Spatiotemporal and Synoptic Analysis of PM10 Based on Self-Organizing Map (SOM) During Asian Dust Events in South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
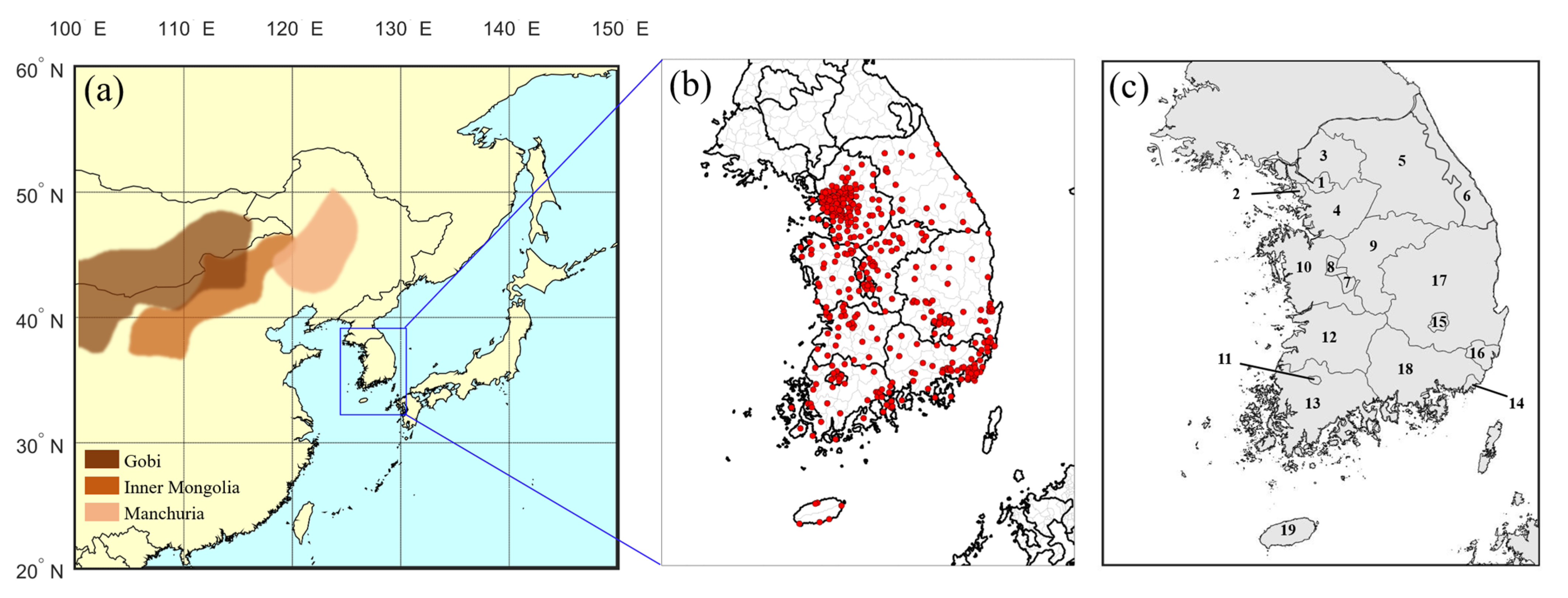
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Case Selection
2.2. Self-Organizing Map (SOM)
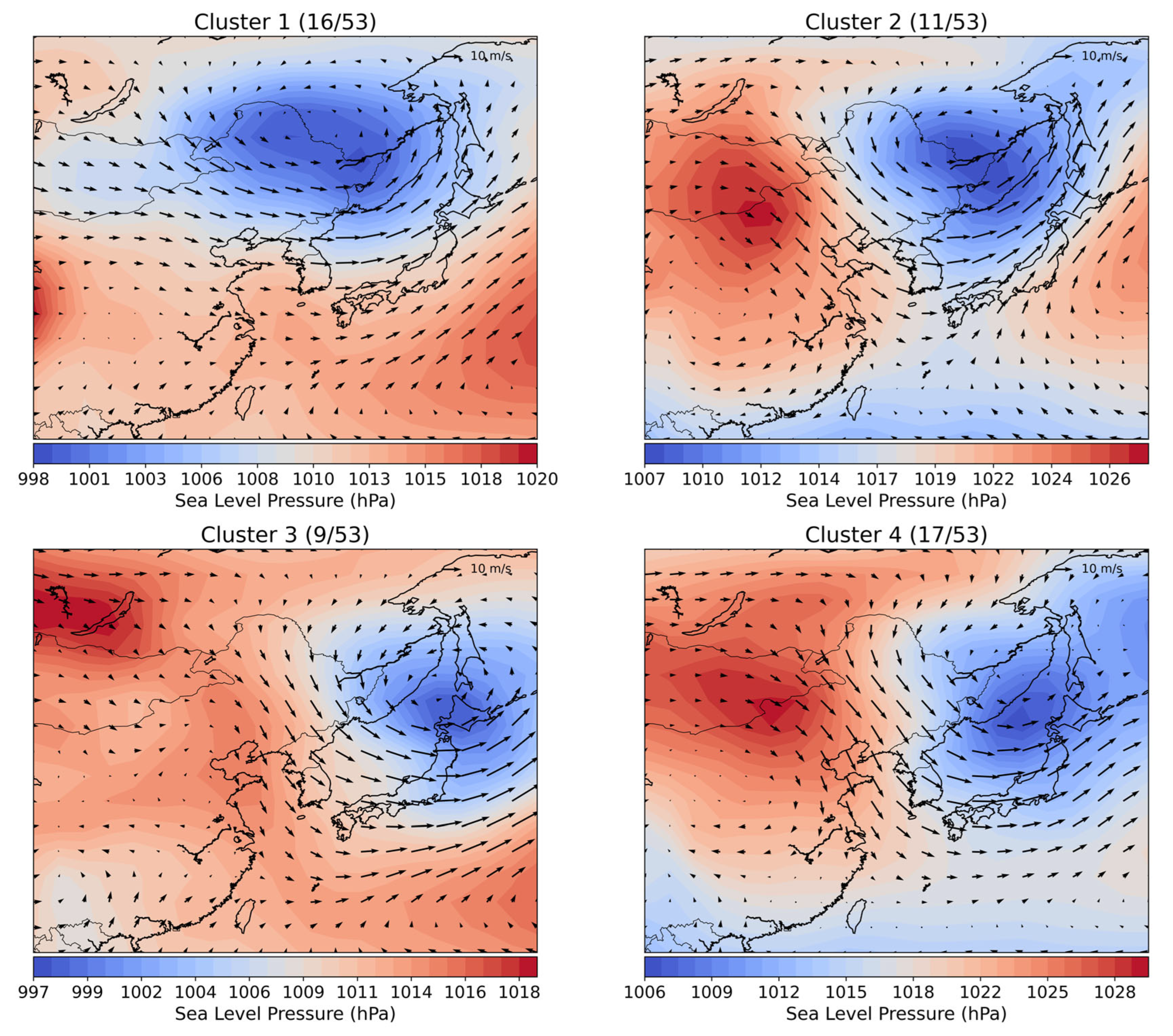
3. Results
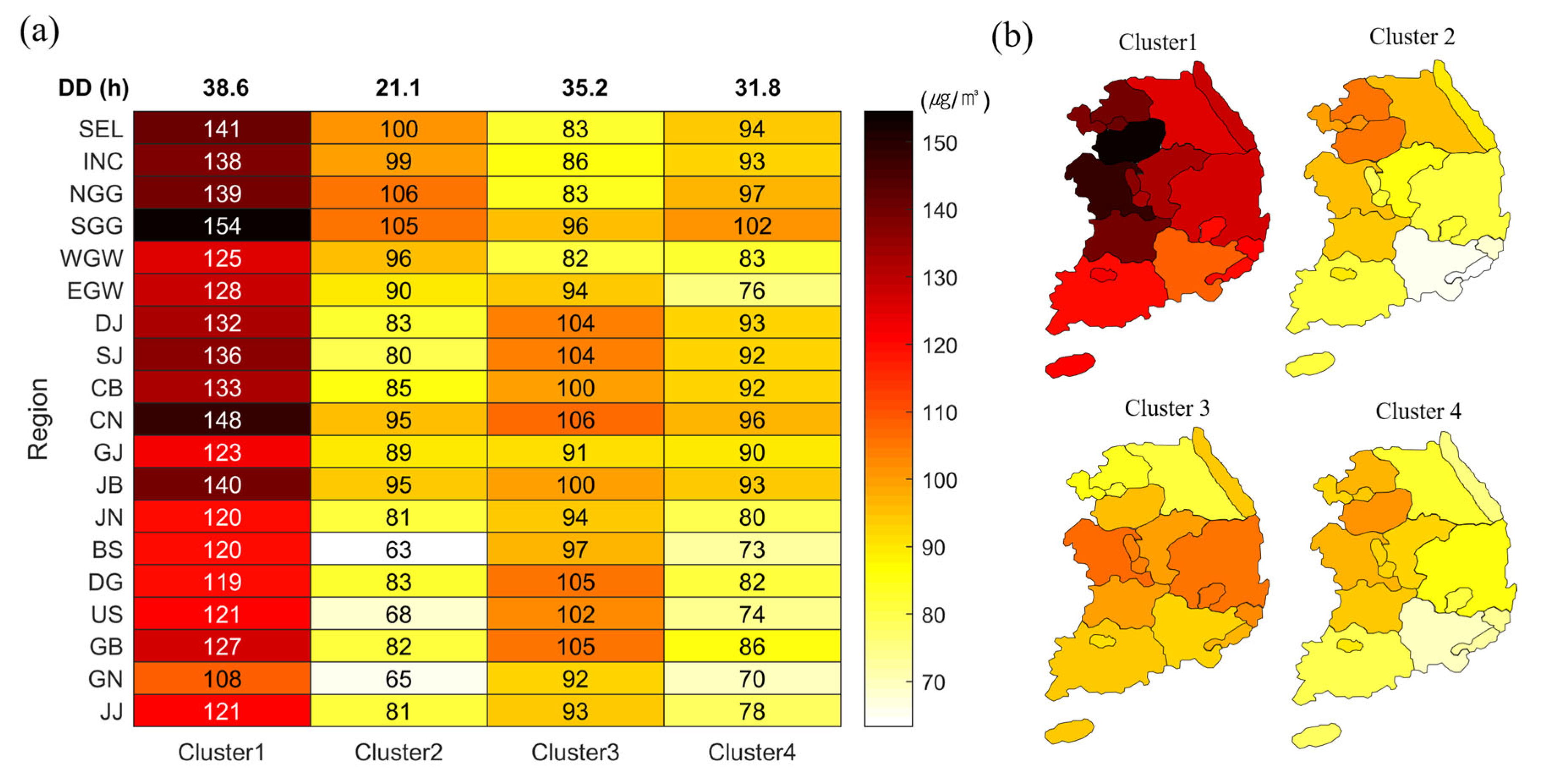
3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of PM10 by Cluster
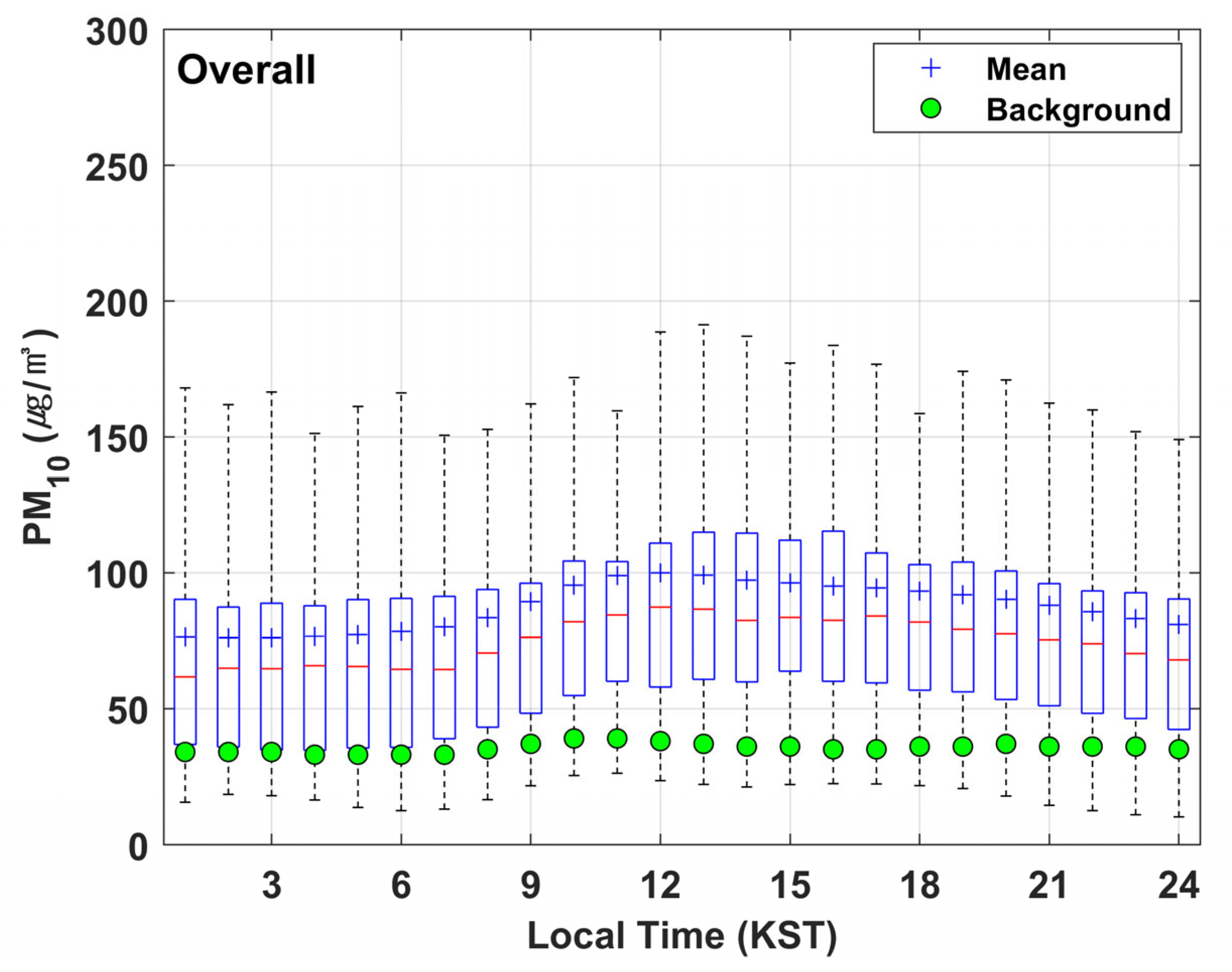
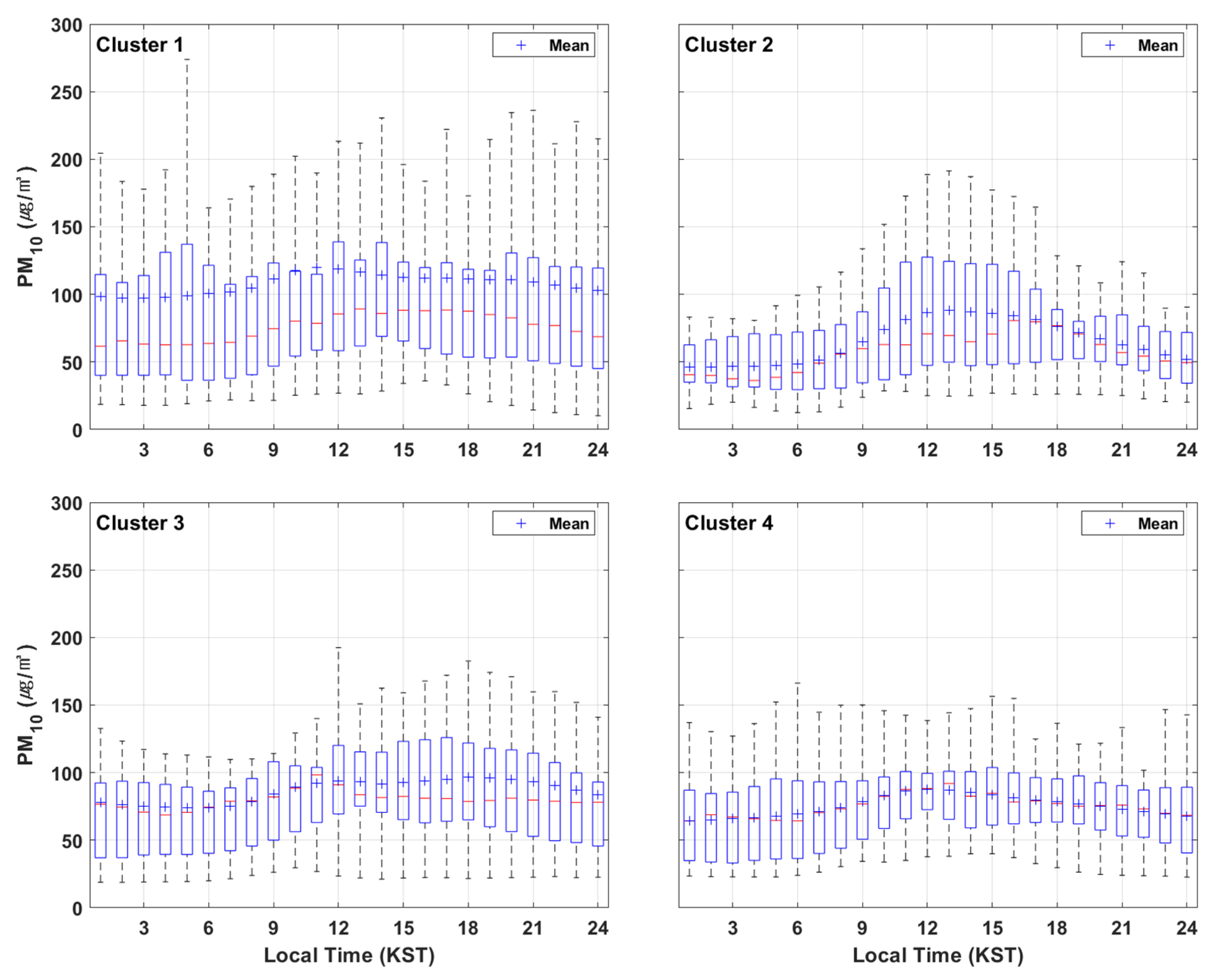
3.2. Temporal Characteristics of PM10
4. Conclusions
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Cluster Type | Date | PM10 Hourly Max (µg m−3) | Highest Concentration Area | PM10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advisory | Warning | |||||
| 1 | Cluster 1 | 22-Apr-19 | 169 | SGG | 6 | - |
| 2 | 29-Oct-19 | 259 | US | 49 | - | |
| 3 | 19-Mar-20 | 172 | GJ | 1 | - | |
| 4 | 11-May-20 | 202 | NGG | 10 | - | |
| 5 | 14-May-20 | 227 | GJ | 27 | 2 | |
| 6 | 04-Jun-20 | 137 | WGW | - | - | |
| 7 | 23-Mar-21 | 265 | EGW | 9 | - | |
| 8 | 29-Mar-21 | 1309 | JJ | 89 | 58 | |
| 9 | 28-Apr-21 | 179 | GJ | 6 | - | |
| 10 | 07-May-21 | 869 | INC | 78 | 64 | |
| 11 | 24-May-21 | 304 | SEL | 37 | 1 | |
| 12 | 11-Apr-23 | 599 | JJ | 114 | 52 | |
| 13 | 07-Dec-23 | 137 | SEL | - | - | |
| 14 | 29-Mar-24 | 509 | INC | 67 | 16 | |
| 15 | 16-Apr-24 | 295 | EGW | 18 | 1 | |
| 16 | 25-Apr-24 | 147 | DG | - | - | |
| 1 | Cluster 2 | 18-Nov-19 | 275 | NGG | 28 | - |
| 2 | 22-Feb-20 | 160 | SGG | - | - | |
| 3 | 22-Oct-20 | 211 | GJ | 23 | - | |
| 4 | 07-Nov-20 | 123 | INC | - | - | |
| 5 | 13-Jan-21 | 174 | SEL | 6 | - | |
| 6 | 16-Apr-21 | 324 | SEL | 11 | 10 | |
| 7 | 17-Apr-21 | 275 | EGW | 41 | - | |
| 8 | 26-Nov-22 | 112 | INC | - | - | |
| 9 | 13-Dec-22 | 395 | NGG | 63 | 12 | |
| 10 | 15-Mar-23 | 134 | INC | - | - | |
| 11 | 12-May-24 | 251 | DG | 31 | 1 | |
| 1 | Cluster 3 | 13-Mar-19 | 71 | SGG | - | - |
| 2 | 05-Apr-19 | 231 | SGG | 38 | - | |
| 3 | 02-May-19 | 240 | JJ | 14 | - | |
| 4 | 14-Jan-21 | 109 | WGW | 2 | - | |
| 5 | 27-Apr-22 | 242 | INC | 25 | - | |
| 6 | 16-Apr-23 | 203 | DG | 24 | - | |
| 7 | 21-Apr-23 | 616 | US | 89 | 37 | |
| 8 | 21-May-23 | 207 | EGW | 8 | - | |
| 9 | 24-Jun-24 | 177 | DG | 4 | - | |
| 1 | Cluster 4 | 28-Jan-19 | 150 | NGG | 1 | - |
| 2 | 04-Feb-19 | 155 | GJ | 8 | - | |
| 3 | 31-Oct-19 | 202 | NGG | 41 | - | |
| 4 | 04-Apr-20 | 233 | GJ | 23 | - | |
| 5 | 21-Apr-20 | 111 | NGG | - | - | |
| 6 | 22-Apr-20 | 254 | NGG | 10 | - | |
| 7 | 25-Apr-20 | 169 | DJ | - | - | |
| 8 | 15-Jan-21 | 185 | US | 1 | - | |
| 9 | 16-Mar-21 | 218 | DG | 29 | 1 | |
| 10 | 04-Mar-22 | 278 | INC | 59 | - | |
| 11 | 16-Mar-22 | 142 | DJ | - | - | |
| 12 | 07-Jan-23 | 251 | SJ | 36 | - | |
| 13 | 20-Jan-23 | 178 | INC | 20 | - | |
| 14 | 02-Mar-23 | 92 | NGG | - | - | |
| 15 | 23-Mar-23 | 358 | INC | 52 | 9 | |
| 16 | 17-Mar-24 | 309 | INC | 41 | 6 | |
| 17 | 19-Mar-24 | 243 | JJ | 5 | - | |
References
- Middleton, N. Desert Dust Hazards: A Global Review. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.; Al-Hemoud, A. Sand and Dust Storms: Recent Developments in Impact Mitigation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Heo, H.H.; Kim, C.S. Effects of the Asian Dust Events on Daily Mortality in Seoul Korea. Environ. Res. 2013, 124, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, M.; Kim, Y.; Ng, C.F.S.; Chung, Y.; Madaniyazi, L.; Bell, M.L.; Guo, Y.L.; Kan, H.; Honda, Y.; Yi, S.-M.; et al. Health Effects of Asian Dust: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 066001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.; Kim, B.-U.; Kim, H.C.; Yoo, C.; Kim, S. Long-Range Transport Influence on Key Chemical Components of PM2.5 in the Seoul Metropolitan Area, South Korea, during the Years 2012–2016. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.H.; Kim, J.; Shim, S.; Seo, J.; Byun, Y.H. Analysis of Weather Patterns Related to Wintertime PM10 Concentration in Seoul Metropolitan Area, South Korea. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.S.K.; Pani, S.K.; Griffith, S.M.; Ou-Yang, C.F.; Ravindra Babu, S.; Chuang, M.T.; Ooi, M.C.G.; Huang, W.S.; Sheu, G.R.; Lin, N.H. Distinct transport mechanisms of East Asian dust and the impact on downwind marine and atmospheric environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, R.J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Guo, J.; Chen, J.; Cao, J.; et al. Aqueous-phase secondary organic aerosol formation on aged dust particles over land. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2025, 12, nwaf221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Li, H.; Tian, M.; Wang, G.; Qin, X.; Zhao, N.; Huo, J.; Yang, F.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Secondary aerosol formation during a special dust transport event: Impacts from unusually enhanced ozone and dust backflows over the ocean. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 13853–13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobías, A.; Querol, X.; Roqué, M.; Lwin, K.S.; Yuan, L.; Ith, S.; Wai, H.Z.; Chua, P.L.; Solá, I.; Renzi, M.; et al. Short-Term Exposure to Desert Dust and Sandstorms and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality and Morbidity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Int. 2025, 181, 109277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S.; Oku, Y.; et al. Dust Cycle: An Emerging Core Theme in Earth System Science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Global Assessment of Sand and Dust Storms; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016; Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/20.500.11822/20764 (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Jin, J.; Pang, M.; Segers, A.; Han, W.; Fang, L.; Li, B.; Feng, H.; Lin, H.X.; Liao, H. Inverse modeling of the 2021 spring super dust storms in East Asia. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 6393–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Why super sandstorm 2021 in North China? Atmosphere 2021, 12, nwab165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Dai, T.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. A Study of a Severe Spring Dust Event in 2021 over East Asia with WRF-Chem and Multiple Platforms of Observations. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Jin, Q.; Idrissa, N.F.; Huang, J.; Dong, W. Attribution of the March 2021 exceptional dust storm in North China. Atmosphere 2023, 104, E749–E755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Tan, C.; Zhao, Z.; Yao, W. The Lower Atmospheric Characteristics of Dust Storms Using Ground-Based Sensor Data: A Comparative Analysis of Two Cases in Jinan, China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Leung, J.C.H.; Ren, J.; Du, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, B. Anomaly-Based Synoptic Analysis and Model Prediction of Six Dust Storms that Originated from Mongolia and Moved to Northern China in Spring 2021. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD036272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, D.L.; Toon, O.B.; Carlson, T.N. A Case Study of Mobilization and Transport of Saharan Dust. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 44, 2349–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, I.; Carmichael, G.R.; Streets, D.G.; Satake, S.; Takahashi, T.; Woo, J.H.; Uematsu, M. Regional Chemical Weather Forecasting System CFORS: Model Descriptions and Analysis of Surface Observations at Japanese Island Stations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 18347–18366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Gong, S.L.; Zhao, T.L.; Arimoto, R.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhou, Z.J. Sources of Asian Dust and Role of Climate Change versus Desertification in Asian dust emission. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yoon, J.W.; Park, S.K. Primary Factors and Synoptic Pattern Classification of Mega Asian Dust Storms in Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 60, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-Y.; Lim, Y.-K.; Cha, J.W. Short-Term Prediction of Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5) in Seoul, South Korea Using Tree-Based Machine Learning Algorithms. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Seo, J.; Kim, G.M.; Jin, H.C.; Chun, Y. Long-Range Transport of Giant Particles in Asian Dust Identified by Physical, Mineralogical, and Meteorological Analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.; Boo, K.-O.; Kim, J.; Park, S.-U.; Lee, M. Synopsis, Transport, and Physical Characteristics of Asian Dust in Korea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 18461–18469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohonen, T. Self-Organizing Maps, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.C.; Feldstein, S.B.; Tremblay, B. The continuum of Northern Hemisphere teleconnection patterns and a description of the NAO shift with the use of self-organizing maps. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 6354–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, D.E.; Johnson, N.C.; Singh, D.; Swain, D.L.; Rajaratnam, B.; Diffenbaugh, N.S. Contribution of changes in atmospheric circulation patterns to Northern Hemisphere temperature extremes (1979–2013) as revealed by self-organizing maps. Nature 2015, 522, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Lu, R.; Zhang, Y. Exploring combined effects of Arctic Oscillation and filled in large-scale pressure patterns using self-organizing maps. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 9107–9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.; Park, C.; Son, S.-W.; Roh, J.-W.; Lee, G.-W.; Lee, Y.-H. Classification of Localized Heavy Rainfall Events in South Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 56, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Chun, H.-Y.; Jang, W.; Son, S.-W. Classification of Synoptic Patterns with Mesoscale Mechanisms for Downslope Windstorms in Korea Using a Self-Organizing Map. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesanto, J.; Alhoniemi, E. Clustering of the Self-Organizing Map. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2000, 11, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S. Relationships between Springtime PM2.5, PM10, and O3 Pollution and the Boundary Layer Structure in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y. Characteristics of Boundary Layer Structure during a Persistent Haze Event in the Central Liaoning City Cluster, Northeast China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Jo, H.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Park, S.M.; Cho, S.; Lee, K.H. Impacts of atmospheric vertical structures on transboundary aerosol transport from China to South Korea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Navas-Guzmán, F.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Pérez-Ramírez, D.; Granados-Muñoz, M.J.; Olmo, F.J.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Study of mineral dust entrainment in the planetary boundary layer by lidar depolarisation technique. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2015, 67, 26180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, A.; Balawender, K.; Kuszewski, H.; Jaremcio, M. The Assessment of PM2.5 and PM10 Immission in Atmospheric Air in a Climate Chamber during Tests of an Electric Car on a Chassis Dynamometer. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Year | Total Events | Events by Cluster | PM10 | Mean Hourly Max (µg m−3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No.1 | No.2 | No.3 | No.4 | Advisories | Warnings | |||
| 2019 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 185 | 0 | 195 |
| 2020 | 11 | 4 | 3 | - | 4 | 94 | 2 | 181 |
| 2021 | 11 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 318 | 134 | 382 |
| 2022 | 5 | - | 2 | 1 | 2 | 147 | 12 | 233 |
| 2023 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 343 | 98 | 278 |
| 2024 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 166 | 24 | 275 |
| Total | 53 | 16 | 11 | 9 | 17 | 1244 | 270 | 261(Mean) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seong, D.; Son, J.; Kim, D.-J.; Yoon, J.; Lee, J.-B. Spatiotemporal and Synoptic Analysis of PM10 Based on Self-Organizing Map (SOM) During Asian Dust Events in South Korea. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101116
Seong D, Son J, Kim D-J, Yoon J, Lee J-B. Spatiotemporal and Synoptic Analysis of PM10 Based on Self-Organizing Map (SOM) During Asian Dust Events in South Korea. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(10):1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101116
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeong, Daekyeong, JeongSeok Son, Dong-Ju Kim, Jongmin Yoon, and Jae-Bum Lee. 2025. "Spatiotemporal and Synoptic Analysis of PM10 Based on Self-Organizing Map (SOM) During Asian Dust Events in South Korea" Atmosphere 16, no. 10: 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101116
APA StyleSeong, D., Son, J., Kim, D.-J., Yoon, J., & Lee, J.-B. (2025). Spatiotemporal and Synoptic Analysis of PM10 Based on Self-Organizing Map (SOM) During Asian Dust Events in South Korea. Atmosphere, 16(10), 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101116





