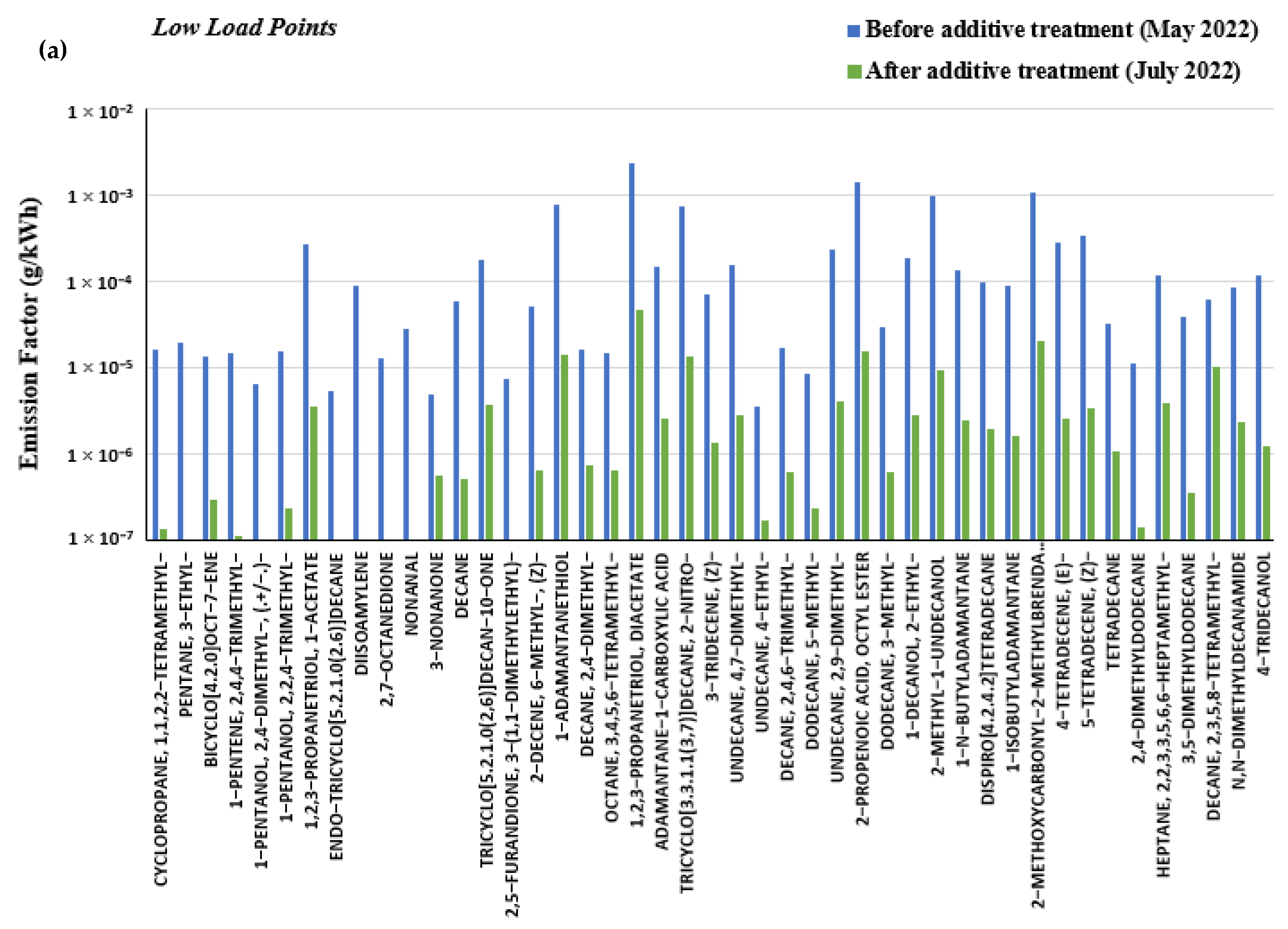
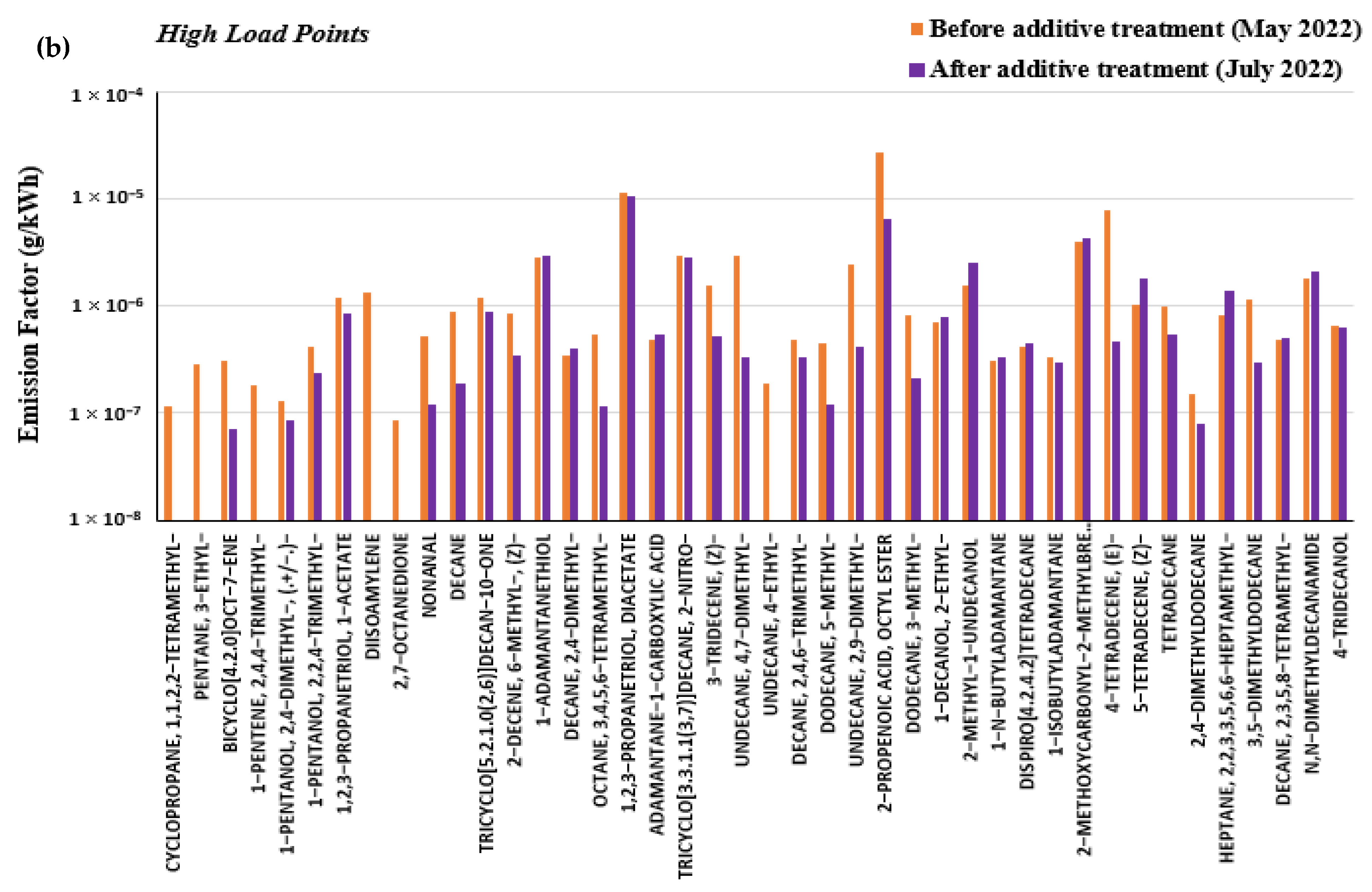
3.4. Effect of Marine Fuel Additive
3.5. Toxicity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kiliç, A.; Deniz, C. Inventory of Shipping Emissions in Izmit Gulf, Turkey. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2010, 29, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICCT (The International Council on Clean Transportation). Air Pollution and Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Ocean-Going Ships: Impacts, Mitigation Options and Opportunities for Managing Growth. Marit. Stud. 2007, 153, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Papaefthimiou, S.; Maragkogianni, A.; Andriosopoulos, K. Evaluation of Cruise Ships Emissions in the Mediterranean Basin: The Case of Greek Ports. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2016, 10, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.J.; Winebrake, J.J.; Green, E.H.; Kasibhatla, P.; Eyring, V.; Lauer, A. Mortality from Ship Emissions: A Global Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8512–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Isaksen, I.S.A.; Berntsen, T.; Collins, W.J.; Corbett, J.J.; Endresen, O.; Grainger, R.G.; Moldanova, J.; Schlager, H.; Stevenson, D.S. Transport Impacts on Atmosphere and Climate: Shipping. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4735–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivié, D.J.L.; Cariolle, D.; Teyssèdre, H.; Salas, D.; Voldoire, A.; Clark, H.; Saint-Martin, D.; Michou, M.; Karcher, F.; Balkanski, Y.; et al. Modeling the Climate Impact of Road Transport, Maritime Shipping and Aviation over the Period 1860–2100 with an AOGCM. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1449–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, M.; Jin, X.; Shang, Y.; Shindell, D.; Faluvegi, G.; Shindell, C.; He, K. Health and Climate Impacts of Ocean-Going Vessels in East Asia. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, C.J.; Quinn, P.K.; Bates, T.S.; Gilman, J.B.; Bon, D.M.; Kuster, W.C.; Prather, K.A. The Impact of Shipping, Agricultural, and Urban Emissions on Single Particle Chemistry Observed Aboard the R/V Atlantis during CalNex. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5003–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoyoglu, S.; Baltensperger, U.; Prévôt, A.S.H. Contribution of Ship Emissions to the Concentration and Deposition of Air Pollutants in Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelle, L.; Thomas, J.L.; Raut, J.-C.; Law, K.S.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Roiger, A.; Schlager, H.; Kim, J.; Reiter, A.; et al. Air Quality and Radiative Impacts of Arctic Shipping Emissions in the Summertime in Northern Norway: From the Local to the Regional Scale. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2359–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becagli, S.; Anello, F.; Bommarito, C.; Cassola, F.; Calzolai, G.; Di Iorio, T.; di Sarra, A.; Gómez-Amo, J.-L.; Lucarelli, F.; Marconi, M.; et al. Constraining the Ship Contribution to the Aerosol of the Central Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2067–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, X.; Feng, J.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X. Influence of Ship Emissions on Urban Air Quality: A Comprehensive Study Using Highly Time-Resolved Online Measurements and Numerical Simulation in Shanghai. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, J.; Silver, J.D.; Christensen, J.H.; Andersen, M.S.; Bønløkke, J.H.; Sigsgaard, T.; Geels, C.; Gross, A.; Hansen, A.B.; Hansen, K.M.; et al. Assessment of Past, Present and Future Health-Cost Externalities of Air Pollution in Europe and the Contribution from International Ship Traffic Using the EVA Model System. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7747–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broome, R.A.; Cope, M.E.; Goldsworthy, B.; Goldsworthy, L.; Emmerson, K.; Jegasothy, E.; Morgan, G.G. The Mortality Effect of Ship-Related Fine Particulate Matter in the Sydney Greater Metropolitan Region of NSW, Australia. Environ. Int. 2016, 87, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakko-Saksa, P.; Koponen, P.; Roslund, P.; Laurikko, J.; Nylund, N.-O.; Karjalainen, P.; Rönkkö, T.; Timonen, H. Comprehensive Emission Characterisation of Exhaust from Alternative Fuelled Cars. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 236, 117643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarainen, H.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; Sainio, M.; Ihantola, T.; Rönkkö, T.J.; Koponen, P.; Rönkkö, T.; Jalava, P.I. Toxicological Evaluation of Exhaust Emissions from Light-Duty Vehicles Using Different Fuel Alternatives in Sub-Freezing Conditions. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alander, T.J.A.; Leskinen, A.P.; Raunemaa, T.M.; Rantanen, L. Characterization of Diesel Particles: Effects of Fuel Reformulation, Exhaust Aftertreatment, and Engine Operation on Particle Carbon Composition and Volatility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2707–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Cappa, C.D.; Langridge, J.; Bahreini, R.; Buffaloe, G.; Brock, C.; Cerully, K.; Coffman, D.; Hayden, K.; Holloway, J.; et al. Impact of Fuel Quality Regulation and Speed Reductions on Shipping Emissions: Implications for Climate and Air Quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9052–9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Saukko, E.; Lehtoranta, K.; Rönkkö, T.; Timonen, H.; Simonen, P.; Karjalainen, P.; Keskinen, J. Particle Emissions Characterization from a Medium-Speed Marine Diesel Engine with Two Fuels at Different Sampling Conditions. Fuel 2016, 186, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, Q.; Ding, X.; Sun, J.; Li, D.; Fu, H.; Teich, M.; Ye, X.; Chen, J. Primary Particulate Matter Emitted from Heavy Fuel and Diesel Oil Combustion in a Typical Container Ship: Characteristics and Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12943–12951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyyränen, J.; Jokiniemi, J.; Kauppinen, E.I.; Joutsensaari, J. Aerosol Characterisation in Medium-Speed Diesel Engines Operating with Heavy Fuel Oils. J. Aerosol Sci. 1999, 30, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvi, A.; Fogelholm, C.-J.; Zevenhoven, R. Emissions from Large-Scale Medium-Speed Diesel Engines: 2. Influence of Fuel Type and Operating Mode. Fuel Process. Technol. 2008, 89, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A.; Weingartner, E.; Hasselbach, J.; Lauer, P.; Kurok, C.; Fleischer, F. Physical Properties, Chemical Composition, and Cloud Forming Potential of Particulate Emissions from a Marine Diesel Engine at Various Load Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3800–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Noor, C.W.; Noor, M.M.; Mamat, R. Biodiesel as Alternative Fuel for Marine Diesel Engine Applications: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, A.; Aufdenblatten, S.; Forss, A.; Mohr, M.; Burtscher, H. Particulate Emissions from a Low-Speed Marine Diesel Engine. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Malloy, Q.G.J.; Welch, W.A.; Wayne Miller, J.; Cocker, D.R. In-Use Gaseous and Particulate Matter Emissions from a Modern Ocean Going Container Vessel. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5504–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Welch, W.A.; Miller, J.W.; Cockert, D.R. Emission Measurements from a Crude Oil Tanker at Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7098–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.M.; Agrawal, H.; Sorooshian, A.; Padró, L.T.; Gates, H.; Hersey, S.; Welch, W.A.; Lung, H.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D.R.; et al. Comprehensive Simultaneous Shipboard and Airborne Characterization of Exhaust from a Modern Container Ship at Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4626–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldanová, J.; Fridell, E.; Popovicheva, O.; Demirdjian, B.; Tishkova, V.; Faccinetto, A.; Focsa, C. Characterisation of Particulate Matter and Gaseous Emissions from a Large Ship Diesel Engine. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2632–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endresen, Ø.; Bakke, J.; Sørgård, E.; Flatlandsmo Berglen, T.; Holmvang, P. Improved Modelling of Ship SO2 Emissions—A Fuel-Based Approach. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3621–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henein, N.A. Analysis of Pollutant Formation and Control and Fuel Economy in Diesel Engines. Progress Energy Combust. Sci. 1976, 1, 165–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Chen, L.; Hong, G.; Yan, F.; Dong, S. Modeling Study of Soot Formation and Oxidation in DI Diesel Engine Using an Improved Soot Model. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 62, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtoranta, K.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; Vesala, H.; Järvinen, A.; Peitz, D.; Jokiluoma, J. Reducing Particle Emissions from Marine Engines—Fuel Choices and Technology Pathways: 30th CIMAC Congress 2023. In Proceedings of the 30th CIMAC World Congress, Busan, Republic of Korea, 12–16 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ristovski, Z.D.; Miljevic, B.; Surawski, N.C.; Morawska, L.; Fong, K.M.; Goh, F.; Yang, I.A. Respiratory Health Effects of Diesel Particulate Matter. Respirology 2012, 17, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aakko-Saksa, P.T.; Lehtoranta, K.; Kuittinen, N.; Järvinen, A.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johnson, K.; Jung, H.; Ntziachristos, L.; Gagné, S.; Takahashi, C.; et al. Reduction in Greenhouse Gas and Other Emissions from Ship Engines: Current Trends and Future Options. Progress Energy Combust. Sci. 2023, 94, 101055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofiev, M.; Winebrake, J.J.; Johansson, L.; Carr, E.W.; Prank, M.; Soares, J.; Vira, J.; Kouznetsov, R.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Corbett, J.J. Cleaner Fuels for Ships Provide Public Health Benefits with Climate Tradeoffs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmer, N.; Comer, B.; Roy, B.; Mao, X.; Rutherford, D. Greenhouse Gas. Emissions from Global Shipping, 2013–2015 Detailed Methodology; International Council on Clean Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, J.; Zhong, B.-J. Soot in Diesel Combustion Systems. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2006, 29, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalde-Santiago, V.; Bailón-García, E.; Davó-Quiñonero, A.; Lozano-Castelló, D.; Bueno-López, A. Three-Dimensionally Ordered Macroporous PrOx: An Improved Alternative to Ceria Catalysts for Soot Combustion. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 248, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadikolaei, M.A.; Yung, K.-F.; Cheung, C.S.; Lau, P.-C. Chemical Properties and Composition of PM Emitted from a Diesel Engine Fueled with Ternary Fuel (Diesel-Biodiesel-Ethanol) in Blended and Fumigation Modes. Fuel 2019, 251, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockhorn, H. (Ed.) Soot Formation in Combustion: Mechanisms and Models; Springer Series in Chemical Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; Volume 59, ISBN 978-3-642-85169-8. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, H.; Howard, J.B. Formation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Growth to Soot—A Review of Chemical Reaction Pathways. Progress Energy Combust. Sci. 2000, 26, 565–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tree, D.R.; Svensson, K.I. Soot Processes in Compression Ignition Engines. Progress Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 272–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvarborna, H.; Kumar, A.; Kim, D.-S. Recent Studies on Soot Modeling for Diesel Combustion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 48, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaqiang, E.; Xu, W.; Ma, Y.; Tan, D.; Peng, Q.; Tan, Y.; Chen, L. Soot Formation Mechanism of Modern Automobile Engines and Methods of Reducing Soot Emissions: A Review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 235, 107373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, S.; Tan, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, B. A Review of the Development and Application of Soot Modelling for Modern Diesel Engines and the Soot Modelling for Different Fuels. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 178, 836–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Maritime Organization. Third IMO GHG Study 2014 Executive Summary and Final Report; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2014; Available online: https://greenvoyage2050.imo.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/third-imo-ghg-study-2014-executive-summary-and-final-report.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Winkel, R.; Weddige, U.; Johnsen, D.; Hoen, V.; Papaefthimiou, S. Shore Side Electricity in Europe: Potential and Environmental Benefits. Energy Policy 2016, 88, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestl, T.; Løvoll, G.; Stensrud, E.; Le Breton, A. The Doubtful Environmental Benefit of Reduced Maximum Sulfur Limit in International Shipping Fuel. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6098–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtoranta, K.; Kuittinen, N.; Vesala, H.; Koponen, P. Methane Emissions from a State-of-the-Art LNG-Powered Vessel. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y. Strategies for Promoting Biodiesel Use in Marine Vessels. Mar. Policy 2013, 40, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, A.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Mohd Nor, S.H.; Mat, R.; Hashim, H.; Ahmad, A.; Yamani Zakaria, Z.; Tuan Abdullah, T.A. The Challenges and Prospects of Palm Oil Based Biodiesel in Malaysia. Energy 2015, 81, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharma, S.; Masjuki, H.H.; Ong, H.C.; Sebayang, A.H.; Silitonga, A.S.; Kusumo, F.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Optimization of Biodiesel Production Process for Mixed Jatropha Curcas–Ceiba Pentandra Biodiesel Using Response Surface Methodology. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 115, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Wang, X.; Li, H. A Review on Regulations, Current Status, Effects and Reduction Strategies of Emissions for Marine Diesel Engines. Fuel 2020, 279, 118477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, M.; Ellis, J.; Lundgren, J.; Landälv, I. Renewable Methanol as a Fuel for the Shipping Industry. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Duan, S.; Sun, P. Comparative Analysis between Natural Gas/Diesel (Dual Fuel) and Pure Diesel on the Marine Diesel Engine. J. Eng. Res. 2015, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afon, Y.; Ervin, D. An Assessment of Air Emissions from Liquefied Natural Gas Ships Using Different Power Systems and Different Fuels. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2008, 58, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Yang, J.; Corbin, J.; Trivanovic, U.; Lobo, P.; Kirchen, P.; Rogak, S.; Gagné, S.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D. Comprehensive Analysis of the Air Quality Impacts of Switching a Marine Vessel from Diesel Fuel to Natural Gas. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grönholm, T.; Mäkelä, T.; Hatakka, J.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Kuula, J.; Laurila, T.; Laakso, L.; Kukkonen, J. Evaluation of Methane Emissions Originating from LNG Ships Based on the Measurements at a Remote Marine Station. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 13677–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagin, Y.V.Z. and S.V. Enhancing Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Specifications of a Marine Diesel When Using Fuel Additives. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Choi, J.H. Comparison of Fuel Consumption and Emission Characteristics of Various Marine Heavy Fuel Additives. Appl. Energy 2016, 179, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.C.; Opris, C.N.; Baumgard, K.J.; Johnson, J.H. A Study of the Regeneration Process in Diesel Particulate Traps Using a Copper Fuel Additive; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, B.; Siebers, D.; Mueller, C.; Aradi, A. Effects of an Ignition-Enhancing, Diesel-Fuel Additive on Diesel-Spray Evaporation, Mixing, Ignition, and Combustion. In Symposium (International) on Combustion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 27, pp. 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerry, E.S.; Raihan, M.S.; Srinivasan, K.K.; Krishnan, S.R.; Sohail, A. Injection Timing Effects on Partially Premixed Diesel–Methane Dual Fuel Low Temperature Combustion. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, J.M.; Peter-Hoblyn, J.D.; Acres, G.K. Emissions Reduction and Improved Fuel Economy Performance from a Bimetallic Platinum/Cerium Diesel Fuel Additive at Ultra-Low Dose Rates; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Nam, J.; Lee, D. A Study on the Variation of Physical & Chemical Properties with Refining Treatment and Additive Mixture for Marine Fuel Oil. Engineering, Environmental Science. 2007. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:106765195 (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Babushok, V.I.; Tsang, W.; McNesby, K.L. Additive Influence on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Formation. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2002, 29, 2315–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrozo, V.B.; May, I.; Dalla Nora, M.; Cairns, A.; Zhao, H. Experimental Analysis of Ethanol Dual-Fuel Combustion in a Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine: An Optimisation at Low Load. Appl. Energy 2016, 165, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Ouyang, M. Dieseline Fueled Flexible Fuel Compression Ignition Engine Control Based on In-Cylinder Pressure Sensor. Appl. Energy 2015, 159, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, W.M.; An, H.; Chou, S.K. Modeling on Blend Gasoline/Diesel Fuel Combustion in a Direct Injection Diesel Engine. Appl. Energy 2015, 160, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Qiao, L.; Jing, S.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, S.; Ma, Y.; Lou, S.; et al. Emission Factors of Particulate and Gaseous Compounds from a Large Cargo Vessel Operated under Real-World Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celo, V.; Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E.; McCurdy, M. Chemical Characterization of Exhaust Emissions from Selected Canadian Marine Vessels: The Case of Trace Metals and Lanthanoids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5220–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sippula, O.; Stengel, B.; Sklorz, M.; Streibel, T.; Rabe, R.; Orasche, J.; Lintelmann, J.; Michalke, B.; Abbaszade, G.; Radischat, C.; et al. Particle Emissions from a Marine Engine: Chemical Composition and Aromatic Emission Profiles under Various Operating Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11721–11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnes, H.; Fridell, E. Particle Emissions from Ships: Dependence on Fuel Type. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Welch, W.A.; Henningsen, S.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker III, D.R. Emissions from Main Propulsion Engine on Container Ship at Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldanová, J.; Fridell, E.; Winnes, H.; Holmin-Fridell, S.; Boman, J.; Jedynska, A.; Tishkova, V.; Demirdjian, B.; Joulie, S.; Bladt, H.; et al. Physical and Chemical Characterisation of PM Emissions from Two Ships Operating in European Emission Control Areas. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3577–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu-Van, T.; Ristovski, Z.; Pourkhesalian, A.M.; Rainey, T.; Garaniya, V.; Abbassi, R.; Jahangiri, S.; Enshaei, H.; Kam, U.-S.; Kimball, R.; et al. On-Board Measurements of Particle and Gaseous Emissions from a Large Cargo Vessel at Different Operating Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Salo, K.; Hallquist, Å.M.; Fridell, E. Characterization of Particles from a Marine Engine Operating at Low Loads. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, A.A.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Orasche, J.; Abbaszade, G.; Lintelmann, J.; Arteaga-Salas, J.M.; Stengel, B.; Rabe, R.; Harndorf, H.; Sippula, O.; et al. Gas Phase Carbonyl Compounds in Ship Emissions: Differences between Diesel Fuel and Heavy Fuel Oil Operation. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzani Lööv, J.M.; Alfoldy, B.; Beecken, J.; Berg, N.; Berkhout, A.J.C.; Duyzer, J.; Gast, L.F.L.; Hjorth, J.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Lagler, F.; et al. Field Test of Available Methods to Measure Remotely SO2 and NOX Emissions from Ships. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2013, 6, 9735–9782. [Google Scholar]
- Westerlund, J.; Hallquist, M.; Hallquist, Å.M. Characterization of Fleet Emissions from Ships through Multi-Individual Determination of Size-Resolved Particle Emissions in a Coastal Area. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alföldy, B.; Lööv, J.B.; Lagler, F.; Mellqvist, J.; Berg, N.; Beecken, J.; Weststrate, H.; Duyzer, J.; Bencs, L.; Horemans, B.; et al. Measurements of Air Pollution Emission Factors for Marine Transportation in SECA. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.A. Exhaust Emissions from Ships at Berth. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3817–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrooten, L.; De Vlieger, I.; Panis, L.I.; Chiffi, C.; Pastori, E. Emissions of Maritime Transport: A European Reference System. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Lou, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Matthias, V. Emission Factors for Gaseous and Particulate Pollutants from Offshore Diesel Engine Vessels in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6319–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Feng, Y.; Shang, Y.; Yang, X.; Gao, H.; Tian, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; et al. Real-World Emission Factors of Gaseous and Particulate Pollutants from Marine Fishing Boats and Their Total Emissions in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4910–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Cui, M.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Tian, C.; Matthias, V.; et al. Emission Factors and Environmental Implication of Organic Pollutants in PM Emitted from Various Vessels in China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagot, B. CAPNAV: CAractérisation des Émissions Particulaires des NAVires-Application à des Navires à Passagers. 2023, Volume 81. Available online: https://librairie.ademe.fr/mobilite-et-transports/6685-caracterisation-des-emissions-particulaires-des-navires-application-a-des-navires-a-passagers.html (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Chen, L.; Song, D.; Tian, Y.; Ding, L.; Yu, A.; Zhang, H. Application of On-Line Microwave Sample-Preparation Techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, W.F.; Hildemann, L.M.; Mazurek, M.A.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Sources of Fine Organic Aerosol. 2. Noncatalyst and Catalyst-Equipped Automobiles and Heavy-Duty Diesel Trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevron. Diesel Fuels Technical Review (FTR-2); Chevron Products Company: San Ramon, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, J.J.; Kleeman, M.J.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Measurement of Emissions from Air Pollution Sources. 2. C1 through C30 Organic Compounds from Medium Duty Diesel Trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, B.; Campbell, D.; Lawson, D.R.; Ireson, R.G.; Weaver, C.S.; Hesterberg, T.W.; Larson, T.; Davey, M.; Liu, L.-J.S. Detailed Characterization and Profiles of Crankcase and Diesel Particular Matter Exhaust Emissions Using Speciated Organics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5661–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-T.; Kim, K.-H.; Jung, K.; Bell, M.L. Characterization of Fine Particulate Matter and Associations between Particulate Chemical Constituents and Mortality in Seoul, Korea. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Ho, K.; Louie, P.K.K.; Qiu, H.; Pun, V.C.; Kan, H.; Yu, I.T.S.; Wong, T.W. Shipping Emissions Associated with Increased Cardiovascular Hospitalizations. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
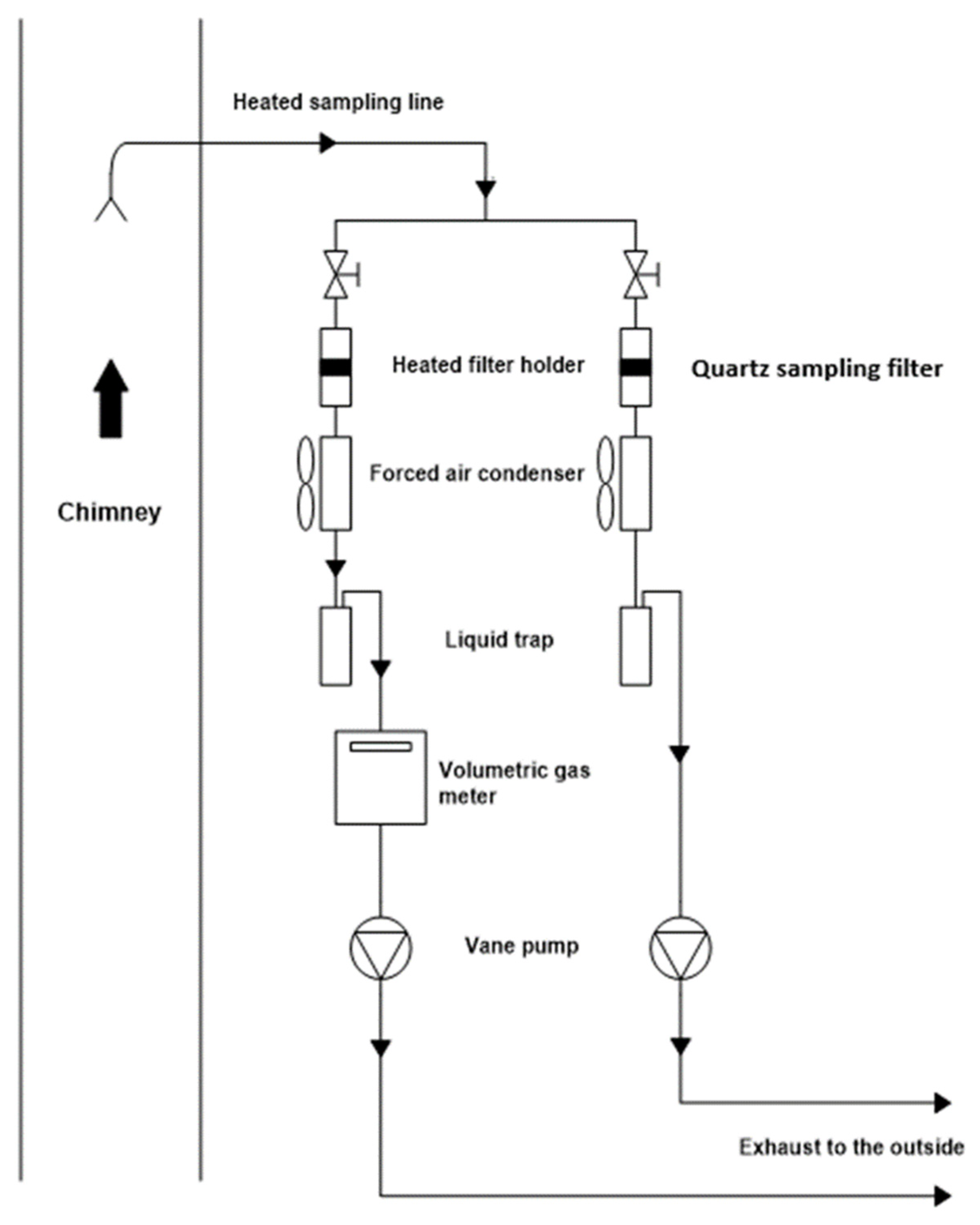

| Specifications | Port Engine |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | ABC, Anglo Belgium Corporation |
| Model | 8 DZC-1000-166-A |
| Type | Straight-eight engine 4-stroke turbocharged diesel cycle mechanical direct injection one injector pump per cylinder |
| Rated speed | 1000 rpm |
| Nominal power | 1650 kW |
| Test cycle | E3 |
| NOX emission value | E3 = 7.6 g/kWh |
| Measurement Campaign | July 2021 | May 2022 | July 2022 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine load (Low/High) | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High |
| Operation mode | At berth, departure, arrival | Cruising | At berth, departure, arrival | Cruising | At berth, departure, arrival | Cruising |
| Average exhaust mass flow rate (kg/h) | 3218 (±2426) | 10,212 (±1300) | 2923 (±1637) | 9993 (±2039) | 5403 (±1243) | 13,137 (±1173) |
| Average exhaust gas flow rate (m3/h) | 4593 (±3463) | 16,806 (±2139) | 4060 (±2274) | 16,560 (±3379) | 8273 (±1903) | 21,641 (±1932) |
| Average engine power (kW) | 48.5 (±37) | 1071.8 (±136) | 5.4 (±3) | 1039.8 (±212) | 368.2 (±85) | 1499.7 (±134) |
| Total mass of soot (mg) | nd | nd | 53 (±0.1) | 25 (±0.1) | 47.5 (±0.1) | 22.6 (±0.1) |
| Sampled gas volume (m3) | nd | nd | 14.1 | 13.6 | 11.8 | 17.2 |
| (µg/kWh) | nd | nd | 10,200 (±5713) | 84.2 (±17) | 169.1 (±39) | 44.0 (±4) |
| (µg/kWh) | nd | nd | 97,328 (±54,510) | 414 (±84) | 1738 (±400) | 597 (±53) |
| (g/kWh) | nd | nd | 2.83 (±1.590) | 0.03 (±0.006) | 0.09 (±0.021) | 0.02 (±0.002) |
| Number of detected OCs | 315 | 166 | 267 | 237 | 315 | 302 |
| Number of identified OCs | 30 | 30 | 45 | 42 | 38 | 36 |
| Identification rate (wt.%) | 7.1 | 4.4 | 10.5 | 20.3 | 9.7 | 7.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahi, R.; Joubert, A.; Villot, A.; Sagot, B.; Le Coq, L. Methodological Development for Studying the Chemical Composition of Exhaust Particle Emissions: Application to a Passenger Vessel Operating on Marine Gas Oil. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020126
Mahi R, Joubert A, Villot A, Sagot B, Le Coq L. Methodological Development for Studying the Chemical Composition of Exhaust Particle Emissions: Application to a Passenger Vessel Operating on Marine Gas Oil. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(2):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020126
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahi, Ridha, Aurélie Joubert, Audrey Villot, Benoit Sagot, and Laurence Le Coq. 2025. "Methodological Development for Studying the Chemical Composition of Exhaust Particle Emissions: Application to a Passenger Vessel Operating on Marine Gas Oil" Atmosphere 16, no. 2: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020126
APA StyleMahi, R., Joubert, A., Villot, A., Sagot, B., & Le Coq, L. (2025). Methodological Development for Studying the Chemical Composition of Exhaust Particle Emissions: Application to a Passenger Vessel Operating on Marine Gas Oil. Atmosphere, 16(2), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020126








