Estimation of Global Solar Radiation in Unmonitored Areas of Brazil Using ERA5 Reanalysis and Artificial Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
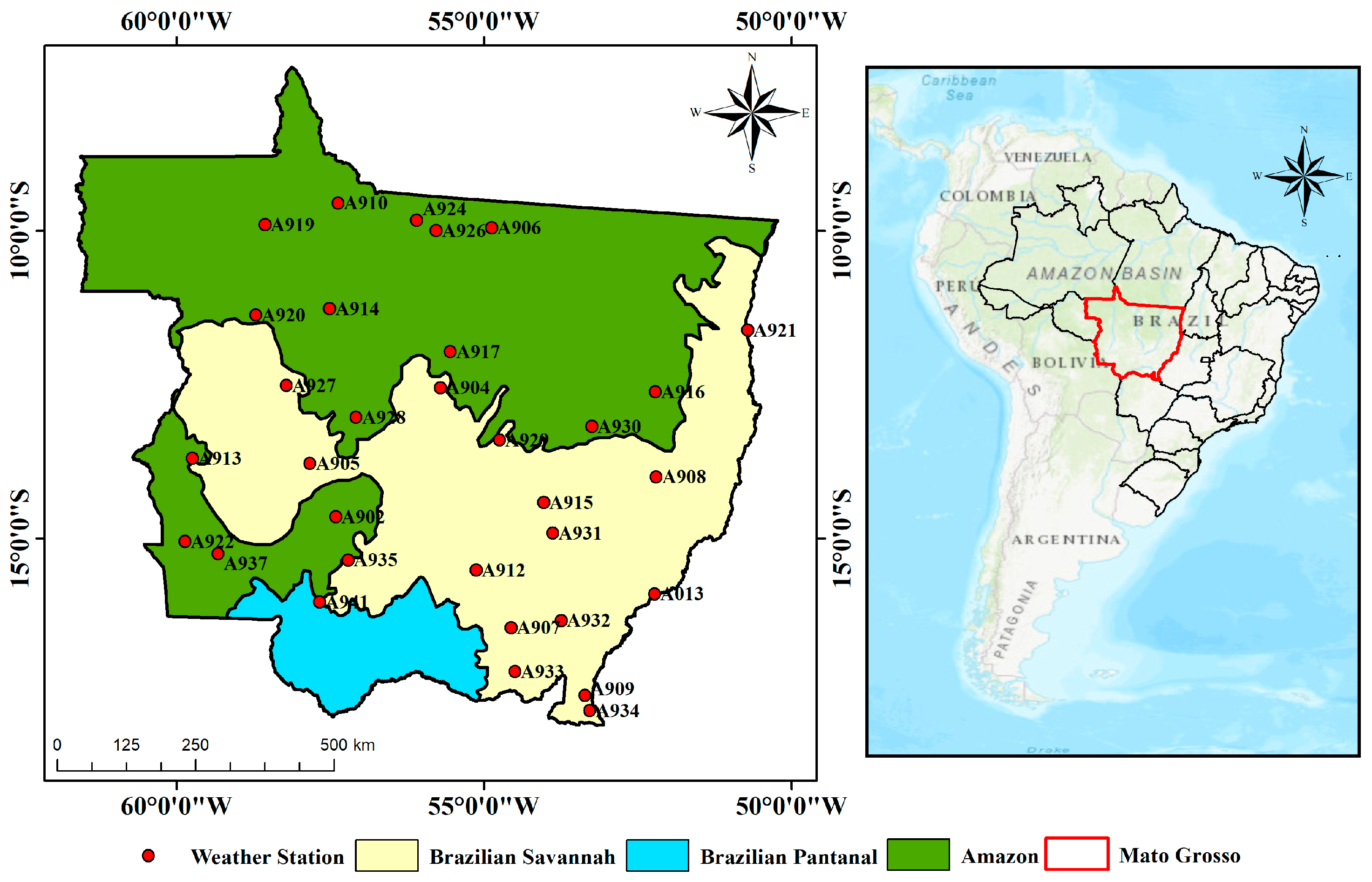
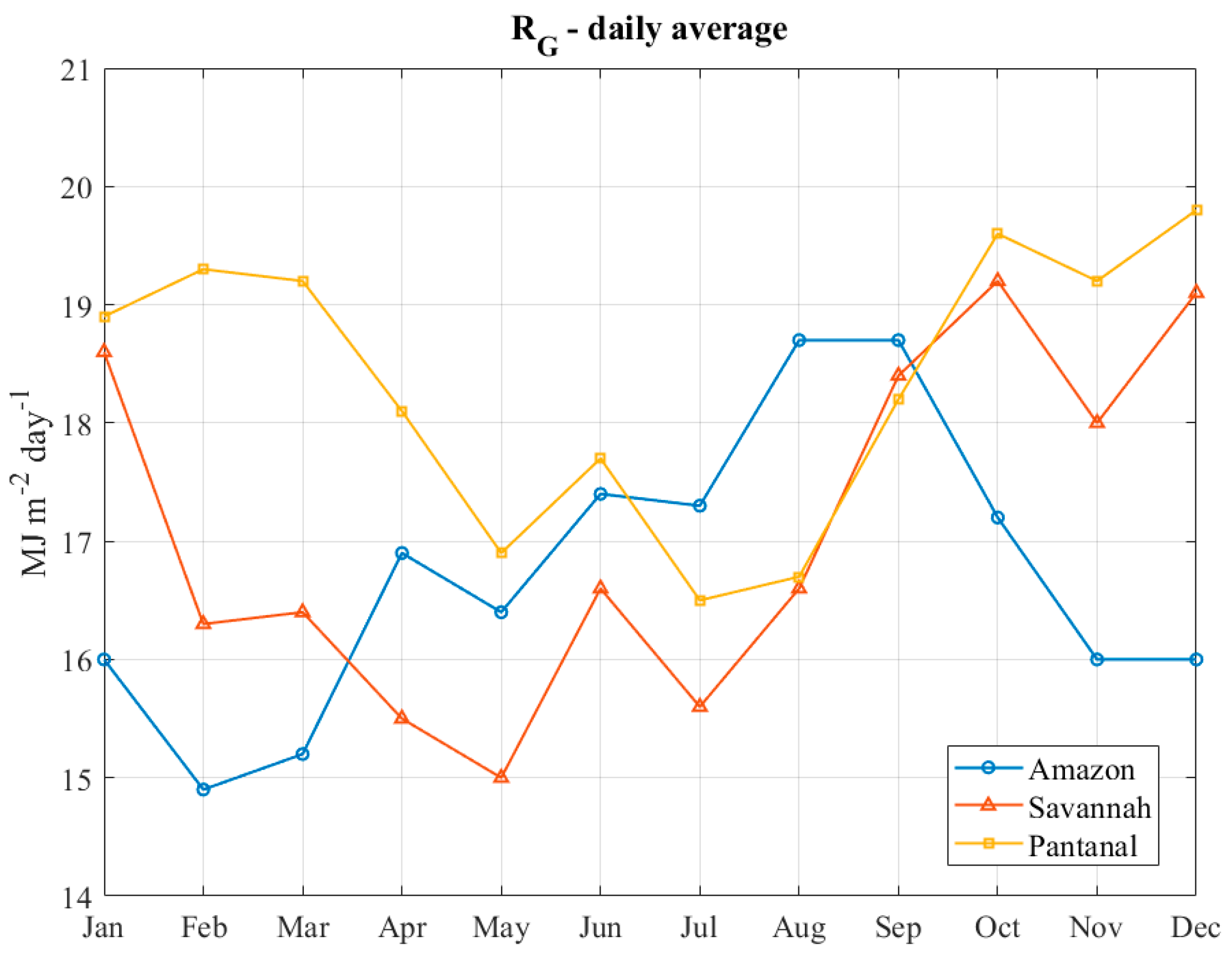
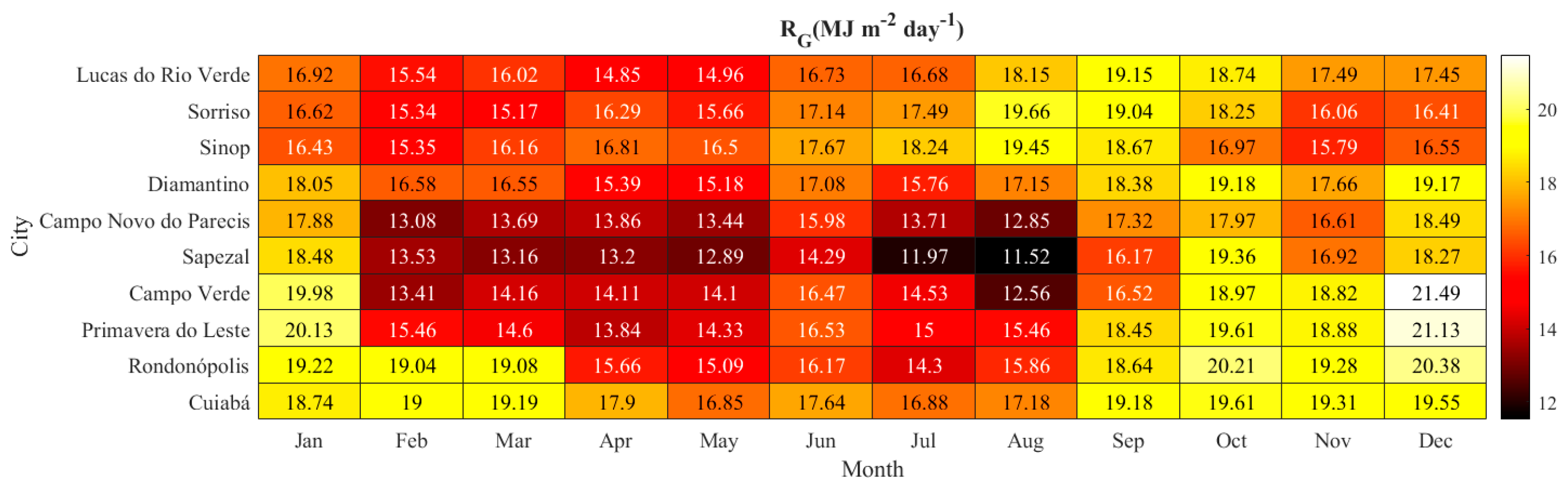
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Meteorological Data
2.3. ERA5 Reanalysis Data
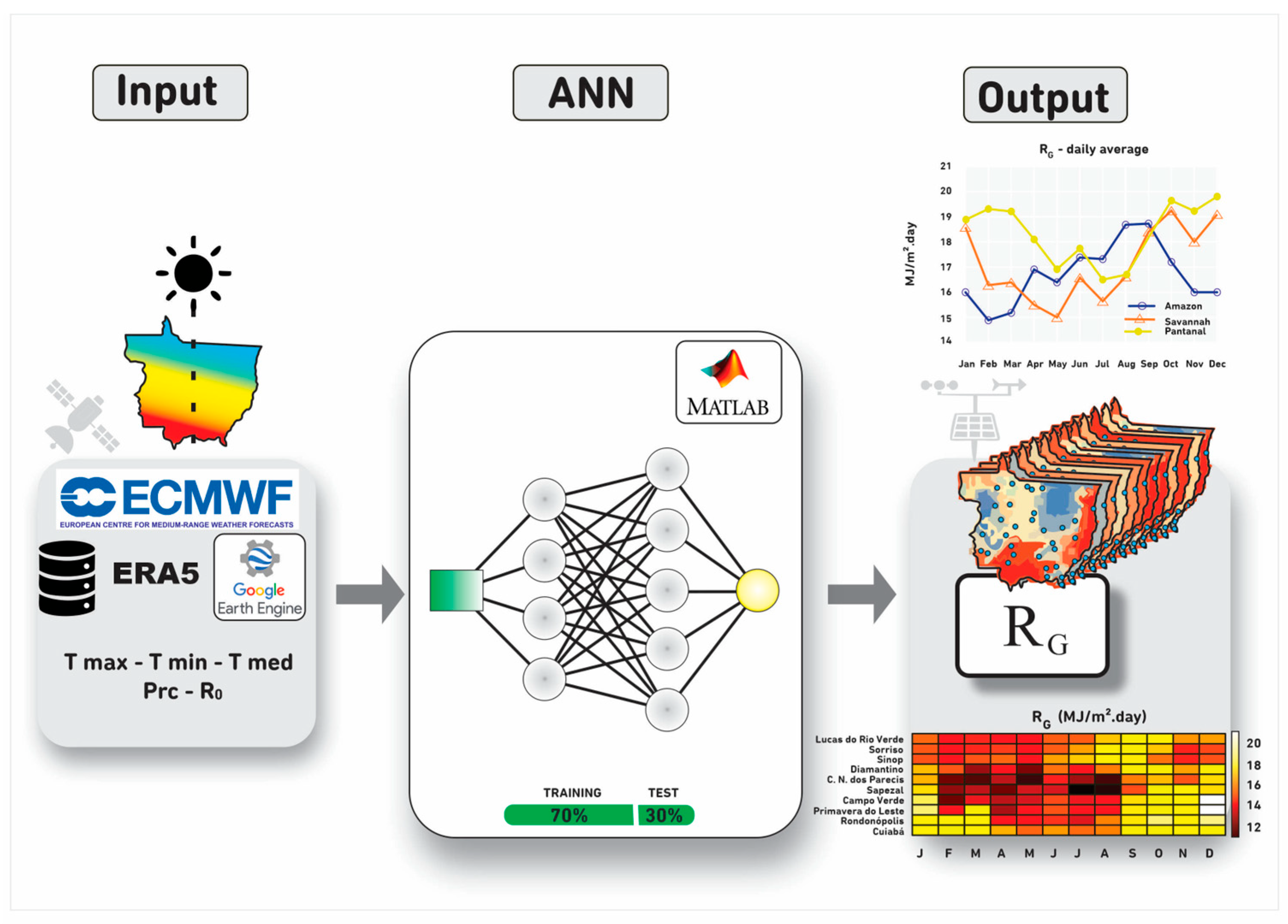
2.4. ANN Architecture and Training
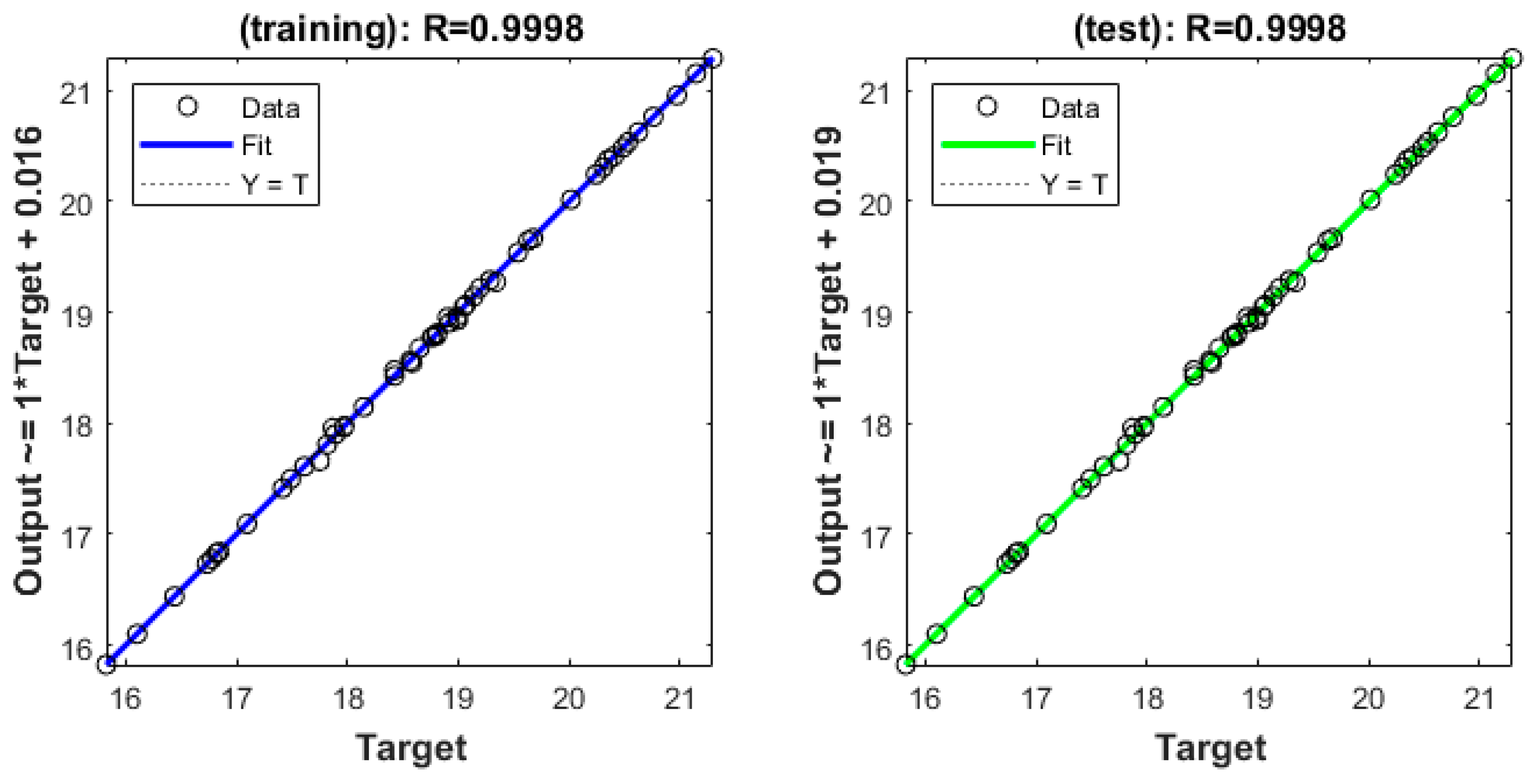
2.5. Model Performance Evaluation
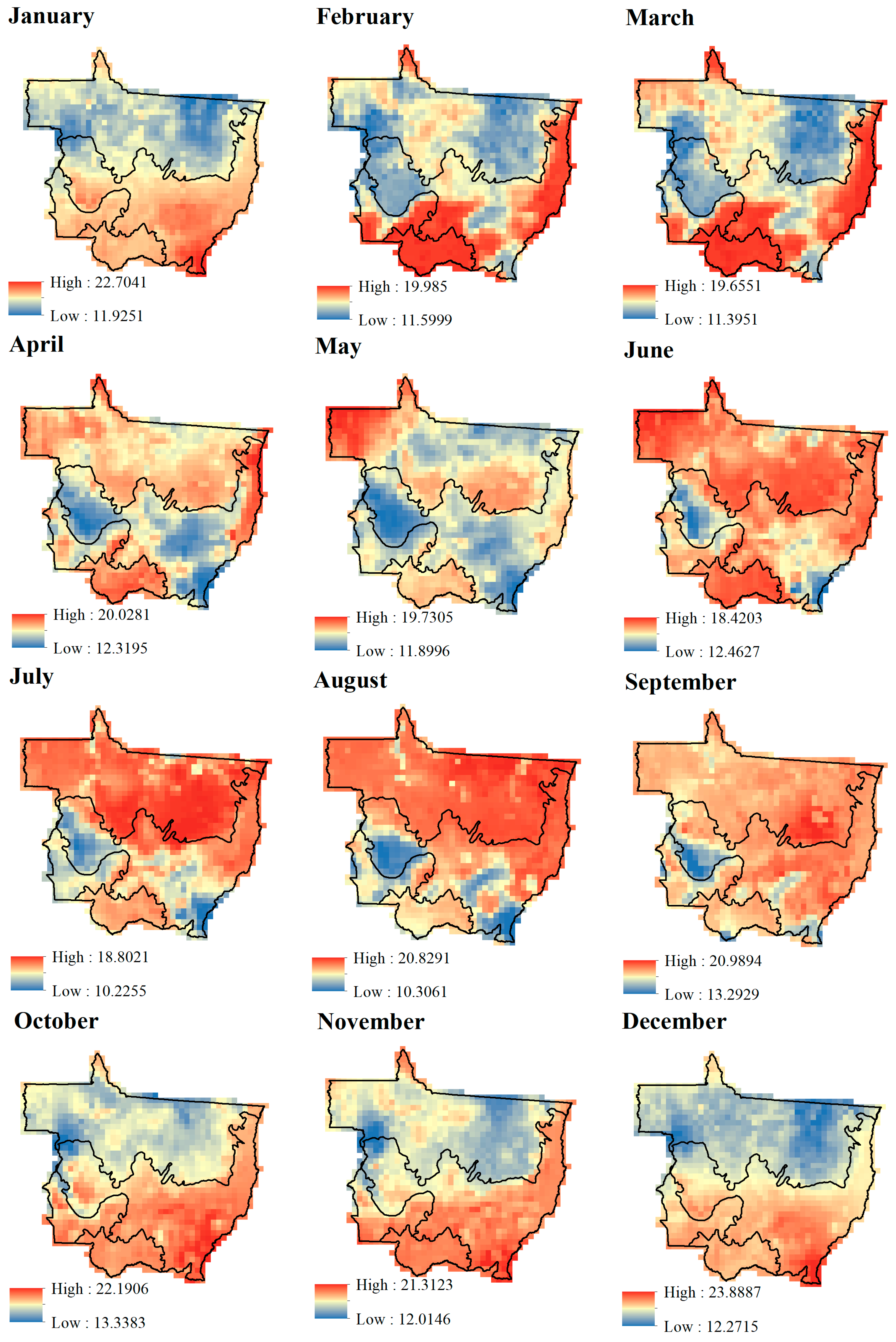
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| ERA5 | Fifth Generation ECMWF Reanalysis |
| GR | Global Radiation |
References
- Porfirio, A.C.; Ceballos, J.C.; Britto, J.M.; Costa, S.M. Evaluation of global solar irradiance estimates from GL1.2 satellite-based model over Brazil using an extended radiometric network. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Canhoto, P.; Salgado, R.; Costa, M.J. Development of an ANN based corrective algorithm of the operational ECMWF global horizontal irradiation forecasts. Sol. Energy 2019, 185, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neher, I.; Crewell, S.; Meilinger, S.; Pfeifroth, U.; Trentmann, J. Photovoltaic power potential in West Africa using long-term satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12871–12888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhiarasan, M.; Louzazni, M.; Belmahdi, B. Statistical analysis of novel ensemble recursive radial basis function neural network performance on global solar irradiance forecasting. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2023, 2023, 2554355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Lu, N.; Yao, L.; Qin, J.; Liu, T. Impact of climate changes on the stability of solar energy: Evidence from observations and reanalysis. Renew. Energy 2023, 208, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawadogo, W.; Bliefernicht, J.; Fersch, B.; Salack, S.; Guug, S.; Diallo, B.; Ogunjobi, K.O.; Nakoulma, G.; Tanu, M.; Meilinger, S.; et al. Hourly global horizontal irradiance over West Africa: A case study of one-year satellite- and reanalysis-derived estimates vs. in situ measurements. Renew. Energy 2023, 216, 119066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paletta, Q.; Terrén-Serrano, G.; Nie, Y.; Li, B.; Bieker, J.; Zhang, W.; Dubus, L.; Dev, S.; Feng, C. Advances in solar forecasting: Computer vision with deep learning. Adv. Appl. Energy 2023, 11, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, N.; Yaghoubirad, M.; Farajollahi, M.; Ahmadi, A. Deep learning based long-term global solar irradiance and temperature forecasting using time series with multi-step multivariate output. Renew. Energy 2023, 206, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Yang, K.; Tang, W.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, H.; Fu, H.; Zheng, J. Convolutional neural network-based homogenization for constructing a long-term global surface solar radiation dataset. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 169, 112952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.H.; Iosifidis, A.; Karstoft, H. IrradianceNet: Spatiotemporal deep learning model for satellite-derived solar irradiance short-term forecasting. Sol. Energy 2021, 228, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljanad, A.; Tan, N.M.; Agelidis, V.G.; Shareef, H. Neural network approach for global solar irradiance prediction at extremely short-time-intervals using particle swarm optimization algorithm. Energies 2021, 14, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, B.; Luppino, L.T.; Boström, T.; Anfinsen, S.N. Random forest regression for improved mapping of solar irradiance at high latitudes. Sol. Energy 2020, 198, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, D.H.; Li, S.; Lam, J.C. Estimating hourly global solar irradiance using artificial neural networks–A case study of Hong Kong. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 556, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kakkar, A. Forecasting daily global solar irradiance generation using machine learning. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2254–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, Q.; Ming, B.; Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Feng, G.; Shang, J. Assessment of wind and solar power potential and their temporal complementarity in China’s Northwestern Provinces: Insights from ERA5 Reanalysis. Energies 2023, 16, 7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Climate Change Service. ERA5: Fifth Generation of ECMWF Atmospheric Reanalyses of the Global Climate. Copernicus Climate Data Store. 2017. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-era5-single-levels?tab=overview (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Wu, Q. geemap: A Python package for interactive mapping with Google Earth Engine. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uliana, E.M.; Aires, U.R.V.; de Sousa Junior, M.F.; da Silva, D.D.; Moreira, M.C.; da Cruz, I.F.; Araujo, H.B. Estimated evaporation of lakes by climate reanalysis data and artificial neural networks. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2024, 136, 104811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa Junior, M.F.; Uliana, E.M.; Aires, U.R.V.; Rápalo, L.M.C.; da Silva, D.D.; Moreira, M.C.; da Silva Rondon, D. Streamflow prediction based on machine learning models and rainfall estimated by remote sensing in the Brazilian Savanna and Amazon biomes transition. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, V.K. Effective and efficient global optimization for conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rápalo, L.M.C.; Uliana, E.M.; Moreira, M.C.; da Silva, D.D.; de Melo Ribeiro, C.B.; da Cruz, I.F.; dos Reis Pereira, D. Effects of land-use and -cover changes on streamflow regime in the Brazilian Savannah. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 38, 100934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiba, C.; Fraidenraich, N.; Lyra, F.J.M.; Nogueira, A.M.B. Atlas Solarimétrico do Brasil: Banco de Dados Terrestres; Editora Universitária da UFPE: Recife, Brazil, 2000; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.P.; Zamadei, T.; Monteiro, E.B.; Casavecchia, B.H. Transmissividade atmosférica da radiação global na região amazônica de Mato Grosso. Rev. Bras. Meteorol. 2016, 31, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.P.; Silva, A.C.; Tanaka, A.A.; Uliana, E.M.; Almeida, F.T.; Klar, A.E.; Gomes, A.W.A. Global radiation by simplified models for the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2017, 52, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamadei, T.; Souza, A.P.; Almeida, F.T.; Escobedo, J.F. Daily global and diffuse radiation in the Brazilian Cerrado–Amazon transition region. Rev. Ciênc. Nat. 2021, 43, 39775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Wei, M.; Yuan, J.; He, W.; Chen, L.; Gao, Y. The Impact of Climate Change on Solar Radiation and Photovoltaic Energy Yields in China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbor, M.E.; Udo, S.O.; Ewona, I.O.; Nwokolo, S.C.; Ogbulezie, J.C.; Amadi, S.O. Potential impacts of climate change on global solar radiation and PV output using the CMIP6 model in West Africa. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; He, W.; He, L.; Yang, J.Y.; Qian, B.; Zhou, W.; He, P. Modelling adaptation strategies to reduce adverse impacts of climate change on maize cropping system in Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Roy, A.; Moghaddasi, P.; Moftakhari, H.; Magliocca, N.; Mekonnen, M.; Moradkhani, H. Assessment of climate change impact on rainfed corn yield with adaptation measures in Deep South, US. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 376, 109230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Input | Function | N1 | N2 | N3 | Stage | MAE | RMSE | RRMSE | Bias | Ens | Ekg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tmax; Tmin; Tmed; Prc; R0 | tansig; tansig; purelin | 4 | 5 | 1 | Training | 0.014 | 0.026 | 0.0014 | 0.0002 | 0.9996 | 0.9993 |
| Test | 0.015 | 0.027 | 0.0014 | 0.0028 | 0.9996 | 0.9990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morgan Uliana, E.; de Abreu Araujo, J.; Roggia Zanuzo, M.; Guedes Araujo, A.H.; Fomaca de Sousa Junior, M.; Venâncio Aires, U.R.; Alves Ramos Filho, H. Estimation of Global Solar Radiation in Unmonitored Areas of Brazil Using ERA5 Reanalysis and Artificial Neural Networks. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111306
Morgan Uliana E, de Abreu Araujo J, Roggia Zanuzo M, Guedes Araujo AH, Fomaca de Sousa Junior M, Venâncio Aires UR, Alves Ramos Filho H. Estimation of Global Solar Radiation in Unmonitored Areas of Brazil Using ERA5 Reanalysis and Artificial Neural Networks. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(11):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111306
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorgan Uliana, Eduardo, Juliana de Abreu Araujo, Márcio Roggia Zanuzo, Alvaro Henrique Guedes Araujo, Marionei Fomaca de Sousa Junior, Uilson Ricardo Venâncio Aires, and Herval Alves Ramos Filho. 2025. "Estimation of Global Solar Radiation in Unmonitored Areas of Brazil Using ERA5 Reanalysis and Artificial Neural Networks" Atmosphere 16, no. 11: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111306
APA StyleMorgan Uliana, E., de Abreu Araujo, J., Roggia Zanuzo, M., Guedes Araujo, A. H., Fomaca de Sousa Junior, M., Venâncio Aires, U. R., & Alves Ramos Filho, H. (2025). Estimation of Global Solar Radiation in Unmonitored Areas of Brazil Using ERA5 Reanalysis and Artificial Neural Networks. Atmosphere, 16(11), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111306






