Quantification of Heavy Metals in Indoor Dust for Health Risk Assessment in Macao
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Locations
- Student Dormitory: A residential room on the 10th floor of a university campus, medium occupancy density with continuous residential activity.
- Office: Third floor of a university campus, standard working environment with regular working hours.
- Restaurant: Commercial food service establishment with cooking emissions.
- Auto Repair Workshop: Industrial setting with vehicle maintenance activities.
- Parking Security Office: Enclosed space with limited ventilation.
2.2. Indoor Dust Collection and Analysis
2.3. Receptor Modeling Source Apportionment
2.4. Exposure Assessment Model
2.5. Health Risks Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution Characteristics
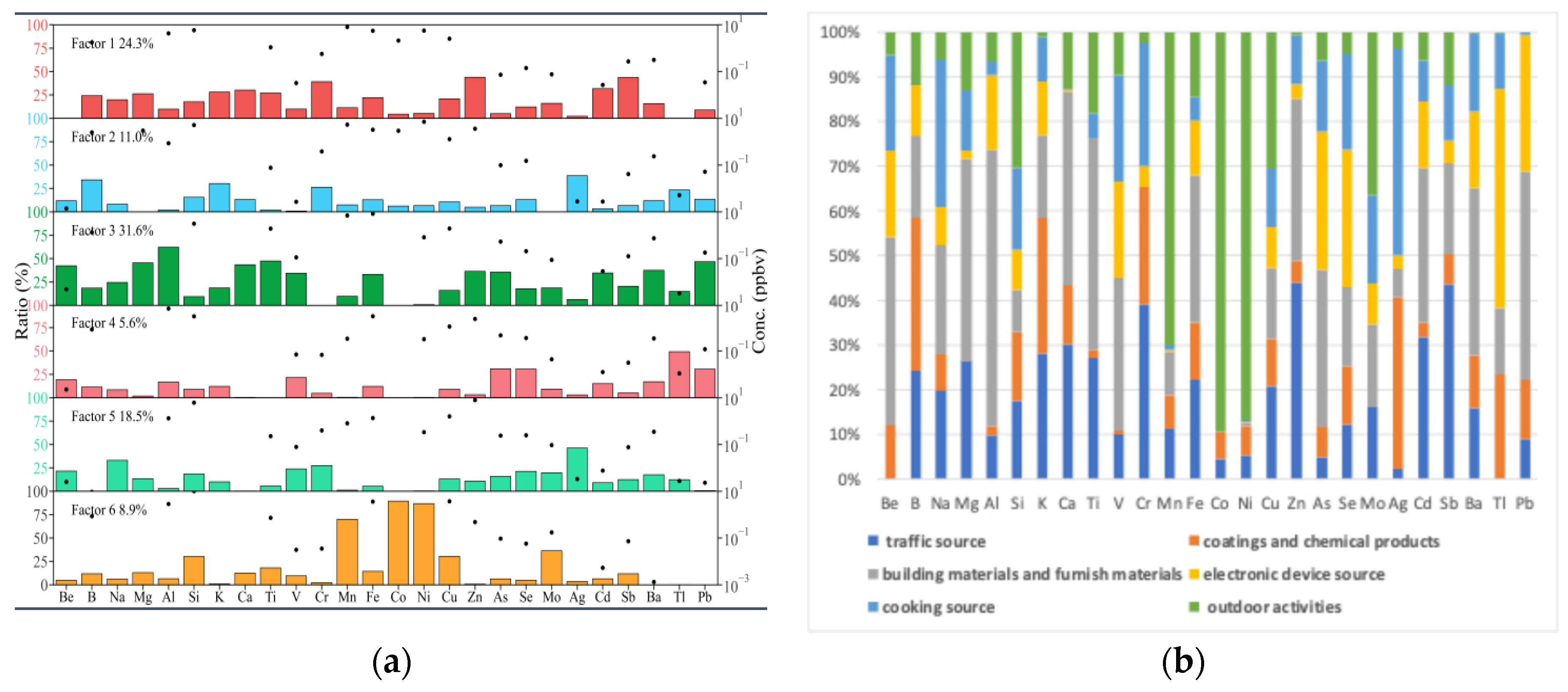
3.2. PMF Heavy Metal Source Analysis
3.3. Heavy Metal Health Risks Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, S.-P.; Cai, M.-J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, J.-B.; Yan, J.-P.; Schwab, J.J.; Yuan, C.-S. Chemical Nature of PM2.5 and PM10 in the Coastal Urban Xiamen, China: Insights into the Impacts of Shipping Emissions and Health Risk. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 227, 117383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA; ORD. EPA IO [Inorganic] Compendium Method IO-3.5: Determination of Metals in Ambient Particulate Matter Using Inductively Coupled Plasma/Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/esam/epa-io-inorganic-compendium-method-io-35-determination-metals-ambient-particulate-matter-using (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Lei, T.M.T.; Chan, Y.W.I.; Mohd Nadzir, M.S. Monitoring PM2.5 at a Large Shopping Mall: A Case Study in Macao. Processes 2023, 11, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Huang, H.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Y. Levels, Sources, and Health Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Indoor Dust in a College in the Pearl River Delta. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 3621–3627. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, G.; Chen, Q.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, P.; Sun, L.; Shen, M.; et al. Propositional Modification for the USEPA Models for Human Exposure Assessment on Chemicals in Settled Dust or Soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20113–20116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, P.T.B.S.; Sousa, S.I.V.; Dudzińska, M.R.; Ruzgar, D.G.; Mutlu, M.; Panaras, G.; Papadopoulos, G.; Saffell, J.; Scutaru, A.M.; Struck, C.; et al. A Review of Relevant Parameters for Assessing Indoor Air Quality in Educational Facilities. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebnikovas, A.; Jasevičius, R. Air Pollution with Fine Particles in Closed Parking and Theoretical Studies of the Interaction of Inhaled Particles in Respiratory Tract. Buildings 2022, 12, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthammer, T. Emerging Indoor Pollutants. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 224, 113423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyi, I.N.Y.; Isley, C.F.; Soltani, N.S.; Taylor, M.P. Human Exposure and Risk Associated with Trace Element Concentrations in Indoor Dust from Australian Homes. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y. Solid Fuel Combustion and Air Pollution: Filling the Data Gap and Future Priorities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Method 6020B (SW-846): Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry; Revision 2; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/6020b.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Dwivedi, S.; Mahanta, S.K.; Mayer, A.C.R.; Lawrence, A. Distribution Assessment and Source Apportionment of Particulate Bound-PAHs in Indoor Air of South Asian Precinct Using IDW and PMF Receptor Model: A Comprehensive Study. Atmos. Environ. X 2024, 23, 100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habre, R.; Coull, B.; Moshier, E.; Godbold, J.; Grunin, A.; Nath, A.; Castro, W.; Schachter, N.; Rohr, A.; Kattan, M.; et al. Sources of Indoor Air Pollution in New York City Residences of Asthmatic Children. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods. Method 7300, 5th ed.; Elements by ICP (Nitric/Perchloric Acid Ashing); National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2003.
- ISO/IEC 17025:2017; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Grzetic, I.; Ghariani, R. Potential Health Risk Assessment for Soil Heavy Metal Contamination in the Central Zone of Belgrade (Serbia). J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2008, 73, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.-H.; Cai, M.-J.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Q.-D.; Wu, S.P. Characterization and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in PM2.5 in Xiamen Port. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2022, 43, 3404–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Hao, K.; Zheng, G.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q.; Yang, W.; et al. Toxic Metals in Outdoor/Indoor Airborne PM2.5 in Port City of Northern, China: Characteristics, Sources, and Personal Exposure Risk Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W. Source Analysis of Heavy Metal Elements of PM2.5 in Canteen in a University in Winter. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-W.; Zhou, H.-J.; Lü, Y.-C.; Sun, B.; Fu, X.-T.; Chun, X.; Wan, Z.-Q. Characteristics and Health Risks of Metal Elements in House Dust in Baotou. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 17734-2:2013; Determination of Organonitrogen and Organophosphorus Compounds in Airborne Particles and Gaseous Phase—Sampling and Analytical Methods—Part 2: Sampling and Gas Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Analysis. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Johnson, G.W.; Ehrlich, R.; Full, W.; Ramos, S. Principal Components Analysis and Receptor Models in Environmental Forensics. In Introduction to Environmental Forensics; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 609–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamy, M.B.; Natesan, U.; Karuppannan, S.; Chandrasekaran, L.N.; Hussain, S.; Almohamad, H.; Al Dughairi, A.A.; Al-Mutiry, M.; Alkayyadi, I.; Abdo, H.G. Multivariate Urban Air Quality Assessment of Indoor and Outdoor Environments at Chennai Metropolis in South India. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Hirano, K.; Masunaga, S. Assessment of the Sources of Suspended Particulate Matter Aerosol Using US EPA PMF 3.0. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 1063–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, T.M.T.; Ma, M.F.C. The Relationship between Roadside PM Concentration and Traffic Characterization: A Case Study in Macao. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Seo, Y.R. An Overview of Carcinogenic Heavy Metal: Molecular Toxicity Mechanism and Prevention. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 20, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, R.; Lam, C.W.K.; Chan, A.; Lee, M.; Chan, I.H.S.; Pang, S.W.; Lai, C.K.W. Indoor Environment of Residential Homes in Hong Kong—Relevance to Asthma and Allergic Disease. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1998, 28, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q. Analysis of Indoor Air Quality and Fresh Air Energy Consumption Based on Students’ Learning Efficiency under Different Ventilation Methods by Modelica. Energies 2024, 17, 4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Costa, M. Carcinogenicity of Metal Compounds. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 5th ed.; Nordberg, G.F., Costa, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 507–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, A.; Harrison, R.M. Sources and Properties of Non-Exhaust Particulate Matter from Road Traffic: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjortenkrans, D.; Bergbäck, B.; Häggerud, A. Metal Emissions from Brake Linings and Tires: Case Studies of Stockholm, Sweden 1995/1998 and 2005. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5224–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, R.; Oldfield, M.; Bryant, J.A.; Riordan, L.; Hill, H.J.; Watts, J.A.; Alexander, M.R.; Cox, M.J.; Stamataki, Z.; Scurr, D.J.; et al. Efficacy of Antimicrobial and Anti-Viral Coated Air Filters to Prevent the Spread of Airborne Pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, S.; Wijesekara, H.; Amarasiri, D.; Zhang, T.; Ragályi, P.; Brdar-Jokanović, M.; Rékási, M.; Lin, J.-Y.; Padhye, L.P.; Zhao, H.; et al. Boron Contamination and Its Risk Management in Terrestrial and Aquatic Environmental Settings. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasnat, M.R.; Hassan, M.K.; Saha, S. A Comprehensive Review of Aluminium Composite Panels: Current Research, Challenges, and Future Research Direction. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamus, J. Applications of Titanium Sheets in Modern Building Construction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Materials Research. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1020, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Li, J. A Systematic Review of the Human Body Burden of E-Waste Exposure in China. Environ. Int. 2014, 68, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, L.; Tian, K.; Li, J. The Fate and Behavior of Thallium During Simulated Municipal Solid Waste Incineration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, A.J.; Eighmy, T.T.; Hjelmar, O.; Kosson, D.S.; Sawell, S.E.; Vehlow, J.; Hartlén, J.; van der Sloot, H.A. Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator Residues; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, C.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Heringa, M.F.; Chirico, R.; Slowik, J.G.; Richter, R.; Crippa, M.; Ezrat, P.; Decarlo, P.; Gianini, M.F.D.; et al. Identification and Quantification of Organic Aerosol from Cooking and Other Sources in Barcelona Using Aerosol Mass Spectrometer Data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1649–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Hammingh, P.; Colette, A.; Querol, X.; Degraeuwe, B.; de Vlieger, I.; van Aardenne, J. Impact of Maritime Transport Emissions on Coastal Air Quality in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Welch, W.A.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D.R. Emission measurements from a crude oil tanker at sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7098–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-M.; Jeong, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Moon, J.-H.; Chung, Y.-S.; Kim, K.-H. The Analysis of PM2.5 and Associated Elements and Their Indoor/Outdoor Pollution Status in an Urban Area. Indoor Air 2011, 21, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Bu, Z.; Liu, W.; Kan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, F.; Huang, C.; Zhao, B.; Zeng, X.; Sun, Y.; et al. Indoor Exposure Levels and Risk Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds in Residences, Schools, and Offices in China from 2000 to 2021: A Systematic Review. Indoor Air 2022, 32, e13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streibel, T.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Czech, H.; Harndorf, H.; Jakobi, G.; Jokiniemi, J.; Karg, E.; Lintelmann, J.; Matuschek, G.; Michalke, B.; et al. Aerosol Emissions of a Ship Diesel Engine Operated with Diesel Fuel or Heavy Fuel Oil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10976–10991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbonna, C.G.; Mbamalu, G.E.; Ahuchaogu, U.E.; Ogbaa, S.I.; Ukpabi, I.J. Indoor Air Pollution and Hypertension Disease Burden among Women Using Low-Grade Fuels. Indoor Environ. 2024, 1, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.P. Indoor Air Pollution and Chronic Respiratory Diseases. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R. National Burden of Disease in India from Indoor Air Pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13286–13293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Luo, L.; Qian, C.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y. Associations between Indoor and Outdoor Size-Resolved Particulate Matter in Urban Beijing: Chemical Compositions, Sources, and Health Risks. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirkkonen, J.; Täubel, M.; Hirvonen, M.-R.; Leppänen, H.; Lindsley, W.G.; Chen, B.T.; Hyvärinen, A.; Huttunen, K. Evaluation of Sampling Methods for Toxicological Testing of Indoor Air Particulate Matter. Inhal. Toxicol. 2016, 28, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tong, X.; Wang, B.; Dai, W.-T.; Cao, J.-J.; Ho, S.S.H.; Kwok, T.C.Y.; Lui, K.-H.; Lo, C.-M.; Ho, K.F. Indoor Air Pollutant Exposure and Determinant Factors Controlling Household Air Quality for Elderly People in Hong Kong. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.V.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Indoor Air Pollution, Related Human Diseases, and Recent Trends in the Control and Improvement of Indoor Air Quality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Chu, X.; Lin, J.; Yang, Q.; Fan, Z.; Wang, D.; Oeser, M. Investigation of the Formation Mechanism and Environmental Risk of Tire—Pavement Wearing Waste (TPWW). Sustainability 2021, 13, 8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wippermann, D.; Zonderman, A.; Zimmermann, T.; Pröfrock, D. Determination of Technology-Critical Elements in Seafood Reference Materials by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 2797–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.J.; Song, A.M.; Song, M.W. Health Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Pearl River Delta. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 260–261, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.M.T.; Cai, J.; Cheng, W.-H.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Molla, A.H.; Mohd Nadzir, M.S.; Kong, S.S.-K.; Chen, L.-W.A. Application of Deep Learning Techniques for Air Quality Prediction: A Case Study in Macau. Processes 2025, 13, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.H.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Chandra, I.; Lei, T.M.T. Modeling PM10 Emissions in Quarry and Mining Operations: Insights from AERMOD Applications in Malaysia. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Rashid, A.; Habib, A.K.M.A.; Mahmud, M.; Motakabber, S.M.A.; Hossain, S.; Rokonuzzaman, M.; Molla, A.H.; Harun, Z.; Khan, M.M.H.; et al. Vehicle to Grid: Technology, Charging Station, Power Transmission, Communication Standards, Techno-Economic Analysis, Challenges, and Recommendations. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter * | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| c | mg/kg | Heavy metal content in dust from sampling sites |
| IR | mg/day | 12.800 |
| EF | days/year | 200.000 |
| ED | years | 30.000 |
| BW | Kg | 55.900 |
| AT | days | ED × 365 (for non-carcinogenic), 70 × 365 (for carcinogenic) |
| PEF | mg/kg | 1.360 × 109 |
| CF | kg/mg | 1.000 × 10−6 |
| FI | 1.000 | |
| SA | cm2/event | 400.000 |
| AF | mg/cm2 | 0.500 |
| ABS | 0.001 |
| Item | RfD Inh * mg/kg-Day | RfD Ing * mg/kg-Day | RfD Der * mg/kg-Day | SF * [mg/kg-Day]−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 3.000 × 10−1 | 3.000 × 10−1 | 3.000 × 102 | |
| Pb | 3.520 × 10−3 | |||
| Cu | 4.020 × 10−2 | 4.000 × 10−2 | 4.000 × 101 | |
| Be | 2.000 × 10−2 | 2.000 × 10−3 | 2.000 | 1.100 |
| As | 1.230 × 10−4 | 3.000 × 10−4 | 1.000 × 10−2 | 4.300 × 10−3 |
| Ni | 2.060 × 10−2 | 2.000 × 10−2 | 2.000 | 0.840 |
| Cr | 2.860 × 10−5 | 3.000 × 10−3 | 3.000 × 10−1 | 42.000 |
| Cd | 1.000 × 10−3 | 5.000 × 10−4 | 5.000 × 10−1 | 6.300 |
| Element | Maximum Value (μg/g) | Indoor Environment Where It Occurs |
|---|---|---|
| Be | 0.020 | Dining Room 1 |
| B | 10.310 | Security Hall 1 |
| Na | 24815.660 | Office 2 |
| Mg | 4693.410 | Dining Room 2 |
| Al | 103.910 | Dining Room 2 |
| Si | 67.220 | Auto Repair Shop 1 |
| K | 4257.890 | Office 2 |
| Ca | 16024.950 | Dining Room 2 |
| Ti | 8.300 | Dining Room 2 |
| V | 0.580 | Dining Room 2 |
| Cr | 3.350 | Office 1 |
| Mn | 448.040 | Auto Repair Shop 2 |
| Fe | 447.950 | Auto Repair Shop 2 |
| Co | 222.410 | Auto Repair Shop 1 |
| Ni | 992.710 | Auto Repair Shop 2 |
| Cu | 30.540 | Auto Repair Shop 1 |
| Zn | 1659.580 | Office 1 |
| As | 3.000 | Dormitory Room 2 |
| Se | 2.310 | Dormitory Room 2 |
| Mo | 1.100 | Auto Repair Shop 1 |
| Ag | 0.020 | Office 3 |
| Cd | 0.210 | Office 1 |
| Sb | 1.820 | Office 2 |
| Ba | 3.240 | Dining Room 1 |
| Tl | 0.060 | Dormitory Room 2 |
| Pb | 1.000 | Dormitory Room 2 |
| Compound | ADD (mg/kg/Day) | HQ | HI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Be | 1.070 × 10−12 | 5.350 × 10−10 | 6.160 × 10−6 |
| Cr | 1.260 × 10−10 | 4.400 × 10−6 | |
| Ni | 1.190 × 10−8 | 5.780 × 10−7 | |
| Cu | 1.080 × 10−9 | 2.670 × 10−8 | |
| Zn | 1.800 × 10−8 | 5.990 × 10−8 | |
| As | 1.320 × 10−10 | 1.070 × 10−6 | |
| Cd | 7.760 × 10−12 | 7.760 × 10−9 | |
| Pb | 3.460 × 10−11 | 9.840 × 10−9 |
| Compound | ADD (mg/kg/Day) | HQ | HI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Be | 1.470 × 10−9 | 7.370 × 10−7 | 1.720 × 10−3 |
| Cr | 1.840 × 10−7 | 6.130 × 10−5 | |
| Ni | 1.740 × 10−5 | 8.690 × 10−4 | |
| Cu | 1.570 × 10−6 | 3.920 × 10−5 | |
| Zn | 2.620 × 10−5 | 8.740 × 10−5 | |
| As | 1.920 × 10−7 | 6.400 × 10−4 | |
| Cd | 1.130 × 10−8 | 2.270 × 10−5 | |
| Pb | 5.060 × 10−8 |
| Compound | ADD (mg/kg/Day) | HQ | HI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Be | 2.300 × 10−11 | 1.150 × 10−11 | 2.270 × 10−5 |
| Cr | 2.870 × 10−8 | 9.570 × 10−8 | |
| Ni | 2.720 × 10−5 | 1.360 × 10−5 | |
| Cu | 2.450 × 10−7 | 6.130 × 10−9 | |
| Zn | 4.100 × 10−6 | 1.370 × 10−8 | |
| As | 9.000 × 10−8 | 9.000 × 10−6 | |
| Cd | 1.770 × 10−10 | 3.540 × 10−10 | |
| Pb | 4.740 × 10−9 |
| Compound | ADD (mg/kg/Day) | Risk | Total Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Be | 4.580 × 10−13 | 5.040 × 10−13 | 6.570 × 10−9 |
| Cr | 5.400 × 10−11 | 2.270 × 10−9 | |
| Ni | 5.100 × 10−9 | 4.290 × 10−9 | |
| As | 5.640 × 10−11 | 2.260 × 10−13 | |
| Cd | 3.330 × 10−12 | 2.100 × 10−11 | |
| Pb | 1.480 × 10−11 | 1.260 × 10−13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, T.M.T.; Ye, W.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, W.H.; Molla, A.H.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Wu, S. Quantification of Heavy Metals in Indoor Dust for Health Risk Assessment in Macao. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111294
Lei TMT, Ye W, Liu Y, Cheng WH, Molla AH, Chen L-WA, Wu S. Quantification of Heavy Metals in Indoor Dust for Health Risk Assessment in Macao. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(11):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111294
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Thomas M. T., Wenlong Ye, Yuyang Liu, Wan Hee Cheng, Altaf Hossain Molla, L.-W. Antony Chen, and Shuiping Wu. 2025. "Quantification of Heavy Metals in Indoor Dust for Health Risk Assessment in Macao" Atmosphere 16, no. 11: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111294
APA StyleLei, T. M. T., Ye, W., Liu, Y., Cheng, W. H., Molla, A. H., Chen, L.-W. A., & Wu, S. (2025). Quantification of Heavy Metals in Indoor Dust for Health Risk Assessment in Macao. Atmosphere, 16(11), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111294








