Impacts of Climate Change on Rice Production in Pakistan: A Perspective from a Deep Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
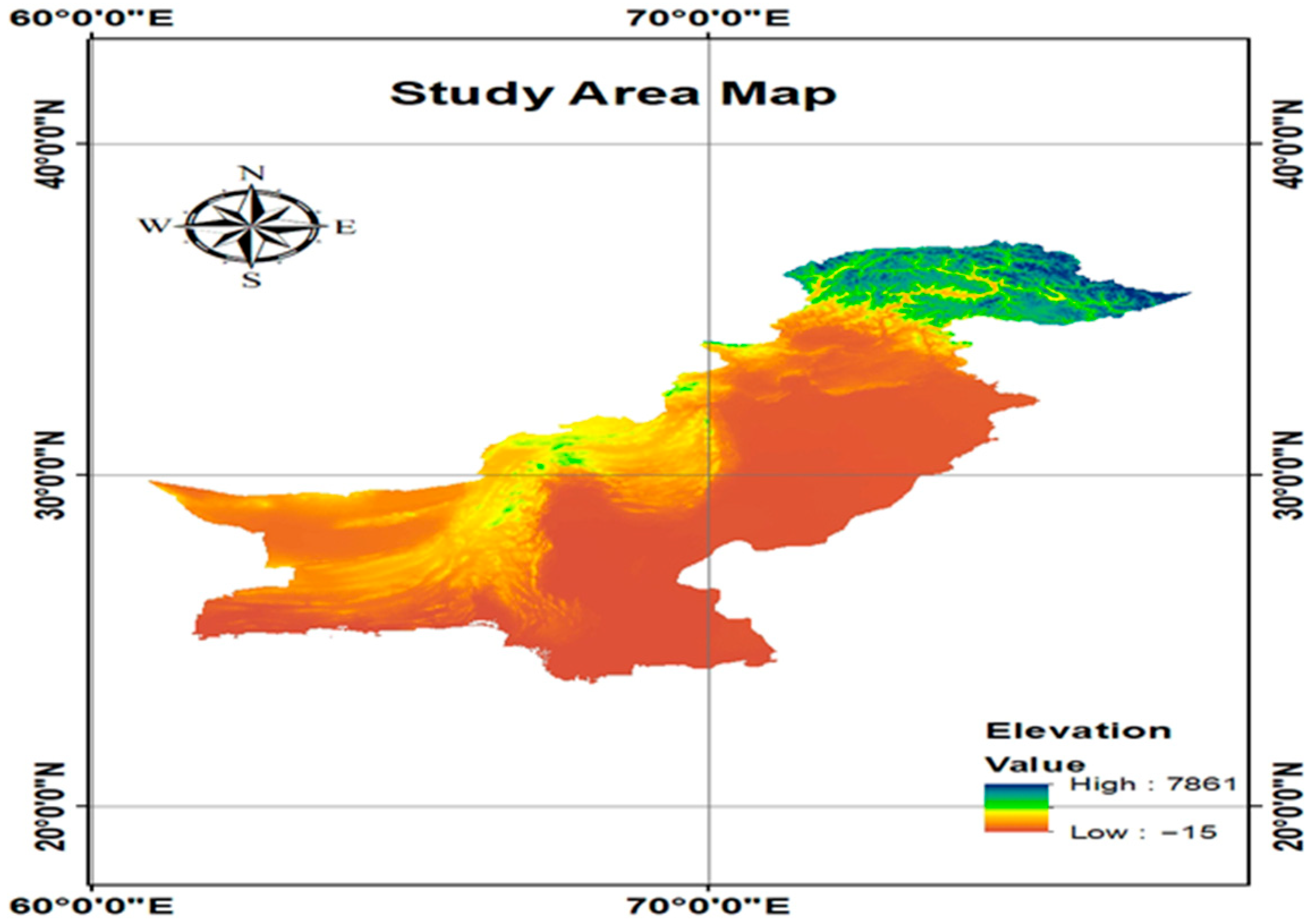
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Observed and CMIP6 Dataset Overview
2.3. Deep Neural Network
2.3.1. Deep Neural Network Theory
Neural Network Architecture
- Input Layer: Receives the raw input data.
- Hidden Layers: Intermediate layers that transform the input data into abstract representations.
- Output Layer: Produces the final prediction or classification.
Mathematical Representation
- For a given layer let represent the weight matrix, and the bias vector of that layer.
- The output of each layer is computed by applying a linear transformation followed by an activation function:
- is the linear combination of the inputs and weights.
- is the output of the activation function f(⋅) applied to .
- ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit): .
- Sigmoid: .
- Tanh: .
- SoftMax is used for multi-class classification: , where C is the number of classes and is the logit (raw output) for class .
Training Deep Neural Networks
- Forward Propagation: Input data is passed through the network, layer by layer, to compute the output:
- Loss Function: The discrepancy between the predicted output y and the actual target y is quantified using a loss function. Common loss functions include the following:
- ○
- Mean Squared Error (MSE) for regression tasks:
- ○
- Cross-Entropy Loss for classification tasks:
Backpropagation
2.4. R-Squared (R2)
2.5. Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
3. Results
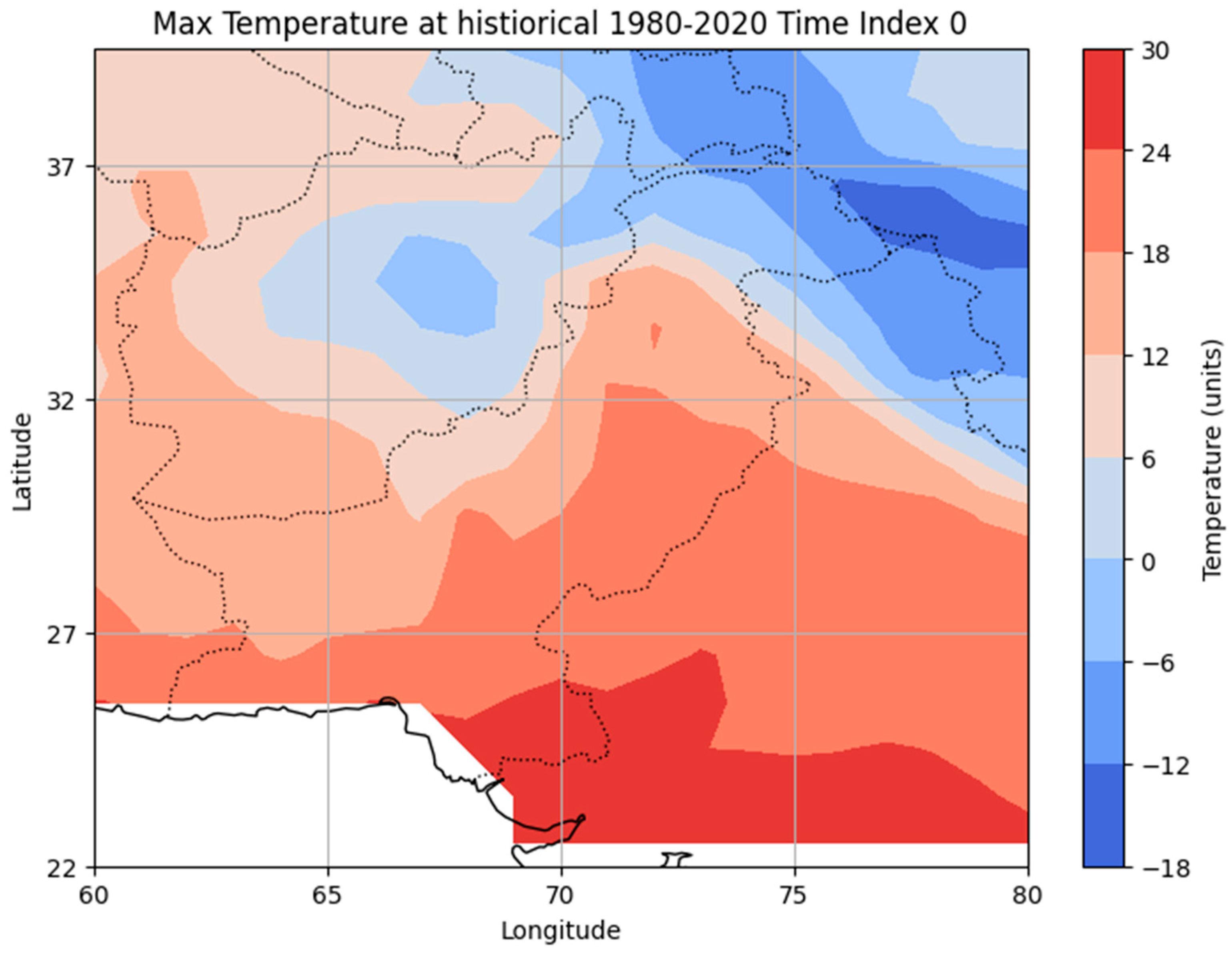
3.1. Historical Maximum Temperature
3.2. Future Maximum Temperature
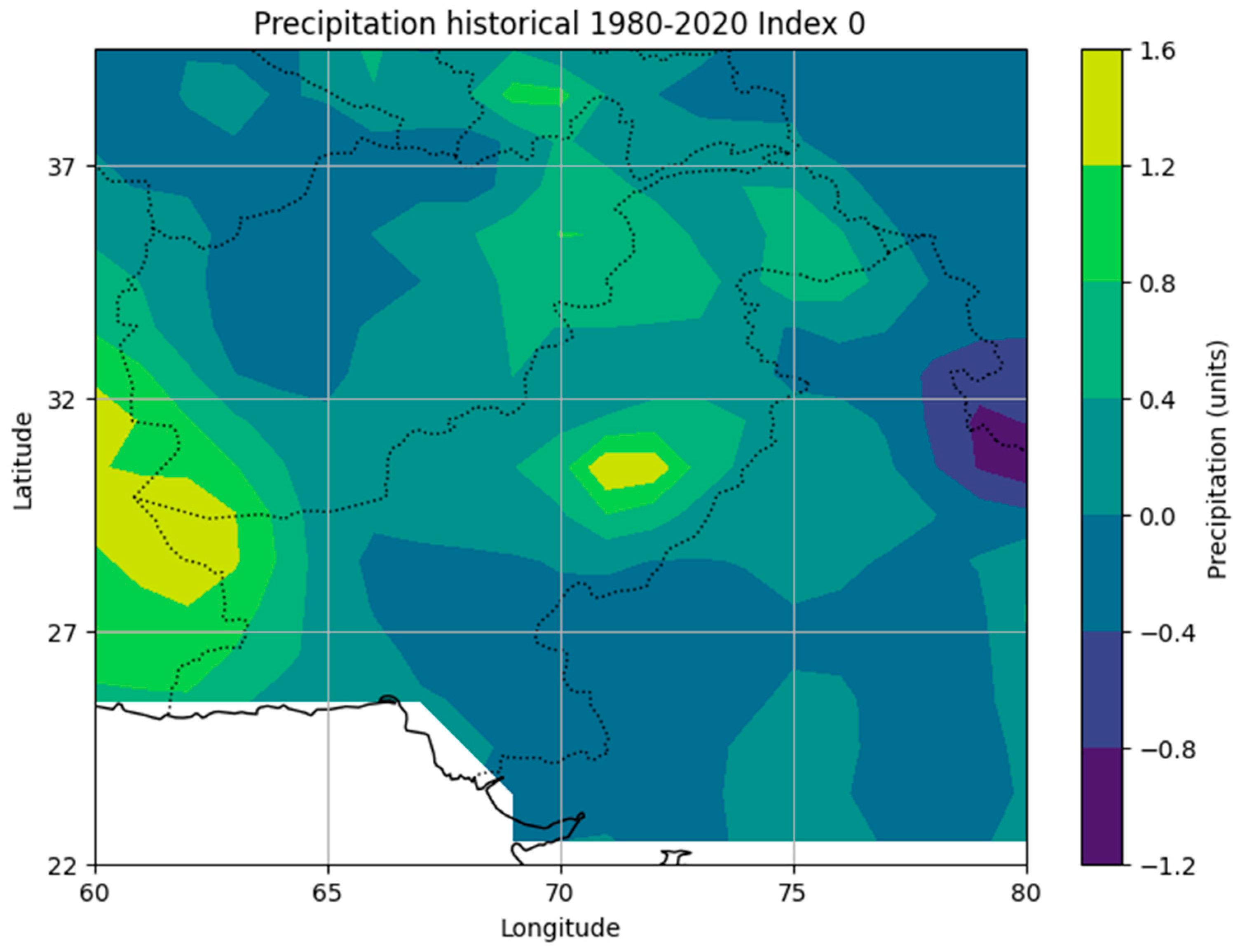
3.3. Historical Precipitation
3.4. Future Precipitation
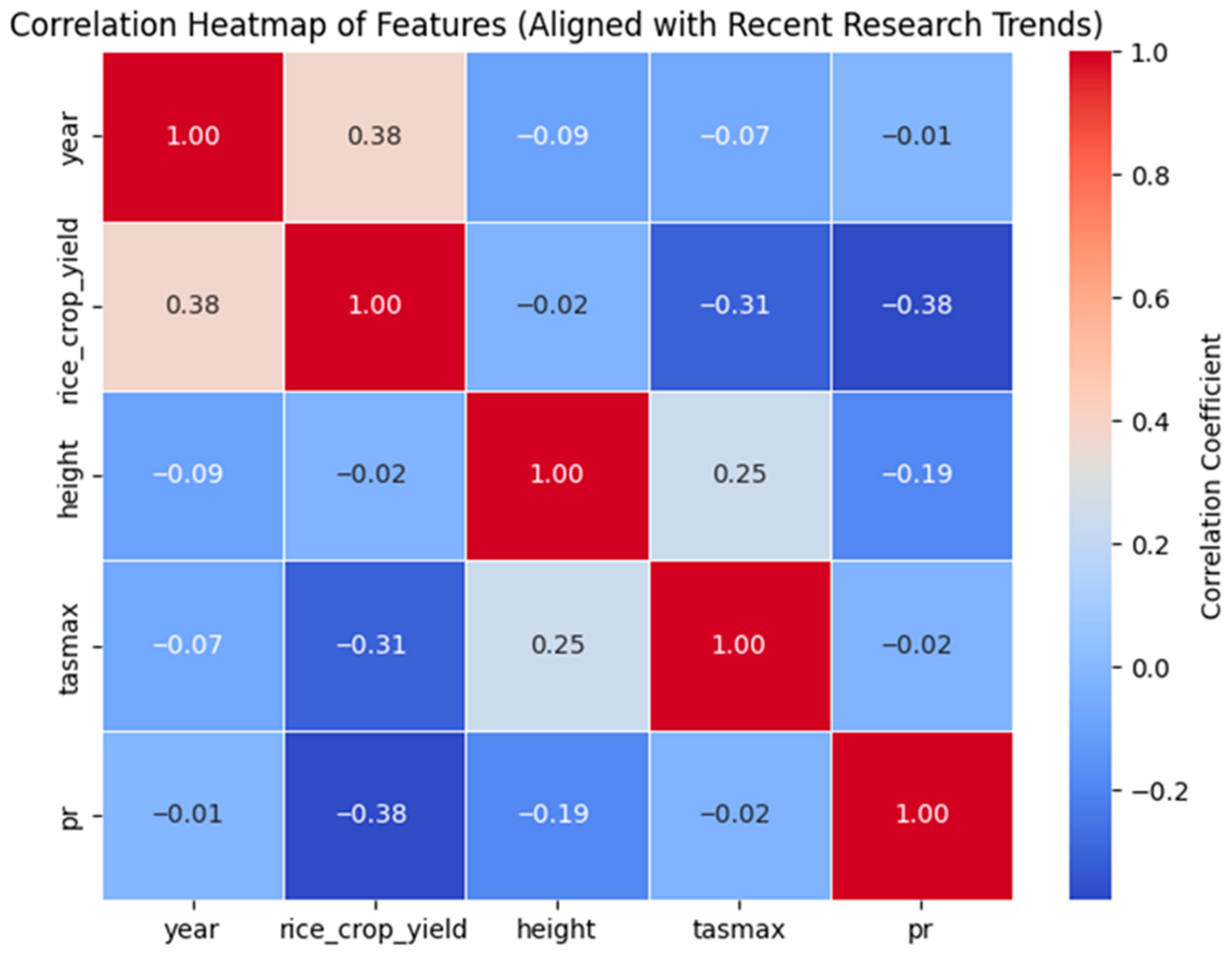
3.5. Maximum Temperature and Precipitation Affect the Crop Yield Using a Deep Learning Model
3.6. Model Performance
3.7. Impact of Water Resources on Rice Production: An Agro-Meteorological Perspective
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahzaman, M.; Zhu, W.; Ullah, I.; Mustafa, F.; Bilal, M.; Ishfaq, S.; Nisar, S.; Arshad, M.; Iqbal, R.; Aslam, R.W. Comparison of Multi-Year Reanalysis, Models, and Satellite Remote Sensing Products for Agricultural Drought Monitoring over South Asian Countries. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzaman, M.; Zhu, W.; Bilal, M.; Habtemicheal, B.; Mustafa, F.; Arshad, M.; Ullah, I.; Ishfaq, S.; Iqbal, R. Remote Sensing Indices for Spatial Monitoring of Agricultural Drought in South Asian Countries. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Khan, J.; Ullah, I.; Khan, F.; Lee, Y. Investigating Drought and Flood Evolution Based on Remote Sensing Data Products over the Punjab Region in Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Lei, H.; Khan, A.; Muhammad, I.; Javeed, T.; Khan, A.; Huo, X. Yield Gap Analysis of Major Food Crops in Pakistan: Prospects for Food Security. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 7994–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyakaremye, V.; Zeng, G.; Ullah, I.; Gahigi, A.; Mumo, R.; Ayugi, B. Recent Observed Changes in Extreme High-Temperature Events and Associated Meteorological Conditions over Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 4522–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Khan, J.; Ullah, I.; Khan, F.; Lee, Y. Assessing Impacts of Flood and Drought over the Punjab Region of Pakistan Using Multi-Satellite Data Products. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, R.; Jie, Z.; Ullah, I.; Akinsanola, A.A.; Syed, S.; Geremew, C.T.; Ullah, K.; Qasim, M. Seasonal Contrast in Dryland Vegetation Response to Meteorological Drought across South Asia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2025, 20, 084065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, W.; Chen, J.; Ullah, I.; Shah, A.A.; Alotaibi, B.A.; Syed, S.; Shah, M.H. Examining the Impacts of Recent Water Availability on the Future Food Security Risks in Pakistan Using Machine Learning Approaches. Water 2024, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, P.; Shrestha, N.S.; Shrestha, M.L.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Panthi, J.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Jha, A.; Lakhankar, T. Drought Risk Assessment in Central Nepal: Temporal and Spatial Analysis. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1913–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, W.; Chen, J.; Ullah, I.; Shah, M.H.; Ullah, I. Application of RNN-LSTM in Predicting Drought Patterns in Pakistan: A Pathway to Sustainable Water Resource Management. Water 2024, 16, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Saleem, F.; Syed, S.; Omer, A.; Habtemicheal, B.A.; Liu, M.; Arshad, M. Observed Changes in Seasonal Drought Characteristics and Their Possible Potential Drivers over Pakistan. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 1576–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffel, E.D.; Horton, R.M.; de Sherbinin, A. Temperature and Humidity Based Projections of a Rapid Rise in Global Heat Stress Exposure during the 21st Century. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Omer, A.; Habtemicheal, B.A.; Saleem, F.; Iyakaremye, V.; Syed, S.; Arshad, M.; Liu, M. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Meteorological Drought Variability and Trends (1981–2020) over South Asia and the Associated Large-Scale Circulation Patterns. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 60, 2261–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwimbabazi, J.; Jing, Y.; Iyakaremye, V.; Ullah, I.; Ayugi, B. Observed Changes in Meteorological Drought Events during 1981–2020 over Rwanda, East Africa. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyakaremye, V.; Zeng, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, G.; Ullah, I.; Gahigi, A.; Vuguziga, F.; Asfaw, T.G.; Ayugi, B. Increased High-Temperature Extremes and Associated Population Exposure in Africa by the Mid-21st Century. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sein, Z.M.M.; Ullah, I.; Syed, S.; Zhi, X.; Azam, K.; Rasool, G. Interannual Variability of Air Temperature over Myanmar: The Influence of Enso and Iod. Climate 2021, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Zeng, X.M.; Mukherjee, S.; Aadhar, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Syed, S.; Ayugi, B.O.; Iyakaremye, V.; Lv, H. Future Amplification of Multivariate Risk of Compound Drought and Heatwave Events on South Asian Population. Earth’s Future 2023, 11, e2023EF003688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Hou, J.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, D.; Khan, M.H.; Ullah, I.; Noor, R.S.; Umair, M.; Hussain, S. Flood Characteristics and Risk Analysis in Small Watersheds on the Loess Plateau under Extreme Heavy Rainfall. Nat. Hazards 2024, 121, 6857–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ma, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Ullah, I.; Arshad, M. Non-stationary Frequency Analysis of Extreme Streamflow Disturbance in a Typical Ecological Function Reserve of China under a Changing Climate. Ecohydrology 2021, 23, e2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, M.M.; Wang, J.; Abbas, H.; Ullah, I.; Khan, R.; Ali, F. Impact of Climate and Land-Use Change on Groundwater Resources, Study of Faisalabad District, Pakistan. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Zeng, X.; Hina, S.; Syed, S.; Ma, X.; Iyakaremye, V.; Yin, J.; Singh, V.P. Recent and Projected Changes in Water Scarcity and Unprecedented Drought Events over Southern Pakistan. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1113554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Zeng, X.; Syed, S.; Ma, X.; Xing, Y.; Singh, V.P. How Significant Is Projected Drought Risk in Pakistan Under a Warmer Climate? Earth Syst. Environ. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Nomman, M.; Schmitz, M. Economic Assessment of the Impact of Climate Change on the Agriculture of Pakistan. Bus. Econ. Horizons 2011, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Chen, X.; Lai, C.; Wang, Z.; Lian, Y.; Yu, H.; Wu, X. Drought Monitoring Utility of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products across Mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodhan, F.A.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Pangali Sharma, T.P.; Koju, U.A. Monitoring of Drought Condition and Risk in Bangladesh Combined Data from Satellite and Ground Meteorological Observations. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 93264–93282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Shao, D.; Liang, Q.; Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Ullah, I. Investigation of the Drainage Loss Effects with a Street View Based Drainage Calculation Method in Hydrodynamic Modelling of Pluvial Floods in Urbanized Area. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KING, R.D.; FENG, C.; SUTHERLAND, A. STATLOG: COMPARISON OF CLASSIFICATION ALGORITHMS ON LARGE REAL-WORLD PROBLEMS. Appl. Artif. Intell. 1995, 9, 289–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayugi, B.O.; Ullah, I.; Chung, E. Observed Flash Drought to Persist in Future over Southern Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sein, Z.M.M.; Ullah, I.; Iyakaremye, V.; Azam, K.; Ma, X.; Syed, S.; Zhi, X. Observed Spatiotemporal Changes in Air Temperature, Dew Point Temperature and Relative Humidity over Myanmar during 2001–2019. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2022, 134, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Ullah, W.; Liu, M.; Ullah, I. Performance Evaluation of ERA-5, JRA-55, MERRA-2, and CFS-2 Reanalysis Datasets, over Diverse Climate Regions of Pakistan. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2021, 33, 100373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eman, K.; Chung, E.; Ayugi, B.O.; Ullah, I. Unravelling Teleconnection-Driven Shifts in Precipitation Extremes Over Pakistan Through HighResMIP-CMIP6 Simulations. Int. J. Climatol. 2025, 45, e8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Asfaw, T.G.; Azam, K.; Syed, S.; Liu, M.; Arshad, M.; Shahzaman, M. Evaluating the Meteorological Drought Characteristics over Pakistan Using in Situ Observations and Reanalysis Products. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 4437–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Ullah, W.; Ali, G.; Ullah, S.; Liu, M.; Shahzaman, M.; Ullah, I. Evaluation of GPM-IMERG and TRMM-3B42 Precipitation Products over Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, F.; Zhang, W.; Hina, S.; Zeng, X.; Ullah, I.; Bibi, T.; Nnamdi, D.V. Population Exposure Changes to Mean and Extreme Climate Events Over Pakistan and Associated Mechanisms. GeoHealth 2023, 7, e2023GH000887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hina, S.; Saleem, F.; Arshad, A.; Hina, A.; Ullah, I. Droughts over Pakistan: Possible Cycles, Precursors and Associated Mechanisms. Geomatics, Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 1638–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Tebaldi, C.; Van Vuuren, D.P.; Eyring, V.; Friedlingstein, P.; Hurtt, G.; Knutti, R.; Kriegler, E.; Lamarque, J.F.; Lowe, J.; et al. The Scenario Model Intercomparison Project (ScenarioMIP) for CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 3461–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, O.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, T.; Orbell, J.; Lobben, A.; Gordon, J. The Relative Importance of Climate Change and Population Growth for Exposure to Future Extreme Droughts. Clim. Change 2016, 138, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Saleem, F.; Iyakaremye, V.; Yin, J.; Ma, X.; Syed, S.; Hina, S.; Asfaw, T.G.; Omer, A. Projected Changes in Socioeconomic Exposure to Heatwaves in South Asia Under Changing Climate. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Arshad, M.; Ma, X.; Ullah, I.; Wang, J.; Shao, W. Evaluating Observed and Future Spatiotemporal Changes in Precipitation and Temperature across China Based on CMIP6-GCMs. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 7703–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Asfaw, T.G.; Yin, J.; Iyakaremye, V.; Saleem, F.; Xing, Y.; Azam, K.; Syed, S. Projected Changes in Increased Drought Risks Over South Asia Under a Warmer Climate. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2022EF002830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hina, S.; Saleem, F.; Hina, A.; Ullah, I.; Bibi, T.; Mahmood, T. Exploring Trends and Variability of Climate Change Indices in the Agro-ecological Zones of Pakistan and Their Driving Mechanisms. Int. J. Climatol. 2024, 44, 3589–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.R.; Doi, T.; Behera, S.K. Predicting Extreme Floods and Droughts in East Africa Using a Deep Learning Approach. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Zeng, X.-M.; Syed, S.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Syed, S.; Wang, N.; Li, Y. A Multivariate Framework for Assessing Propagation Thresholds from Meteorological to Hydrological Drought across Indus River Basins-South Asia. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2025, 39, 5415–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-Z.Z.; Liu, S.-J.J.; Zeng, X.-M.M.; Lu, B.; Zhang, Z.-X.X.; Zhu, J.; Ullah, I. A Study of Precipitation Forecasting for the Pre-Summer Rainy Season in South China Based on a Backpropagation Neural Network. Water 2024, 16, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yao, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, X. Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Carbon during Drought and Flood Events: A Phase-by-Stages Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, I.; Mukherjee, S.; Syed, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Ayugi, B.O.; Aadhar, S. Anthropogenic and Atmospheric Variability Intensifies Flash Drought Episodes in South Asia. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zeng, X.-M.; Wang, N.; Ullah, I.; Lv, H. Attribution of Moisture Sources for Summer Precipitation in the Upstream Catchment of the Three Gorges Dam. J. Hydrometeorol. 2024, 25, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sein, Z.M.M.; Zhi, X.; Ullah, I.; Azam, K.; Ngoma, H.; Saleem, F.; Xing, Y.; Iyakaremye, V.; Syed, S.; Hina, S.; et al. Recent Variability of Sub-seasonal Monsoon Precipitation and Its Potential Drivers in Myanmar Using In-situ Observation during 1981–2020. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 3341–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Wang, X.; Yin, Y.; Ma, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, P.; Ullah, I. Comparing Spatio-Temporal Propagation Patterns of Hydrological and Meteorological Droughts: Insights from SWAT Modelling in the Poyang Lake Basin. CATENA 2024, 243, 108183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, A.; Zhu, F.R.; Sa’adi, Z.; Mamun Hridoy, M.A.A.; Ullah, I. Study of Meteorological Parameters and Classification of Aerosols Using Remote Sensing over LHAASO. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2025, 156, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Ren, G.; Yin, J.; Iyakaremye, V.; Syed, S.; Lu, K.; Xing, Y.; Singh, V.P. Recent Changes in Drought Events over South Asia and Their Possible Linkages with Climatic and Dynamic Factors. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shen, C.; Ullah, I.; Curio, J.; Chen, D. Evaluating Heat Stress and Occupational Risks in the Southern Himalayas under Current and Future Climates. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Shao, D.; Lin, Q.; Ullah, I.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Towards More Efficient Urban Flood Assessment: Issue of Spatial Resolution in Urban Flood Hydrodynamic Modeling from Flood Exposure Perspective. Water Resour. Manag. 2025, 39, 6683–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Liu, M.; Ullah, I. Characteristics and Propagation of Meteorological and Hydrological Droughts in Eastern Gansu, a Typical Semi-arid Region, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 5327–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Zeng, X.; Li, C.; Wang, N.; Shao, S.; Ullah, I. A Numerical Simulation of a Fog Event in the Sichuan Basin, China: The Sensitivity to Terrain Elevations. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Taha Bakheit Taha, A.; Tian, F.; Yuan, X.; Ajmal, M.; Ullah, I.; Ahmad, M. Flood Modelling and Risk Analysis of Cinan Feizuo Flood Protection Area, Huaihe River Basin. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafadi, K.; Sun, J.; Ullah, I.; Srivastava, A.K.; Ewert, F.; Larbi, B.R.; Bi, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, F.; Cao, W. Urbanization’s Dual Role in the Exacerbation and Mitigation of Drought Dynamics in China. npj Urban Sustain. 2025, 5, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Syed, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J. Warming Asian Drylands Inducing the Delayed Retreat of East Asian Summer Monsoon and Intensifying Autumn Precipitation in Northern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2024JD041811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Zeng, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, N.; Ullah, I.; Fang, W.; Bai, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J. Strong Spatial Propagation Strength of Meteorological Droughts Exhibits in the Humid—Arid Transition Regions of Mainland China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2025, 52, e2025GL115891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sein, Z.M.M.; Ullah, I.; Saleem, F.; Zhi, X.; Syed, S.; Azam, K. Interdecadal Variability in Myanmar Rainfall in the Monsoon Season (May–October) Using Eigen Methods. Water 2021, 13, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Liang, Q.; Shao, D.; Ullah, I. Effects of Urban Topographical Features on Drainage Efficiency for Pluvial Flash Flood Occurrence. Nat. Hazards 2025, 121, 14513–14529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremew, T.; Ullah, I.; Akinsanola, A.A.; Muleta, D. Unravelling Southern Ocean Sea Surface Temperatures Impacts on Long Rainfall Variability in East Africa. Atmos. Res. 2026, 327, 108406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldi, C.; Wehner, M.F. Benefits of Mitigation for Future Heat Extremes under RCP4.5 Compared to RCP8.5. Clim. Change 2018, 146, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edokossi, K.; Jin, S.; Mazhar, U.; Molina, I.; Calabia, A.; Ullah, I. Monitoring the Drought in Southern Africa from Space-Borne GNSS-R and SMAP Data. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 7947–7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Nie, M.; Wang, N.; Ullah, I.; Bai, G. Attributing Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Meteorological Drought across Yangtze River Basin, China. Atmos. Res. 2025, 323, 108155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.-M.; Li, C.; Wang, N.; Ullah, I. Impacts of Land–Atmosphere Interactions on Boundary Layer Variables: A Classification Perspective from Modeling Approaches. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



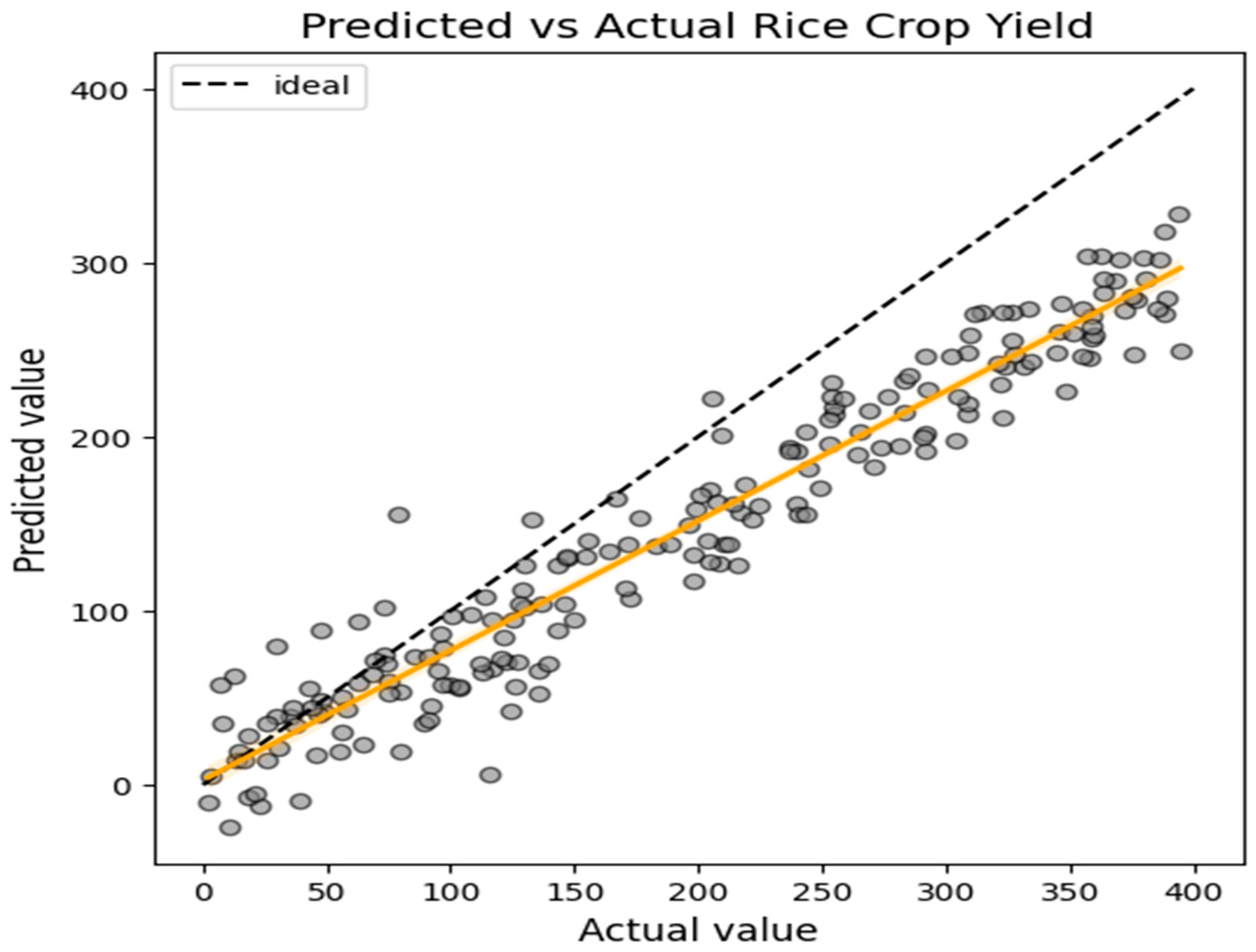
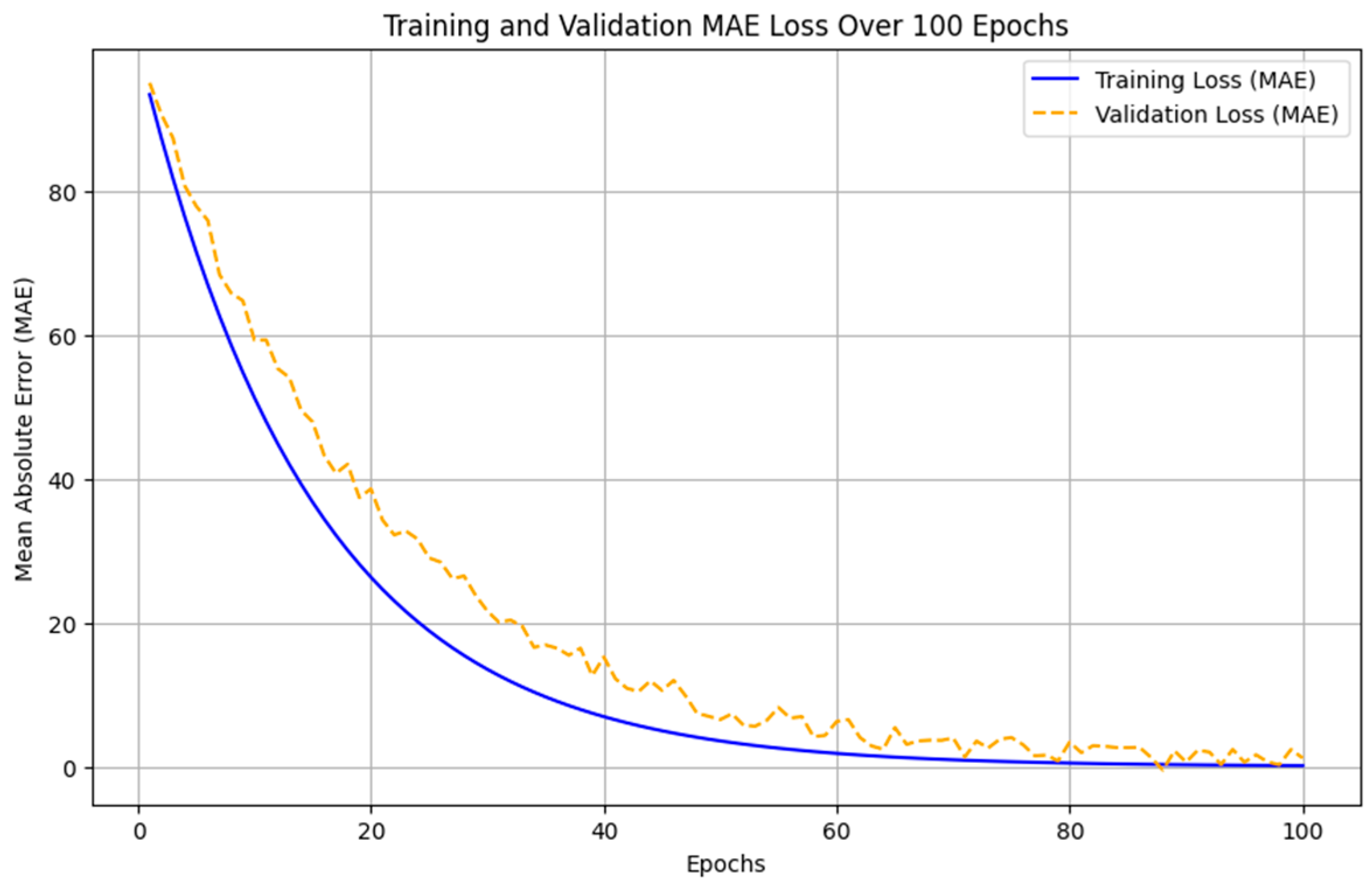
| Metrics | Values | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R-squared (R2) | 0.89 | Explains 89% variation in the variation in crops |
| 2 | Mean Absolute Error (MAE) | 70.33 | Average Deviation of Model Predictions from the actual values. |
| 3 | Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) | 82.95 | Penalizes larger deviations, indicating consistent performance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shah, M.H.; Shah, W.; Syed, S.; Ullah, I.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Impacts of Climate Change on Rice Production in Pakistan: A Perspective from a Deep Learning Approach. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111305
Shah MH, Shah W, Syed S, Ullah I, Wang Y, Wang Y. Impacts of Climate Change on Rice Production in Pakistan: A Perspective from a Deep Learning Approach. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(11):1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111305
Chicago/Turabian StyleShah, Muhammad Haroon, Wilayat Shah, Sidra Syed, Irfan Ullah, Yaoyao Wang, and Yuanyuan Wang. 2025. "Impacts of Climate Change on Rice Production in Pakistan: A Perspective from a Deep Learning Approach" Atmosphere 16, no. 11: 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111305
APA StyleShah, M. H., Shah, W., Syed, S., Ullah, I., Wang, Y., & Wang, Y. (2025). Impacts of Climate Change on Rice Production in Pakistan: A Perspective from a Deep Learning Approach. Atmosphere, 16(11), 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111305







