Diverging Carbon Balance and Driving Mechanisms of Expanding and Shrinking Cities in Transitional China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. Identification of Urban Expansion and Shrinkage
2.3.2. Carbon Source and Sink Estimation
Carbon Emissions
Carbon Storage
2.3.3. Carbon Balance Zoning
Carbon Compensation Rate
Economic Contribution Coefficient of Carbon Emissions
Ecological Support Coefficient of Carbon
Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.3.4. Driving Mechanism Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Classification and Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Urban Expansion and Contraction in China
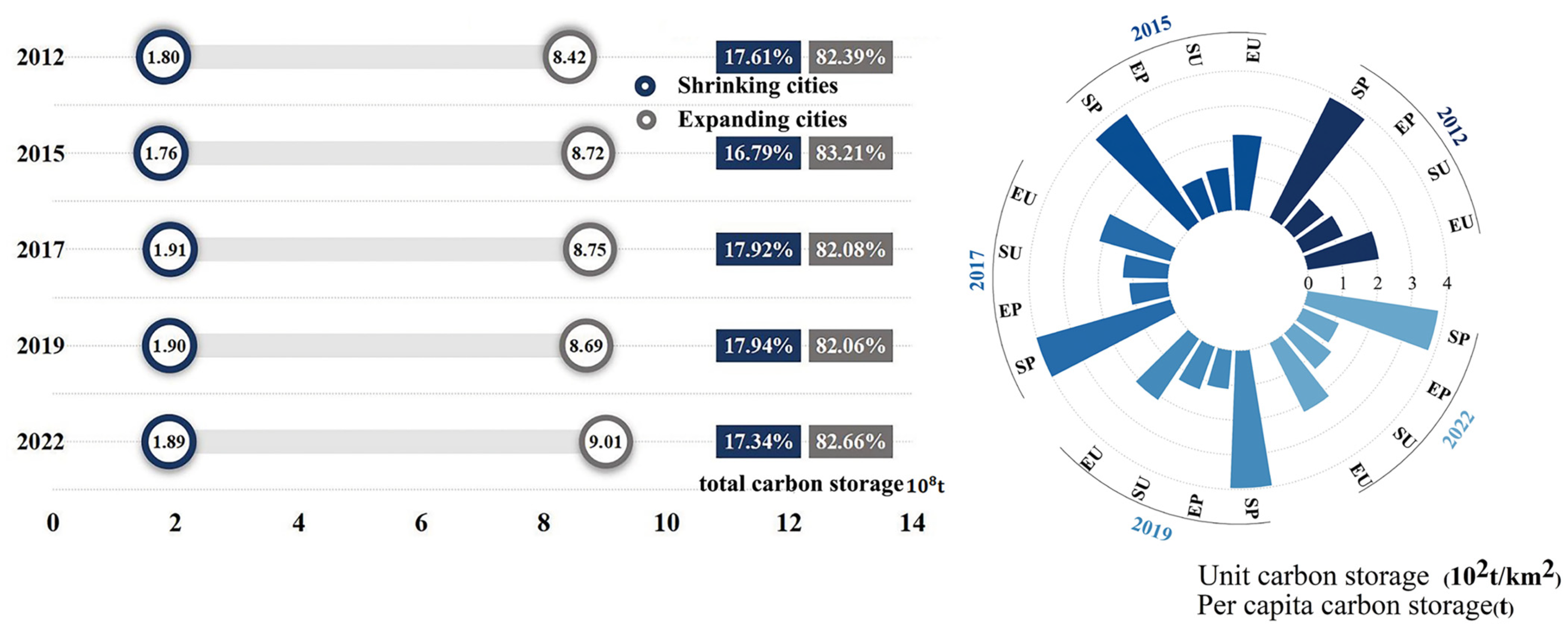
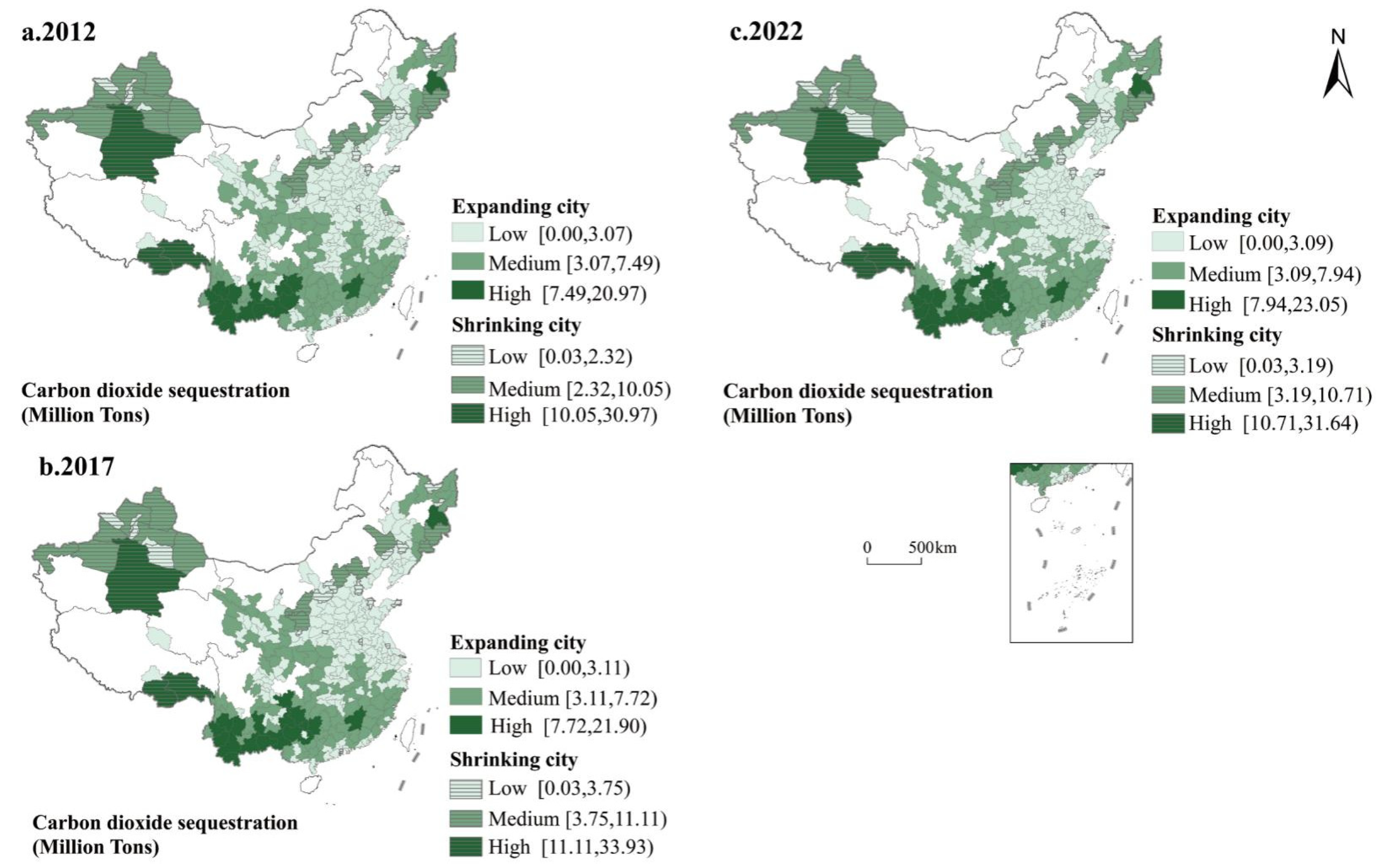
3.2. Carbon Sources and Sinks in China
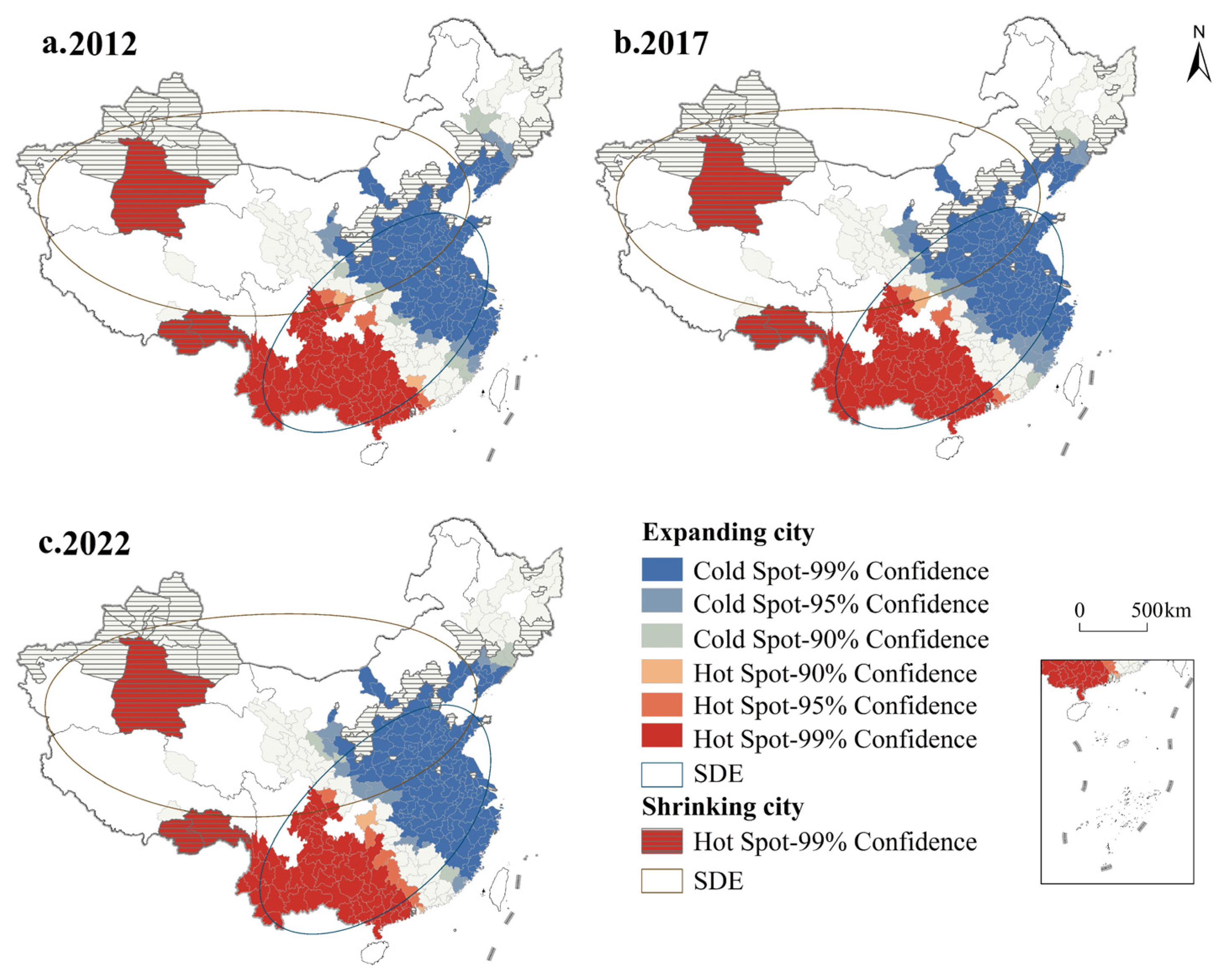
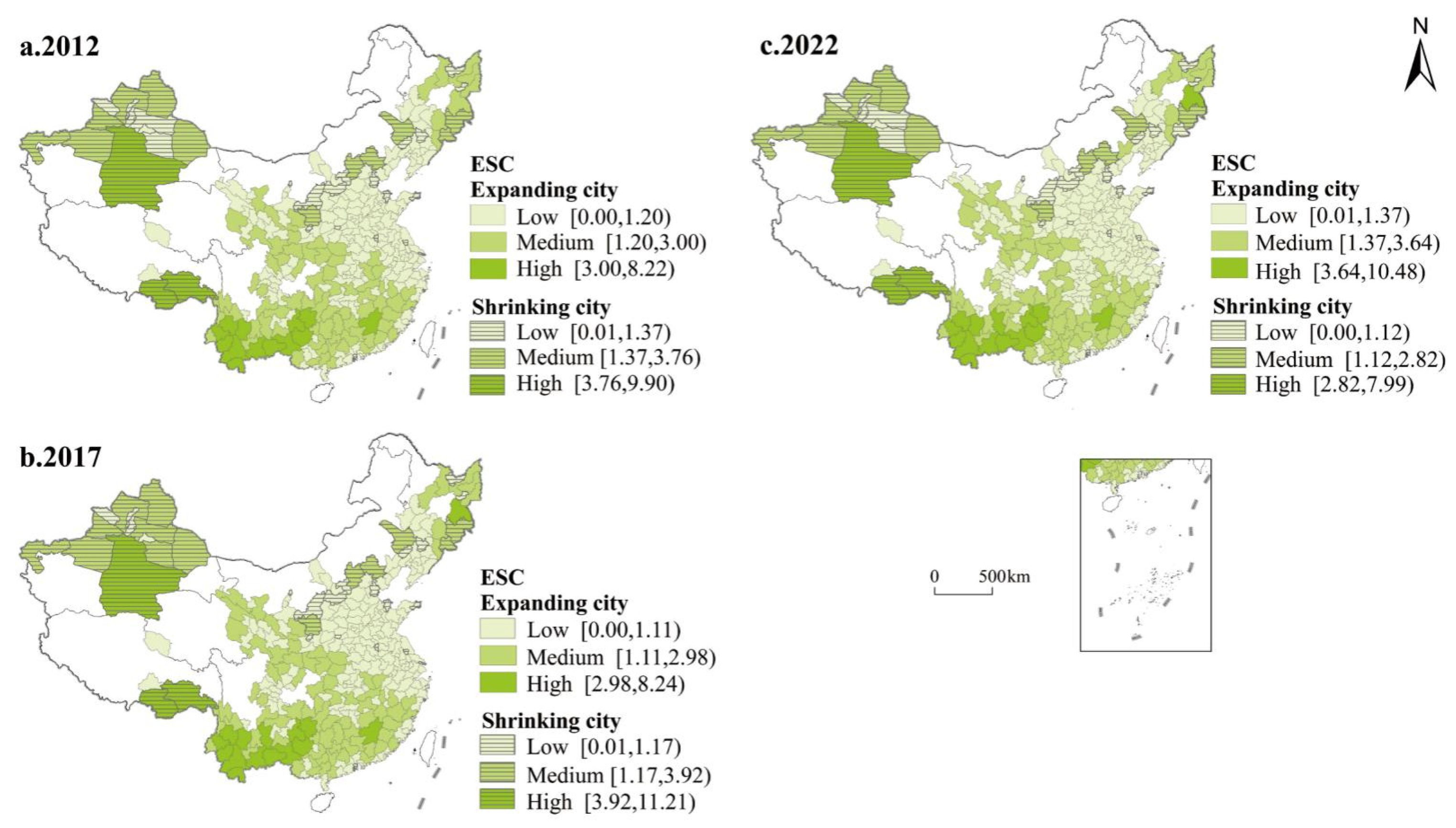
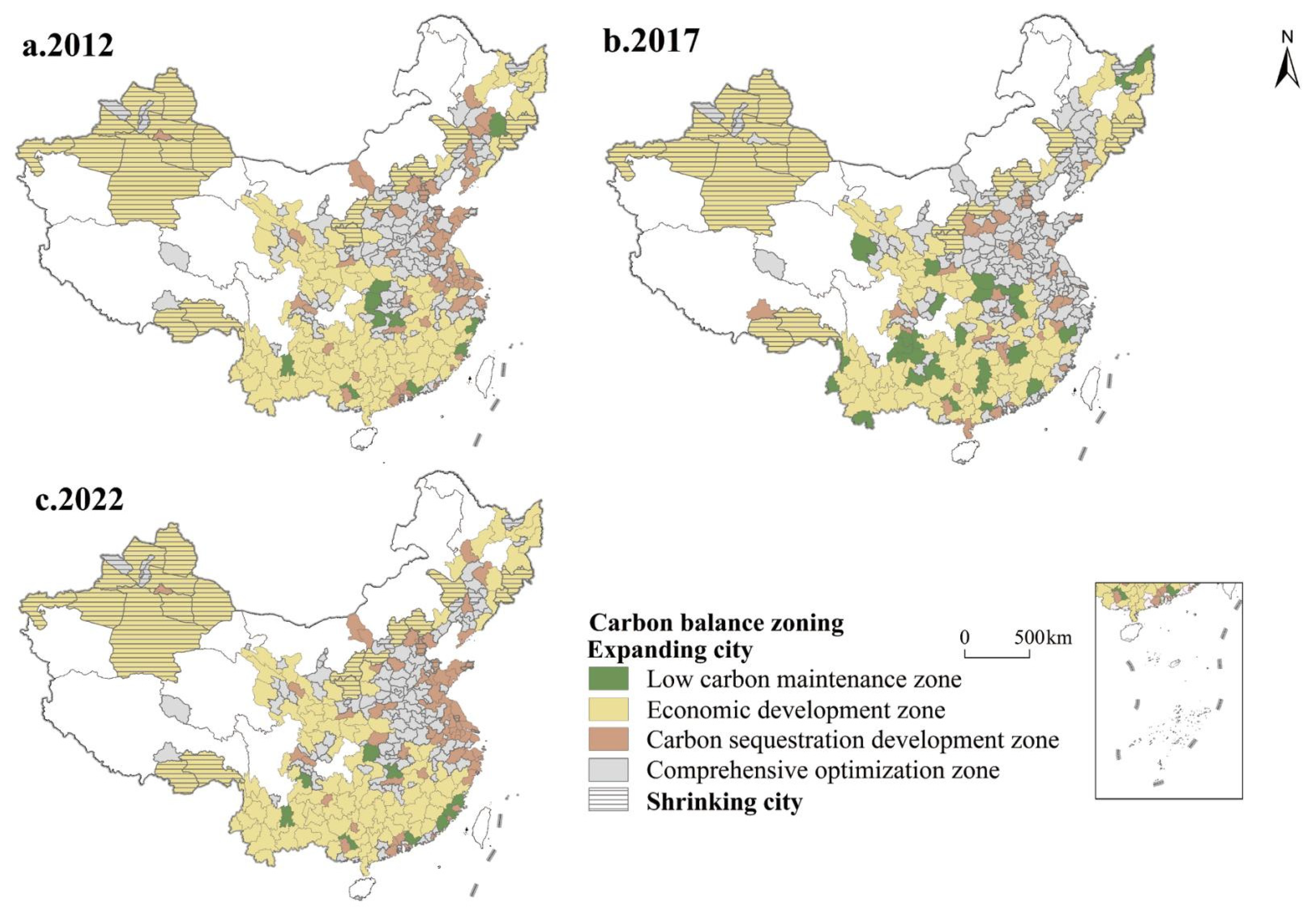
3.3. Carbon Balance Zoning
3.4. Driving Force Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Trends and Key Areas of Carbon Source and Sink Under Urban Spatial Morphological Transformation
4.2. Carbon Balance Zoning and Driving Force Heterogeneity Based on Urban Expansion–Contraction Evolution
4.3. Research Significance and Innovation Points
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Semenov, S.M. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Results, Problems, and Prospects. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2024, 60, S323–S330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y. Climate Change, Carbon Neutrality: The Role of Spatial Economics. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2024, 73, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Sinha, A.; Sharif, A.; Siddique, M.; Irshad, S.; Anwar, W.; Malik, S. The Nexus between Urbanization, Renewable Energy Consumption, Financial Development, and CO2 Emissions: Evidence from Selected Asian Countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 6556–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Msigwa, G.; Yang, M.; Osman, A.I.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.-S. Strategies to Achieve a Carbon Neutral Society: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2277–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouez, F.; Ifa, A. Assessing the Sustainability of Southeast Asia’s Energy Transition: A Comparative Analysis. Energies 2025, 18, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, H.; Lu, C. Research on the Economic Abatement Pathway of Carbon Peaking in China Based on Marginal Abatement Costs and Abatement Tasks Allocation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 7956–7972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urata, T.; Yamada, T.; Itsubo, N.; Inoue, M. Modeling and Balancing for Costs and CO2 Emissions in Global Supply Chain Network among Asian Countries. Procedia CIRP 2015, 26, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yue, T.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Long, R.; Wang, Y. Carbon Neutrality Research Hotspots and Evolution Trend: Based on the Scientific Knowledge Map. Resour. Sci. 2022, 44, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielke, R.; Burgess, M.G.; Ritchie, J. Plausible 2005–2050 Emissions Scenarios Project between 2 °C and 3 °C of Warming by 2100. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 024027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ahmed, R.; Mashud, A.H.M.; Malik, A.I.; Miah, S.; Abedin, M.Z. Consumption-Based CO2 Emissions on Sustainable Development Goals of SAARC Region. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddle, B. Consumption-Based Accounting and the Trade-Carbon Emissions Nexus in Asia: A Heterogeneous, Common Factor Panel Analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, W.P.; Cooper, C.J. Implications of Fossil Fuel Constraints on Economic Growth and Global Warming. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Cai, T. Revisiting the Environmental Kuznets Curve for City-Level CO2 Emissions: Based on Corrected NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J. Using a Combination of Nighttime Light and MODIS Data to Estimate Spatiotemporal Patterns of CO2 Emissions at Multiple Scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, S.; Yue, C.; Ding, J.; Guo, Z. Perspectives on the Role of Terrestrial Ecosystems in the ‘Carbon Neutrality’ Strategy. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubau, W.; Lewis, S.L.; Phillips, O.L.; Affum-Baffoe, K.; Beeckman, H.; Cuni-Sanchez, A.; Daniels, A.K.; Ewango, C.E.N.; Fauset, S.; Mukinzi, J.M.; et al. Asynchronous Carbon Sink Saturation in African and Amazonian Tropical Forests. Nature 2020, 579, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.M.; Ju, W.; Ciais, P.; Viovy, N.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X. Vegetation Structural Change since 1981 Significantly Enhanced the Terrestrial Carbon Sink. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Ruiz, G.; Mena-Nieto, A.; Golpe, A.A.; Garcia-Ramos, J.E. CO2 Emissions and Causal Relationships in the Six Largest World Emitters. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 162, 112435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Rahman, M.M.; Haneklaus, N.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y. Green Transition Initiatives to Reduce Environmental Degradation: Adaptation, Mitigation and Synergistic Effects. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 115, 107993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopczewska, K.; Elhorst, P. New Developments in Spatial Econometric Modelling. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2024, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Identification of the Driving Factors’ Influences on Regional Energy-Related Carbon Emissions in China Based on Geographical Detector Method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9626–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, M.; Wiechmann, T. Urban Growth and Decline: Europe’s Shrinking Cities in a Comparative Perspective 1990–2010. Eur. Urban Reg. Stud. 2018, 25, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiechmann, T.; Pallagst, K.M. Urban Shrinkage in Germany and the USA: A Comparison of Transformation Patterns and Local Strategies. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2012, 36, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Long, Y. Shrinking Cities in China: Evidence from the Latest Two Population Censuses 2010–2020. Environ. Plan.-Econ. Space 2022, 54, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Fernandez, C.; Audirac, I.; Fol, S.; Cunningham-Sabot, E. Shrinking Cities: Urban Challenges of Globalization. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2012, 36, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Crooks, A.; Wang, W.; Xie, Y. Simulating Urban Shrinkage in Detroit via Agent-Based Modeling. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morckel, V. Population Decline and Data Discrepancies: Evaluating ACS Estimates and Comprehensive Plan Projections for a Subset of U.S. Shrinking Cities. Plan. Pract. Res. 2025, 40, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Gueneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global Forecasts of Urban Expansion to 2030 and Direct Impacts on Biodiversity and Carbon Pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, S.; Li, G. Changing Urban Forms and Carbon Dioxide Emissions in China: A Case Study of 30 Provincial Capital Cities. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavar, Y.; Delavar, A.; Suzanchi, K.; Ochoa, K.S. GreenPlotter: An AI-Driven Low-Carbon Design Algorithm for Land Partitioning and Sustainable Urban Development. Technol. Des. 2024, 8, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncero-Tarazona, M.; Ribo-Perez, D.; Rodolfo-Martinez, L.; Gil-Chong, P.; Montagud-Montalva, C.; Gomez-Navarro, T. Scale Matters: A 3 Scope Urban Carbon Footprint Accounting at the Neighborhood Level. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 130, 106429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, L.; O’Regan, A.C.; McGookin, C.; Nyhan, M.M. Modelling Urban Carbon Emissions for Multiple Sectors in High Spatial Resolution for Achieving Sustainable & Net-Zero Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 126, 106370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, N.B.; Campos, P.C.D.O.; Paz, I.; Marques, M.E.S. Geoprocessing Applied to the Assessment of Carbon Storage and Sequestration in a Brazilian Medium-Sized City. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, R. Identification of Shrinkage Patterns in Japan’s Four Major Metropolitan Areas Based on Nighttime Light and Population Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 136, 104391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Zhang, Q.; de Miguel, A.S.; Roman, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote Sensing of Night Lights: A Review and an Outlook for the Future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivand, R.S.; Wong, D.W.S. Comparing Implementations of Global and Local Indicators of Spatial Association. Test 2018, 27, 716–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shi, W.; Miao, Z. Confidence Analysis of Standard Deviational Ellipse and Its Extension into Higher Dimensional Euclidean Space. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Xu, C. An Optimal Parameters-Based Geographical Detector Model Enhances Geographic Characteristics of Explanatory Variables for Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis: Cases with Different Types of Spatial Data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Cui, X.; Chen, W.; Yao, X. Impact of Urban Expansion on the Supply-Demand Balance of Ecosystem Services: An Analysis of Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 99, 107003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Lamonica, G.R. Containing Urban Expansion: Densification vs. Greenfield Development, Socio-Demographic Transformations and the Economic Crisis in a Southern European City, 2006–2015. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, G.; Hou, X. Conceptualizing the Nexus between Spatiotemporal Shrinkage Patterns of Natural Cities and Driving Mechanisms: Insights into Urban Shrinkage in Northeast China. Cities 2024, 152, 105179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, A.; Bontje, M.; Couch, C.; Marcinczak, S.; Rink, D.; Rumpel, P.; Wolff, M. Factors Driving the Regrowth of European Cities and the Role of Local and Contextual Impacts: A Contrasting Analysis of Regrowing and Shrinking Cities. Cities 2021, 108, 102942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.; Li, X.; Cai, W.; Zuo, J.; Jia, F.; Wei, H. Exploring the Impact of Urbanization on Urban Building Carbon Emissions in China: Evidence from a Provincial Panel Data Model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 56, 102068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.; Ma, Y.; Xu, L.; Feng, W.; Cai, W. Carbon Emissions in China’s Urban Residential Building Sector through 2060: A Dynamic Scenario Simulation. Energy 2022, 254, 124395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Krigsvoll, G.; Johansen, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Carbon Emission of Global Construction Sector. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, M.; Tang, Z.; Mei, Z. Urbanization, Land Use Change, and Carbon Emissions: Quantitative Assessments for City-Level Carbon Emissions in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Anan, N.; Mashud, A.H.M.; Hasan, M.; Tseng, M.-L. Consumption-Based CO2 Emissions Accounting and Scenario Simulation in Asia and the Pacific Region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 34607–34623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Qiang, W.; Wu, K.; Wang, X. Urban Form, Shrinking Cities, and Residential Carbon Emissions: Evidence from Chinese City-Regions. Appl. Energy 2020, 261, 114409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Liang, H.; Dong, L.; Ren, J.; Wang, G. Synergistic CO2 Reduction Effects in Chinese Urban Agglomerations: Perspectives from Social Network Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Gong, J.; Luo, F.; Pan, Y. Effectiveness and Driving Mechanism of Ecological Restoration Efforts in China from 2009 to 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 910, 168676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Meadows, M.E. Ecological Restoration for Sustainable Development in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; He, N. Forest Carbon Storage along the North-South Transect of Eastern China: Spatial Patterns, Allocation, and Influencing Factors. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalm, C.R.; Anderegg, W.R.L.; Michalak, A.M.; Fisher, J.B.; Biondi, F.; Koch, G.; Litvak, M.; Ogle, K.; Shaw, J.D.; Wolf, A.; et al. Global Patterns of Drought Recovery. Nature 2017, 548, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bie, Q.; Huang, C. Land Use/Cover Changes Lead to a Decrease in Carbon Storage in Arid Regions-a Case Study of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 992, 179993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Kinoshita, T.; Li, H.; Luo, S.; Su, D.; Yang, X.; Hu, Y. Toward Green Equity: An Extensive Study on Urban Form and Green Space Equity for Shrinking Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 90, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safransky, S. Greening the Urban Frontier: Race, Property, and Resettlement in Detroit. Geoforum 2014, 56, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, L.; Qi, P.; Ren, X.; Sun, X. Energy Endowment, Industrial Structure Upgrading, and CO2 Emissions in China: Revisiting Resource Curse in the Context of Carbon Emissions. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Aktar, M.; Das Gupta, A.; Abedin, M.Z. The Impact of Economic Development on Environmental Sustainability: Evidence from the Asian Region. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 3523–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Bao, Z.; Ng, S.T.; Song, W.; Chen, K. Land-Use Carbon Emissions and Built Environment Characteristics: A City-Level Quantitative Analysis in Emerging Economies. Land Use Policy 2024, 137, 107019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiao, L.; Li, F.; Lu, X.; Hou, J.; Li, R.; Cai, D. Spatial Disequilibrium and Influencing Factors of Carbon Emission Intensity of Construction Land in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 136464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xiong, R.; Ni, T. Spatial Network Characteristics of Carbon Balance in Urban Agglomerations—A Case Study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei City Agglomeration. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 169, 103343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, X.; Xu, J. Study on the Spatial-Temporal Pattern and Evolution of Surface Urban Heat Island in 180 Shrinking Cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 84, 104018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, M.; Wang, L.; Liang, Y.; Tang, F.; Li, S.; Wu, C. Impact of Urban Shrinkage on Pollution Reduction and Carbon Mitigation Synergy: Spatial Heterogeneity and Interaction Effects in Chinese Cities. Land 2025, 14, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T. Implementation Pathways for Carbon Emission Reduction Through Environmental Regulations: Synergistic Mechanisms of Industrial Intelligence and Green Technological Innovation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Industrial Structure, Technical Progress and Carbon Intensity in China’s Provinces. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yuan, H.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, F. What Determines the Diversity of CO2 Emission Patterns in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region of China? An Analysis Focusing on Industrial Structure Change. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Wang, E.; Qiu, Y.; Moest, D. Impact Assessment of Population Migration on Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions in China: A Spatial Econometric Investigation. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 93, 106744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Pan, J. How Do Trade-Offs between Ecological Construction and Urbanization Affect Regional Carbon Balance? A Case Study from China’s Yellow River Basin. Catena 2024, 247, 108534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.-F.; Pan, S.-Y.; Yu, H.; Wei, Y.-M. Potential Impacts of Industrial Structure on Energy Consumption and CO2 Emission: A Case Study of Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunko, M. Postsocialism through the Lens of Shrinking Cities and Urban Infrastructure. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2025, 66, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Teo, T.S.H. Green Technology Innovation, Environmental Externality, and the Cleaner Upgrading of Industrial Structure in China—Considering the Moderating Effect of Environmental Regulation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 184, 122020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Ou, J. Temporal-Spatial Variation and Regulatory Mechanism of Carbon Budgets in Territorial Space through the Lens of Carbon Balance: A Case of the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Types | Data | Precision | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote sensing image | Nighttime light data | 500 m | https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/ (assessed on 19 December 2024) |
| Land cover data | 30 m | https://zenodo.org/records/12779975 (assessed on 1 September 2024) | |
| Meteorological data | monthly | https://data.cma.cn/ (assessed on 22 March 2025) | |
| NDVI raster data | 1000 m | https://www.resdc.cn/ (assessed on 14 October 2024) | |
| Statistical data | Socioeconomic data | yearly | http://www.stats.gov.cn/ (assessed on 2 June 2025) |
| Other auxiliary data | Administrative boundary | GS(2024)0650 | https://cloudcenter.tianditu.gov.cn (assessed on 3 February 2025) |
| Carbon Emission Sources | Discount Factor for Standard Coal (t Standard Coal/t) | Carbon Emission Coefficient (104 t Carbon/104 t Standard Coal) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw coal | 0.71 | 0.76 |
| Coke | 0.97 | 0.86 |
| Crude oil | 1.43 | 0.59 |
| Gasoline | 1.47 | 0.55 |
| Kerosene | 1.47 | 0.57 |
| Diesel | 1.48 | 0.59 |
| fuel oil | 1.43 | 0.62 |
| natural gas | 1.33 | 0.45 |
| Heat | 34.12 | 0.67 |
| Electricity | 0.345 | 0.272 |
| Year | Shrinking Cities (%) | Expanding Cities (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Significant Shrinkage | Non-Significant Shrinkage | Significant Expansion | Non-Significant Expansion | |
| 2012–2017 | 0.78 | 22.14 | 65.65 | 39.74 |
| 2017–2022 | 2.08 | 9.68 | 45.78 | 42.08 |
| 2012–2022 | 1.81 | 14.35 | 28.38 | 55.06 |
| Year | Shrinking Cities | Expanding Cities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | Z | Moran’s I | Z | |
| 2012 | 0.167767 | 1.597566 | 0.218301 *** | 26.409825 |
| 2017 | 0.155989 | 1.524104 | 0.231272 *** | 27.964083 |
| 2022 | 0.161509 | 1.571922 | 0.232322 *** | 28.123701 |
| Types | Variables | EL | UR | PZ | CA | RA | IS | TA | ES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expanding cities | q | 0.0744 | 0.2343 | 0.5089 | 0.0803 | 0.1661 | 0.5237 | 0.0851 | 0.3656 |
| p | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Shrinking cities | q | 0.2951 | 0.4558 | 0.8633 | 0.3865 | 0.2609 | 0.7462 | 0.1603 | 0.2367 |
| p | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0051 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, J.; Luo, K.; Xia, L.; Wang, Z. Diverging Carbon Balance and Driving Mechanisms of Expanding and Shrinking Cities in Transitional China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101155
Lei J, Luo K, Xia L, Wang Z. Diverging Carbon Balance and Driving Mechanisms of Expanding and Shrinking Cities in Transitional China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(10):1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101155
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Jiawei, Keyu Luo, Le Xia, and Zhenyu Wang. 2025. "Diverging Carbon Balance and Driving Mechanisms of Expanding and Shrinking Cities in Transitional China" Atmosphere 16, no. 10: 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101155
APA StyleLei, J., Luo, K., Xia, L., & Wang, Z. (2025). Diverging Carbon Balance and Driving Mechanisms of Expanding and Shrinking Cities in Transitional China. Atmosphere, 16(10), 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101155





