Mortality Burden Attributed to the Synergy Between Human Bio-Climate and Air Quality Extremes in a Climate Change Hotspot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Mortality, Air Quality and Human Thermal Bioclimate Data
2.3. GAM Modelling Framework
2.4. Attributable Fraction
3. Results
3.1. Observations on Population Dynamics, Mortality Trends, and Statistical Confidence
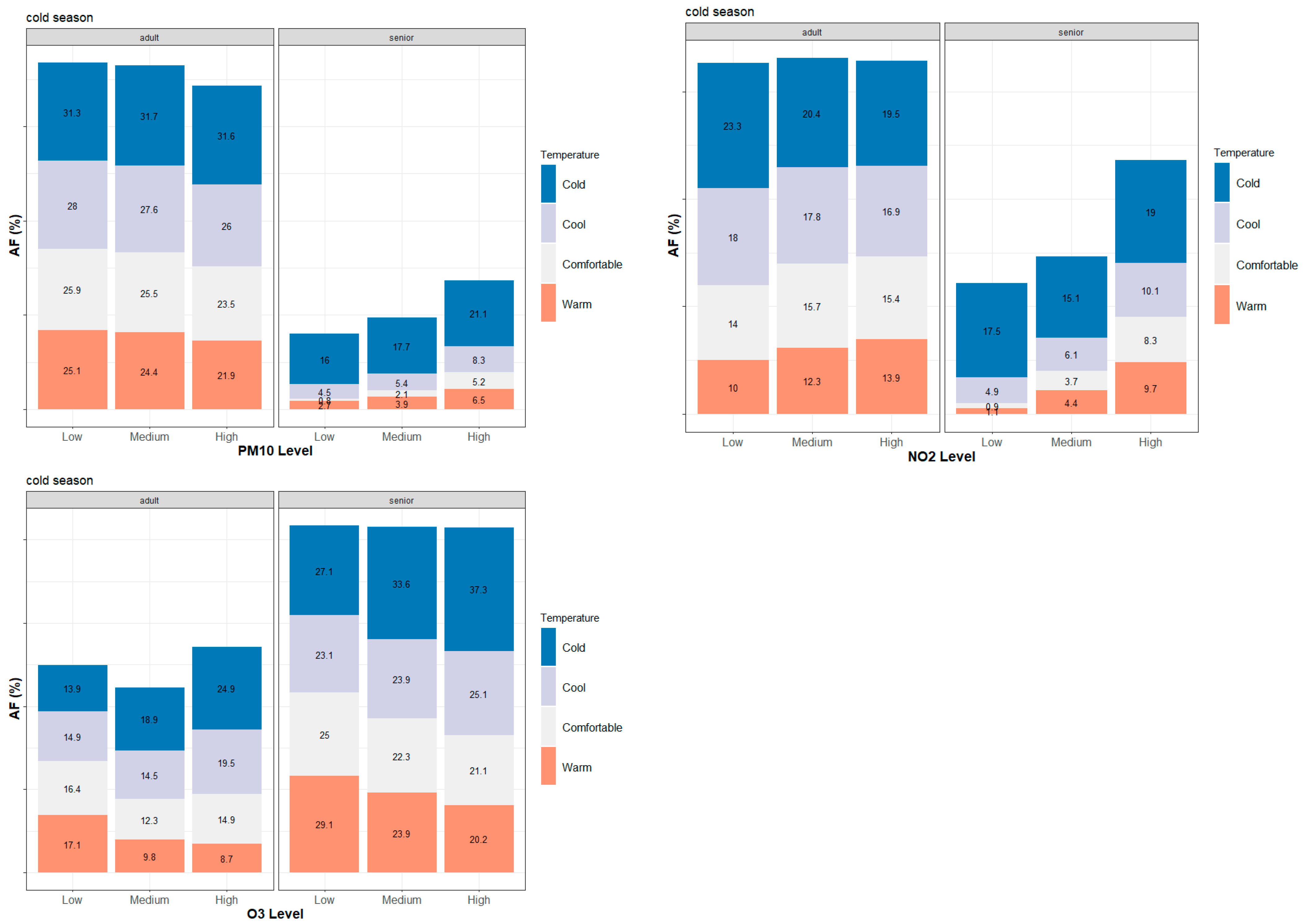
3.2. Seasonal and Age-Specific Patterns of Attributable Mortality Fractions
3.3. Intra-Urban Differences in Attributable Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Attributable Fraction |
| DLNM | Distributed Lag Non-Linear Models |
| GAM | Generalized Additive Model |
| mPET | Modified Physiologically Equivalent Temperature |
| REML | Restricted Maximum Likelihood |
| TUA | Thessaloniki Urban Area |
Appendix A
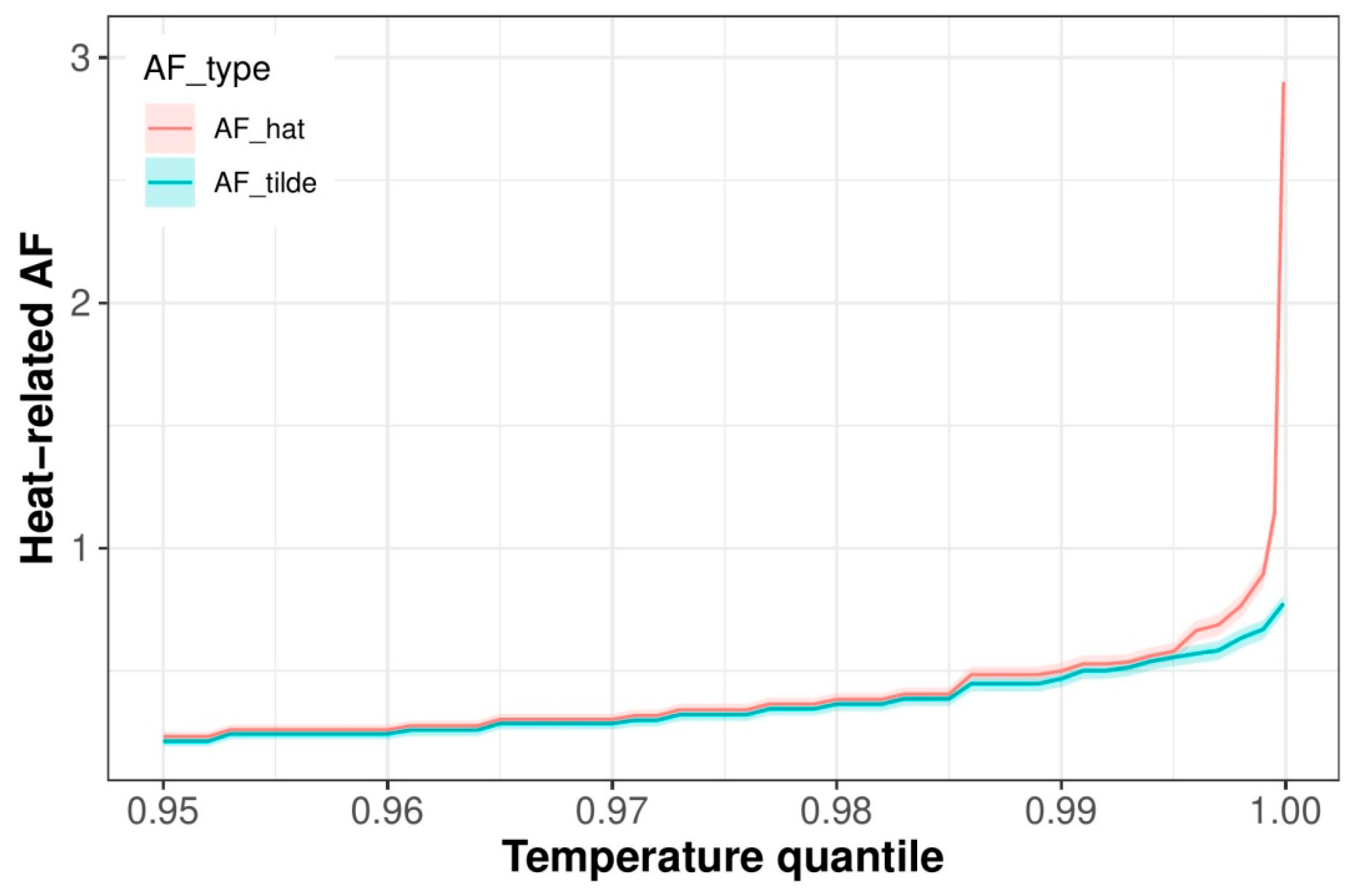
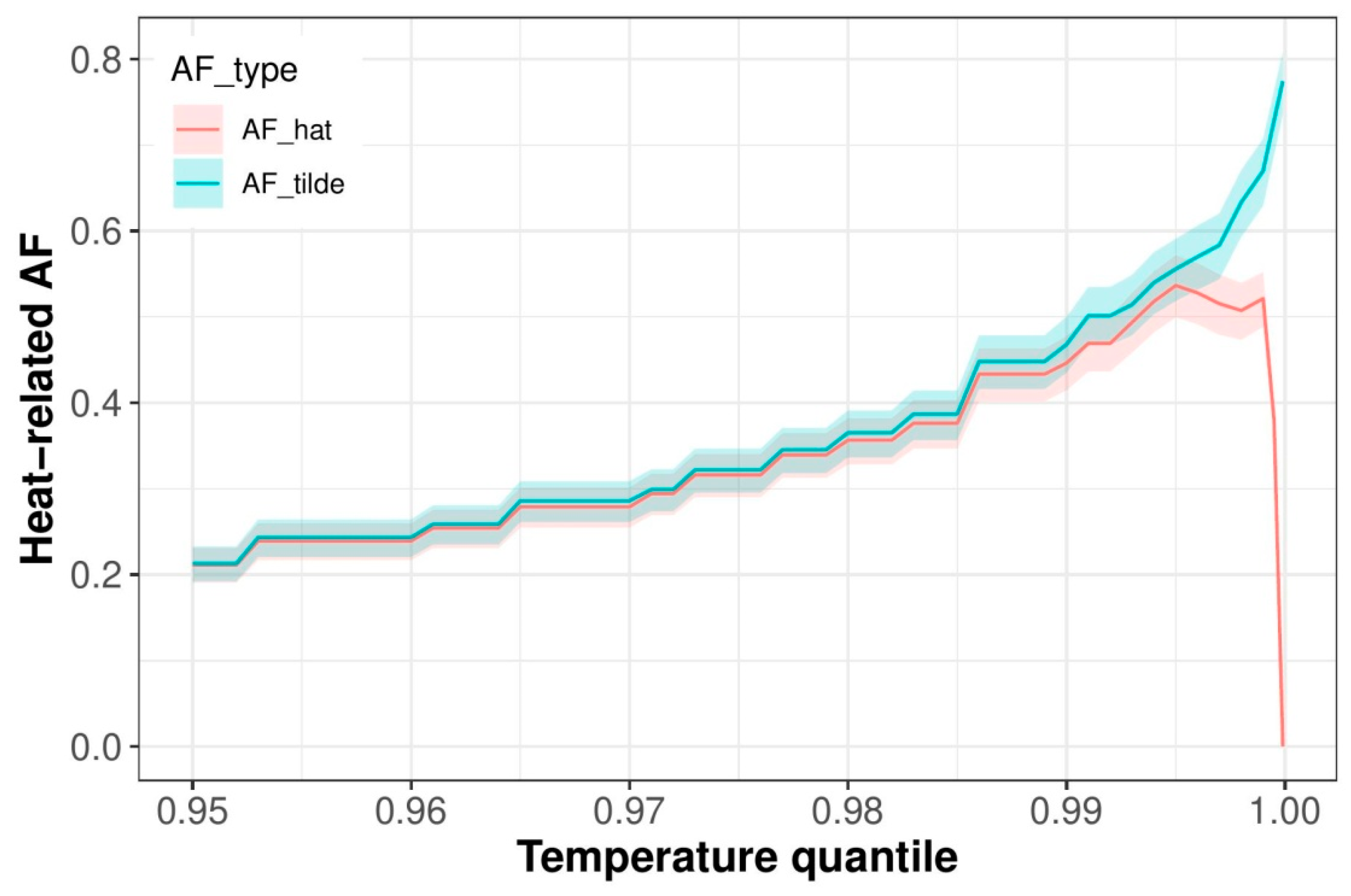
References
- Lazoglou, G.; Papadopoulos-Zachos, A.; Georgiades, P.; Zittis, G.; Velikou, K.; Manios, E.M.; Anagnostopoulou, C. Identification of climate change hotspots in the Mediterranean. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founda, D.; Pierros, F.; Katavoutas, G.; Keramitsoglou, I. Observed trends in thermal stress at european cities with different background climates. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulias, A.K.; Akritidis, D.; Kalisoras, A.; Kapsomenakis, J.; Melas, D.; Zerefos, C.S.; Zanis, P. Climate change projections for Greece in the 21st century from high-resolution EURO-CORDEX RCM simulations. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271, 106049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppas, S.; Parliari, D.; Kontos, S.; Poupkou, A.; Papadogiannaki, S.; Tzoumaka, P.; Kelessis, A.; Dimitrios, M. Urban Heat Island and Future Projections: A Study in Thessaloniki, Greece. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Environmental Protection and Disaster Risks (ENVIRORISK 2020), Sofia, Bulgaria, 29–30 September 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamnisos, D.; Giannakou, K.; Jakovljevic, M. Demographic forecasting of population aging in Greece and Cyprus: One big challenge for the Mediterranean health and social system long-term sustainability. Health Res. Policy Syst. 2021, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriopoulos, I.; Athanasakis, K.; Tsoli, S.; Mossialos, E.; Papanicolas, I. Addressing public health and health system challenges in Greece: Reform priorities in a changing landscape. Lancet Public Health 2025, 10, e794–e803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekeri, E.; Kolokotsa, D.; Santamouris, M. On the association of ambient temperature and elderly mortality in a Mediterranean island—Crete. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environmental Agency. Air Quality Status Report 2025; European Environmental Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2025; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/publications/air-quality-status-report-2025 (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Akritidis, D.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Steffens, B.; Pozzer, A.; Zanis, P. The future health burden of air pollution in Greece and the associated drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 994, 179897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psistaki, K.; Kouis, P.; Michanikou, A.; Yiallouros, P.K.; Papatheodorou, S.I.; Paschalidou, A.Κ. Temporal trends in temperature-related mortality and evidence for maladaptation to heat and cold in the Eastern Mediterranean region. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 943, 173899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafoggia, M.; Michelozzi, P.; Schneider, A.; Armstrong, B.; Scortichini, M.; Rai, M.; Achilleos, S.; Alahmad, B.; Analitis, A.; Åström, C.; et al. Joint effect of heat and air pollution on mortality in 620 cities of 36 countries. Environ. Int. 2023, 181, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, E.; Quijal-Zamorano, M.; Turrubiates, R.F.M.; Tonne, C.; Basagaña, X.; Achebak, H.; Ballester, J. Heat-related mortality in Europe during 2023 and the role of adaptation in protecting health. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 3101–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loupa, G.; Kryona, Z.P.; Pantelidou, V.; Rapsomanikis, S. Are PM2.5 in the atmosphere of a small city a threat for health? Sustainability 2021, 13, 11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomenko, S.; Cirach, M.; Pereira-Barboza, E.; Mueller, N.; Barrera-Gómez, J.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Hoek, G.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Premature mortality due to air pollution in European cities: A health impact assessment. Lancet Planet Health 2021, 5, e121–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Han, W.; Wang, Y.; Aunan, K.; Pan, X.; Huang, J.; Li, G. Does air pollution modify temperature-related mortality? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2021, 210, 112898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Stafoggia, M.; De’Donato, F.; Scortichini, M.; Zafeiratou, S.; Fernandez, L.V.; Zhang, S.; Katsouyanni, K.; Samoli, E.; Rao, S.; et al. Heat-related cardiorespiratory mortality: Effect modification by air pollution across 482 cities from 24 countries. Environ. Int. 2023, 174, 107825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-N.; Chou, C.C.-K.; Matzarakis, A. Concepts and new implements for modified physiologically equivalent temperature. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Matzarakis, A. Modified physiologically equivalent temperature—Basics and applications for western European climate. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2018, 132, 1275–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannaros, C.; Galanaki, E.; Agathangelidis, I. Climatology and long-term trends in population exposure to urban heat stress considering variable demographic and thermo–physiological attributes. Climate 2024, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannaros, C.; Economou, T.; Parliari, D.; Galanaki, E.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K.; Matzarakis, A. A thermo-physiologically consistent approach for studying the heat-health nexus with hierarchical generalized additive modelling: Application in Athens urban area (Greece). Urban Clim. 2024, 58, 102206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Region of Central Macedonia. Air Quality Action Plan of Central Macedonia, Greece; Region of Central Macedonia: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kalogeropoulos, K.; Fragkopoulos, D.; Andreopoulos, P.; Tragaki, A. Shifting sands: Examining and mapping the population structure of Greece through the last three censuses. Economies 2024, 12, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, A.; Foscolou, A.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Thodis, A.; Kouris-Blazos, A.; Brazionis, L.; Sidossis, A.C.; Polychronopoulos, E.A.; Kokkinos, P.; Panagiotakos, D.; et al. Successful aging and lifestyle comparison of Greeks living in Greece and abroad: The epidemiological Mediterranean Islands Study (MEDIS). Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2021, 97, 104523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Progiou, A.; Liora, N.; Sebos, I.; Chatzimichail, C.; Melas, D. Measures and Policies for Reducing PM Exceedances through the Use of Air Quality Modeling: The Case of Thessaloniki, Greece. Sustainability 2023, 15, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyrichidou, I.; Balis, D.; Koukouli, M.E.; Drosoglou, T.; Bais, A.; Gratsea, M.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Liora, N.; Poupkou, A.; Giannaros, C.; et al. Adverse results of the economic crisis: A study on the emergence of enhanced formaldehyde (HCHO) levels seen from satellites over Greek urban sites. Atmos. Res. 2019, 224, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizos, K.; Meleti, C.; Kouvarakis, G.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Melas, D. Determination of the background pollution in the Eastern Mediterranean applying a statistical clustering technique. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 276, 119067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannaros, C.; Agathangelidis, I.; Galanaki, E.; Cartalis, C.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K.; Giannaros, T.M.; Matzarakis, A. Hourly values of an advanced human-biometeorological index for diverse populations from 1991 to 2020 in Greece. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzarakis, A.; Rutz, F.; Mayer, H. Modelling radiation fluxes in simple and complex environments—Application of the RayMan model. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2007, 51, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2011, 73, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Economou, T.; Parliari, D.; Tobias, A.; Dawkins, L.; Steptoe, H.; Sarran, C.; Stoner, O.; Lowe, R.; Lelieveld, J. Flexible distributed lag models for count data using mgcv. Am. Stat. 2025, 79, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, Y.; Kondo, M.; McGregor, G.; Kim, H.; Guo, Y.-L.; Hijioka, Y.; Yoshikawa, M.; Oka, K.; Takano, S.; Hales, S.; et al. Heat-related mortality risk model for climate change impact projection. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2014, 19, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparrini, A.; Leone, M. Attributable risk from distributed lag models. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglan, A.; Synn, A.J.; Nurhussien, L.; Chen, K.; Scheerens, C.; Koutrakis, P.; Coull, B.; Rice, M.B. Personal and community-level exposure to air pollution and daily changes in respiratory symptoms and oxygen saturation among adults with COPD. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2023, 6, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, W.; Mfarrej, M.F.B.; Saleem, M.H.; Khan, K.A.; Ma, J.; Raposo, A.; Han, H. Breathing in danger: Understanding the multifaceted impact of air pollution on health impacts. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 280, 116532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.Y.; Tan, A.X.; Nadeau, K.C.; Odden, M.C. Aging hearts in a hotter, more turbulent world: The impacts of climate change on the cardiovascular health of older adults. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2022, 24, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, R.D.; Akerman, A.P.; Notley, S.R.; McGinn, R.; Poirier, P.; Gosselin, P.; Kenny, G.P. Physiological factors characterizing heat-vulnerable older adults: A narrative review. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastl, C.; Arnberger, A.; Gallistl, V.; Stein, V.K.; Dorner, T.E. Heat vulnerability: Health impacts of heat on older people in urban and rural areas in Europe. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2024, 136, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalt, E.W.; Curl, C.L.; Allen, R.W.; Cohen, M.; Adar, S.D.; Stukovsky, K.H.; Avol, E.; Castro-Diehl, C.; Nunn, C.; Mancera-Cuevas, K.; et al. Time–location patterns of a diverse population of older adults: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis and air pollution (MESA Air). J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepeis, N.E.; Nelson, W.C.; Ott, W.R.; Robinson, J.P.; Tsang, A.M.; Switzer, P.; Behar, J.V.; Hern, S.C.; Engelmann, W.H. The national human activity pattern survey (NHAPS): A resource for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoussaïd, T.; Coll, I.; Charreire, H.; Makni, I.; Costes, M.; Etuman, A.E. Reassessing air pollution exposure: How daily mobility and activities shape individual risk in greater Paris. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2025, 122, 102340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parliari, D.; Economou, T.; Giannaros, C.; Kushta, J.; Melas, D.; Matzarakis, A.; Lelieveld, J. A comprehensive approach for assessing synergistic impact of air quality and thermal conditions on mortality: The case of Thessaloniki, Greece. Urban Clim. 2024, 56, 102088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anenberg, S.C.; Haines, S.; Wang, E.; Nassikas, N.; Kinney, P.L. Synergistic health effects of air pollution, temperature, and pollen exposure: A systematic review of epidemiological evidence. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; McConnell, R.; Schlaerth, H.; Ko, J.; Silva, S.; Lurmann, F.W.; Palinkas, L.; Johnston, J.; Hurlburt, M.; Yin, H.; et al. The effects of coexposure to extremes of heat and particulate air pollution on mortality in California: Implications for climate change. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Breitner, S.; Stafoggia, M.; Donato, F.D.; Samoli, E.; Zafeiratou, S.; Katsouyanni, K.; Rao, S.; Palomares, A.D.-L.; Gasparrini, A.; et al. Effect modification of air pollution on the association between heat and mortality in five European countries. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, E.S.; Cleland, S.E.; McVea, D.; Stafoggia, M.; Henderson, S.B. The synergistic effects of PM2.5 and high temperature on community mortality in British Columbia. npj Clean Air 2025, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.P.; Harris, M.H.; Apte, J.S.; Marshall, J.D. National and intraurban air pollution exposure disparity estimates in the united states: Impact of data-aggregation spatial scale. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brekel, L.v.D.; Lenters, V.; Mackenbach, J.D.; Hoek, G.; Wagtendonk, A.; Lakerveld, J.; E Grobbee, D.E.; Vaartjes, I. Ethnic and socioeconomic inequalities in air pollution exposure: A cross-sectional analysis of nationwide individual-level data from the Netherlands. Lancet Planet Health 2024, 8, e18–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentschler, J.; Leonova, N. Air Pollution Kills–Evidence from a Global Analysis of Exposure and Poverty. World Bank Blogs, 2022. Available online: https://blogs.worldbank.org/en/developmenttalk/air-pollution-kills-evidence-global-analysis-exposure-and-poverty?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 31 October 2025).
- Tobias, A.; Ng, C.F.S.; Kim, Y.; Hashizume, M.; Madaniyazi, L. Compilation of open access time-series datasets for studying temperature-mortality association. Data Brief 2024, 55, 110694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
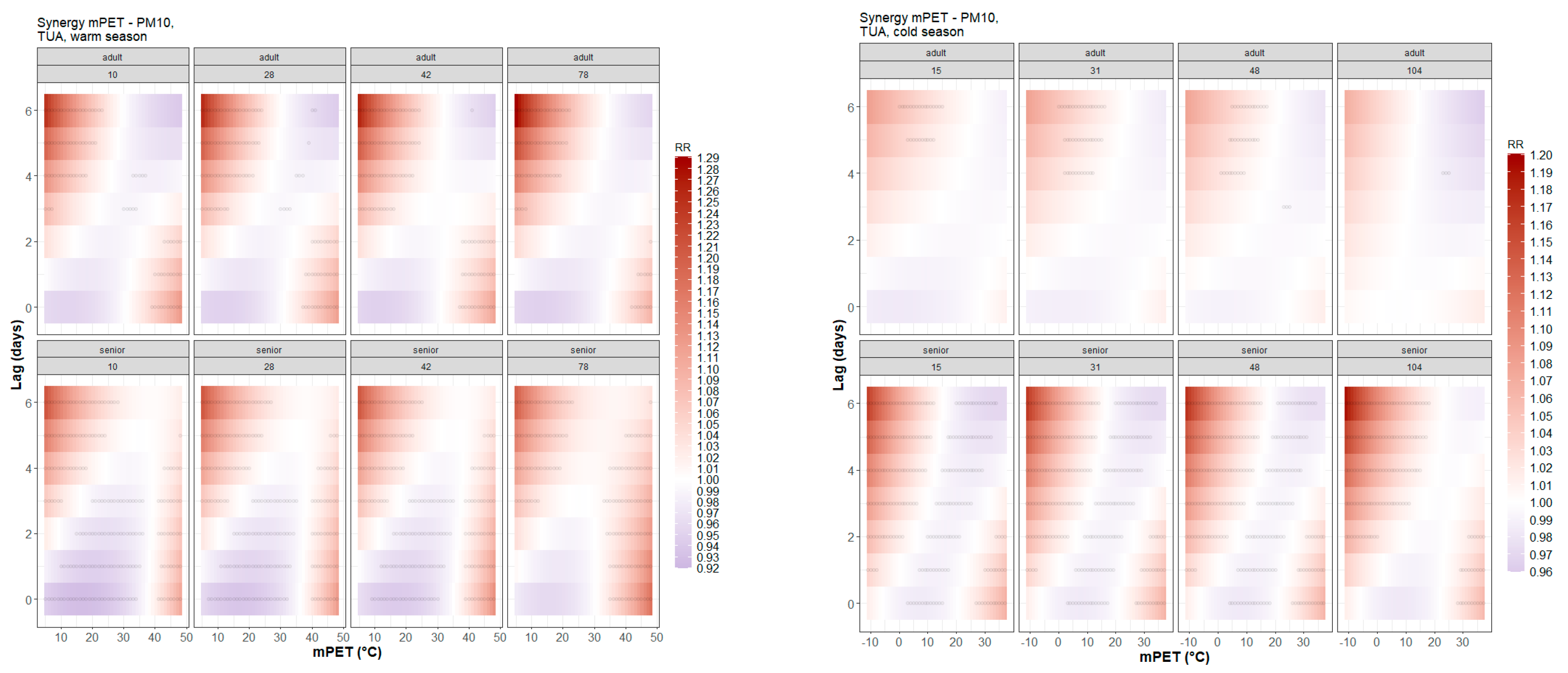
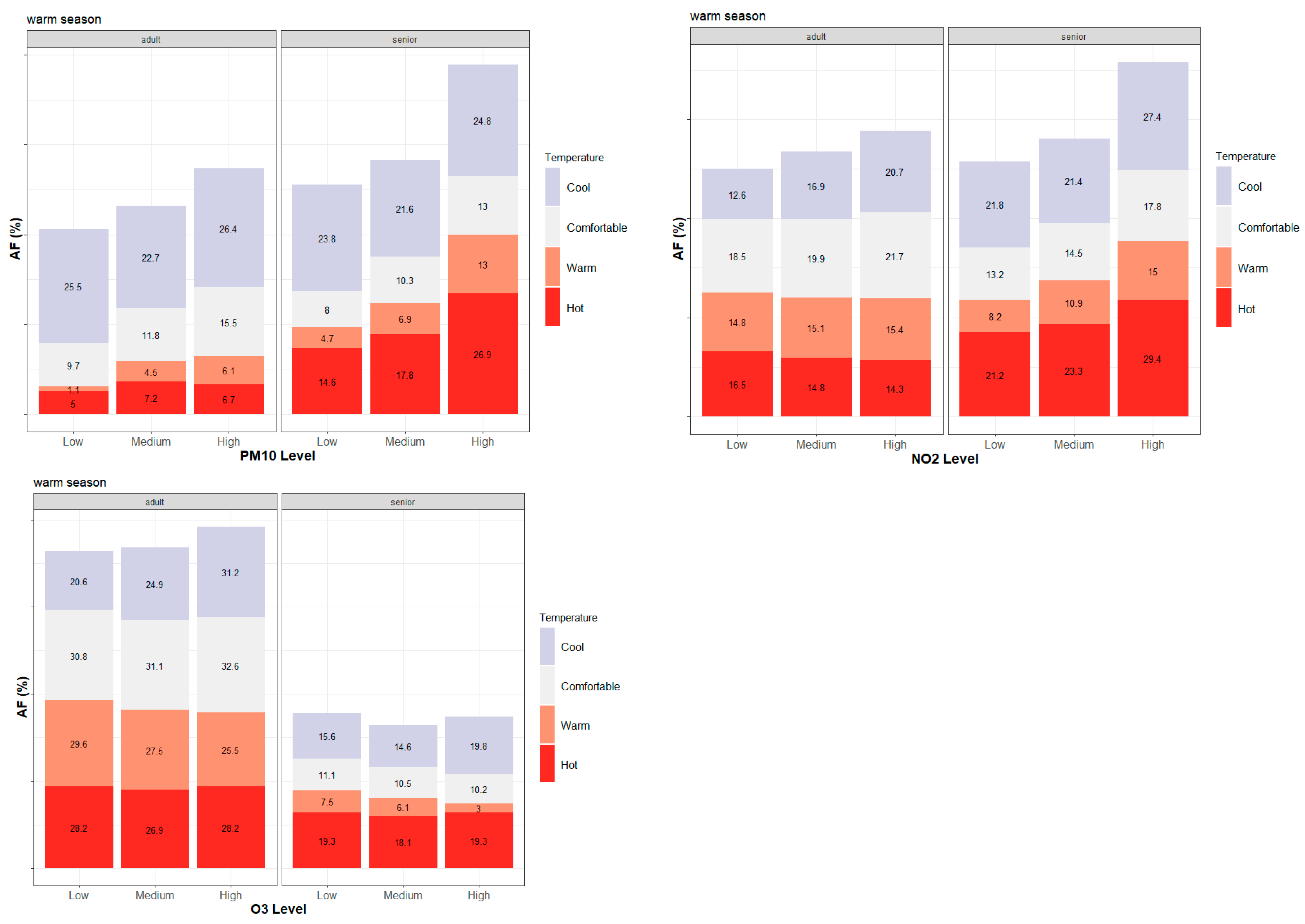
| Station Name | Longitude | Latitude | Altitude (m) | Measured Pollutants | Type of Stations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO2 | O3 | PM10 | |||||
| AUTH | 22.955444° E | 40.633143° N | 29 | YES | YES | YES | Urban Traffic |
| Agias Sofias | 22.945099° E | 40.633724° N | 12 | YES | YES | YES | Urban Traffic |
| Kordelio | 22.893219° E | 40.673453° N | 30 | YES | YES | YES | Urban Industrial |
| Thermal Sensation | Warm Period mPET Thresholds | Cold Period mPET Thresholds |
|---|---|---|
| “Cold” | - | <8 °C |
| “Cool” | <18 °C | 8 °C–18 °C |
| “Comfortable” | 18 °C–23 °C | 18 °C–23 °C |
| “Warm” | 23 °C–35 °C | >23 °C |
| “Hot” | >35 °C | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parliari, D.; Economou, T.; Giannaros, C.; Matzarakis, A. Mortality Burden Attributed to the Synergy Between Human Bio-Climate and Air Quality Extremes in a Climate Change Hotspot. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121313
Parliari D, Economou T, Giannaros C, Matzarakis A. Mortality Burden Attributed to the Synergy Between Human Bio-Climate and Air Quality Extremes in a Climate Change Hotspot. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(12):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121313
Chicago/Turabian StyleParliari, Daphne, Theo Economou, Christos Giannaros, and Andreas Matzarakis. 2025. "Mortality Burden Attributed to the Synergy Between Human Bio-Climate and Air Quality Extremes in a Climate Change Hotspot" Atmosphere 16, no. 12: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121313
APA StyleParliari, D., Economou, T., Giannaros, C., & Matzarakis, A. (2025). Mortality Burden Attributed to the Synergy Between Human Bio-Climate and Air Quality Extremes in a Climate Change Hotspot. Atmosphere, 16(12), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121313









