Multi-Scale Mechanisms of Heavy Rainfall Event over North China: Nocturnal Low-Level Jet Intensification and Afternoon Synoptic Forcing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
3. Results
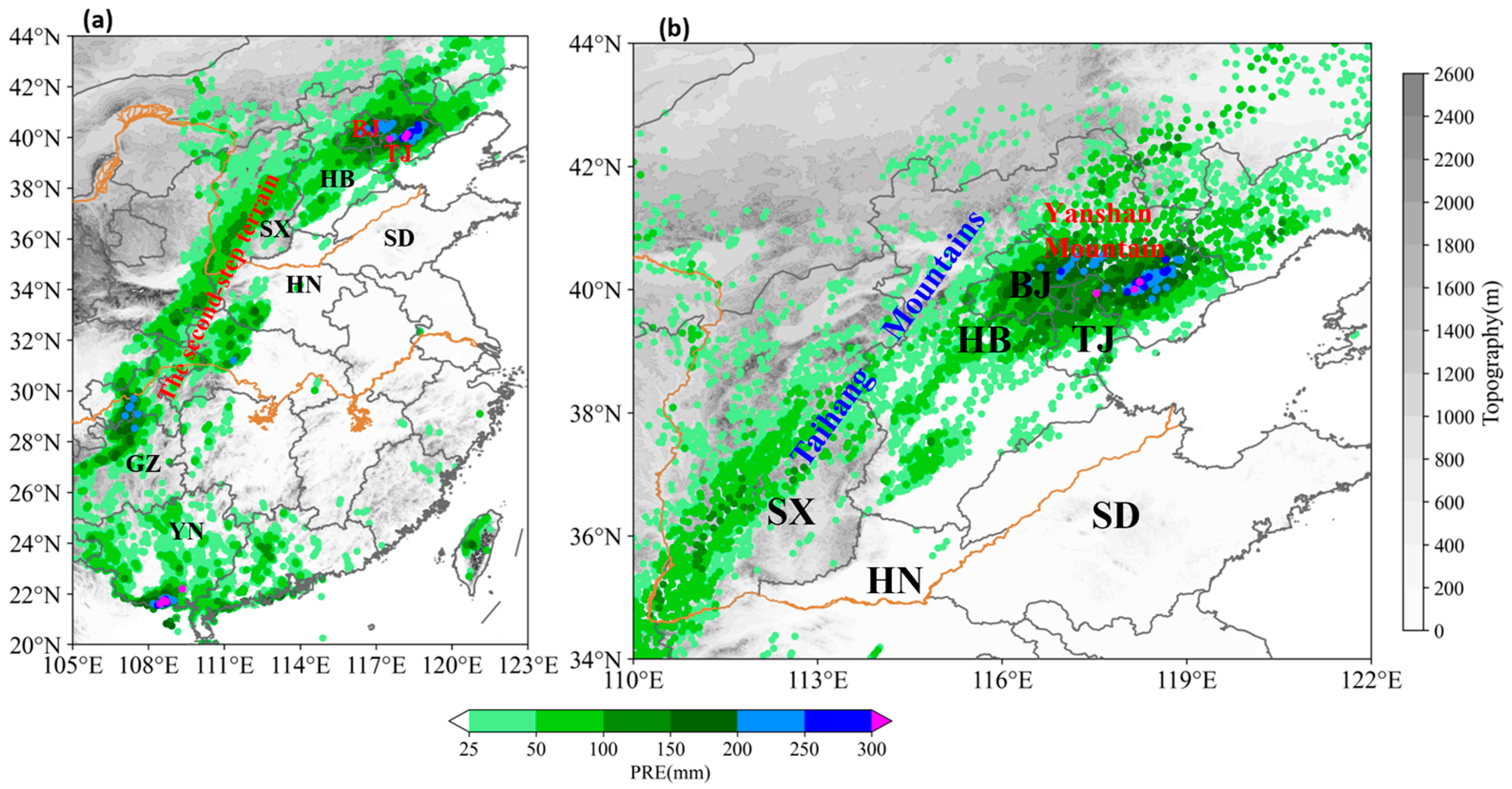
3.1. The Persistent Heavy Rainfall and Its Synoptic Circulation
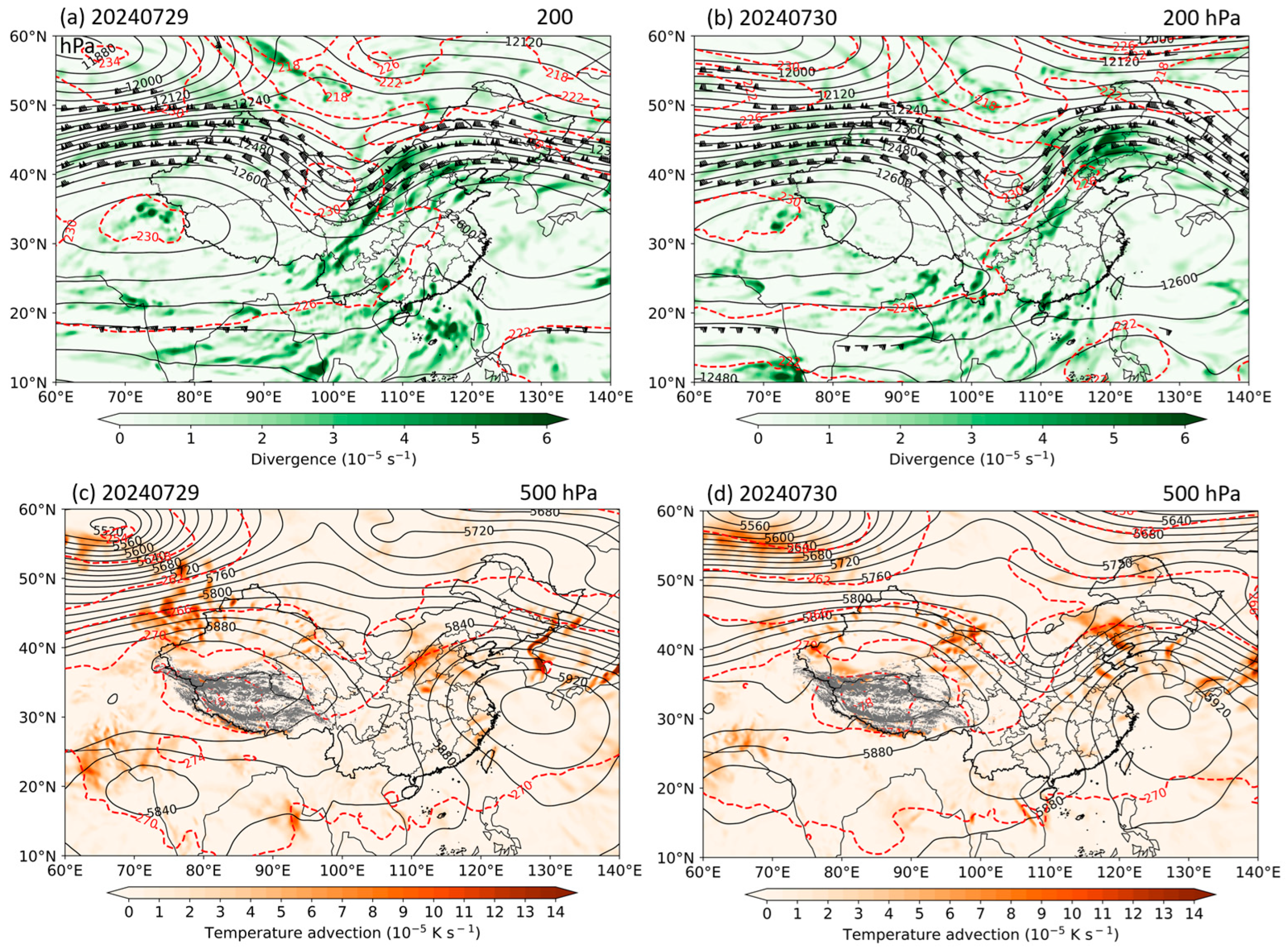
3.2. Multi-Scale Mechanisms During This Heavy Rainfall Event
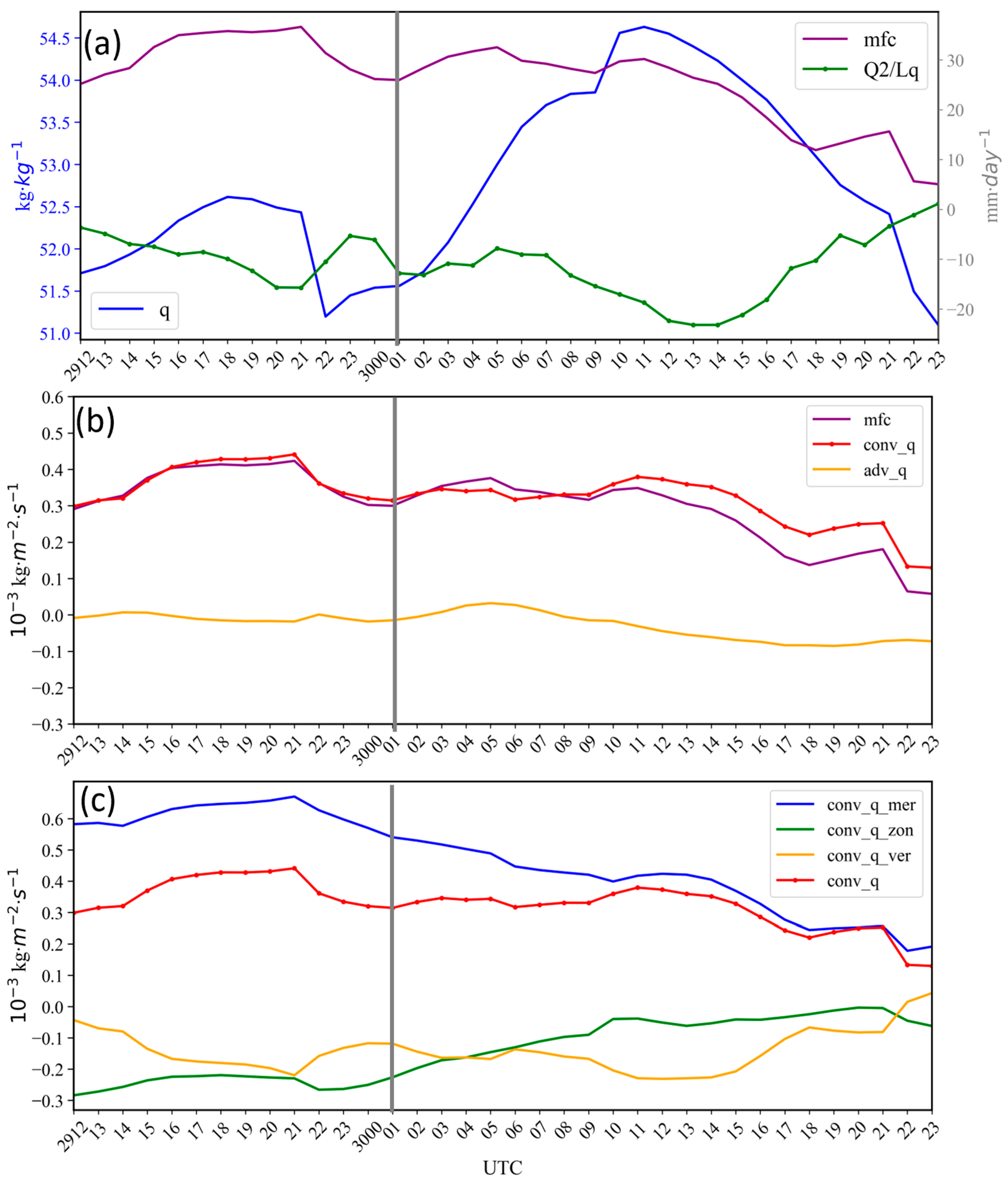
3.2.1. Temporal Variation in Moisture
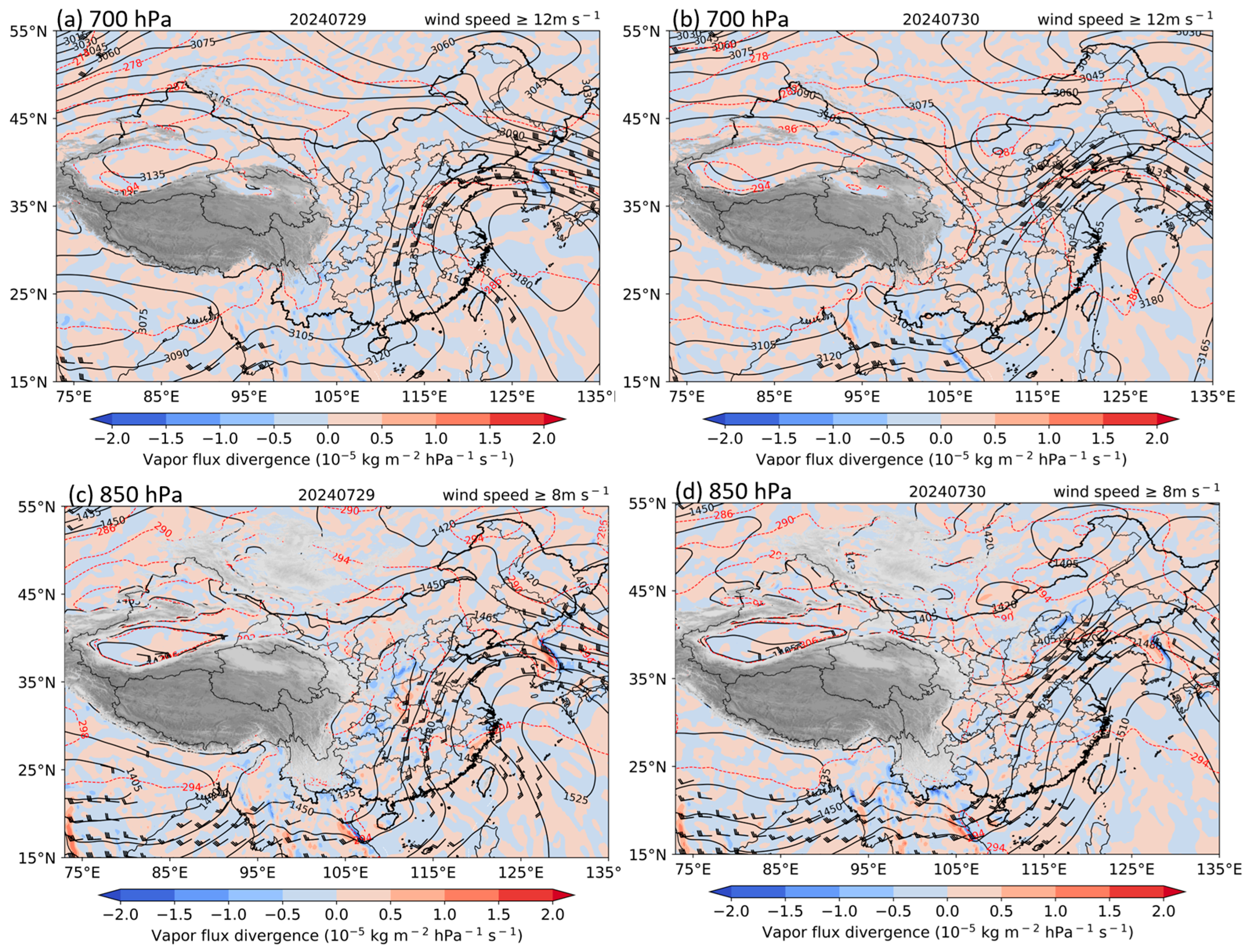
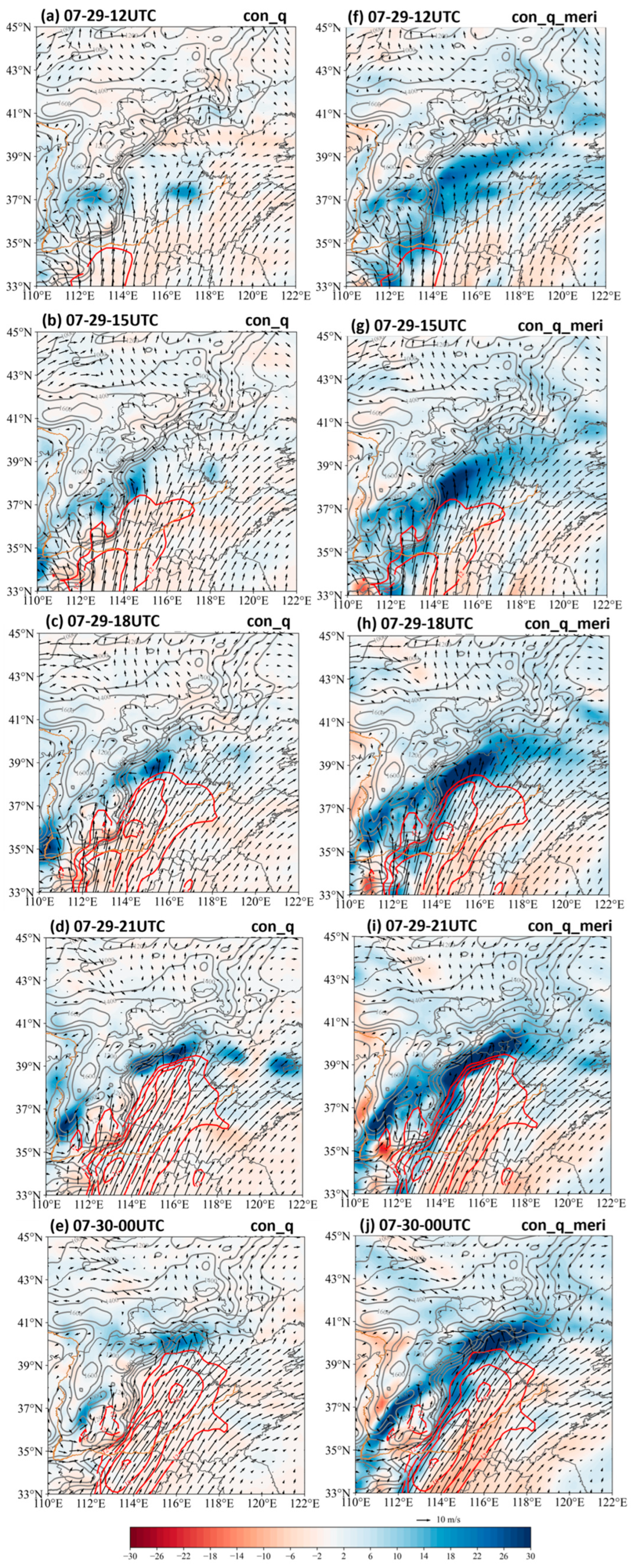
3.2.2. Meridional Moisture Convergence and Nocturnal Rainfall Intensification
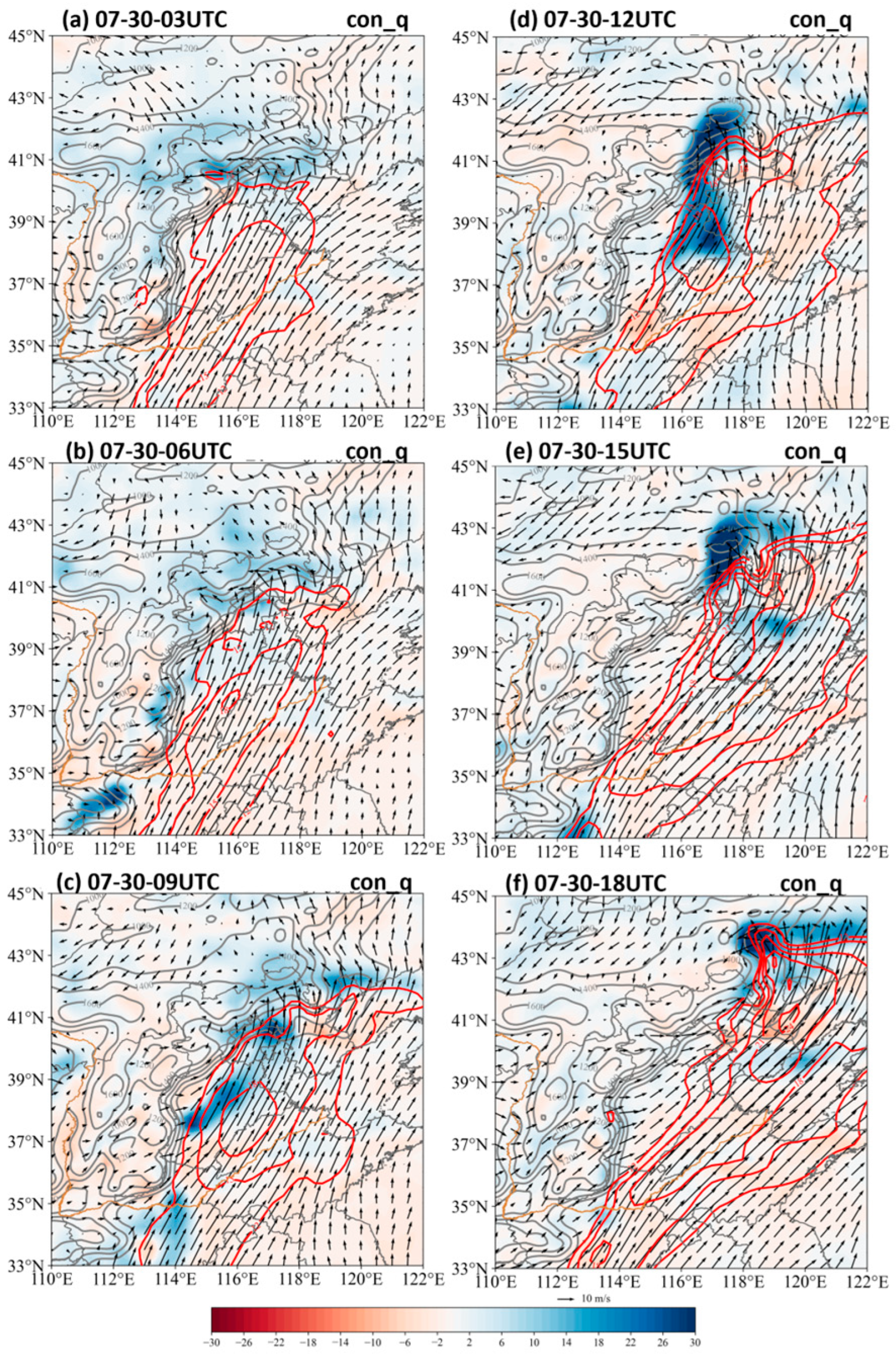
3.2.3. Moisture Convergence for the Afternoon Precipitation Maximum
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doswell, C.A.; Brooks, H.E.; Maddox, R.A. Flash flood forecasting: An ingredients based methodology. Weather Forecast. 1996, 11, 560–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebora, N.; Molini, E.; Casella, E.; Comellas, A.; Fiori, E.; Pignone, F.; Siccardi, F.; Silvestro, F.; Tanelli, S.; Parodi, A. Extreme rainfall in the Mediterranean: What can we learn from observations? J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 906–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sha, W.; Iwasaki, T.; Wen, Z. Diurnal cycle of a heavy rainfall corridor over East Asia. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 3365–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, S.N.; Zong, Z.P.; Chen, T.; Fang, C.; Sheng, J. Analysis and thinking on the extremes of the 21 July 2012 torrential rain in Beijing. PartI: Observation and thinking. Meteorol. Mon. 2012, 38, 1255–1266. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. The effects of vertical distribution of the lower-level flow on precipitation location. Plateau Meteorol. 2005, 24, 62–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, P.; Yu, X.D.; Wang, S.Q.; Kang, H.W.; Ding, Y.H. The Beijing extreme rainfall of 21 July 2012: “Right results” but for wrong reasons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1426–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Mu, R.; Zhang, D.L.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wang, N. An observational analysis of warm-sector rainfall characteristics associated with the 21 July 2012 Beijing extreme rainfall event. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 3274–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Ma, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.D.; Sun, J.; Quan, W.Q.; Yang, S.N.; Shen, X.L. Characteristics and synoptic mechanism of the July 2016 extreme precipitation event in North China. Meteorol. Mon. 2017, 43, 528–539. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Zhang, D.; Fu, S.; Yin, J.F.; Wang, H.Y. On the anomalous development of a series of heavy rainfall events from central to North China during 19–21 July 2016. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 148, 272–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Sun, J.; Yin, J.; Abulikemu, A. The impact of mountain-plain thermal contrast on precipitation distributions during the “23⋅7” record-breaking heavy rainfall over North China. Atmos. Res. 2024, 310, 107582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Ruan, Y.; Sun, J.; Liang, X.D.; Wu, C.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Yin, J.F.; Bao, X.H.; Li, M.X.; et al. Distinct mechanisms governing two types of extreme hourly rainfall Rates in the mountain foothills of North China during the passage of a typhoon remnant vortex from July 30 to August 1, 2023. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 42, 761–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, T.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Fu, J.L.; Huang, X.; Shi, Y.; Shen, Y. Observational analysis of Mount Taihang’ s orographic effects on the “23·7” extreme precipitation event in North China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 49, 629–644. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.X.; Li, J.B.; Wang, X. Investigation of extreme flash-rain events on the impact of Taihang Mountain. Meteorol. Mon. 2017, 43, 425–433. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Peng, X.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Shang, K.; Lu, S. Observational analyses of topographic effects on convective systems in an extreme rainfall event in northern China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 229, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin Ra Neiman, P.; Wick, G. Satellite and CALJET aircraft observations of atmospheric rivers over the eastern North Pacific Ocean during the winter of 1997/98. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1721–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.; Houze, R., Jr. Modification of precipitation by coastal orography in storms crossing northern California. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 3110–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, D.; Pu, Z. Characteristics and variations of low-level jets in the contrasting warm season precipitation extremes of 2006 and 2007 over the Southern Great Plains. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 136, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Du, Y. The roles of low-level jets in “21·7” Henan extremely persistent heavy rainfall event. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 350–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wan, Q.; Wang, B.; Wong, W.K.; Hu, Z.; Jou, B.J.-D.; Lin, Y.; Johnson, R.H.; Chang, C.P.; et al. The southern China monsoon rainfall experiment (SCMREX). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yuan, W.; Yu, R. The extraordinary rainfall over the eastern periphery of the Tibetan Plateau in August 2020. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Chiao, S.; Wang, T.; Kaplan, M.L.; Weglarz, R.P. Some common ingredients for heavy orographic rainfall. Weather Forecast. 2001, 16, 633–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.; Houze, R.A. Air motions precipitation growth in Alpine storms. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 129, 345–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotunno, R.; Ferretti, R. Orographic effects on rainfall in MAPcases IOP2b IOP8. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 129, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q. Moist dynamics and orographic precipitation. Tellus A 2003, 55, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B.; Barstad, I. Alinear theory of orographic precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 1377–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, S.W.; Hagos, S.; Chang, C.-C.; Balaguru, K.; Leung, L.R. Cross-equatorial surges boost MJO’s southward detour over the Maritime Continent. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL104770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Y.; Zhu, C.W.; Jiang, N. A Super Cluster of extreme rainfall event over North China in July 2023: Role of typhoon-monsoon interaction, Environ. Res. Commun. 2025, 7, 051007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Wei, J.; Zhao, S.X. A study on severe heavy rainfall in North China during the 1990s. Clim. Environ. Res. 2005, 3, 492–506. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Multi-Scale Mechanisms of Heavy Rainfall Event over North China: Nocturnal Low-Level Jet Intensification and Afternoon Synoptic Forcing. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111241
Wang H, Zhang Y. Multi-Scale Mechanisms of Heavy Rainfall Event over North China: Nocturnal Low-Level Jet Intensification and Afternoon Synoptic Forcing. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(11):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111241
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huijie, and Yuanchun Zhang. 2025. "Multi-Scale Mechanisms of Heavy Rainfall Event over North China: Nocturnal Low-Level Jet Intensification and Afternoon Synoptic Forcing" Atmosphere 16, no. 11: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111241
APA StyleWang, H., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Multi-Scale Mechanisms of Heavy Rainfall Event over North China: Nocturnal Low-Level Jet Intensification and Afternoon Synoptic Forcing. Atmosphere, 16(11), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111241



